Chapter 14: Psychological Disorders & Chapter 15: Therapies
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Psycopatholody
the scientific study of the origins, symptoms, and development of psychological disorders
Psychological Disorder
a pattern of behavioral or psychological symptoms that causes significant personal distress, impairs the ability to function in one or more important areas of life
DSM-5
the abbreviation for the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual Disorders, Fifth Edition, which describes the symptoms of a disorder and diagnostic guidelines
Neurodevelopmental Disorders
wide range of developmental, behavioral, learning, and communication disorders that are usually first diagnosed in infancy, childhood, or adolescence. Symptoms of a particular disorder may vary depending on a child’s age and developmental level.
Autism Spectrum Disorder
Onset of symptoms prior to age of 3. Characterized by: (1) deficits in social communication and social interaction and (2) restricted, repetitive behaviors, interests, and activities; diagnosed according to level of symptom of severity, ranging from “requiring support” to “requiring very substantial support.”
Tourette’s Disorder
Onset prior to age of 18. Characterized by motor tics, such as recurring spasmodic movements of the head or arms, and vocal tics, such as recurring and sudden clicking, grunting, or snorting sounds. Sometimes involves uncontrollable utterances of profane or obscene words.
Substance-related and Addictive Disorders
Cluster of cognitive, behavioral, and psychological symptoms indicating that the individual continues using the substance or engaging in the behavior despite significant problems.
Substance Use Disorder
Recurrent substance use that involves impaired control, disruption of social, occupational, and interpersonal functioning, and the development of craving, tolerance, and withdrawal symptoms
Gambling Disorder
Persistent gambling that disrupts personal, family, and/or vocational pursuits
Somatic Symptoms and Related Disorders
Persistent, recurring complaints of bodily (or somatic) symptoms that are accompanied by abnormal thoughts, feelings, and behaviors in response to these symptoms.
Somatic Symptom Disorder
Characterized by excessive worry or distress that is out of proportion to the seriousness of physical symptoms that are present
Illness Anxiety Disorder
Excessive worry or distress that is out of proportion to the seriousness of physical symptoms that are present.
Disruptive, Impulse-Control, and Conduct Disorders
Problems in the self-control of emotions and behaviors as manifested in behaviors that harm or violate the rights of others
Kleptomania
the recurrent failure to steam items that are not needed for personal use or their monetary value.
Pyromania
Deliberately setting fires on more than one occasion, accompanied by pleasure, gratification, or relief of tension.
Anxiety
an unpleasant emotional state characterized by physical arousal and feelings of tension, apprehension, and worry
Anxiety Disorders
a category of psychological disorders in which extreme anxiety is the main diagnostic feature and causes significant disruptions in the person’s cognitive, behavioral, or interpersonal functioning
General Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
an anxiety disorder characterized by excessive, global, and persistent symptoms of anxiety
Panic Attack
Problems in the self-control of emotions and behaviors as manifested in behaviors that harm or violate the rights of others
Panic Disorder
the recurrent failure to steam items that are not needed for personal use or their monetary value.
Agoraphobia
Deliberately setting fires on more than one occasion, accompanied by pleasure, gratification, or relief of tension.
Catastrophic Cognitions Theory
people with panic disorder are not only oversensitive to physical sensations, they also tend to catastrophize the meaning of their experience
Phobia
a persistent and irrational fear of a specific object, situation, or activity
Specific Phobia
an excessive, intense, and irrational fear of a specific object, situation, or activity that is actively avoided or endured with marked anxiety
Social Anxiety Disorder
an anxiety disorder involving the extreme and irrational fear of being embarrassed, judged, or scrutinized by others in social situations
Taijin Kyofusho
a disorder that usually affects young Japanese men
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
a disorder triggered by extreme trauma that results in intrusive memories; avoidance of stimuli; negative changes in thoughts and emotions; and a persistent state of heightened physical arousal
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
a disorder characterized by intrusive, repetitive, and unwanted thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors or mental acts that an individual feels driven to perform (compulsions)
Obsessions
repeated, intrusive, uncontrollable irrational thoughts or mental images that cause extreme anxiety and distress
Compulsions
repetitive behaviors or mental acts that a person feels driven to perform in order to prevent or reduce anxiety and distress or to prevent a dreaded event or situation
Major Depressive Disorder
a mood disorder characterized by extreme and persistent feelings of despondency, worthlessness, and hopelessness, causing impaired emotional, cognitive, behavioral, and physical functioning
Panic Attack
a mood disorder involving periods of incapacitating depression alternating with periods of extreme euphoria and excitement; formerly called manic depression
Manic Episode
a sudden, rapidly escalating emotional state characterized by extreme euphoria, excitement, physical energy, and rapid thoughts and speech
Cyclothymic Disorder
people experience moderate but frequent mood swings for two years or longer
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
recurring depressive episodes that follow a seasonal pattern, typically occurring in the fall and winter and subsiding in the spring and summer
Persistent Depressive Disorder
chronic depressed feelings that are often less severe than those that accompany major depressive disorder
Eating Disorders
a category of psychological disorders characterized by severe disturbances in eating behavior
Anorexia Nervosa
an eating disorder characterized by excessive weight loss, an irrational fear of gaining weight, and distorted body self-perception
Bulimia Nervosa
an eating disorder characterized by binges of extreme overeating followed by self-inducing vomiting, misuse of laxatives, or other methods to purge excess food and prevent weight gain
Hikikomori
pattern of extreme social withdrawal in Japan
Personality Disorder
inflexible, maladaptive, and stable pattern of thoughts, emotions, behavior, and interpersonal functioning that deviate from the expectations of the individual’s culture
Antisocial Personality Disorder
a personality disorder characterized by a pervasive pattern of disregarding and violating the rights of others; psychopath or sociopath
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)
a personality disorder characterized by instability of interpersonal relationships, self-image, and emotions, and marked impulsivity
Dissociative Experience
a break or disruption in consciousness during which awareness, memory, and personal identity become separated or divided
Dissociative Disorders
a category of psychological disorders in which extreme and frequent disruption of awareness, memory, and personal identity impair the ability to function
Dissociative Amnesia
dissociative disorder involving the partial or total inability to recall important information
Dissociative Fugue
a type of dissociative amnesia involving sudden and unexpected travel away from home, extensive amnesia, and identity confusion
Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID)
a dissociative disorder involving extensive memory disruptions for personal information along with the presence of two or more distinct identities, or “personalities,” within a single person
Schizophrenia
a psychological disorder in which the ability to function is impaired by severely distorted beliefs, perceptions, and thought processes
Positive Symptoms
an excess or distortion of normal functioning including delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized thoughts and behavior
Negative Symptoms
defects or deficits in normal functioning, including flat affect
Delusion
a false belief that persists despite compelling contradictory evidence
Hallucination
a false or distorted perception that seems vividly real to the person experiencing it
Psychotherapy
treatment of emotional, behavioral, and interpersonal problems through psychological techniques that promote understanding of problems and modify troubling feelings, behaviors, or relationships
Clinical Psychologist
Holds an academic doctorate (Ph.D., Psy.D., or Ed.D.) and is required to be licensed to practice. Assesses and treats mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders. Has expertise in psychological testing and evaluation, diagnosis, psychotherapy, research, and prevention of mental and emotional disorders.
Counseling Psychologist
Holds an academic doctorate and must be licensed to practice. Assesses and treats mental, emotional, and behavioral problems and disorders. Historically treated disorders of lesser severity, but now there is less distinction between the practices of clinical and counseling psychologists.
Psychiatrist
Holds a medical degree (M.D. or D.O.) and is required to be licensed to practice. Has expertise in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental and emotional disorders. Often has training in psychotherapy. May prescribe medications and medical procedures.
Psychoanalyst
Usually a psychiatrist or clinical psychologist who has received additional training in the specific techniques of psychoanalysis, the form of psychotherapy originated by Sigmund Freud.
Licensed Professional Counselor
Holds at least a master's degree in counseling, with supervised training in assessment and therapy techniques. May be certified in specialty areas. Most states require licensure or certification.
Psychiatric Social Worker
Holds a master's degree in social work (M.S.W.). Training includes an internship in a social service agency or mental health center. Usually has certification or licensing. May have training in psychotherapy.
Marriage and Family Therapist
Usually holds a master's degree, with extensive supervised experience in couple or family therapy. May also have training in individual therapy. Many states require licensing.
Psychiatric Nurse
Holds an R.N. degree and has selected psychiatry or mental health nursing as a specialty. May or may not have training in psychotherapy.
Biomedical Therapies
use of medication, electroconvulsive therapy, or other medical treatments to treat the symptoms associated with psychological disorders
Psychoanalysis
originated by Sigmund Freud in which free association and transference are used to explore repressed or unconscious impulses, anxieties, and internal conflicts
Free Association
psychoanalytic technique in which the patient spontaneously reports all thoughts, feelings, and mental images that arise, revealing unconscious thoughts and emotions
Resistance
the patient’s conscious or unconscious attempts to block the process of revealing repressed memories and conflicts
Interpretation
a psychoanalytic technique in which the psychoanalyst offers carefully timed explanations of the patient’s dreams, feelings, or behaviors to help explore unconscious conflicts or motivations
Transference
the process by which emotions and desires associated with a significant person in the patient’s life, such as a parent, are unconsciously transferred onto the psychoanalyst
Short-term Dynamic Therapy
type of psychotherapy based on psychoanalytical theory but differing in that it is time-limited, has specific goals, and involves an active, rather than neutral, role for the therapist
Interpersonal Therapy (IPT)
a brief psychodynamic psychotherapy that focuses on current relationships and is based on the assumption that symptoms are caused and maintained by interpersonal problems
Client-Centered Therapy
type of psychotherapy in which the therapist is nondirective and reflective, and the client direct the focus of each therapy session
Three Qualities of a Therapist
genuineness, unconditional positive regard, empathetic understanding
Motivational Interviewing
a technique designed to help clients overcome the mixed feelings or reluctance they might have about committing to change
Comparing Psychodynamic and Humanistic Therapies
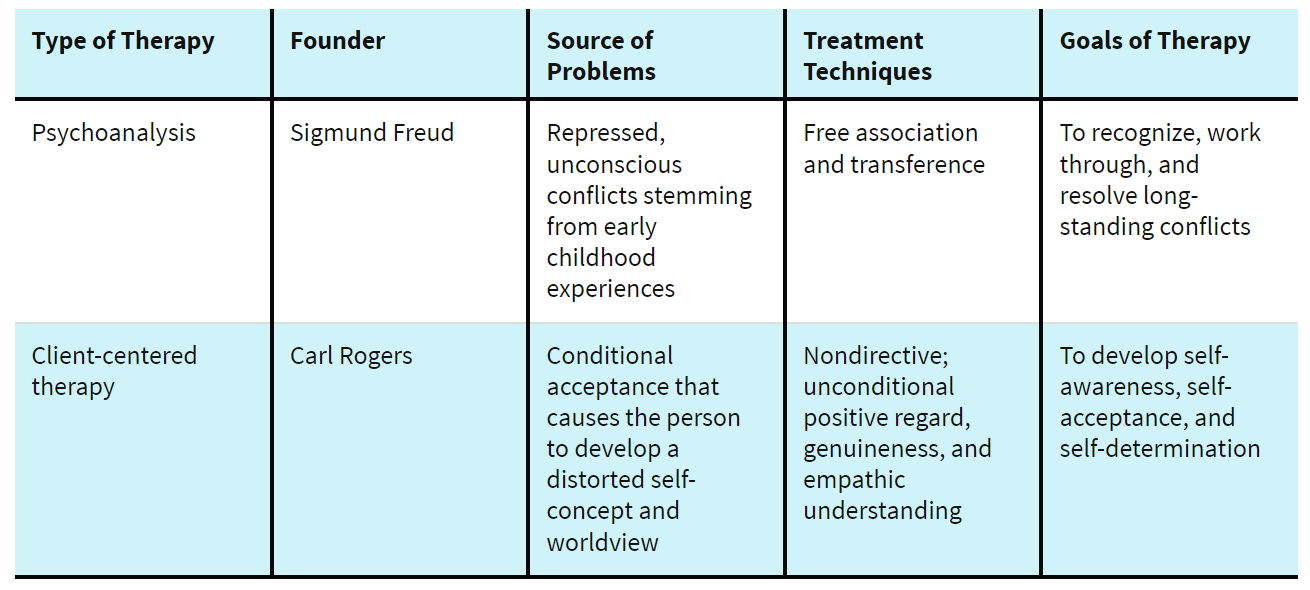
Behavior Therapy
type of psychotherapy that focuses on directly changing maladaptive behavior patterns by using basic learning principles and techniques; Behavior Modification
Counterconditioning
a behavior therapy technique that involves learning a new conditioned response that is incompatible with a previously learned response
Exposure Therapy
behavioral therapy for phobias, panic disorder, PTSD, or related anxiety disorders in which the person is repeatedly exposed to the disturbing object or situation under controlled conditions
Systematic Desensitization
type of behavior therapy that involves learning a new conditioned response (relaxation) that is incompatible with or inhibits the old conditioned response (fear and anxiety)
Basic Steps in Systematic Desensitization
progressive relaxation, exposure therapy, feared experiences
Aversive Conditioning
a relatively ineffective type of behavior that involves repeatedly pairing an aversive stimulus with the occurrence of undesirable behavior or thoughts
Operant Conditioning
model of learning based on the simple principle that behavior is shaped and maintained by its consequences
Shaping
involves reinforcing successive approximations of a desired behavior
Token Economy
a form of behavior therapy in which the therapeutic environment is structures to reward desired behaviors with tokens or points that may eventually be exchanged for tangible rewards
Cognitive Therapies
group of psychotherapies based on the assumption that psychological problems are due to illogical patterns of thinking; techniques focus on recognizing and altering unhealthy thinking patterns
Rational-Emotive Behavior Therapy
type of cognitive therapy that focuses on changing the client’s irrational beliefs
ABC Model
(A) Activating Events, (B) Beliefs, (C) Consequences
Cognitive Therapy
therapy developed by Aaron T. Beck that focuses on changing the client’s unrealistic and maladaptive beliefs
Arbitrary Inference
drawing a negative conclusion when there is little or no evidence to support
Selective Abstraction
focusing on a single negative detail taken out of context and ignoring the more important aspects of the situation
Overgeneralization
drawing a sweeping, global conclusion based on an isolated incident and applying that conclusion to other unrelated areas of life
Personalization
taking responsibility, blaming oneself, or applying external events to oneself when there is no basis or evidence for making the connection
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy
therapy that integrates cognitive and behavioral techniques and that is based on the assumption that thoughts, moods, and behaviors are interrelated
Mindfulness-based Cognitive Therapy
was developed to treat major depressive disorder
Group Therapy
a form of psychotherapy that involves one or more therapists working simultaneously
Cognitive Therapy
a form of psychotherapy that involves one or more therapists working simultaneously with a small group of clients
Family Therapy
a form of psychotherapy that is based on the assumption that the family is a system and that treats the family as a unit
Network Therapy
kind of extended-family therapy, including a wide range of a patient’s community in their treatment
Behavioral Couple Therapy
based on the assumption that couples are satisfied when they experience more reinforcement than punishment in their relationship
Eclecticism
the pragmatic and integrated use of techniques from different psychotherapies
Psychotropic Medications
prescription drugs that alter mental functions, alleviate psychological symptoms, and are used to treat psychological disorders