Lab Quiz 2
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
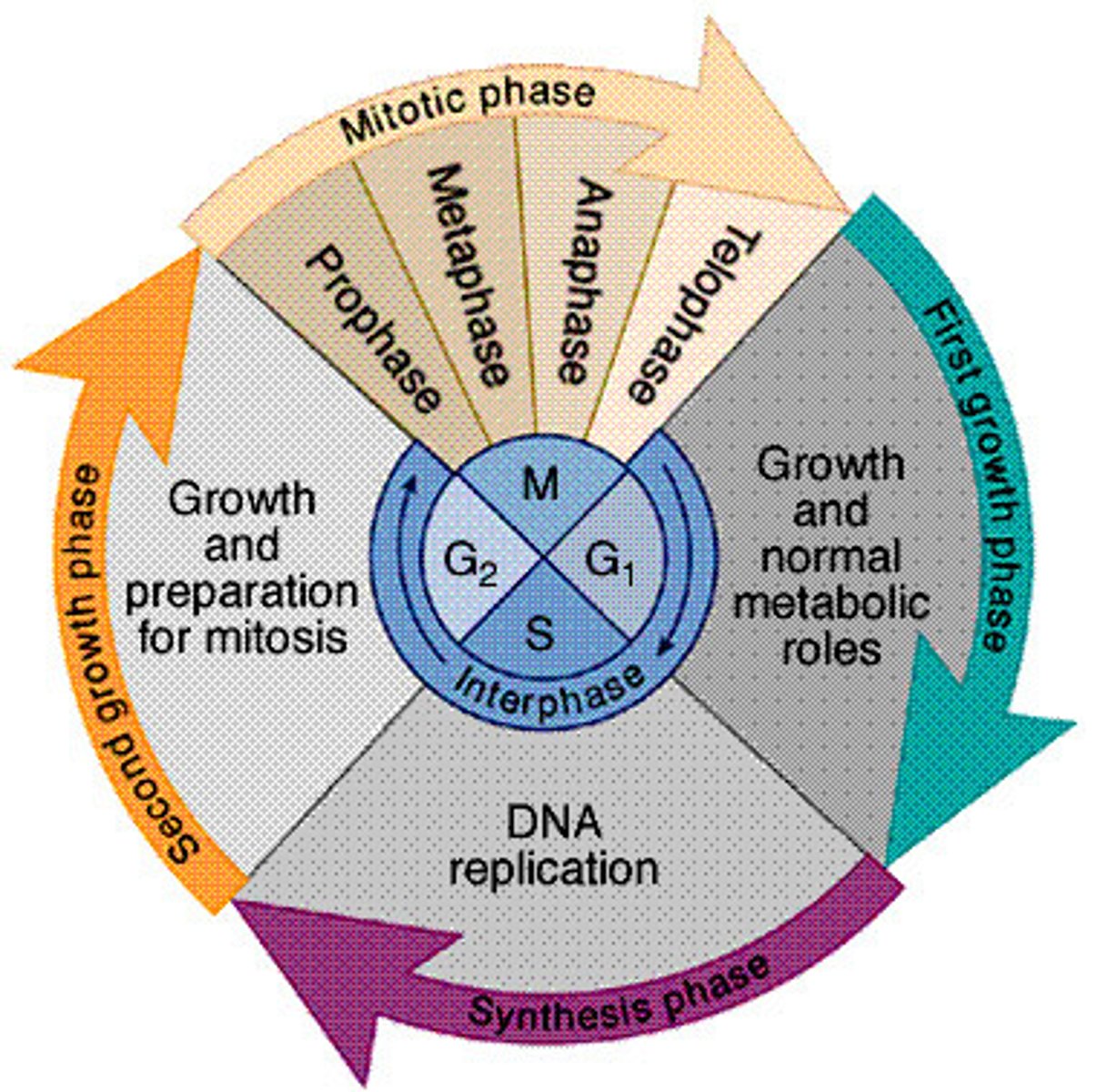
cell cycle
interphase, mitosis, cytokinesis
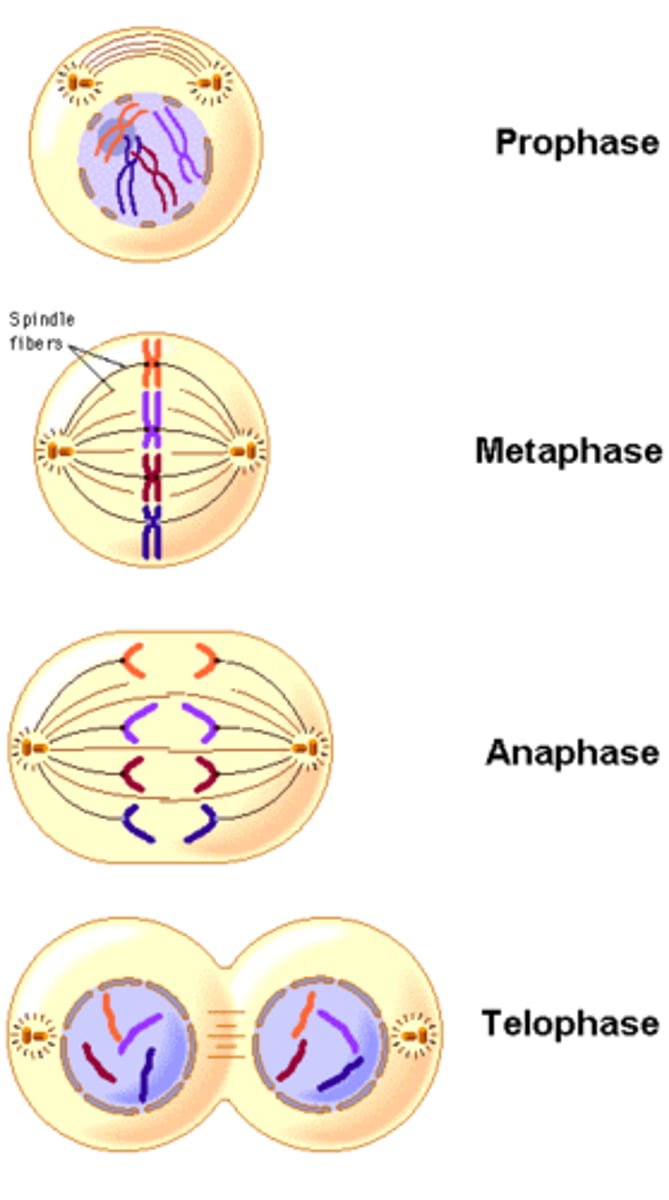
Mitosis
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Homologous Chromosomes
same type of chromosome containing the same type of genes. One maternal and one paternal
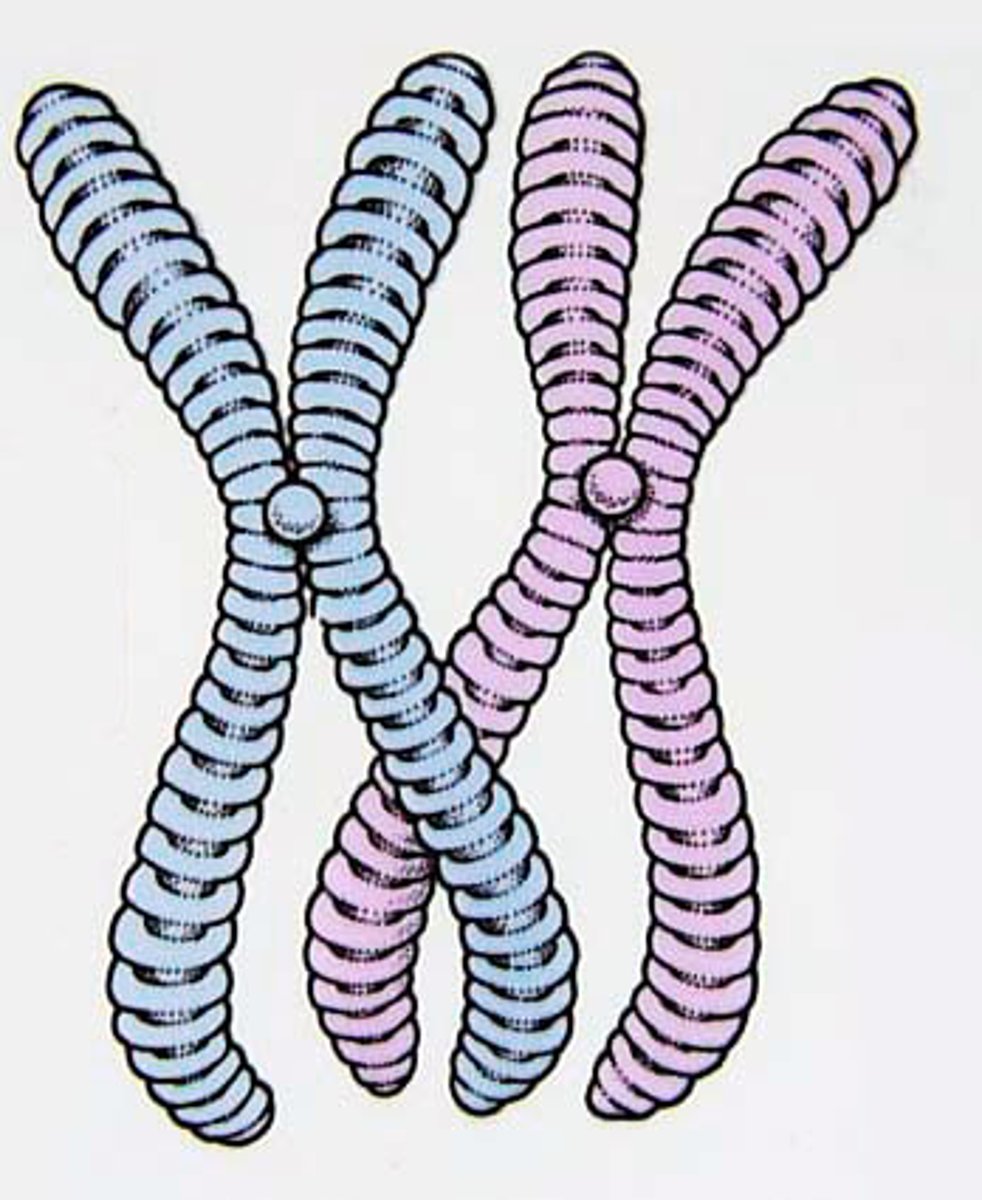
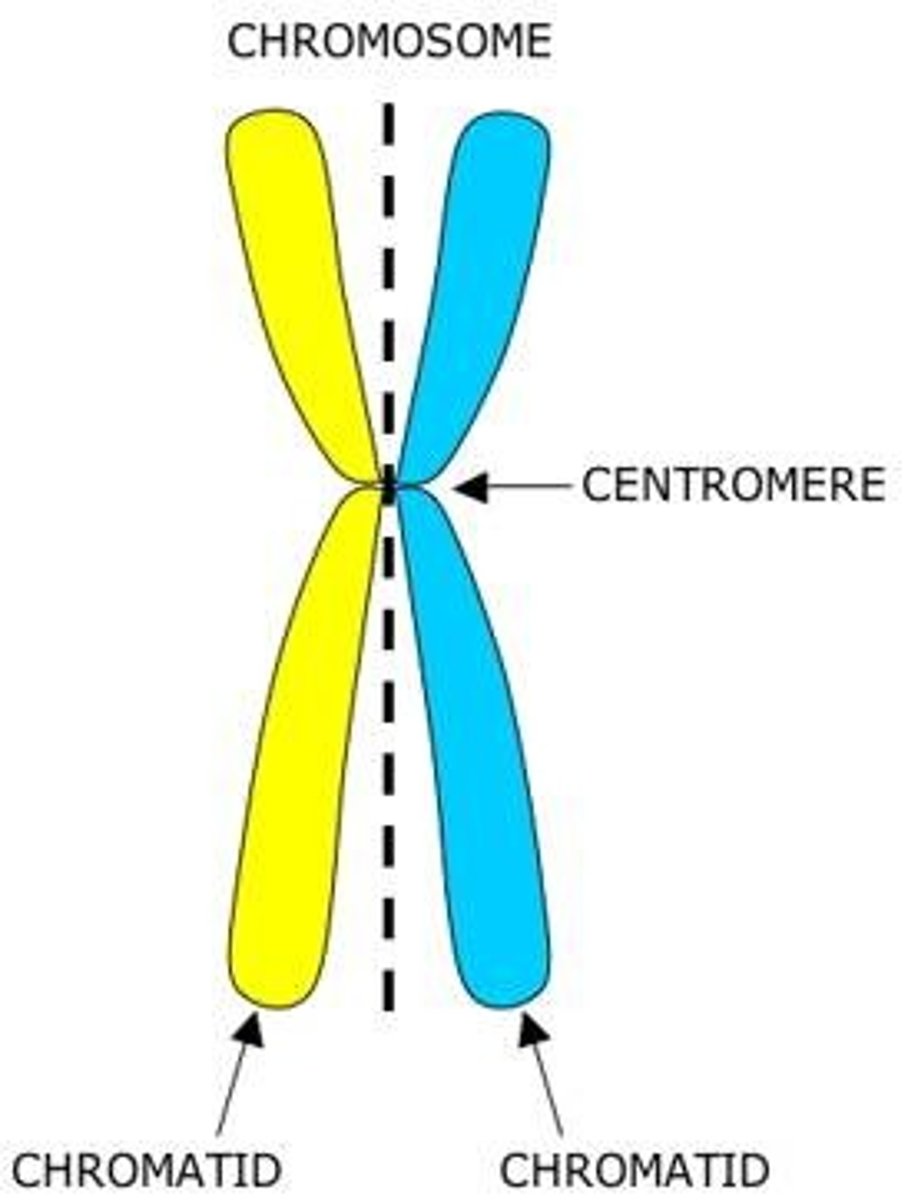
Centromere
where sister chromatids are held together AND where the spindle fibers attach during mitosis
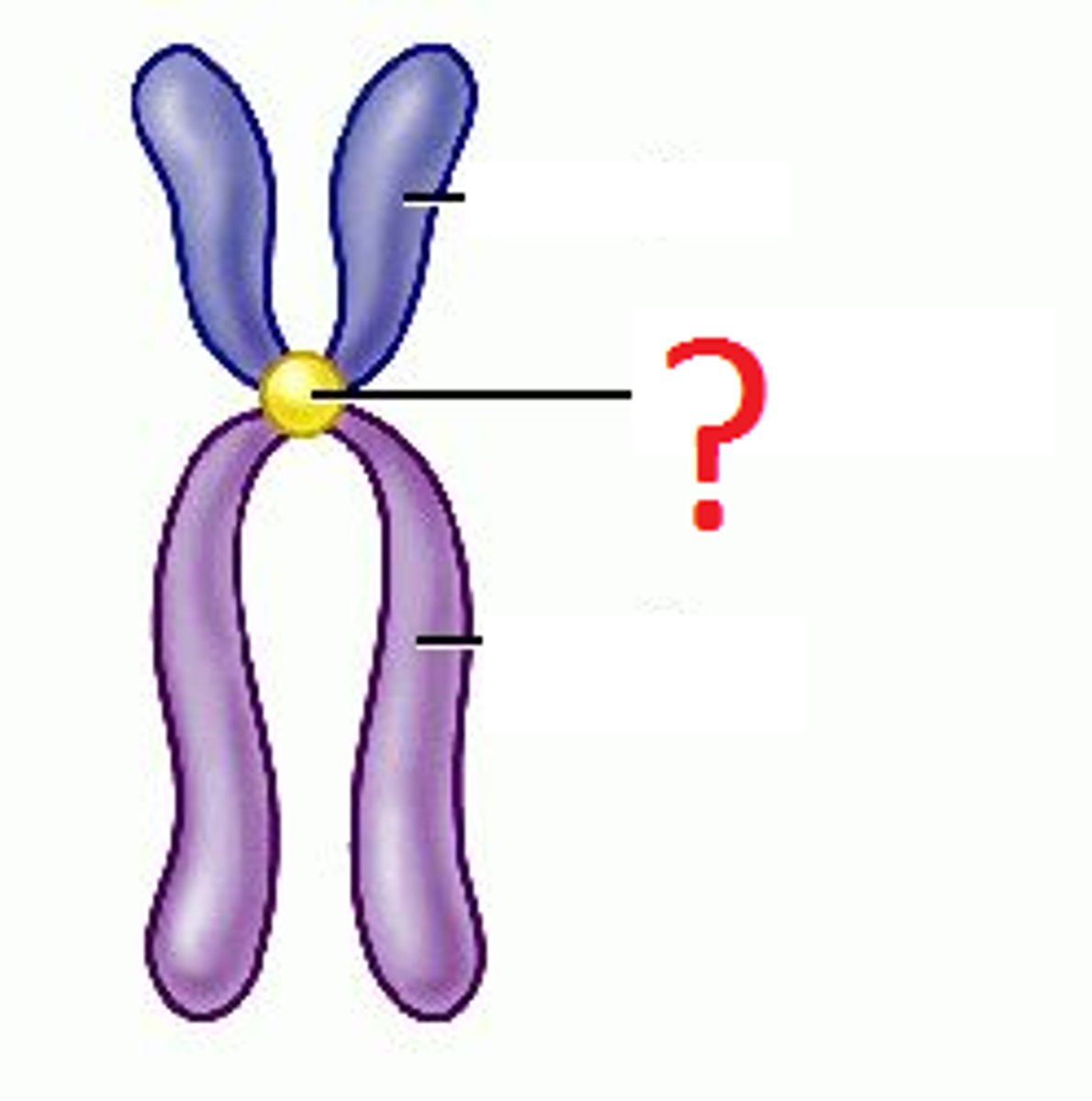
Sister Chromatids
identical copy of chromosomes formed by DNA replication (which takes place during interphase)
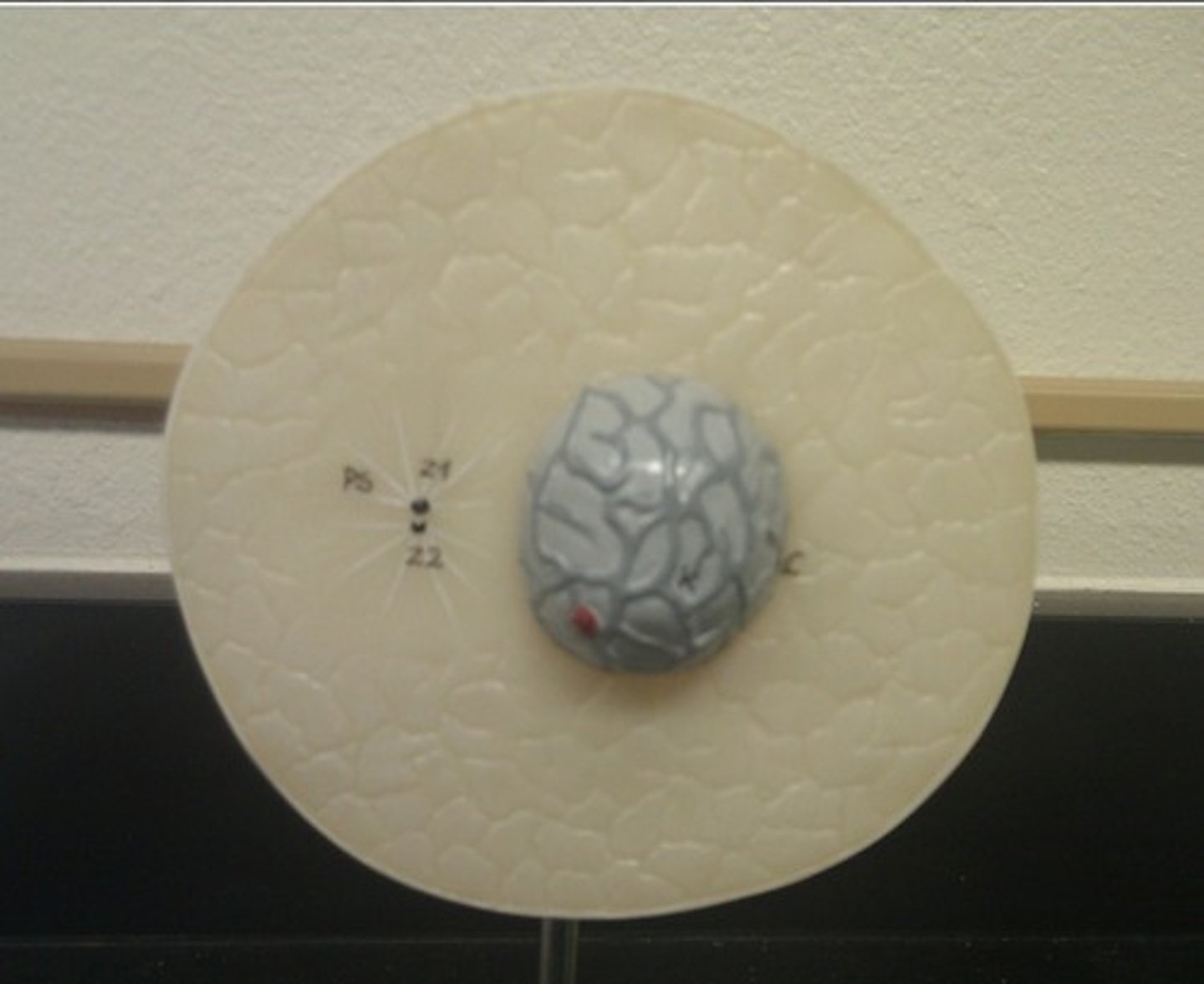
Interphase
proteins are being made, chromosomes are replicated, and the cell replicated the organelles
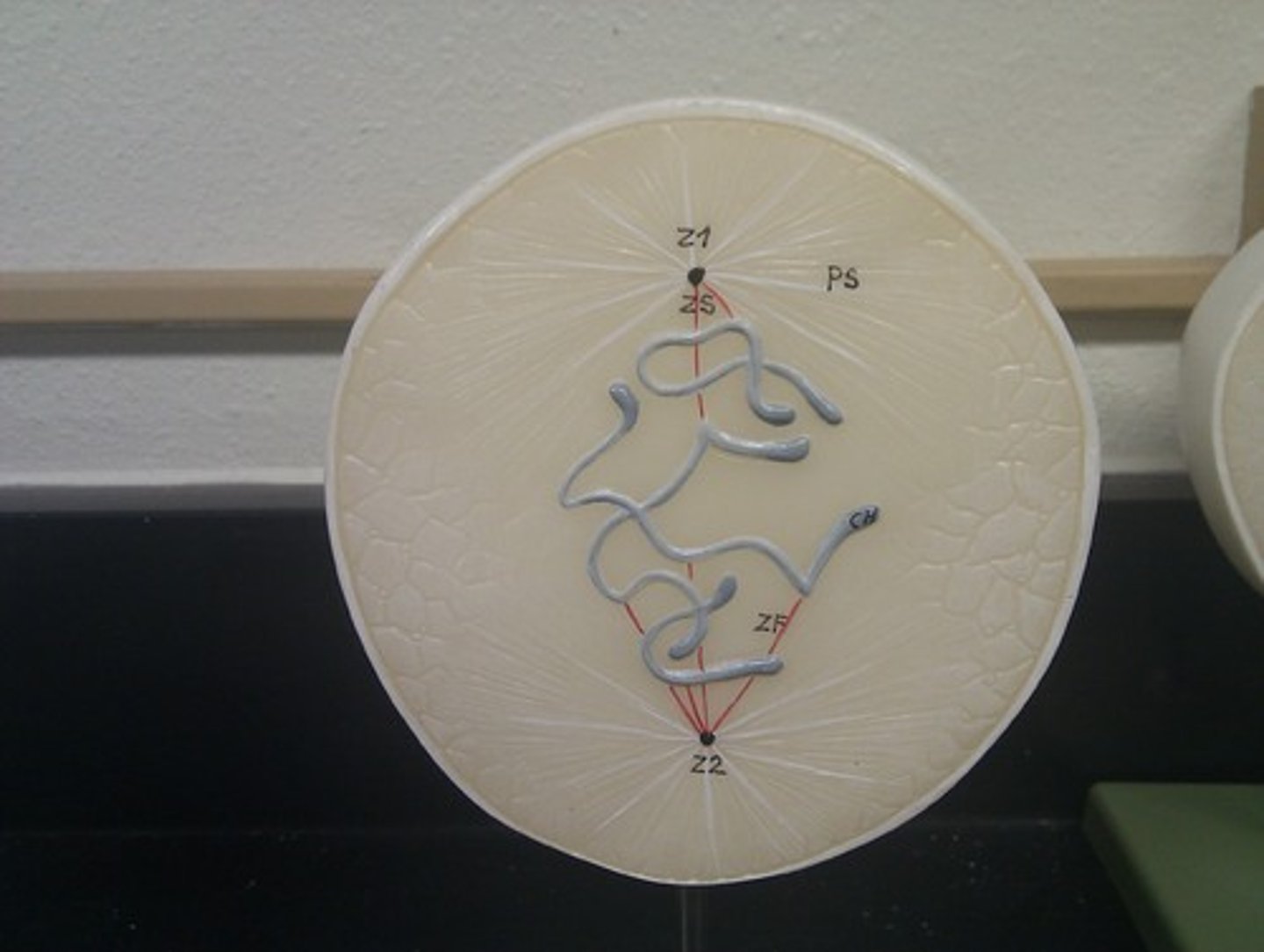
prophase
first phase of mitosis nuclear envelope breaks down, centrioles begin producing spindle fibers, sister chromatids become visible.
Metaphase
second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
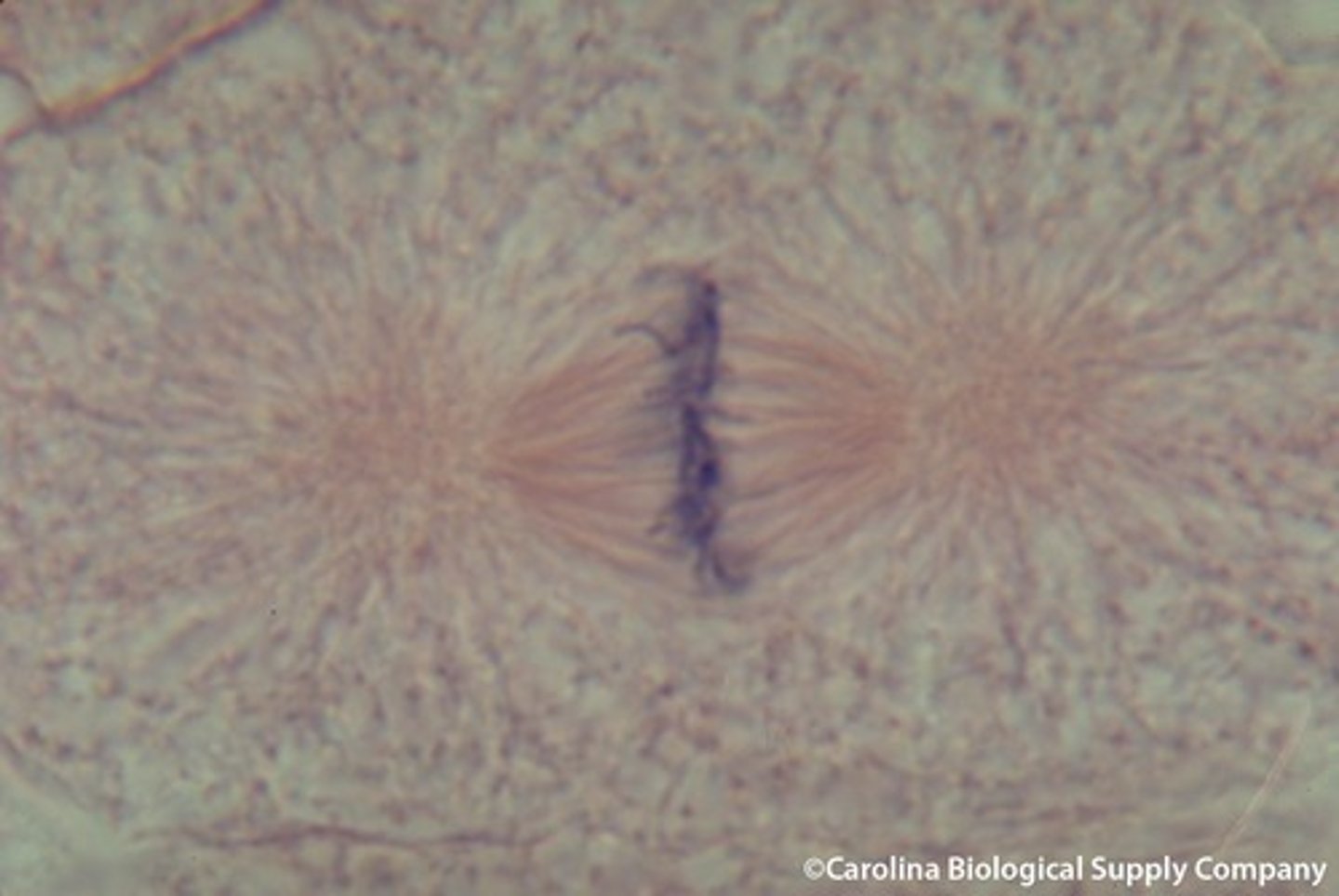
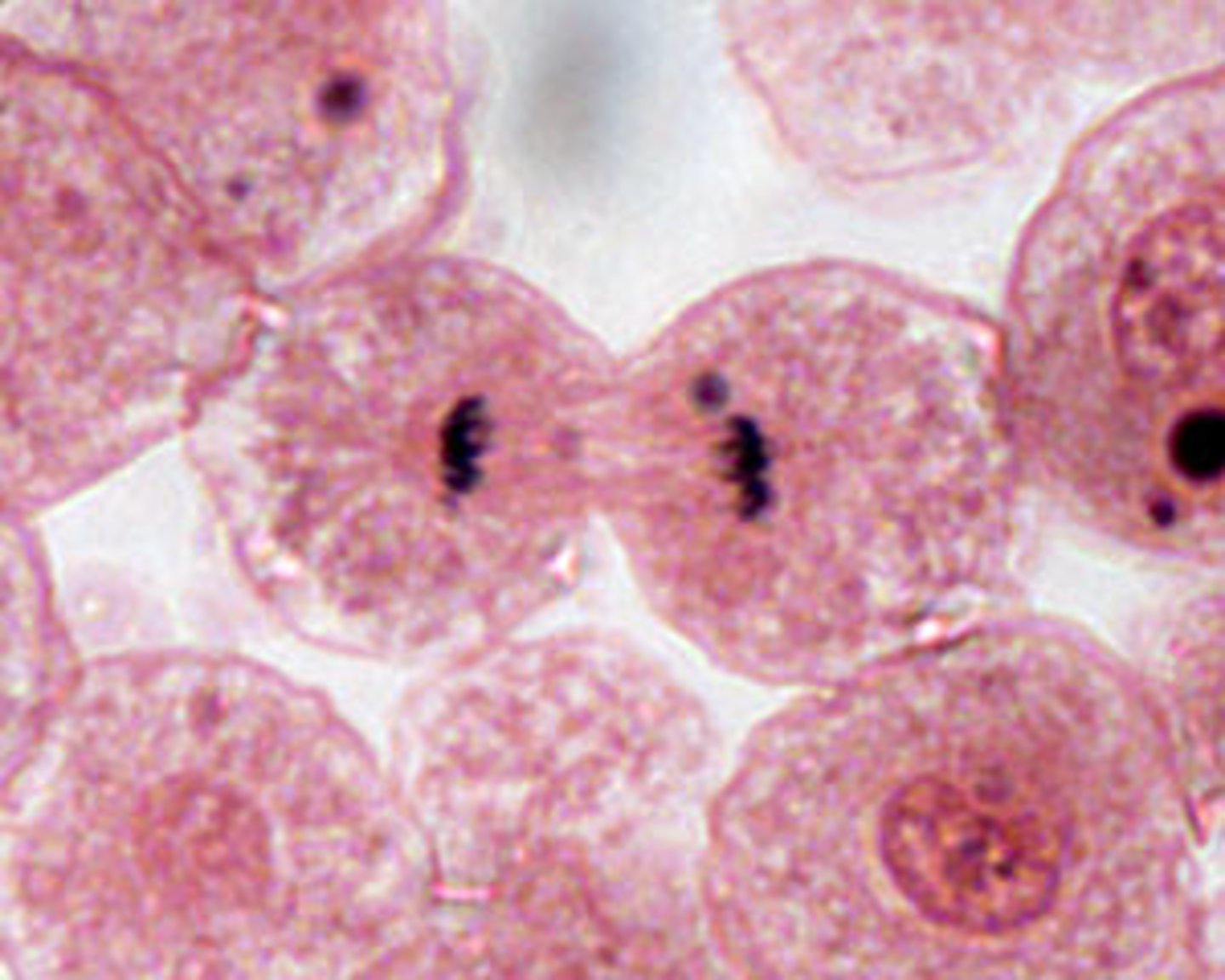
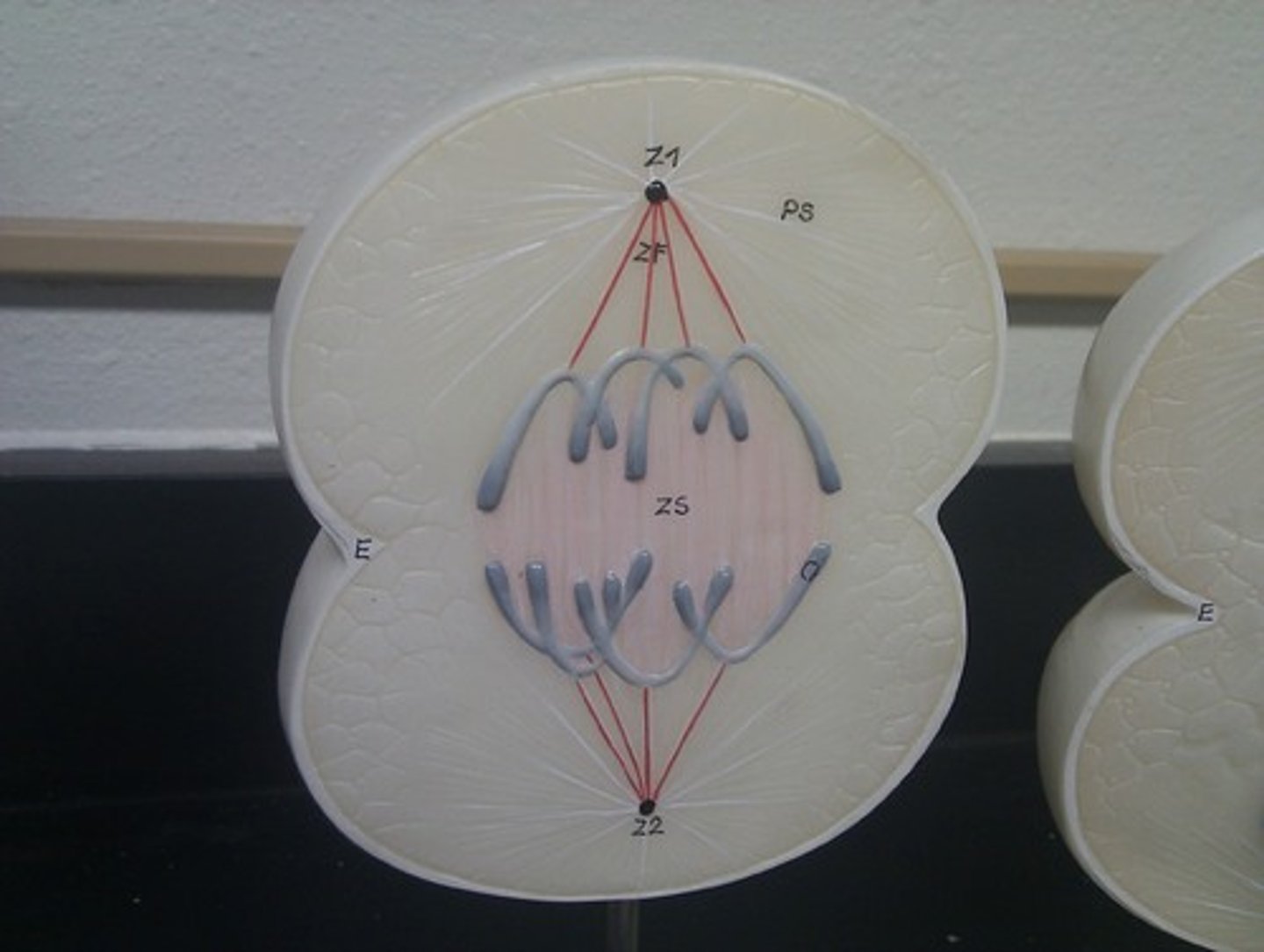
anaphase
the third phase of mitosis, during which the sister chromatids pulled apart at their centers, Each chromatid moving to opposite poles of the cell
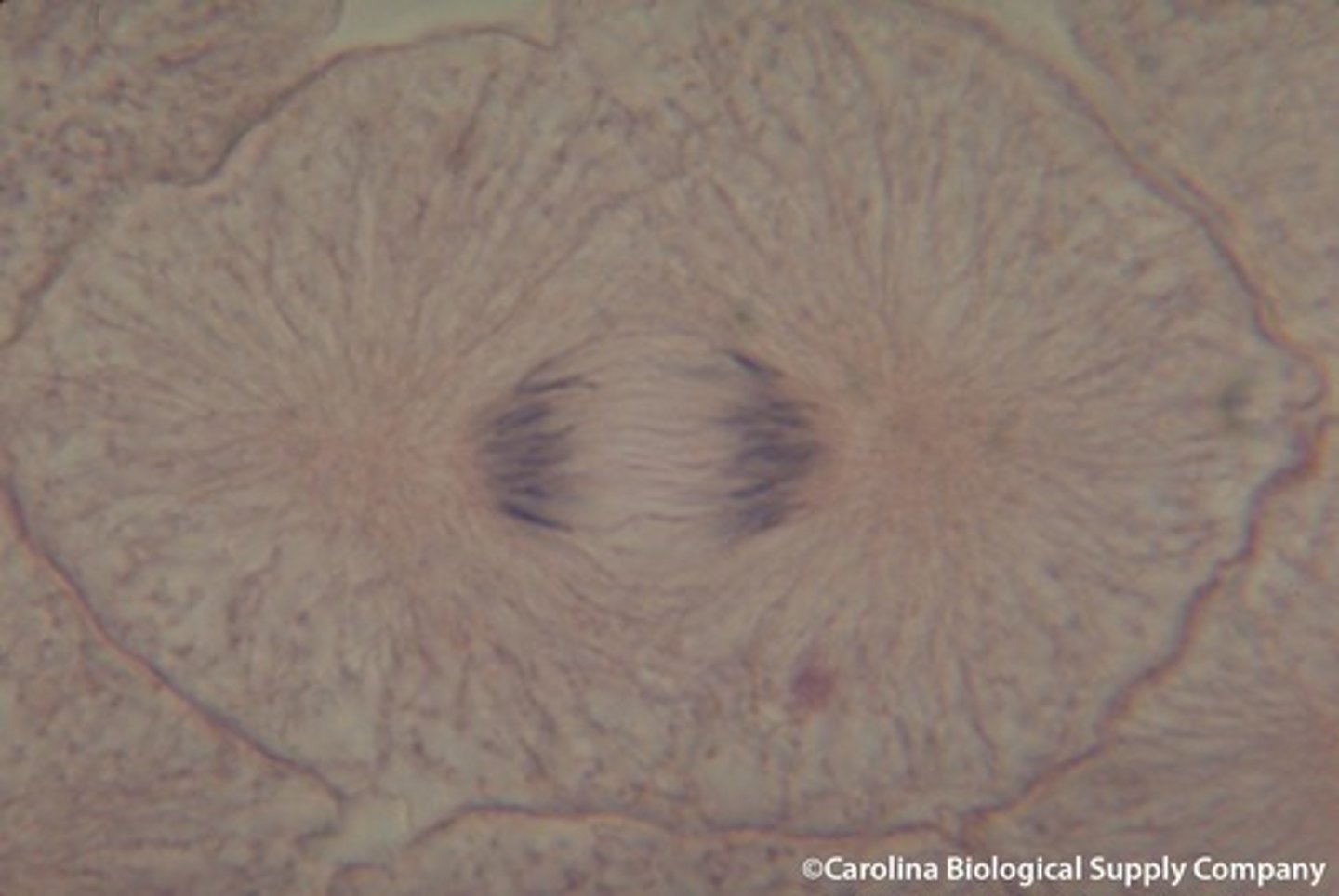
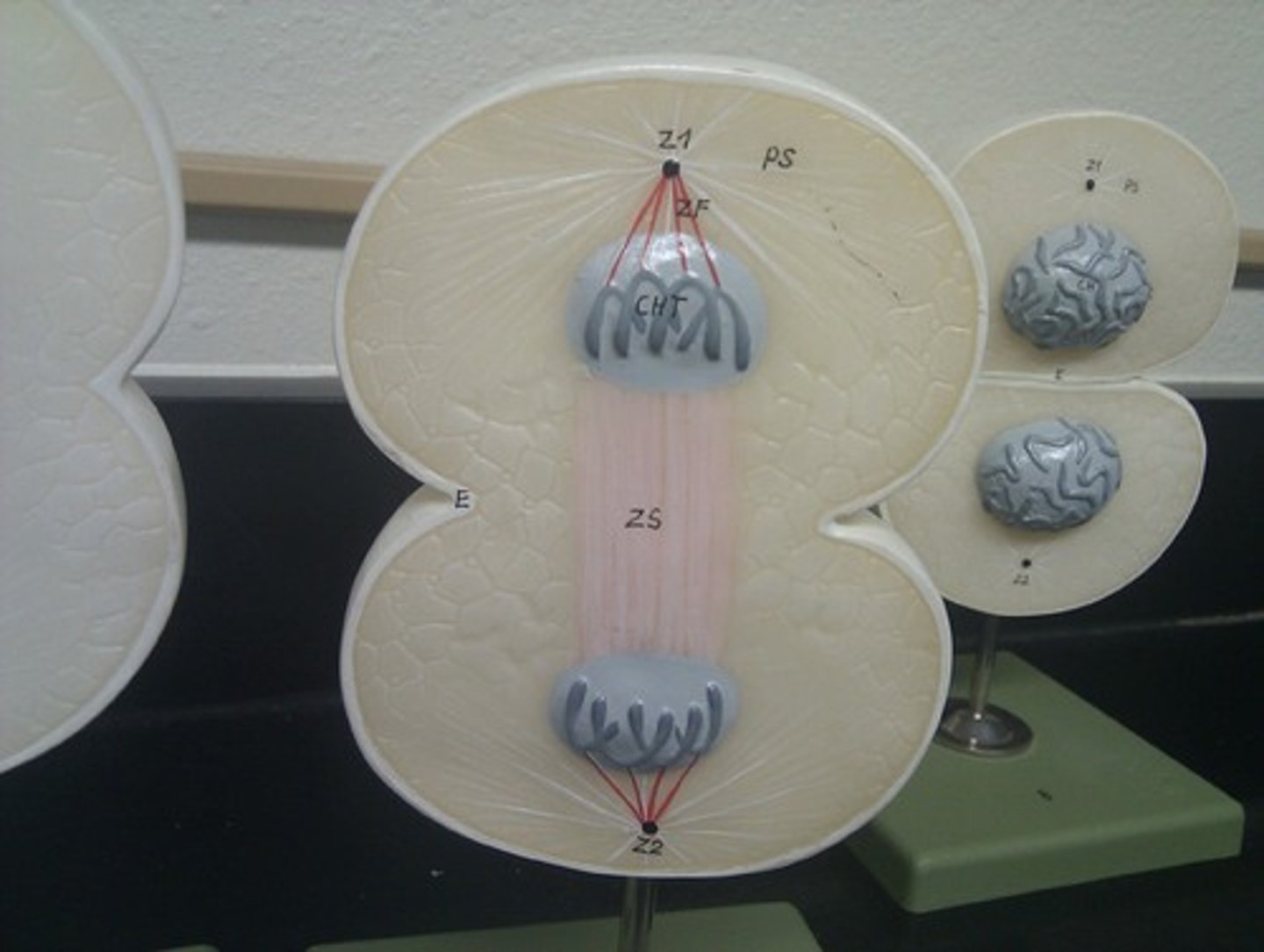
Telophase
The 4th and final stage of mitosis, in which daughter nuclei are forming, plasma membrane begins to fold into cleavage furrow
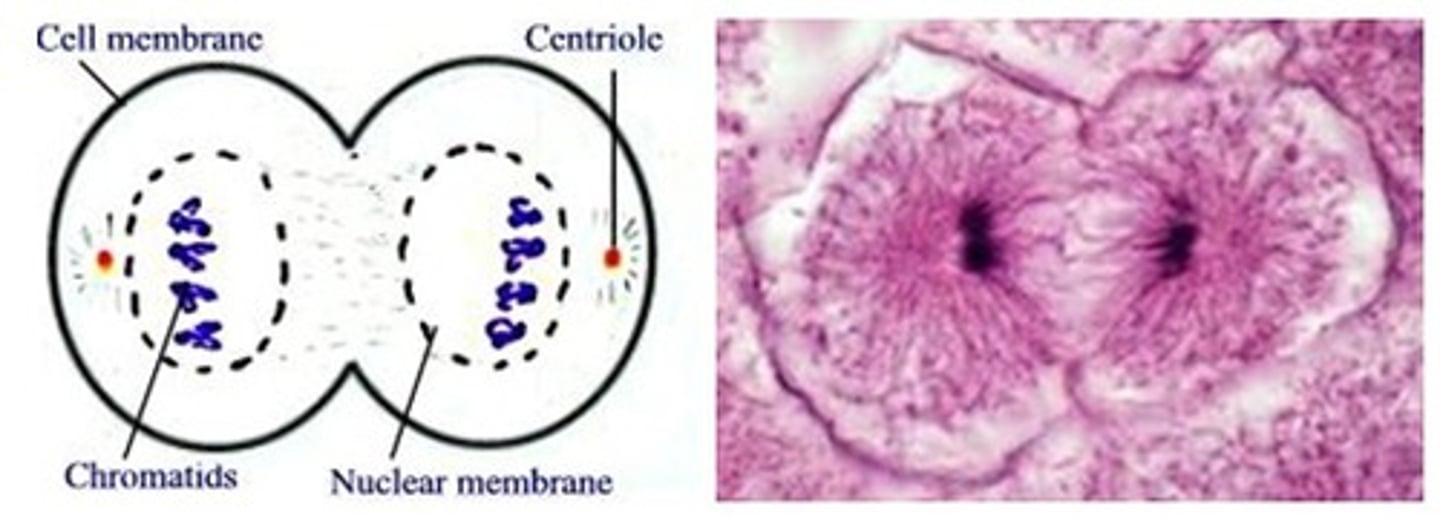
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells
Interphase model
no spindle fibers
Telophase model
cleavage furrow
anaphase model
pulling apart
prophase model
condensing & forming
metaphase model
center line
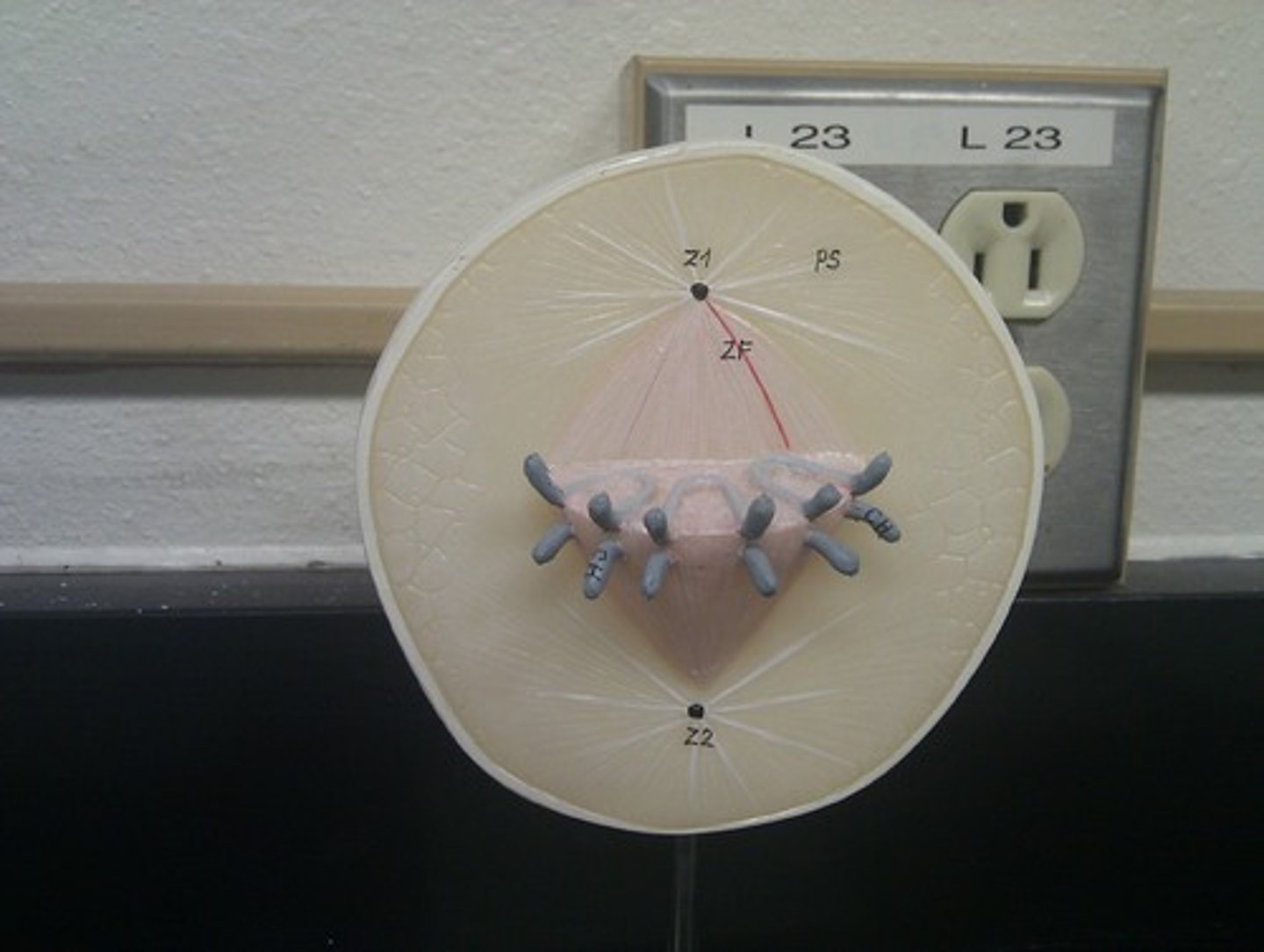
Tisssues
groups of cells that perform a similar task
Epithelial Functions
1. covers organs and lining of body cavities 2. Lines GI Tract 3. Skin (epidermis)
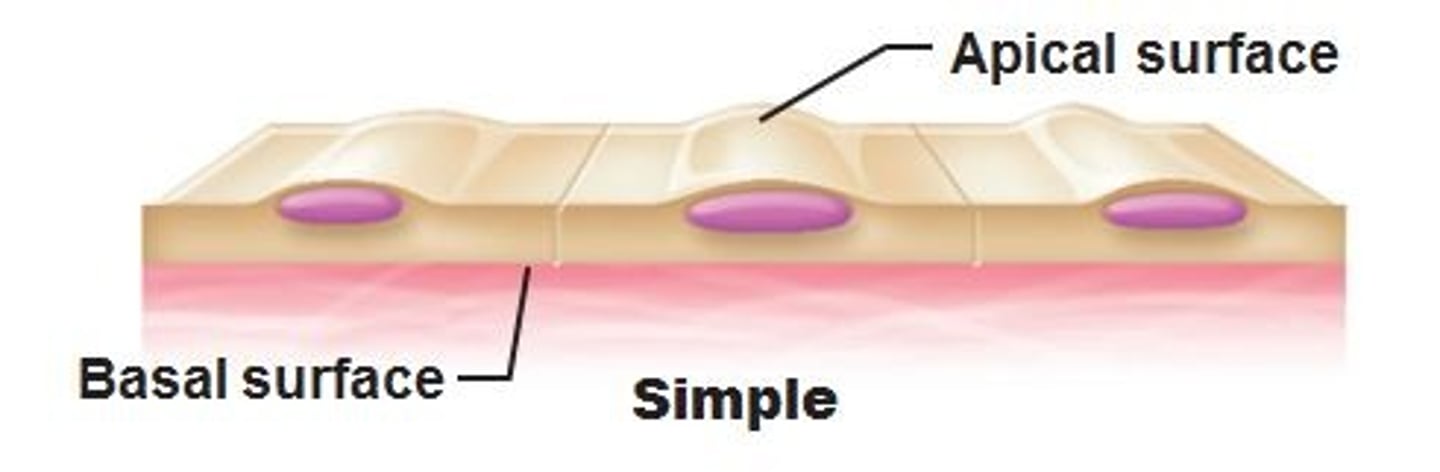
Apical, basement Membrane
All epithelial tissues have a free surface known as the _____ surface, and the side attached at the surface is known as the _____
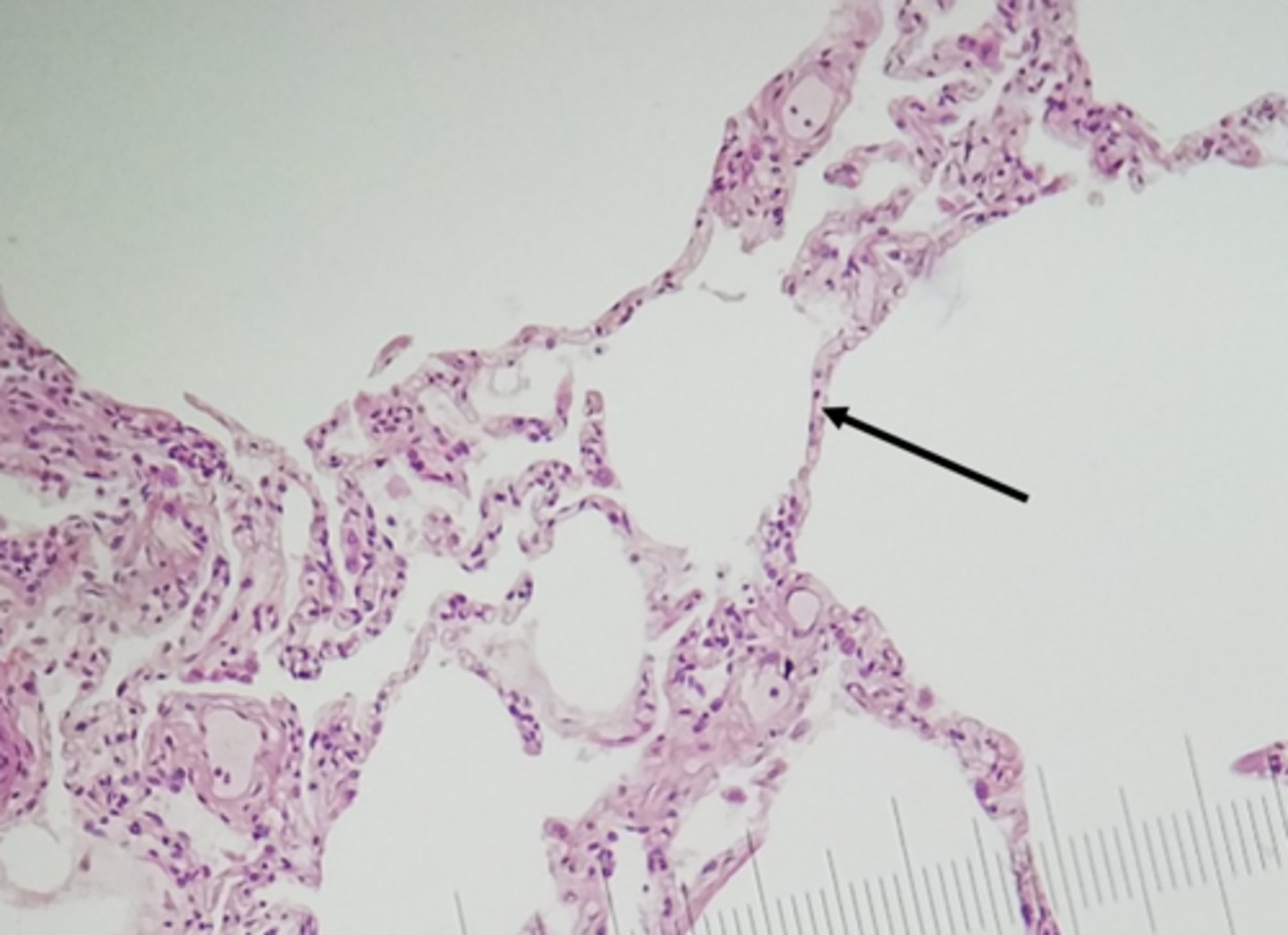
simple squamous epithelium
(Single Layer) Function: Allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration, osmosis
Location:lungs, walls of capillaries, blood and lymph vessels
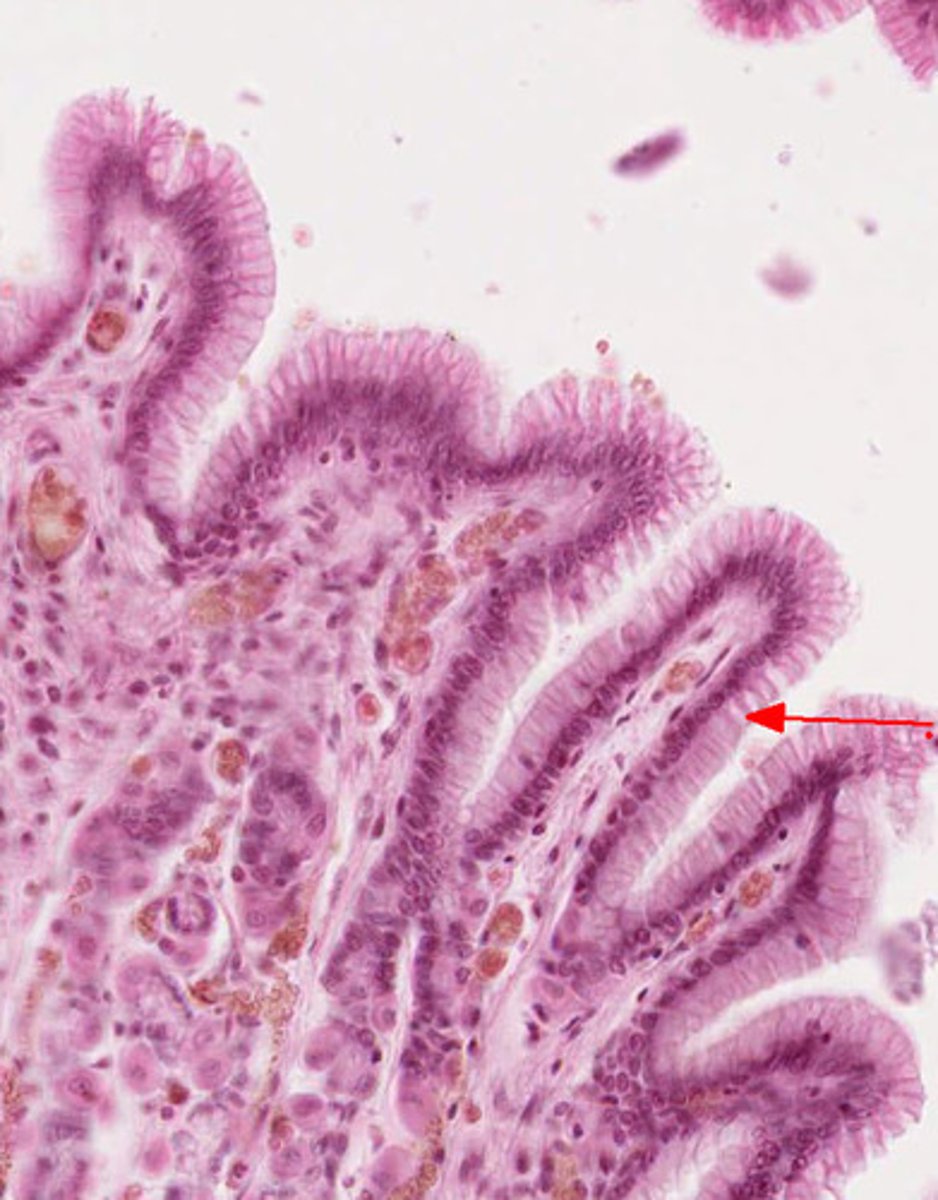
simple columnar epithelium
(Single Layer) Function: Absorption; secretion, and movement of eggs
Location: nonciliated type lines most of the digestive tract (stomach to anal canal), ; ciliated ovaries and uterus.
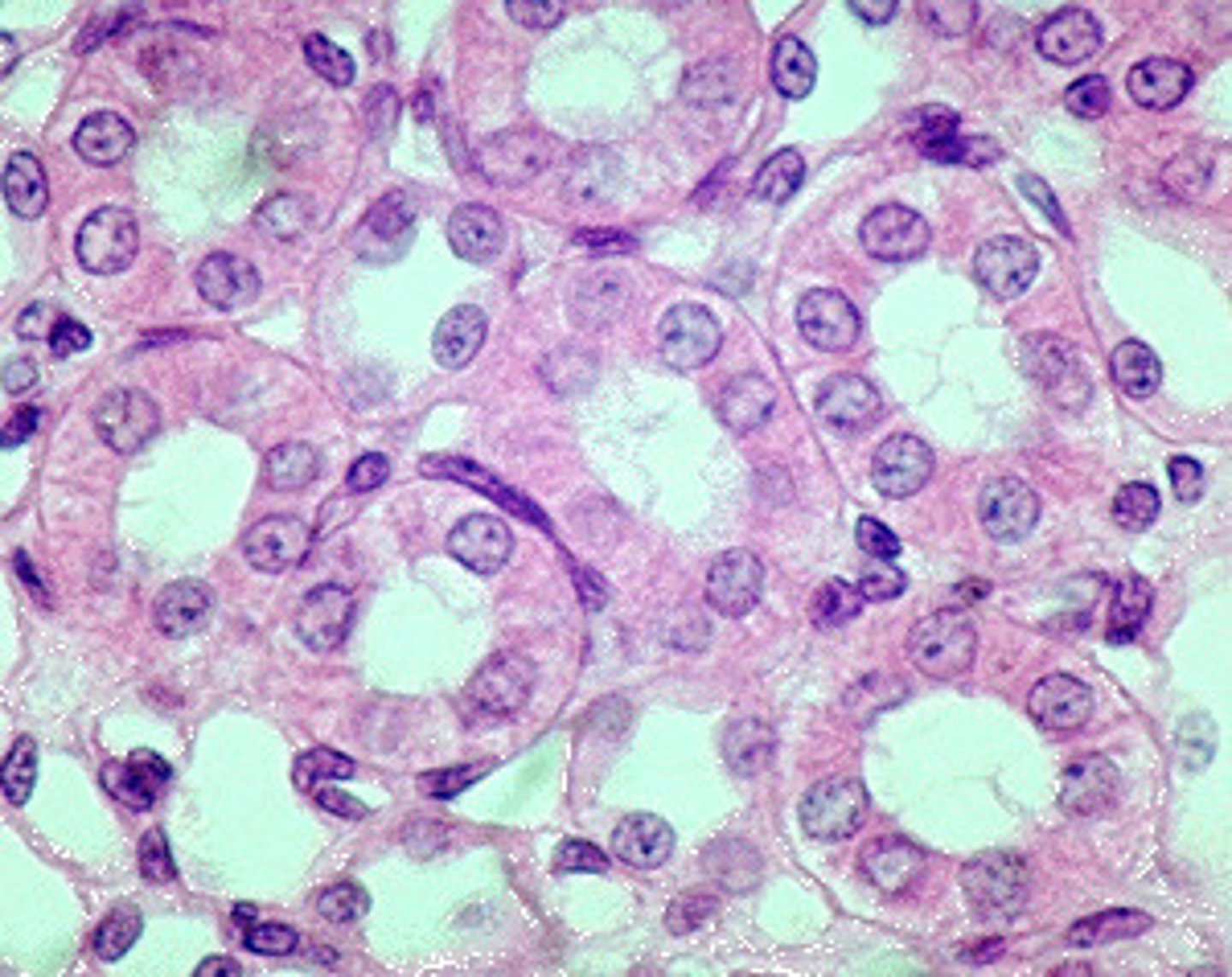
simple cuboidal epithelium
(Single Layer)Function: secretion and absorption
Location: Kidney & Ovaries
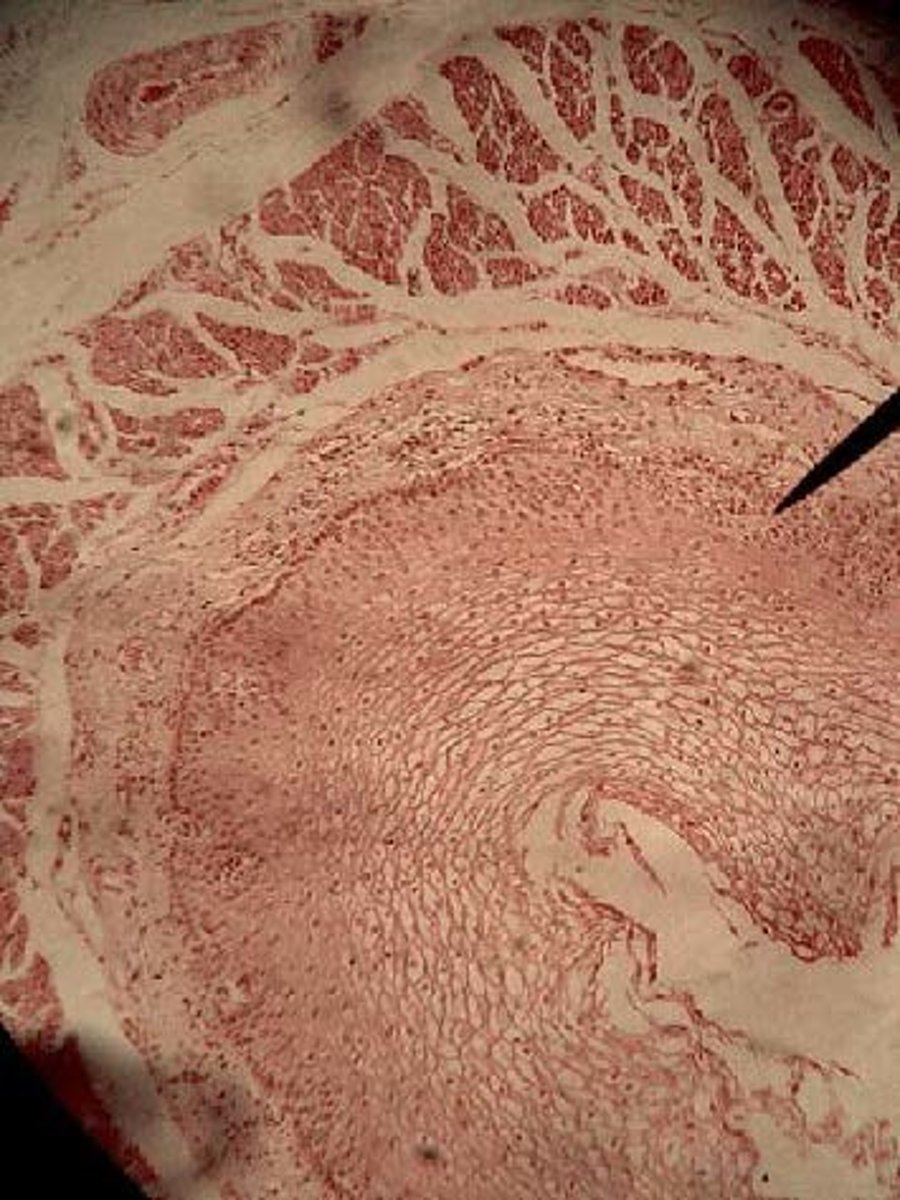
stratified squamous epithelium
Location with keratinized surface rough Epidermis (skin)
Location with non keratinized surface smooth oral, esophagus, vagina, anal canal
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
tissue that consists of a single layer of irregularly shaped and sized cells that give the appearance of multiple layers; found in ducts of certain glands and the upper respiratory tract
Function: protection, secretion, movement of mucus
Special Features: Goblet Cell
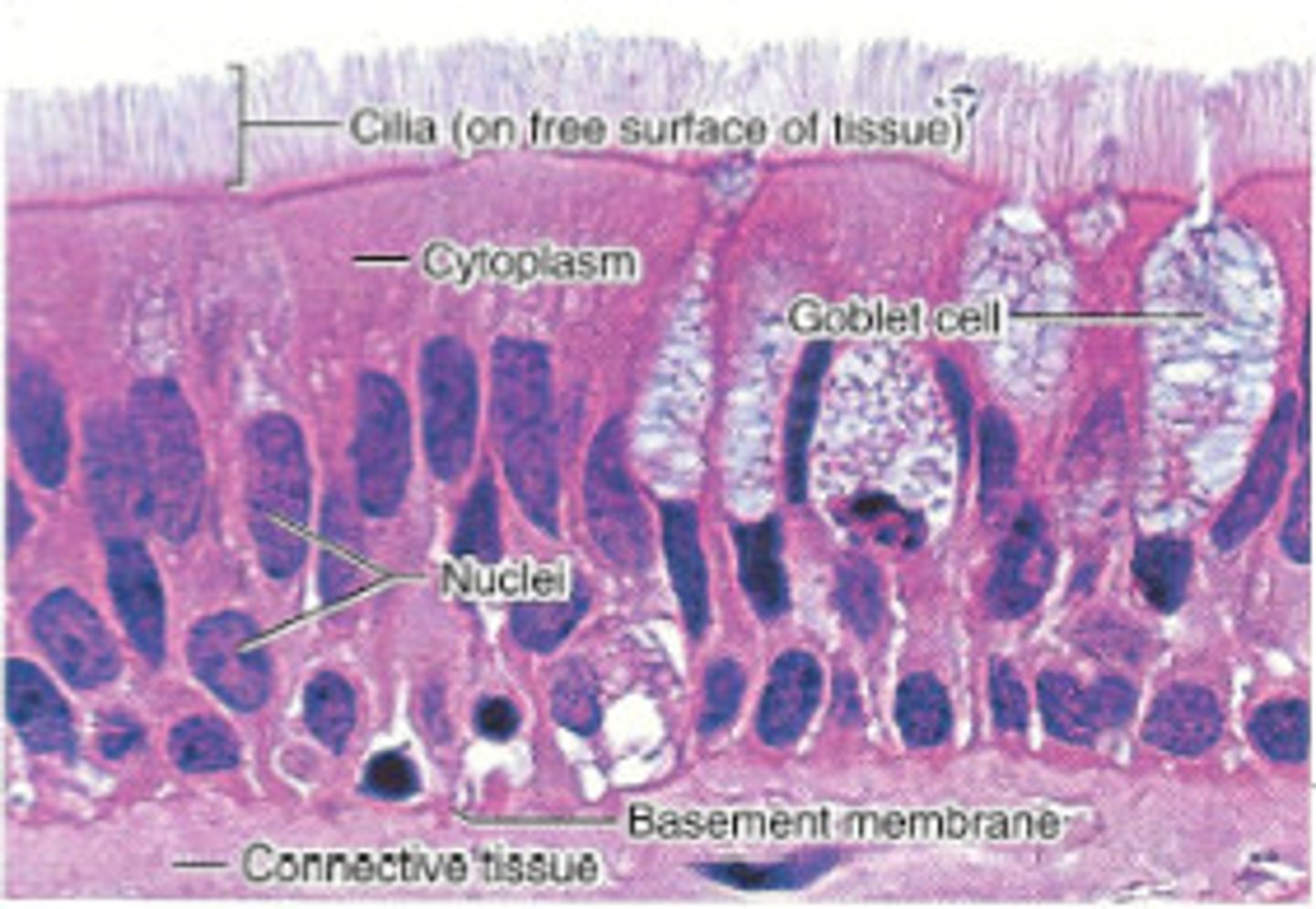
goblet cells
special feature of pseudostratified columnar epithelium
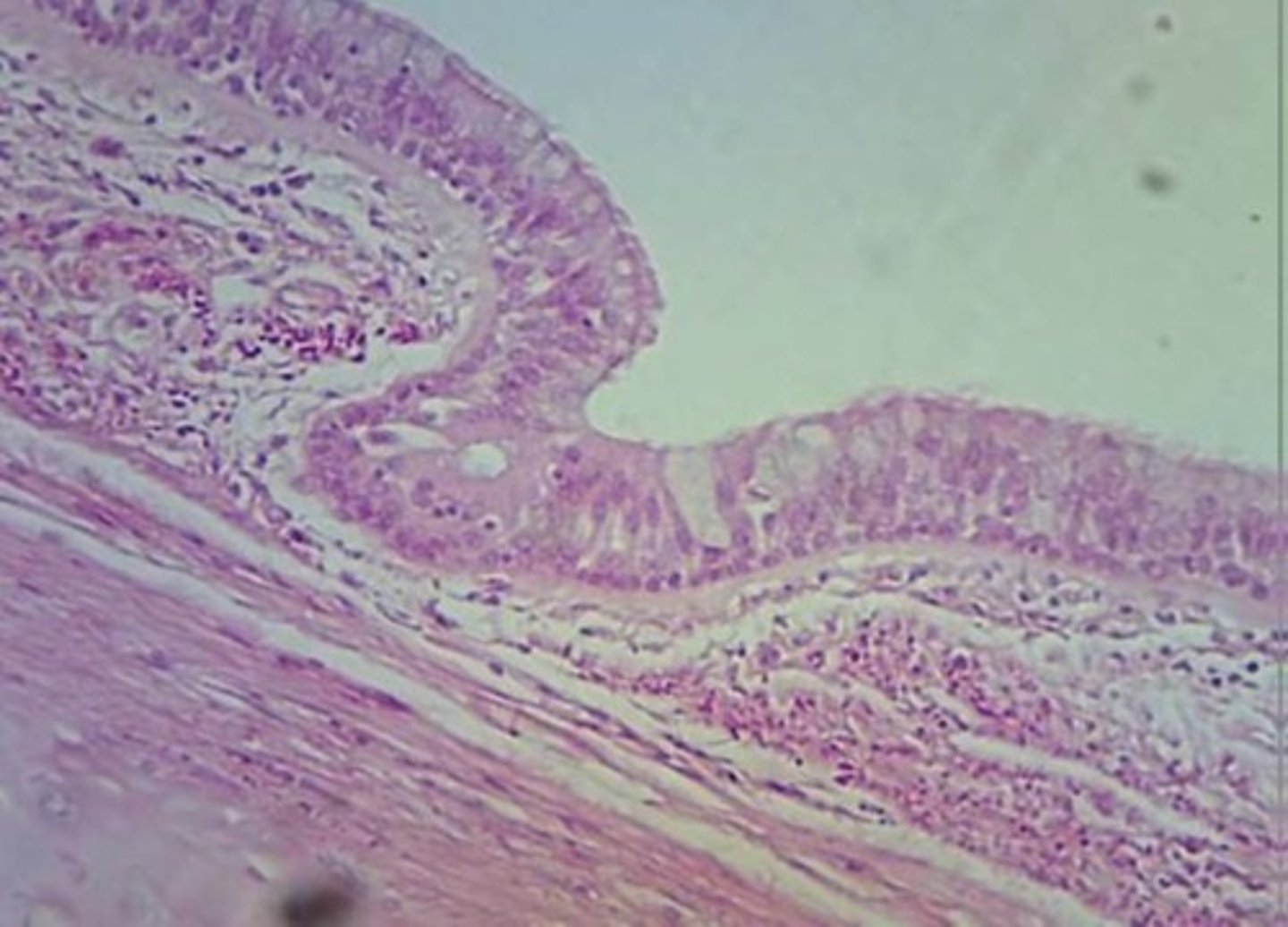
transitional epithelium
Location: bladder
Function: stretchability and protection
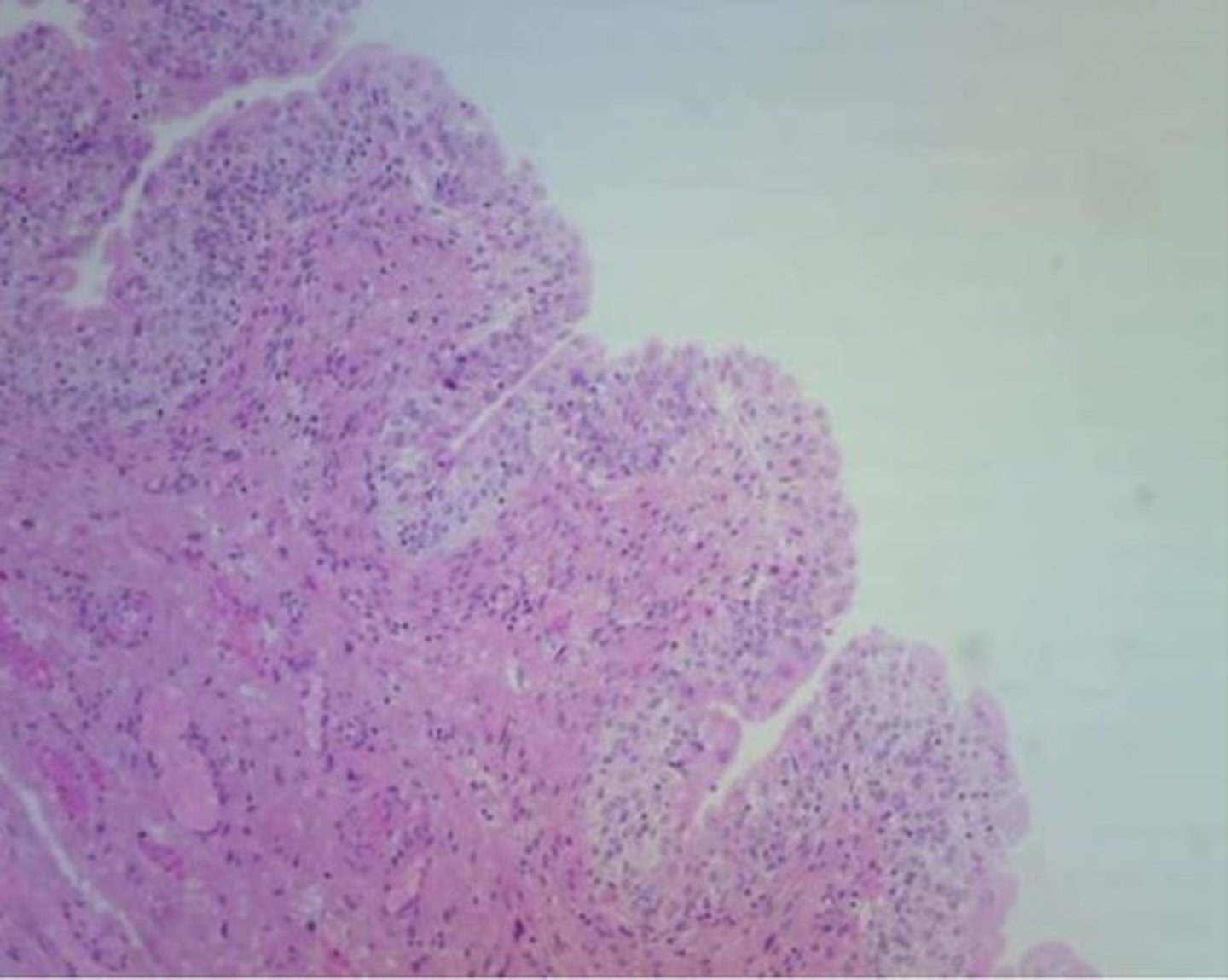
Connective Tissue
binds, supports, and protects structures in the body. types: Areolar, Dense Regular Connective Tissue, Hyaline Cartilage, Elastic Cartilage, Fibrocartilage, Adipose Tissue, Blood Connective Tissue, Bone Connective tissue
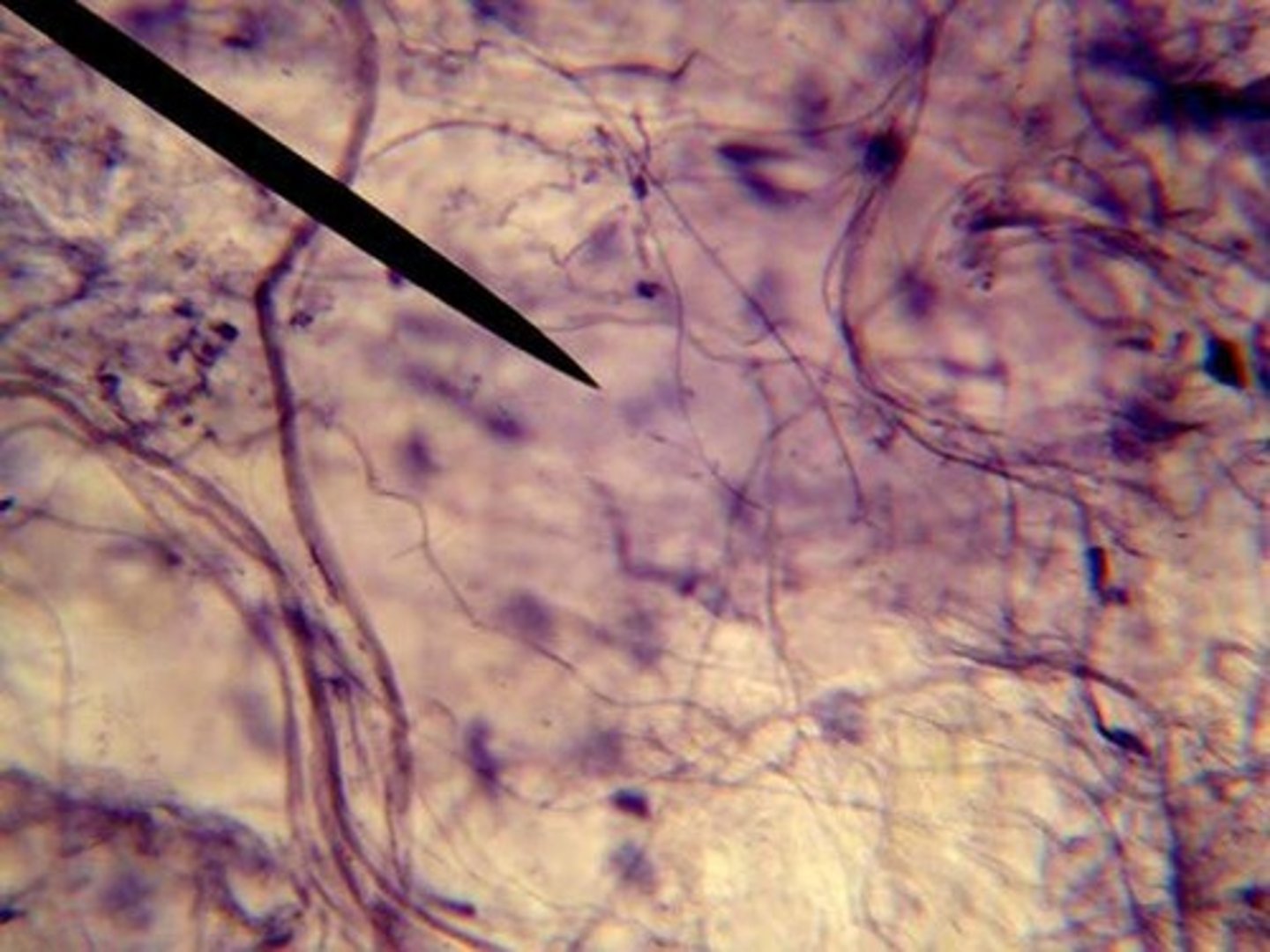
Areolar Tissue
loose connective tissue. Location: beneath skin, between muscle tissues, beneath epithelial tissue. Function: binds organs and tissue together.
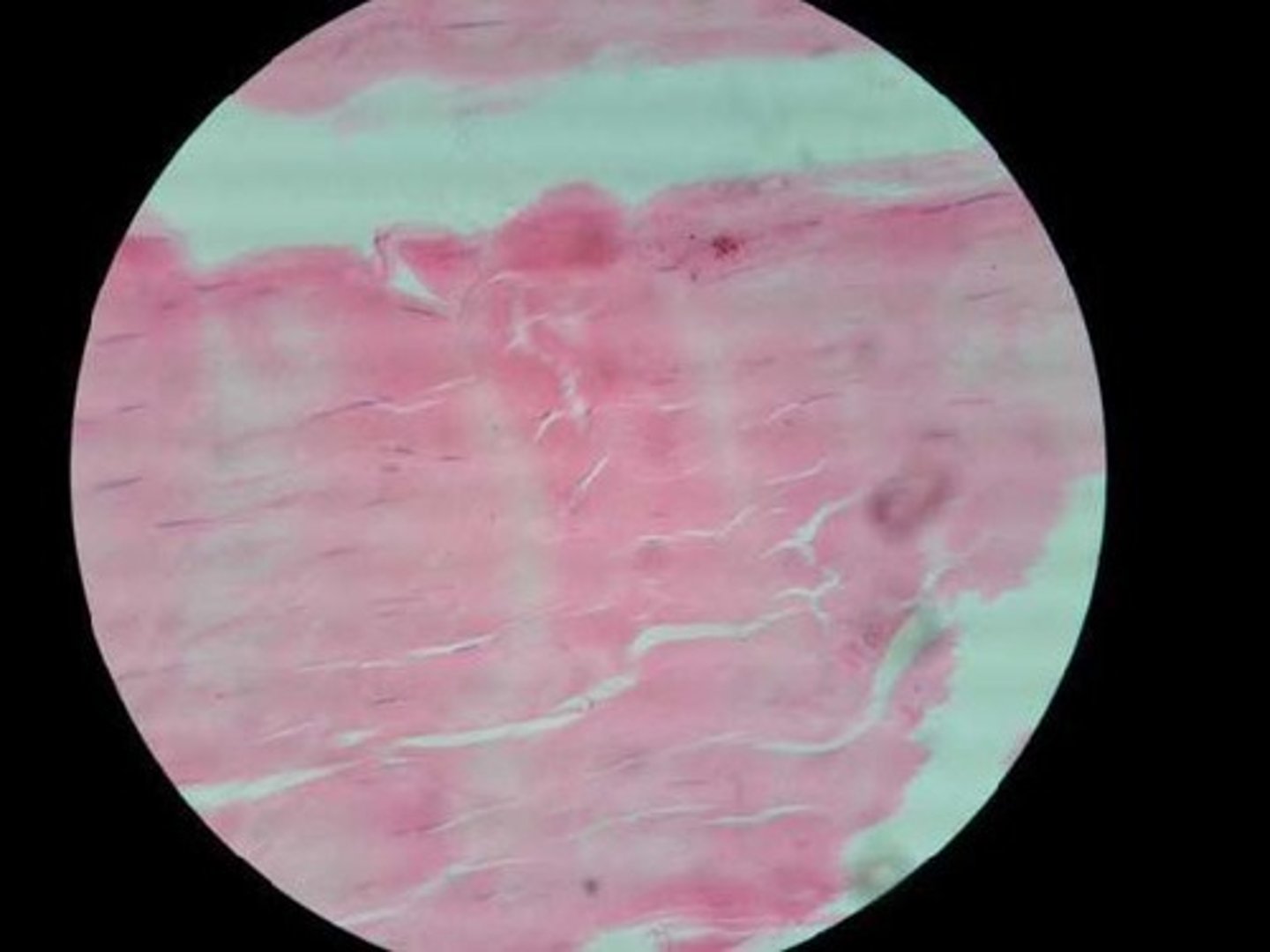
dense regular connective tissue
Function: attaches muscles to bones or to muscles; attaches bones to bones; withstands great tensile stress when pulling force is applied in one direction
Location: tendons, most ligaments
hyaline cartilage
Location: Most common type of cartilage; it is found on the ends of long bones, ribs, and nose
Function: development and growth of bones.
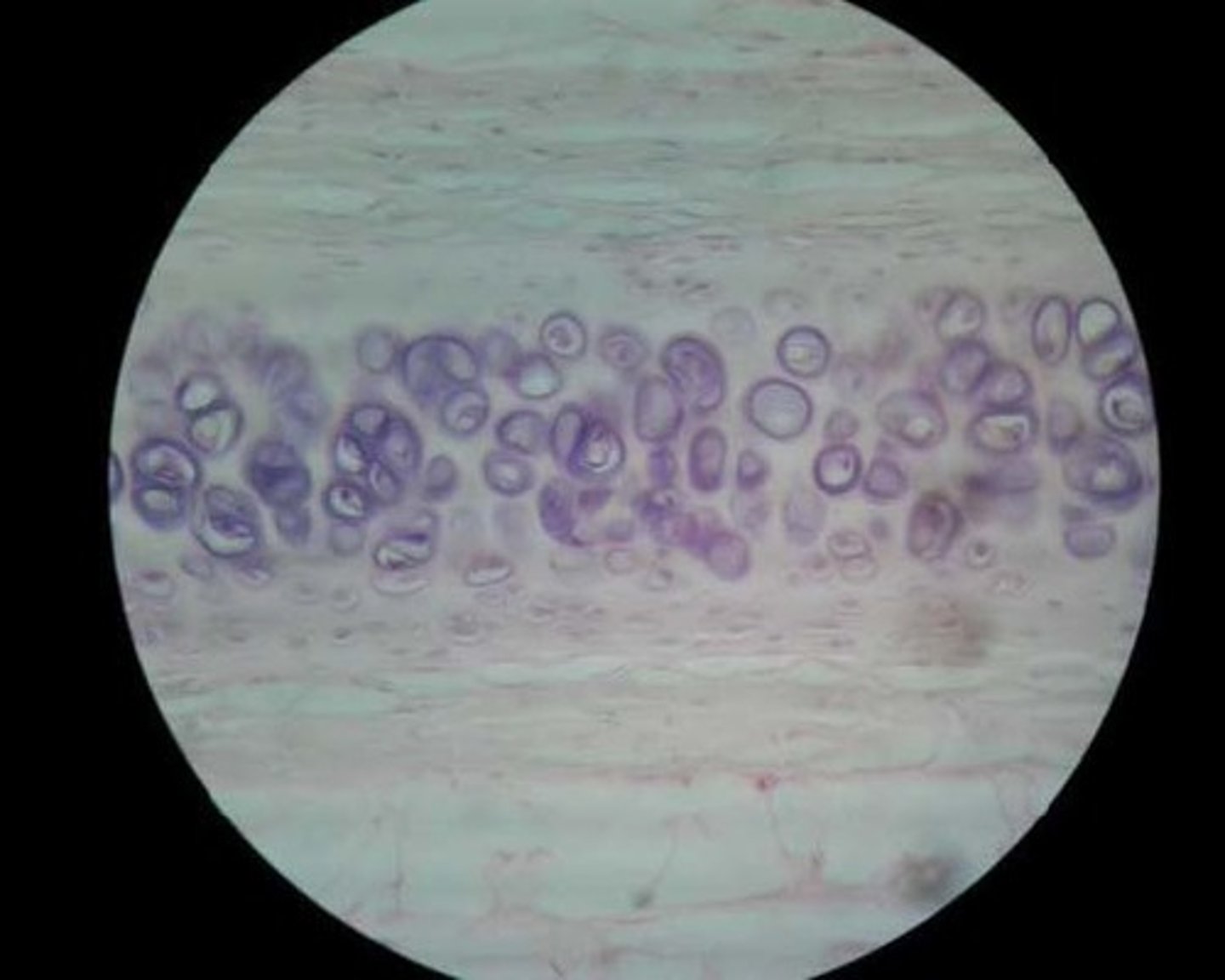
Chondrocytes
(cartilage cells) occupy small chambers called lacunae and are surrounded by extracellular matrix containing very fine collagenous fibers.
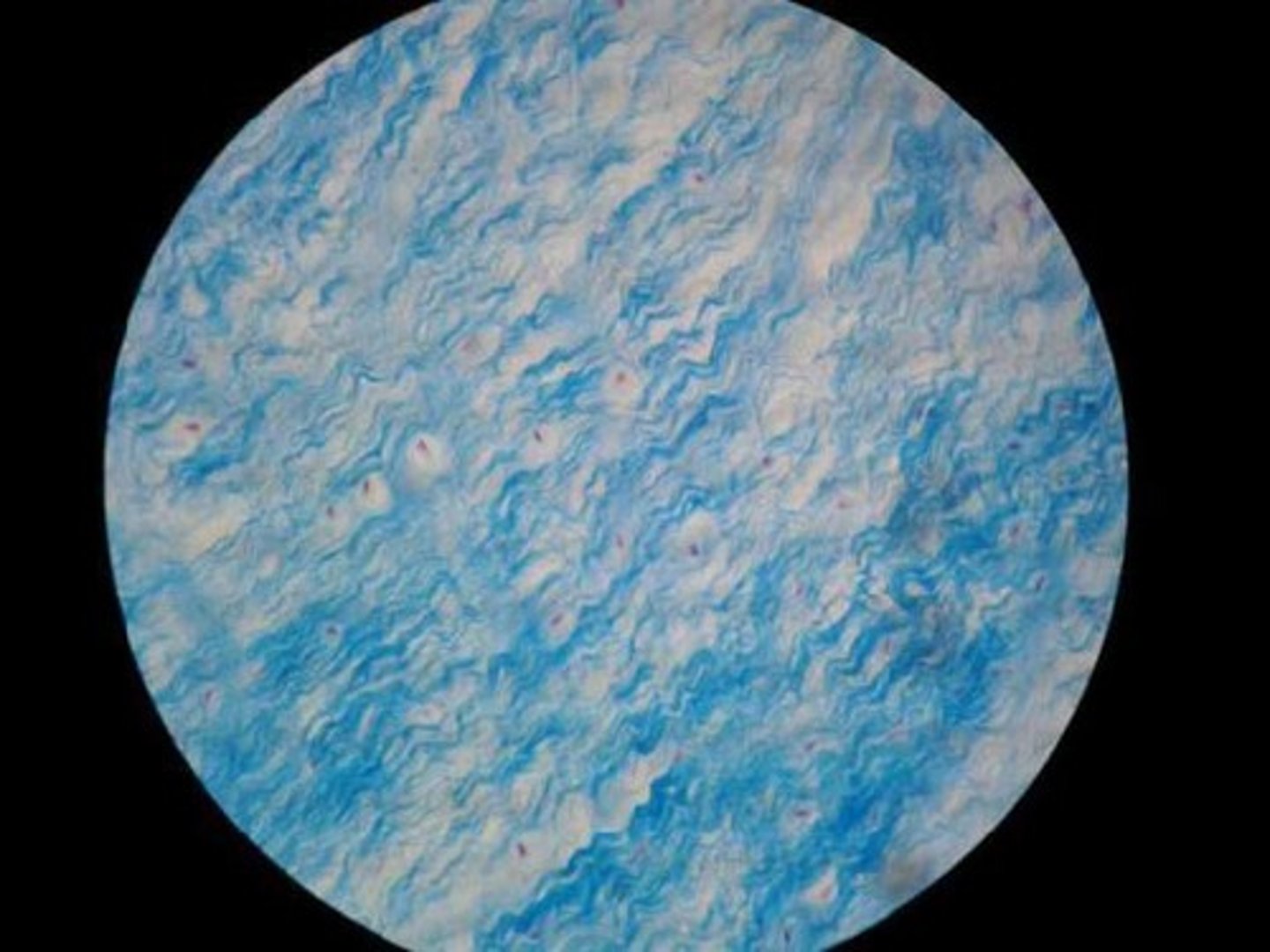
elastic cartilage
Location: Framework for external ears and parts of the larynx
Function: Support, protect, and provide a flexible framework (*more compact and smaller than hyaline, usually stain darker)
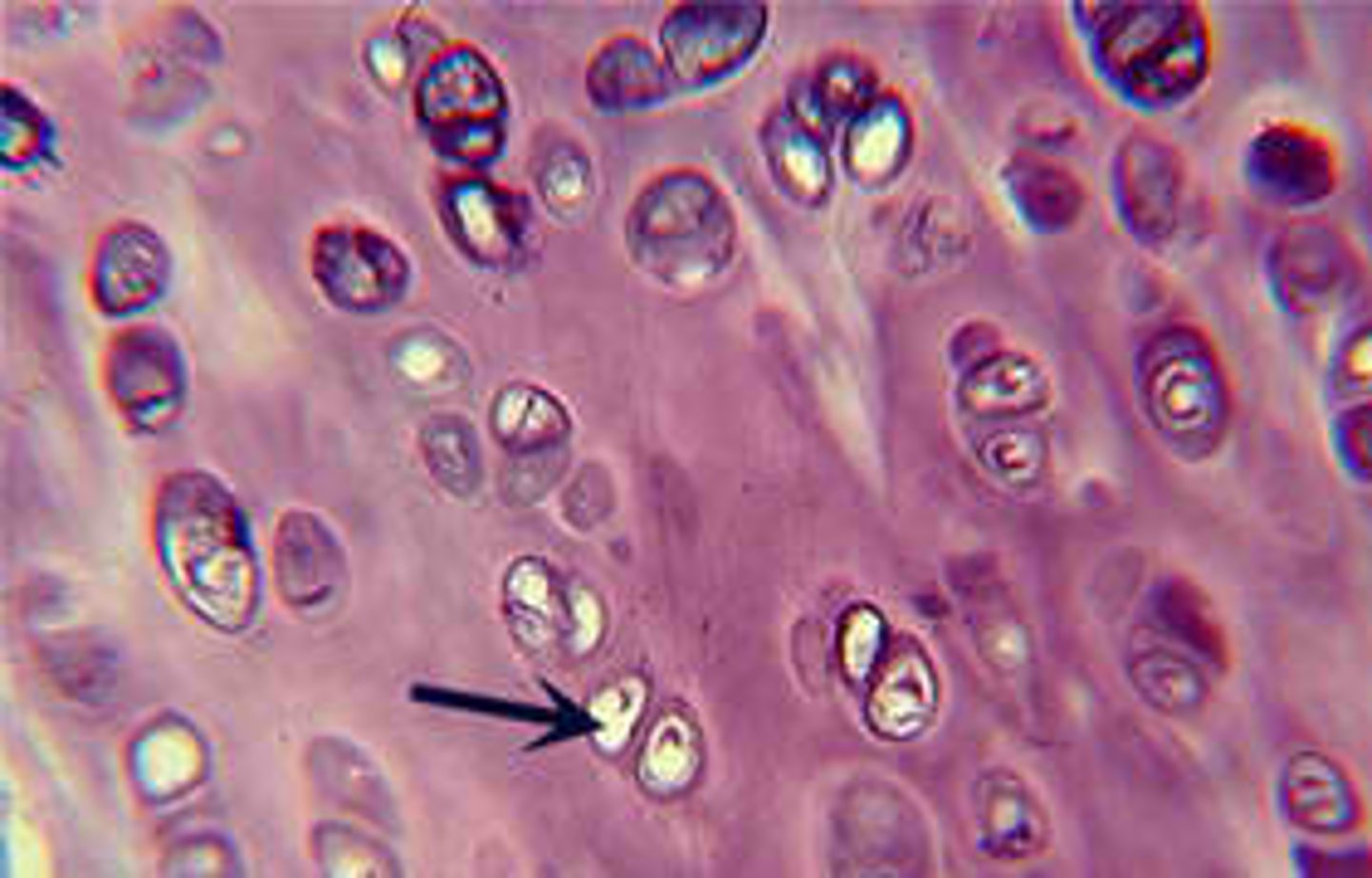
Fibrocartilage
Location: Pads between the vertebrae and cushions bones of the knees and pelvic girdle
Function: Shock absorber (*usually looks wavy, small dark spots are chondrocytes)
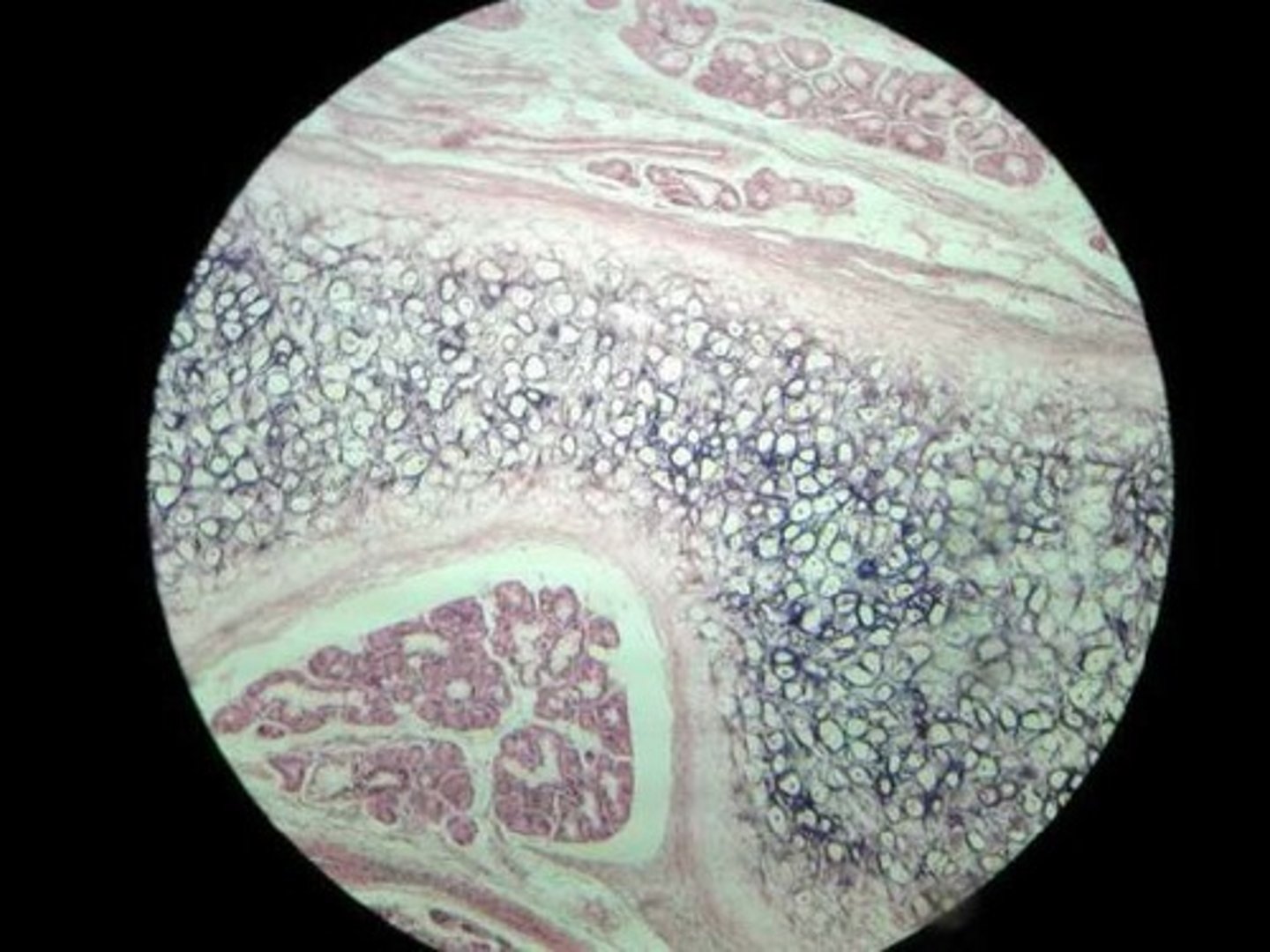
Adipose Tissue
Location: cushions joints and some organs.
Function: cushion, insulation, and energy storage
Blood Connective Tissue
red cells: Erythrocytes, White Cells: Leukocyte, Platelets will appear as small speck on closer images
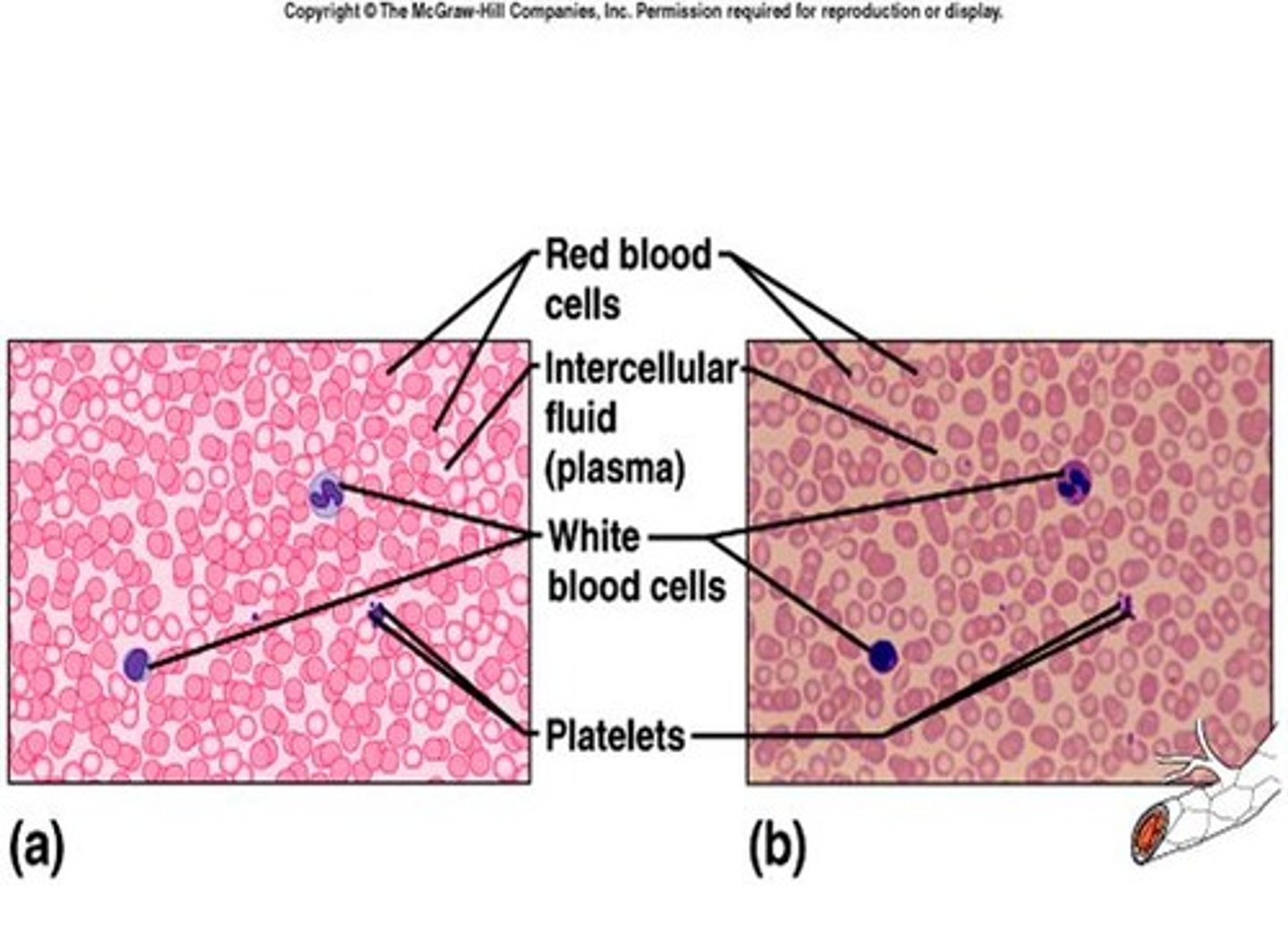
Blood Connective Tissue
Location: Throughout the body within a closed system of blood vessels and heart chambers.
Function: Transports substances
Bone Connective Tissue
Location: Skeletal system
Functions:Support, Protection, Skeletal Framework
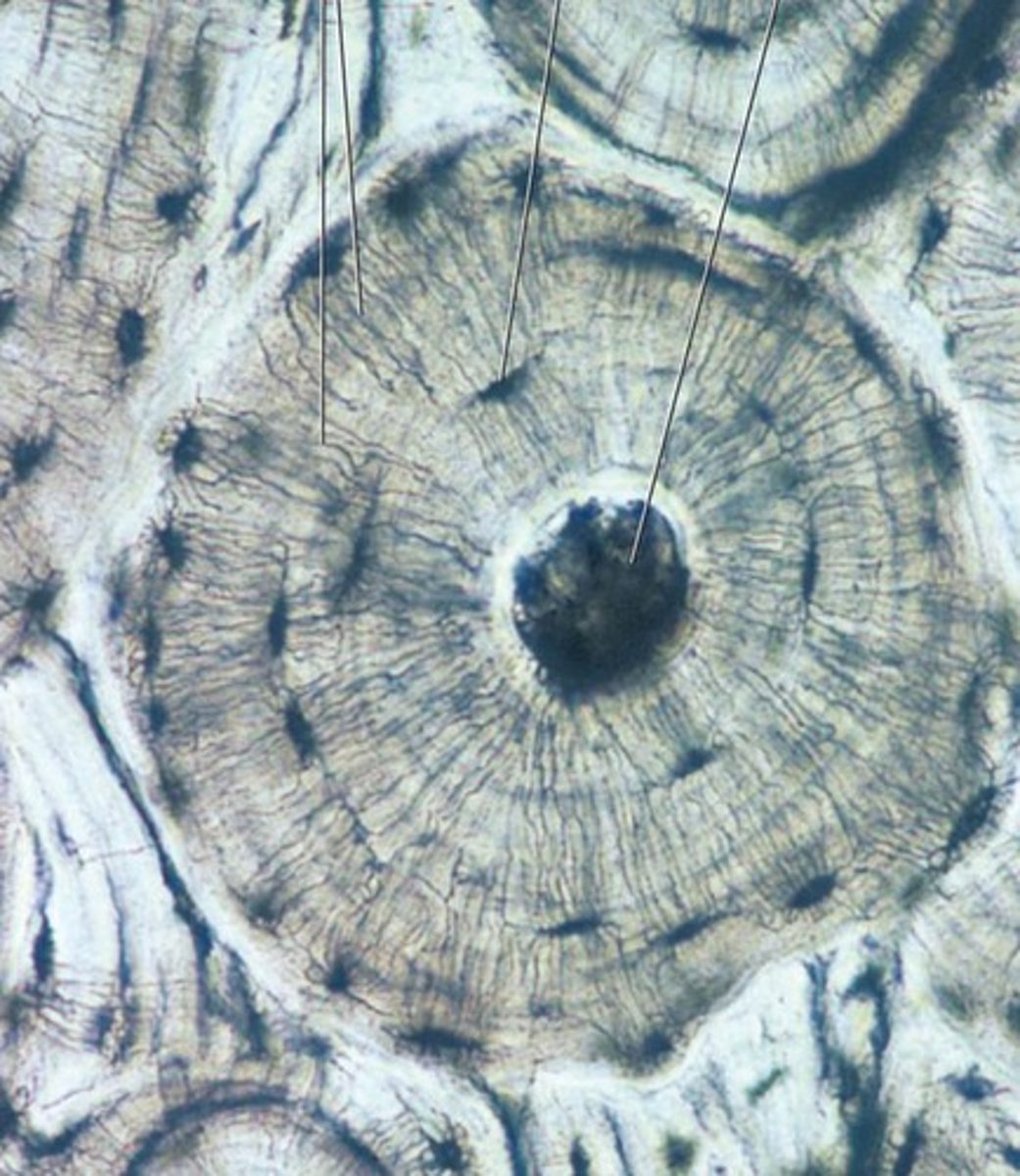
Osteocytes
bone cells
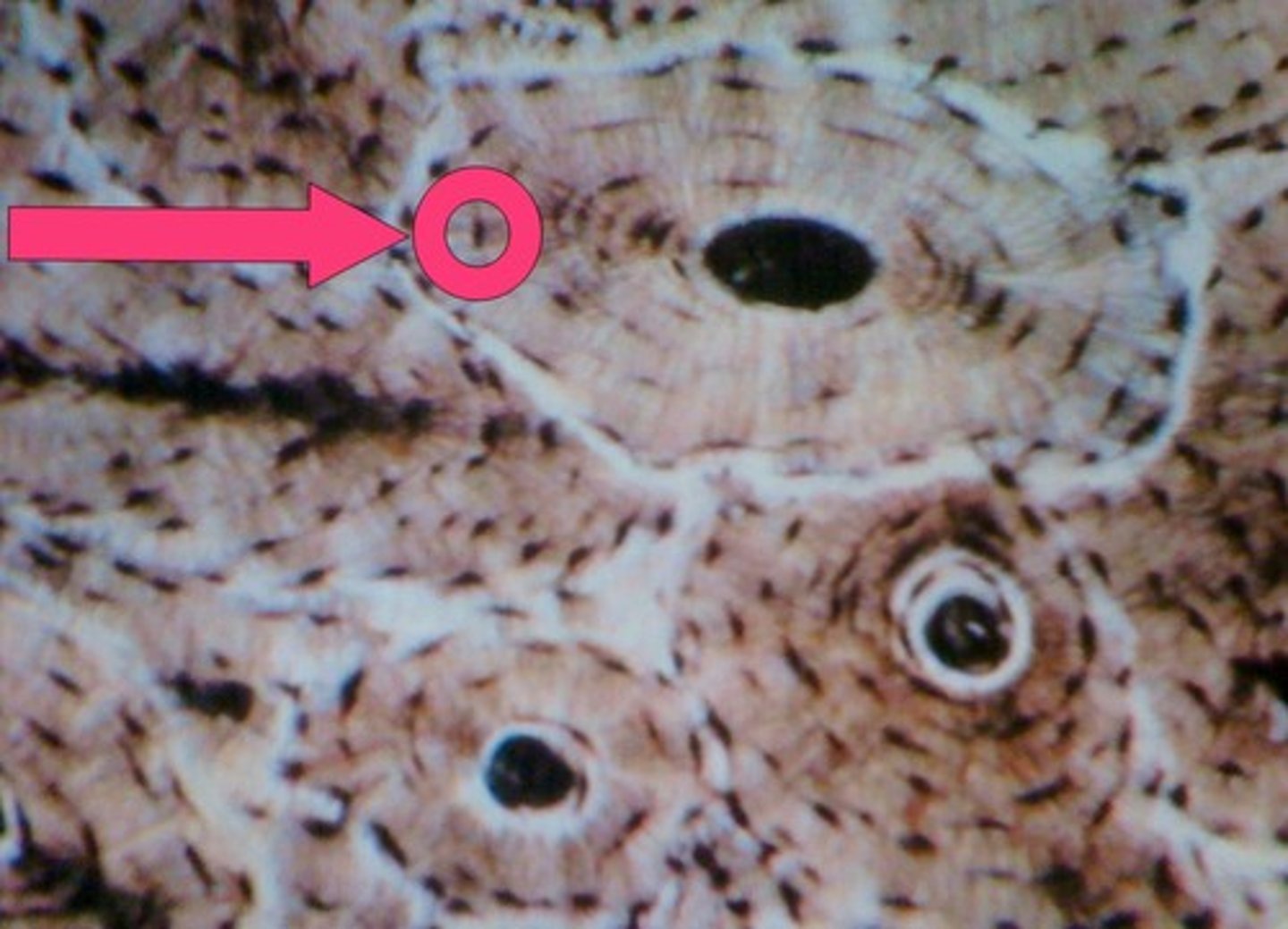
Muscle Tissue
skeletal, smooth, cardiac
skeletal muscle
tissue is striated and voluntary
Location: Muscles typically attached to bones
Function: Voluntary movements of skeletal parts
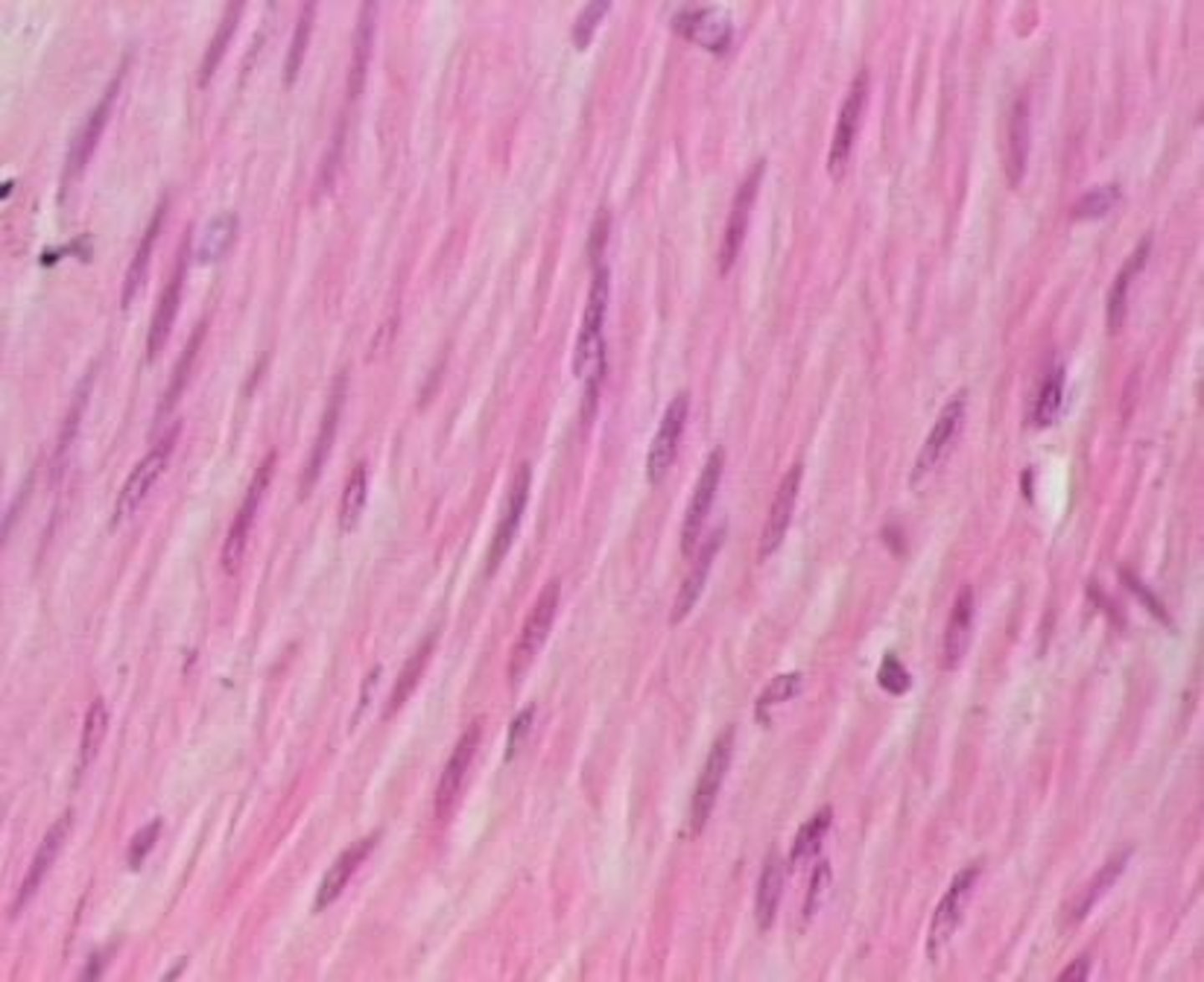
smooth muscle
tissue is not striated and is involuntary
Location: walls of hollow internal organs
Function:involuntary movements of internal organs
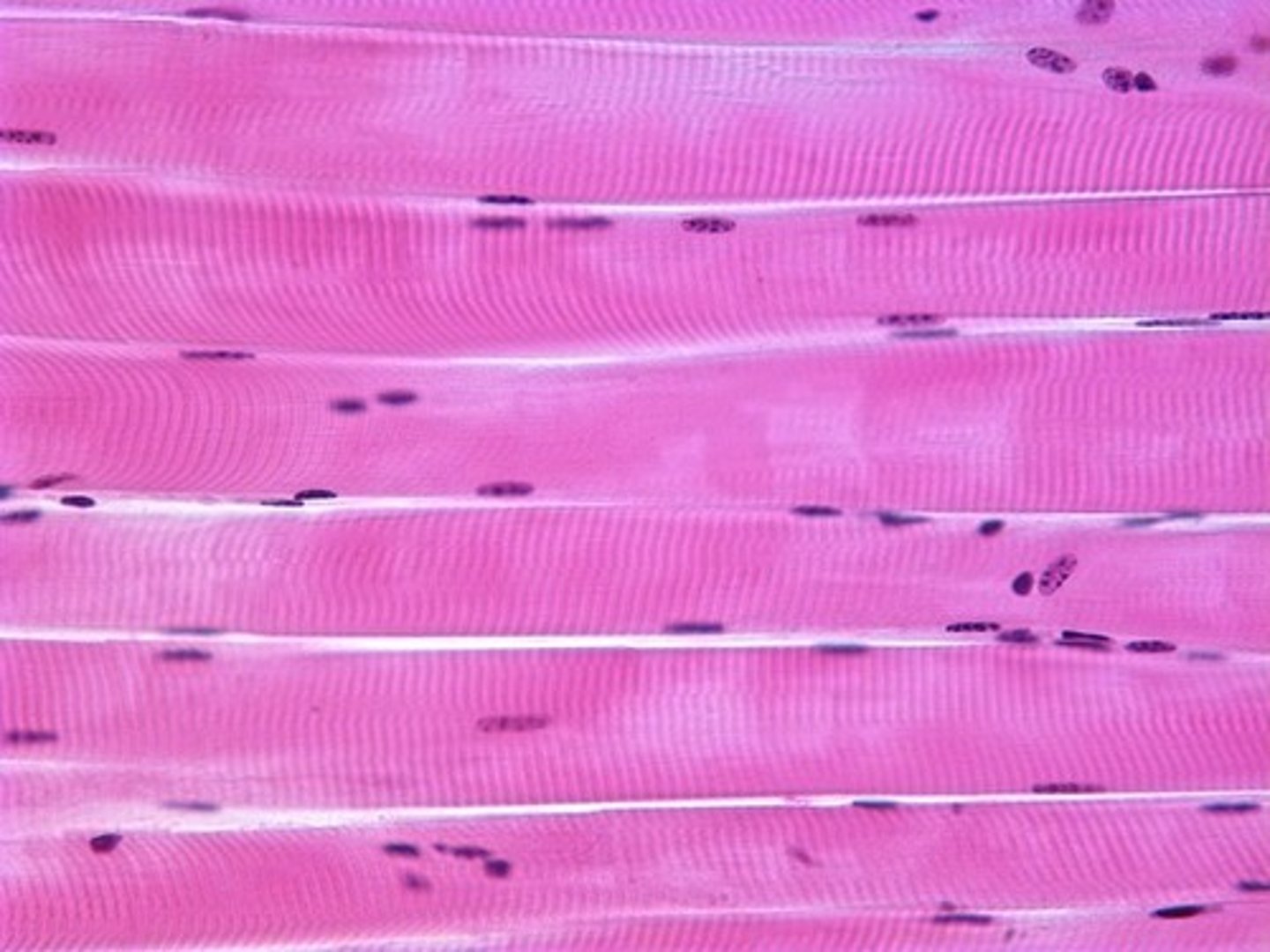
cardiac muscle
tissue is striated and involuntary (contains intercalated discs)
Location: Heart Muscle
Function: Heart movements
intercalated discs
allow the heart cells to act as a single unit and beat together
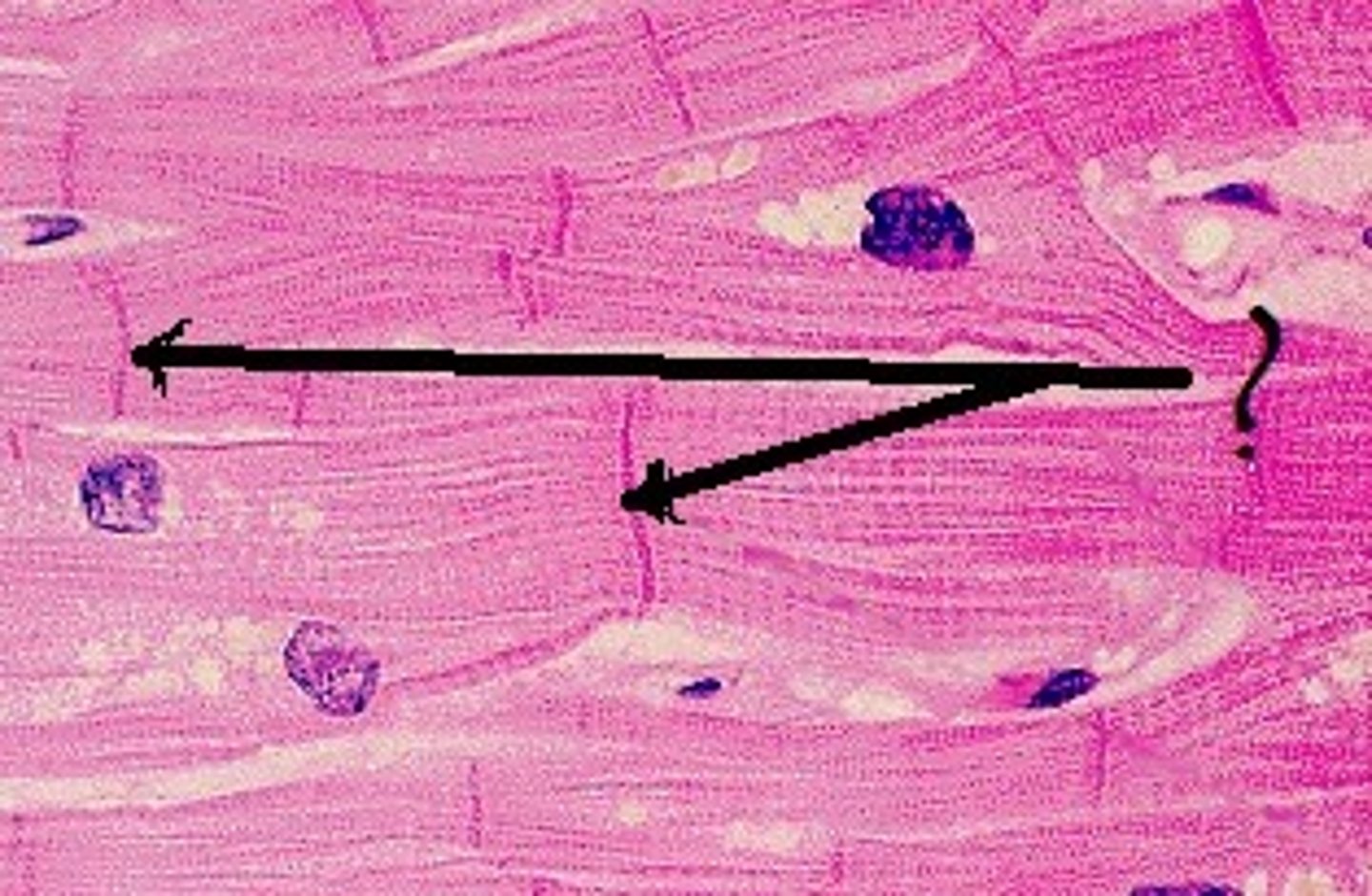
nervous tissue
Location: brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves
Function: sensory reception and conduction of electrical impulses
(contains neurons and neuroglia)
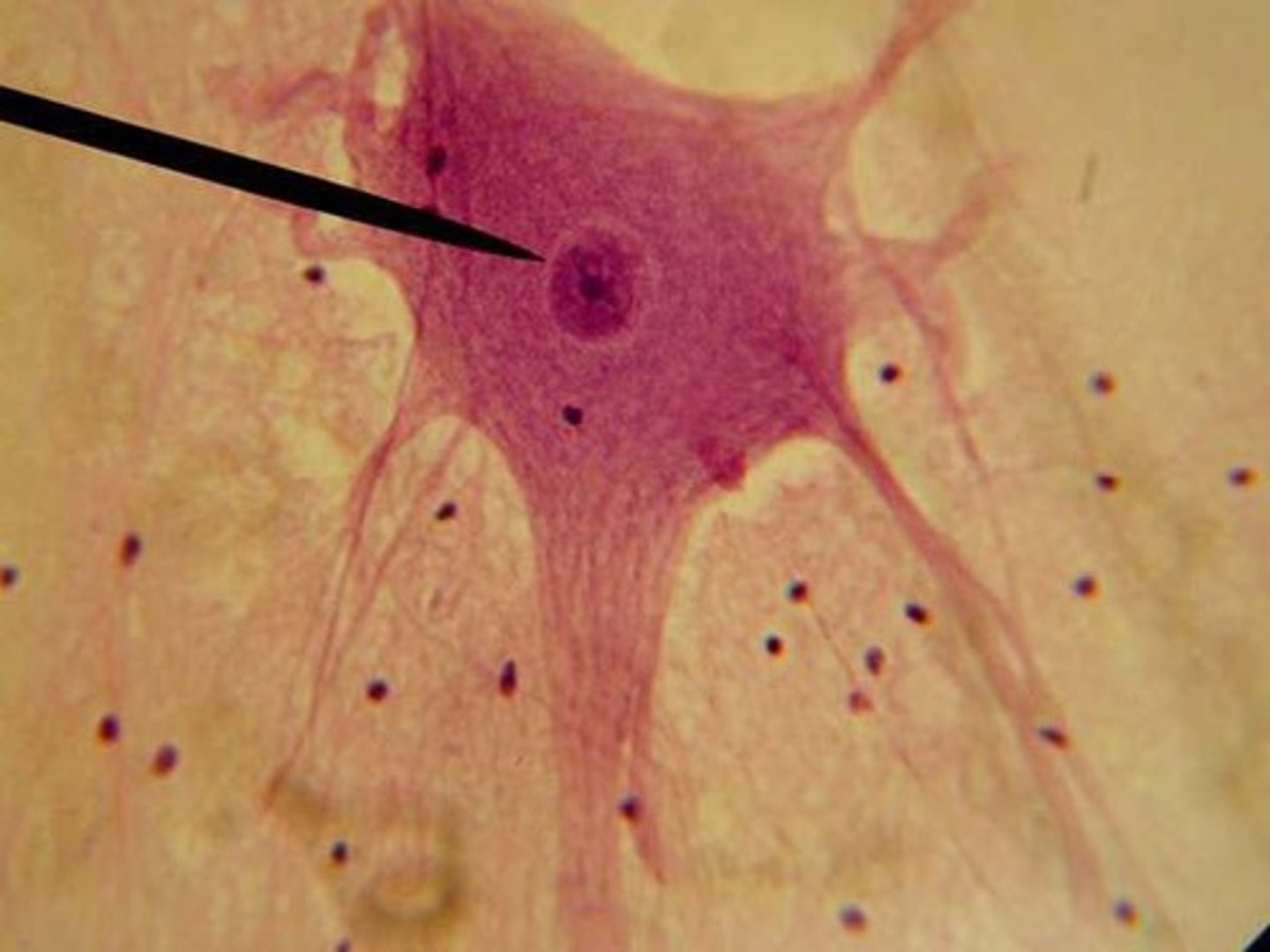
neurons
main type of nervous cell. Receives nerve impulses at the dendrites and sends impulses through the axon.
Neuroglia
these supporting cells act as 'nerve glue' to support and bind the components of the nervous tissue.
integumentary system
The skin, the largest organ in the body, and its accessory structures (hair, nails, sensory receptors, and glands)
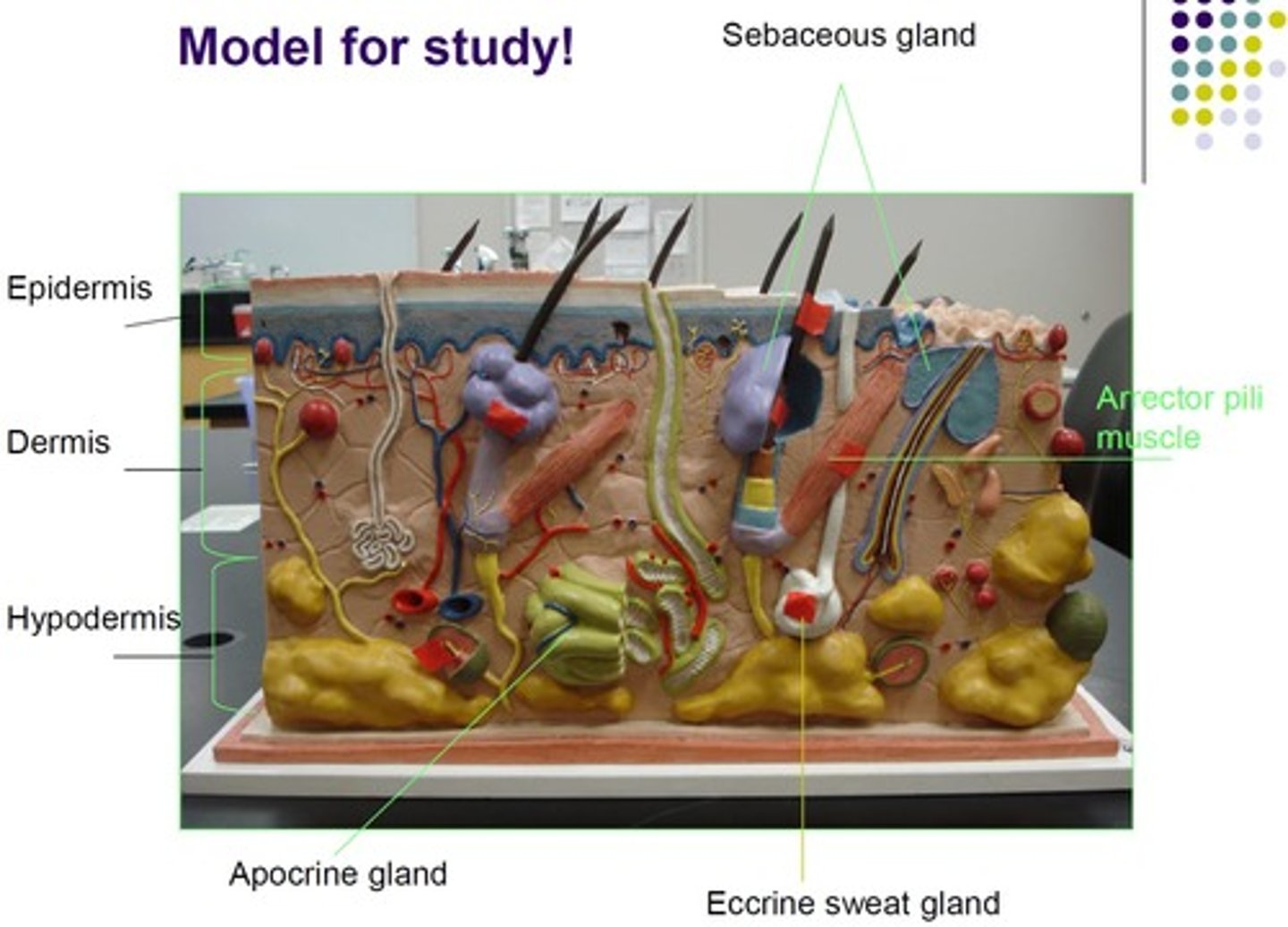
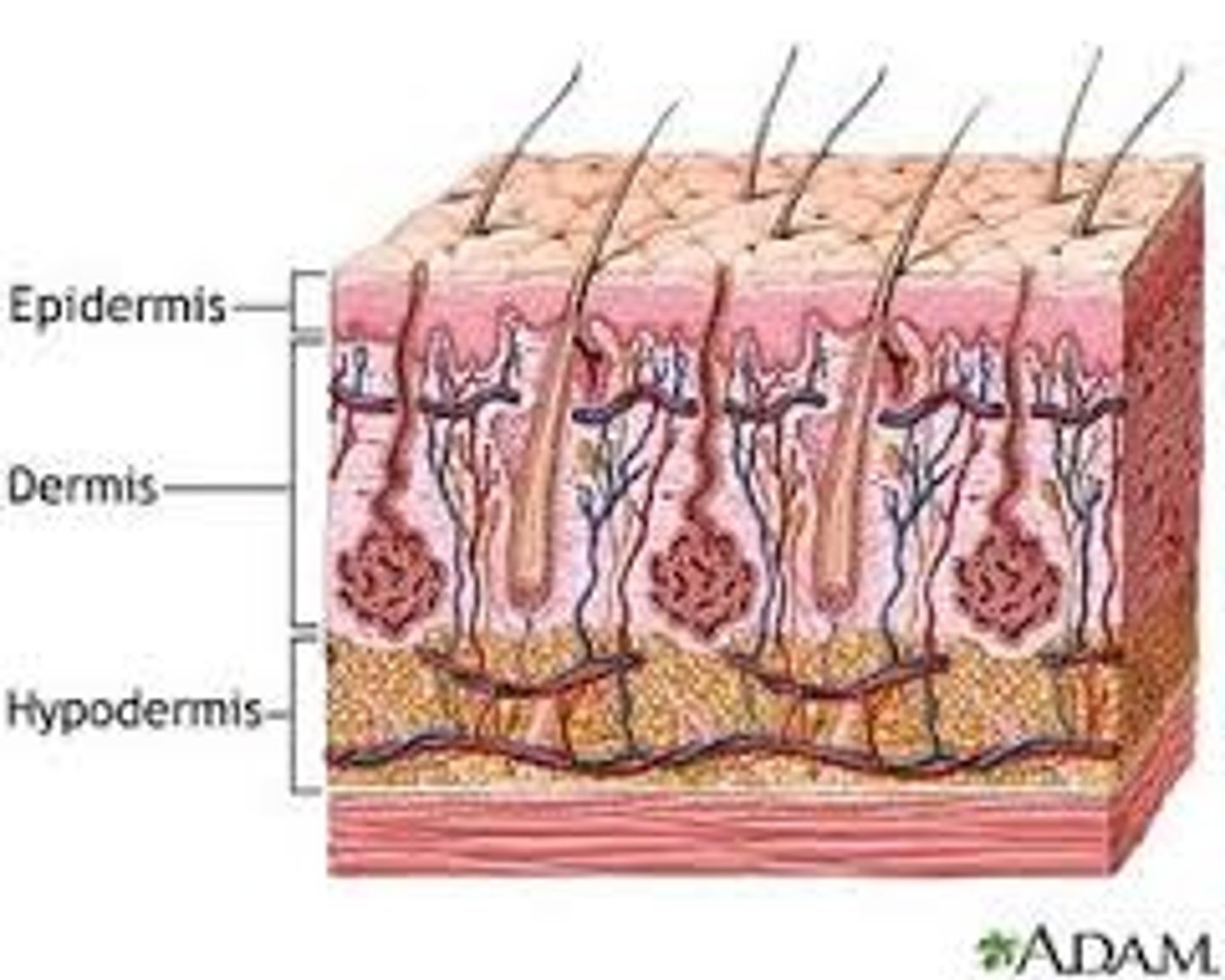
Skin Layers
1. Epidermis
2. Dermis
3. Hypodermis
Epidermis
outermost layer, composed of stratified squamous epithelium contains stratum corneum and stratum basale Note: as the cells regenerate, older cells are pushed towards the surface where they become nutrient poor and eventually die.
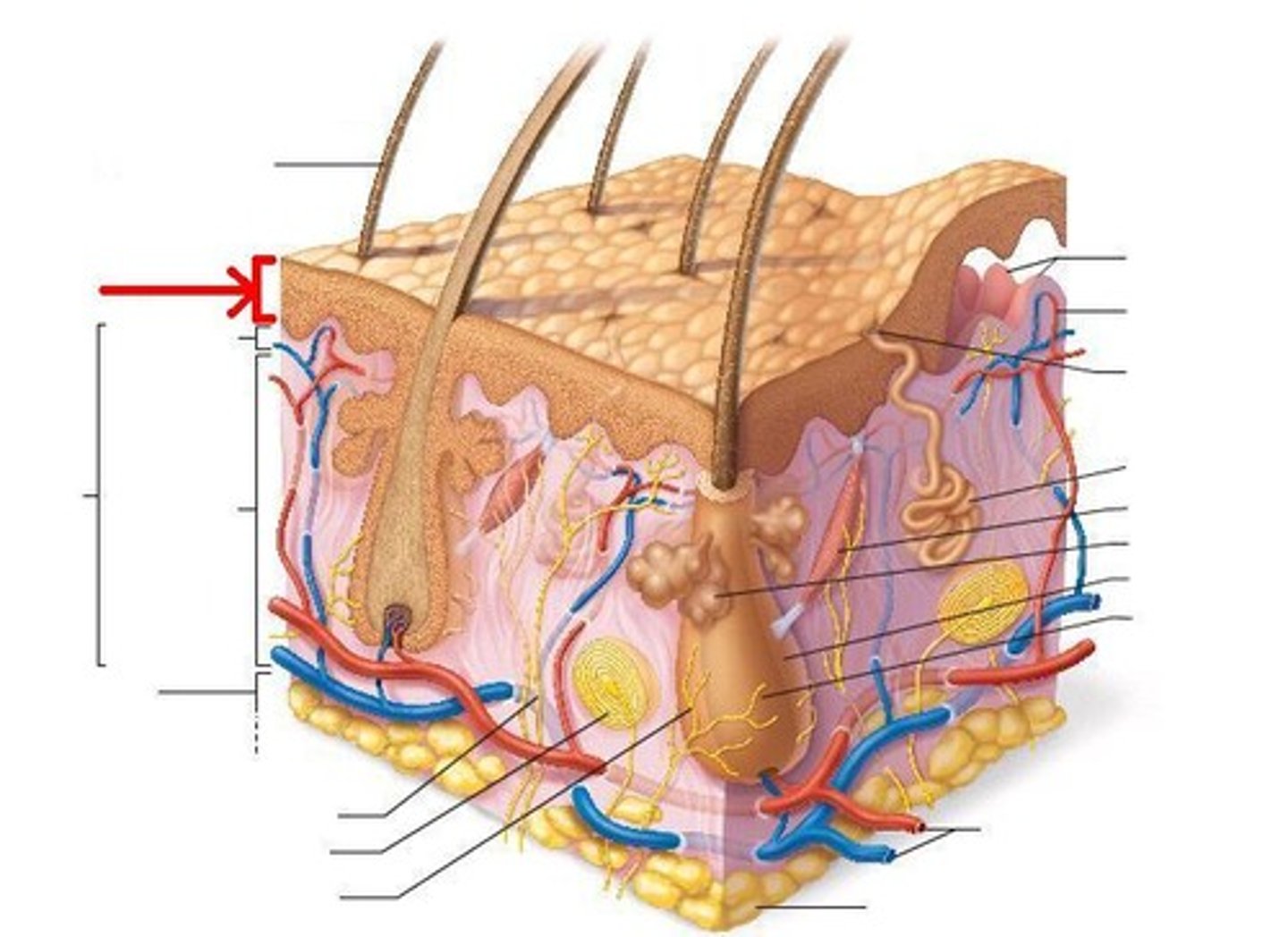
Stratum corneum
outermost layer made of many layers of tough, tightly packed dead cells
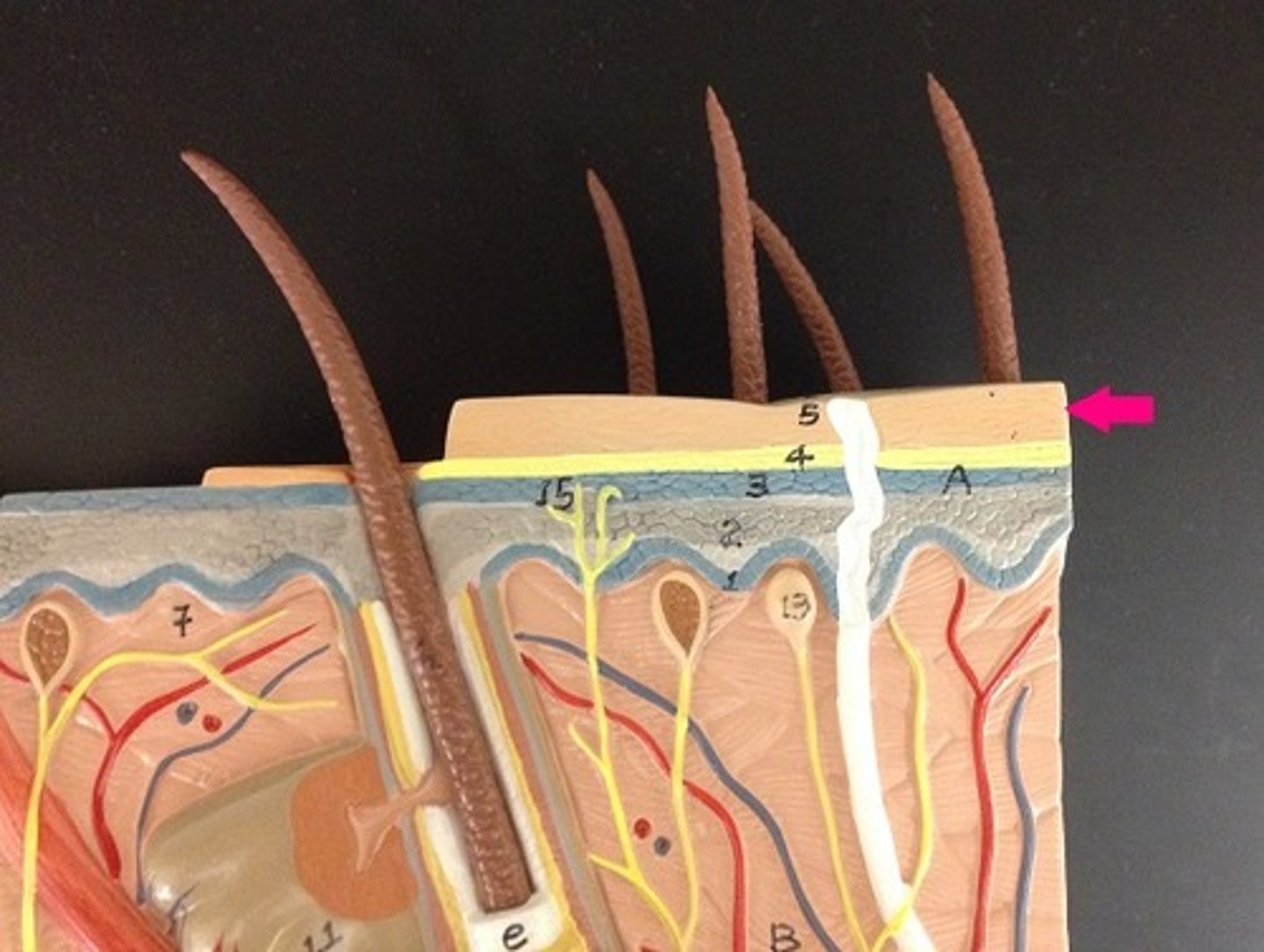
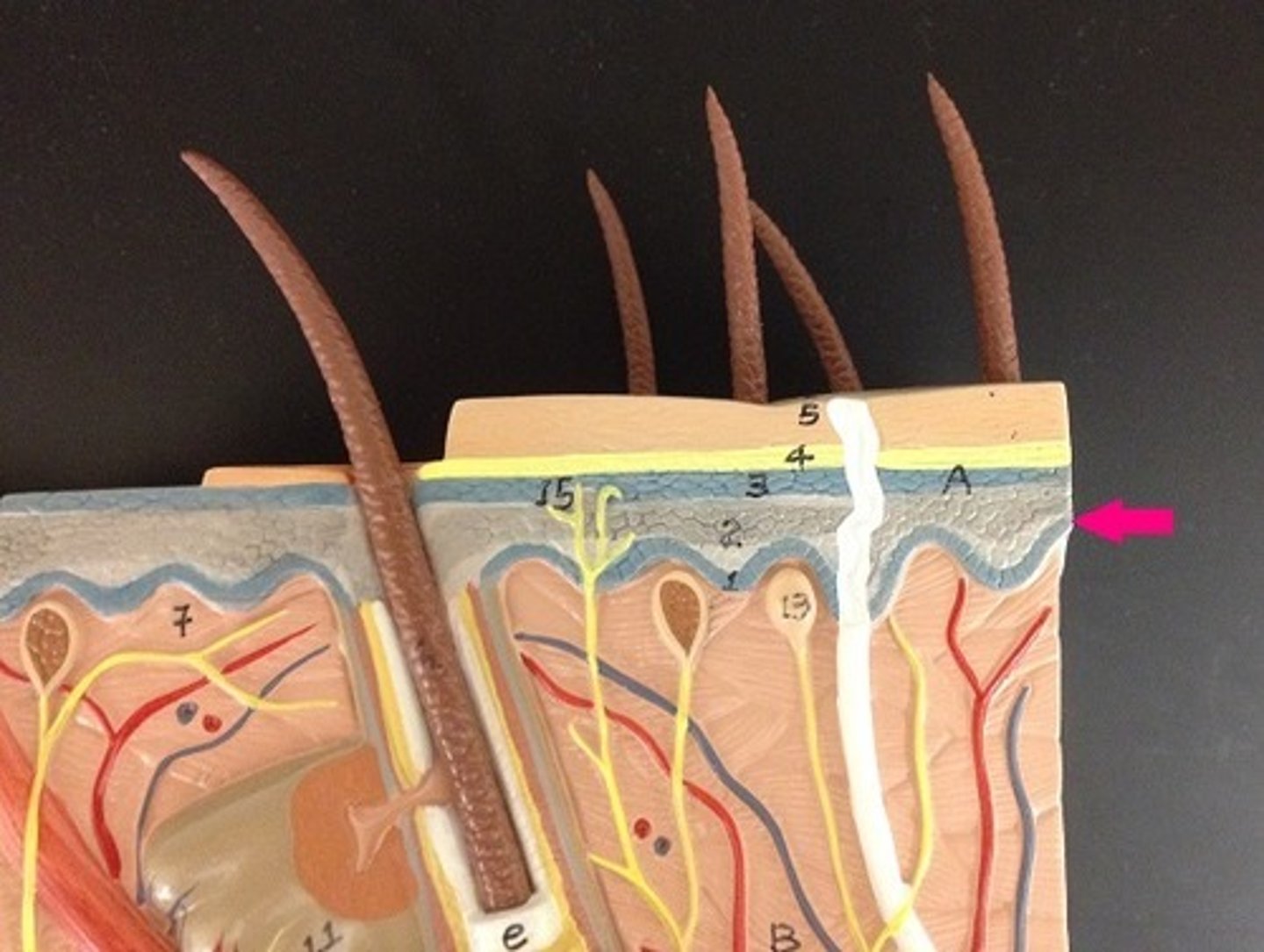
Stratum basale
innermost layer located close to the dermis and and nourished by the dermal blood vessels. Therefore, this layer of cells actively grows and divides
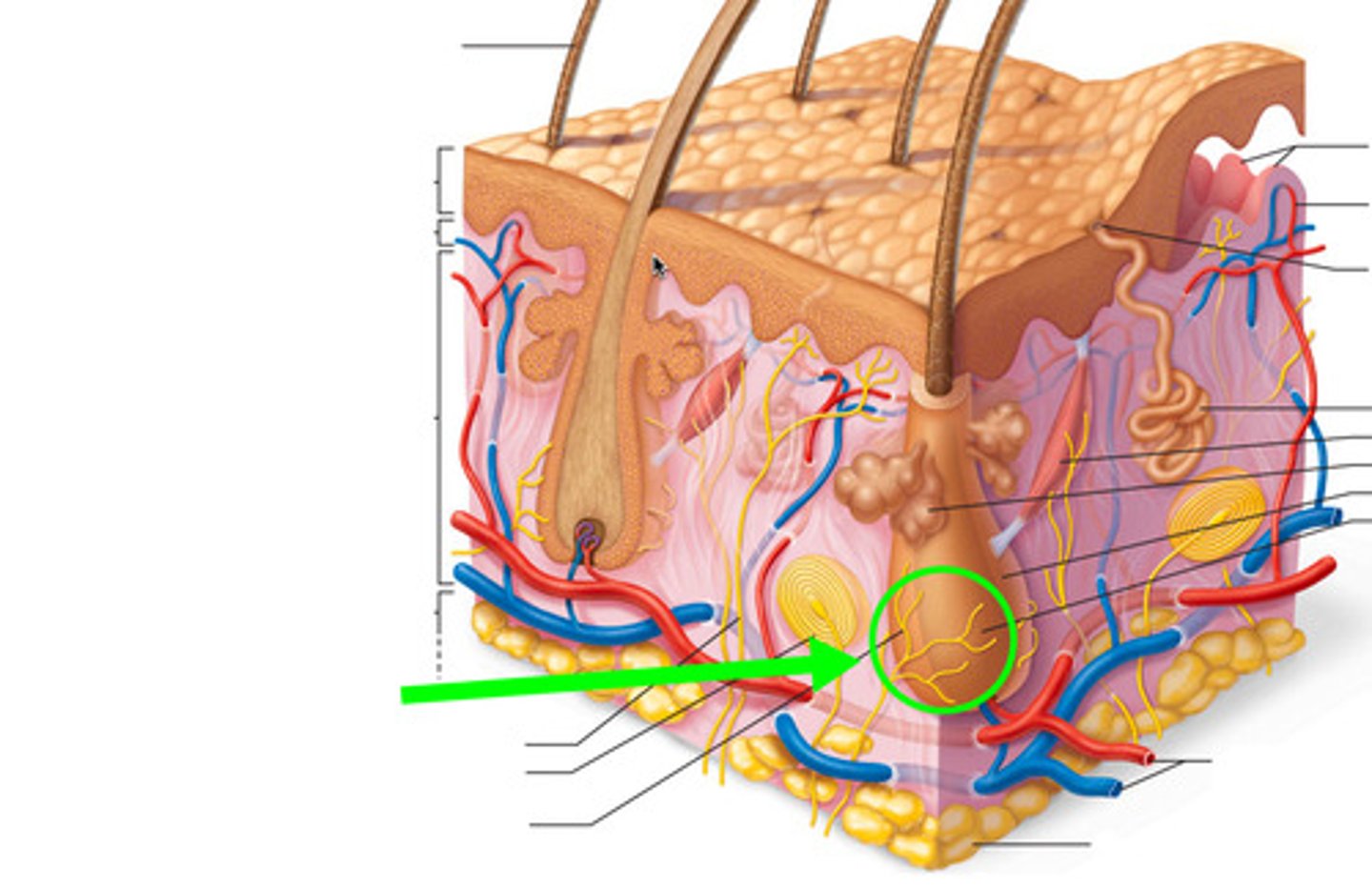
hair follicle
sheath that surrounds hair
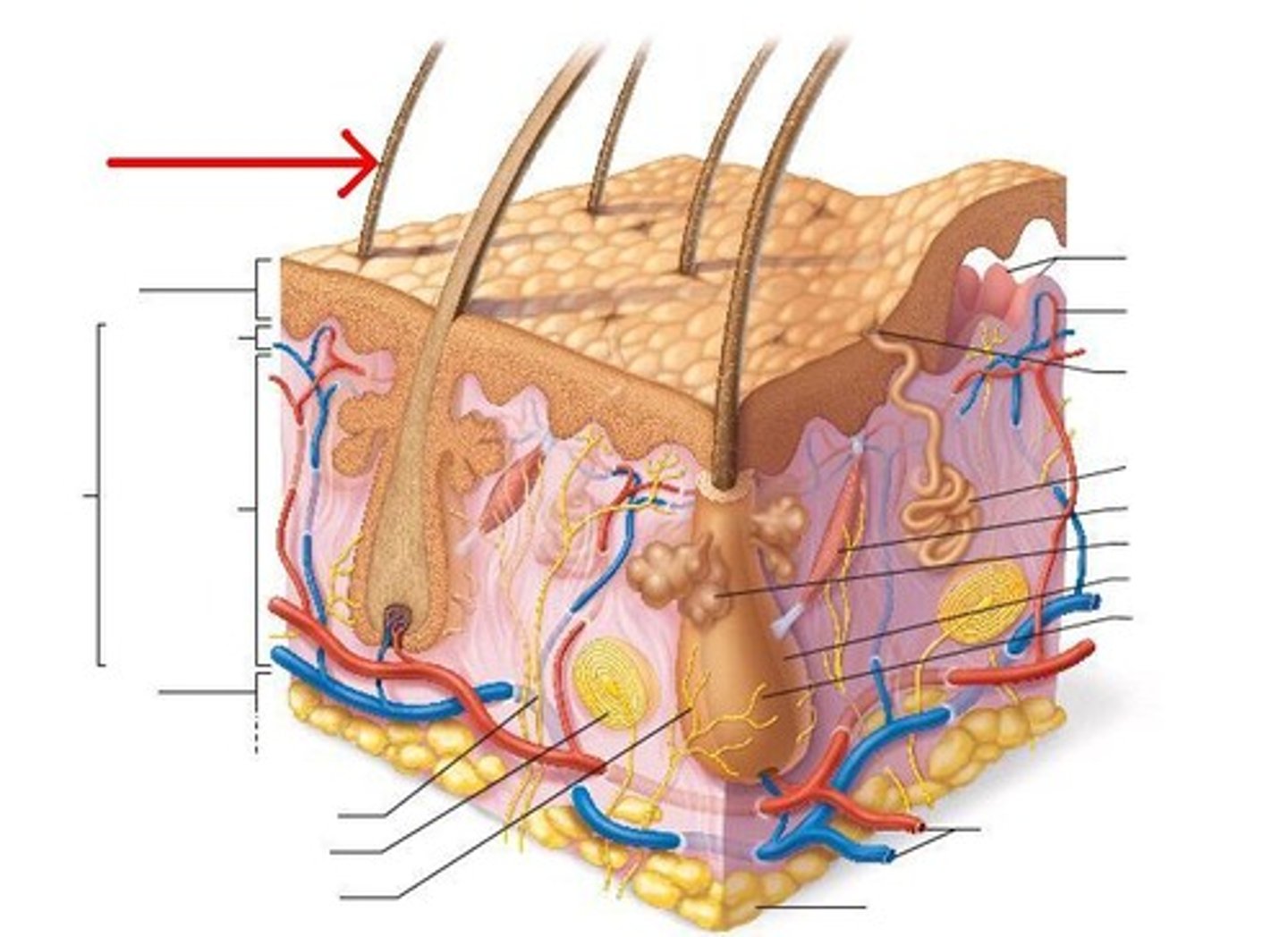
Hair shaft
visible part of the hair
arrector pili muscle
bundle of smooth muscles associated with hair follicle. Causes goosebumps.
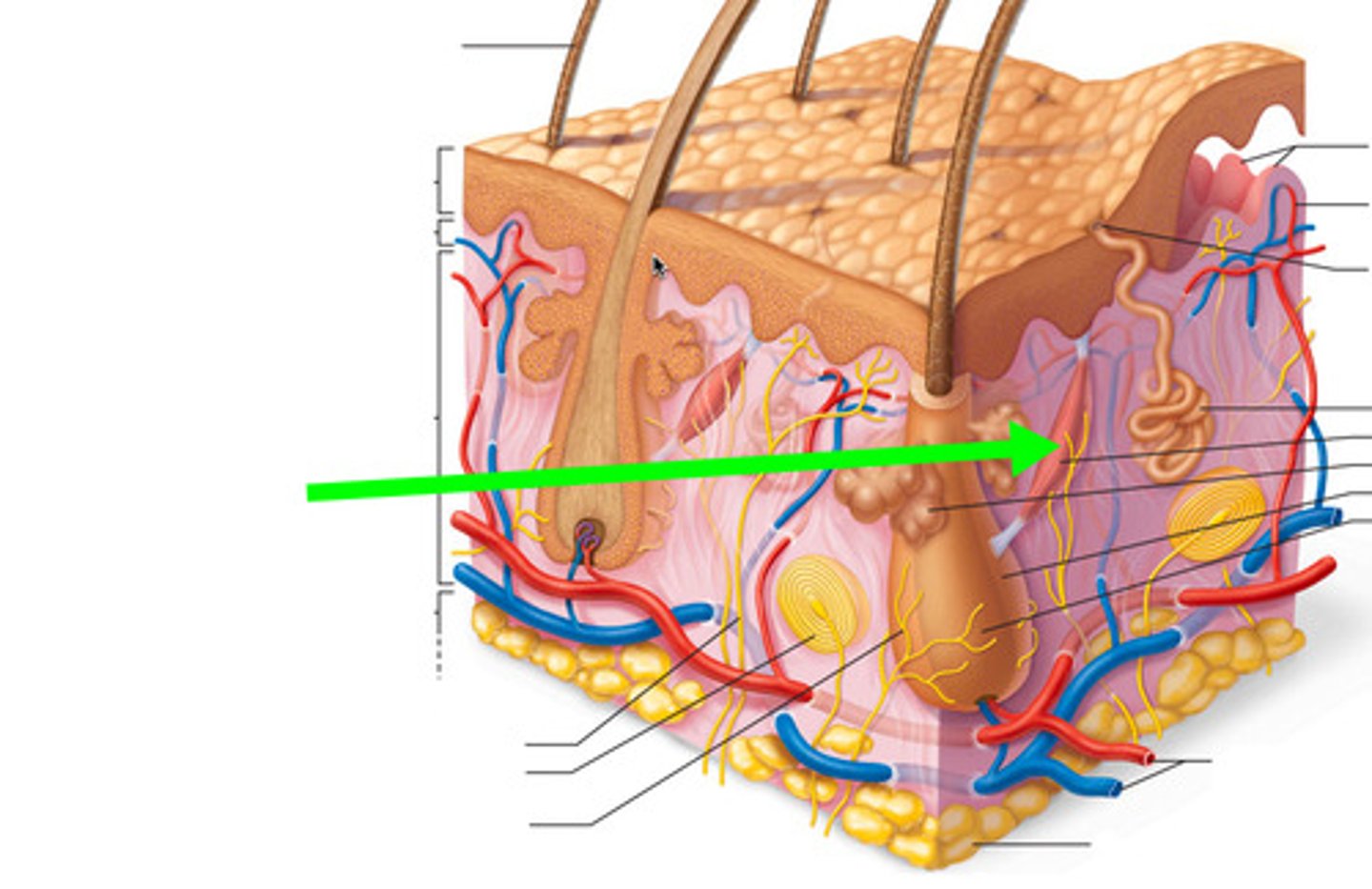
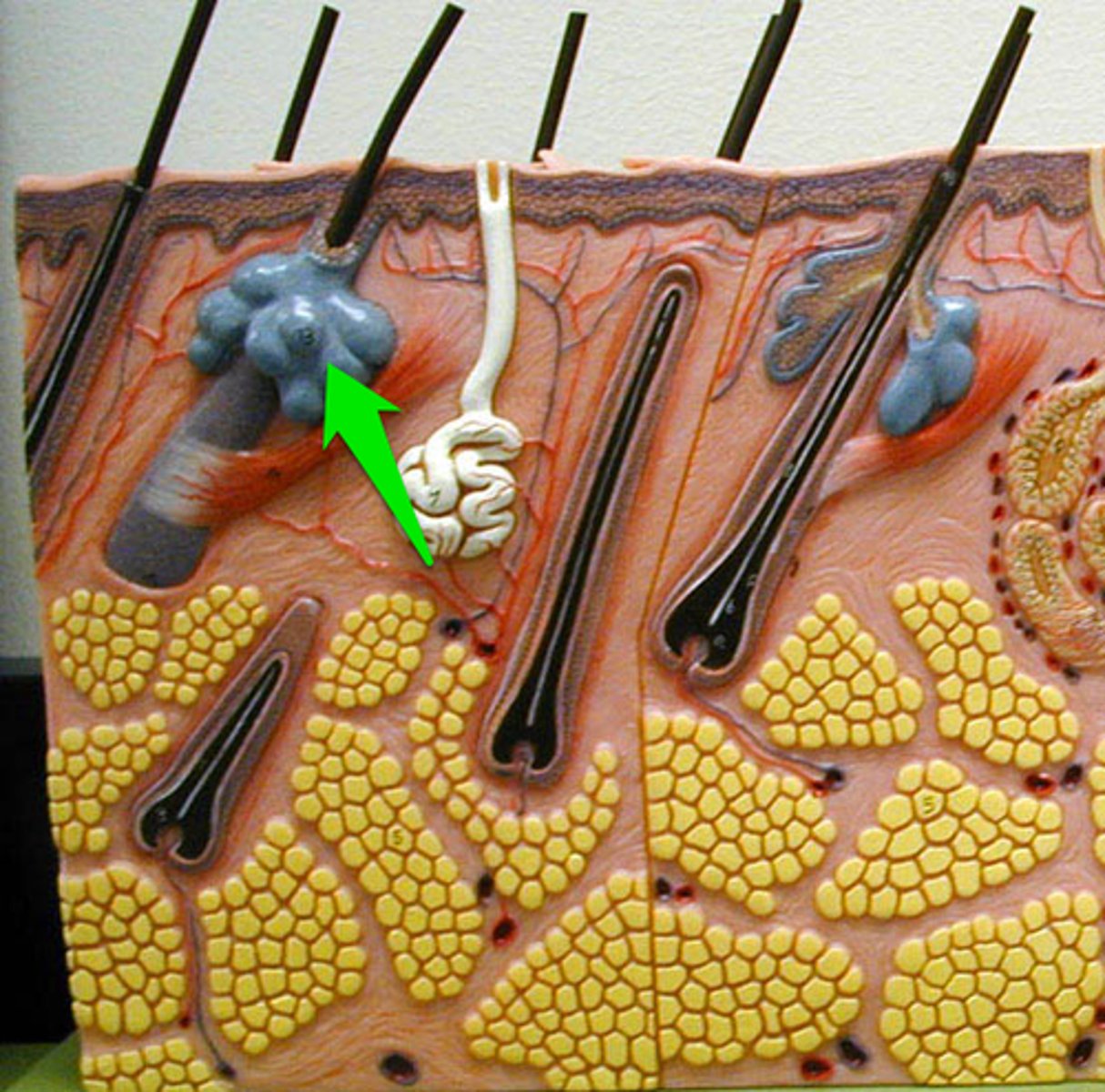
Sebaceous gland
surrounds hair follicle; secretes oily sebum.
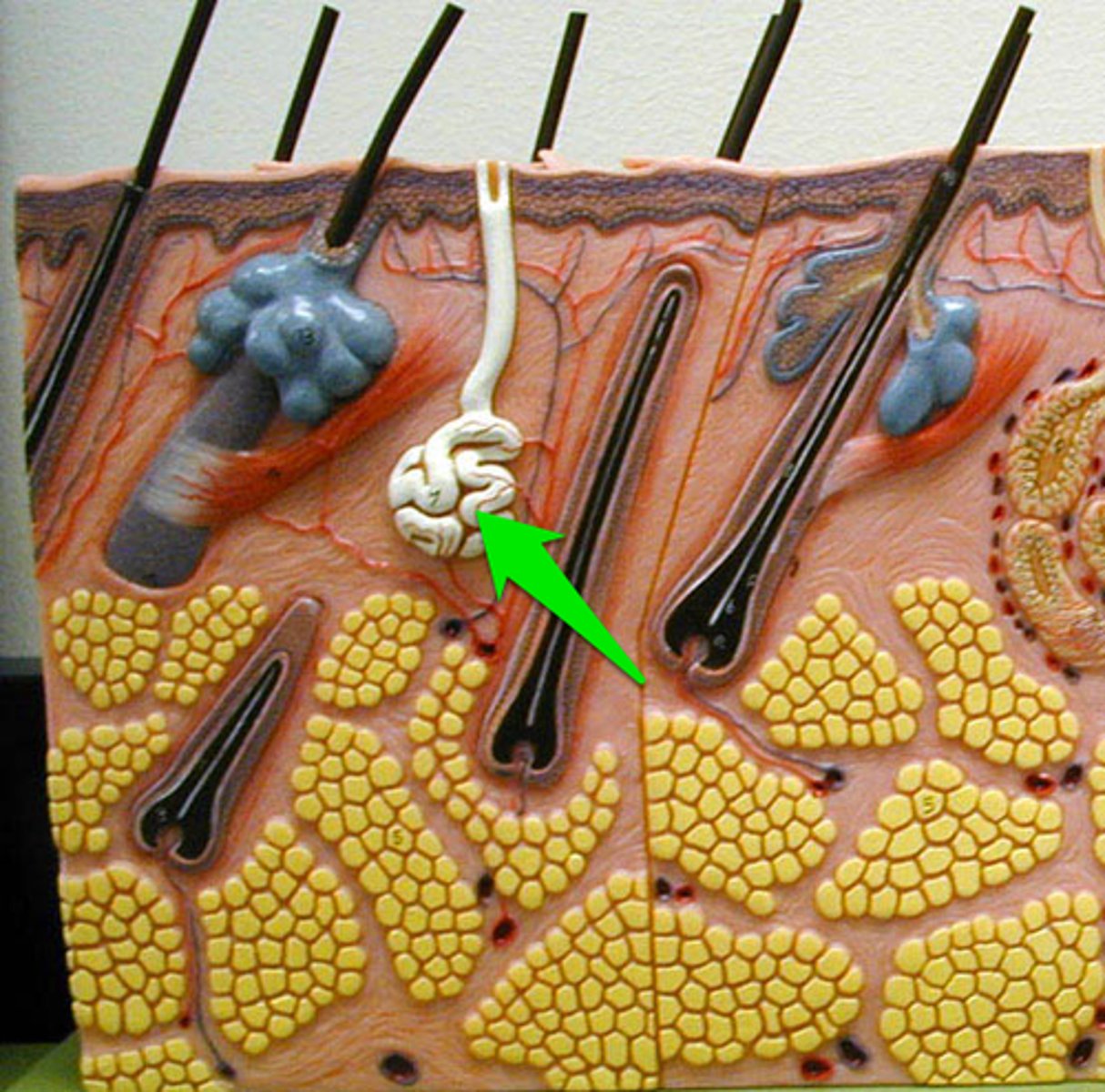
Eccrine sweat gland
numerous gland that has an opening (pore) to the surface of the skin to secrete sweat. Non-stinky sweat
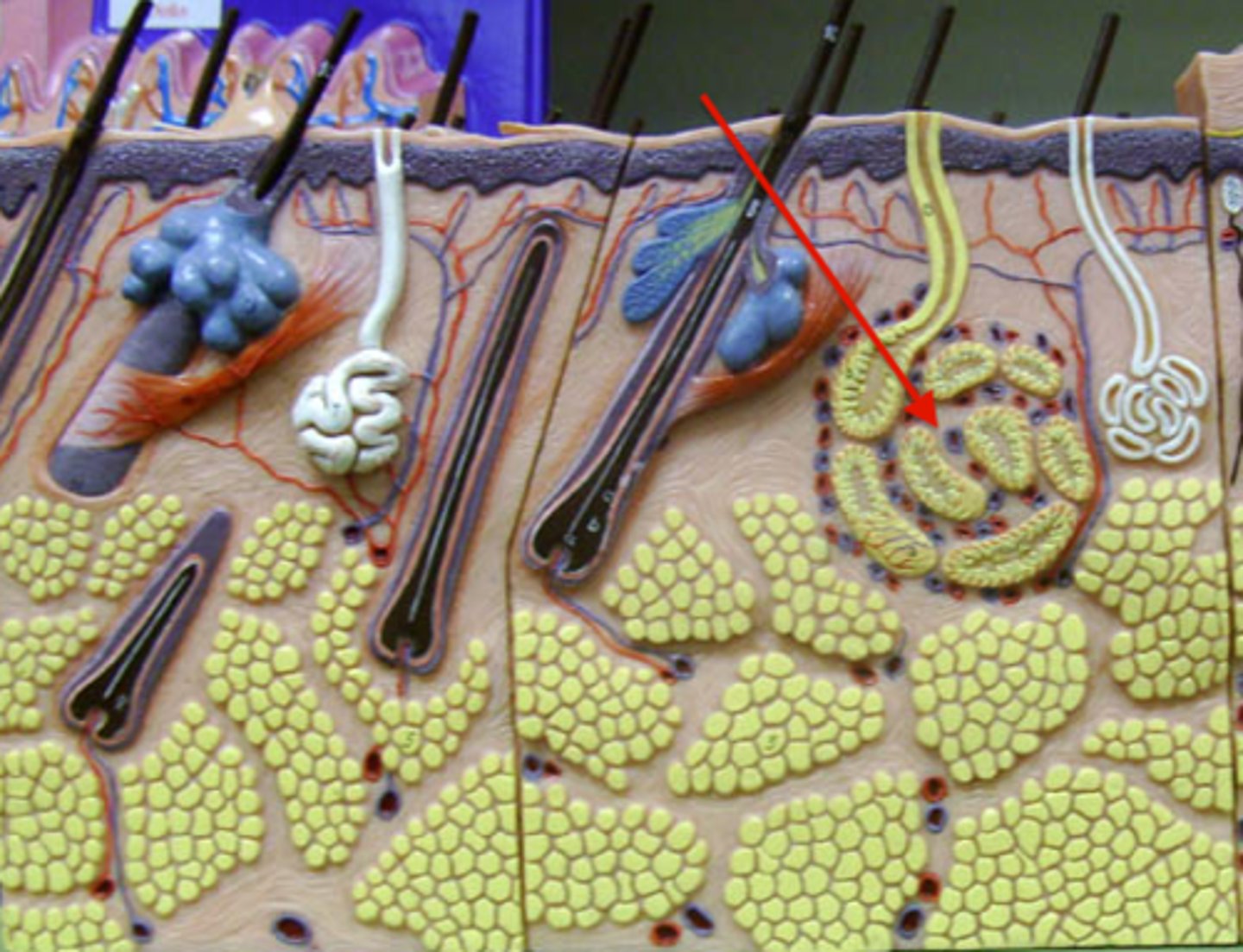
Apocrine gland
large sweat gland found in the armpits and groin that become active at puberty. Secretes 'stinky' sweat
Skin Model