Ochem - Ch. 19: Amino Acids and Proteins
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chem 106
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Biological functions of proteins?
Enzymes, structure, transport, signaling, immune defense, movement.
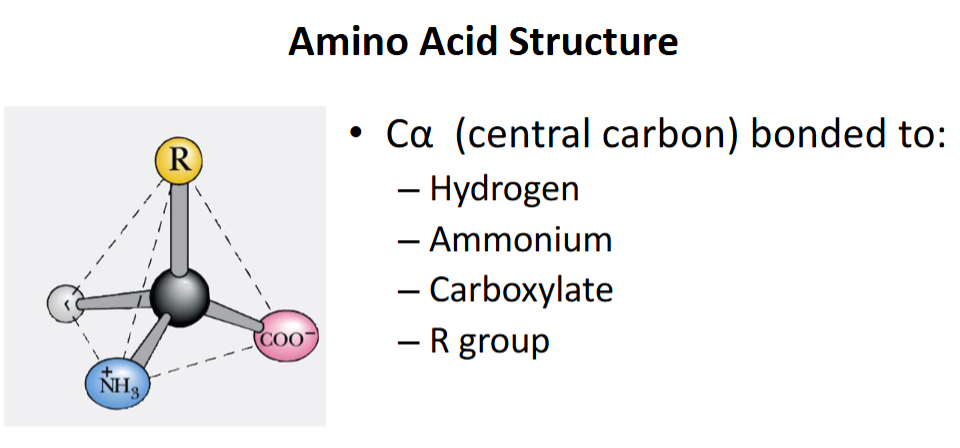
Basic structure of an amino acid?
Central C with –NH₂, –COOH, –H, and R group.
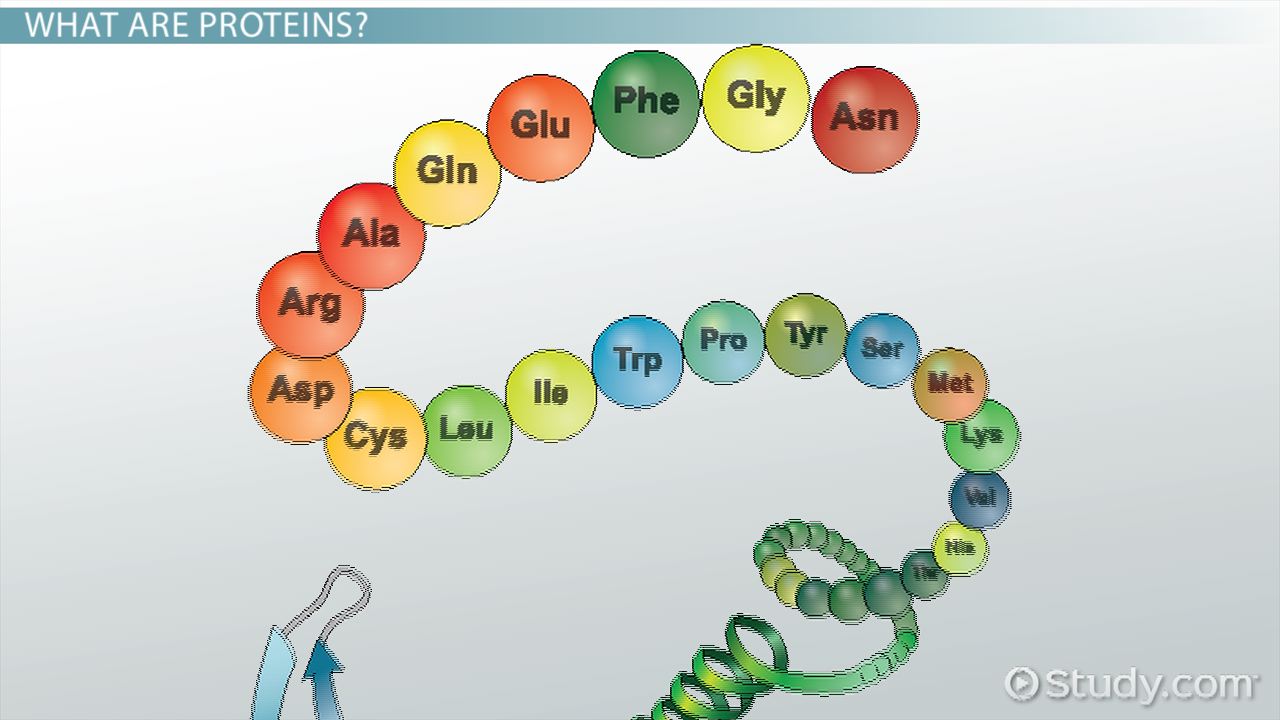
What is a polypeptide?
Chain of amino acids joined by peptide bonds.
What is a protein?
One or more polypeptides folded into a functional structure.
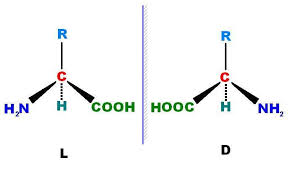
How to distinguish D and L amino acids?
In Fischer projection, –NH₂ on left = L (naturally occurring); right = D.
How does pH affect amino acids?
Low pH = positive charge (protonated); high pH = negative charge (deprotonated).
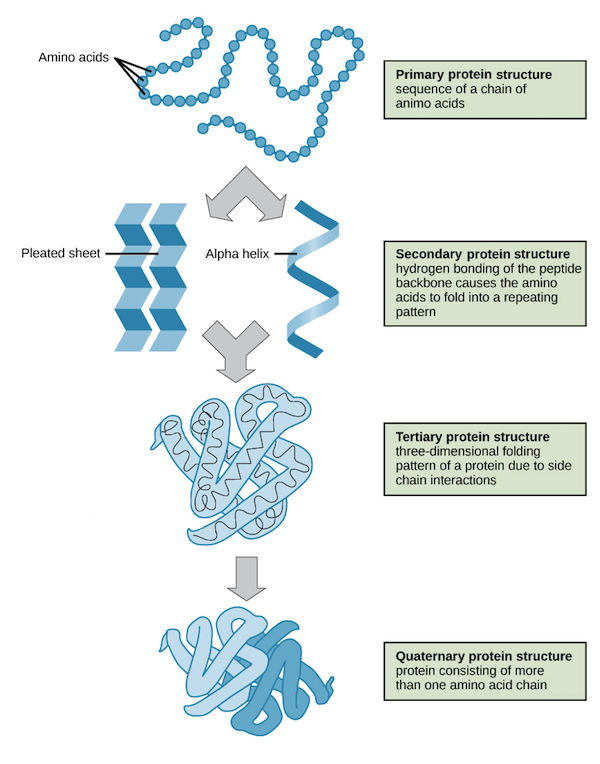
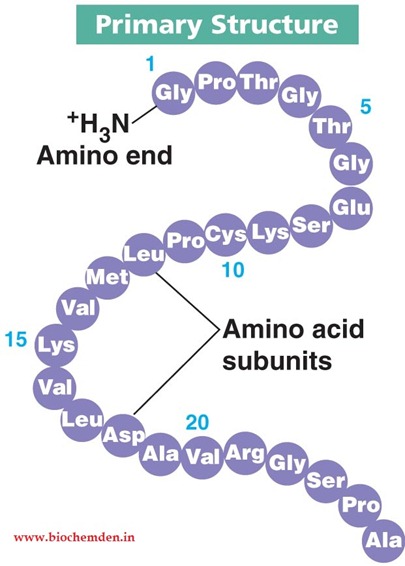
Primary protein structure?
Sequence of amino acids (peptide bonds).
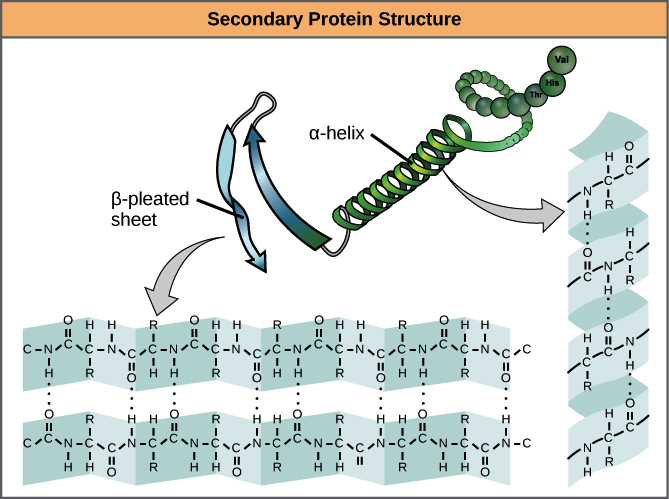
Secondary protein structure?
α-helix or β-sheet (hydrogen bonding).
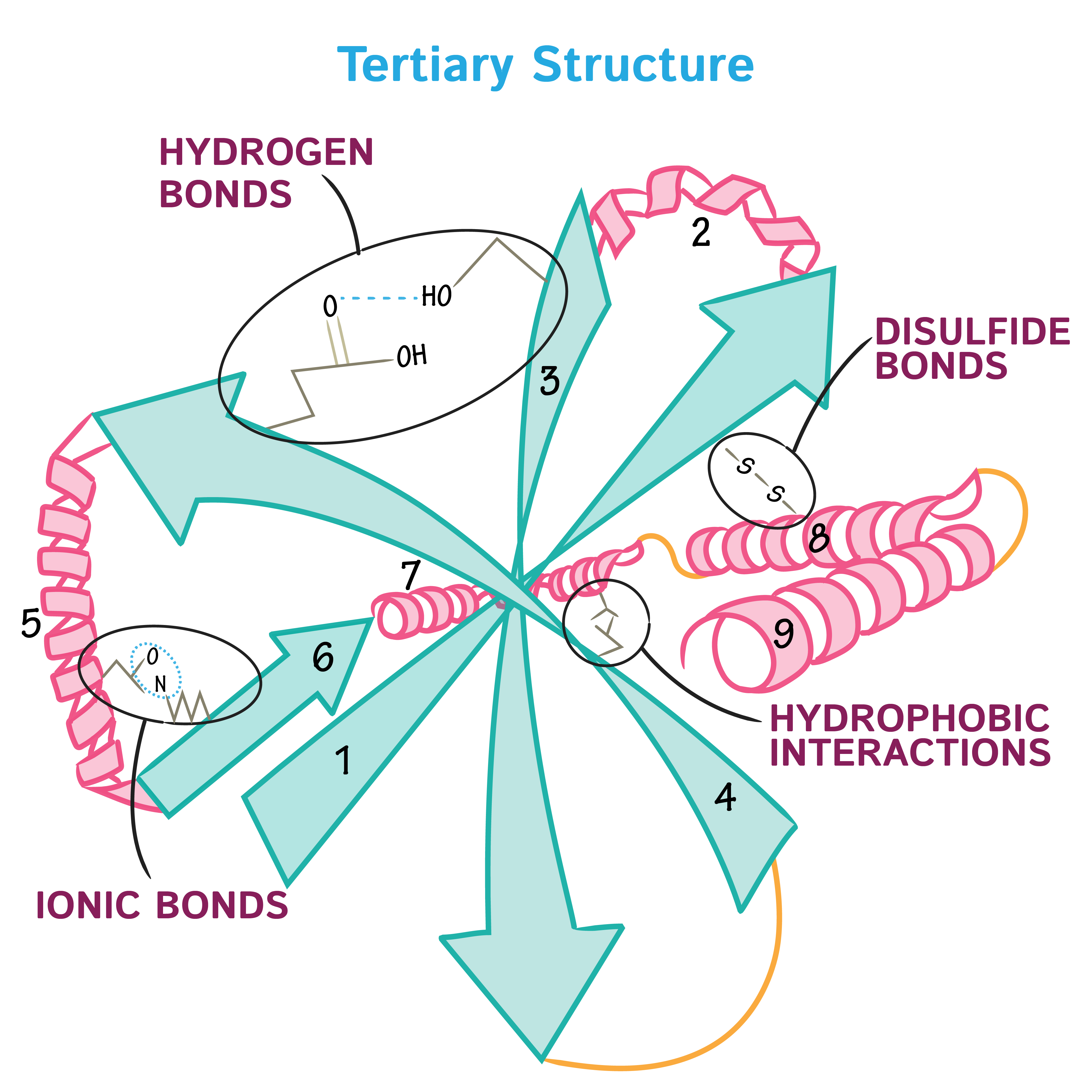
Tertiary protein structure?
3D folding from side chain interactions (H-bonds, ionic, disulfide, hydrophobic).
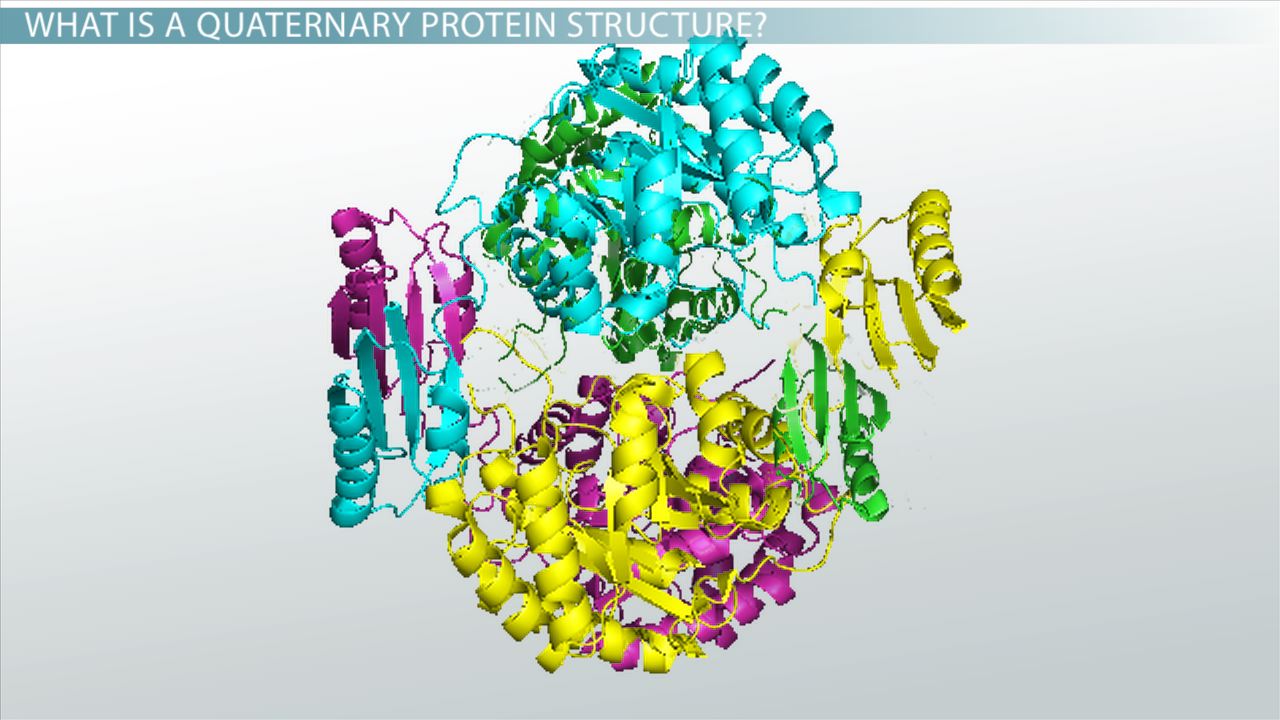
Quaternary protein structure?
Multiple polypeptides forming a functional unit (e.g., hemoglobin).
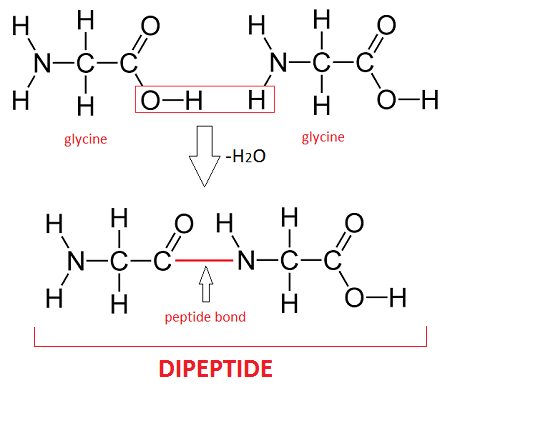
How to draw a dipeptide or tripeptide?
Join amino acids via peptide bonds –CO–NH–, removing water between each.
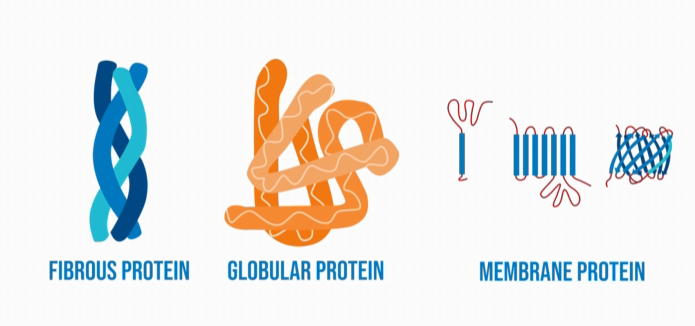
Types of proteins by shape?
Fibrous = structural (e.g., collagen); Globular = functional (e.g., enzymes); Membrane = embedded in cell membranes.
Difference between hydrolysis and denaturation?
Hydrolysis = breaks peptide bonds (chemical); Denaturation = unfolds protein (no bond breaking, just shape change).