Chapter 11 - Pricing strategies
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Potentially a short-answer question
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Psychological pricing
Even though the price difference is little, subconsciously we tend to think the prices are cheaper based on the first number we read.
Odd-even pricing
Odd numbers convey a bargain image --> $.79, $9.99 etc
Even numbers can convey quality --> $5, 10, 15, 20
The importance of pricing
A strategic opportunity to create value
Not an after thought to the rest of the marketing mix
Pricing signals quality or a lack of quality
The role of price in the marketing mix
One of the most important factors in purchase decisions
The only element in the marketing mix that generates revenue
The most challenging of the four Ps to manage, partly because it is often the least understood.
Misunderstood by managers
The 5 C's of Pricing
Company objectives
Customers
Costs
Compeitition
Channel members
The 5 C's of Pricing : Company objectives
Profit Orientation
Target profit pricing
Maximize profits
Target return pricing
Sales Orientation
Competitor Orientation
Customer Orientation
Example of company objectives: Tiffany & Co.
Tiffy & Co. keeps its prices high even during a recession to protect its prestigious image, symbolized by its famous blue box
The 5 C's of Pricing: Customers
The most important C!!!
It’s all about understanding consumers reactions to different prices
Consumers want value
Price is half of the value equation
Demand curves and pricing
Knowing demand curves enables to see the relationship between price and demand
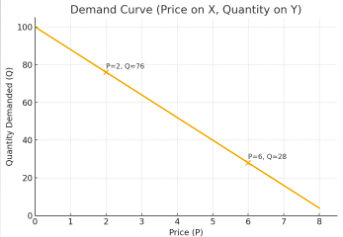
Price elasticity of demand
How do consumers respond to price increases or decreases?
Based on:
Income effect
Substituion effect
Equation: % Change in Qd/ % Change in Price
Factors influencing Price elasticity of demand: Income effect
Generally, as people’s income increases, their spending behavior changes
Demand shifts from lower-priced products to higher-priced products
Factors influencing Price elasticity of demand: Substitution effect
The greater the availability of substitute products, the higher the price elasticity of demand for any given product
Many substitutes = very responsive to change
Demand Curves and Pricing (cross elasticity of demand)
Substitute goods
Coca-cola vs Pepsi
Complementary goods
Printer and ink jet
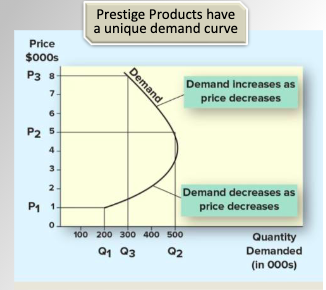
Demand Curves and Pricing (Prestige Products)
Prestige products have a unique demand curve
Graph:
Demand increases as the price decreases
Demand also decreases as price decreases
The 5 C's of Pricing: Costs
Includes:
Fixed Costs
Variable Costs
Total Costs
Costs: Fixed Costs
Does not change with output or production volume
Example: Rent, insurance, salaried manager
The same whether you make 10 or 1000 units
Costs: Variable Costs
Changes directly wth production volume
Examples: Raw materials, packaging and hourly wages
Increases as you make/sell more
Costs: Total costs
Sum of all costs
(TC = FC + VC)
Increases with production, but not proportionally
Costs: break-even point
The number of units we should sell to recover TC
At this point, the profit is zero and the total revenue = total costs
The 5 C's of Pricing: Competition
Monopoly
On firm controls the market
Oligopoly
A handful of firms control the market
Monopolistic competition
Many firms sell differentiated products at different prices
Pure / Perfect competition
Many firms selling commodities for the same price (no market control)
The 5 C's of Pricing: Channel members
Manufacturers, wholesalers and retailers can have different perspectives on pricing strategies
Manufactures must protect against grey market transactions
Pricinig strategies
Cost
Value
Competitor
Cost-based pricing
Start with cost
All costs are calculated on a per-unit basis
Assumes costs don’t vary for different levels of production
Competitor-based pricing
Set prices to signal information on how the product compares with competitors
Premium pricing
Value-based pricing
Setting prices that focus on the overall value of the product
Consumer perceptions
Psychological Factors Affecting Value-based pricing stratgies
Everyday low pricing (EDLP)
High/Low
Everyday Low Pricing (EDLP)
Saves search costs of finding the lowest overall pricing
High/Low pricing
Provides the thrill of the chase for the lowest price
Relies on the promotio of sales
Prices at this time are temporarily reduced to encourage purchases
New Product pricing strategies
Price skimming
Market penetration pricing
Price skimming
Sets new product prices high and lowers them as competitors enter the market
(High —> Low)
Market penetration pricing
Newly launched products are low to build a big customer base at the outset
(Low —> High)
Pricing tactics
Price lining
Price bundling
Leader pricing
Price lining
Marketers establish a price floor & a price ceiling & set prices in between
Allows for easy comparison
Price bundling
Encourage sales of slow-moving items
Encourage stock up
Encourage trial of a new brand
Incentive to purchase
Leader Pricing
Enticing consumers into the store with the popular aggressively priced item and hoping they will pick up other items while shopping
Consumer Price Reduction
Markdowns
Coupons and rebates
Quantity discounts for consumers
Markdowns
An integral component of high/low pricing strategy
Enable retailers to get rid of slow moving or obsolete merchandise
Used to generate store traffic.
**** Usually a retail tactic, not a typical pricing tool firms use
It’s a reduction in price to clear out slow-moving or outdated inventory
Quantity Discounts for Consumers
Size discount
The more you buy the cheaper the unit cost
Coupons and Rebates
Coupons
Retailer handles
Rebate
Manufacturer issues
B2B Pricing tactics
Seasonal discounts
Cash discounts
Allowances
Quantity discouts
Uniform delivered vs geographic pricing
Seasonal discounts
Designed to spur buyers into purchasing merchandise early
Cash discount
Reduced invoice cost if buyer pays prior to the end of the discount period
Encourages buyers to pay before the discount period ends
Seller benefits either way

Allowances
Lowers the final cost in return for specific behaviour
Advertising allowance
Listing allowance
Uniform Delivered vs Geographic pricing
Addresses the impact of shipping, which is often a major cost for manufacturer
Quantity Discounts
Cumulative quantity discount
Noncumulative quantity discount
Legal and ethical aspects of pricing
Deceptive/illegal price advertising
Predatory pricing
Price discrimination
Price fixing
Legal & Ethical aspects of pricing: Deceptive or illegal price advertising
Deceptive refrence prices
Bait & Switch
Loss leader pricing
Legal and ethical aspects of pricing – Predatory pricing
When a firm sets a very low price for one or more of its products with the intent to drive its competition out of business
Legal and ethical aspects of pricing – Price discrimination
When firms sell the same product to different resellers (Wholesalers, distribuors or retailers) at different prices, usually larger firms receive lower price
Legal and ethical aspects of pricing – Price Fixing
Practice of colluding with other firms to control prices
Examples of monetary sacrifices included in the overall price
Travel Costs
Shipping
The overall sacrifice a consumer makes to acquire a product or service is known as:
Price
BMW offers free scheduled maintenance on its cars for the first four years. BMW expects that consumers will pay more for its cars because the cars are less expensive to drive over their lifetimes than competitors' cars. BMW is using a(n) ______ pricing method.
Cost of ownership
Shrinkflation
When items shrink in size or quantity while their price remains the same or increases
Which of the following is not a type of price tactic typically aimed at consumers?
Cash discount
The cost-of-ownership pricing method involves setting prices based on…
How expensive it will be to use the product throughout its lifetime
Price discrimination is illegal under all conditions (true/false)
False!