Structure and Function of Muscular, Nervous, and Skeletal Systems
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Epimysium
Connective tissue surrounding the muscle belly.
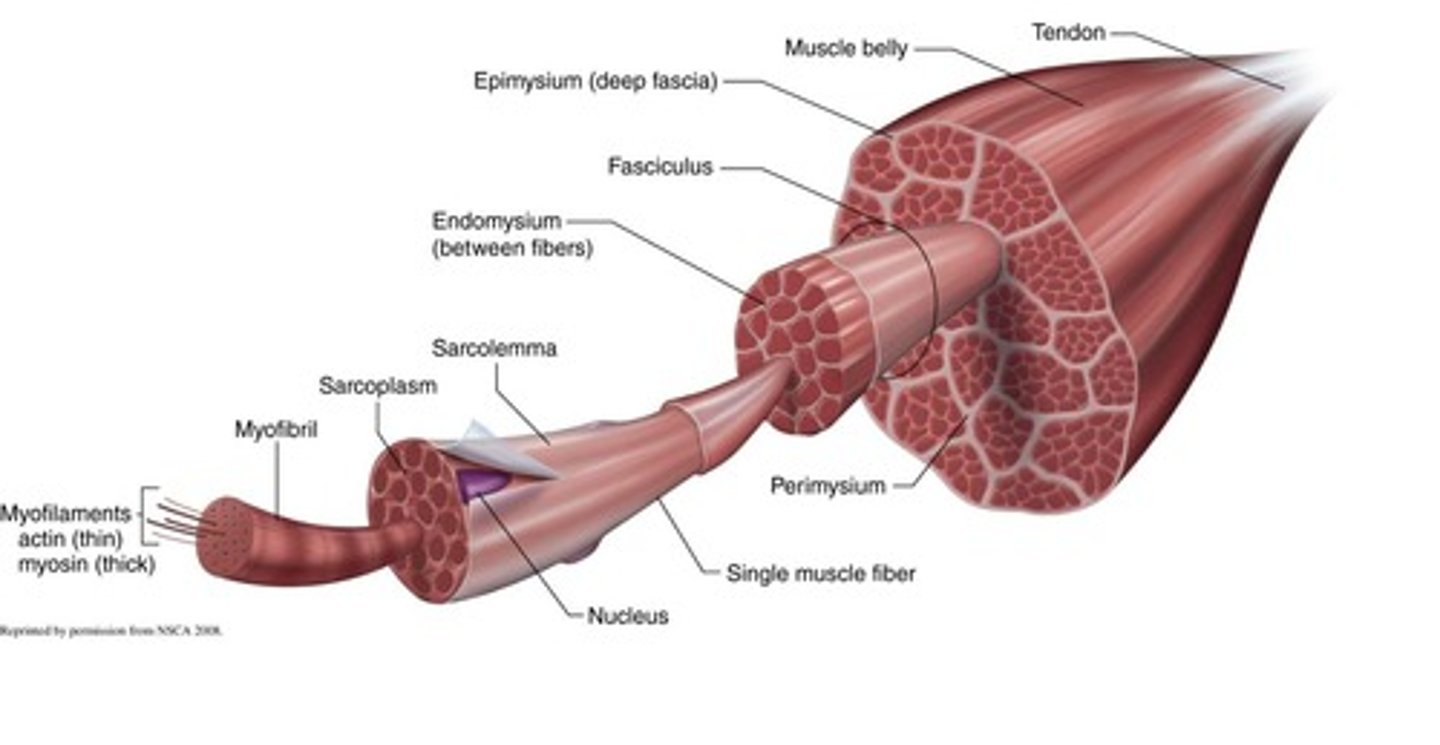
Perimysium
Connective tissue surrounding a fasciculus.
Endomysium
Connective tissue surrounding individual muscle fibers.
Sarcoplasm
Cytoplasm of muscle fibers containing energy sources.
Myofibril
Contractile unit of muscle fibers.
Myosin
Thick filament involved in muscle contraction.
Actin
Thin filament that interacts with myosin.
Tropomyosin
Covers myosin binding sites on actin.
Troponin
Regulatory protein that binds calcium.
Sliding Filament Theory
Mechanism of muscle contraction via filament sliding.
Action Potential
Electrical signal triggering muscle contraction.
Neuromuscular Junction
Site where motor neuron meets muscle fiber.
Muscle Spindle
Sensory receptor detecting muscle length changes.
Golgi Tendon Organ (GTO)
Receptor preventing excessive muscle force.
Stretch Reflex
Involuntary response to muscle stretching.
Cortical Bone
Dense outer layer of long bones.
Cancellous Bone
Spongy interior of bones, site of hematopoiesis.
Tendons
Connect muscle to bone, withstand tensile forces.
Ligaments
Connect bone to bone, contain elastin.
Osteoporosis
Condition of weak, brittle bones.
Wolff's Law
Bone adapts to stresses placed on it.
Type 1 Muscle Fibers
Slow oxidative, fatigue-resistant muscle fibers.
Type 2A Muscle Fibers
Fast oxidative glycolytic, moderate fatigue resistance.
Type 2X Muscle Fibers
Fast glycolytic, highly fatigable muscle fibers.
Delayed-Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS)
Pain after exercise, primarily from eccentric actions.
Central Nervous System
Includes brain and spinal cord, creates impulses.
Peripheral Nervous System
Relays nerve impulses between limbs and CNS.
Somatic Nervous System
Controls voluntary skeletal muscle movements.
Autonomic Nervous System
Regulates involuntary body functions.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Prepares body for fight or flight response.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Promotes rest and digest functions.
Motor Unit Recruitment
Activating more motor units for increased force.
Rate Coding
Increasing firing rate of active motor units.
Size Principle
Order of motor unit recruitment by size.