Production possibilities and opportunity cost
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards based on lecture notes for Chapter 2, focusing on production possibilities and opportunity cost.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What are the three fundamental economic questions related to production?
What?, How?, and For Whom?
What is opportunity cost?
What you give up when you choose one option over another
It’s the next best alternative you didn’t choose.
To what types of decision-making does opportunity cost apply?
Personal, group, and national decision-making.
What is marginal analysis?
decision-making tool in economics. It means:
Comparing the extra benefits to the extra costs of doing a little more or a little less of something.
What is marginal cost?
how much it costs to make one more item
What is marginal benefit?
the extra benefit from one more unit of something
What should you do if the marginal benefit of the last unit of a good exceeds its marginal cost?
Increase production of that good.
What concepts are illustrated by the Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)?
Efficiency, tradeoffs, opportunity cost, and economic growth.
What is the production possibilities frontier (PPF)?
A curve showing the maximum combinations of two outputs an economy can produce with fixed resources, full employment, and unchanged technology.
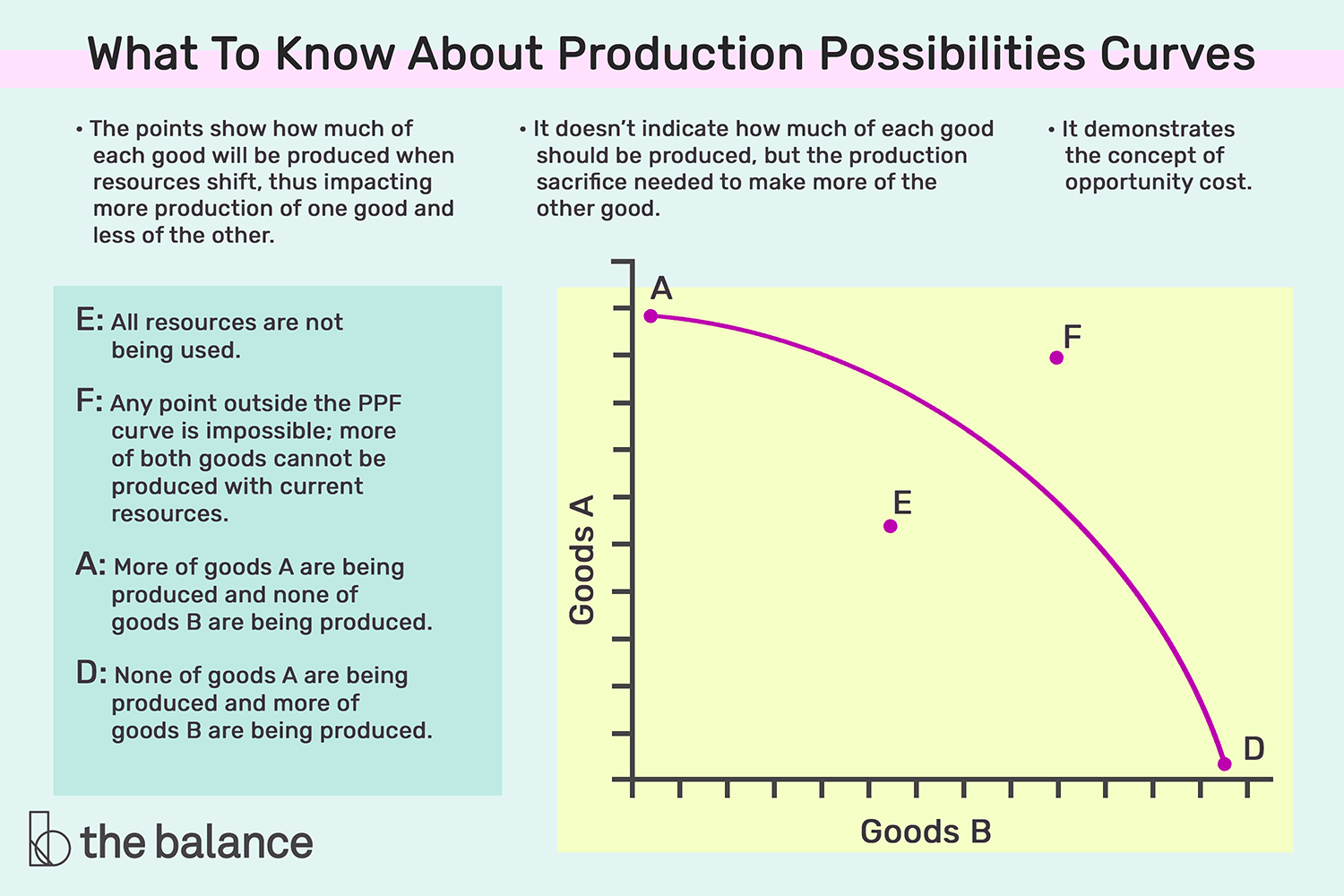
What does efficiency imply in the context of resource use?
We cannot produce more of any good without giving up something that we value even more highly.
What do points outside the PPF represent?
They represent unattainable production possibilities, given current resources and technology.
What do points inside the PPF represent?
They represent an inefficient use of current resources.
What is the law of increasing costs?
Opportunity cost increases as production of one output expands at the expense of another.
How is economic growth represented by the PPF?
By an outward shift of the production possibilities curve.
What could cause growth that shifts the PPF?
An increase in the number of productive resources available or technological change.