STATISTICS CH.1
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
population
the whole set of items that are of interest
census
observes or measures every member of a population
sample
a selection of observations taken from a subset of the population which is used to find out information about the population as a whole
census advantage
it should give a completely accurate result
census disadvantages
time consuming and expensive
cannot be used when the testing process destroys the item
hard to process large quantity of data
sample advantages
less time consuming and expensive than a census
fewer people have to respond
less data to process than in a census
sample disadvantages
data may not be as accurate
sample may not be large enough to give information about small sub-groups of the population
sampling units
individual units of a population
sampling frame
sampling units of a population that are individually named / numbered to form a list
random sampling
every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected (representative of pop. and removes bias)
what are the 3 methods of random sampling?
simple random sampling
systematic sampling
stratified sampling
simple random sampling
every sample of size n has an equal chance of being selected
what are the 2 methods of choosing the numbers for simple random sampling?
generating random numbers (e.g. a calculator)
lottery sampling (e.g. pick numbers from a hat)
systematic sampling
the required elements are chosen at regular intervals from an ordered list
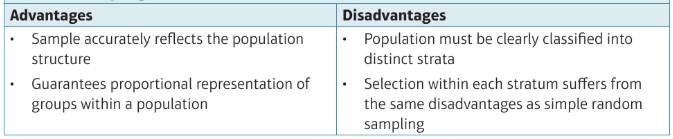
stratified sampling
population is divided into mutually exclusive strata (e.g. males and females) and a random sample is taken from each
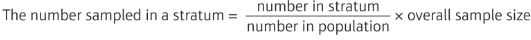
pros and cons of simple random sampling
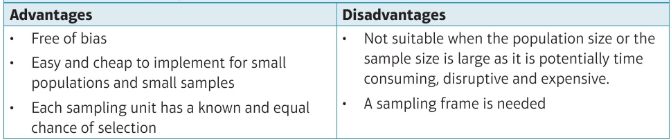
pros and cons of systematic sampling
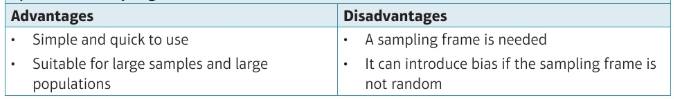
pros and cons of stratified sampling
what are the 2 types of non-random sampling?
quota and opportunity sampling
quota sampling
researcher selects a sample that reflects the characteristics of the whole population
opportunity sampling
takes the sample from those available at the time and fit the criteria
quota pros and cons
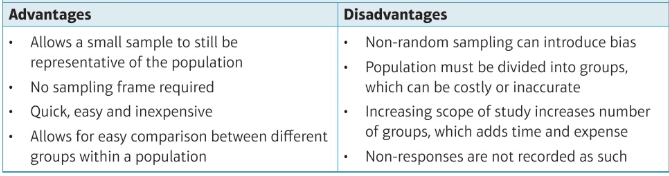
opportunity pros and cons
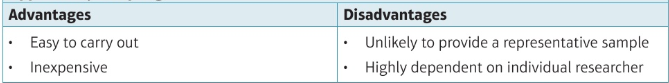
what are the 4 data types?
qualitative
quantitative
discrete
continuous
qualitative
non-numerical data
quantitative
numerical
discrete
can only take certain values (often integers)
continuous
can take any value in a range, must be grouped