Radiology Final Non-traumatic X-ray
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
2
How many x-ray views do you typically need?
X-ray
What type of imaging is best used to visualize bone cortex?
True
T/F: X-rays can detect significant soft tissue swelling?
STS
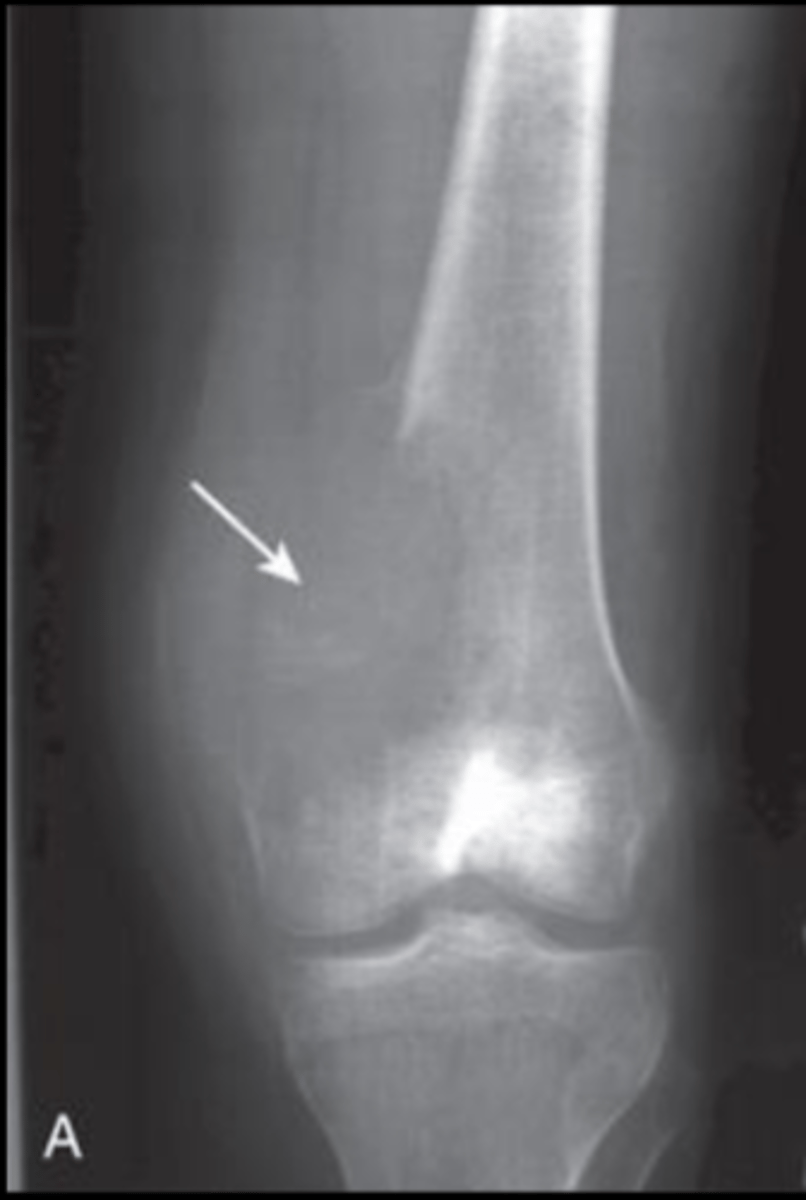
What is the arrow pointing to?
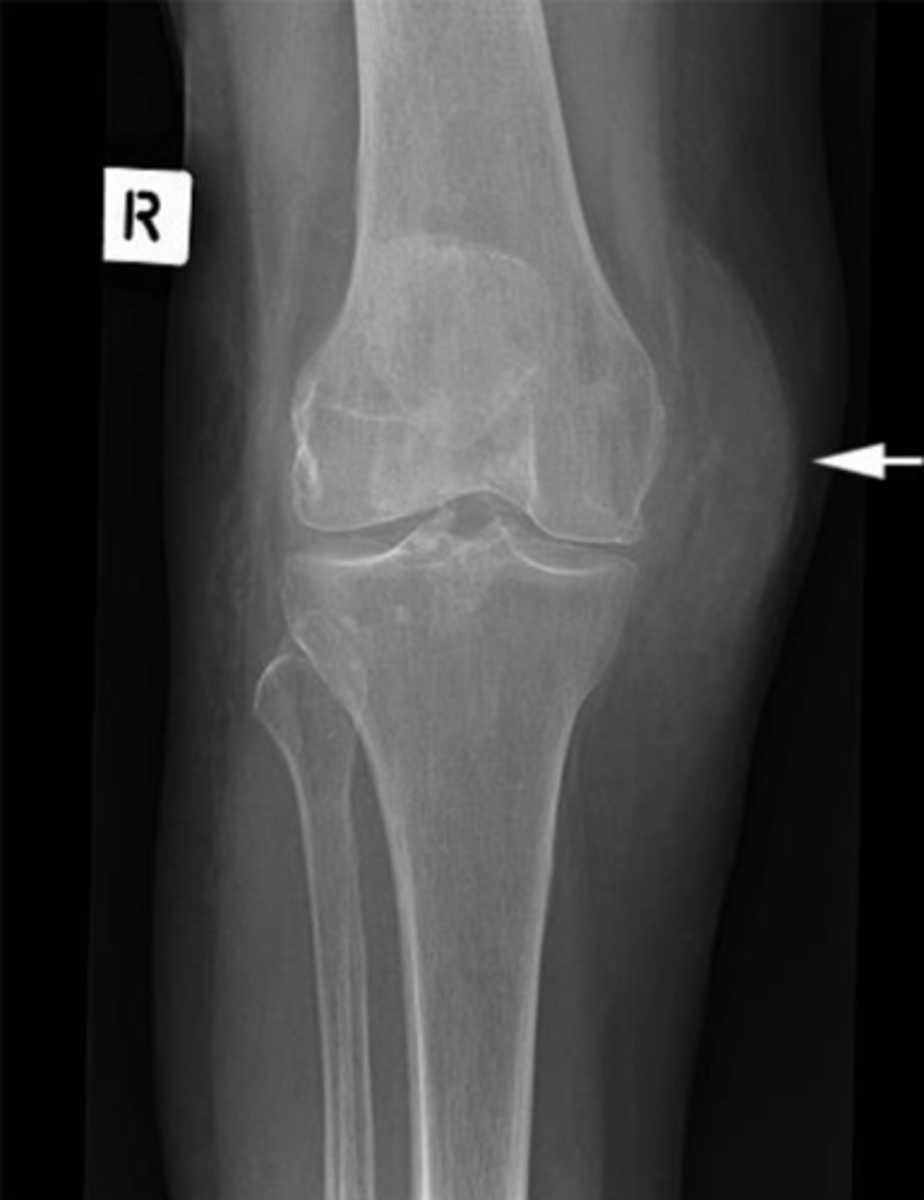
Bone density
Amount of bone mineral in bone tissue
Osteoblastic metastases sclerosis
Diffusely increased density could be indicative of ....
Focally increased density
Localised osteoblastic metastases/tumor, Avascular necrosis of bone (such as in hip), and Paget disease or CCPD would look like what
Diffusely decreased density
Osteoporosis and Hyperparathyroidism would look like ...
Focally decreased density
Localized osteoclastic metastases, multiple myeloma, osteomyeloma would look like ...
False! Metastases to bone are more common
T/F: Metastases to bone are less common than primary bone tumors?
Prostate CA
What is the MC cause in older men of osteoblastic metastasis?
Diffuse
Image on the left is normal, is the image on the right diffuse or local?
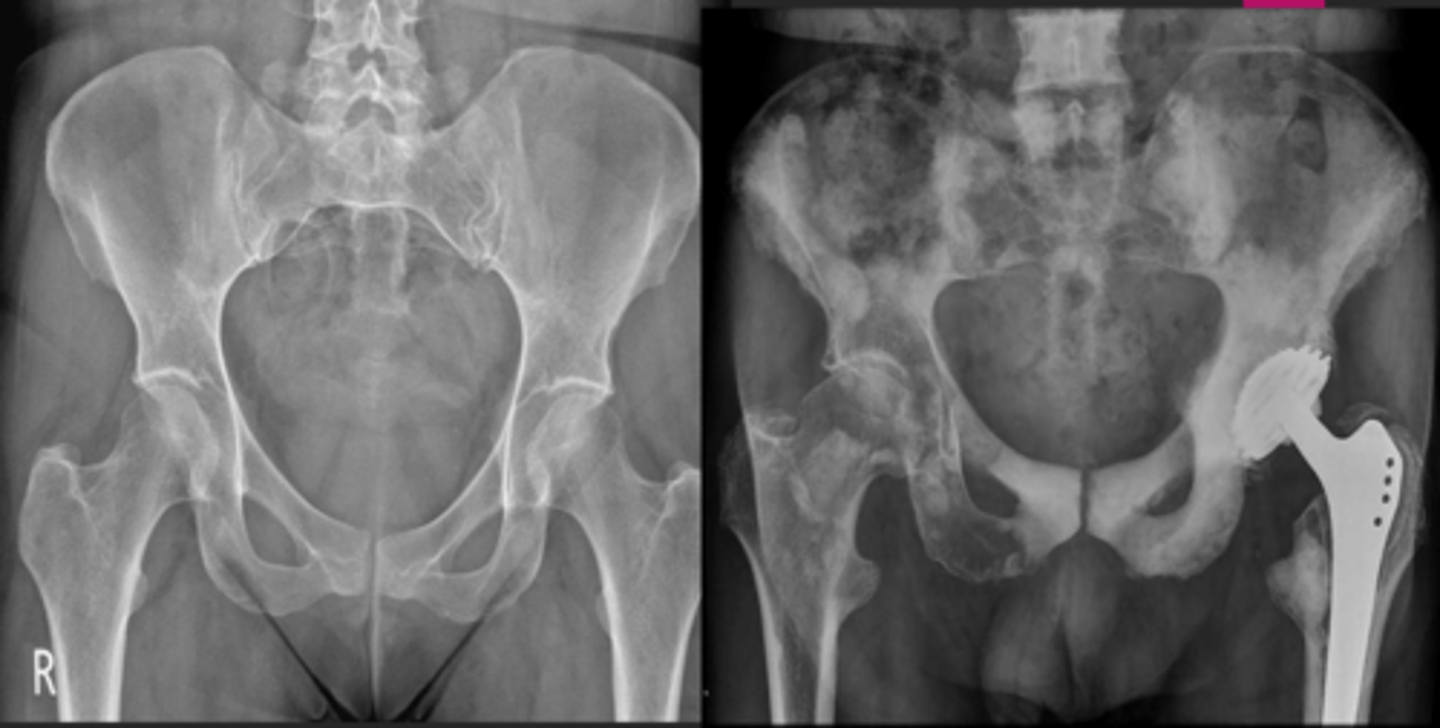
Local
Osteoblastic/sclerotic bone lesion - is this diffuse or local?
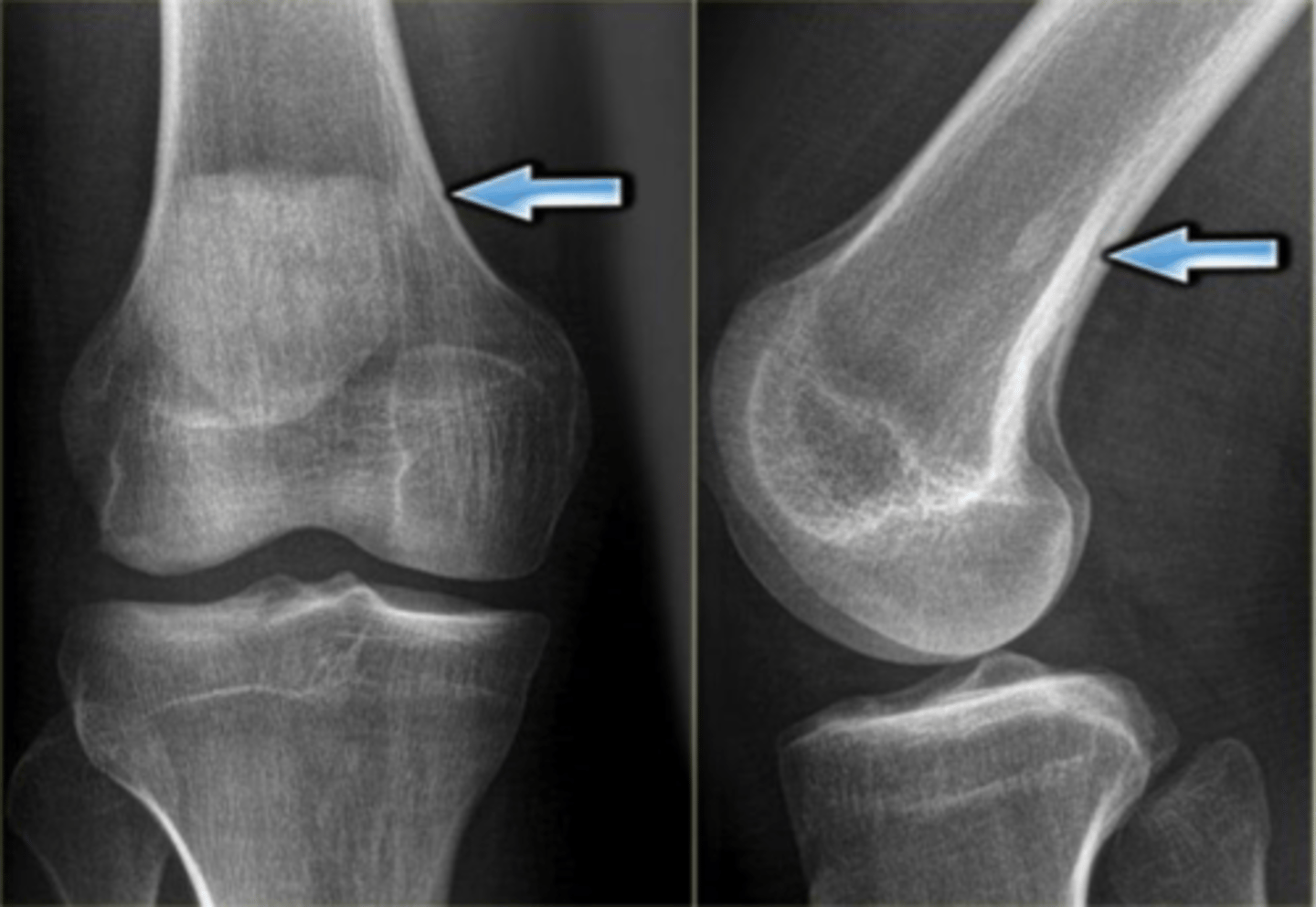
Increased
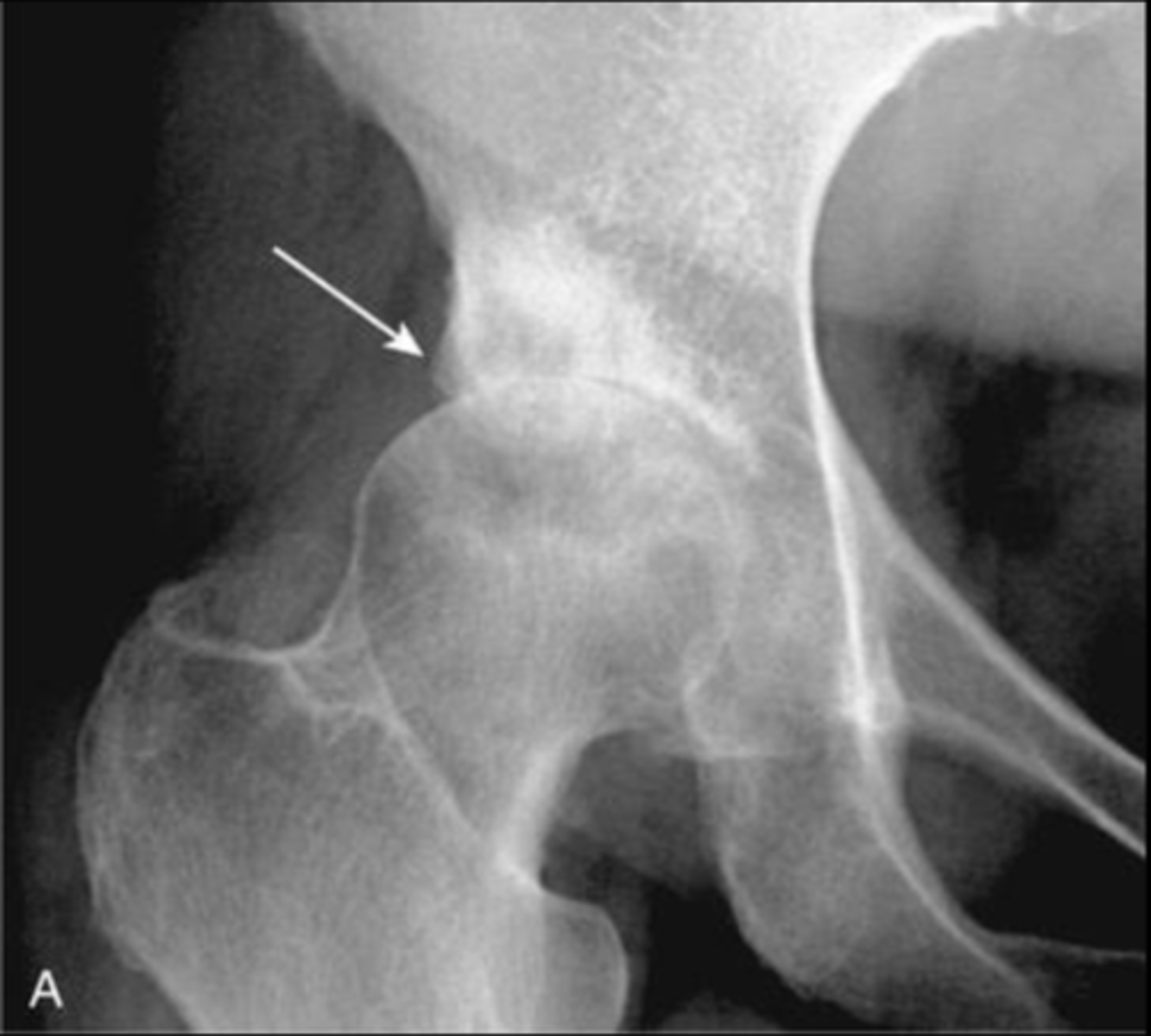
AVN - in later stages, will the lesion appear as increased or decreased density?
MRI
What imaging test is most sensitive for detecting AVN?
AVN
Legg-Calve-Perthe's disease is one of the many causes of
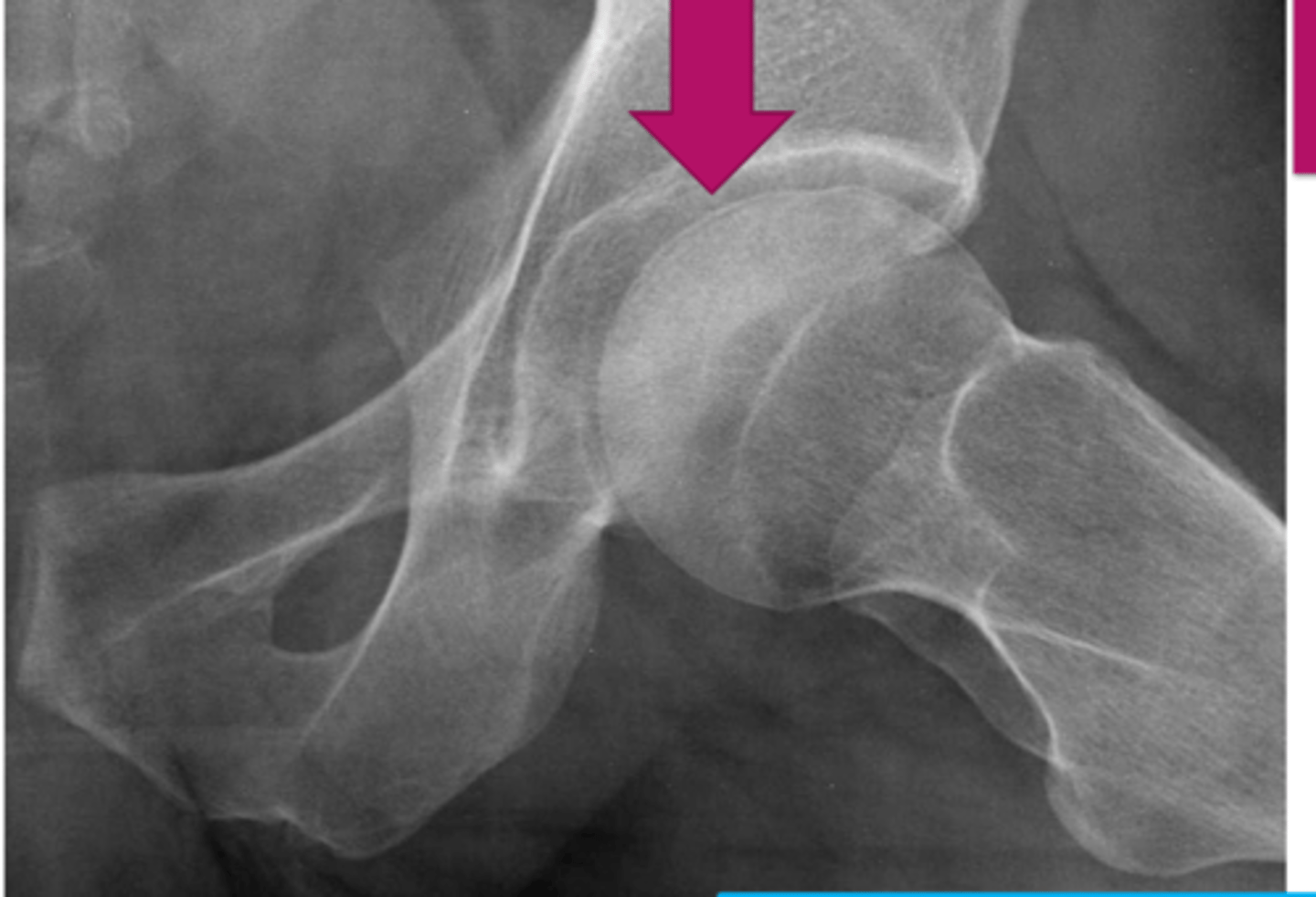
Crescent sign
AVN of femoral head- What is the name of this sign?
Paget's disease
This is a chronic disease of bone characterized by varying degrees of increased bone resorption and increased bone formation
1. thickening of the cortex
2. coarsening and thickening of the trabecular pattern
what are the 2 hallmarks of Paget's disease?
Conventional radiography (x-ray)
What radiologic test would you use to diagnose Paget's disease?
Paget's disease ? (not sure can someone confirm)
Identify
CCPD seen in pseudogout
Pls identify
Osteoclastic
Hyperparathyroidism leads to an increase in _______ activity
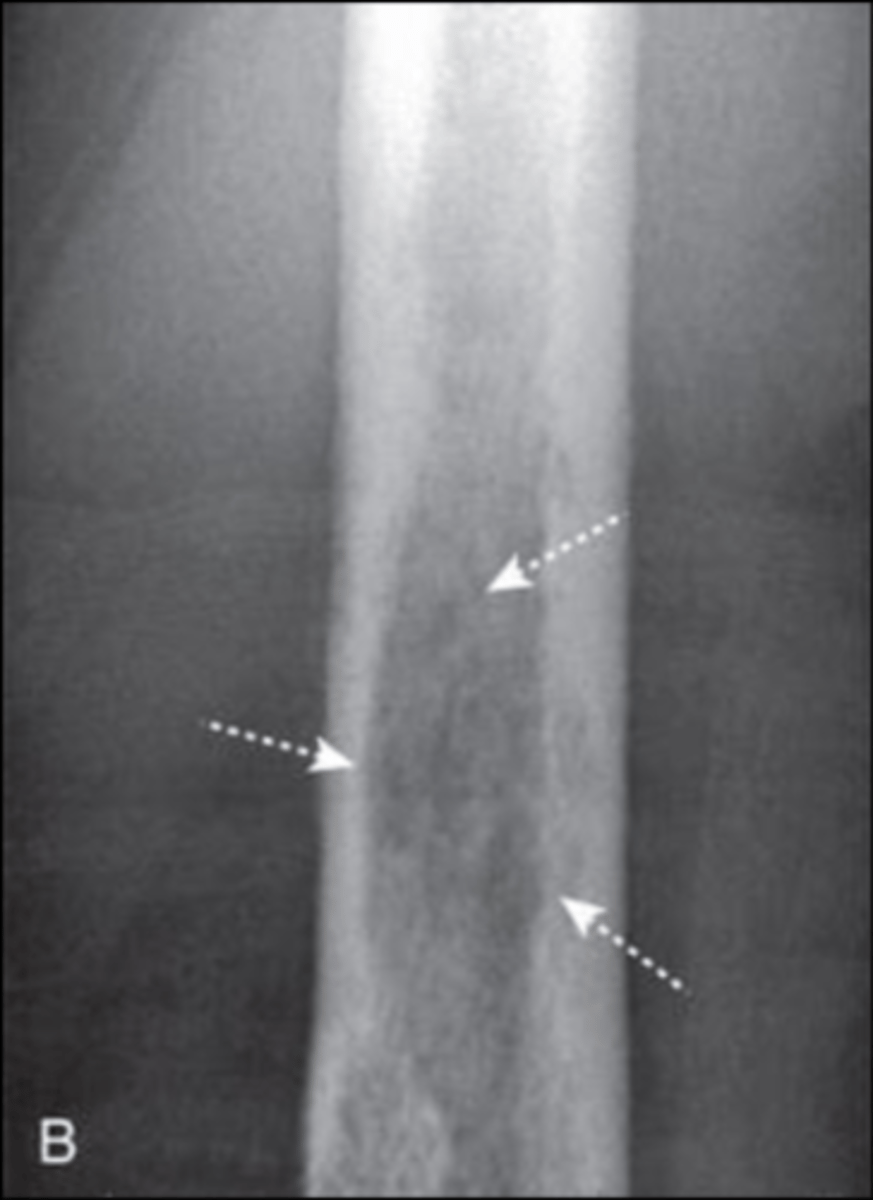
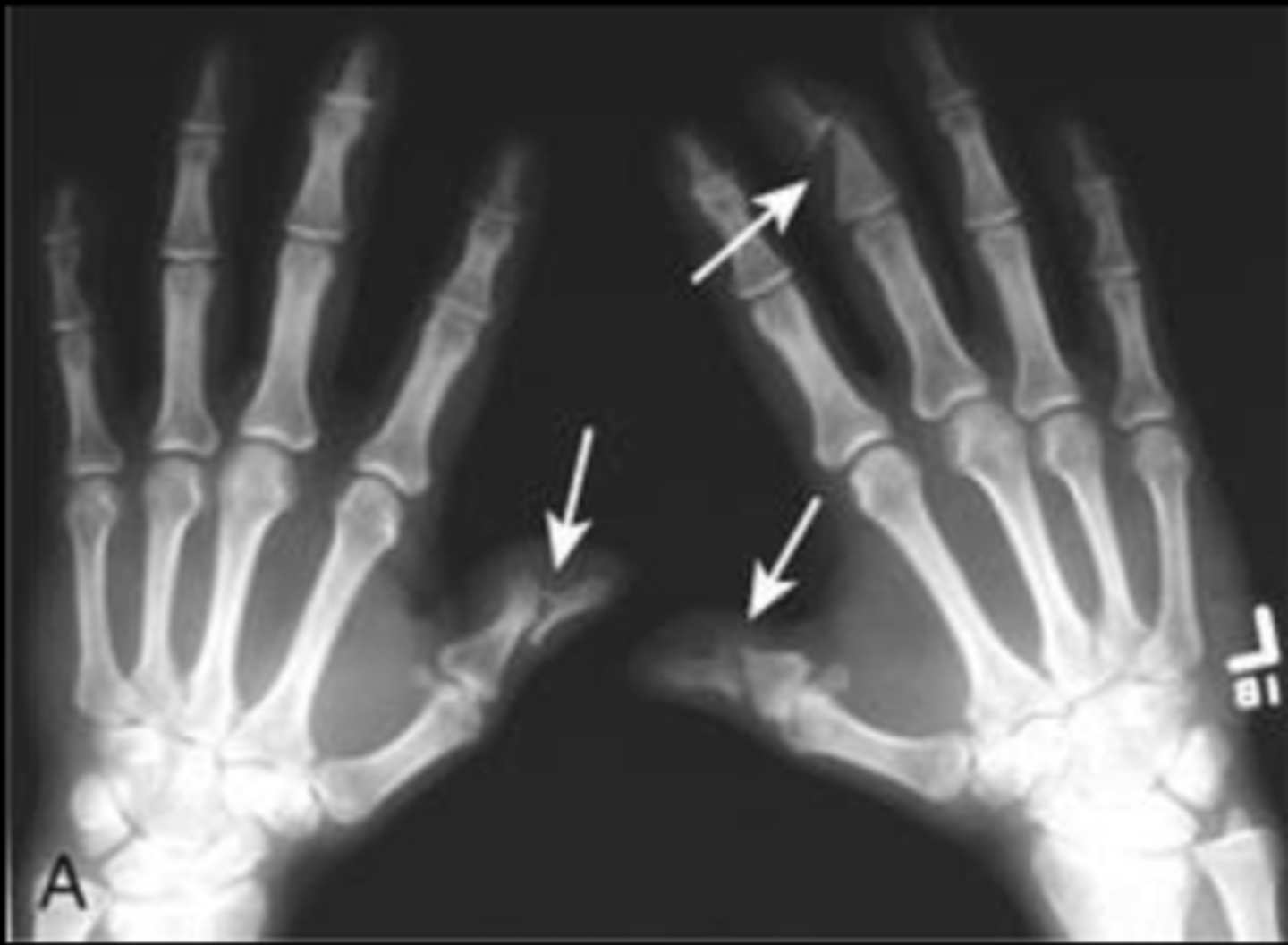
Focal lesion
What are the white arrows pointing to?
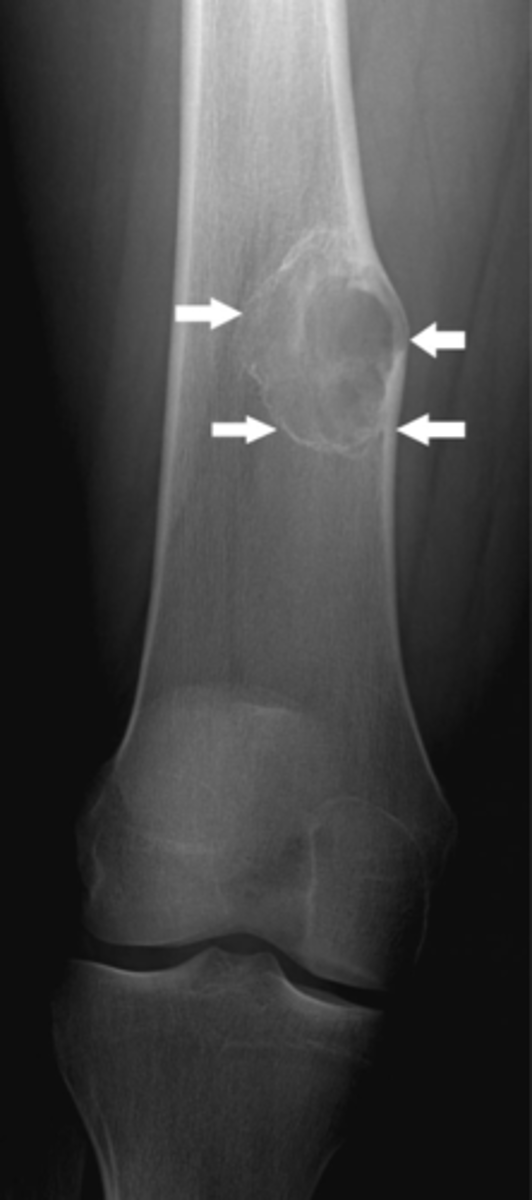
Focal lesions
These are examples of ...
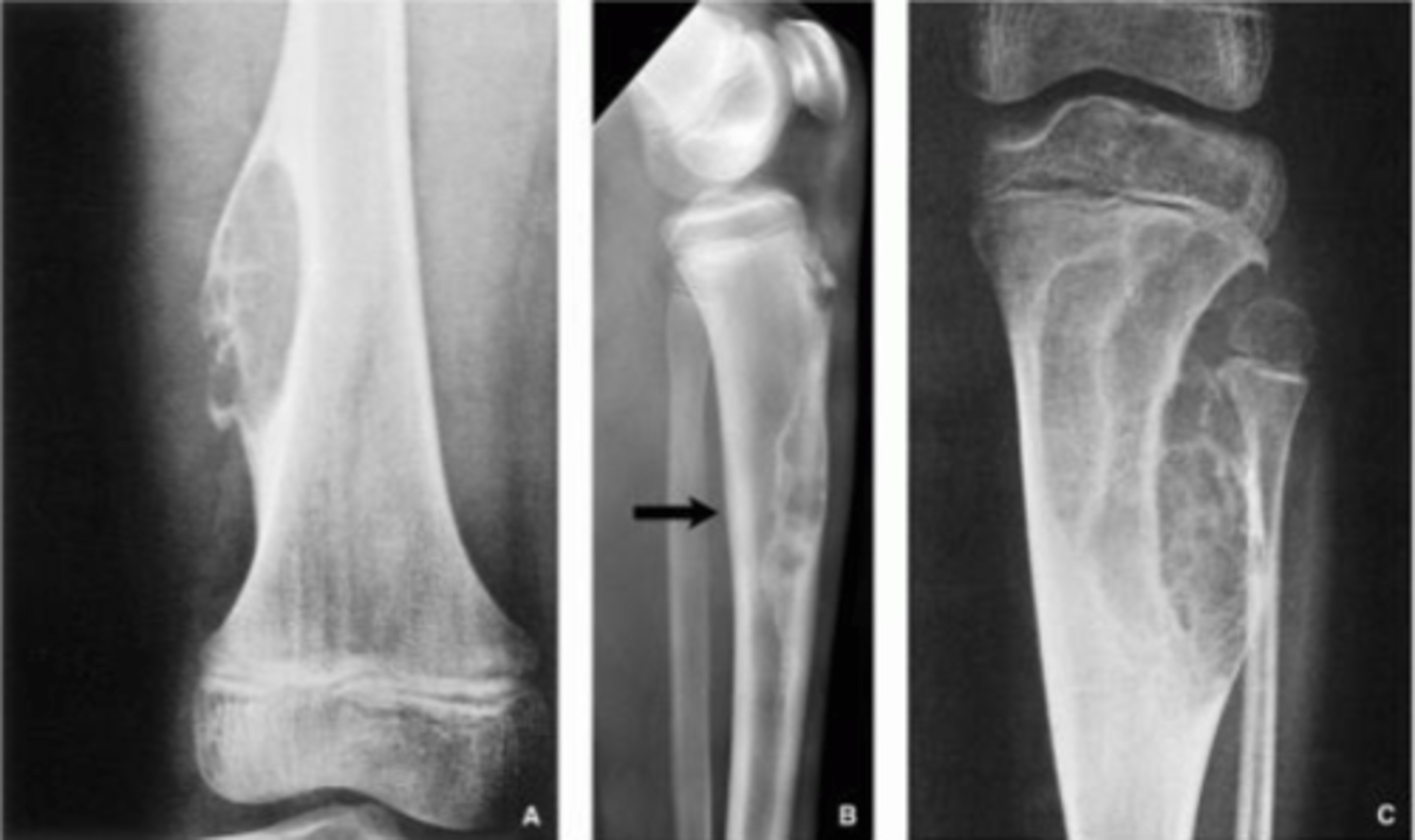
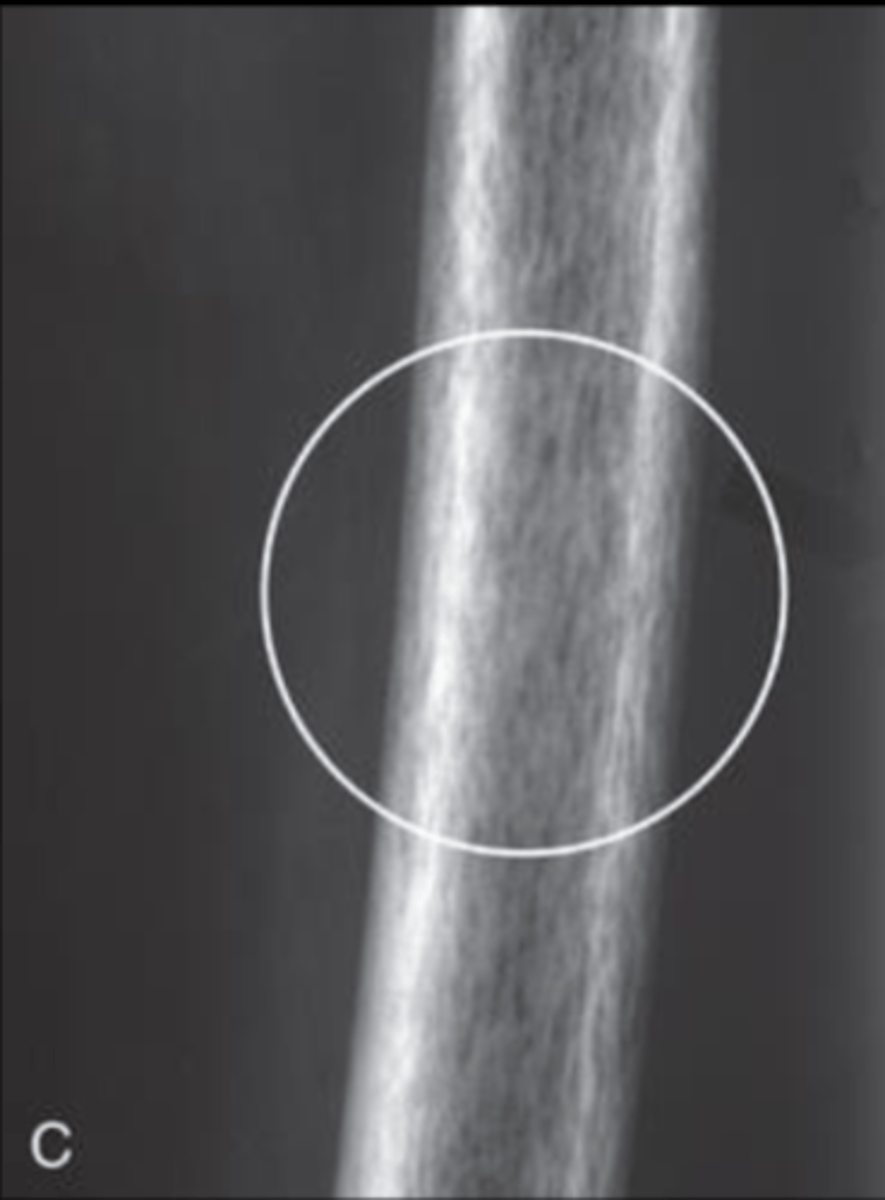
Geographic
Accurately describe this pattern of bone destruction
Mottled (moth eaten appearance)
Accurately describe this pattern of bone destruction
Permeative
Accurately describe this pattern of bone destruction
Multiple Myeloma
What is the most common primary malignancy of bone (marrow) in adults?
Lytic lesions "punched out"
Multiple myeloma creates what type of lesions?
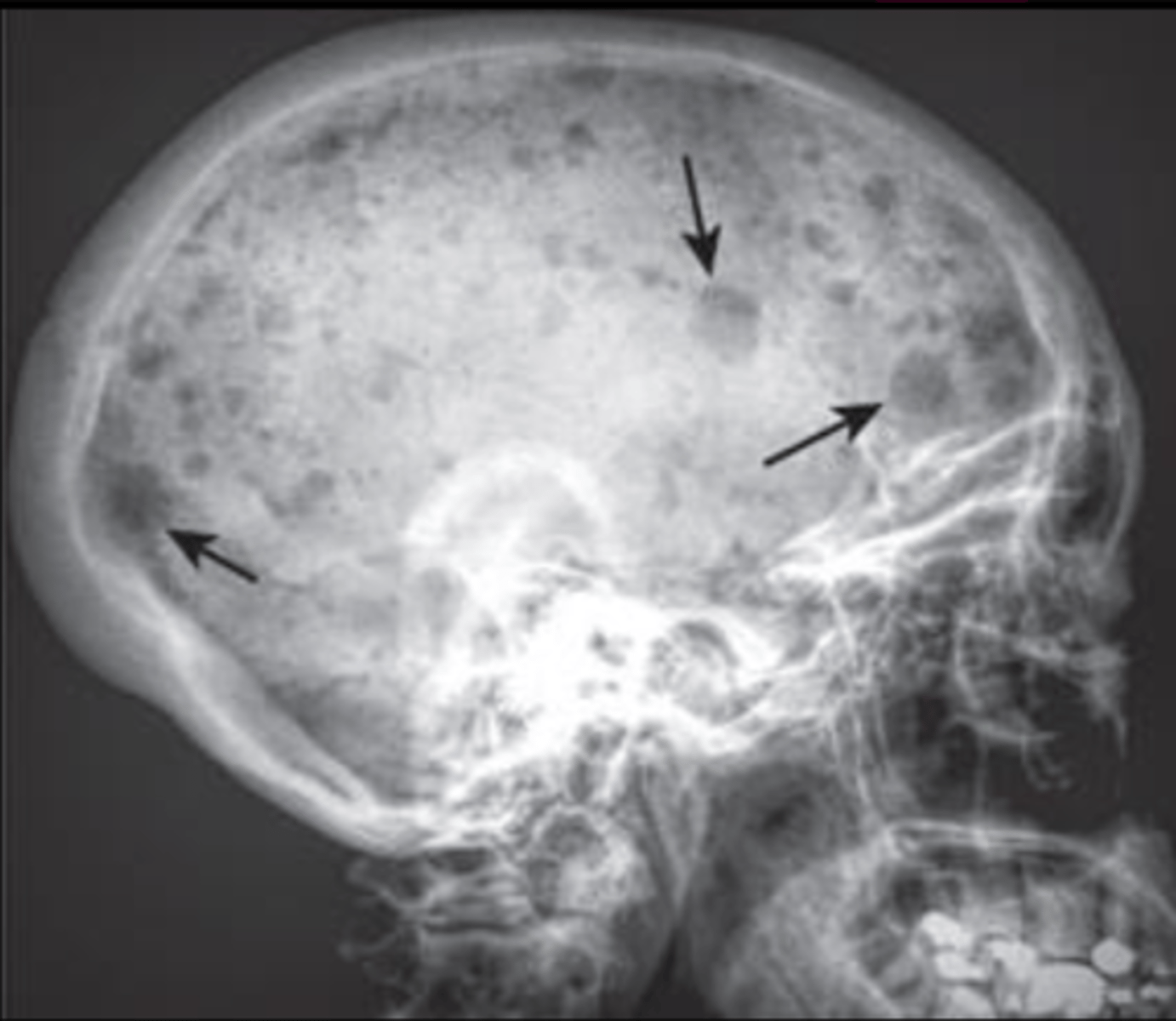
Diffuse spinal osteoporosis
What is the hallmark of MM?
MM
diffuse lytic lesions in skull - think?
Osteomyelitis
Hallmark on radiograph is destruction of the articular cartilage, release of synovial fluid
Can be both!
Would arthritis be increased or decreased in density on x-ray?
Arthritis
Joint space narrowng think
Joint
Is arthritis more of a joint or bone disease?
Osteophyte formation
What is the hallmark of hypertrophic arthritis?
Degenerative joint disease (DJD)
MC type of arthritis?
excessive wear and tear
MC cause of DJD
OA
68 YOM pt comes in complaining of joint pain and this is what the x-ray shows. Dx?
Erosive arthritis
RA, gout, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis are examples of ...
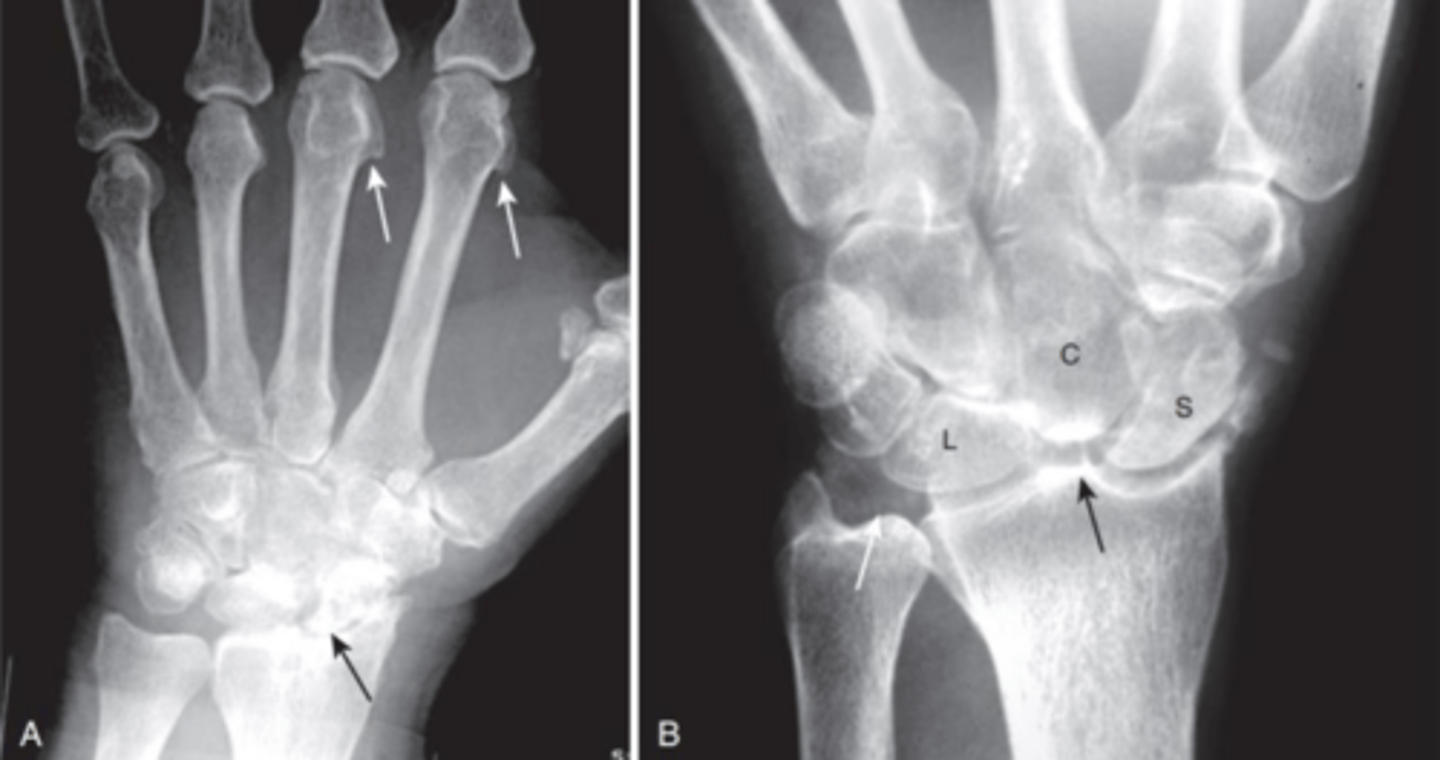
Rheumatoid arthritis
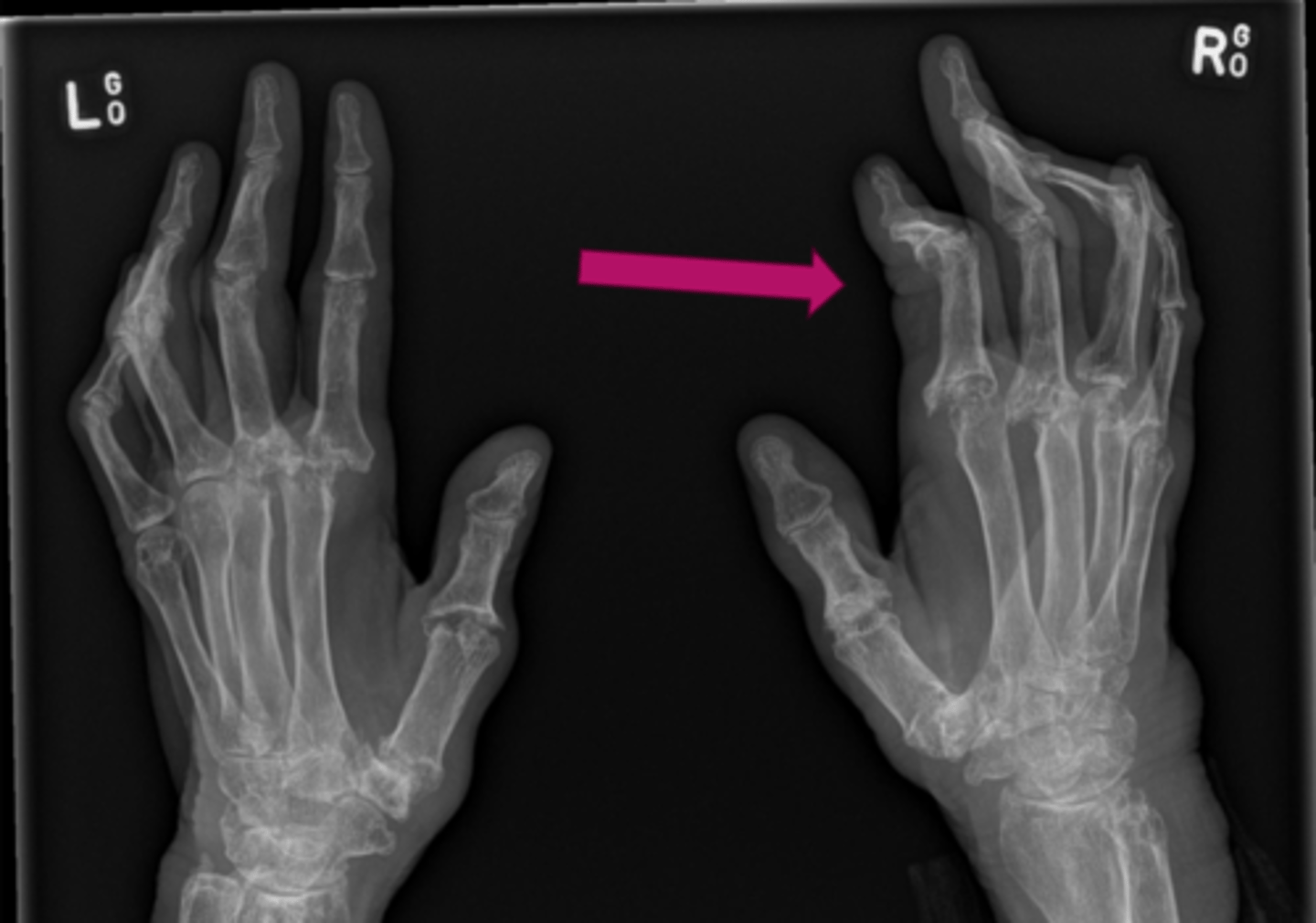
45 YOF presents with joint pain involving proximal joints of hands and wrists, symmetrically, bilaterally. You also see ulnar deviation of the fingers at the MCP joints, subluxation of the MCP joints as well as swan neck and boutonniere deformities. Most likely dx?
Boutonniere and Swan neck deformity
What do you see?
Gout
Calcium urate crystal deposition think ...
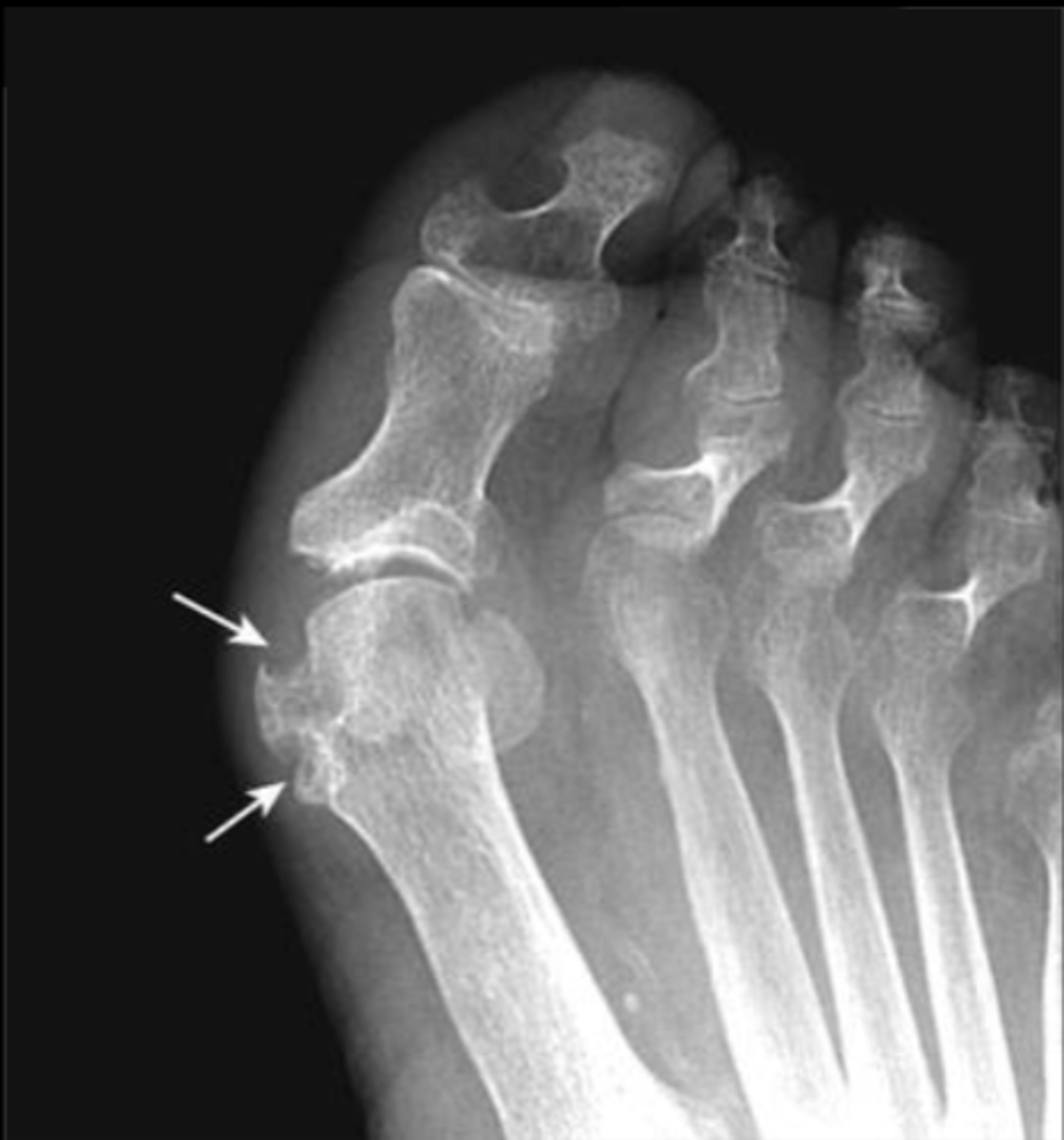
Metatarsal phalangeal joint of great toe
Where (anatomically) does gout MC affect?
Gout
Hallmark of this disease is sharply marginated, juxtaarticular erosion that tends to have a sclerotic border ("rat bites")
Gout
Please identify most likely dx
Pencil in a cup
What sign is this?
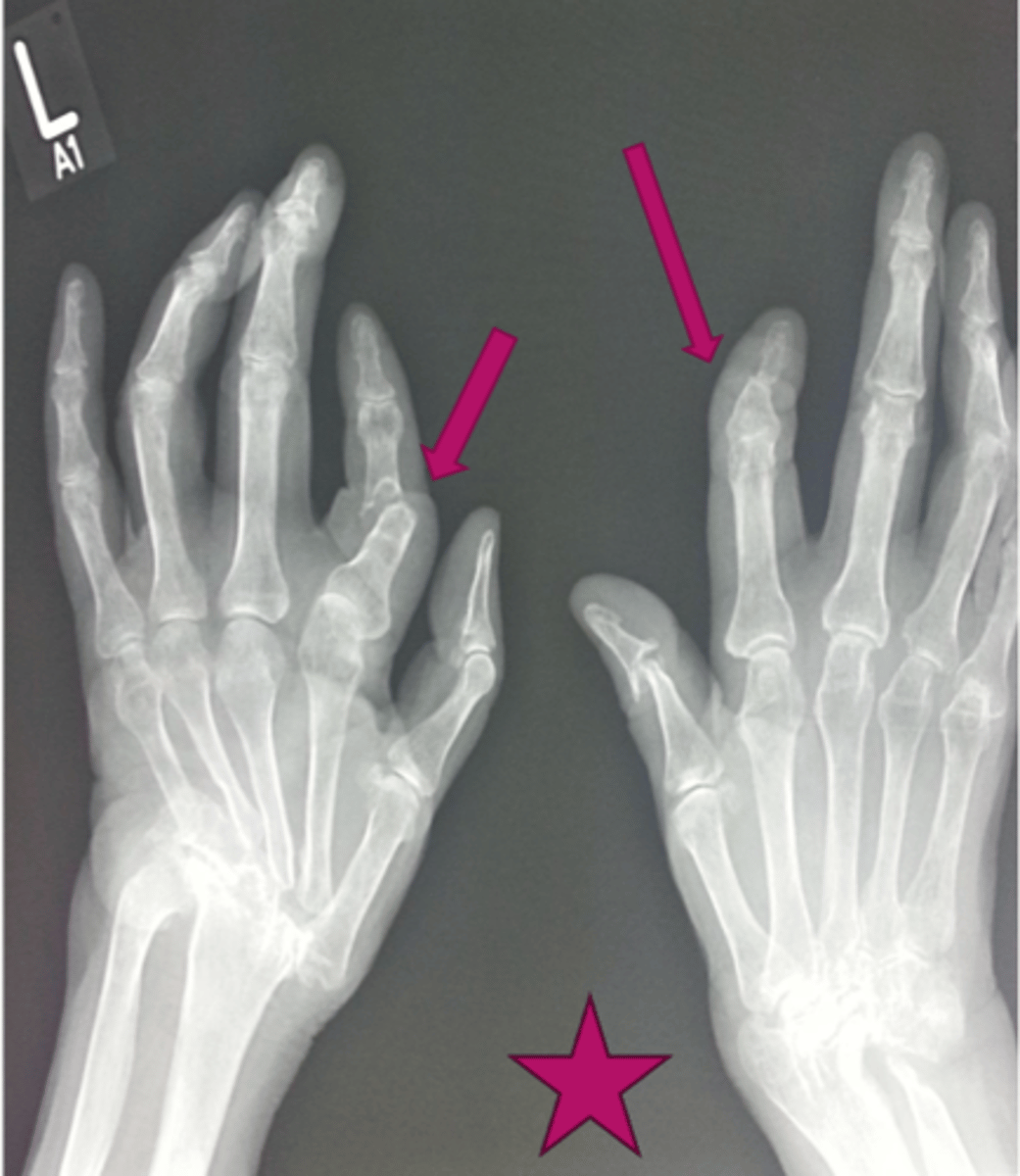
Psoriatic arthritis
Most likely Dx here?
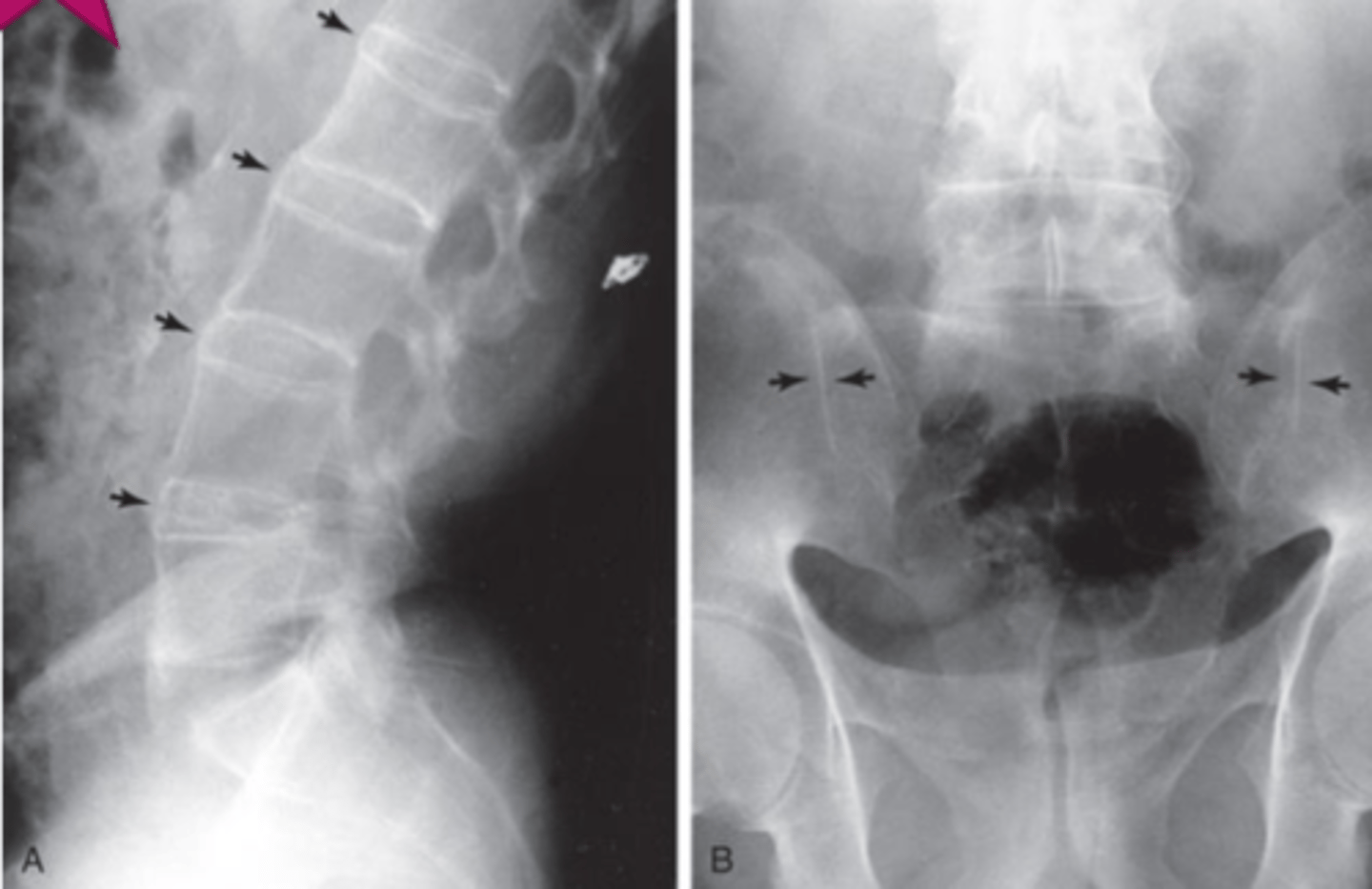
Bamboo spine - Ankylosing spondylitis
What's this sign and what dx?
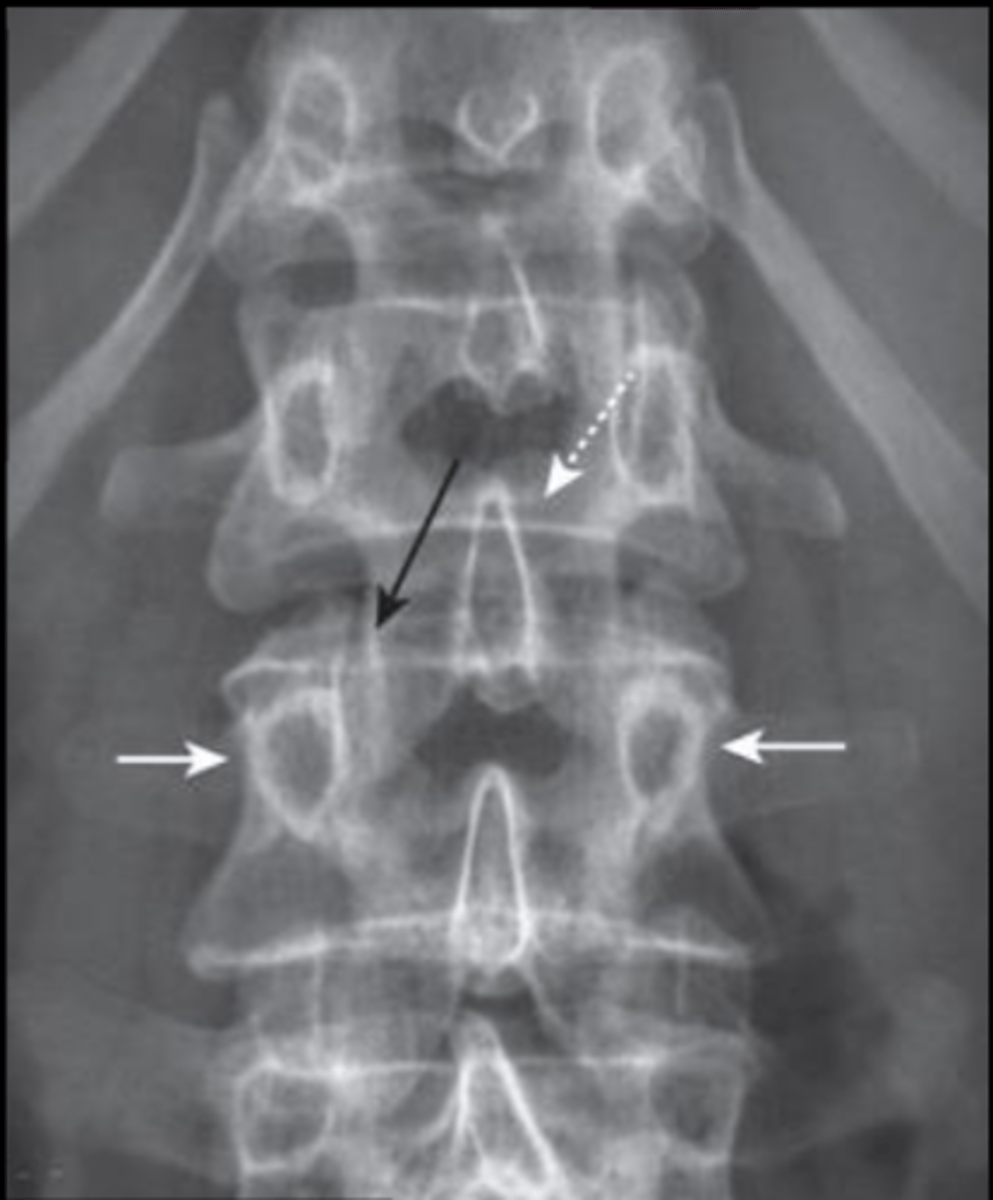
Ankylosing spondylitis
Louis, 25 YOM, presents with complaints of lower back pain and stiffness. X-ray came back with Bamboo spine deformity, fusion of lumbar and sacroiliac joints. Pt also tested positive for HLA-B27. Hx of UC. Most likely Dx?
Normal L-spine
Please identify
MRI
What is the test of choice for spine diseases?
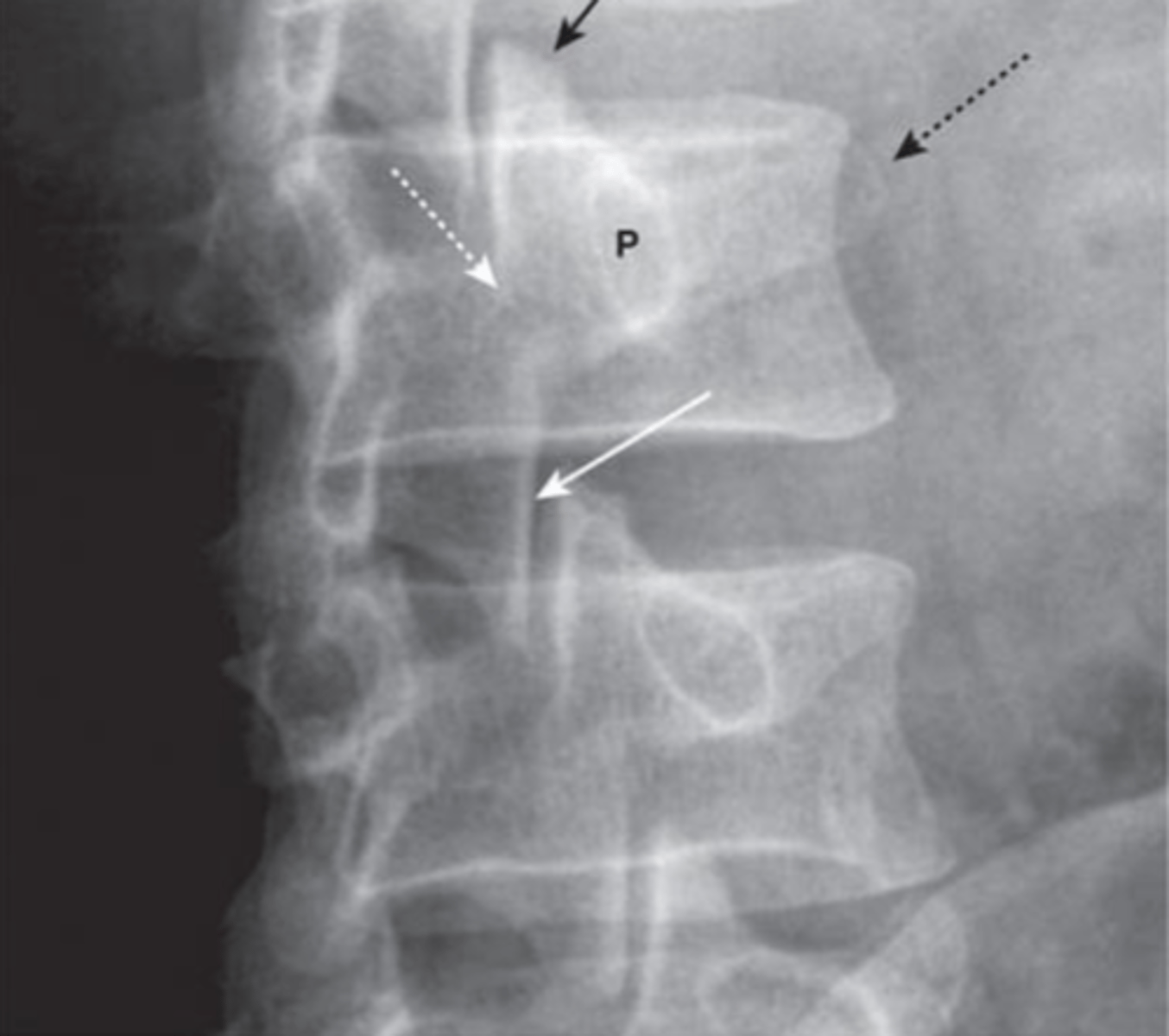
Scottie dog sign
Oblique view- what's this sign?
Degenerative disk disease
spaces above and below are not uniform
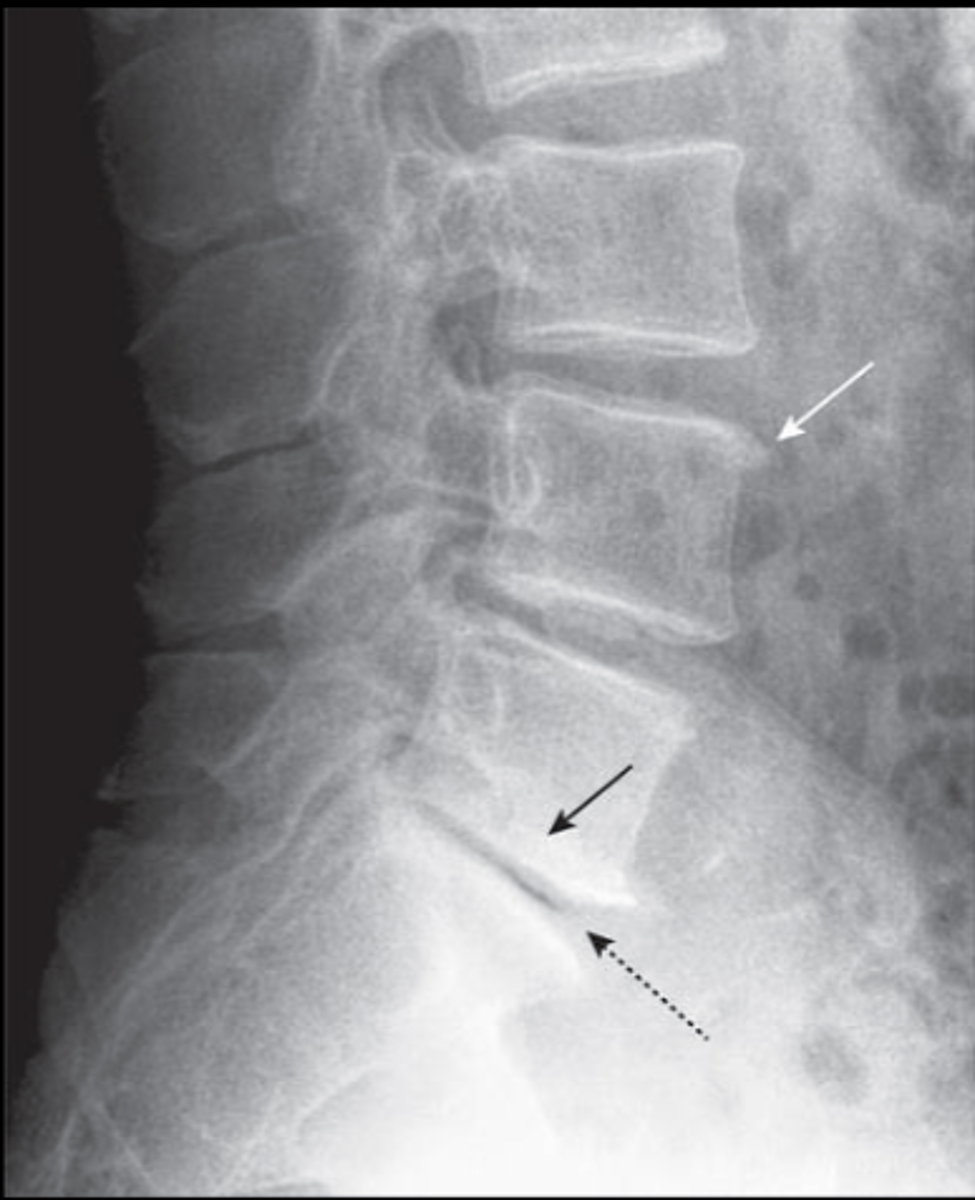
Compression fracture
Please identify
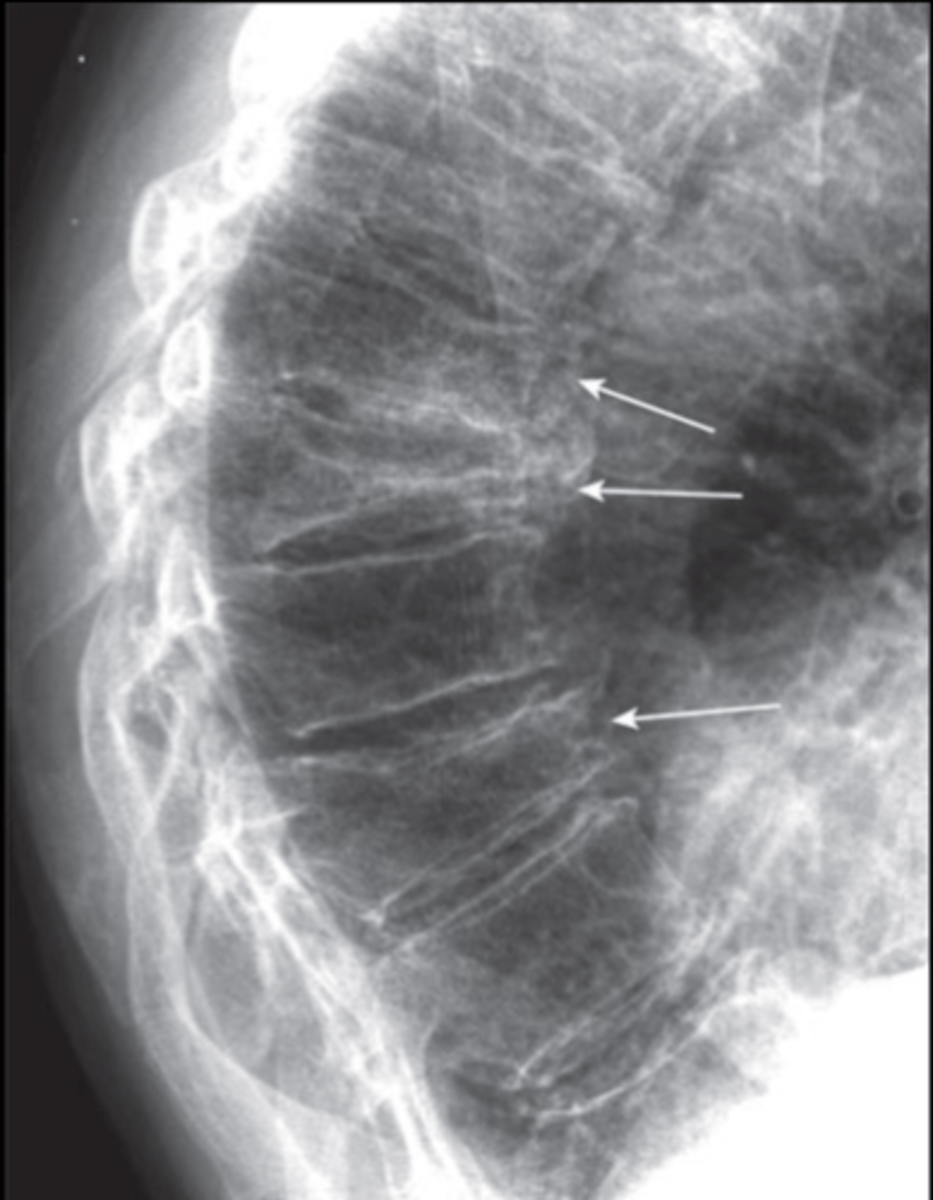
Conventional spine radiographs (X-ray)
Study of first choice for compression fractures
Anterior and Superior
Osteoporotic compression fractures usually involve the _____ and _____ aspects of the vertebral body
Compression fracture
Identify
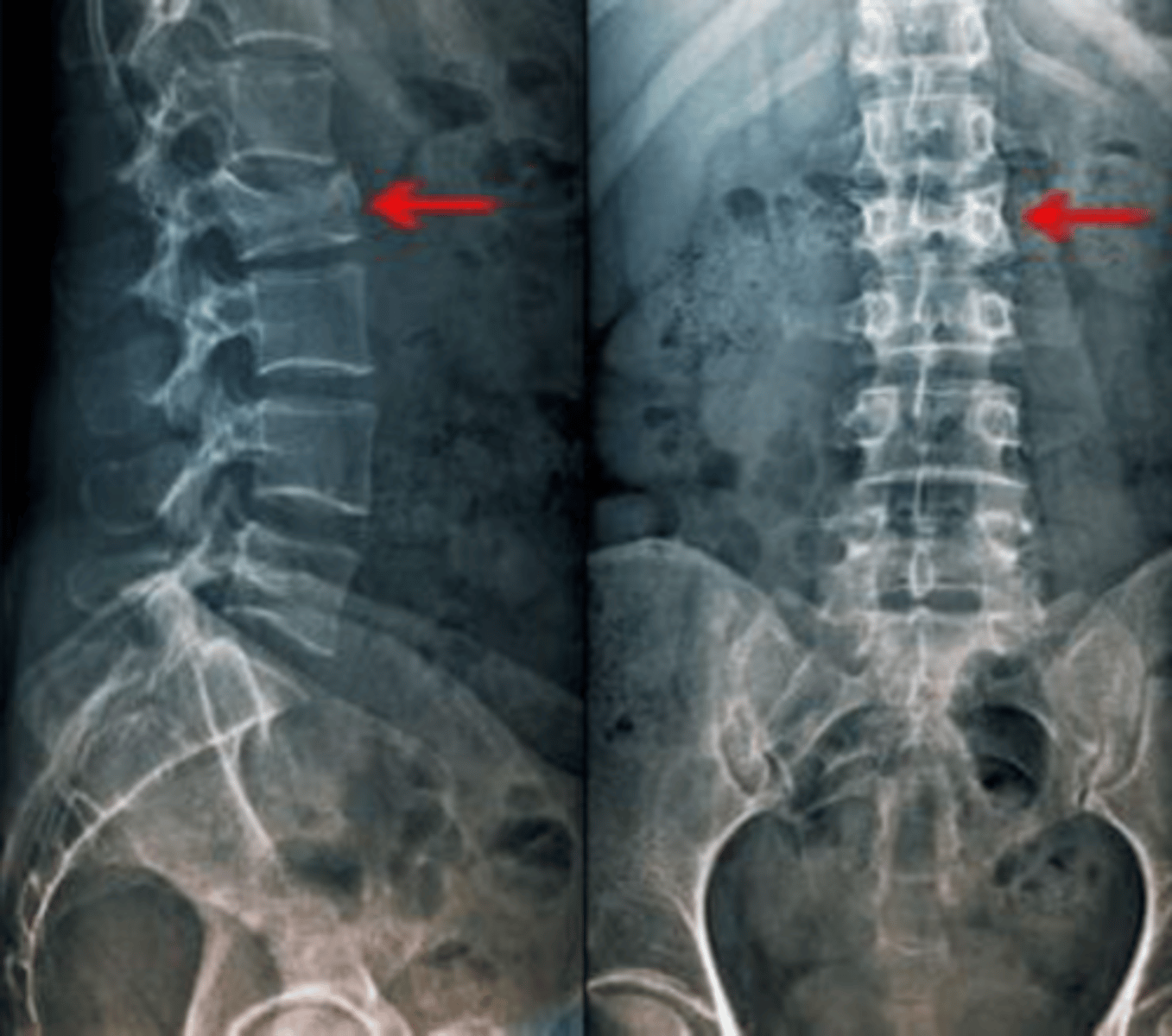
Spinal stenosis
Narrowing of the spinal canal
Cervical and lumbar areas
Where is spinal stenosis most common
Flexing
Neurogenic claudication is relieved by ______ the spine
X-ray
First test for spinal stenosis
MRI
Test of choice for spinal stenosis
Complete fracture
Identify
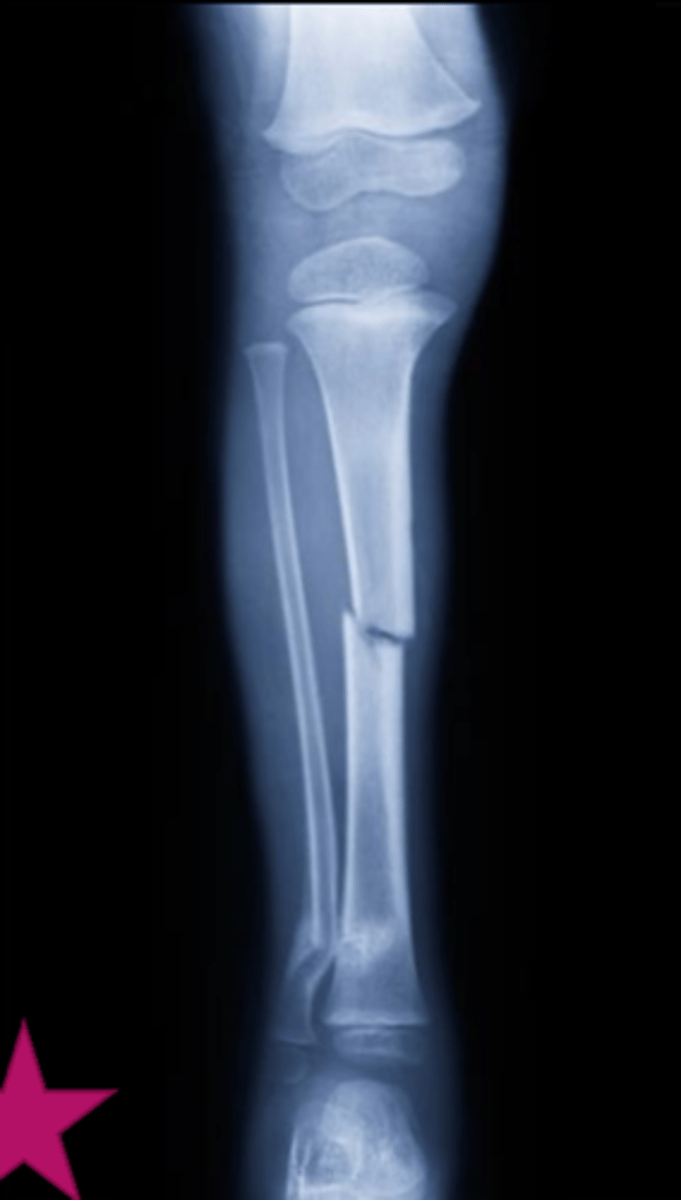
Fracture
disruption in the continuity of all or part of the cortex of a bone
Incomplete fracture
Only part of the cortex is fractured
Complete fx
Fracture through and through
True
T/F: in growing bone there are added calcifications because of the growth plate involvement
Type 3
Fracture below the growth plate - Salter Harris classification?
False! Type 3 can develop arthritic changes or plate fusion
T/F: Salter Harris fx Type 1-3 heal well
Type 4 and 5
Which salter harris fx type is more likely to develop early fusion of the growth plate with angular deformities and shortening of the bone when healing
Type 3
Fracture of epiphyseal plate and epiphysis itself
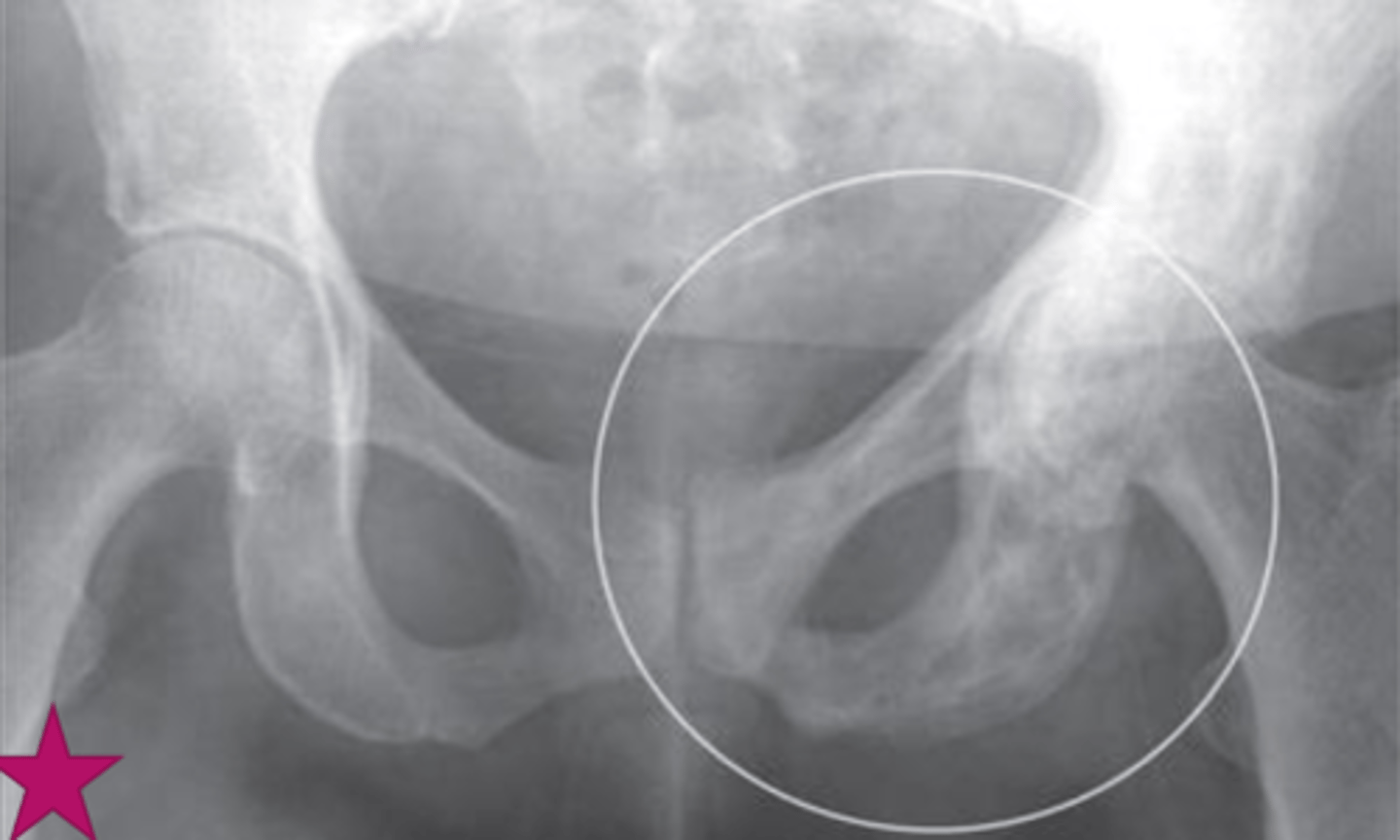
Klein's line
What is the name of line the arrow is pointing to
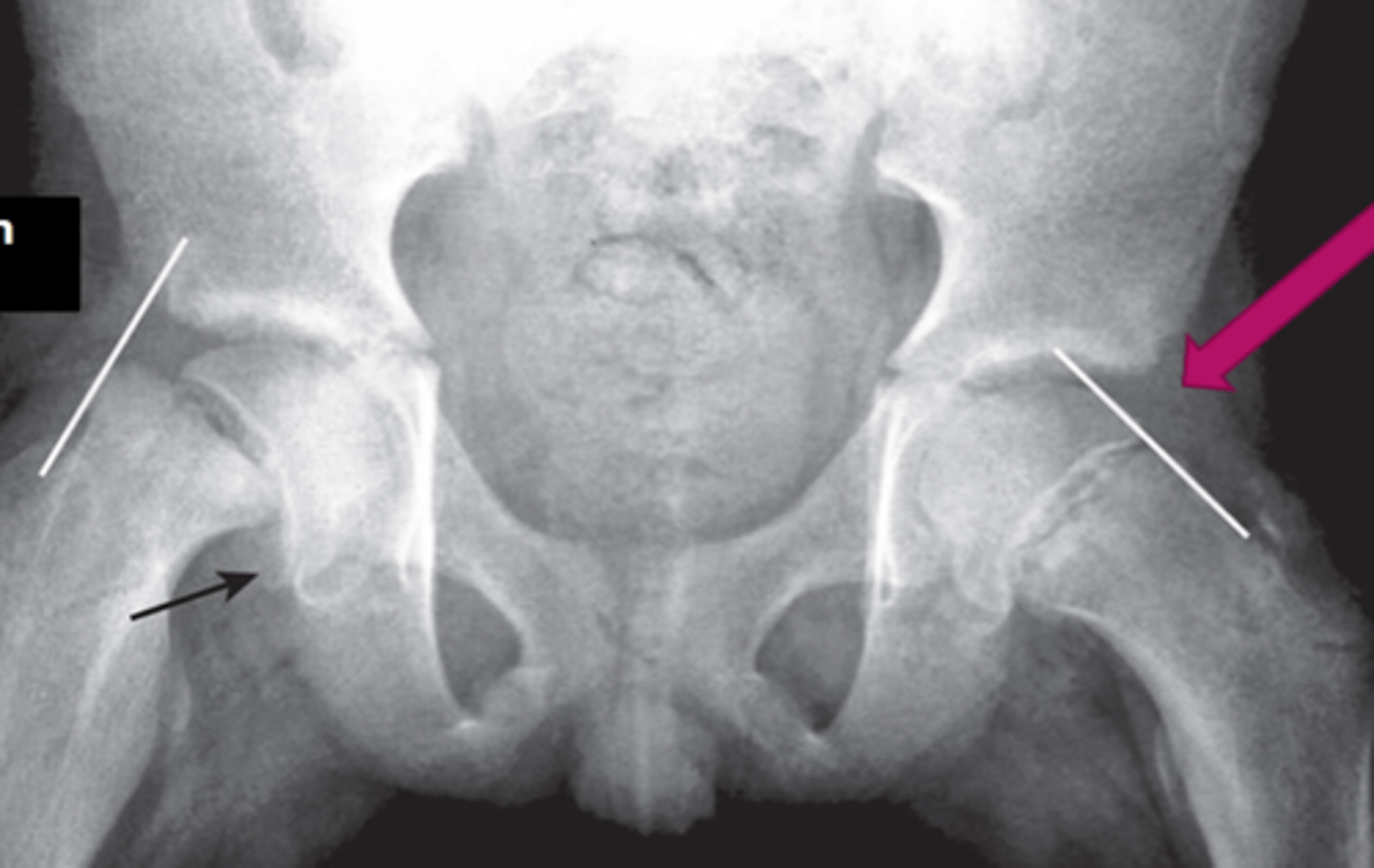
Trethowan sign
What is this sign called
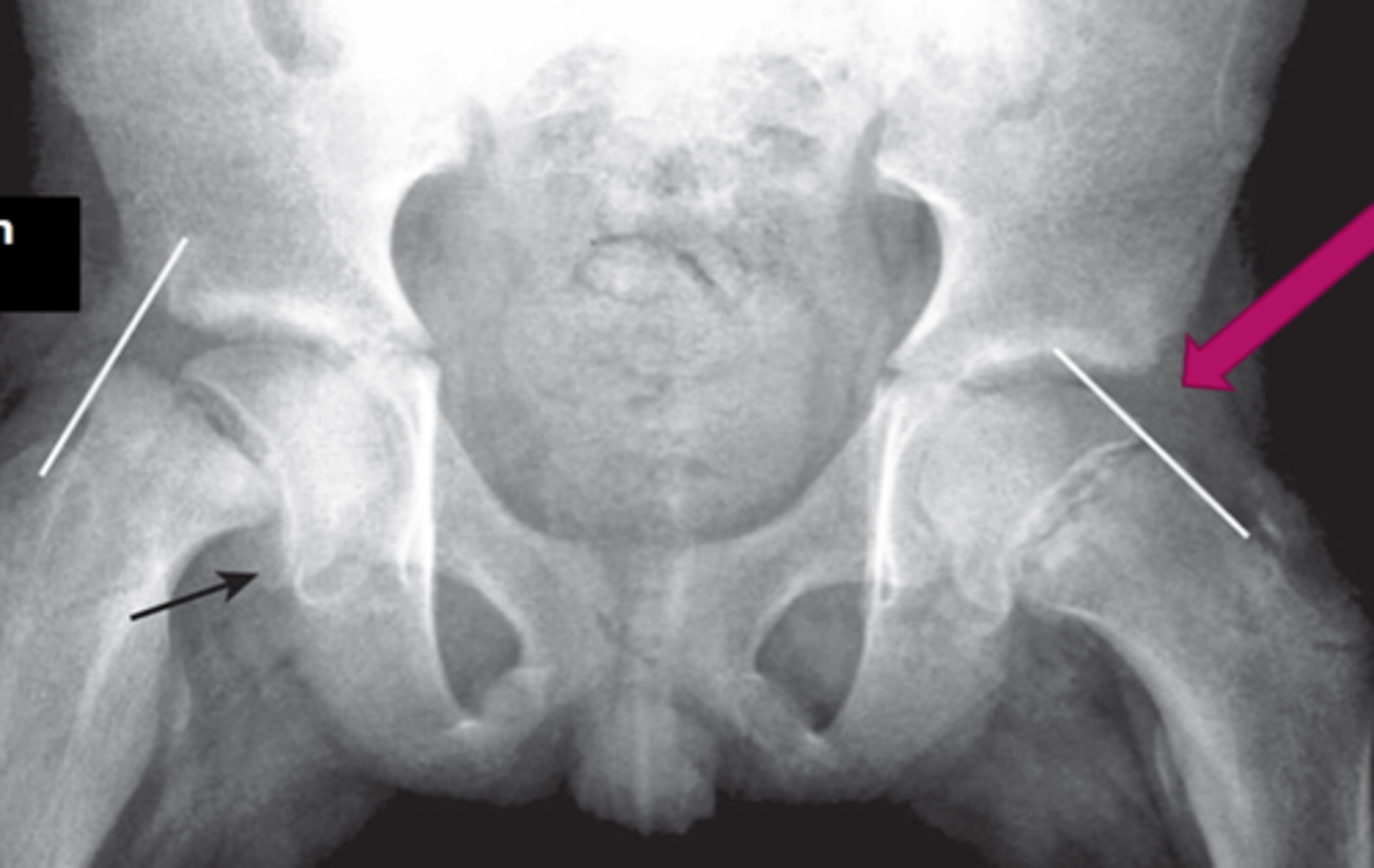
early slipped upper femoral epiphysis
What is Klein's line used to detect?
Type 2
MC type of SH fx?
Corner sign
Type 2 SH fx produces what sign
Type 2
Fracture of epiphyseal plate and metaphysis
SH Type 2 (A= above the growth plate)
Fx type?
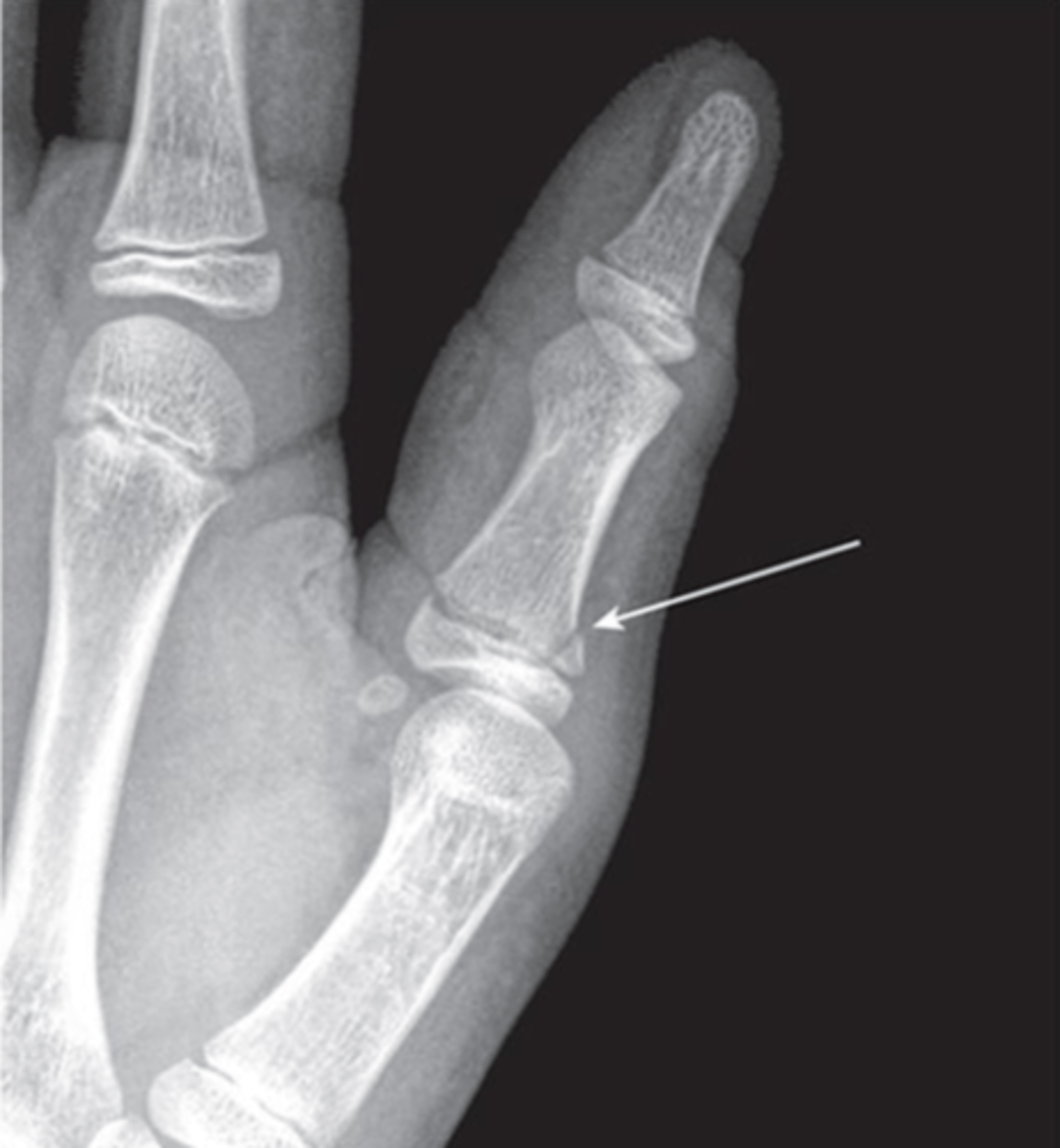
Type 3
Which SH type can cause premature closure of the growth plate?
Type 3 (L=beLow the growth plate)
Fx?
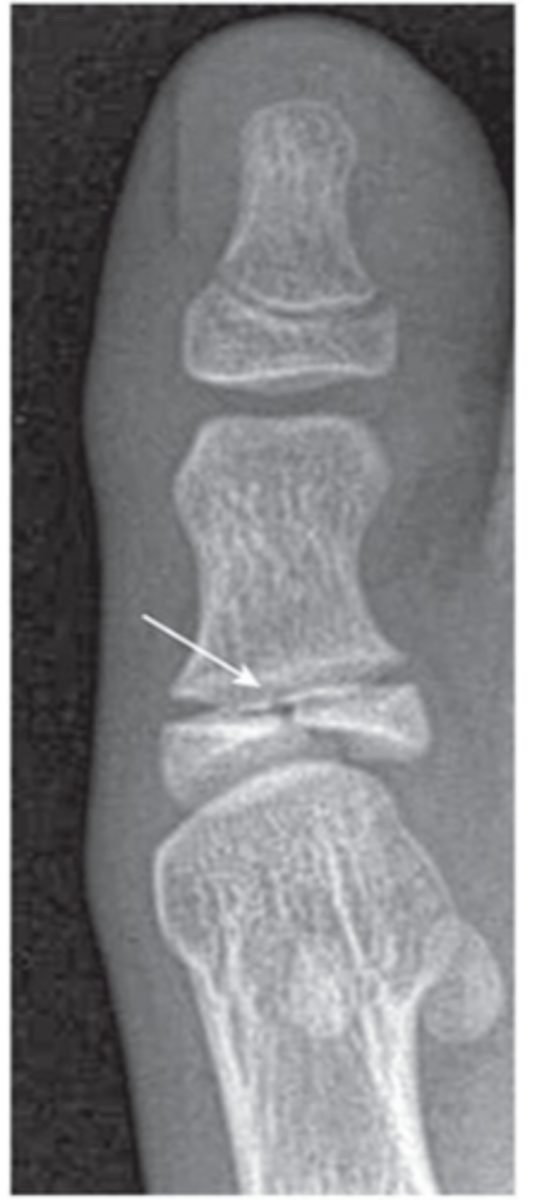
Type 4
Fracture of epiphyseal plate, metaphysis, and epiphysis
Type 4
Premature and asymmetric closure of the growth plate - can cause leg length differences
Type 4
Fx?
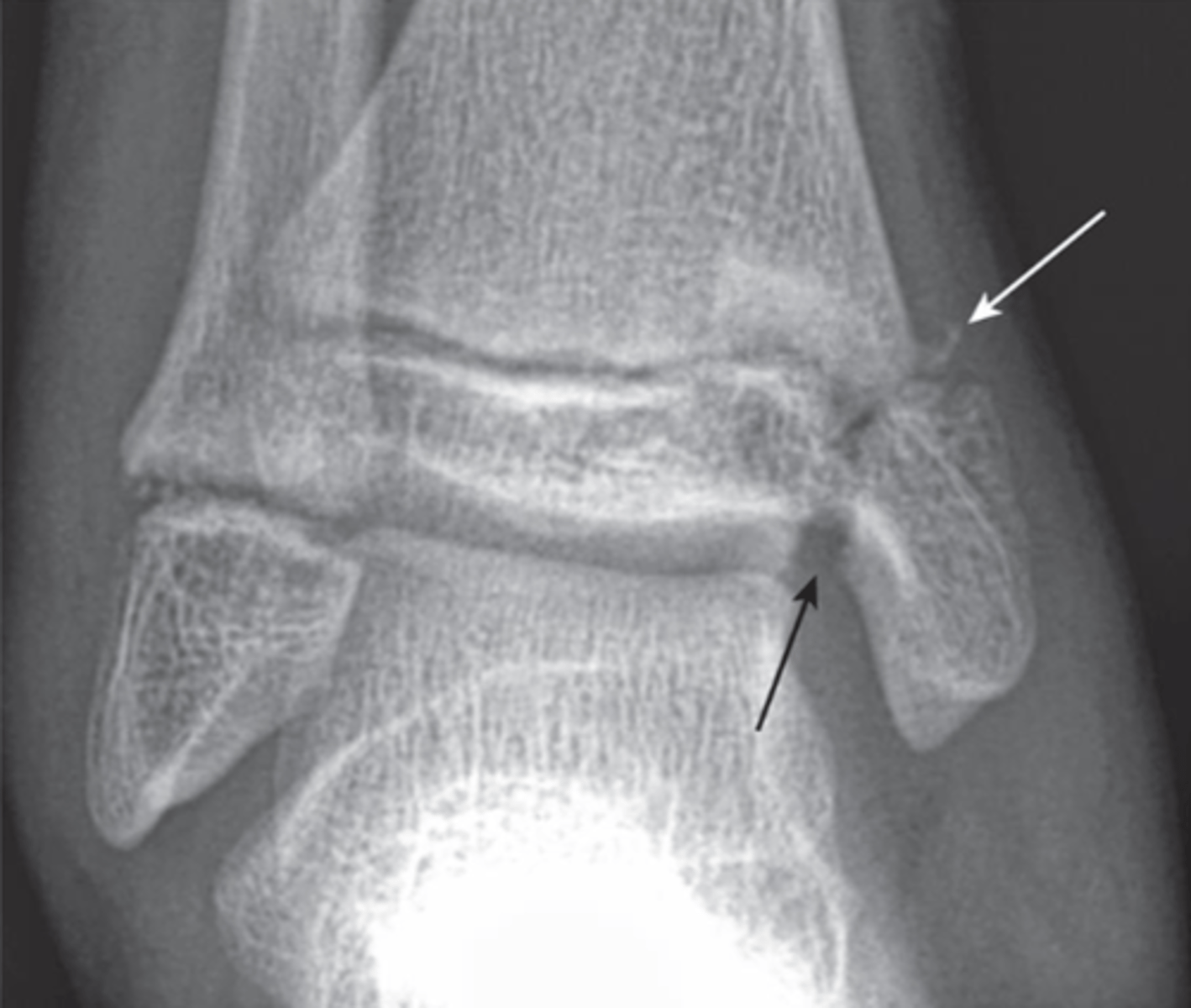
Type 5
Crush type of fx
Type 5
SH fx?
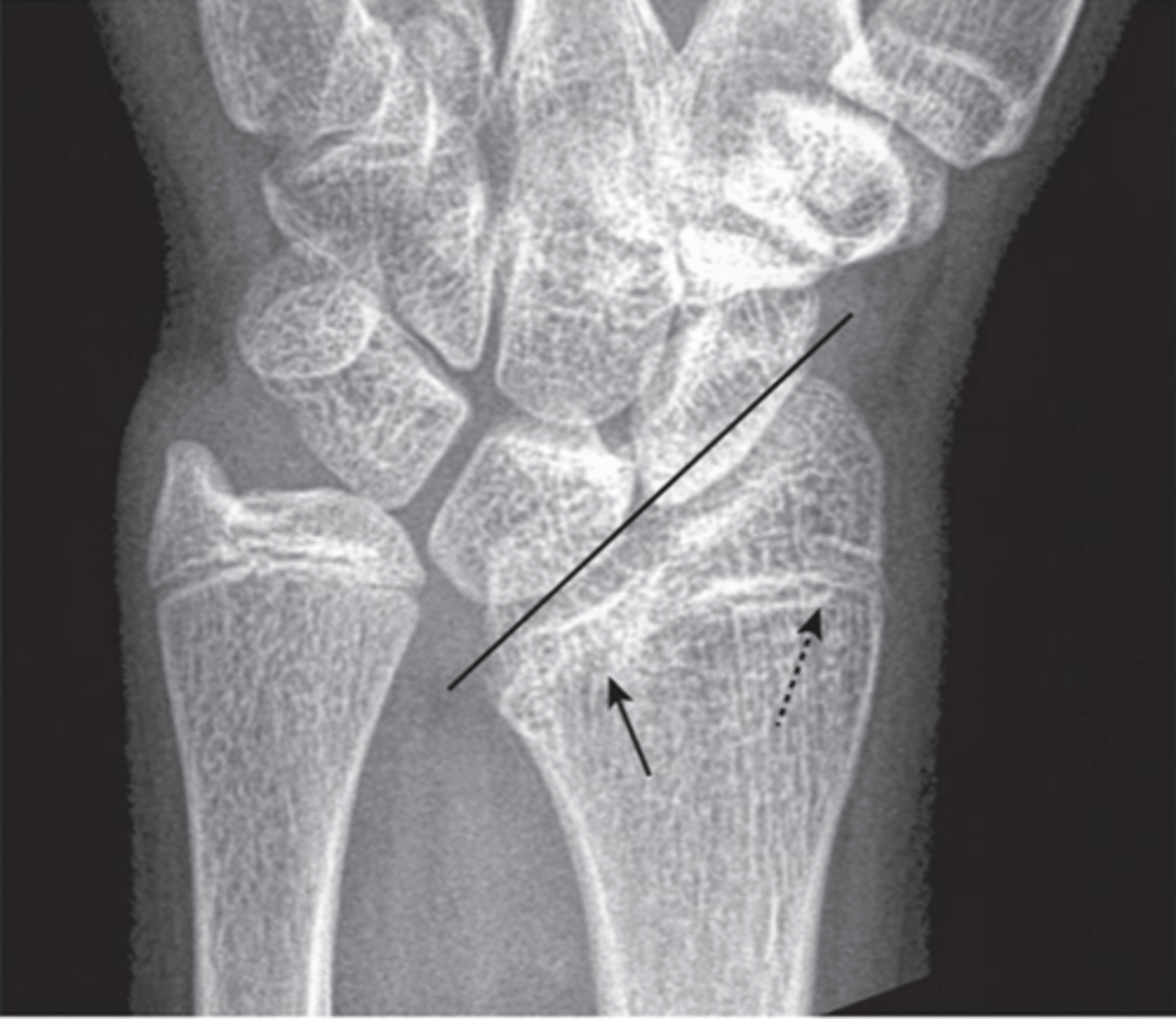
Accidental
Are SH fx accidental or intentional?
Metaphyseal corner fractures
Rib fx
Head injuries
3 injuries that should raise your suspicion for child abuse?
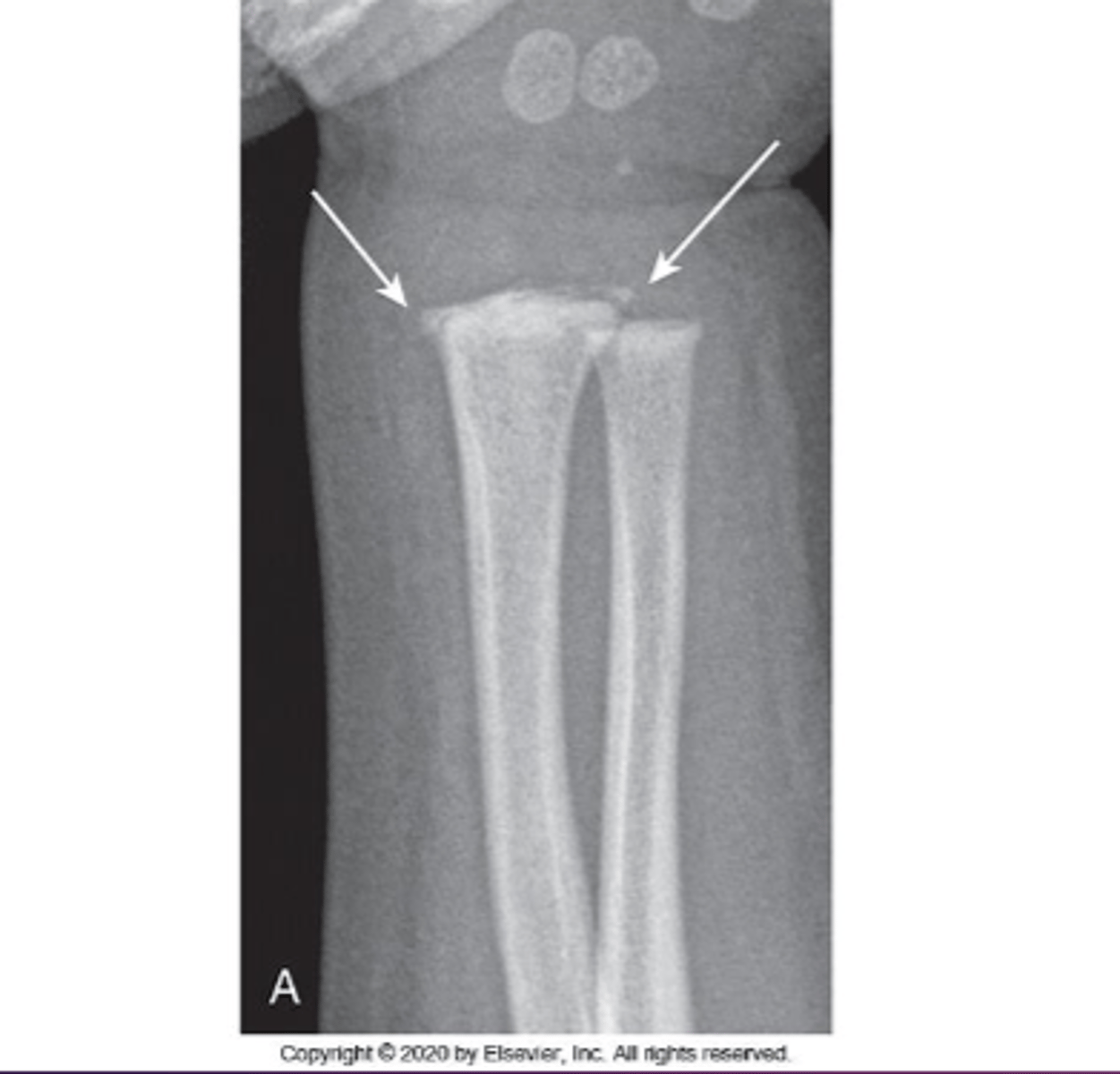
Metaphyseal corner fx
Identify
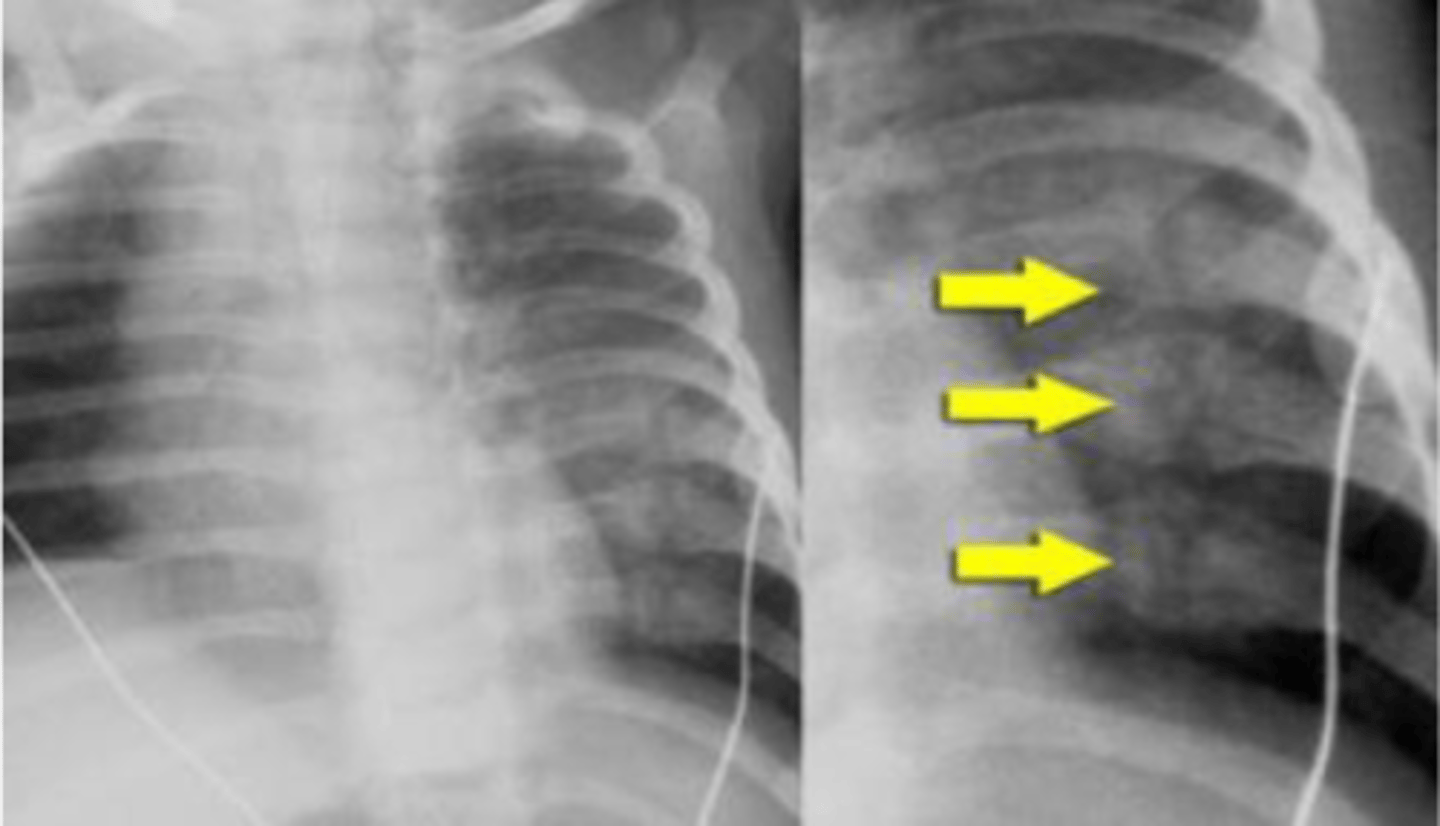
Rib fx
identify
Child abuse
3 y/o pt with broken sternum
1
Spiral fracture in children less than ___ y/o is child abuse