Memory in the Real world
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
The normal everyday operation of long-term memory
The continual, coordinated, cooperative processes of interaction between episodic and semantic memory.
Schacter’s Seven Sins of Memory
Transience
Absent-mindedness
Blocking
Misattribution
Suggestibility
Bias
Persistence
Sins of Omission (TAB)
1.Transience: The tendency to lose access to information across time, whether through forgetting, interference, or retrieval failure.
2.Absent-mindedness: Everyday memory failures in remembering information and intended activities.
3.Blocking: Temporary retrieval failure or loss of access in either episodic or semantic memory
Sins of Commission ( MSBP)
4.Misattribution: Remembering a fact correctly from past experience but attributing it to an incorrect source or context
5.Suggestibility: The tendency to incorporate information provided by others into your own recollection and memory representation
6.Bias: The tendency for knowledge, beliefs, and feelings to distort recollection of previous experiences and to affect current and future judgments and memory
7.Persistence: The tendency to remember facts or events, including traumatic memories, that one would rather forget
Proposition
represents the meaning of a single simple idea
the nature of propositions is remembering the gist of an idea rather than the exact details
Strengths of the propositional theory
•Accurately reflect the meaning of the sentence
•Ignore the surface form of the sentence
•Have the power to represent complex sentence-based connections
Sachs study
ON PROPOSITION
Ps heard a passage a text
tested them after various lengths of delay on the critical sentence they had heard.
The test was to recognize the critical sentence among 4 alternatives
Sachs study conclusion
We quickly lose information about the actual verbatim string of words that we hear (or read), but we do remember the meaning
Anderson Study: assumptions
1.A node in a network has multiple links to other concepts
2.People have limited cognitive resources
Anderson Study
PROPOSITIONS AND INTERFERENCE
Participants memorized a list of sentences about people in locations.
how ever he would varied the number of associations the person and location by 1-3
Then were given a recognition test
Anderson Study: results
There was an interference effect!
Fan effect: when more words are associated with a concept, response times were longer.
Situation Models
representations of events that serve as mental simulations
Levels of representations (S2T)
Surface form: verbatim mental representation
Situation Model: Representation of the overall idea/state of affairs described by the text
Textbase: basic idea units present in text (e.g., propositional network)
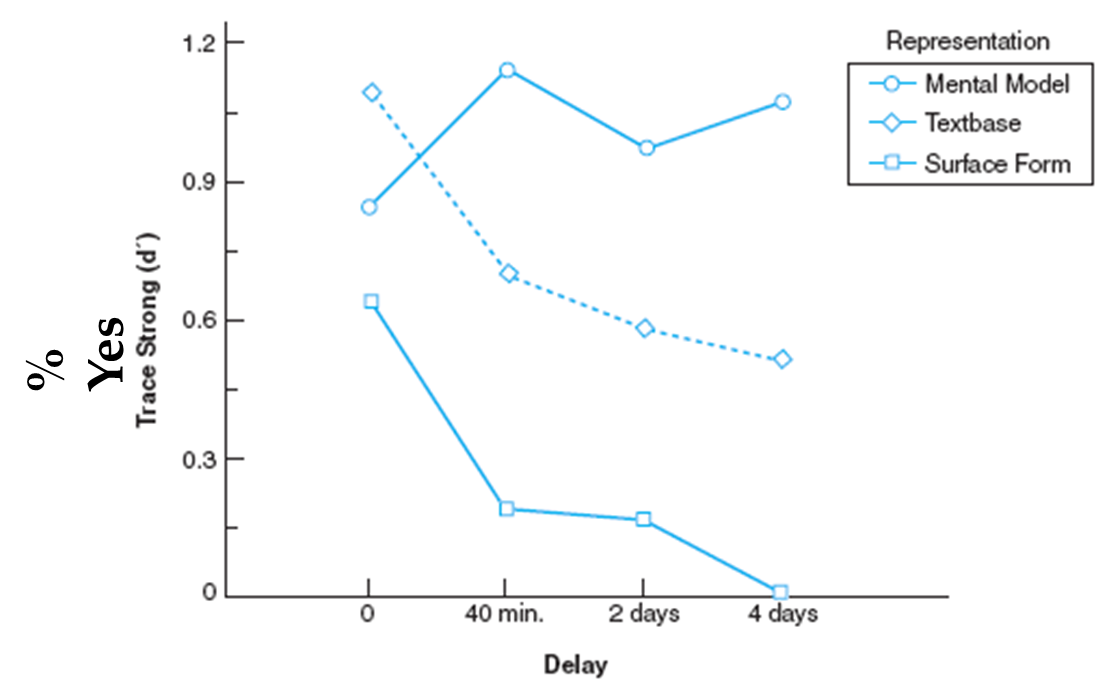
Kitch et al.
SITUATUATION MODELS
looked at how information form each level is remembered over time
Ps read a text & were given recognition test on what they could remember using 4 types of memory probes
kintsch et al. memory probes
1.Verbatim probes: exact sentences that they read (surface form)
2.Paraphrases: captured the idea of the text with different wording (textbase)
3.Inferences: ideas that were likely to be true, but weren’t mentioned in the text (situation model)
4.Wrongs: incorrect probes that were thematically consistent, but incorrect
Kintsch et al. findings
Metamemory
the knowledge about one’s own working, memory including how it works and how it fails to work.
Source monitoring
The ability to accurately remember the source of a memory, whether it be a actual or imagined experience
Source monitoring failure
remember the content of information however is unable to attribute it to a particular source.
Cryptomnesia
in which a person unconsciously plagiarizes something they have read/ seen before. However, since the have forgotten the source, they mistakenly think it is a new idea in which they created.
Prospective memory
the ability to remember to do something in the furture
Types of prospective memory
Time-based: remember to do something based on the passage of time
Event-based: remembering to do something when a certain event occurs
Judgements of learning ( JOL)
in which you make a prediction, after studying a material, about whether it will be remembered at a later date
JOL accuracy
if judgments are made directly after them are estimations tends to be poorer. Due to us over estimate how well we know the material
Feeling of knowing
an estimate of how familiar something is to you
Tip of the tongue state
the temporary inability to remember some shred of information that they have already stored in the LTM
False memory
a memory of something that did not happen
Hyman et al.
asked people to recall childhood stories about themselves. they would add real stores ( collected from parents) and one Pseudo-event
Ps were questioned about events in 3 separate interview. With every interview the percentage of recall for fable memories increased
Wade et al.
Showed people photos of themselves as children; some real and one false.
Ps were questioned about events in 3 separate interview. With every interview the percentage of recall for fable memories increased
Lindsey et al.
obtained and showed people a class photo
read people stores of childhood events ( 2 true; 1 false)
then Ps were asked to recall anything hey could about the first interview
Memory Distortion due to… ( LIM SOM)
•Leading Questions
•Integration
•Misinformation Effect
•Source Misattribution
•Overconfidence in Memory
•Misinformation Acceptance
Memory Integration
an inappropriate combination of information from difference sources or events, which becomes a linked/fused memory
Leading questions
Suggestion what answer to a question is appropriate or desired
Misinformation effect
people claim to remember information that was not in the original experience, but was provide later as a piece of misinformation
Source misattributions
the inability to distinguish whether the original event or some later event was true source of information
Misinformation acceptance
When people accept additional information as being apart of a earlier experience without actually remembering that information.
Reconsolidation
when a memory is retrieved it puts it in a malleable state in which it can be changed before it was stored again
Overconfidence in Memory
certainty int he the accuracy of memory
Overconfidence in memory two factors
Source Memory: memory of the exact source of the information
Processing Fluency: the ease with which something comes to mind
Repression
the intentional forgetting of painful or traumatic experience
Recovered memories
Spontaneous or deliberate retrieval of repressed memories
difficult to verify or disprove
Autobiographical memory
one’s lifetime collection of personal event memories
Bahrick et al.
looks to test long term memory of high school classmates’ names and faces.
free recall, name recognition, and more
Results: there is a steep decay of memory for free recall however there is better memory ( although still decay) in terms of recognition
Superior Autobiographical memory
overall nearly perfect memory.
FlashBulb Memories
extremely detailed memories for surprising or unusual events. seemly very accurate