BY 124L Topic Plant Anatomy
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
How can you treat a poison Ivy/oak/sumac rash?
wash with an oil fighting soap (dawn dish soap)
What causes the itch from poisonous plants?
the oils (some people are immune to the itch and burn
What are the two main parts of land plants?
shoot and root
What are some (5) characteristics of the shoot?
leaves for photosynthesis, stems, divided into nodes and internodes
What are the two parts of a leaf?
blade and petiole
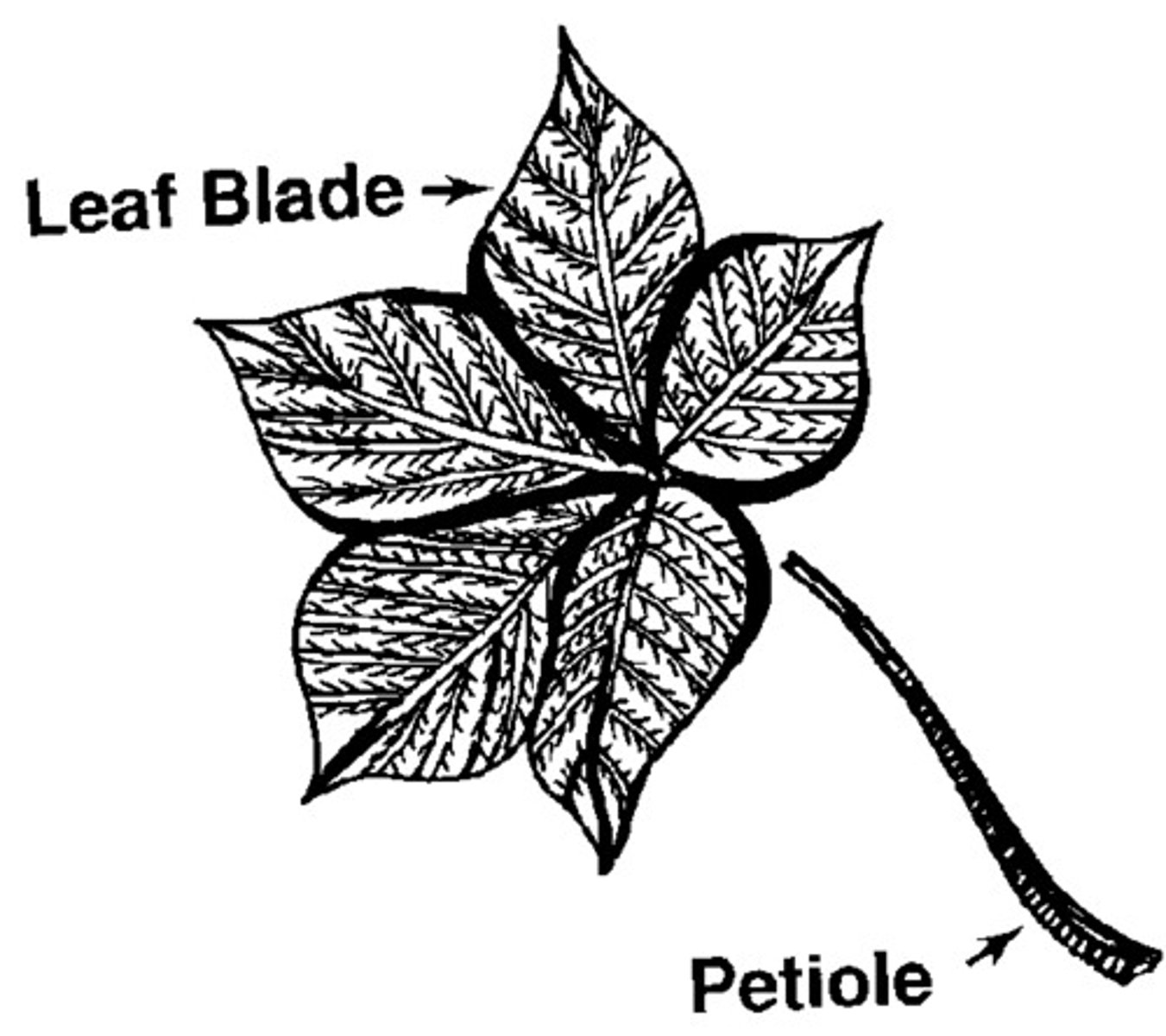
What is the overall function of stems?
to support the plant and to transport water and minerals, terminal and lateral bud for growth, flowers for reproduction
What are nodes?
where the leaves attach
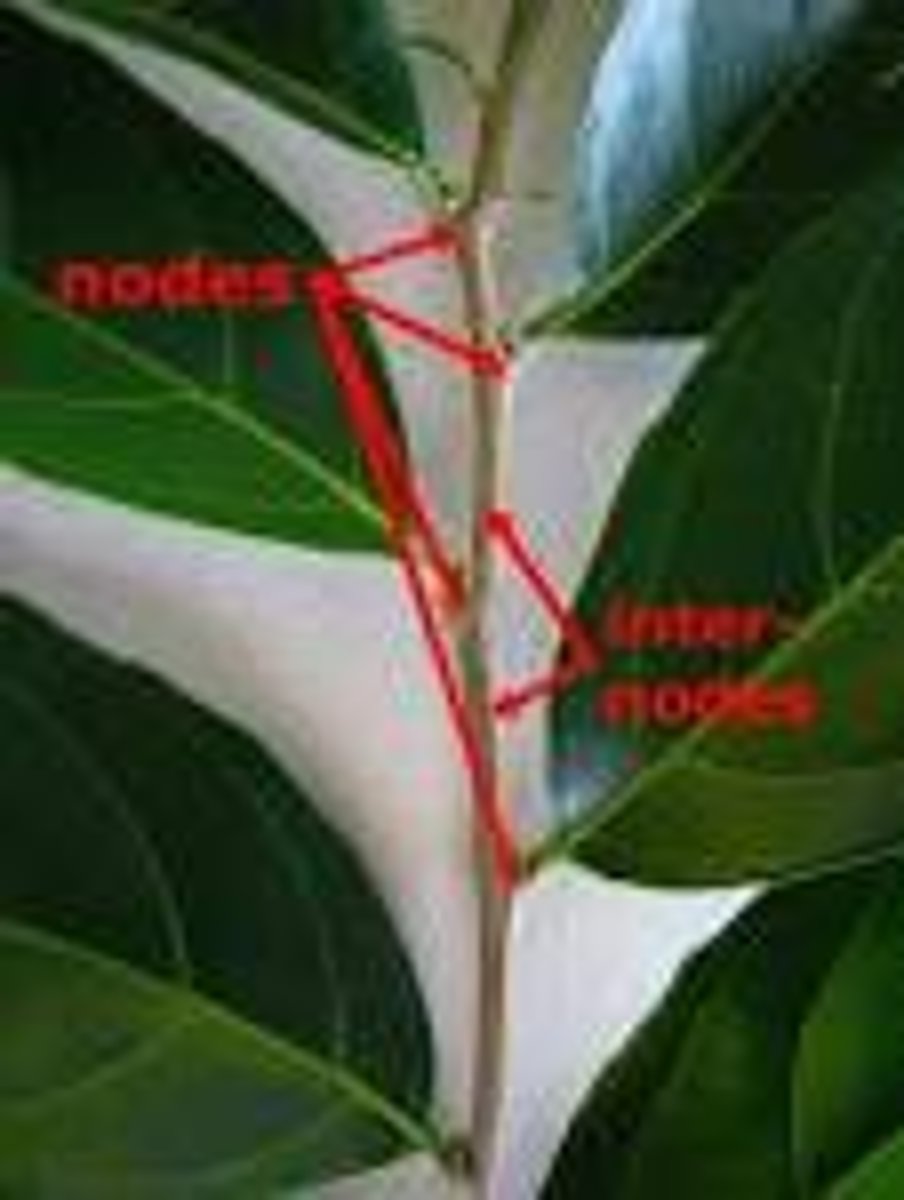

What are internodes?
regions in the nodes
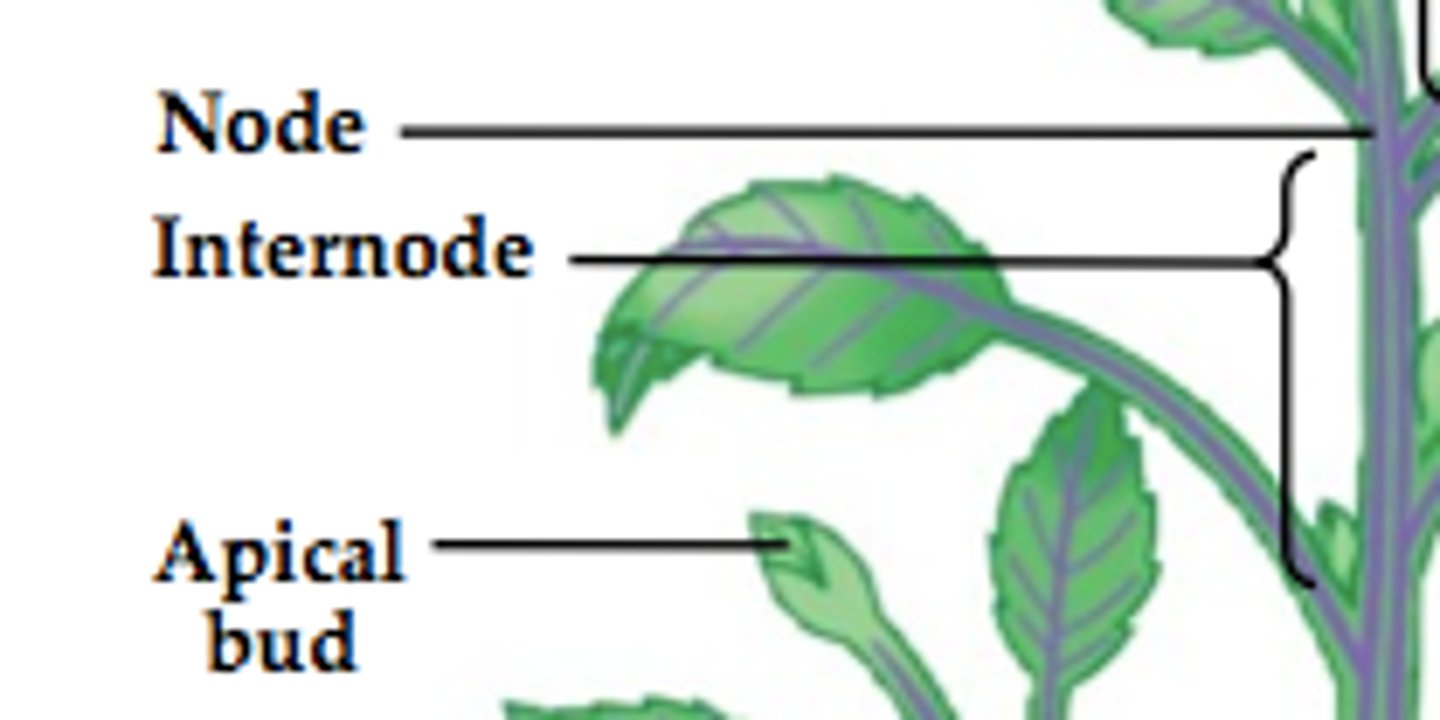
What is the terminal bud also called?
apical bud/meristem
What is the lateral bud also called?
axillary bud
On a lead, the epidermis has waxy covering called a what?
cuticle (keeps water inside)
What are the openings in the epidermis called?
stomata
What are the function of guard cells?
regulate/control the stomata
What is the function of stomata?
regulate gas exchange and transpiration
What is mesophyll?
the green tissue in the interior of the leaf
What are the two types of mesophyll?
palisade and spongy
What is palisade (mesophyll)?
directly beneath the upper epidermis, where photosynthesis takes place
What is spongy (mesophyll)?
directly above the lower epidermis, helps with gas exchange
What are some characteristics of roots?
Anchors the plant, Storage of nutrients, Water and minerals enter here, Root hairs increase surface area (more water)
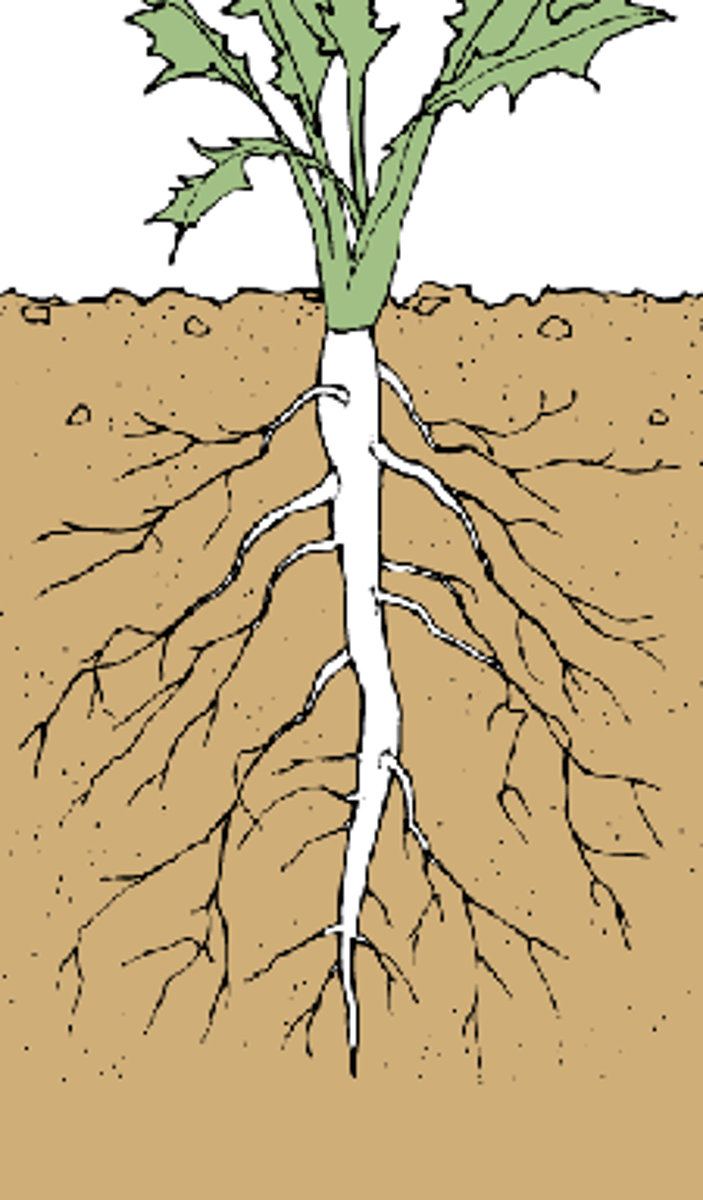
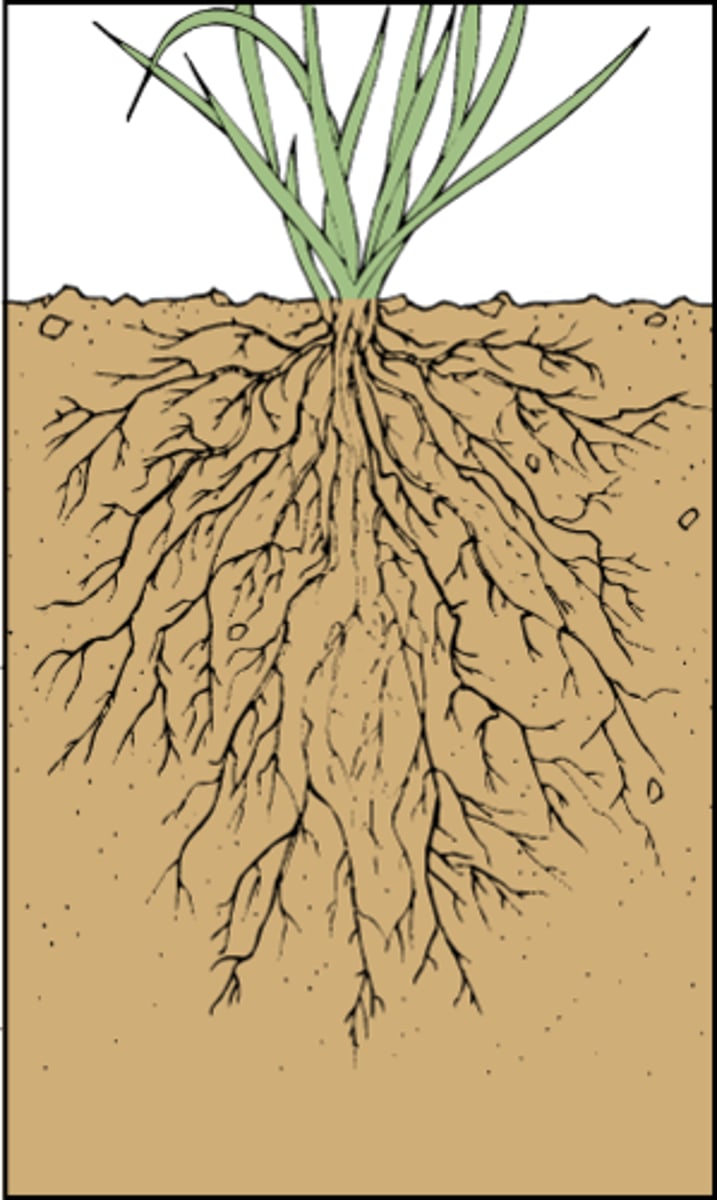
What are the three types of roots?
adventitious, taproot, fibrous
What is an example of adventitious roots?
strawberries (another one pops up from roots)

What is an example of taproots?
shrubs and carrots
What is an example of fibrous roots?
grasses
The meristematic tissue (embryonic tissue) includes what 4 parts of the plant?
apical meristem, lateral meristem, shoots and roots
What are the three types of tissue that undifferentiated meristematic tissue will become?
protoderm, procambium, ground meristem
What is protoderm tissue?
gives rise to epidermal tissue
What is procambium tissue?
vascular tissue
What is ground meristem tissue?
ground tissue
What are the three types of plant cells?
parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma
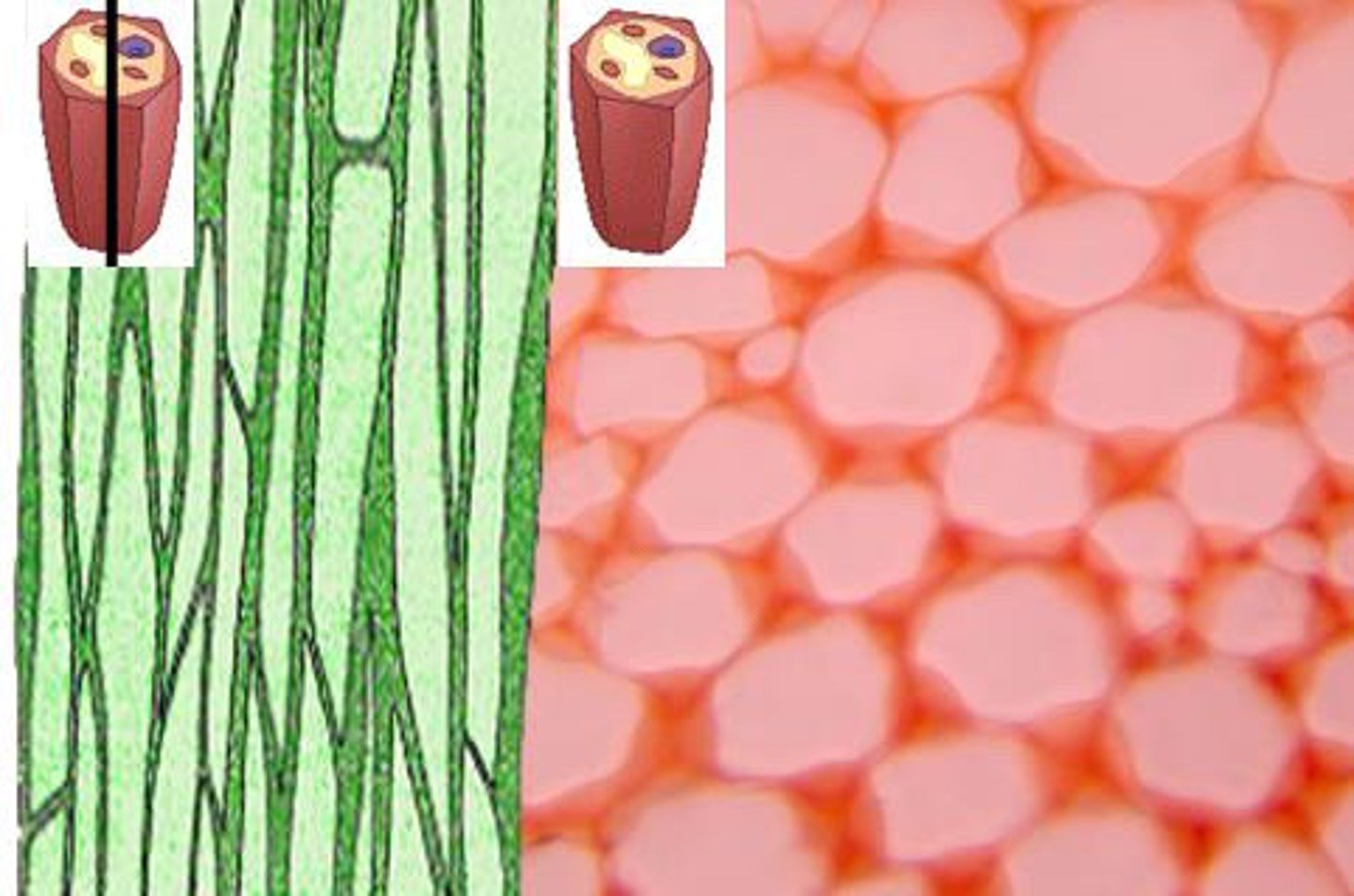
What are parenchyma cells? 5 characteristics
Least specialized, NO secondary cell wall, Thin, primary cell wall, Holds water and stores nutrients in large central vacuole, Does MOST of the metabolism to support the plant
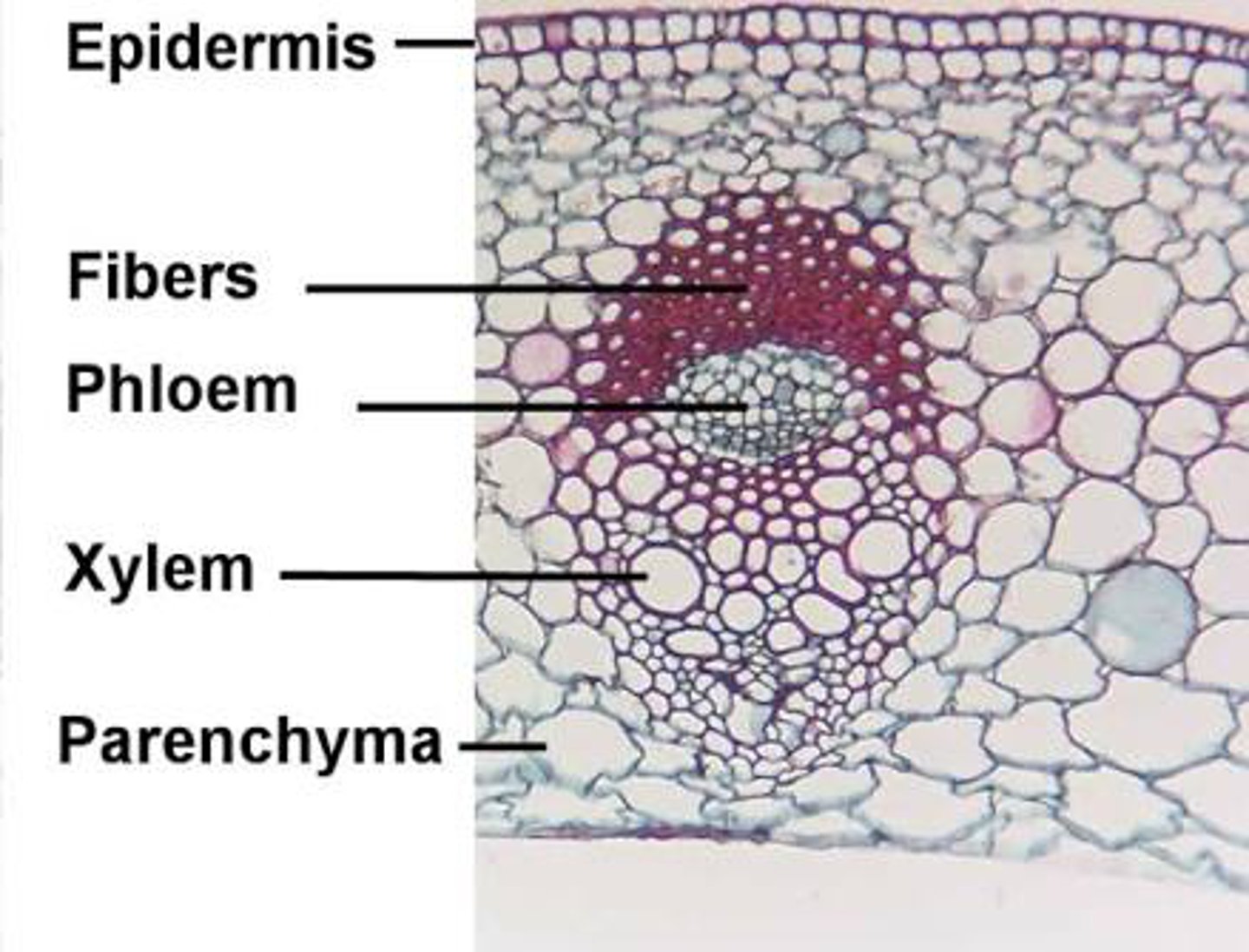
Which type of plant cell does most of the metabolism to support the plant?
parenchyma cells
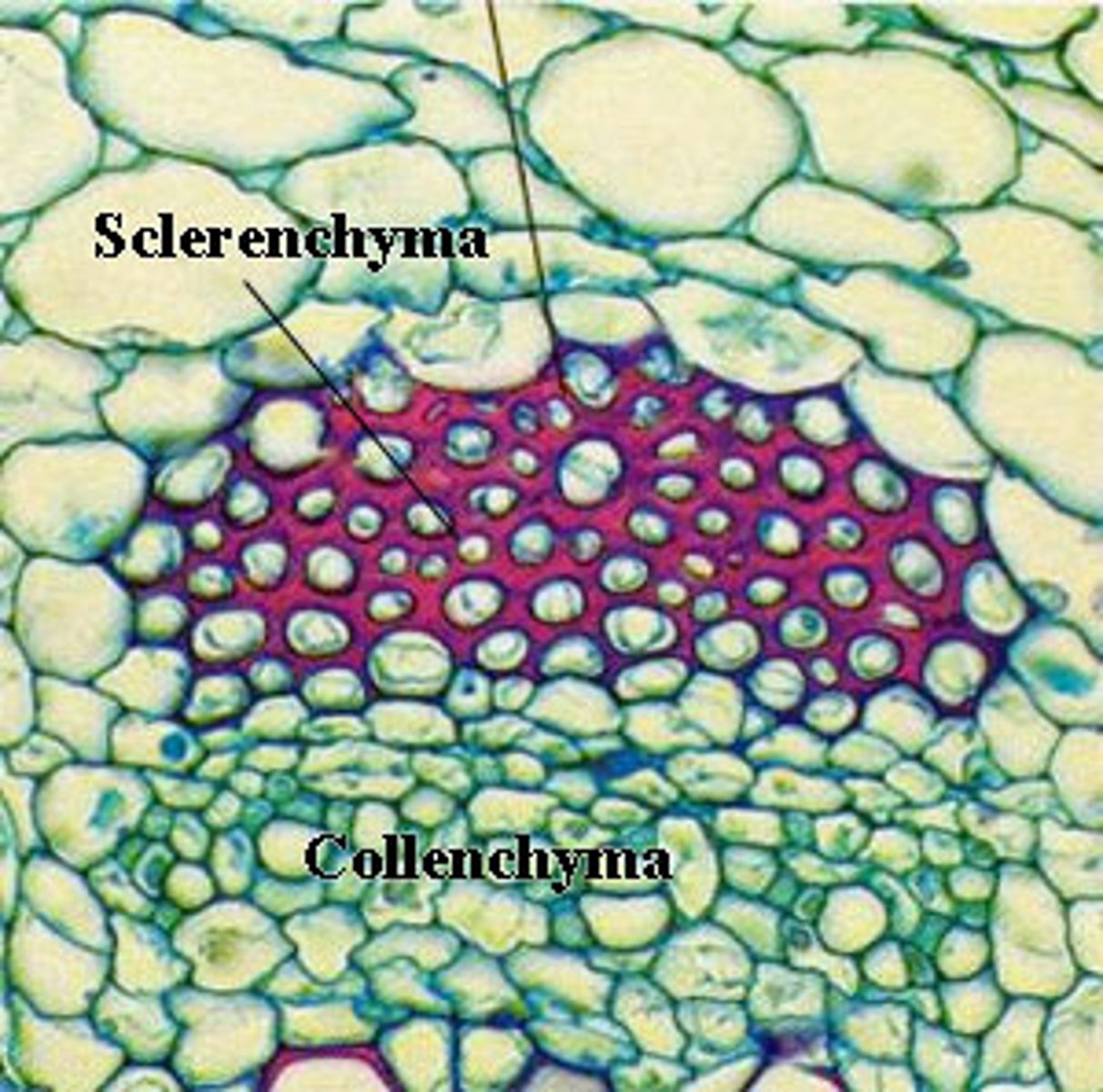
What are collenchyma cells? 4 characteristics
More rigid primary cell walls, NO secondary cell walls, Important in supporting young plants and stems of NON-woody plants (herbaceous plants), Capable of ELONGATION
What are sclerenchyma cells?
HAS SECONDARY CELL WALLS (They contain LIGNIN), This is DEAD tissue, but important in support, Areas that have STOPPED growing
What are the three types of tissue?
dermal, vascular, and ground tissue
What are the two types of dermal tissue?
epidermis and periderm
What are the four characteristics of the epidermis?
PROTECTION, but possibly other functions, "Dermal Tissue", Single layer of tightly packed cells, The "skin" of the plant covering leaves, roots, and stems, CUTICLE
What are some possible other functions of the epidermis?
spines or sensory
What are the three characteristics of periderm?
(woody plants), replaces the epidermis in secondary growth, forms cork and the cork cambium, comes from ground meristem
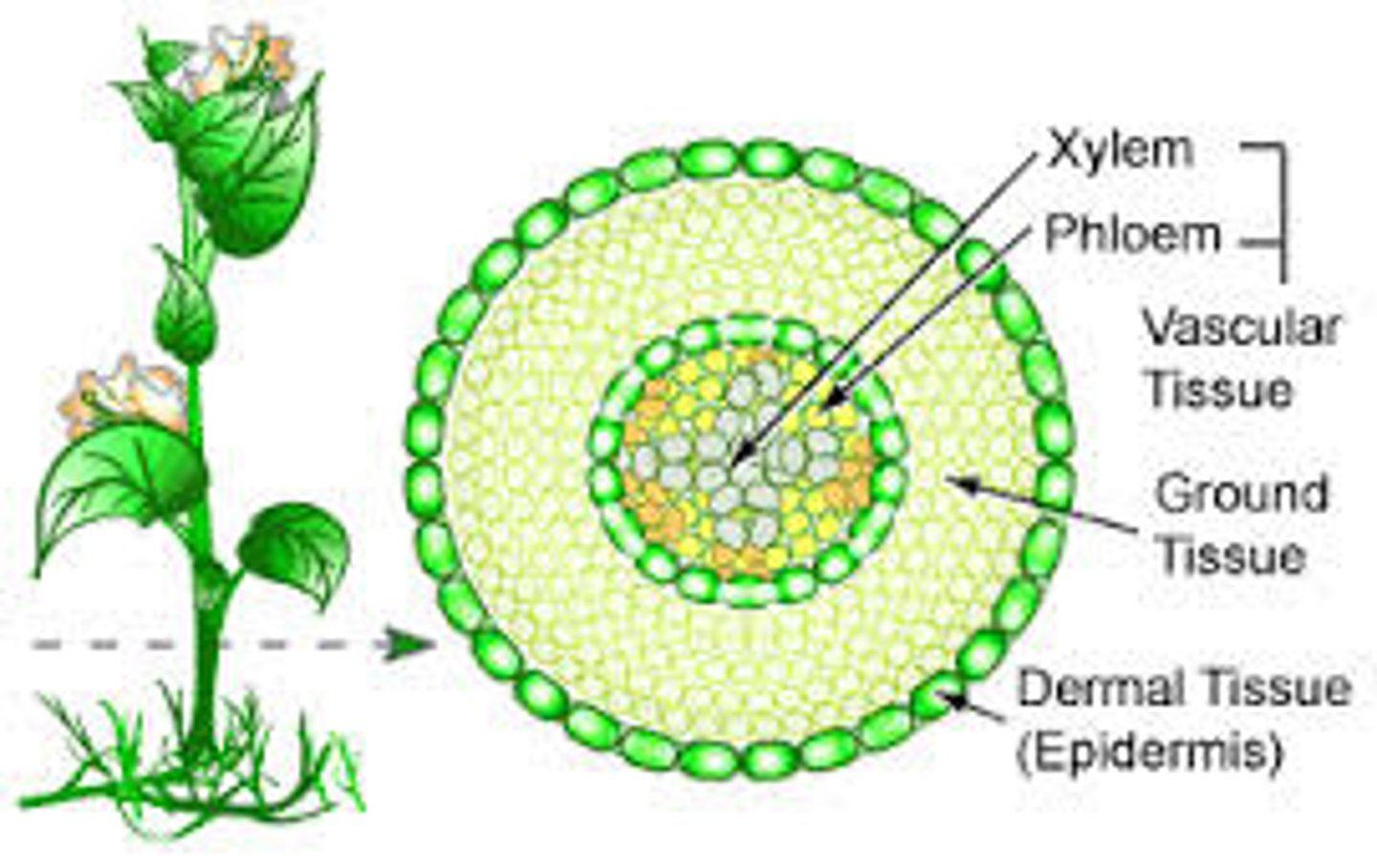
What is vascular tissue important for?
water, mineral, photosynthetic product transport, Support for the plant
What are the two types of vascular tissue?
xylem and phloem
What are some characteristics of xylem tissue?
DEAD AT MATURITY, Transports water, two cell types
What are the two cells types of xylem tissue?
tracheids and vessel elements
What are some characteristics of phloem?
transports sucrose and some mineral ions, 2 cell types
What are the two cell types of phloem tissue?
sieve and companion cells
What are sieve-tube cells?
loses their nuclei
What are companion cells?
coordinates the function of sieve-tube cells
What are some characteristics of ground tissue?
Usually PARENCHYMA cells, Located between dermal and vascular tissues, Does photosynthesis, storage, and supplies
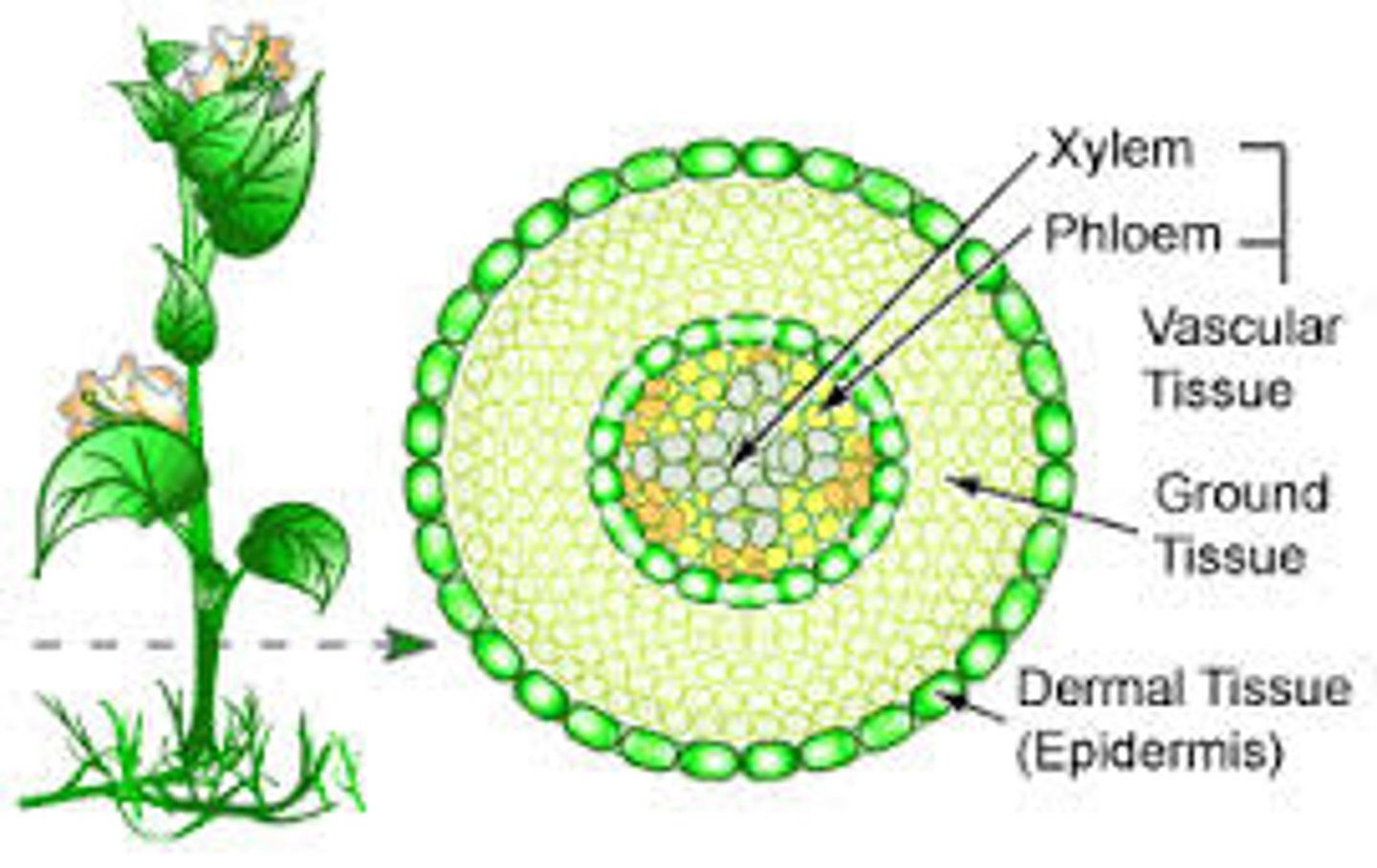
Plant growth is by what two things?
mitosis and cell elongation
What are the two types of plant growth?
indeterminate growth and determinate grown
What is indeterminate growth
Will grow as long as the organism lives with growth occurring at the meristems
What is determinate growth?
Growth will stop after a certain size is reached
What are the three life cycle groups of plants?
annuals, biennials, perennials
What are annuals?
Year or less to go from germination to flowering, then death
What are biennials?
Live 2 years; first year is vegetative growth, second is flowering
What are perennials?
Live for many years; death usually occurs NOT from old age, but injury or disease
What type of meristems are present in roots?
apical
What is the root cap?
Protects the apical meristem and secretes a slimy substance to help root movement
What are the 3 regions to the meristem in the root?
zone of cell division, elongation, cell differentiation
What happens at the zone of cell division?
mitosis growth
What happens at the zone of elongation?
Cells here take in water and elongate
What happens at the zone of cell differentiation? (aka zone of cell maturation)
Major tissue types present, contains root hairs and lateral roots
When looking at the cross section of a root (out to in) what are the four things you will see?
epidermis, cortex, endodermis, stele
What is the function of the epidermis in roots?
one-cell thick, used for absorption
What is the function of the cortex in roots?
storage
What is the function of the endodermis in roots?
Selective on material movement based on Casparian Strip (woody plants)
What is the function of the stele in roots (what are the three parts)?
most inner part of a root, xylem, phloem, pericycle
In monocots, they will have what additional thing in the root?
pith
What are 5 characteristics of monocots?
one cotyledon (seed covering), root xylem and phloem in a ring, vascular bundles scattered in stem, leaf veins form a parallel pattern, flower parts in threes and multiples of three
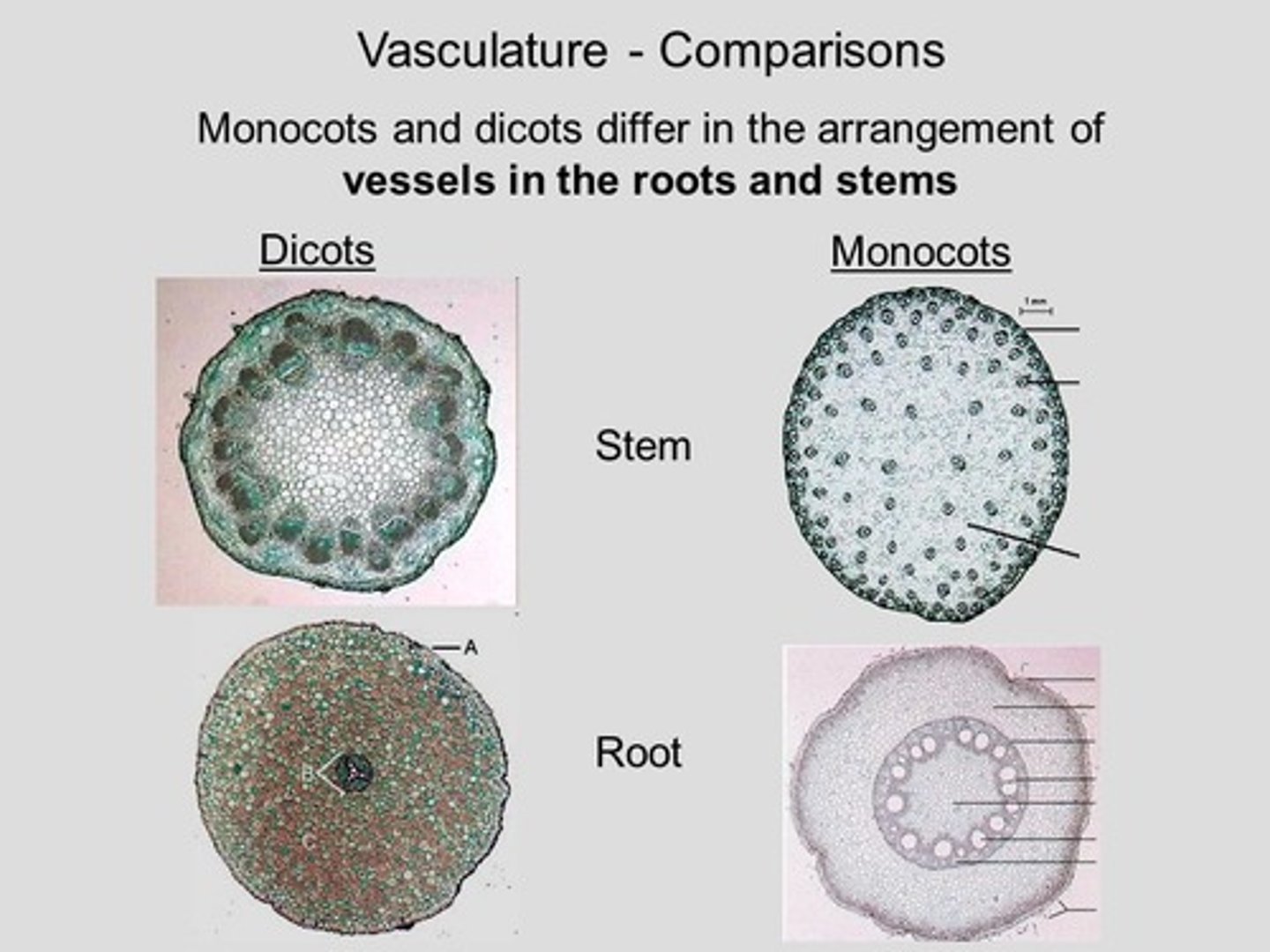
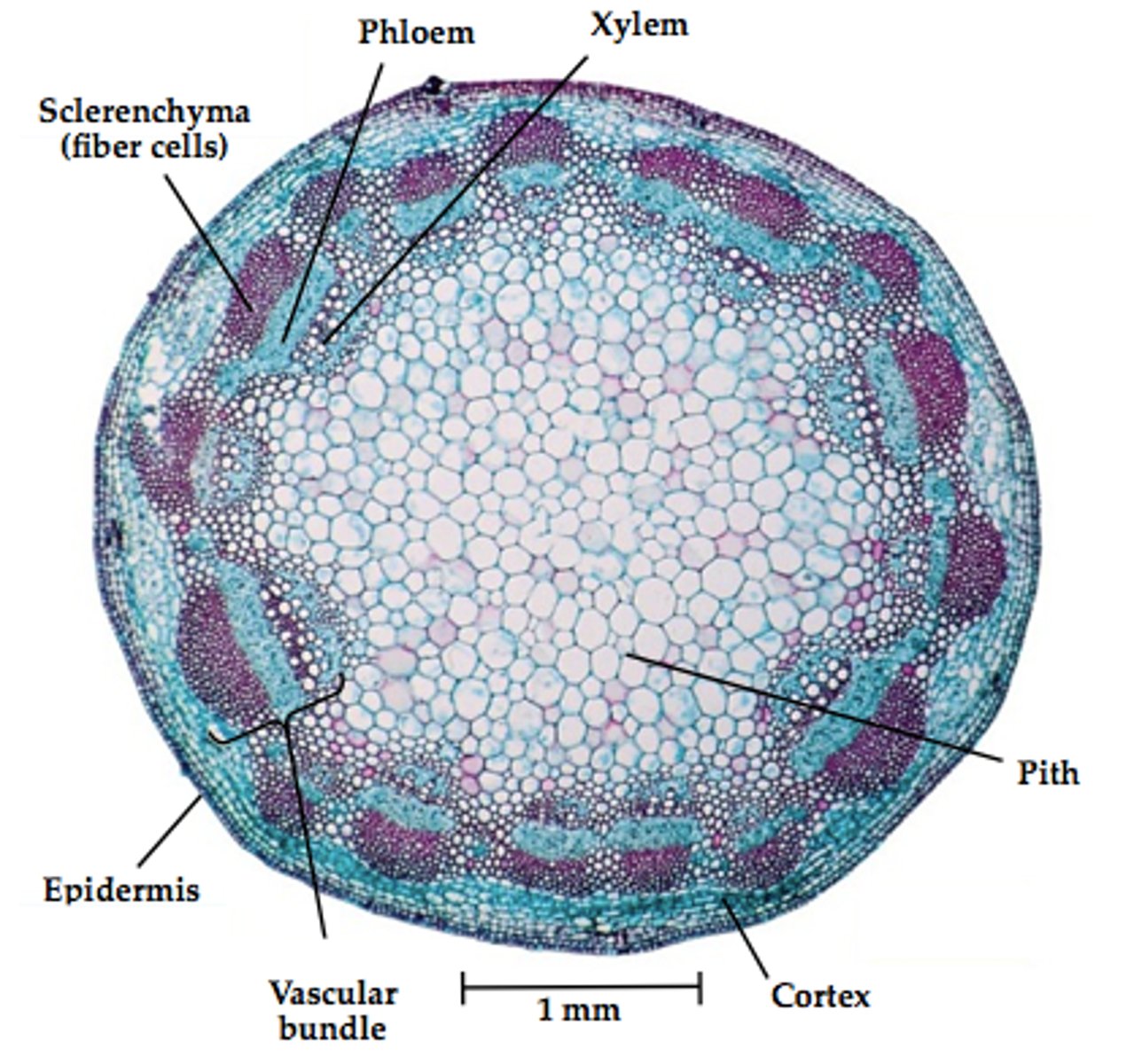
What are 5 characteristics of dicots?
two cotyledons, root phloem between arms of xylem, vascular bundles in a distinct ring, leaf veins form a net pattern, flower parts in fours or fives and their multiples
What are ALL monocots?
herbaceous
What are some characteristics of monocots pertaining to them being herbaceous?
Usually short-lived, fleshy, and limited diameter, Produced from Primary Growth
What is primary growth? (general)
The increase in length of the shoot and the root
Dicots can be what two things?
herbaceous or woody
The woody tissue in dicots comes from what?
secondary growth
What is secondary growth? (general)
thickness of roots and stems, seen in woody and perennial dicots
What are some examples of monocots?
grasses, grains, coconut palms, lilies, and orchids
What are some examples of dicots?
Oak tress, roses, apple trees, kudzu, dogwoods, beans, venus' fly trap
What are the three parts of woody dicots surrounding xylem?
heartwood, sapwood, xylem forms the bulk of the tree (larger and smaller xylem)
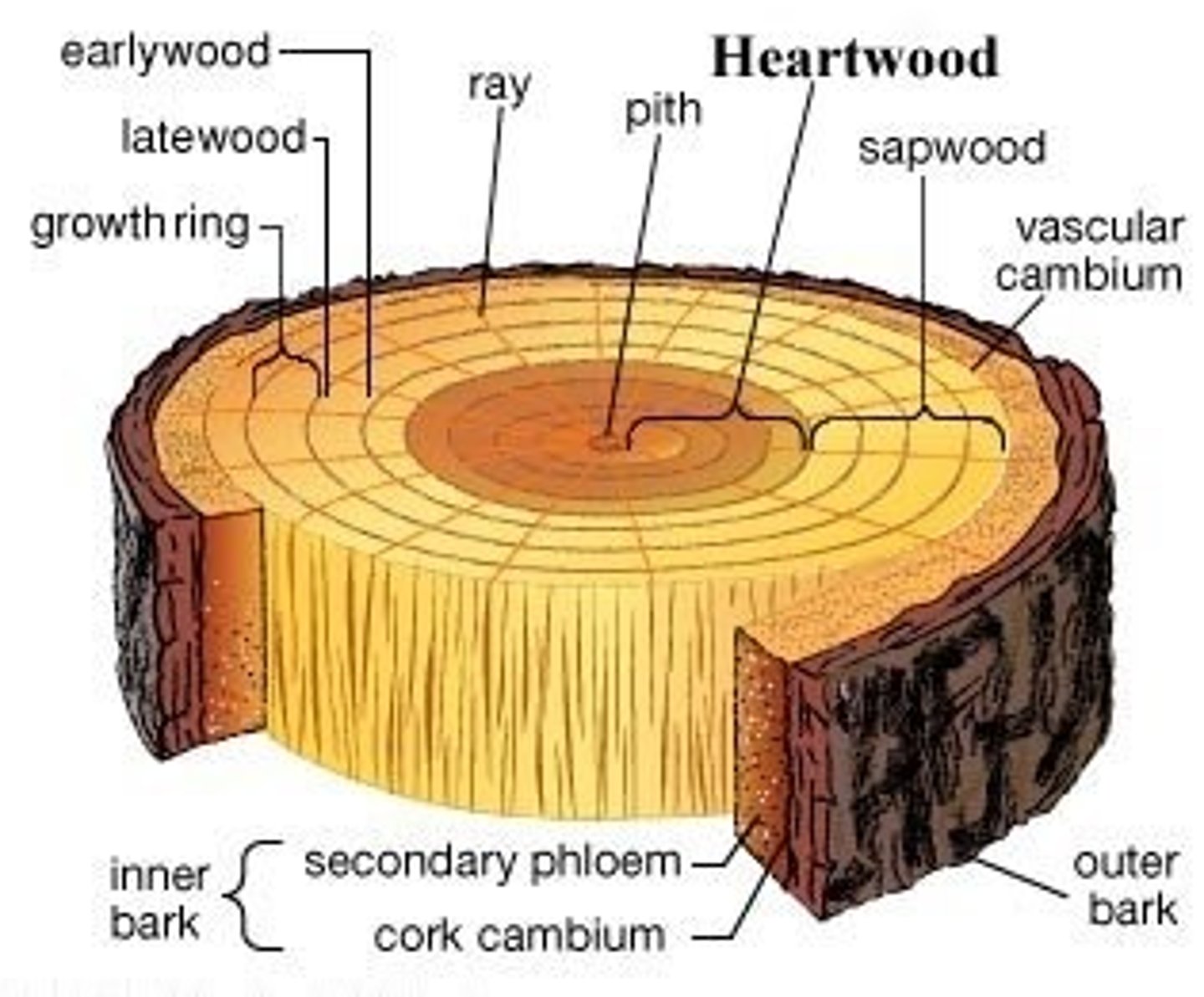
What is heartwood?
Older xylem forms it (NON-functional, near center of tree)
What is sapwood?
New Xylem forms it (external to heartwood)
What is the larger celled xylem of the bulk of the tree?
lighter color, are spring wood, More water from rainfall
What is the smaller celled xylem of the bulk of the tree?
darker color, are summer wood, THESE ARE THE ANNUAL RINGS OF A TREE
The rings of a tree look different based on the ___________ of the environment?
coniditions
Little fact, turtles show their age by the ________ on their shell?
rings
What is the main component of secondary growth?
cork cambium (Secondary growth with secondary meristematic tissue)
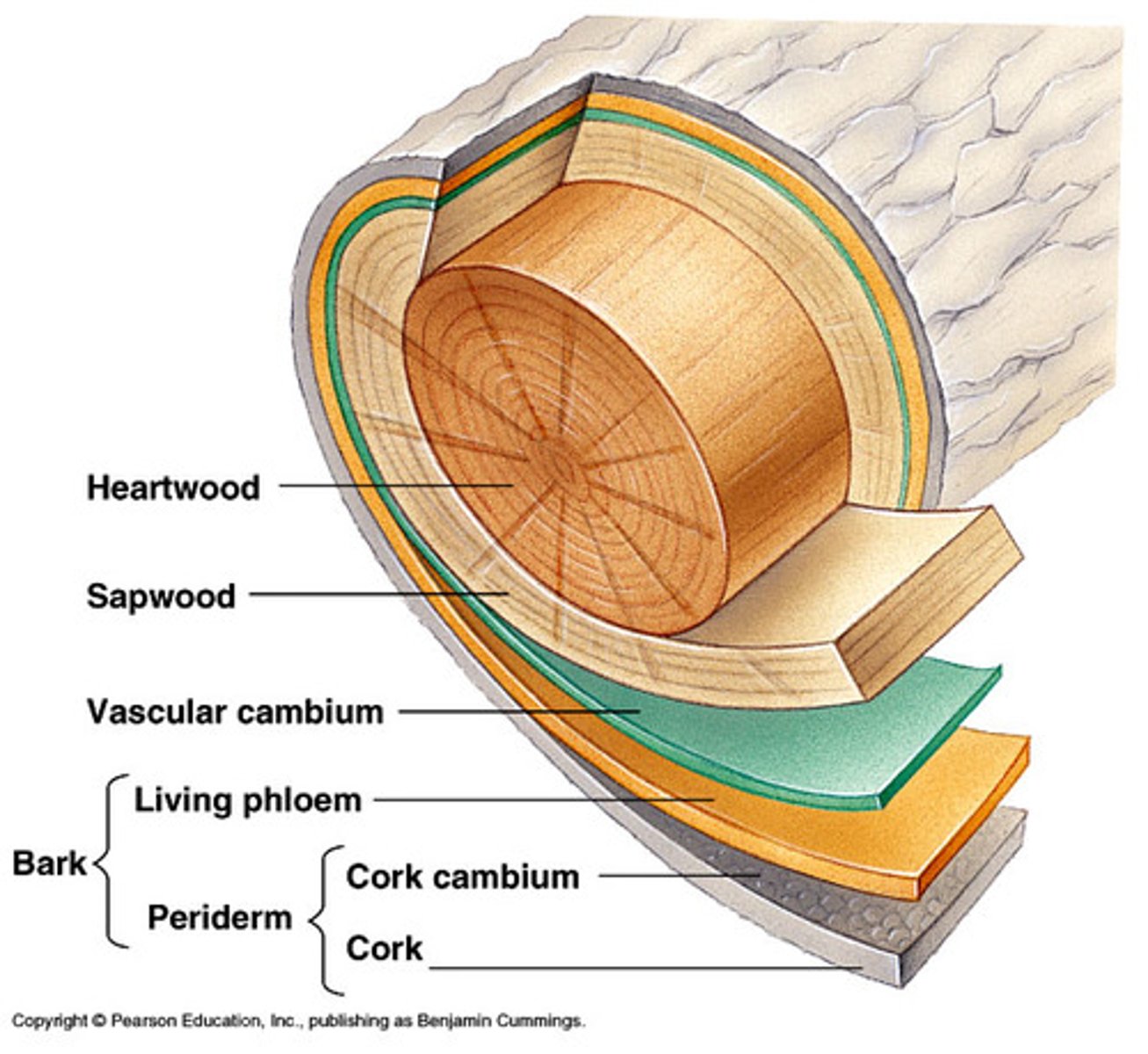
What are the two types of cells of cork cambium?
periderm, cork cells
What are cork cells?
Suberin, a waxy substance, is added and the cork cells die
What is bark the term for?
phloem, cork cambium, phelloderm, and the cork from the periderm
What is the epidermis replaced with?
secondary growth
What are the 13 fruit types?
Aggregate, Multiple, Pome, Drupe, Legume, Hesperidium, Pepo, Berry, Grain, Achene, Nut, Sumara, Capsule
What is an example of agrregate?
raspberry and blackberry
What is an example of multiple?
pineapple, mulberry, fig
What is an example of pome?
apple, pear
What is an example of drupe?
cherry, peach, plum, coconut, almond, olive
What is an example of hesperidium?
orange, lemons, limes, grapefruit
What is an example of pepo?
squash, cucumber, watermelon
What is an example of berry?
grape, pepper, tomato
What is an example of grain?
wheat, corn, rice
What is an example of achene?
sunflower, strawberry
What is an example of a nut?
oak, hickory