Bio 130 Exam 1
1/47
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Characteristics of life
Cellular, homeostasis, response to stimuli, movement, stores energy
Requirements of life
Energy
Essential nutrients
Liquid water
Maintenance & reproduction
Information storage & transfer
Populations of individuals
Capacity to evolve
Abiotic factors
non-living aspects of the physical environment, like temperature, water availability, mineral nutrients
Biotic factors
the interactions and effects of other organisms living in the environment that might compete with, prey on, or form beneficial mutualisms with an organism
Ecological Niche Concept
the full combination of abiotic conditions and biotic factors across which individuals can survive, grow, reproduce, and sustain viable populations in the long term
Niche axis
any continuous abiotic or biotic factor important to a species’ survival (e.g., temperature, food resources, abundance of breeding sites)
Fundamental niche
the full range of abiotic conditions (temperature, water, nutrients, etc.) under which a species is physiologically capable of surviving and reproducing to form a population
Realized niche
The environmental niche space actually occupied by a species in the real world – in the face of negative biotic interactions
Negative biotic interactions
reduce survival & performance of most species, constricting the range of abiotic conditions under which the species can actually survive & reproduce at a rate sufficient to form a self-sustaining population
Red Queen Hypothesis
intense biotic interactions, such as parasitism, mutualism, and predation, drive species to continuously evolve adaptations to maintain relative fitness in an ever-changing environment
ecological arms races
Coevolutionary interactions between species that drive evolutionary change in ecosystems and lead to increased biodiversity
“Empty” niches
empty potential niches that a species has not evolved into yet, usually because they do not exist
Niche “construction”
a niche that comes from a species substantially modifying their environment in order to create the unique niche conditions that can support their populations
Competitive displacement (ecological time)
when the presence of one species narrows the realized niche of another in ecological time; ecological time is relatively quick, as the niche shifts as soon as the competition leaves
Character displacement (evolutionary time)
when competition between species causes niche divergence over evolutionary time; the niche might need a while to expand after competition leaves
Niche “differentiation” or “partitioning” (between similar, competing species)
the process by which competing species use the environment differently in a way that helps them to coexist
Natural selection
the process of how organisms “fit” into their niche; survival of the fittest phenotype
Artificial selection
when humans consciously select for or against particular features in organisms (ex. domestication of dogs and creating different breeds)
Evolution (not equivalent to natural selection)
change in gene frequencies across generations; the change in the inherited traits of a population of organisms through successive generations
Genotype
genetic makeup, genome
Phenotype
outward appearance/characteristics resulting from interaction of genotype and environment
Dominant alleles
alleles that are so “powerful” that only one is required for a trait to present itself; masks recessive alleles
Recessive alleles
the “weaker” allele that requires two for a trait to present
Microevolution
small gradual changes over time
Macroevolution
longer and larger processes that result in the formation of a new species (e.g. horses)
Natural selection — “fitness”
natural selection generates fit for a species, or when individuals vary in traits that affects survival and reproductive success
Heritable traits
traits that can evolve and are passed down genetically from parent to offspring
Heritability
whether or not a trait is heritable, which can be tested by comparing the mean of the trait in the parent to the mean of the offspring
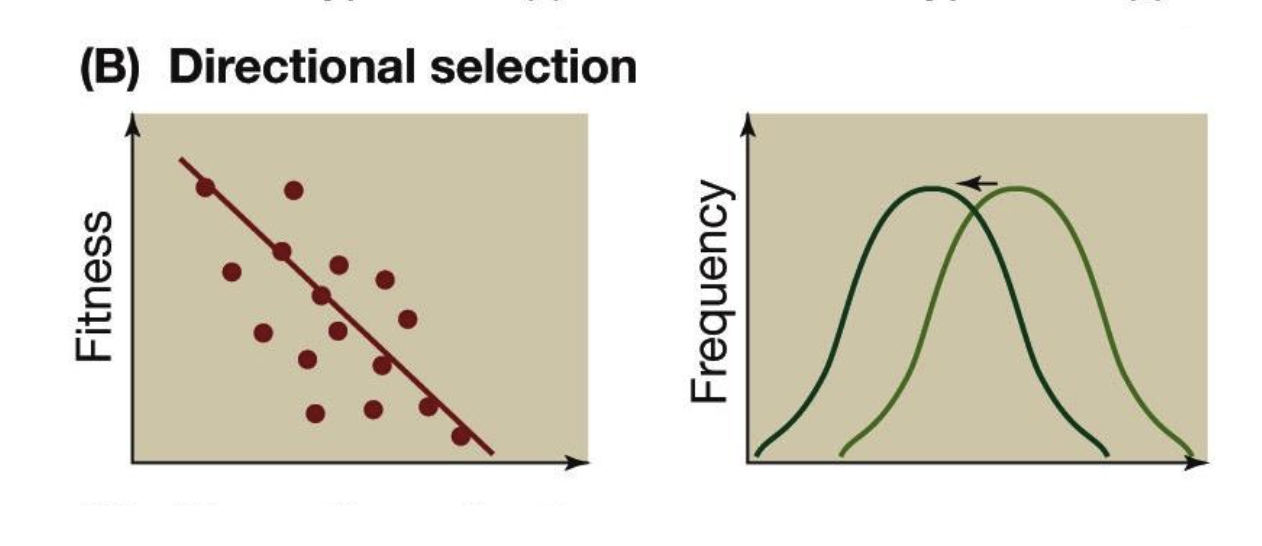
Directional natural selection
occurs when environmental pressures favor one phenotype more than the other causing the allele frequency to continuously shift in one direction
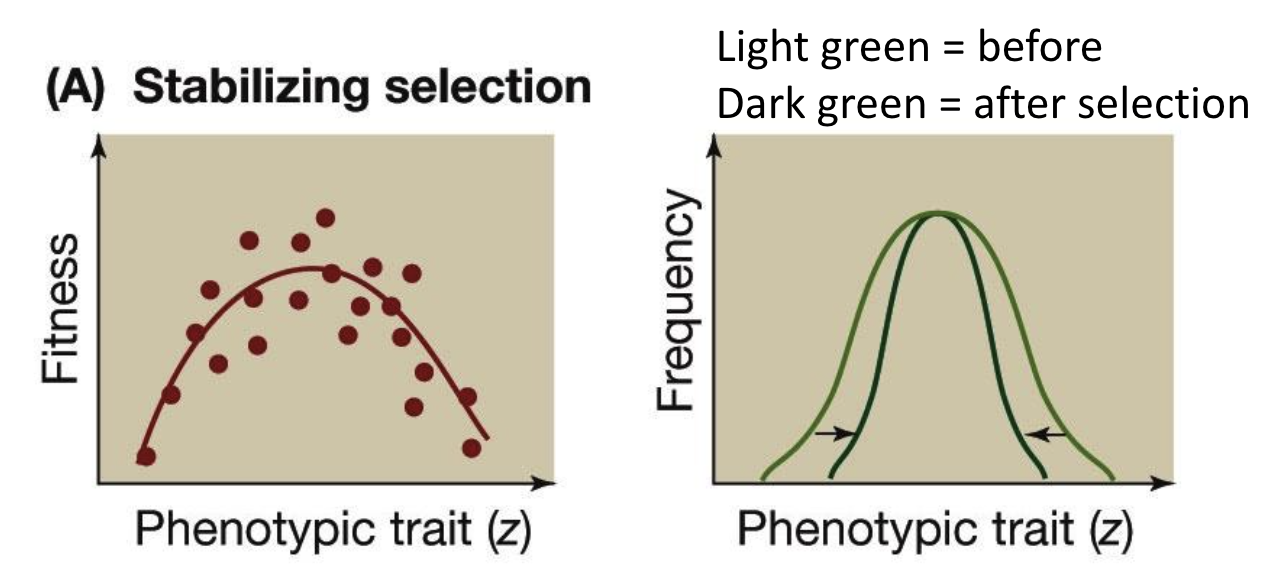
Stabilizing natural selection
a type of natural selection in which genetic diversity decreases as the population stabilizes on a particular trait value
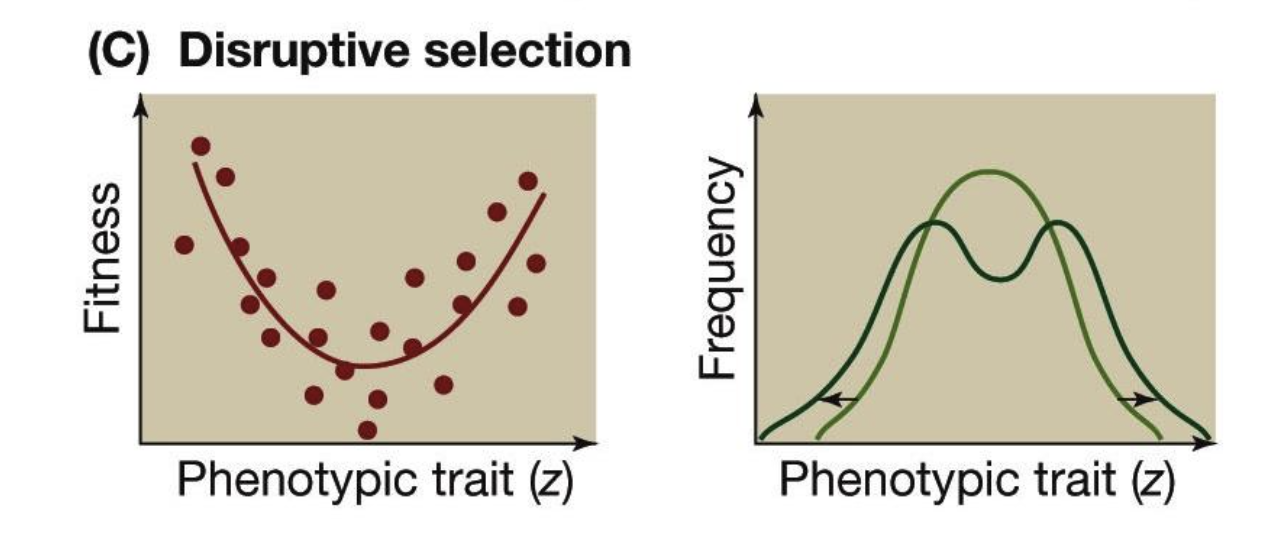
Disruptive natural selection
a mode of natural selection in which extreme values for a trait are favored over intermediate values
Convergent evolution
two or more species each independently evolve to have similar forms or adaptations
Evolutionary traps
when ‘adaptive’ traits or behaviors represent changes favored in past generations and not the present; (ex. male australian jewel beetles being attracted to the glossy surface of a beer bottle, baby sea turtles heading toward streetlights and not the horizon)
Adaptive traits
a characteristic or feature of an organism that enhances its survival or reproductive success in a particular environment
Maladaptive traits
a trait that is (or has become) more harmful than helpful
Darwinian algorithms
set behavioral response encoded in DNA by past natural selection on ancestors triggering automatic and stereotyped response to environmental cues that were important to the survival and fitness of its ancestors
Teleonomy
Apparently future goal-directed activities seen in biotic systems that actually emerge from past natural selection leading to the evolution of “Darwinian algorithms”
Speciation
When a group within a species separates from other members of its species and develops its own unique characteristics i.e. turns into a new species
Anagenesis
evolutionary change within a single lineage over time, meaning no new species and no increase in diversity
Cladogenesis
evolutionary change leading to the splitting of one lineage into two or more new species (aka speciation)
Species
hard to scientifically define, but usually similar individuals who can interbreed
Morphological species concept
a concept that characterizes a species based on its physical features or morphology, and cannot explain why or how a species exists
Biological species concept
defines species as groups of actually or potentially interbreeding natural populations that are reproductively isolated from other such groups; cannot be applied to fossils, prokaryotes, or organisms that live far apart
Phylogenetic species concept
uses analysis of evolutionary trees to guide demarcation of a species, grouping organisms together by an irrefutable common ancestor
Reproductive isolation & gene flow
implies distinct groups/species can form when there is little or no “gene flow” or sexual reproduction between two populations, gene flow meaning the sharing of genes from one population to the other
Allopatric speciation
speciation triggered by geographic separation and barriers that cut off reproduction and gene flow between populations
Monophyletic groups
(a common ancestor and all its descendants) identified by shared, recently evolved, unique traits that are found only in that group due to common ancestry – i.e., inherited from their common ancestor that first evolved the trait or unique genetic characteristic
Cryptic species
Groups of morphologically indistinguishable but evolutionarily distinct related species