Unit 1 Checklist Cards
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
for practical part of exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
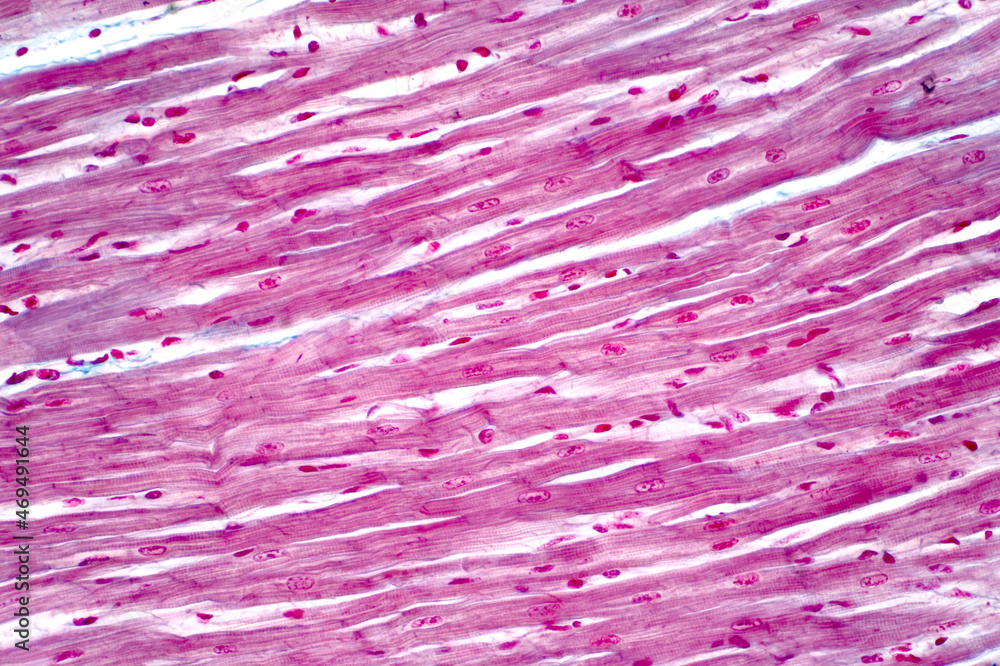
skeletal muscle tissue

smooth muscle tissue
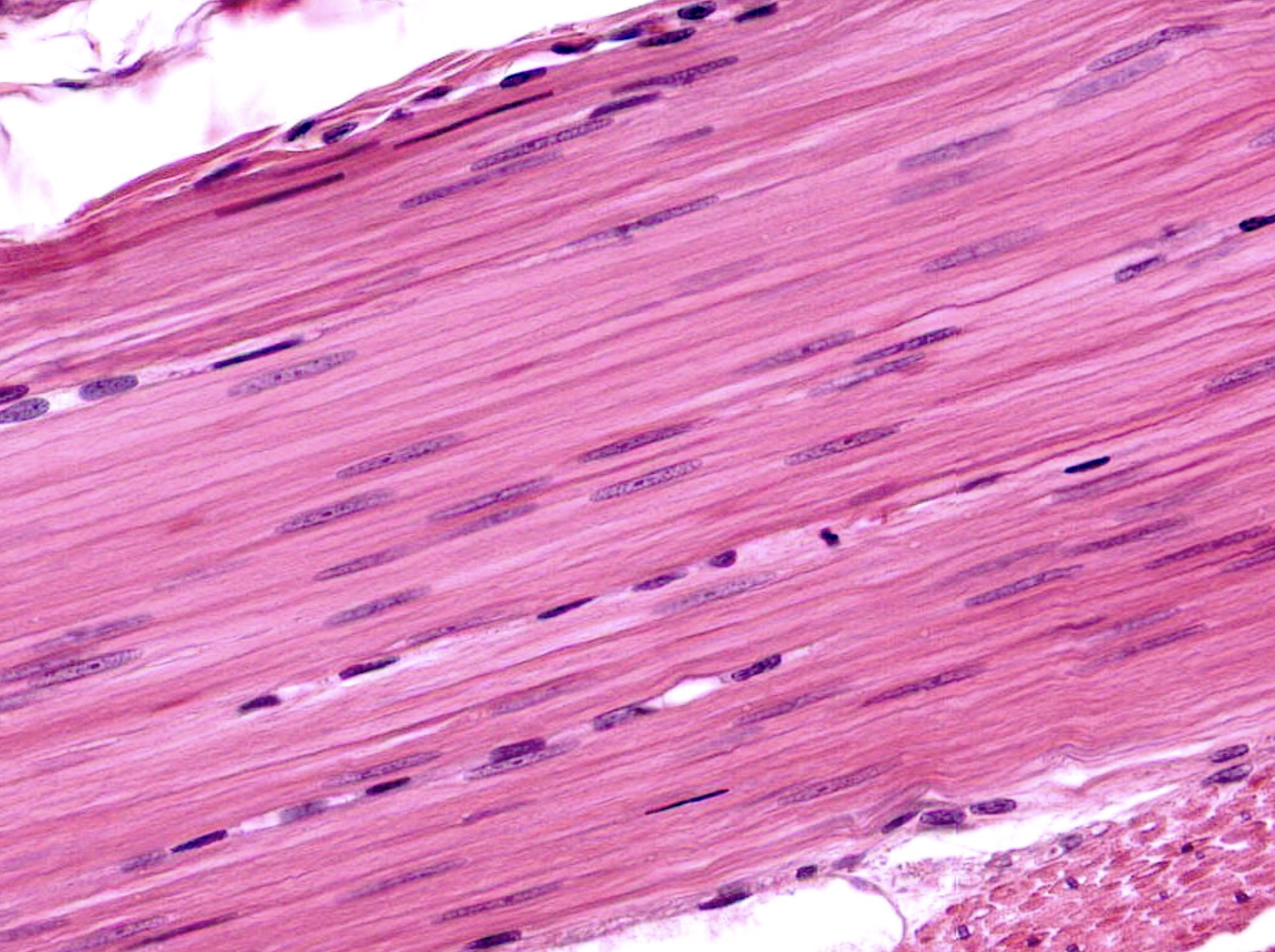
cardiac muscle tissue
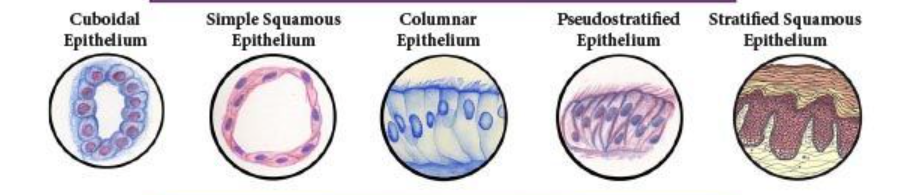
epithelial tissue
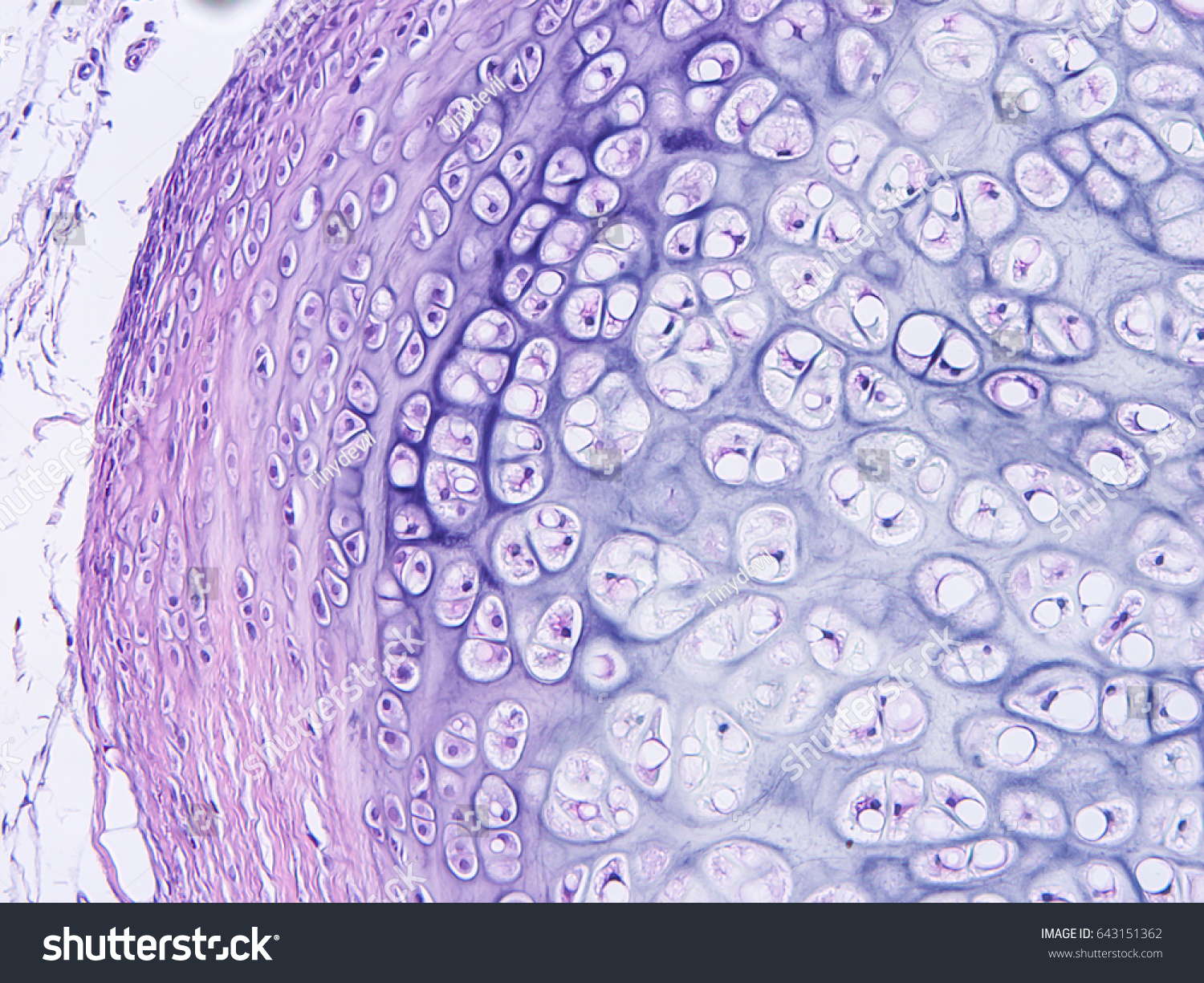
cartilage tissue
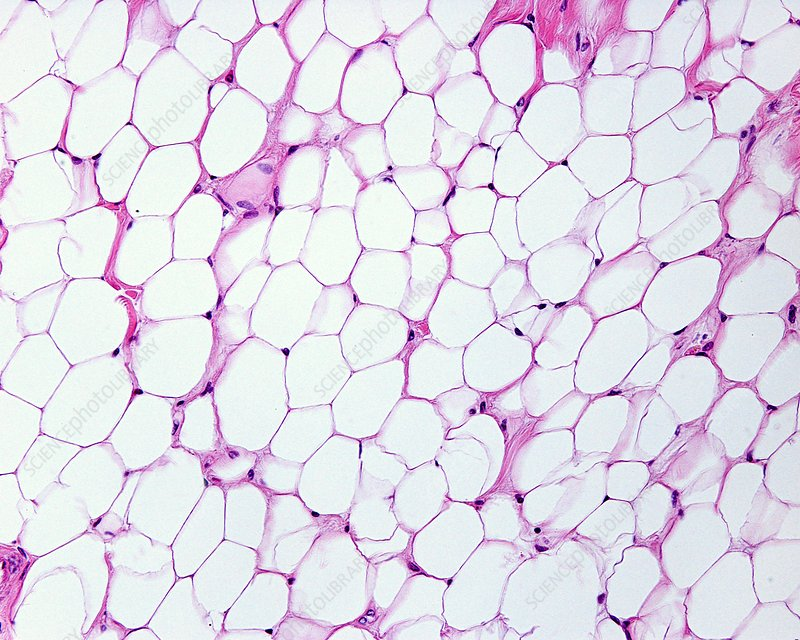
adipose tissue
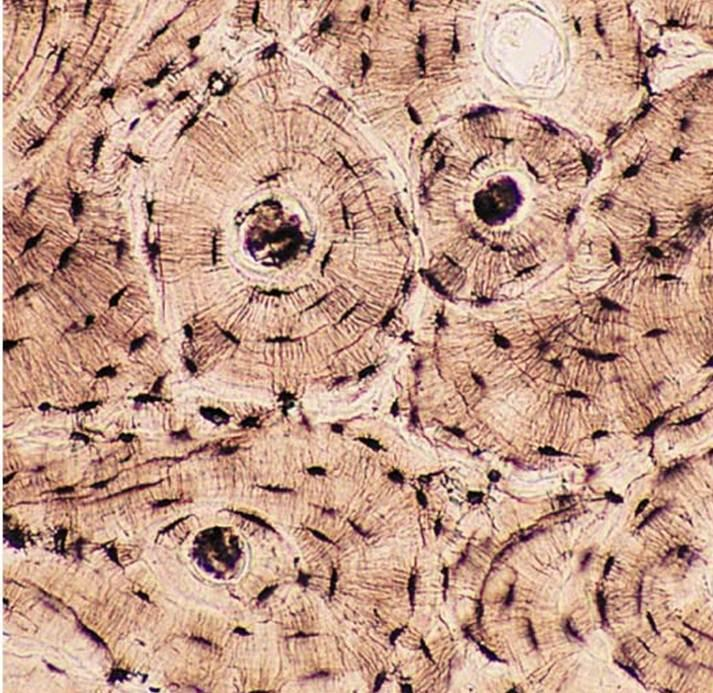
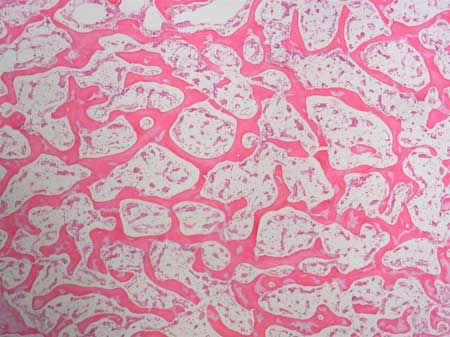
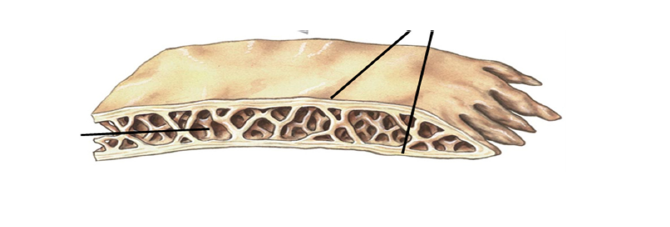
cortical (compact )bone tissue
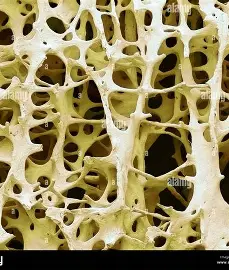
spongey bone tissue
long bone
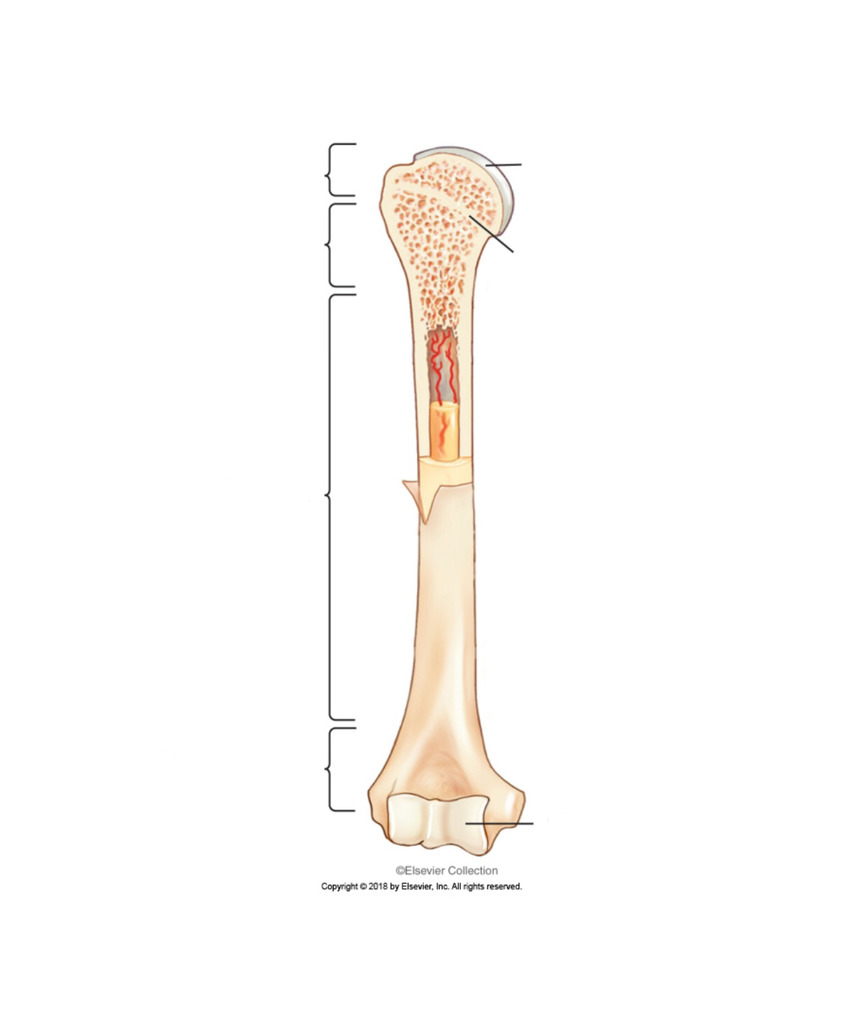
flat bone
irregular bone
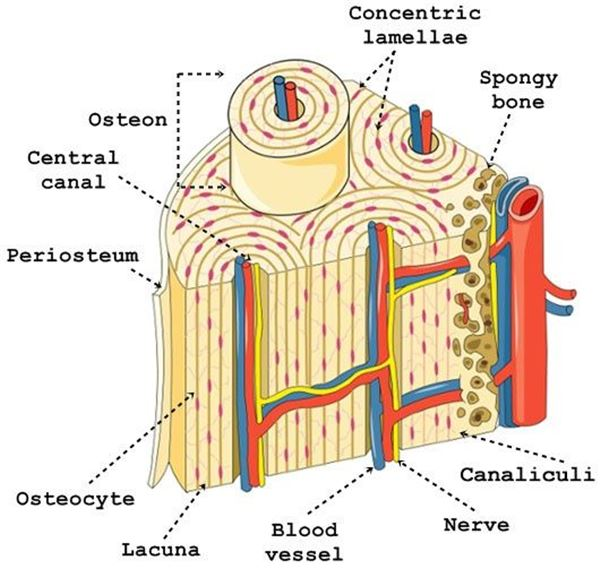
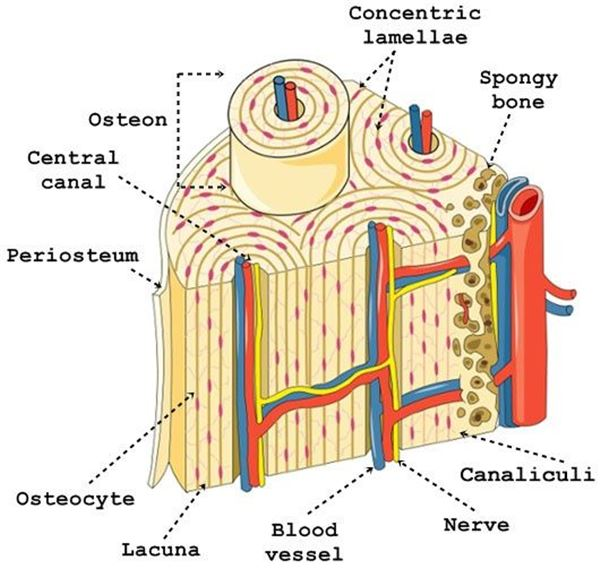
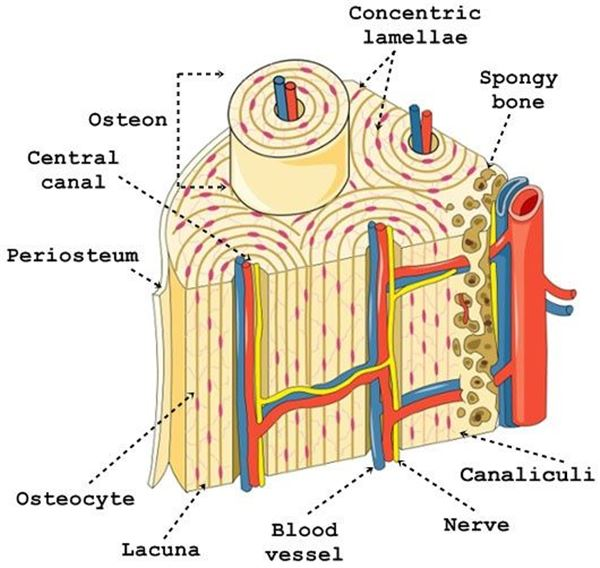
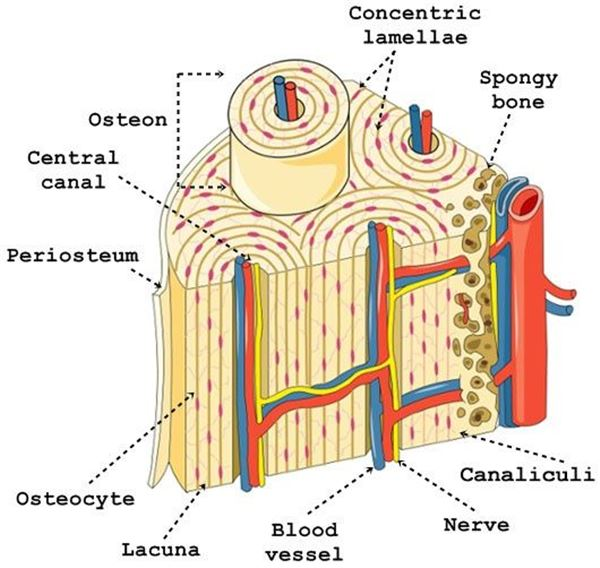
osteon
what is this structure
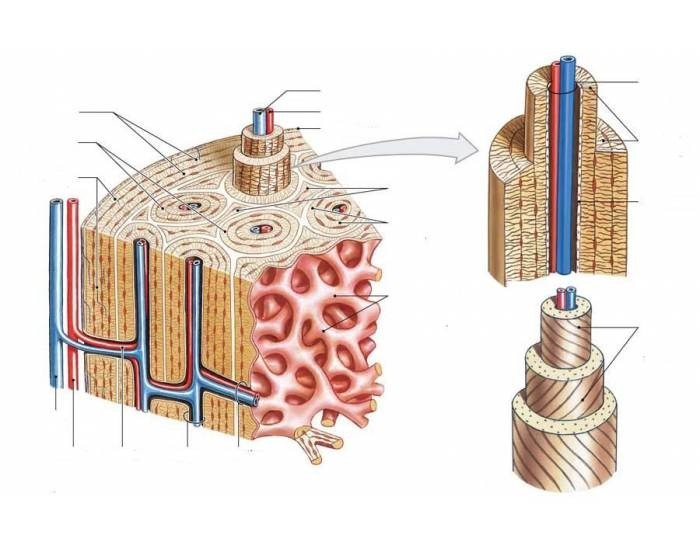
concentric lamellae
rings that form around the haversian canal of an osteon
interstitial lamellae
fills the space between osteons
central artery
the artery found in the central canal is called…
perforating artery
connects the central canal to the periosteum
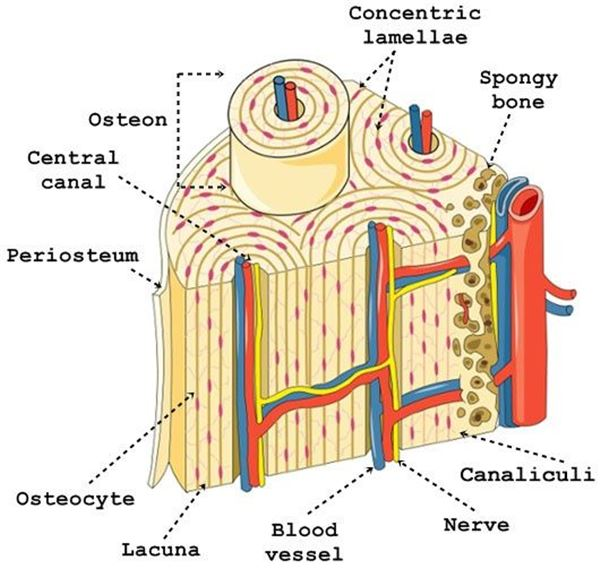
periosteum
dense connective tissue that covers the external surface of the osteon
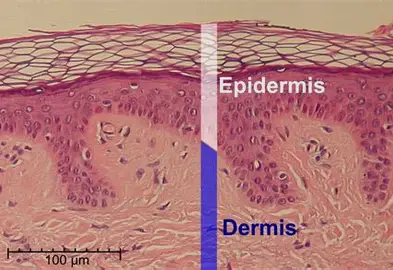
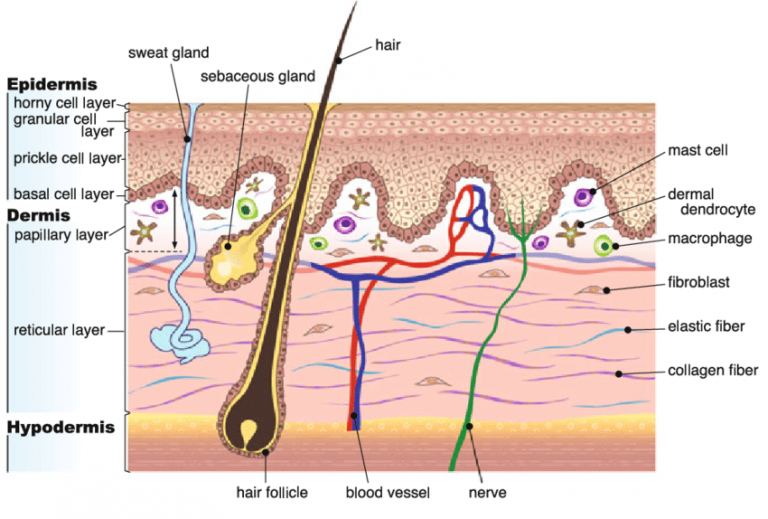
epidermis
outermost layer of the skin made up of stratified squamous epithelium
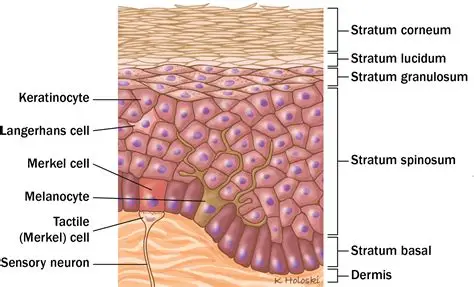
stratum corneum
Outermost layer (visible, dead skin cells)
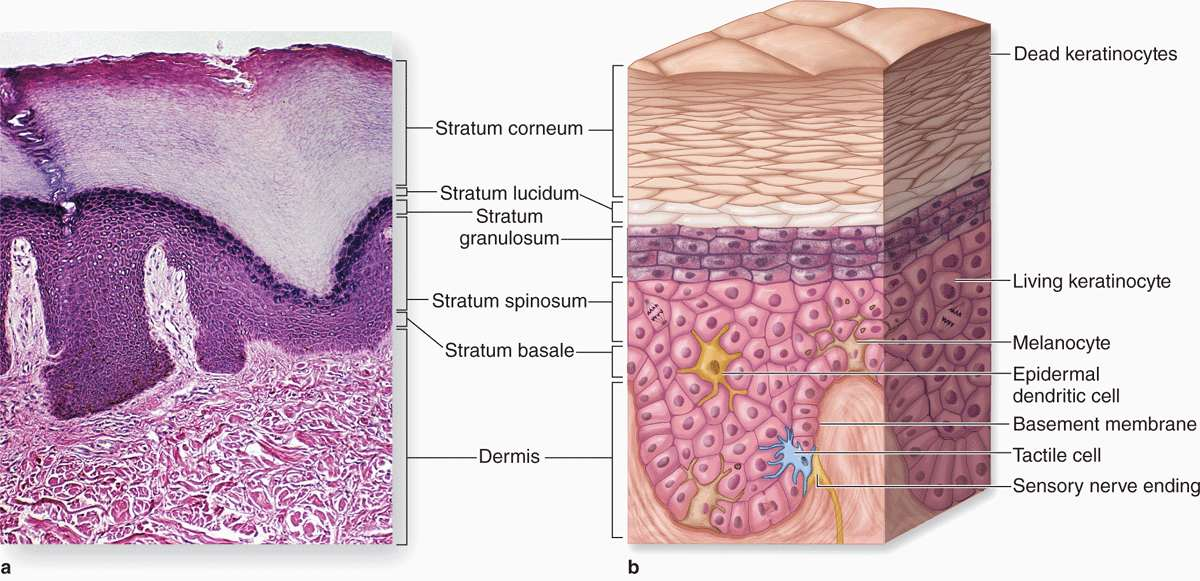
stratum lucidum
only found in thick skin (palms) & contains cornified cells that gives of translucent look
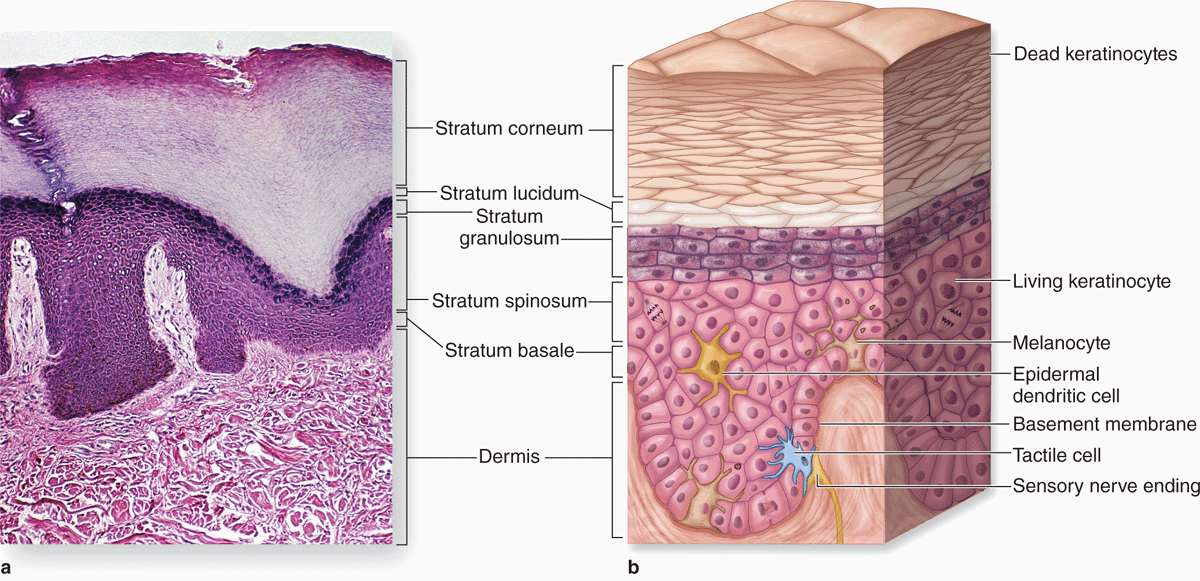
stratum granulosum
full of granules
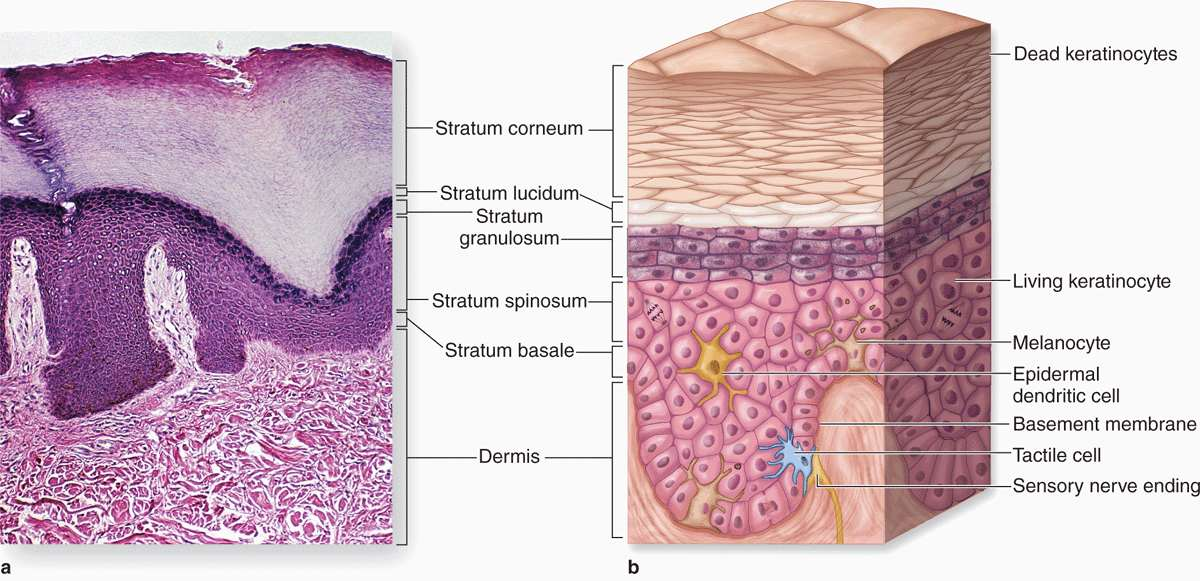
stratum spinosum
contains langerhans cells & has many layers of keratinocytes
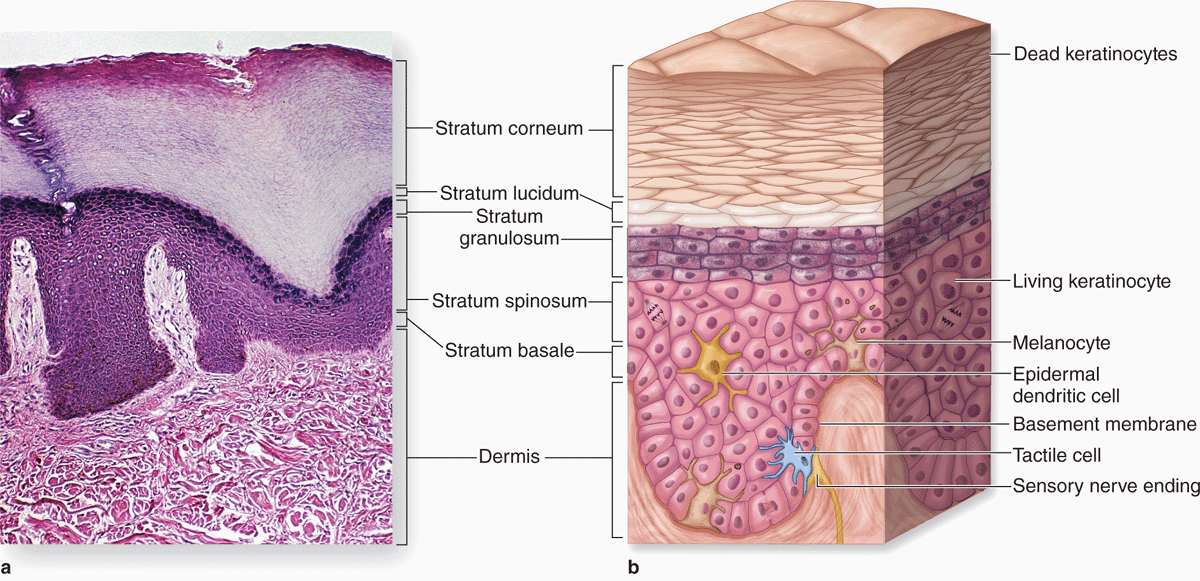
stratum basale
deepest layer, where cell division happens to make keratinocytes
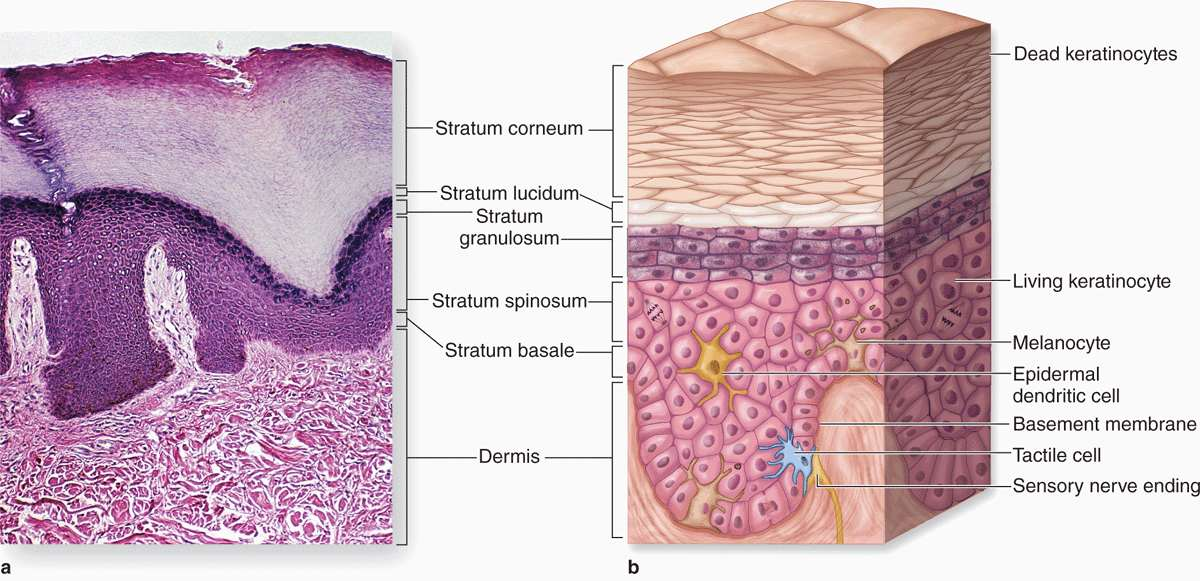
dermis
middle layer of the skin
hair follicle
found in the (deep) reticular layer, where the hair grows out of
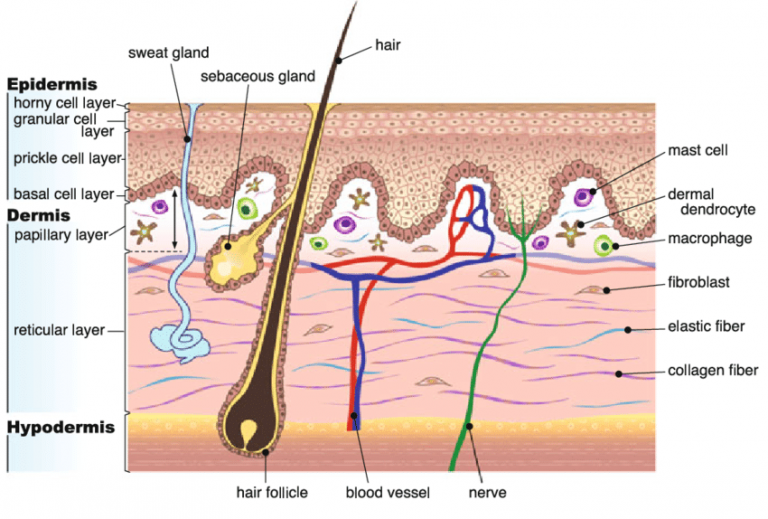
arrector pili muscle
smooth muscle attached near the hair follicle that pulls hair in erect
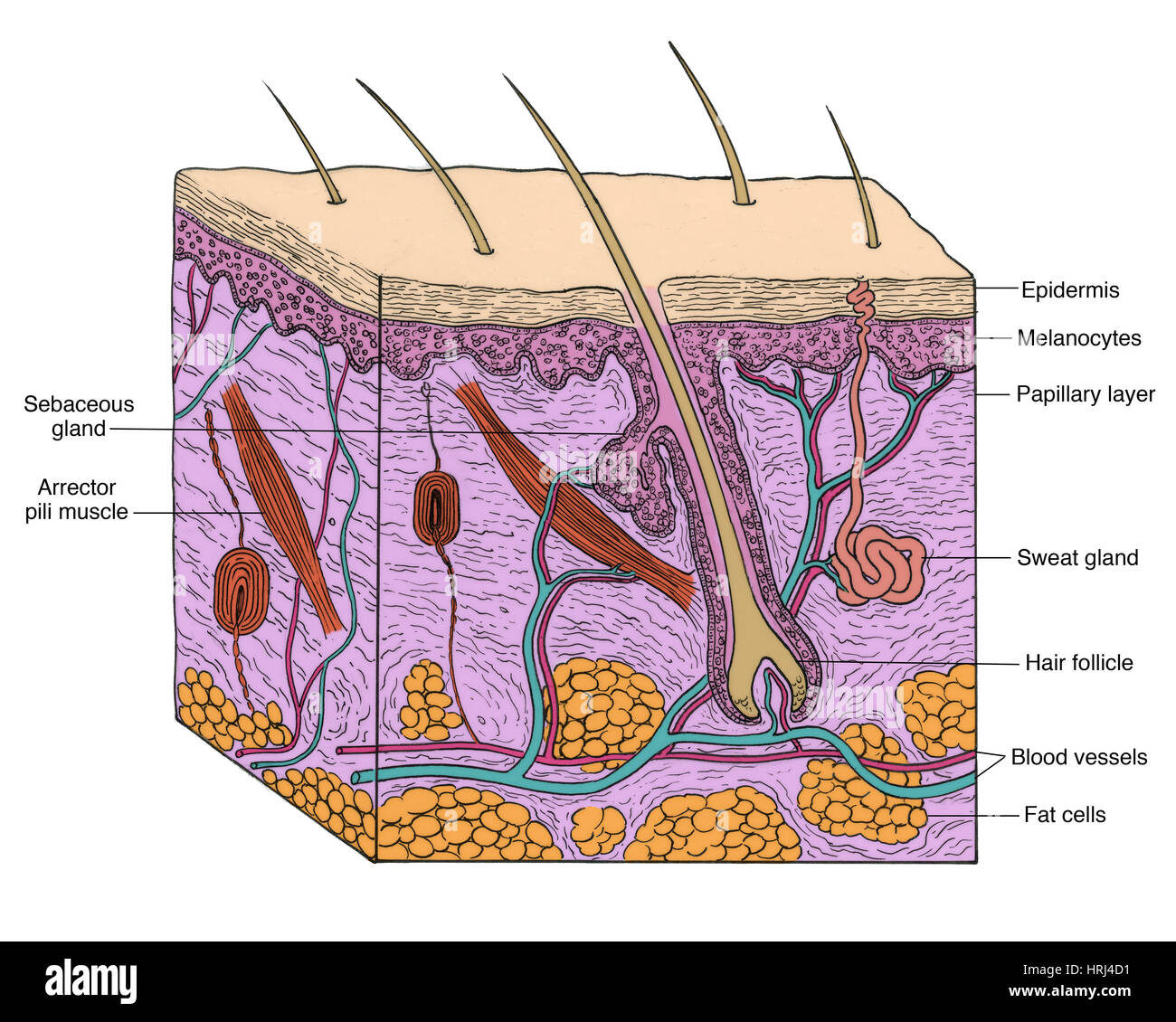
sebaceous gland
secretes sebum (oil)
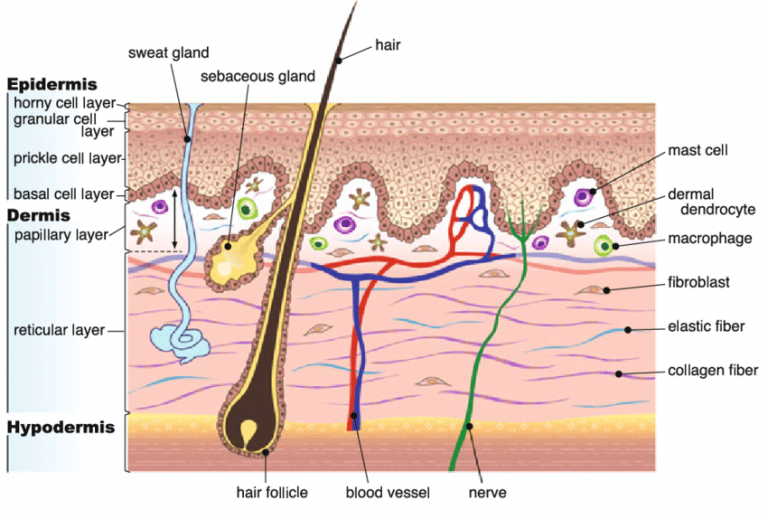
sweat gland
thermoregulation & “body odor”
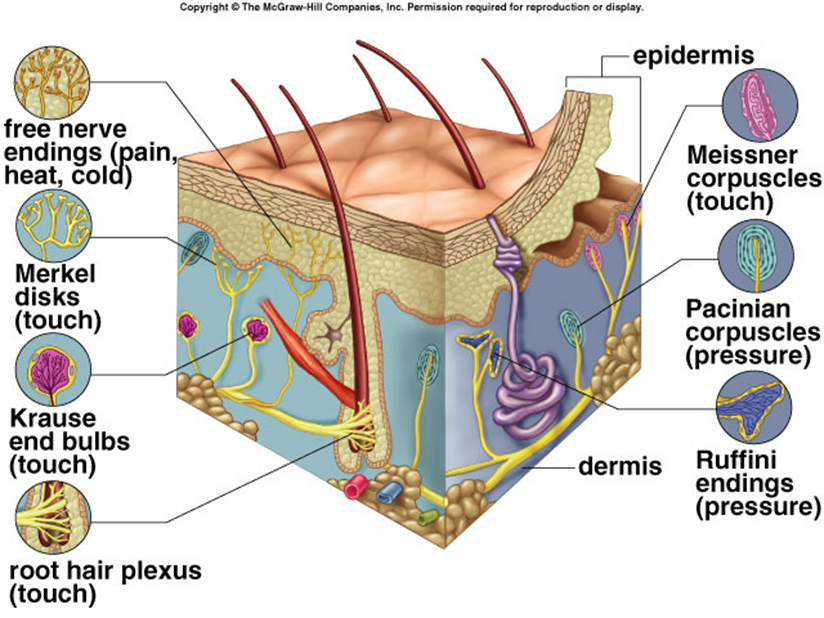
Pacinian gland
touch receptor involving deep pressure and vibration; shaped like an onion
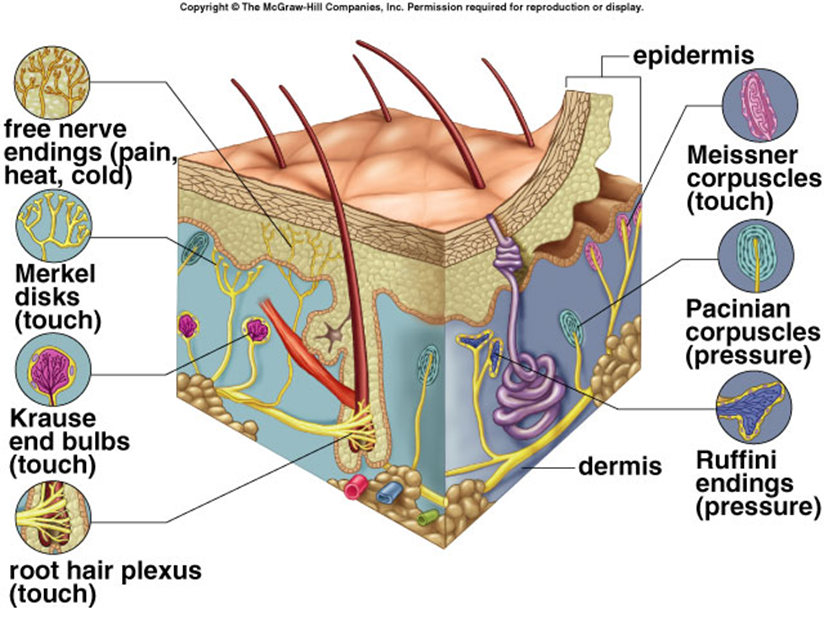
Meissner gland
touch receptor responsible for light touch; shaped like an onion
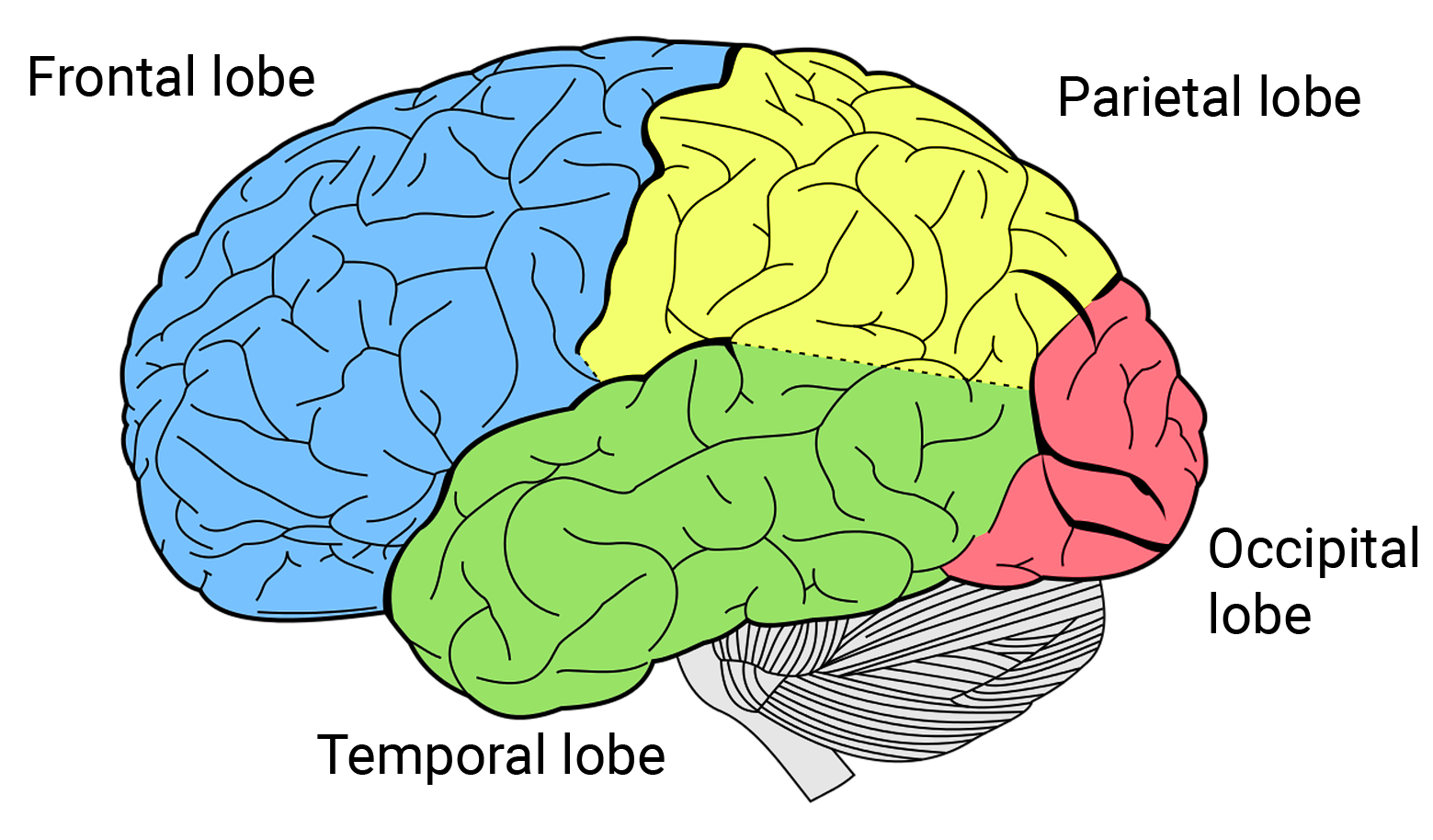
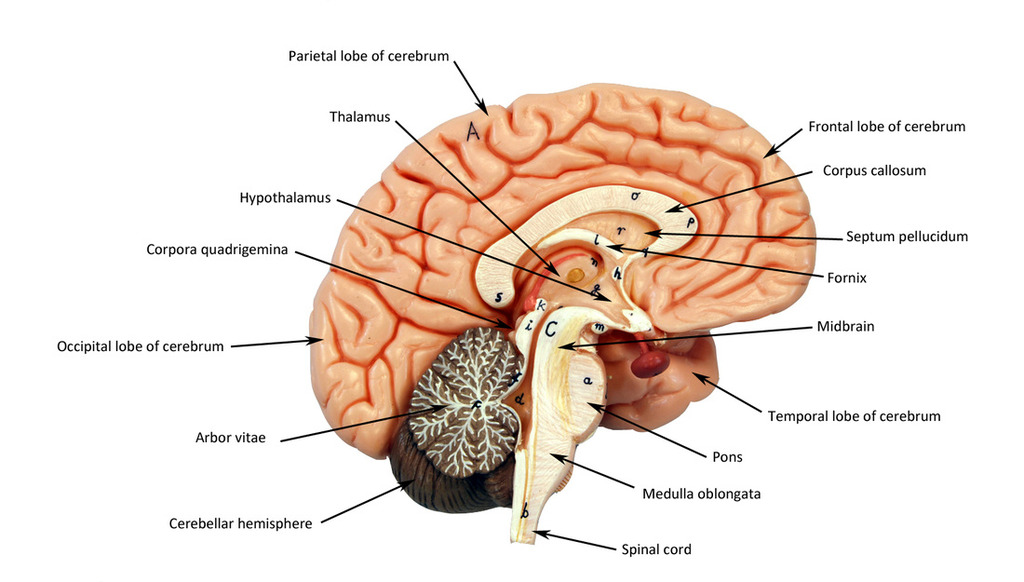
frontal lobe
motor control, abstract thought, planning and personality
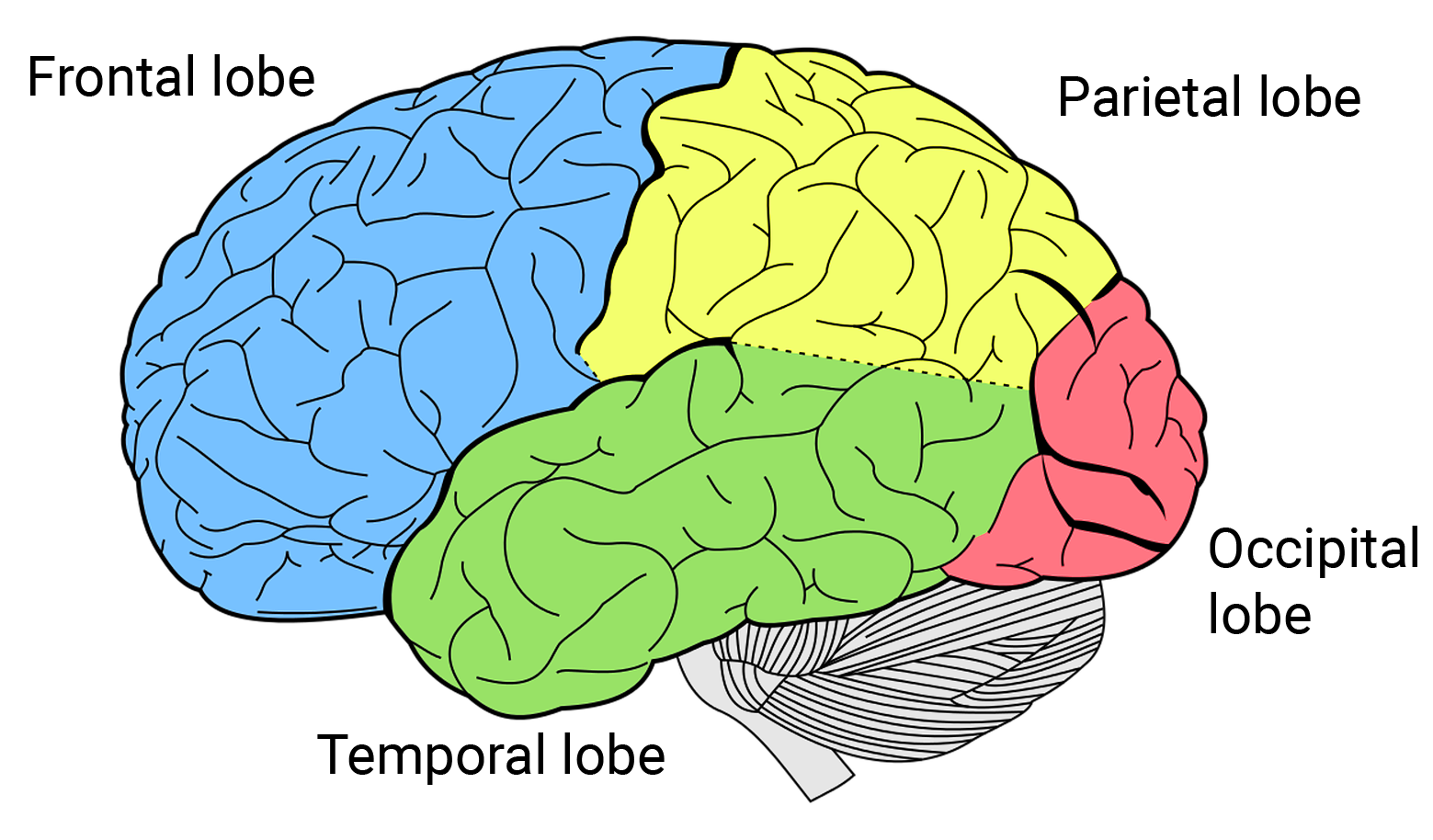
parietal lobe
sensation, association, spatial awareness
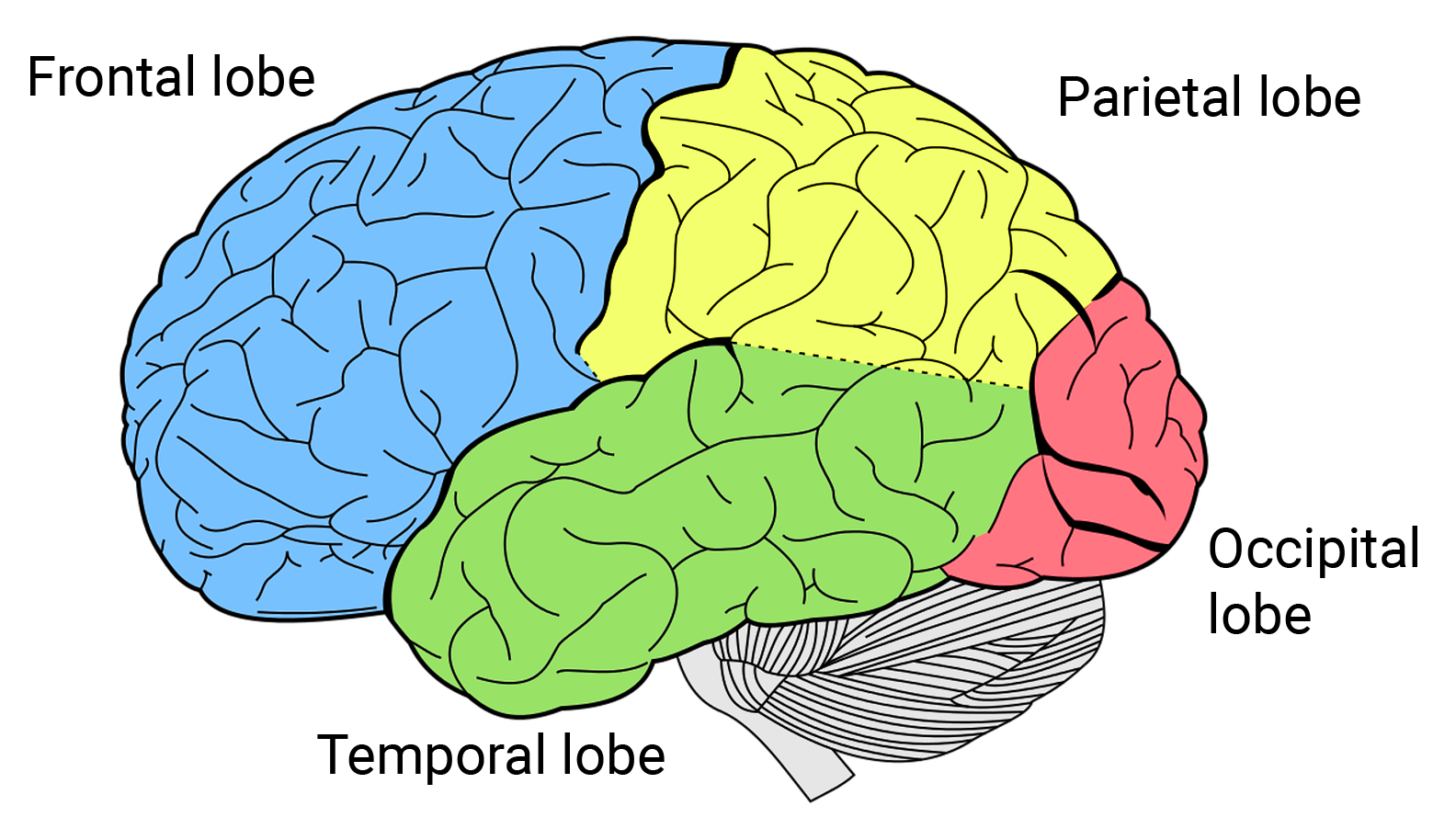
temporal lobe
memory, language
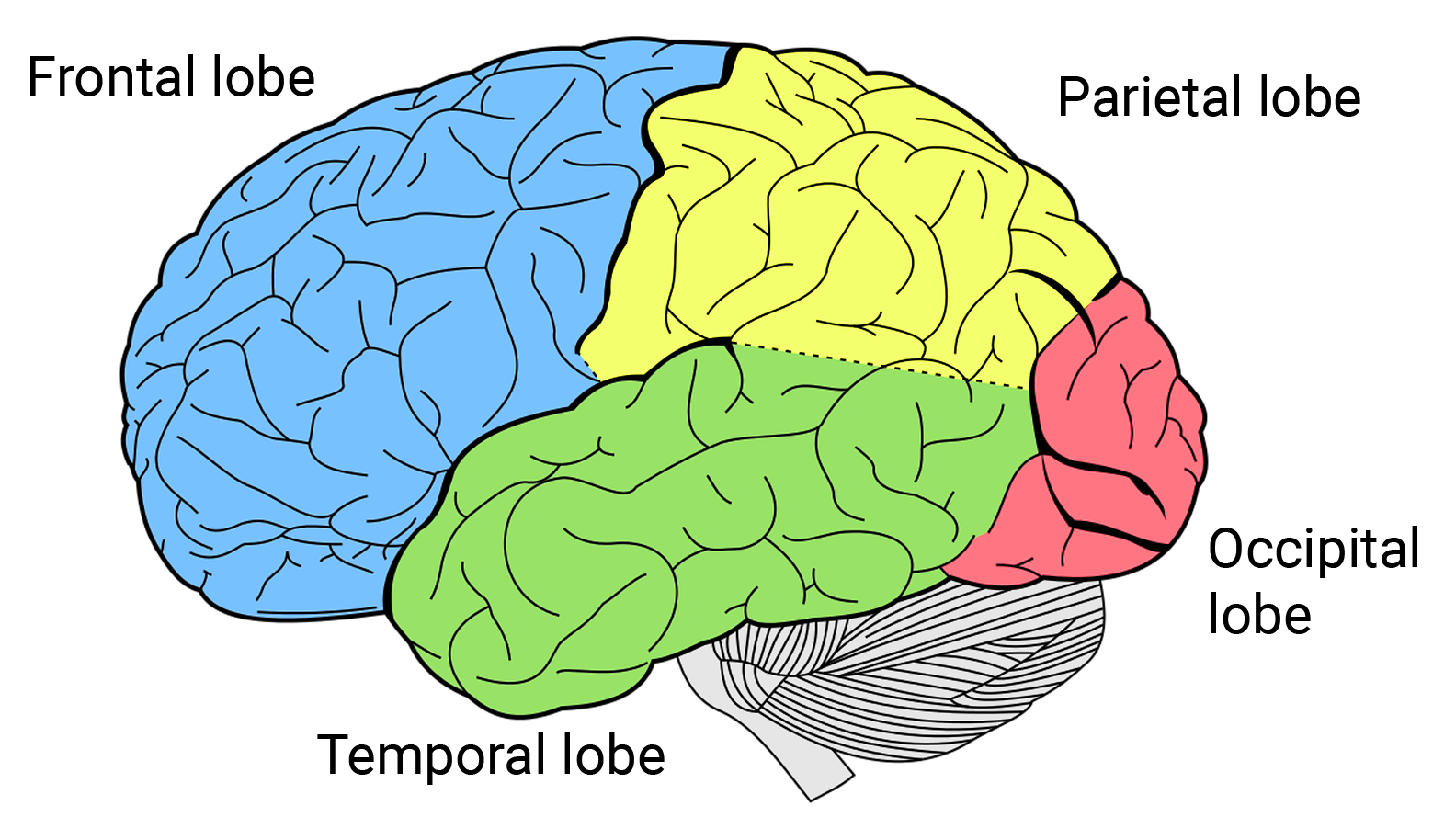
occipital lobe
vision, back of the brain
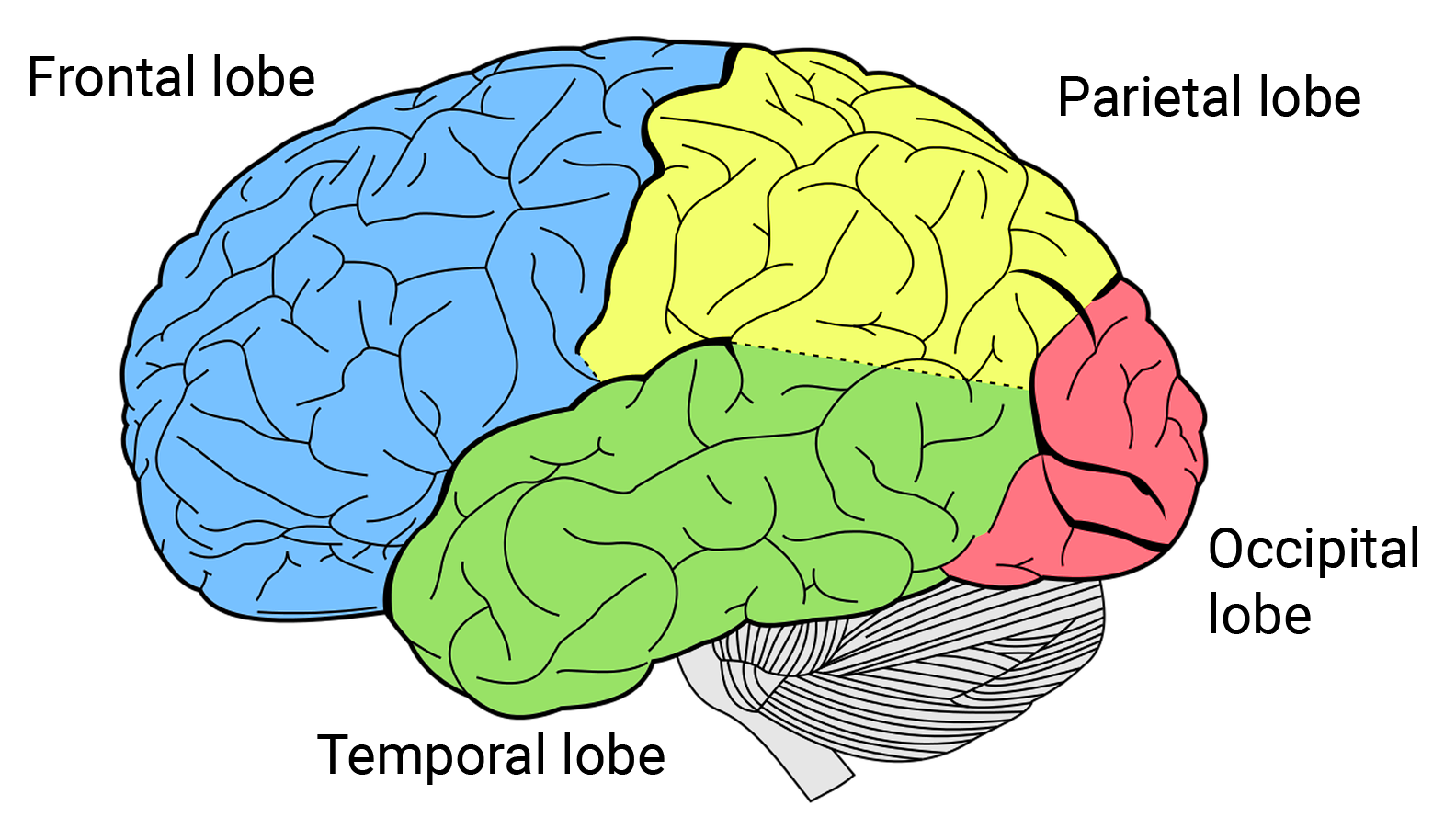
cerebellum
“Little brain;” balance coordination
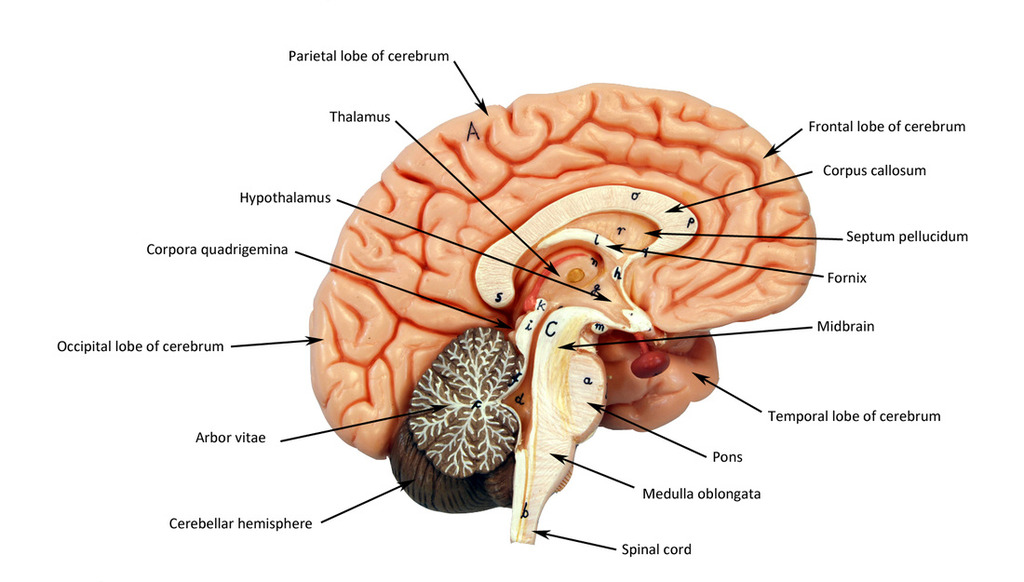
thalamus
directs signals to different lobes of the brain
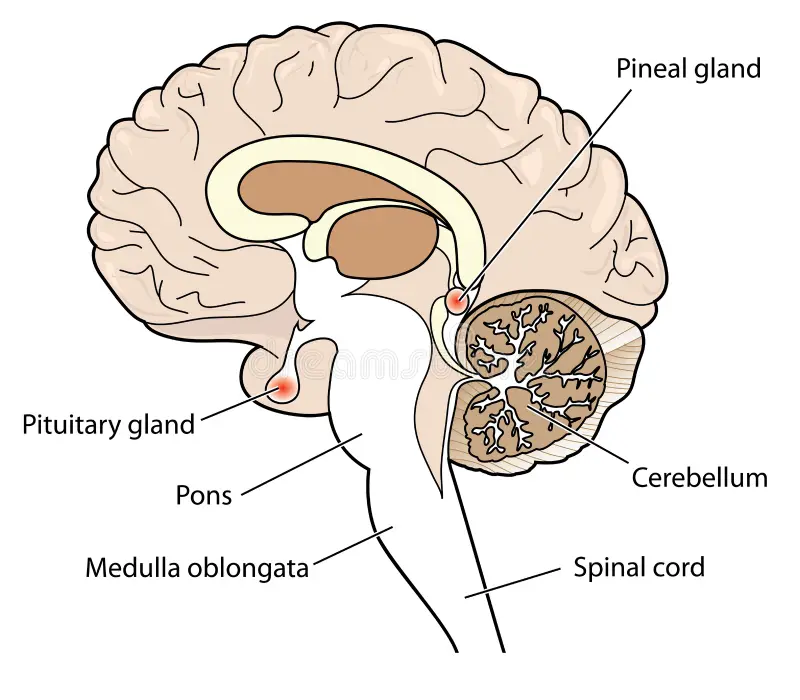
hypothalamus
in charge of homeostasis, secretes hormones and maintains general body functions (sleep, hunger, etc…)
pituitary gland
small, pea sized; in charge of hormone production
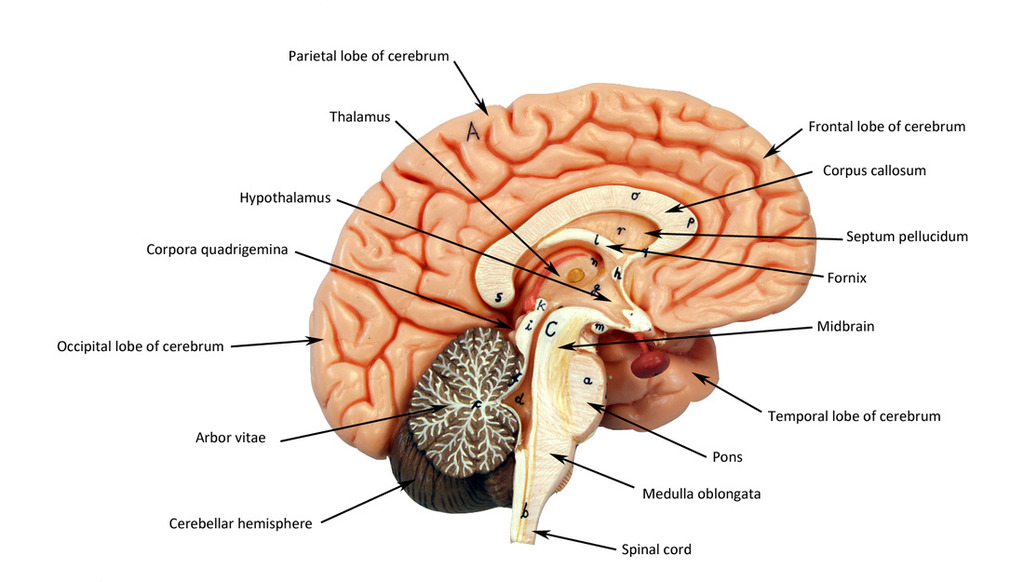
corpus callosum
connects hemispheres
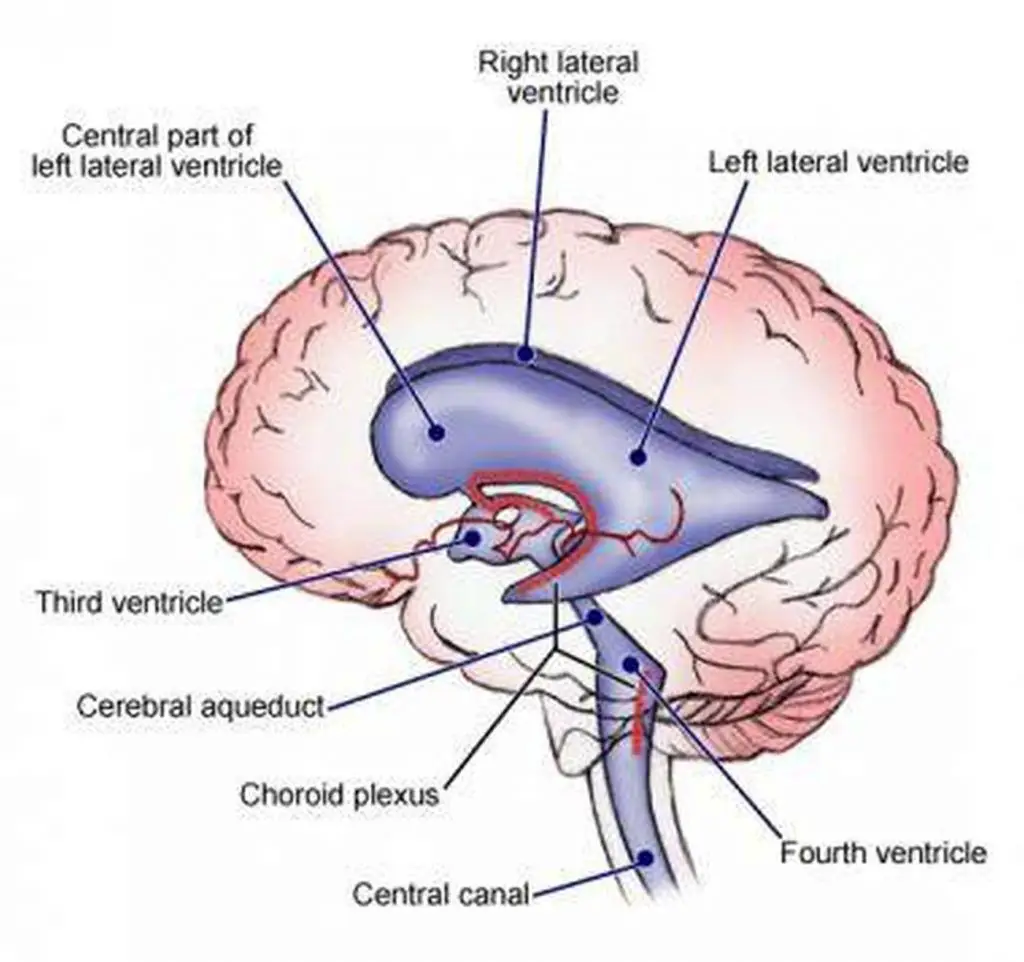
third ventricle
in between the area of the corpus callosum idrk
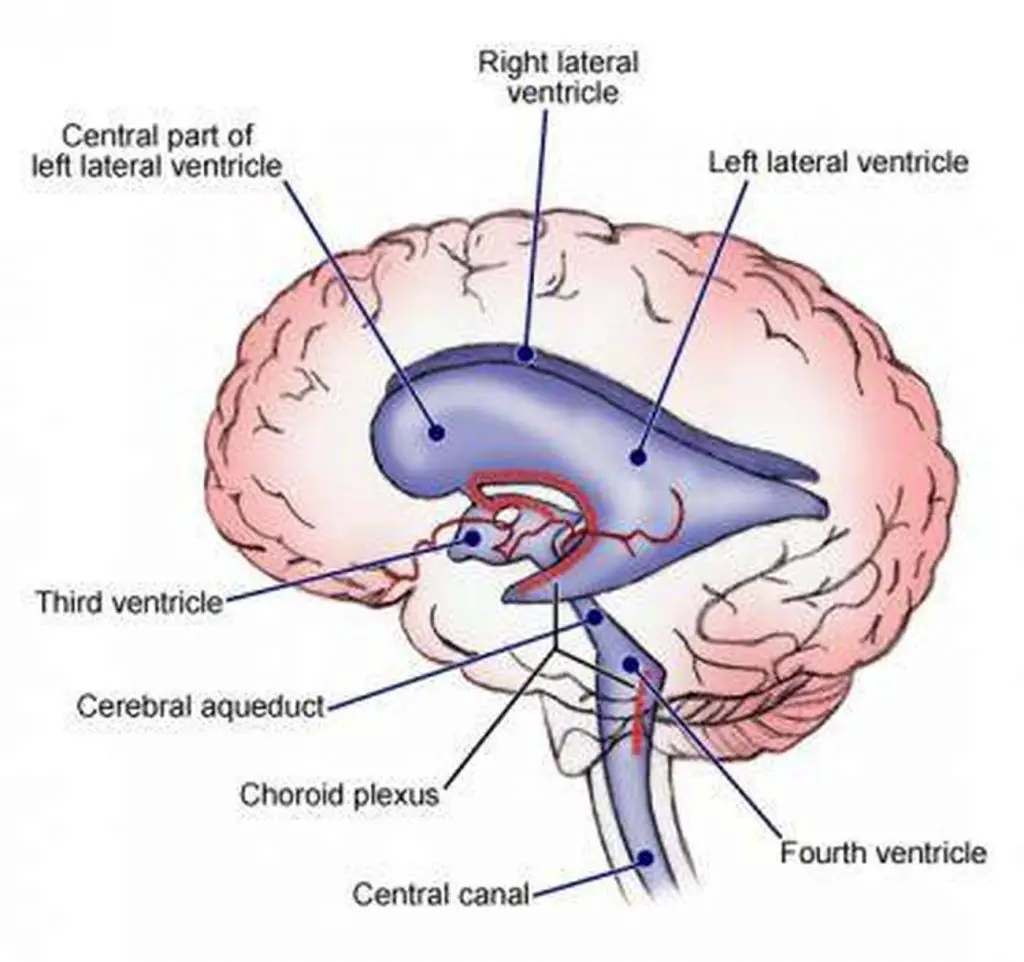
fourth ventricle
goes through temporal lobe and brainstem and cerebellum in midsagittal view
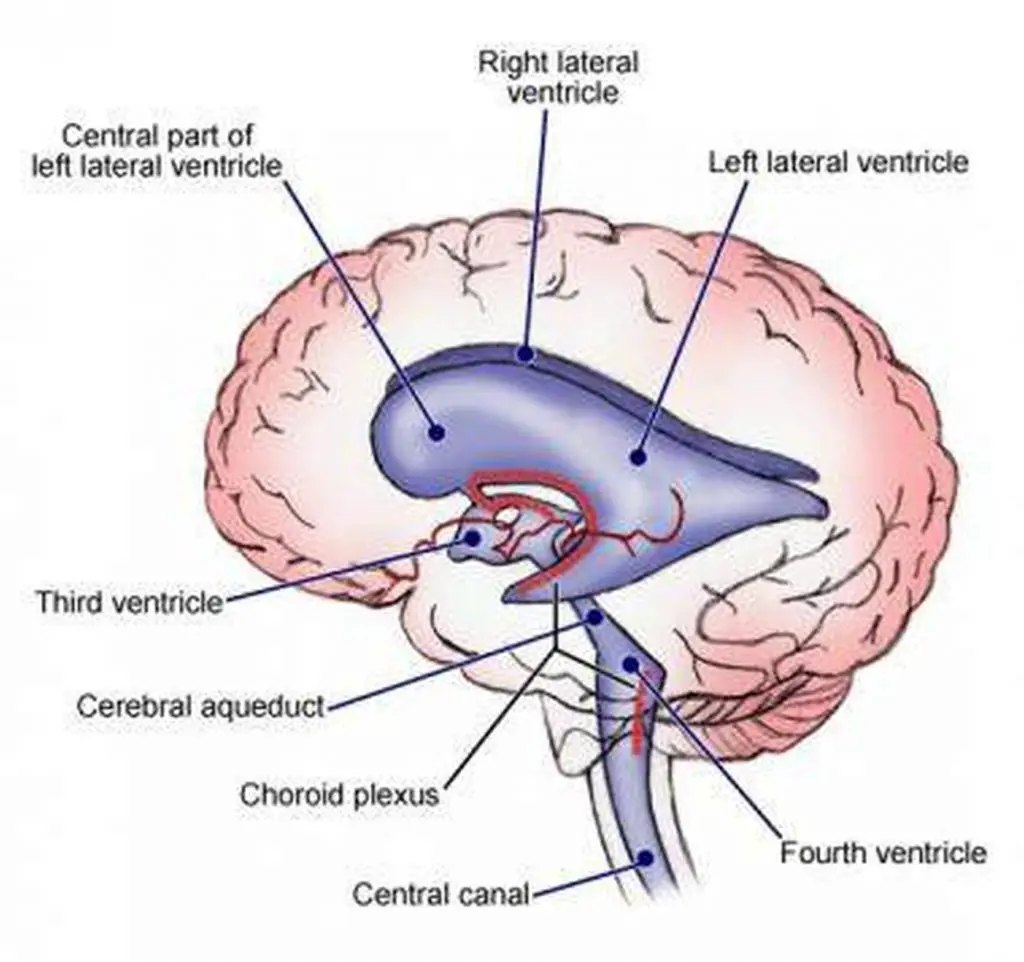
fifth ventricle
guess somewhere below the 4th ventricle i guess… supposedly at the bottom of the spinal cord
brainstem
made up of the midbrain, pons and medulla
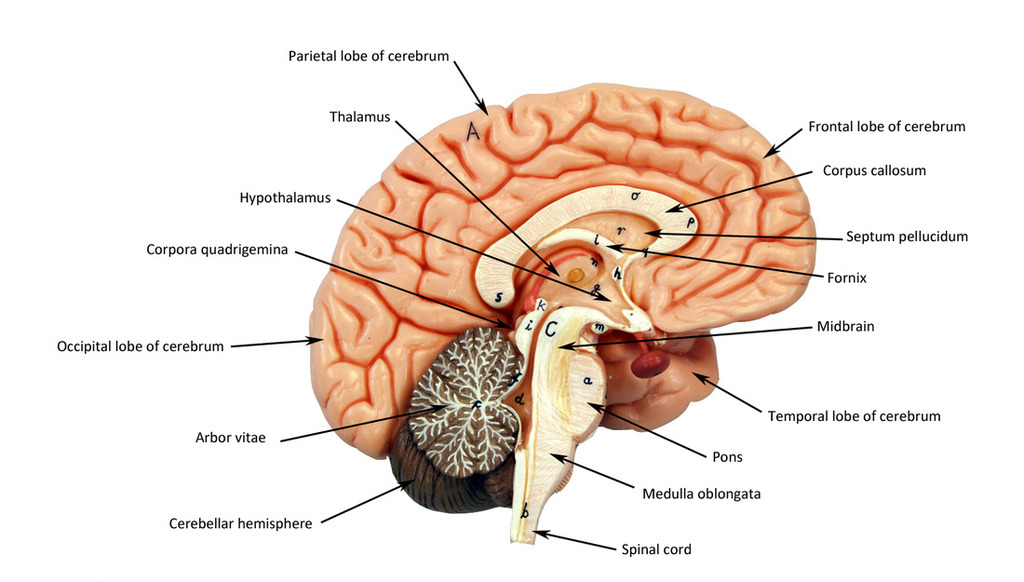
mid brain
closest to the brain, part of the brainstem
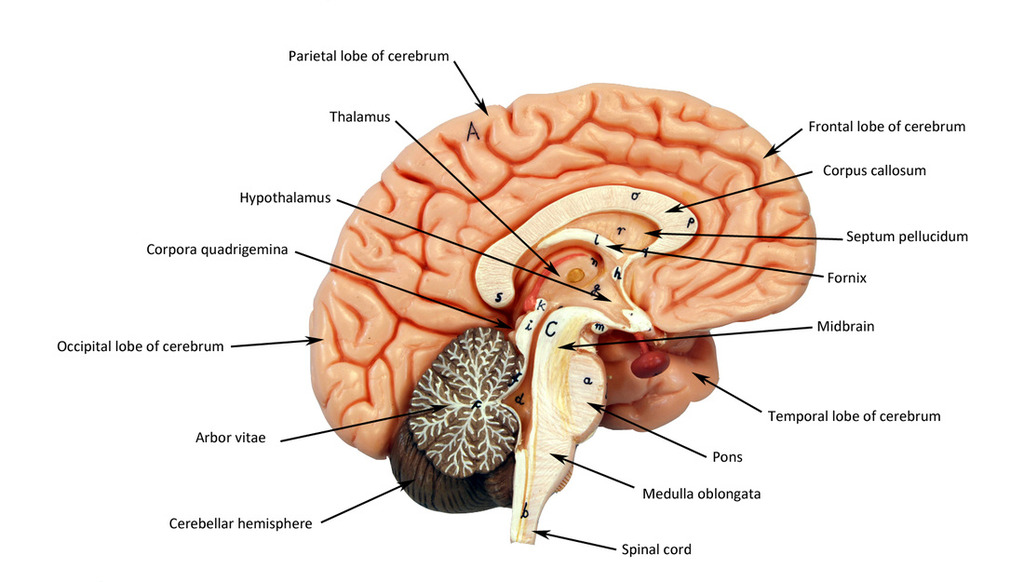
pons
fattest part and in the middle of the brainstem
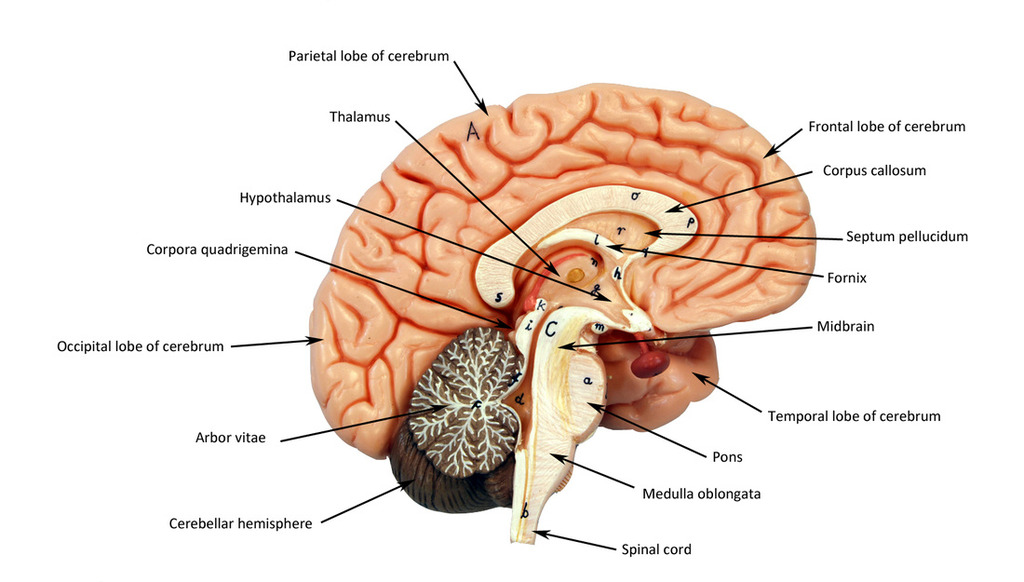
medulla
closest to the spinal cord
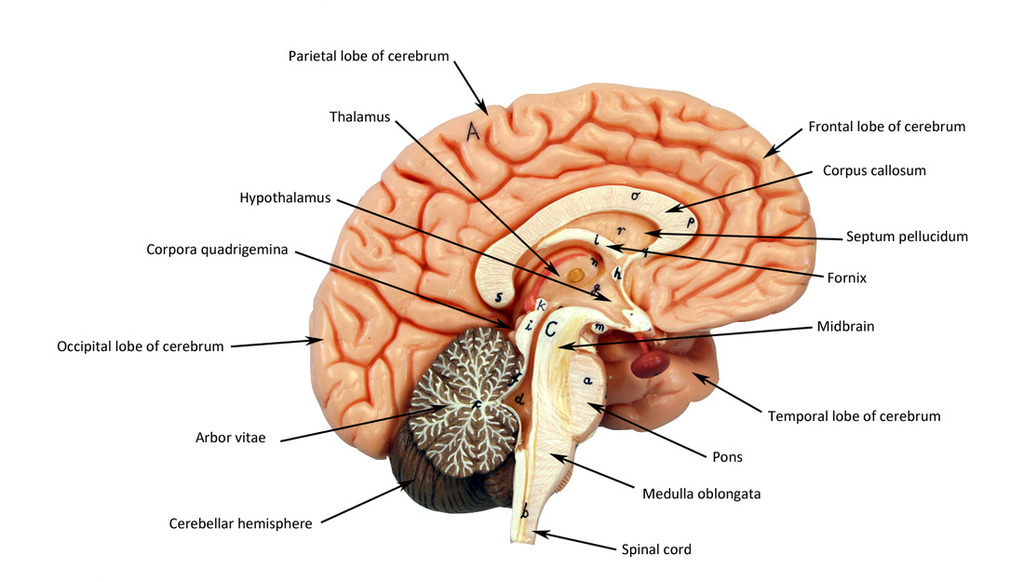
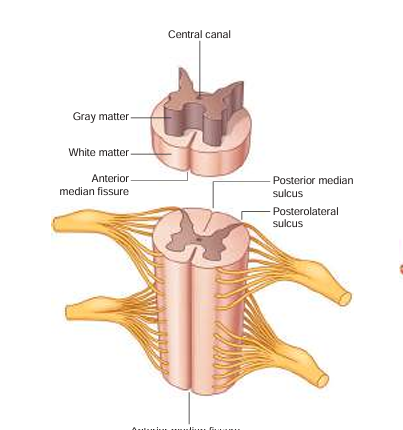
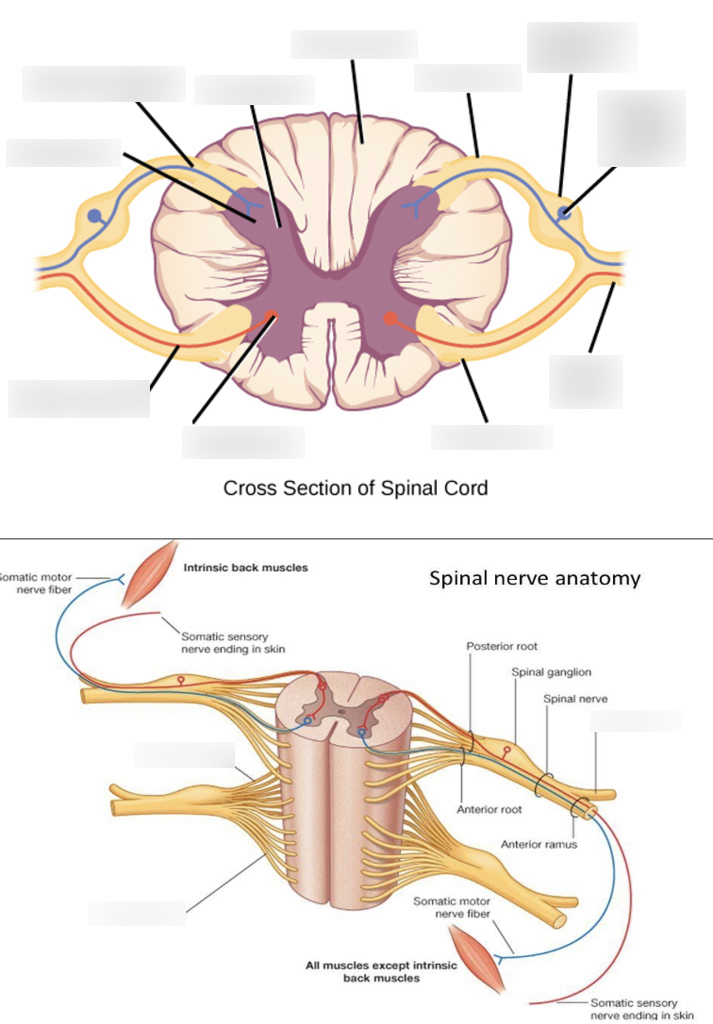
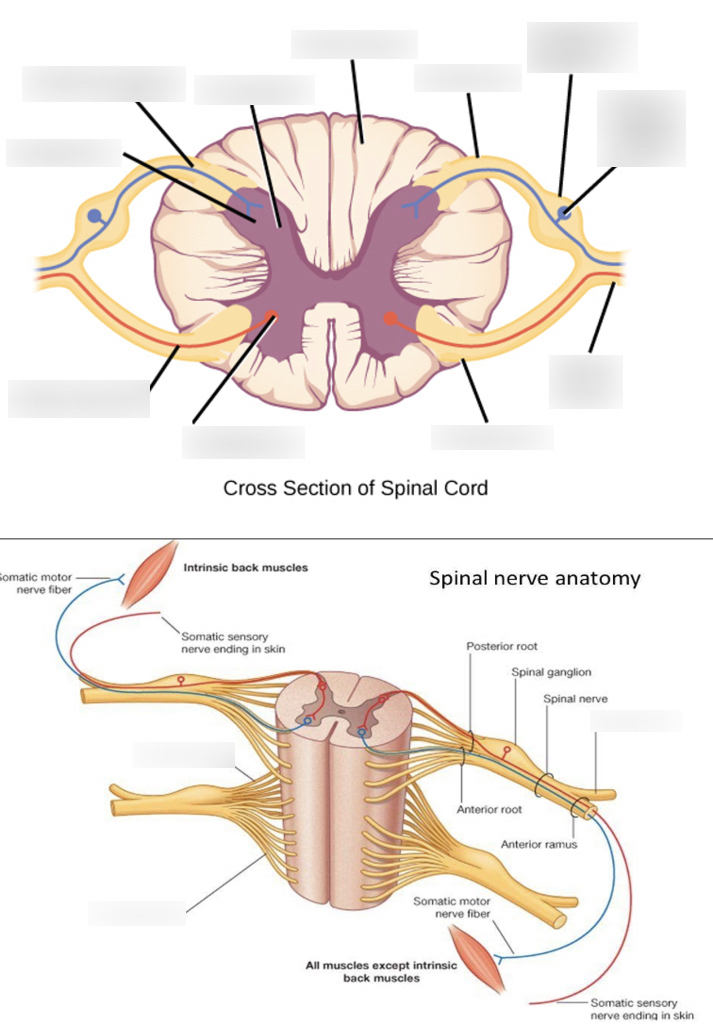
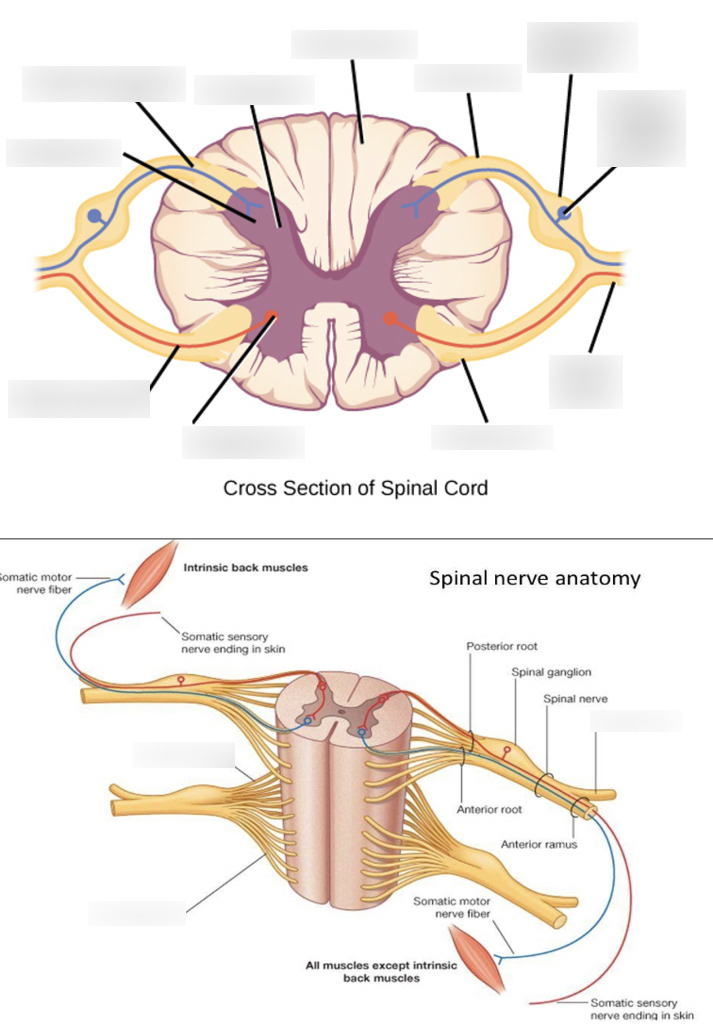
white matter
where the posterior/anterior horns sit on top of; it surrounds the gray matter
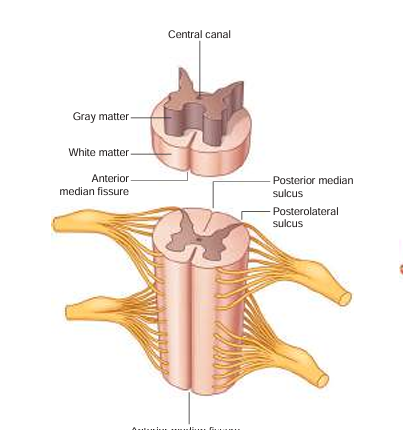
anterior median fissure
booty crack of the anterior
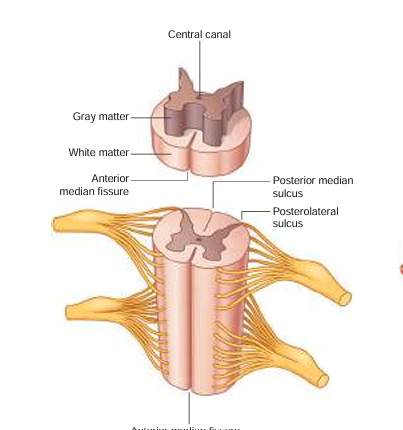
anterior horn
fatter part of the gray matter; closer towards the anterior median fissure
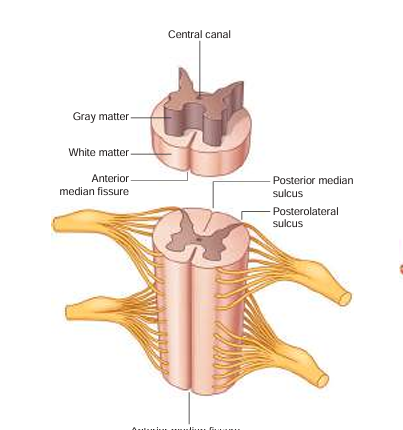
posterior horn
longer, skinnier part of the gray matter
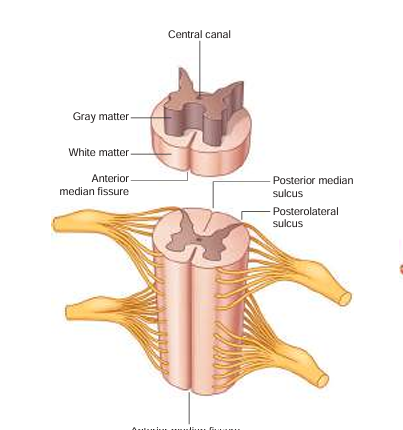
lateral horn
in between the anterior and posterior horns; processes autonomic information
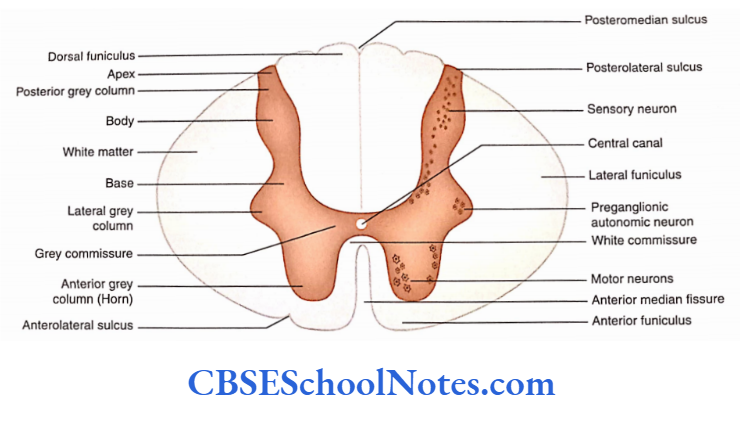
central canal
in the middle of the gray matter, contains CSF (cerebrospinal fluid)
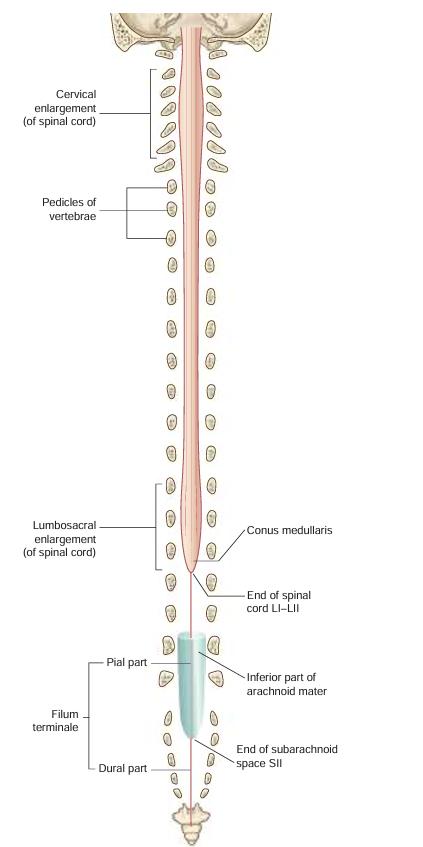
conus medullaris
tapered at the end of the spinal cord; “cone shaped end”
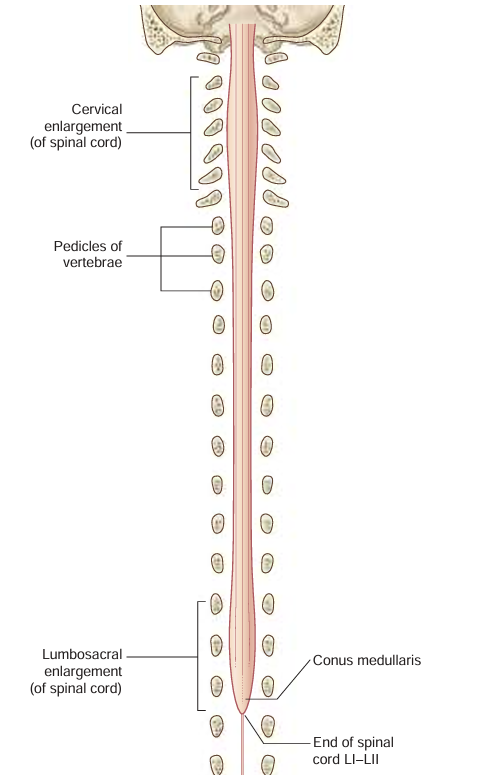
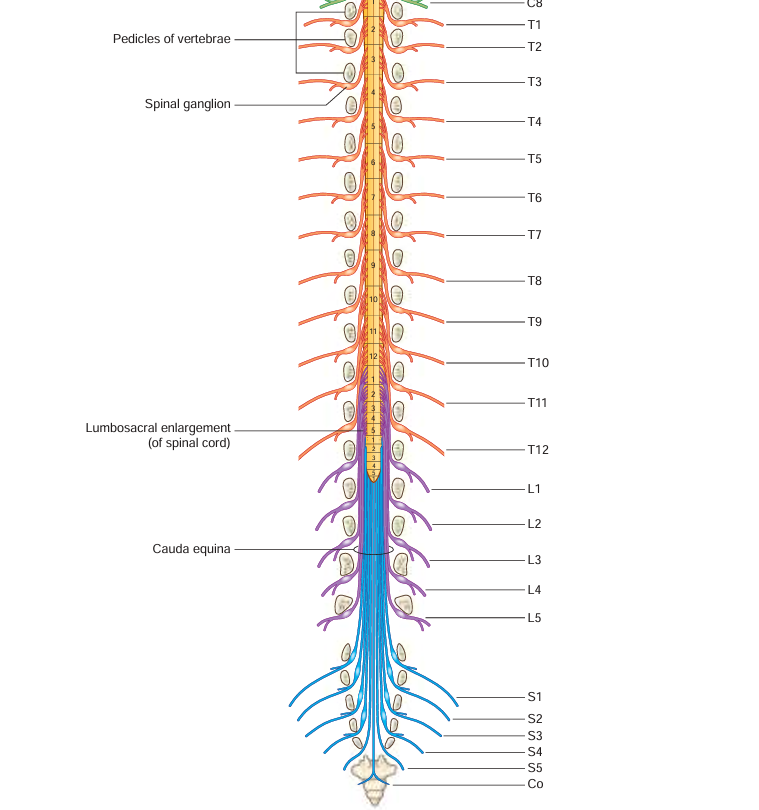
cauda equina
collection of nerve roots the end before the sacral region
filum terminale
part of the spinal cord that is anchored to the coccyx
anterior root (Spinal nerve component)
passes motor information
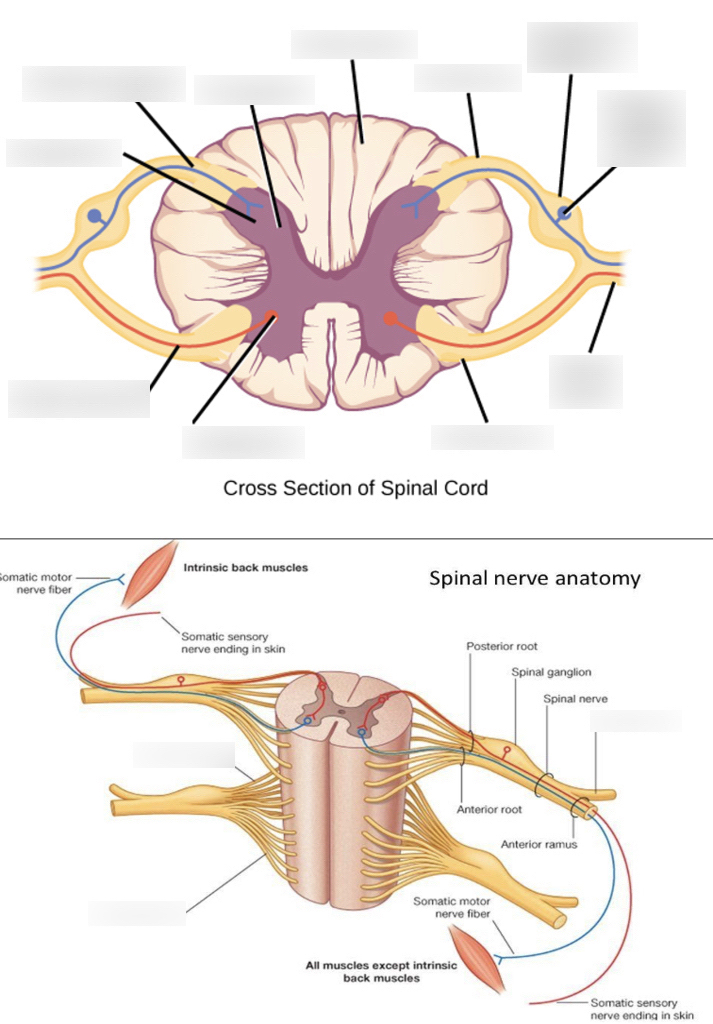
posterior root (Spinal nerve component)
passes sensory information; comes here after passing through the spinal ganglion
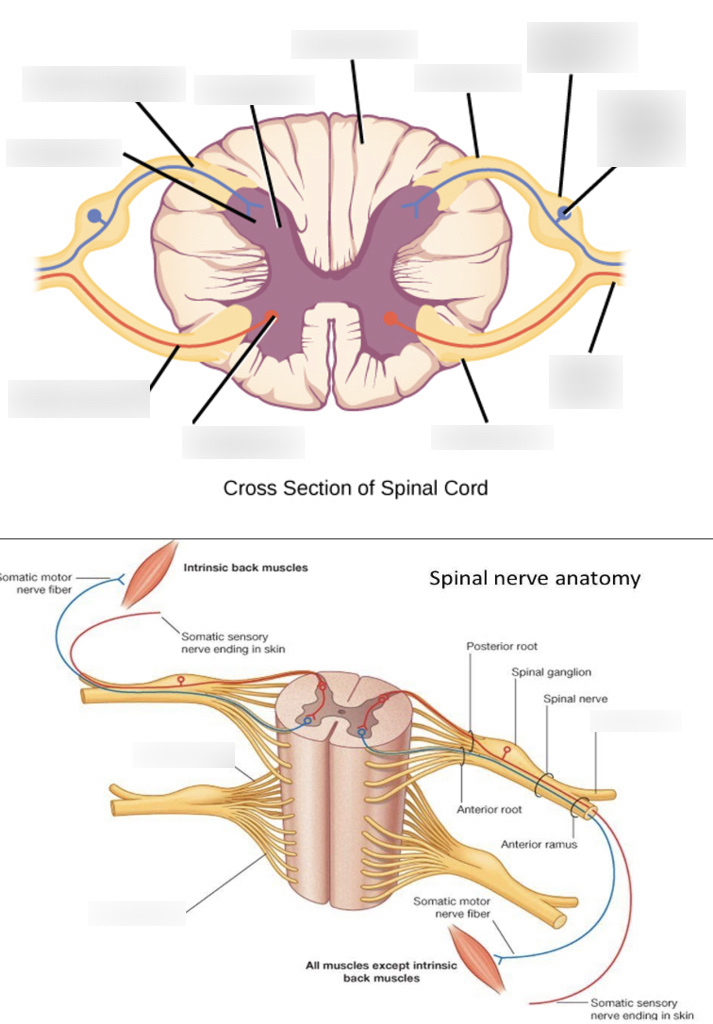
anterior ramus (Spinal nerve component)
passes both sensory and motor information; comes here after passing anterior root.
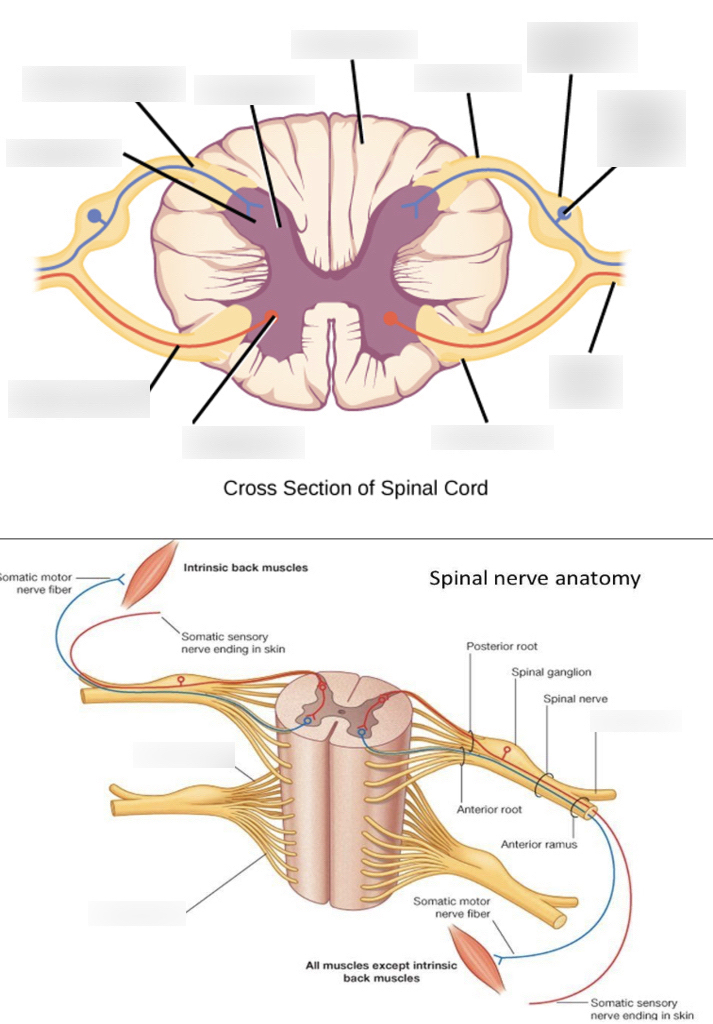
posterior ramus (Spinal nerve component)
passes both sensory and motor information; start of the signal pathway through the spinal nerve
spinal ganglion (Spinal nerve component)
usually labeled on the posterior side; comes here after passing through posterior ramus → spinal nerve -→ -blank-
spinal nerve (Spinal nerve component)
contains the rami, ganglion; the component before the split of the roots
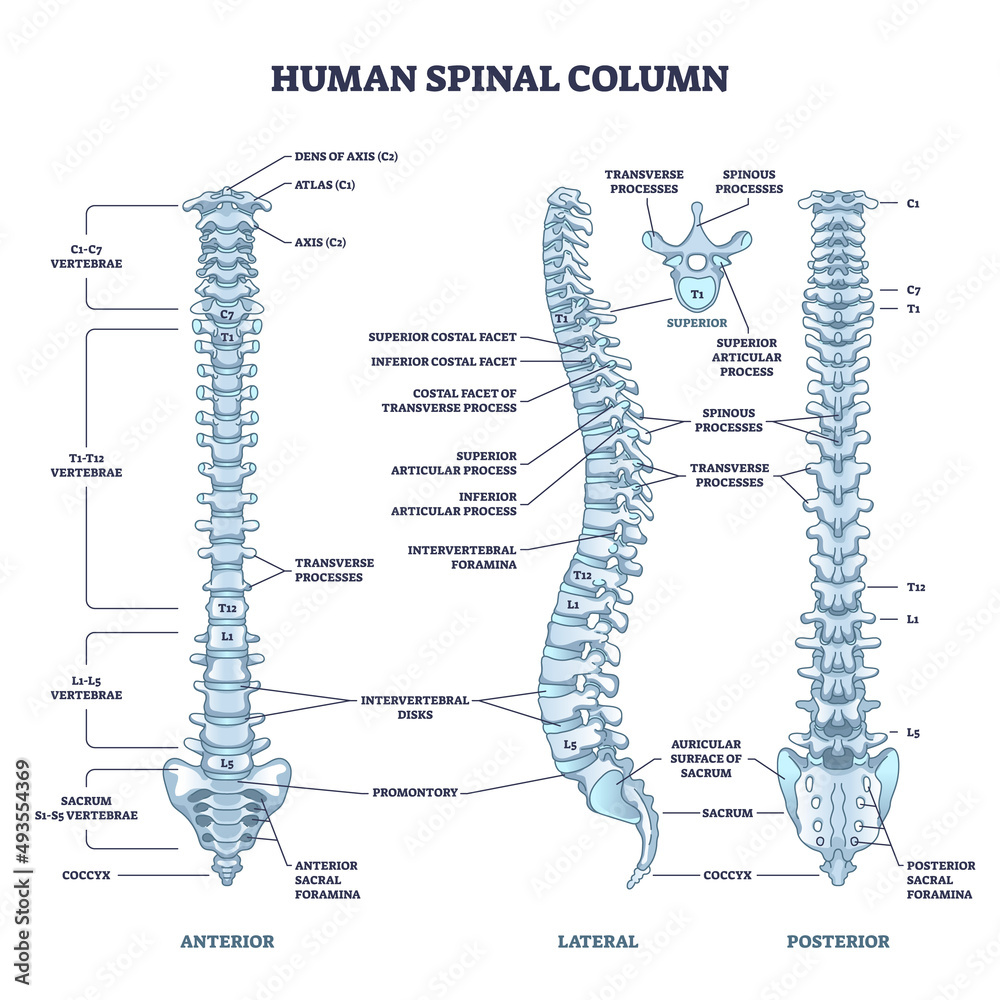
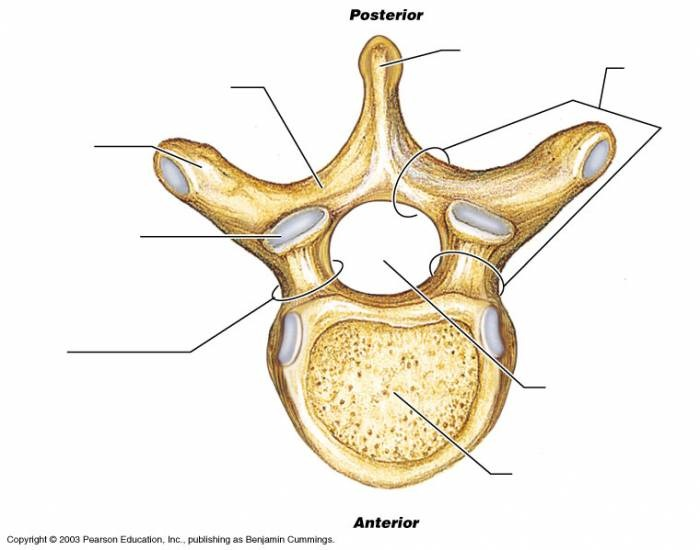
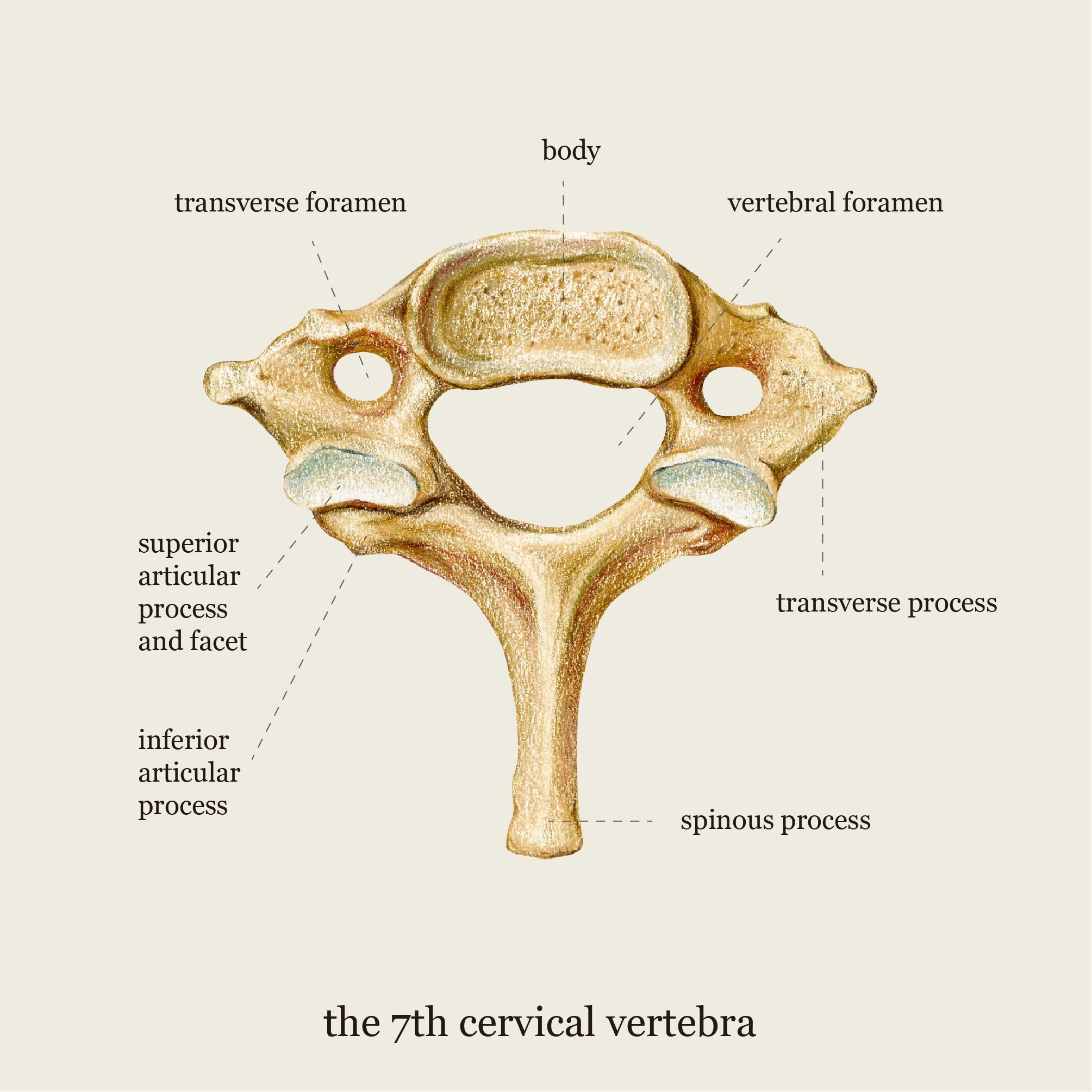
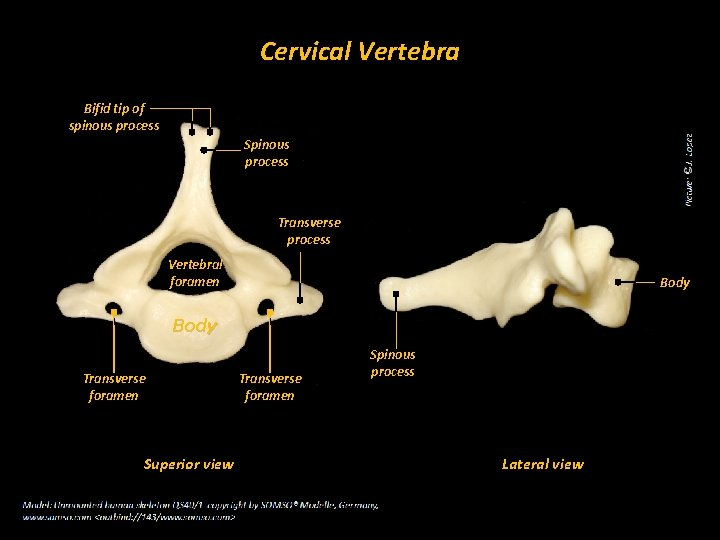
cervical vertebra
top part of the spinal cord
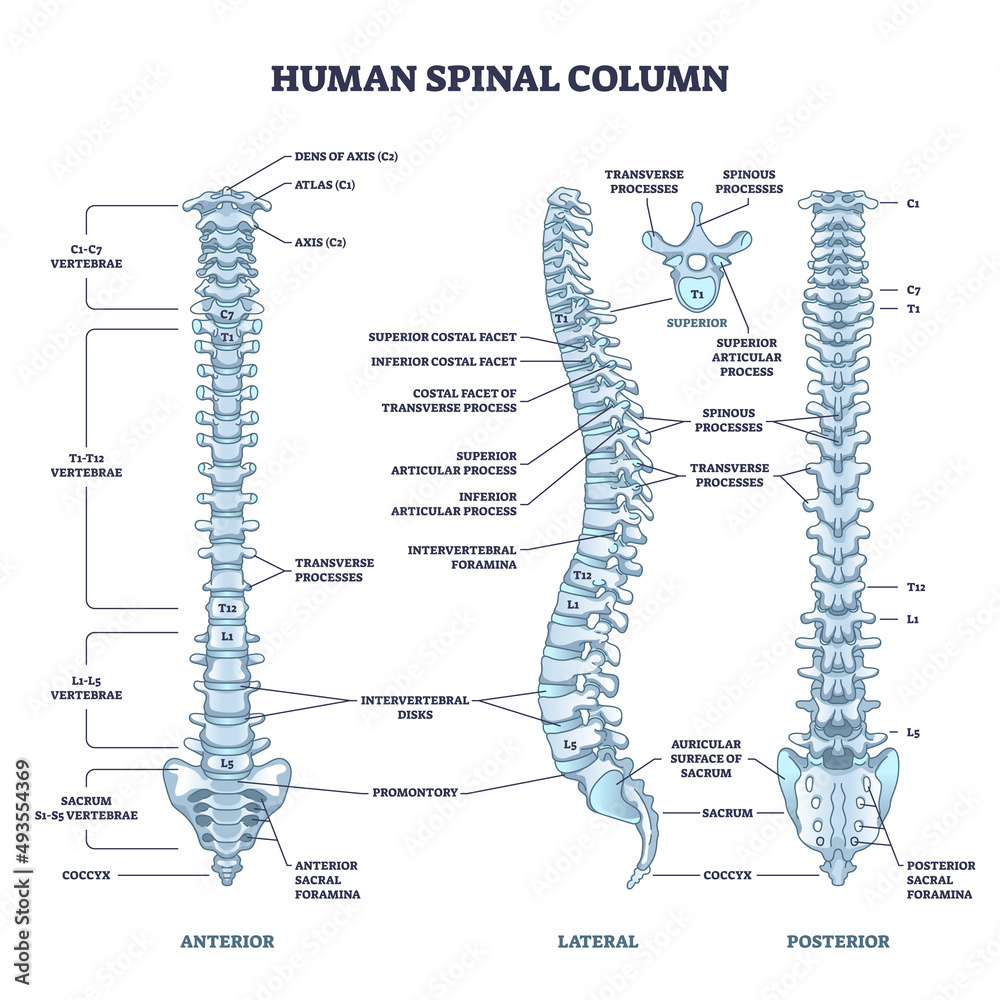
Atlas (C1)
hold the skull; first vertebra of the cervical vertebrae
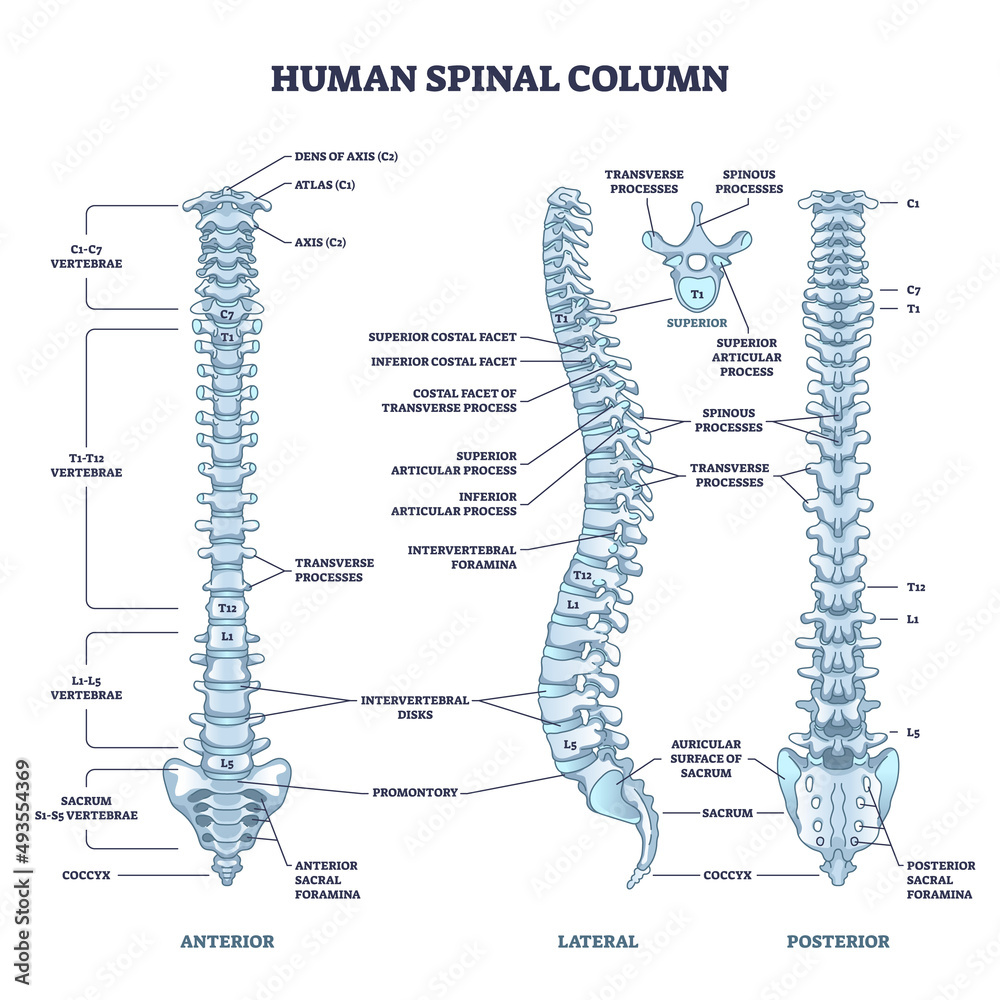
axis (C2)
contains the dens and is the second vertebra of the cervical vertebrae
Dens landmark on Axis (C2)
the protrusion on the axis that acts as a pivot that allows the atlas and attached head to rotate on the axis, side to side.
body of a cervical vertebra
fairly smaller than the thoracic and lumbar body.
bifid spinous process of a cervical vertebra
long portion of the vertebra, splits into 2
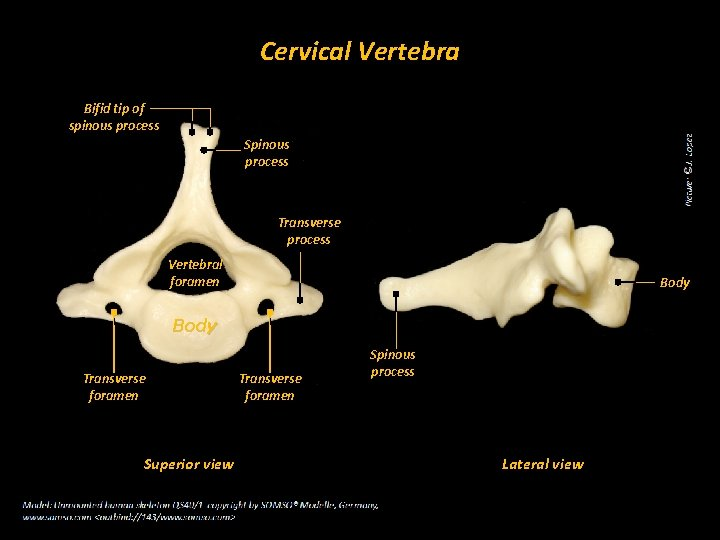
transverse process of a cervical vertebra
“wings” of the body; protrude transversely
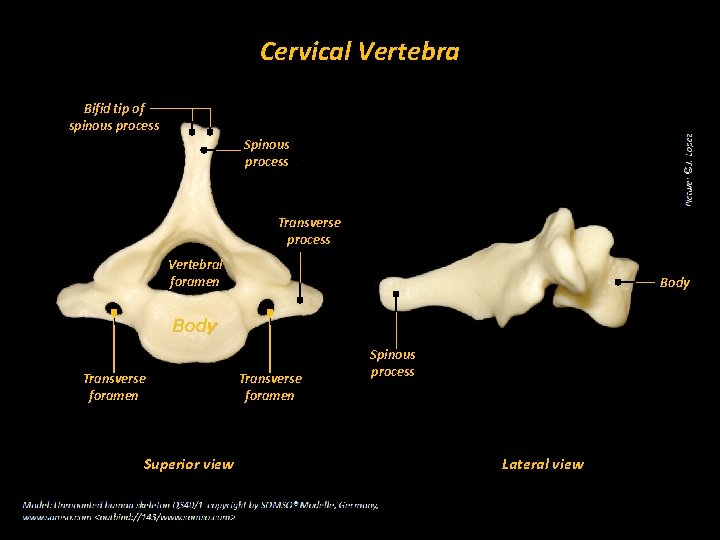
transverse foramen of a cervical vertebra
holes on the transverse process
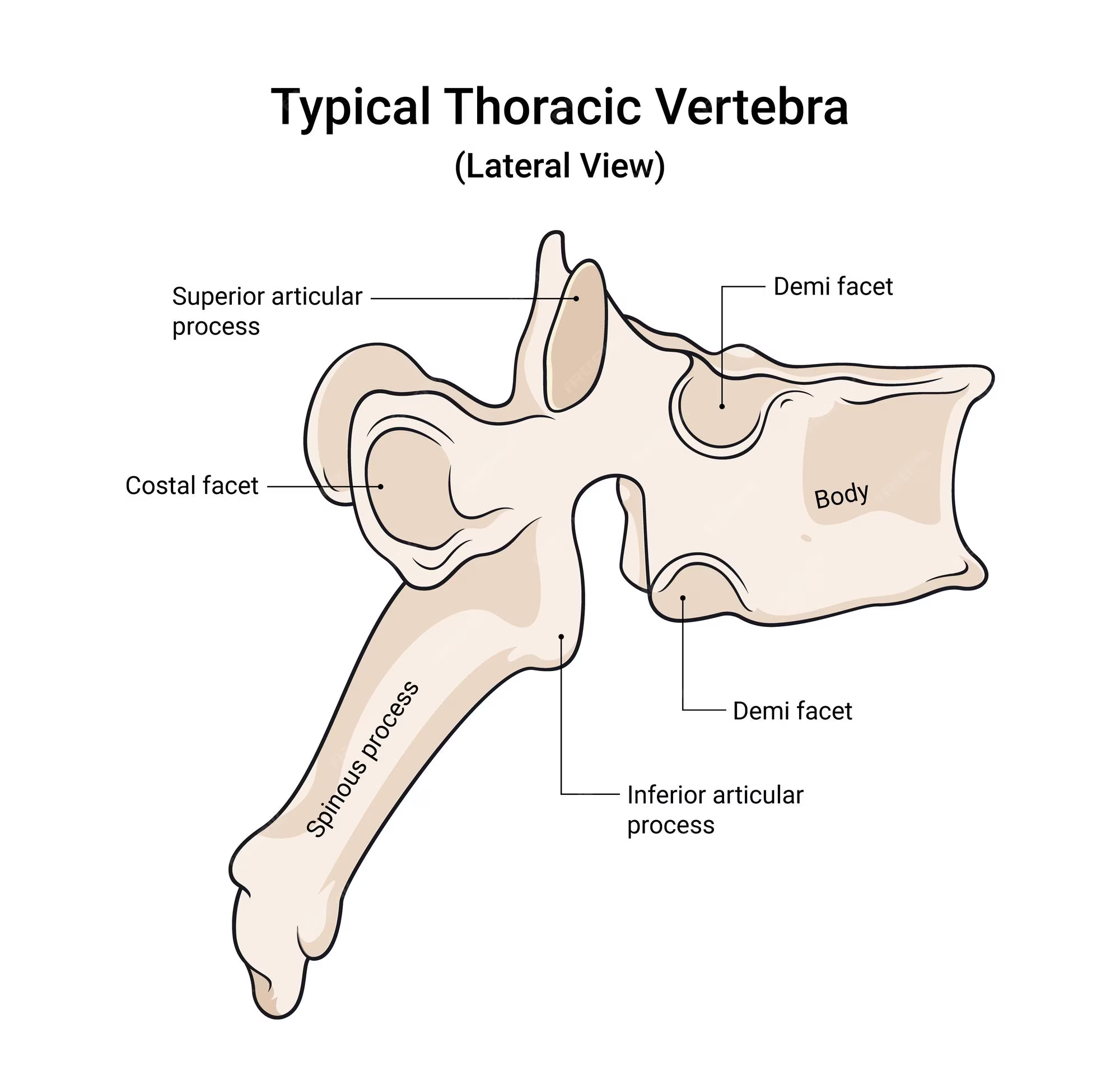
body of a thoracic vertebra
looks like a crow overall; body is fairly big but smaller than the lumbar vertebrae
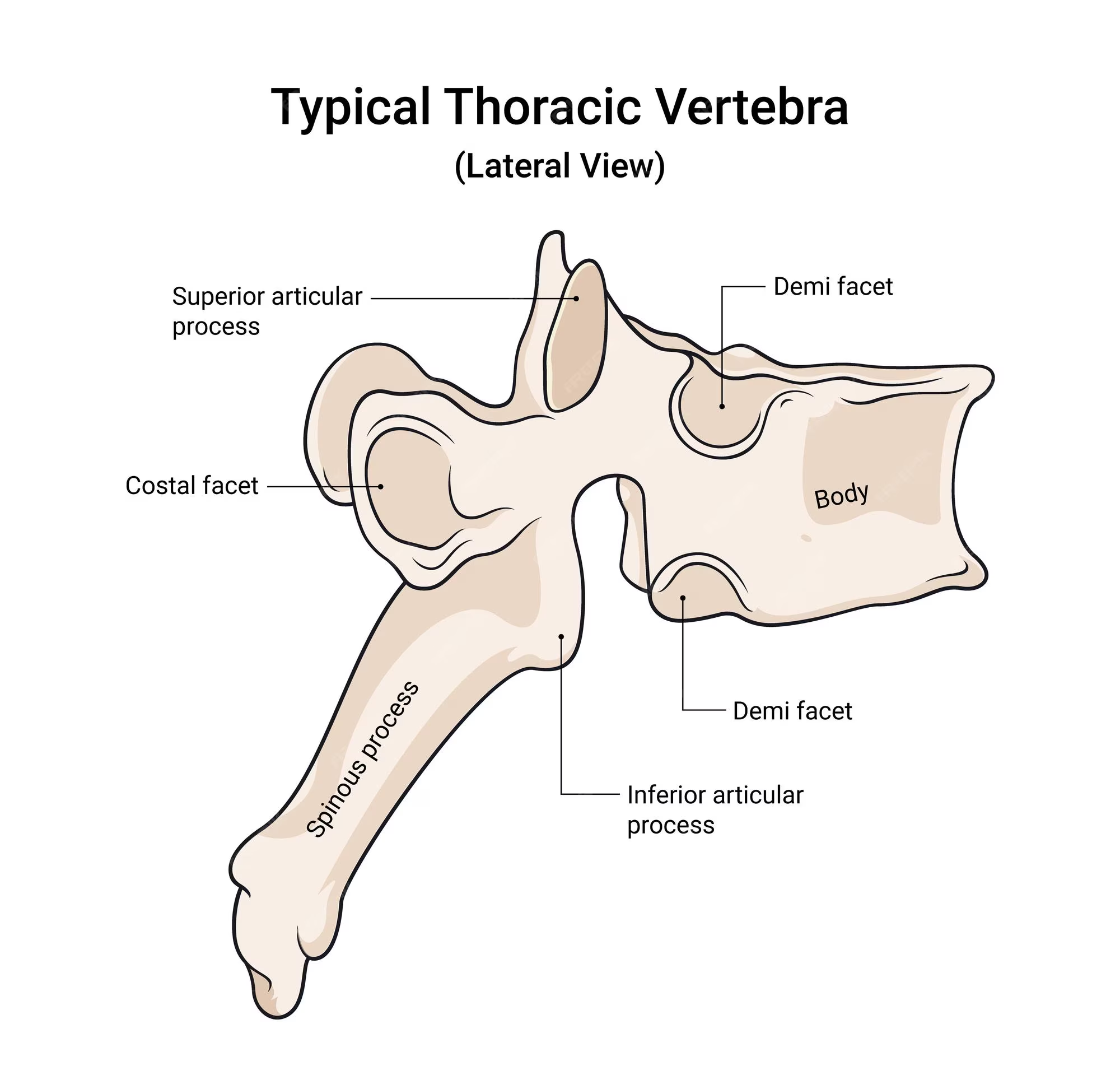
spinous process of a thoracic vertebra
Long, inferiorly angled
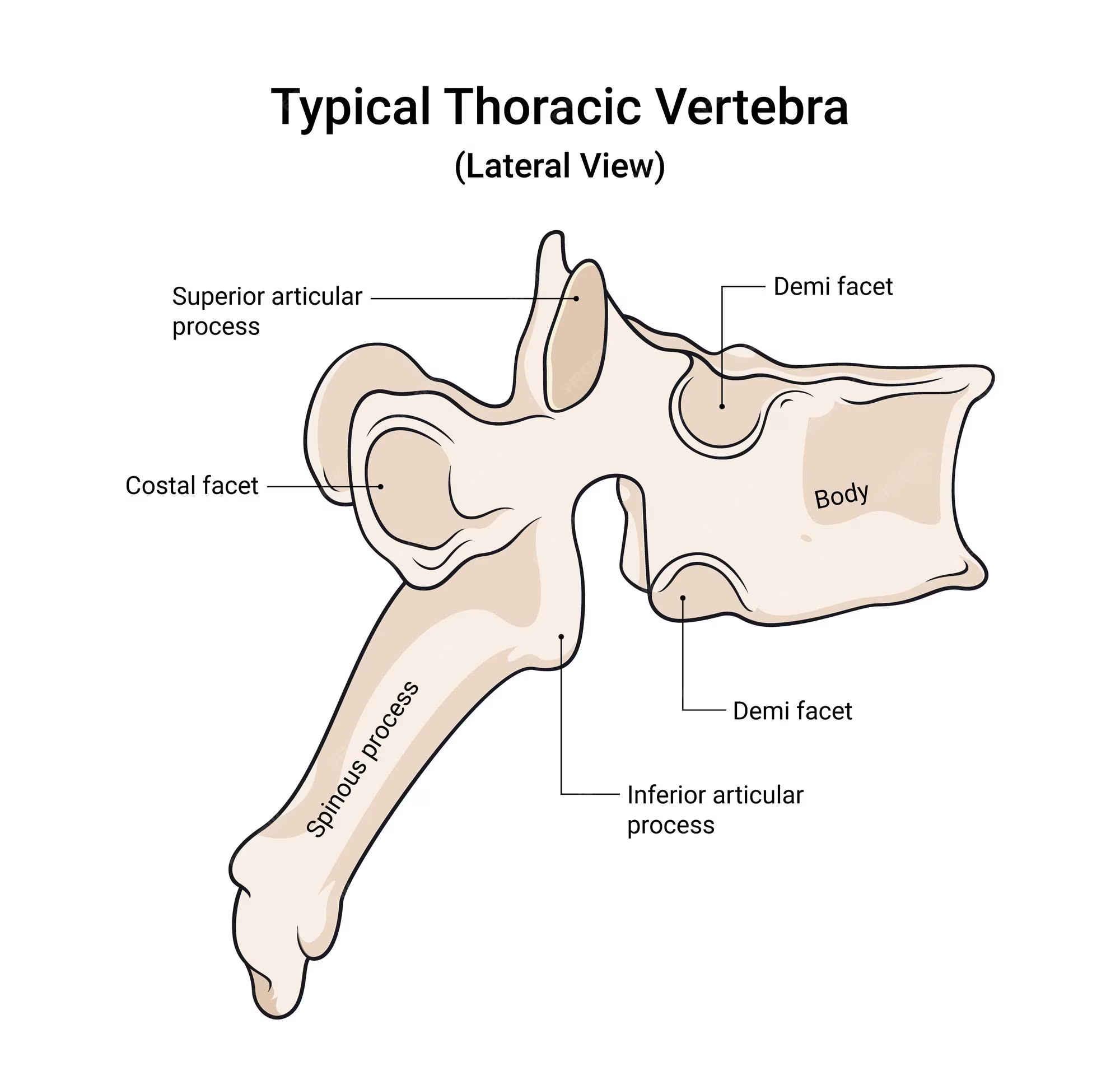
transverse process of a thoracic vertebra
wings that protrude but NOT from the body; connected with pedicle
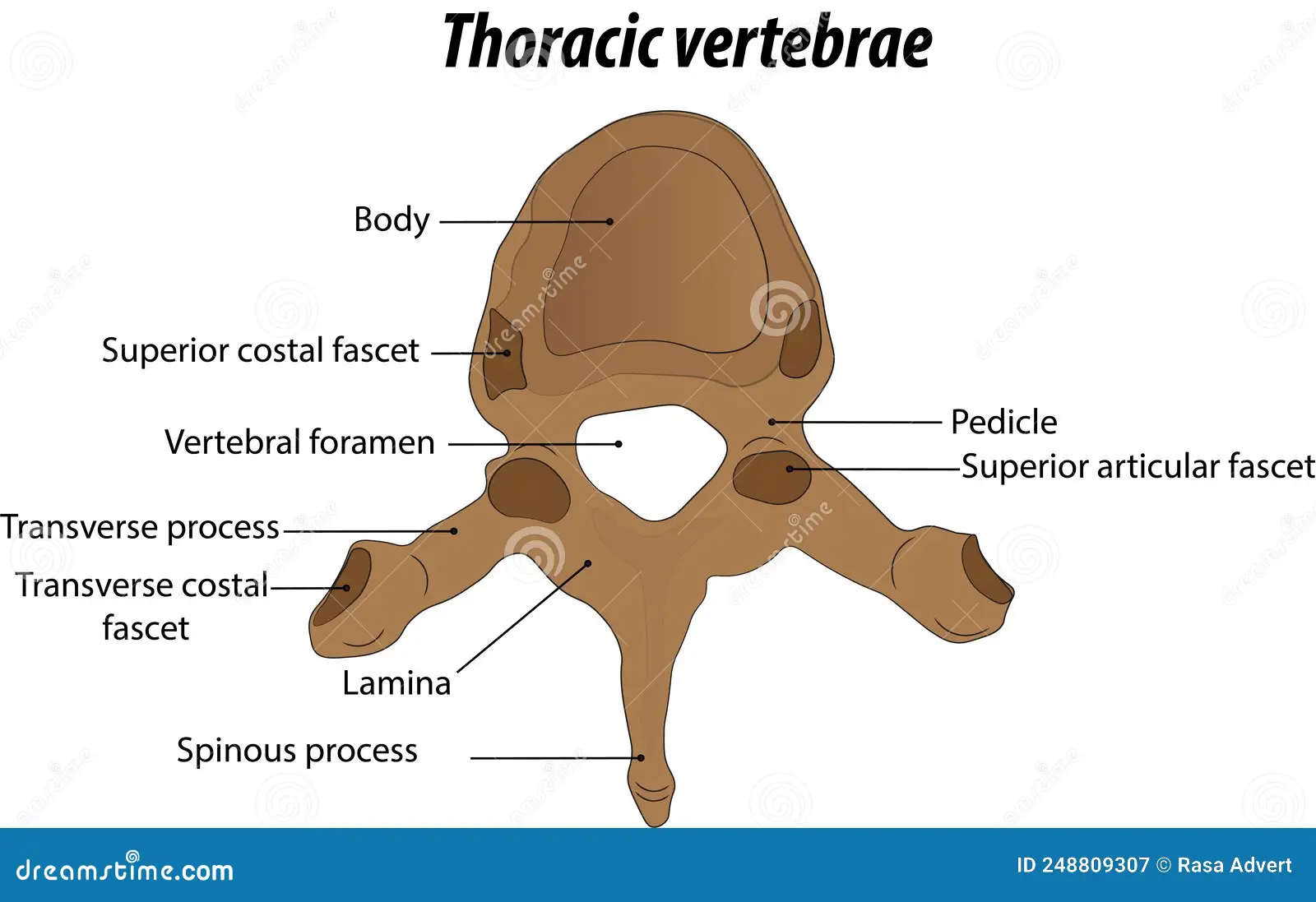
transverse costal facet of a thoracic vertebra
functions for rib articulation, end of the transverse process
superior articular process of a thoracic vertebra
on the lateral view; pointy part; superior to the spinous process of thoracic vertebra
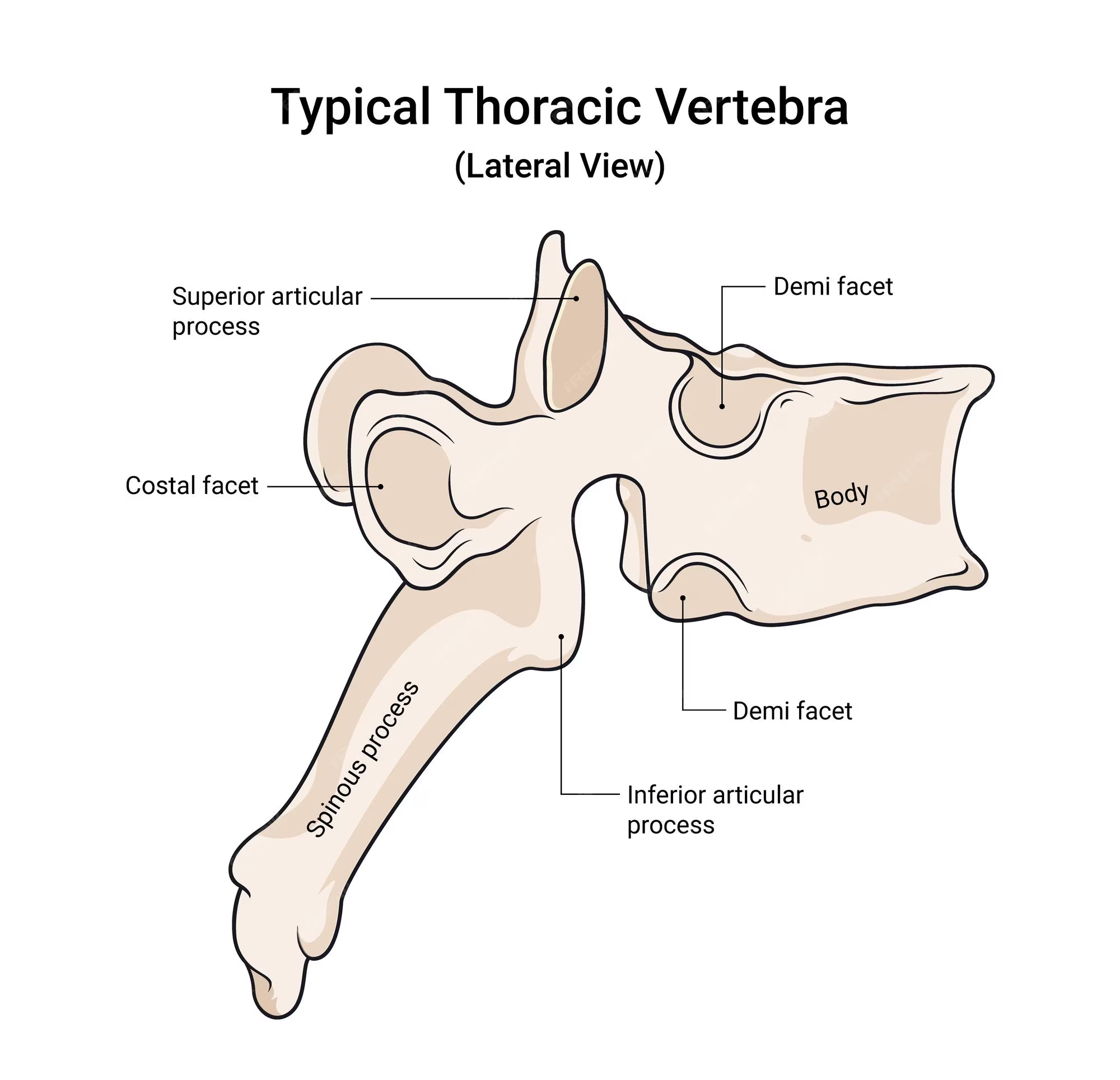
inferior articular process of a thoracic vertebra
can be seen in lateral view; first large bump before the spinous process of thoracic body extends
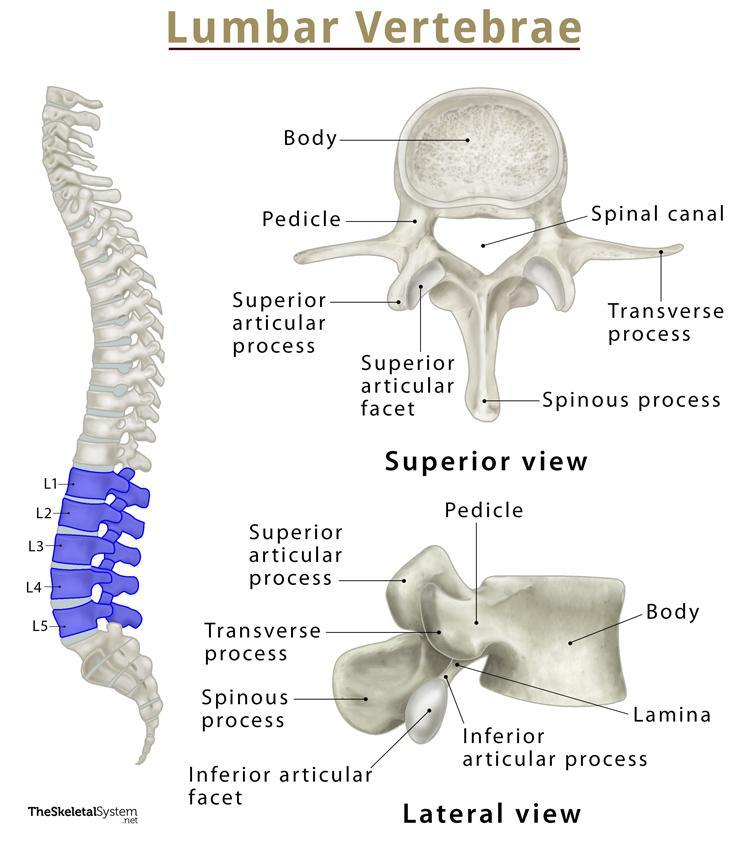
body of a lumbar vertebra
biggest part out of the three types of vertebrae because it’s used for support
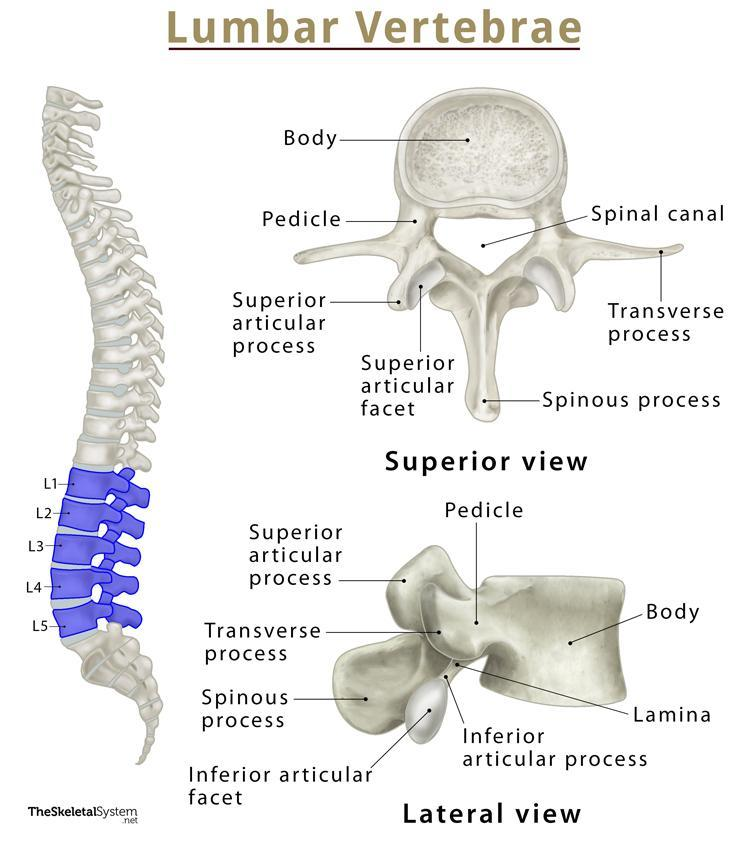
spinous process of a lumbar vertebra
somewhat stubbier than the other two types of vertebrae;
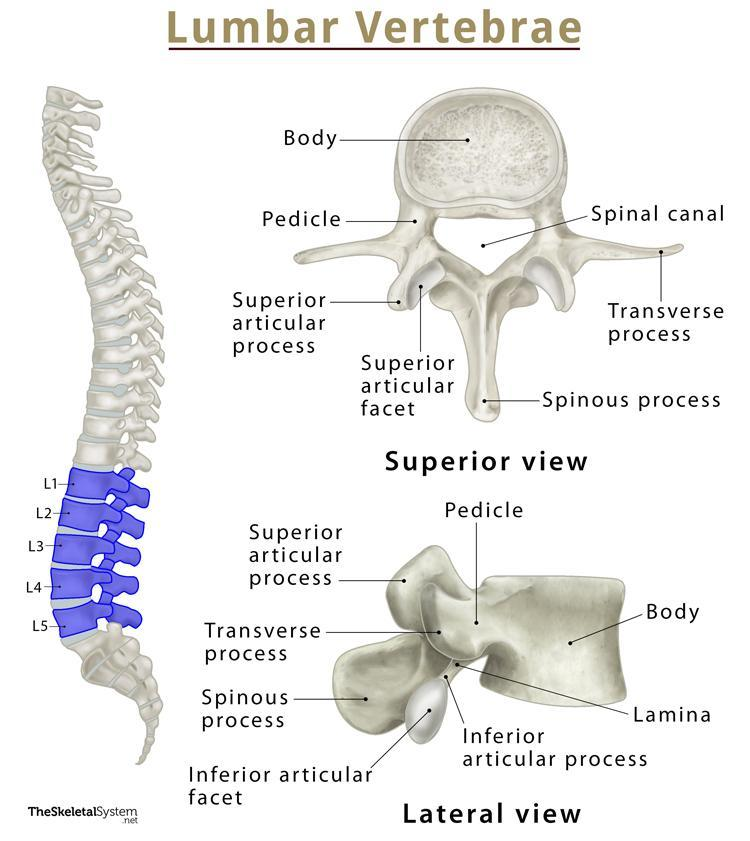
transverse process of a lumbar vertebra
also extends after a pedicle; but look for a bigger body and smaller spinous process to tell the difference.
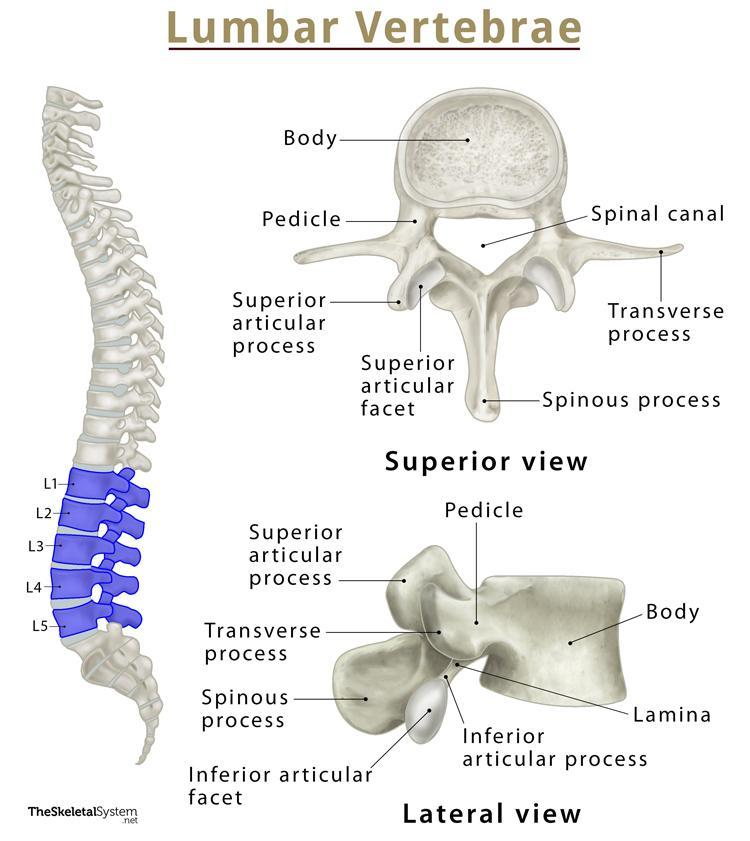
superior articular process of a lumbar vertebra
most superior part of the lumbar vertebrae; it sticks out the most so you can see; easy to tell
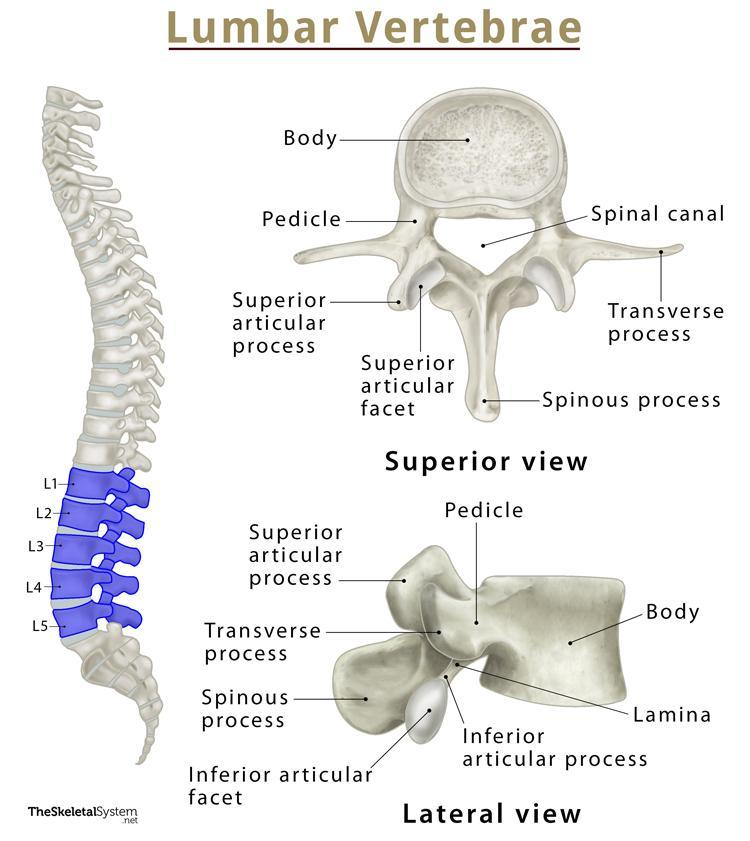
inferior articular process of a lumbar vertebra
can be seen in lateral view; lowkey extends out a lot more than other inferior processes
sacral promontory of a sacrum
anterior (front) projecting edge; can be seen better in lateral view
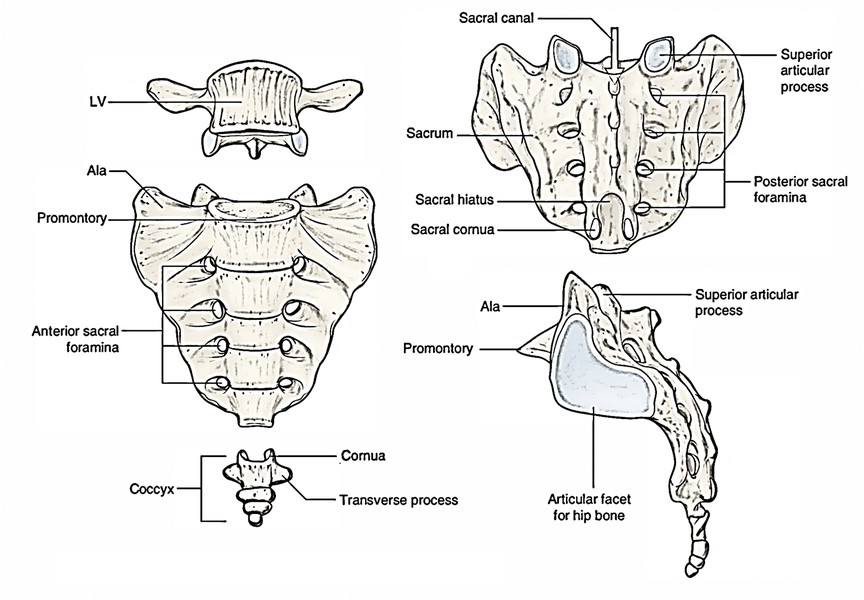
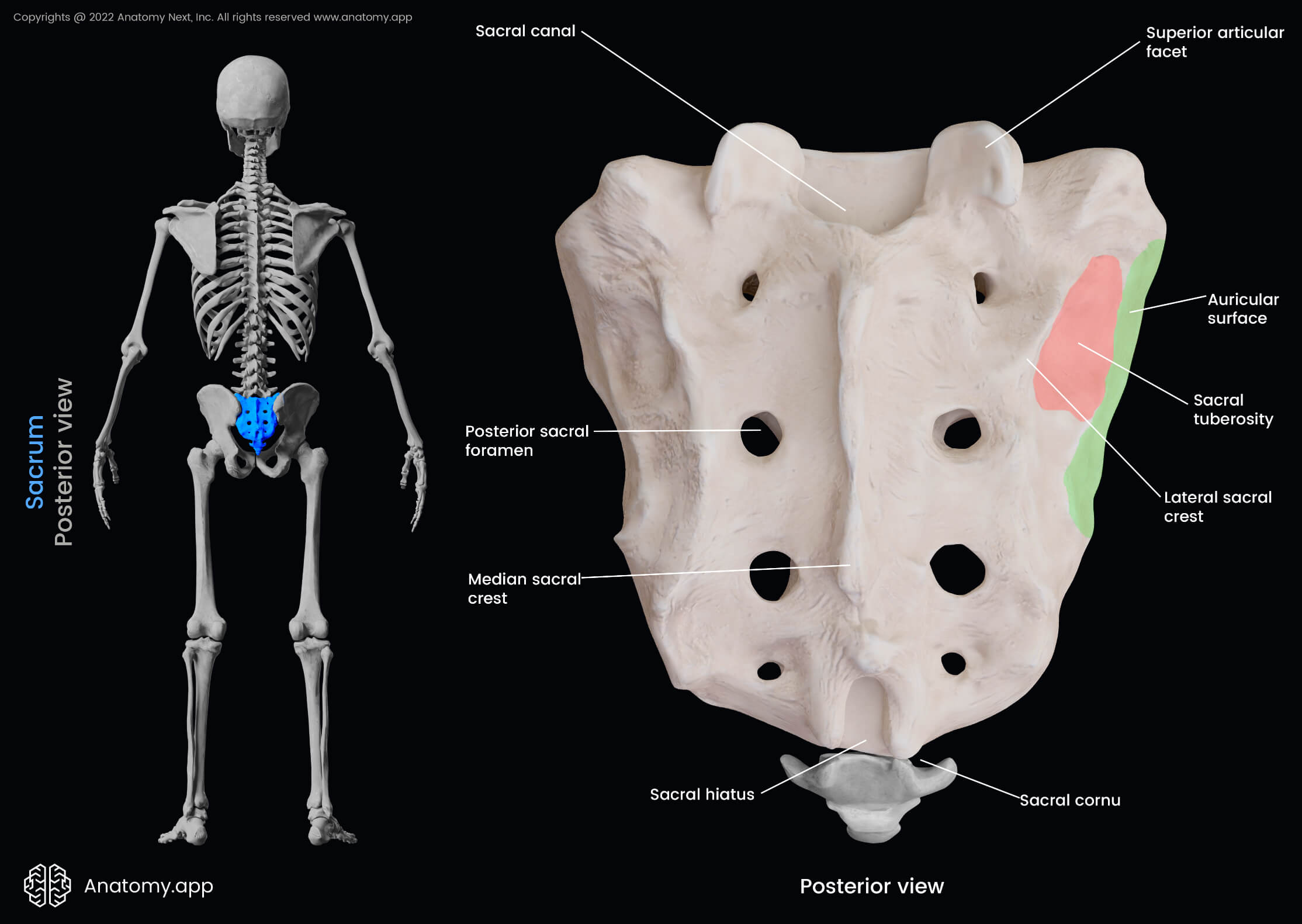
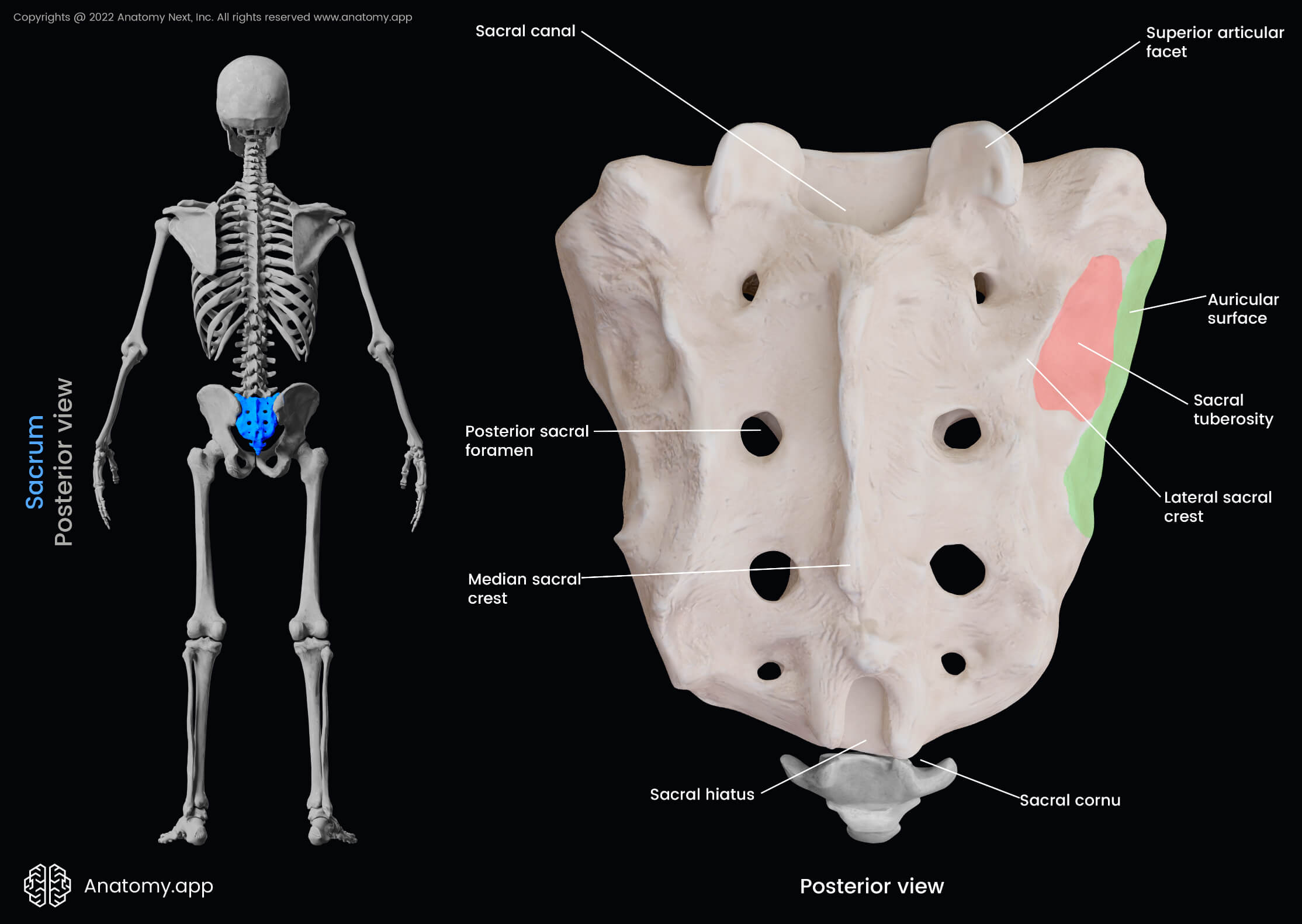
median sacral crest of a sacrum
the most protruding, middle part of the sacrum in posterior view; DO NOT MIX UP WITH MEDIAL
anterior sacral foramina of a sacrum
the holes of the sacrum; exit for the rami
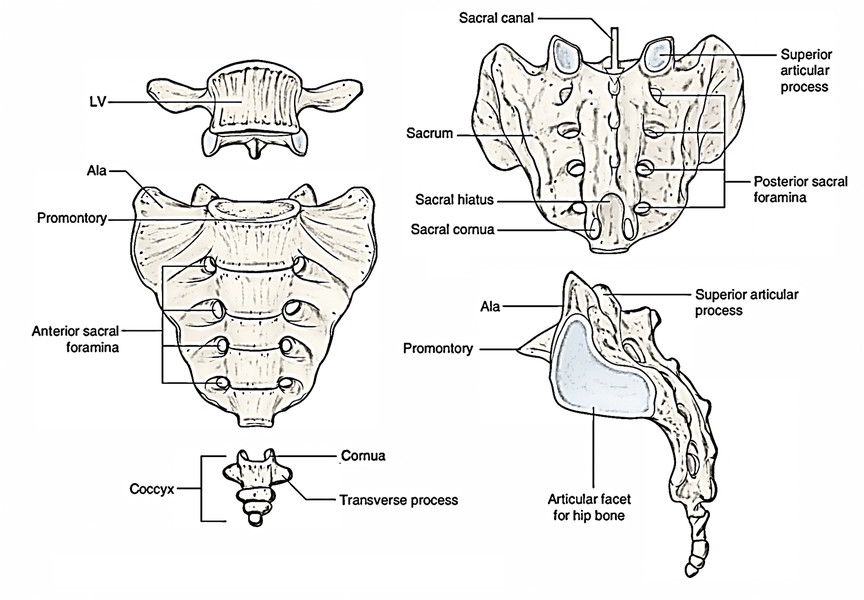
posterior sacral foramina of a sacrum
on the back side; next to the MEDIAN sacral crest; exit for the rami
coccyx
small, triangular bone that articulates with inferior end of sacrum; AKA: tailbone (3-4 infused series of vertebrae)