CS 215 After Midterm
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
In PHP, what happens if you pass too many or too little parameters?
Too many parameters - the extra will be ignored
Too little paramenters - the rest of the spots will become null
What is AJAX?
Asynchronous JavaScript and XML.
It provides web-based applications with the ability to implement rich and responsive user inferfaces.
This is done through a combination of client-side (JavaScript) and server-side (PHP, for this course) programming, and a mechanism for allowing JavaScript code to retrieve information from the web server after the page has been loaded.
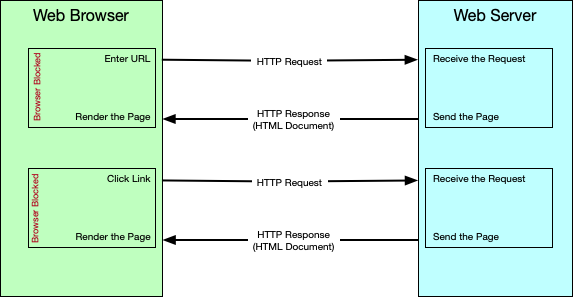
How does synchronous communication works?
When you enter a URL or click on a link in the browser, the request is sent to the server and the browser waits for the response. When the response comes back, the browser parses it and updates the browser window.
In such communications, both the client and the server give their full attention to the communication.
You can think of synchronous communication like a polite telephone call.
Example:
the web browser requests a document
the web server process this request
the web browser waits for the document to be sent
the web browser renders and displays the document
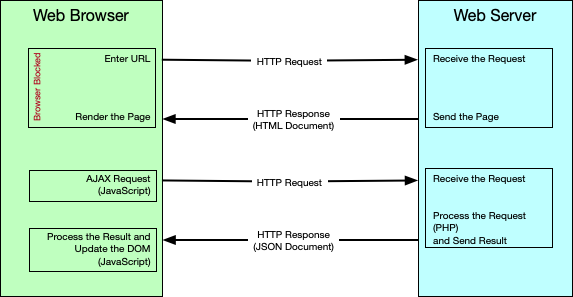
How does asynchronous communication works?
After the client makes the request, it may continue to do other things. When the response comes back from the server, the client is notified and will do something about it. As a result, the client and the server may be performing different operations at the same time (the client continues to do other things while the server is processing the request).
In such communications, the client sends the request to the server, and then specifies a function to execute when the request comes back (rather than waiting).
You can think of asynchronous communication is like a series of back-and-forth text messages.
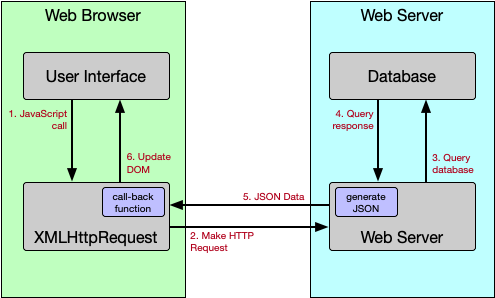
What is the AJAX process?
There are four fundamental steps in AJAX programming. The first is making the asynchronous request to the web server using the XMLHttpRequest object. On the server-side, this request is processed and a response is generated. The response is sent back to the browser. When the response is received, a call-back function is executed to process the request and update the page with the content.
For security reasons, an XMLHttpRequest connection can only be made to the site that provided the document in which it was loaded.
How do you create a new instance of XMLHttpRequest and what set of methods can be used with it?
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
onreadystatechange : set to a function that will execute whenever the state of the request changes
open : set the URL for the request
send : initiates the request. Null for GET requests, encoded parameters for POST requests.
What are the important properties of the XMLHttpRequest object that we need to monitor?
readyState (values 0 – 4):
0: request not initialized
1: sever connection established
2: request received
3: processing request
4: request finished and the response is ready
status (HTTP status values):
200: OK
404: Page not found
500: Server error
Where is the programming for AJAX done?
AJAX code is generally a combination of client-side (JavaScript) and server-side (PHP, or other languages) coding. JavaScript code is written to access the server after the page has been loaded. On the server side, the code could access information from the database, and return data in a format that can easily be processed in JavaScript (e.g., JSON). When this information is received successfully on the client-side, JavaScript is used to manipulate the DOM to make the associated change in the browser.
What type of web applications would benefit from using AJAX?
Generally, a website with static content would not benefit from AJAX. However, if the content is dynamic, and if there is a need to check back frequently for new information (sports scores, status of some external resource), AJAX can be very useful for keeping the web page updated without the need to hit the reload button. It can also be useful to check for user input against data on the server as it is being entered (e.g., verifying the availability of a product added to a shopping cart).
Why don’t we want the web server to return complete HTML documents when we are doing AJAX programming?
The purpose of AJAX programming is to have your page make a request to the server outside of the normal page reload mechanism. As a result, we don't want the whole page back (if we did, we might as well just reload the whole page). Instead, we want just the new or updated data, which we can then parse in JavaScript and update elements of the page as needed.
What is the benefit of using JSON as the return data type when doing AJAX programming?
While there are a wide variety of data types that can be used to provide data from the web server back to the browser via AJAX, JSON is the preferred data format. Other formats are either too simple or too complex. JSON is easy to generate in PHP (constructed with just associative and normal arrays), and easy to parse and use in JavaScript (one command to produce the JavaScript object from the JSON data, and then we can use dot-notation and array indexing to access the data). Although it can take some practice, reading the JSON document is a matter of knowing what the objects are (encapsulated in curly brackets) and what the arrays are (encapsulated in square brackets).
Why do we need to store data on the server?
There are only two places within a web environment to save data: on the browser or on the server. Saving data on the browser only makes that data available for one user on one computer. Saving data on the server makes it available for all users who access the website. Furthermore, saving the data on the server is more reliable, maintainable, and secure.
reliable - the servers are often highly reliable computers with good backup strategies
maintainable - the web application designer can easily access the data on the server
secure - the servers are often maintained by security professionals, preventing unauthorized access
What are some important elements of Database management systems (DBMS) software?
data independence
data representation and storage are handled independently of the application program
efficient data access
data storage and retrieval can occur with minimal delay
data integrity and security
rules regarding valid data can be automatically enforced
access to the data can be restricted depending on who or what application is accessing it
data administration
the data can be administered independently of the application
concurrent access
multiple users can access the data at the same time
maintains the illusion that each has dedicated access
crash recovery
if the computer crashes, no data is corrupted or lost
any changes to the data either happen completely or don’t happen at all
What is a data model?
A data model is a set of high-level data description constructs that allow us to specify what the data should look like without having to worry about the low-level storage details.
Most common one is the relational data model.
the central data construct in this model is the relation, which can be thought of as a set of records
be careful to not confuse this with a relationship, which is also present in the relational model
What are the three levels of abstraction?
conceptual
physical
external
At each of these, we can describe the data using a schema.
What is conceptual schema?
It describes the database in terms of the data model:
information about entities
relationships between the entities
In short, it specifies the details of the specific database (relations, relationships).
What is physical schema?
It specifies storage details for the conceptual schema:
which file organizations to use to store the relations
what auxiliary data structures can be created to speed up storage and/or retrieval operations (indexes)
Decisions are made based on an understanding of how the data is typically accessed.
What is external schema?
This will allow data access to be customized and authorized at the level of individual users and groups:
different users can share access to the same database, but with different rights and privileges
simple example: table-level access controls
complex example: custom views that combine different elements from different related tables
e.g., a view that shows student enrollment in a course, their grades, but not their login information
Such are guided by the end-user requirements for the application.
What is data independence and its different types?
Application programs are insulated from changes in the way the data is structured and stored.
There are two different types of data independence:
logical data independence
physical data independence
As much as possible, we want to ensure that we can maintain our database without the need to update the software that is using the database. Adding a new table or even a new field to a table should not cause our software to no longer work. Changing how the data is stored or sorted should also not cause things to break.
What is logical data independence?
users are shielded from changes in the logical structure of the data or changes in the relations
achieved through the use of views
What is physical data independence?
changes in how the data is stored internally within the database have no impact on how the users access the data
What are entities in ERD?
Basic objects of ERDs
represent a “thing” with an independent existence
may be physical or conceptual
car, car type, manufacturer, engine
student, course, faculty, instructor
room, booking, user, invitation
represented as blocks in the ERD
What are relationships in ERD?
Associations between the entities:
can be inclusion (like in OO programming) or a more abstract connection
Three types:
one to one: for each booking, there is a single room, and for each room there is a single booking (this creates a strict limitation on the relationship)
one to many: each booking is for a single room, but each room may be associated with multiple bookings
many to many: each booking can include multiple rooms, and each room can be associated with multiple bookings
What are attributes in ERD?
These can be assigned to the entities and/or the relationships
for entity attributes, these can be listed within the entity box
relationship attributes are normally added as bubbles connected to the relationship line
What is the value of ERDs?
It allows you to sketch the conceptual schema before you build it in the DBMS.
Why do we want to use databases for persistent data storage on the server?
Managing all of the complications of storing data for a multi-user concurrent application such as a web application is complicated. Database management systems have been developed for this very purpose. As a result, using a DBMS is much easier and reliable than writing your own data storage code.
What is the difference between conceptual, physical, and external levels of abstraction?
The conceptual schema specifies the details of the specific database (relations, relationships). The physical schema specifies specific storage details for the conceptual schema (settings in the chosen DBMS). The external schema specifies a security mechanism for which users gets access to what data.
Why is transaction management such an important part of a database management system?
The transaction management features built into modern DBMS software ensures that if there is a system failure, data can be recovered automatically. By using a transaction log, incomplete transactions can be completed when the DBMS software starts again. This is done by writing to the transaction log first, forcing that to be written to the disk, and then performing the transaction.
What is the purpose of normalization in database design?
It is the process of separating your data into tables that are linked together. The goal is to ensure that each unique piece of data is in the database only once. First normal form (1NF) ensures that there are no repeating columns with the same data, that each column contains a single value (no comma-separated lists of values), and that there is a primary key on each table. Second normal form (2NF) eliminates redundancy across multiple rows by creating new tables that hold repeating information once (e.g., moving the room information into a separate table, rather than repeating it with each booking entry). Third normal form (3NF) takes the elimination of redundancy to the extreme, such that any data that is dependent on another value is moved to a separate table (e.g., since a city can be derived from a postal code, it can be moved to another table so that the city is not repeated multiple times).
How can we use natural language to assist in the construction of Entity Relationship Diagrams?
When we think about the problem at hand, think about what are the nouns, what are the attributes, and what are the verbs. The nouns represent things, telling us what the entities are (e.g., rooms, bookings). The adjectives represent descriptions of those things, telling us what the attributes are (e.g., a room's building, number, capacity, and format). The verbs represent interactions between nouns, telling us what the relationships are (e.g., rooms are reserved in bookings, giving the relationship between rooms and bookings).
What is the primary benefit of performing entity relationship diagraming?
It can readily be converted into tables and relationships in the database
Suppose you were to design a new database (relations, relationships) for a web application. At what level of abstraction would your database design occur?
conceptual
Which of the following features do we get for free by using a database management system in our web application?
concurrent access
At what level of normalization do we ensure that all columns in the database contain a single value?
first normal form
In transaction management, which types of queries can use a shared lock on the relation?
reading data
What is Structured Query Language (SQL)?
Standard language for specifying access to and modifications of relational databases. This language allows you to write human-readable commands that tell a database what to do.
What is MySQL?
It is a database management system. This is an open-source database that is very popular for web-based applications. It uses the same core SQL as other major database vendors, which means that what you learn here can easily be transferred to other DBMS software.
How do you specify foreign key when making a table?
FOREIGN KEY (field_in_this_table) REFERECES OtherTable (field_in_other_table)
Make these modifications to a table structure using sql language:
change the data type of name from what it was to VARCHAR(100)
add a new field called last_name to the table
change the existing field name to first_name, and change its data type to VARCHAR(100)
drop the field name from the table
ALTER TABLE Users MODIFY name VARCHAR(100);ALTER TABLE Users ADD last_name VARCHAR (100);ALTER TABLE Users CHANGE name first_name VARCHAR (100);ALTER TABLE books DROP name;What is the command to insert data into a table?
INSERT INTO table_name
(column_name_1, column_name_2, …, column_name_n)
VALUES
(value_1, value_2, …, value_n);What is the command to update a table?
UPDATE table_name
SET
column_name_1 = value_1,
column_name_2 = value_2,
…
column_name_n = value_n
WHERE conditionWhat is the command to delete from a table?
DELETE FROM table_name
WHERE conditionWhat are the differences between left, right, inner, and full outer joins?
LEFT JOIN will choose all rows from the first table, and link these to the second table even if there isn’t a matching row
RIGHT JOIN will choose all rows from the second table, and link these to the first table even if there isn’t a matching row
INNER JOIN will choose only rows where there is a match (same as specifying the join in the WHERE clause)
FULL OUTER JOIN will choose all rows in both tables, even including data for where this is no match
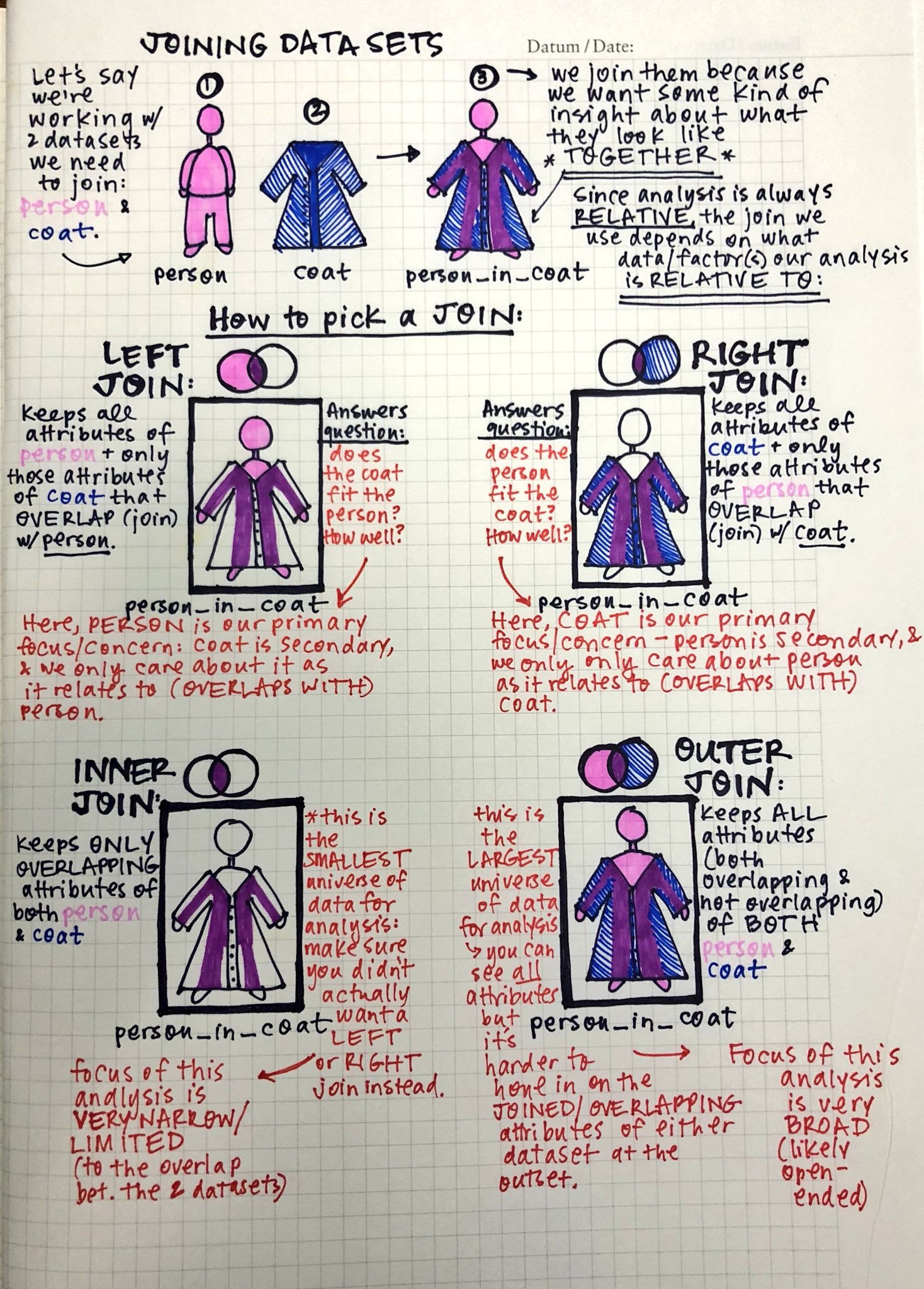
What are foreign keys and why are they so important?
Foreign keys allow tables to be explicitly linked together in the database. They ensure data validity, since any record that has an entry in a column that is specified as a foreign key will be guaranteed to have the required corresponding record in the table that is references. That is, if user_id is a foreign key in the Bookings table, then for every record in Bookings, the values for the user_id fields all have records in the Users table.
Is it better to ALTER a table, or just DROP it and CREATE it again?
This depends on whether you have data in the table already. If there is no data (or none that you need to keep), it may be simpler to DROP the table and the CREATE it again. However, if there is data in the table, it is best to use the ALTER statement to make the required changes. Of note is the fact that you may be restricted from dropping a table if it is part of a foreign key relationship, and there is data in other tables that references data in the table you are trying to drop.
Which of the SQL statements have the ability to make use of the WHERE clause?
Because the WHERE clause filters records (rows of data), it can be applied to any clause that operates on the rows. The ones we have discussed are UPDATE, DELETE, and SELECT. Of note is that it is not valid for INSERT, since that statement does not need filter logic applied to it.
When using a SELECT or UPDATE statement, is it necessary to list the columns in the order they were created?
No, this is not necessary. You can specify the columns in whatever order makes sense for your query.
Supposed you have two tables that are linked together using a foreign key relationship (bookings and rooms as an example), how do you get a list of all the rooms and their bookings?
To do this, you should use a JOIN clause. The trick is what kind of join do you want to do. If you only want the rooms that have bookings, then you should do an INNER JOIN. If you want to include the rooms that do not have any bookings, then you should do either a LEFT JOIN or RIGHT JOIN (depending on whether Rooms is the first table or the second table).
What is the mechanism for ensuring that an integer-valued primary key field is automatically assigned the next available value?
using the AUTO_INCREMENT constraint on the field
If we have a table of Bookings with a booking_id primary key and we want to link this to an Invitations table as a foreign, which line of code is correct?
FOREIGN KEY (booking_id) REFERENCES Bookings (booking_id)
If we try to delete a record that is referenced in a foreign key relationship with another table, what will happen?
we will get an error, and the record will not be deleted
Suppose our Bookings table has a primary key of b_id, and it is linked to the Invitations table which has a foreign key with this same name. Which JOIN clause will give us only the bookings and their matching invitations, excluding bookings without invitations or invitations without bookings?
Bookings INNER JOIN Invitations ON Bookings.b_id = Invitations.b_id
Suppose we want to retrieve the records from the Users table where user_id has values 1, 3, or 5. Which of the following will work for our WHERE clause?
WHERE user_id IN (1, 3, 5)
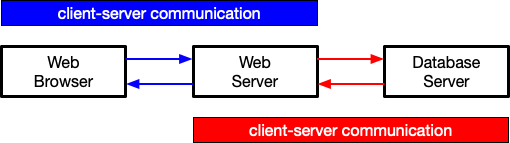
Explain the three-tier architecture
the Web server is both a server (to the browser) and a client (to the database server)
the Web browser is a client of the Web server, not the database server
the three-tier architecture remains valid even if the Web server and database server software are installed on the same computer (they run independently of one another)
PHP (or some other server-side programming language) is the glue between the server’s server and client mode
It is important to know what is the communication mechanism between each tier
web browser & web server: HTTP Request and HTTP Response
web server & database: SQL Query & Result Set
In php, how do you extract the data from the object $result?
if ($result->rowCount() > 0) {
while ($row = $result->fetch()) {
print ($row["email"] . "<br />");
}
} else {
print ("There are no users in the database.");
}
If the type of query issued does not return a result (insert, update, delete), what will our variable be when we $db→query it?
It will come back true or false.
Why does the introduction of a database turn the client-server architecture of the web into a three-toer architecture?
The communication between the web browser and web server follows the traditional client-server architecture. However, since the web browser cannot communicate directly with the database server, we write the code to do so on the web server, which then becomes the client of the database. The result is a three-tier architecture, where the web server acts as both server to the browser and client to the database.
Why is it important to check that the connection to the database has been made successfully?
If there is a problem with connecting to the database, the rest of the page will not work the way you expect. That is, every query you try to issue will fail. Rather than letting the page continue to load and produce such errors, it is better to just stop. The die function is what we use to do this. Alternately, we can redirect the browser to some standard error page, or even execute some custom code to alert a system administrator of the problem.
Even though the PHP engine will automatically close any open database connections when the page finished processing, why should we close the connections ourselves?
It is good programming practice to always be responsible for the objects you create. If you open the connection, you should explicitly close it when you are finished. This way, things get closed at an appropriate time (when you as the programmer decide that you don't need it anymore).
What is the difference between the PDO::FETCH_ASSOC, PDO::FETCH_NUM, and PDO::FETCH_OBJ options when using the fetch() method of the result set object?
These all do the same thing: retrieve one row of data from the result set object. The difference is in the data type of what is returned: an associative array, a numerically indexed array, or an object. As a result, the method that you use impacts how you get the data out of the row.
Why are session variables so important once we start using databases in our web application?
As we start to build up a web application to the point of needing a database, we often then need to keep track of other information as well. For example, if a user has logged into the web application, there may be other pages where we want to show the user's name. Rather than querying the database for this information over and over, we can instead query once as the user logs in, and then save the information we need later in session variables.
Where is the AJAX callback function executed?
web browser
After parsing JSON data in JavaScript, what is/are the primary data types of the result?
Strings and Objects
When generating JSON data in PHP, what is/are the primary data types to use?
Strings and Arrays
What are the readyState and status that indicate an AJAX response has been received and has been processed successfully?
readyState==4 && status==200
Which of the following statements are not true about the XMLHttpRequest object?
The request can only be asynchronous
In a three-tier architecture of a web application, which of the following statements are false?
The web browser communicates directly with the database server.
With respect to the example code provided to illustrate how to build a login system, how does the application know which order to load in the details page?
this was passed to the detail page using the GET method
Where does PHP code execute?
web server
Which is the superglobal variable we use to store information we want to access on the server in future page requests from the same browser?
$_SESSION
Suppose you are doing a single SELECT query of the database, and then iterating through the results set to produce some dynamic content on a web page. Where should you close the database connection?
after iterating over the result set