6/24 Memorization
1/200
Earn XP
Description and Tags
rounding, within- and cross-system conversions, Si prefixes, unit abbreviations, apothecary symbols, roman numerals, compounding instructions, dosage forms, routes, frequency, frequency modifiers and misc. abbrev., indications, units of concentration
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
201 Terms
are conversions between systems accurate?
not accurate
are conversions within systems accurate?
accurate
golden rule #1
Only change systems when necessary
golden rule #2
Use a conversion appropriate to the scale of the quantity being converted. If possible, use a
direct conversion
golden rule #3
You must use leading zeroes, but do NOT use trailing zeroes. Even if you are asked to give an answer to a certain number of decimal places, if the last digit would be zero, it still must be dropped!
leading zeros
zeros that appear to the left of the first non-zero digit in a number
trailing zeros
zero digits that appear at the end of a number after the last non-zero digit
writing ratios
Ratio strength should be written as a ratio of active ingredient to whole product, simplified to
least whole numbers and separated by a colon.
how to measure tbsp/tps
Write teaspoonful or tablespoonful rather than teaspoon or tablespoon
final answer rounding
If you round intermediate steps you must round to at least one decimal place more than
your final answer, but do not double round
rounding to increments not a multiple of 10
answer will be the multiple of the stated increment that is CLOSEST to the
value being rounded (ex: 1.6mL rounded to 1.5mL, not 1.75mL)
rule of rounding for days
IF asks how many days (weeks, etc.) a prescription will last the patient, round down; prescription will run out during partial day if rounded up.
IF asks how long a medication must be given in order to reach a specified total dose, round up; patient will not have reached the target at the beginning of the partial day
rounding rule for drops
round to nearest whole drop
rounding for Discrete dispensing units (tablets or capsules, bottles, jars, IV bags)
IF the question asks how many will be required to compound a prescription, or the number to be dispensed, round up; patient should receive a full unit for effective treatment.
If the question asks how many units a prescription will make, ROUND DOWN –
the partially completed unit will not be dispensed.
infusion pump setting rounding
Round to the nearest 0.1 mL/h unless instructed otherwise.
Freezing point depressions and sodium chloride gram equivalents rounding
If possible, do not round these values. If rounding is necessary, keep at least 3
decimal places.
specific gravity/density rounding
Keep at least 3 decimal places unless instructed otherwise.
density of water
1g/mL
“microdrop
infusion set
60 gtt/mL
normal adult BSA (body surface area)
1.73 m²
density
mass/volume
specific gravity
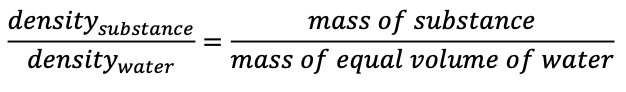
specific volume
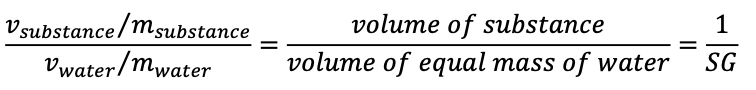
1 nanogram (ng)
0.001 mcg
1 microgram (mcg or μg)
1000ng = 0.001mg
1 milligram (mg)
1000μg = 0.001g
1 gram (g)
1000 mg = 0.001 kg
1 kilogram (kg)
1000 g
1 lb in gr
7000
1 lb in oz
16
1 microliter (mcL or µL)
0.001 mL
1 milliliter (mL)
1000 mcL = 0.001 L
1 cc
1 mL
100mL
1 deciliter (dL) = 0.1 L
1 Liter (L)
1000 mL = 10 dL
1 tablespoonful (T)
3 teaspoonsful (tsp)
1 fl oz
2 tablespoonsful (T) = 1/8 cup (c)
1 cup [c]
8 fl oz
1 pint (pt)
2 c = 16 fl oz
1 quart
2 pt = 4 c = 32 fl oz
1 gallon (gal)
4 qt = 8 pt = 16 c = 128 fl oz
1 nanometer (nm)
0.001 µm
1 micrometer (µm)
1 micron = 1000 nm = 0.001 mm
1 millimeter (mm)
1000 µm = 0.001 m
1 centimeter (cm)
10 mm = 0.01 m
1 decimeter (dm)
10 cm = 0.1 m
1 meter (m)
100 cm = 1000 mm = 0.001 km
1 kilometer (km)
1000 m
1 foot (ft or ')
12 inches (in or ")
1 yard (yd)
3 ft
gr i (1 grain) (cross)
65 mg
1 oz (cross)
28.4g
1 lb (cross)
454g
1 kg (cross)
2.2 lb
1 tsp (cross)
5 mL
1 tbsp (cross)
15 mL
1 fl oz (cross)
29.57 mL
1 c (cross)
240 mL
1 pt (cross)
473 mL
1 qt (cross)
946 mL
1 gal (cross)
3785 mL (most accurate)
1 in (cross)
2.54 cm ≈ 25.4 mm
nano (n)
10^-9 (or 0.000000001)
micro (mc OR μ)
10^-6 (or 0.000001)
milli (m)
10^-3 (or 0.001)
centi [c]
10^-2 (or 0.01)
deci (d)
10^-1 (or 0.1)
kilo (k)
10^3 (or 1,000)
mega (M)
10^6 (or 1,000,000)
giga (G)
10^9 (or 1,000,000,000)
U, IU
unit, International Unit
gr (non abbrev.)
grain
lb (non abbrev.)
(Avoirdupois) pound
minim
♏︎,︎ smallest unit of volume
scruple
℈
dram or fluid dram
ʒ (or dr)
ounce or fluid ounce
℥ (bottles)
apothecary pound
℔
forty in roman numerals
XL
fifty in roman numerals
L
sixty in roman numerals
LX
ninety in roman numerals
XC
one hundred in roman numerals
C
five hundred in roman numerals
D
one thousand in roman numerals
M
building roman numerals
List numerals in descending order of size until the sum equals the number to be expressed.
Exception: A smaller numeral preceding a larger numeral indicates that the smaller value should be subtracted from the larger.
aa (comp)
of each
ad
up to (meaning to fill to the stated quantity)
aq (aq pur; aq dest)
water (purified water; distilled water)
dtd
give of such doses
div
divide
et
and
ft
make
M (compounding)
make
qs
enough; sufficient quantity
cap or caps
capsule(s)
chart
powder paper
gtt
drops
inh
inhalation
IVBP
IV piggyback (a small IV bag, often hung with, or “piggybacked” onto, a larger-volume IV infusion)