Honors Biology Final Study Guide - Unit 3
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
What is the activation energy?
The amount of energy needed to break apart the bonds in the reactants, determining the rate of reaction.
How do enzymes affect biochemical reactions?
Enzymes speed up biochemical reactions by lowering the activation energy.
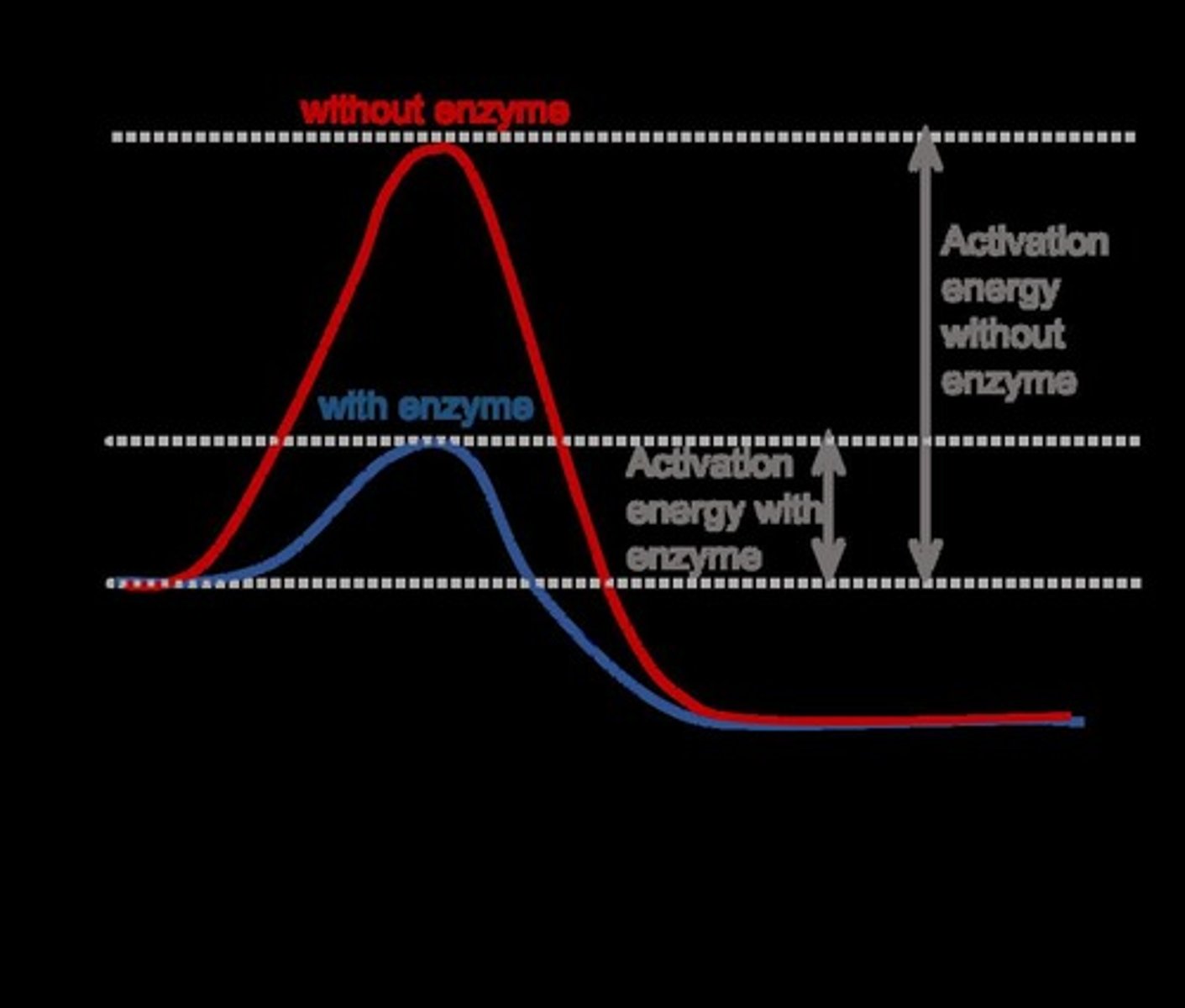
What happens to enzymes during a reaction?
Enzymes are not changed during the reaction.
What is the active site of an enzyme?
The region within an enzyme where the substrate binds and undergoes catalysis, fitting only one type of substrate.
What is produced at the end of a biochemical reaction?
The final molecule of a biochemical reaction is the product.
How do rates of enzyme-catalyzed reactions compare to uncatalyzed reactions?
Rates of enzyme-catalyzed reactions are much faster than rates of uncatalyzed reactions.
What characterizes endothermic reactions?
More energy is absorbed to break bonds in the reactants than is released when new bonds are formed in the products.
What characterizes exothermic reactions?
More energy is released when new bonds are formed in the products than is absorbed to break bonds in the reactants.
What is the lock and key model in enzyme activity?
The lock represents the active site, and the key represents the substrate.
How do enzymes lower activation energy?
By stabilizing the transition state of the reaction.
What happens to enzyme activity with increased substrate concentration?
Increasing substrate concentration can overcome inhibition until all active sites are occupied.
What is malonate's effect on enzyme activity?
Malonate inhibits enzyme action by binding to the active site due to its similar shape to succinate.
What happens to amylase in response to changes in hydrogen ion concentration?
Amylase loses critical secondary and tertiary structure.
Why are covalent bonds not used to bind substrates to enzymes?
Covalent bonds are stronger and permanent, making them unsuitable for temporary binding.
What factors affect enzyme activity?
Enzyme activity is sensitive to temperature range, pH range, and solvent type.
What is enzyme denaturation?
The loss of enzyme shape due to deviations from optimum temperature and pH.
What are enzyme inhibitors?
Molecules that cause an enzyme to lose activity by preventing substrate binding.
What is the overall equation for cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 -> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O.
What are the starting materials for cellular respiration?
Glucose and oxygen.
What are the three steps of aerobic cellular respiration?
1. Glycolysis, 2. Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle), 3. Oxidative Phosphorylation.
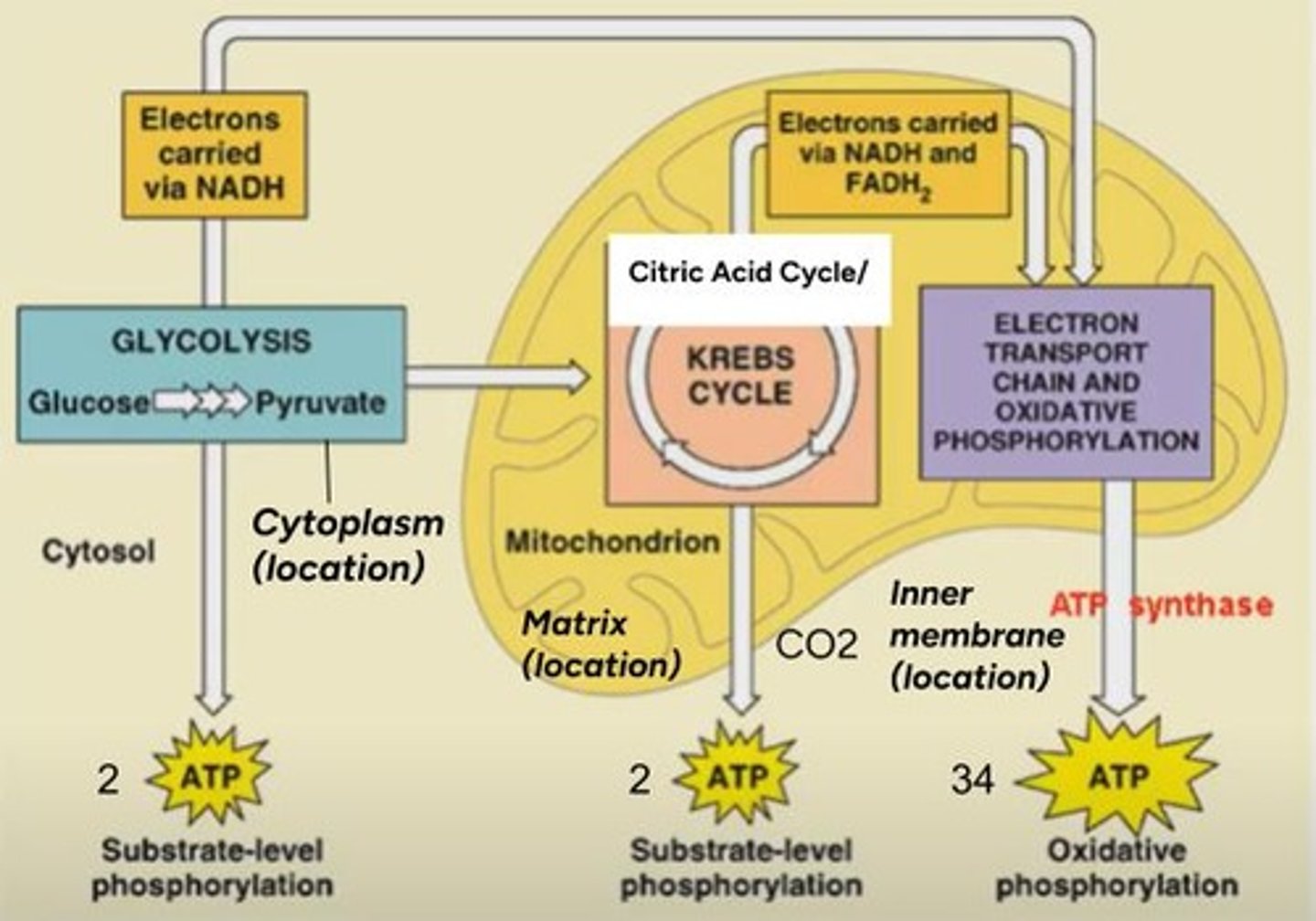
Where does glycolysis occur?
In the cytoplasm of cells.
What is produced during glycolysis?
2 pyruvate, 2 NADH, and a net gain of 2 ATP.
Where does the Citric Acid Cycle occur?
In the matrix of the mitochondria.
What does one turn of the Citric Acid Cycle produce?
3 NADH, 1 FADH2, 2 CO2, and 1 ATP.
Where does oxidative phosphorylation occur?
In the inner membrane of mitochondria.
What is the role of the electron transport chain?
It moves electrons through protein complexes, releasing energy used to create a hydrogen ion gradient.
What is chemiosmosis?
The process where H+ ions pass through ATP synthase, releasing energy to produce ATP from ADP and P.
What is the total ATP produced from one glucose molecule?
32 ATP.
What is fermentation?
Pathways that oxidize glucose to generate ATP without oxygen, using an organic molecule as the ultimate hydrogen acceptor.
What is lactic acid fermentation?
A process where lactic acid builds up in muscle cells, causing fatigue during exercise.
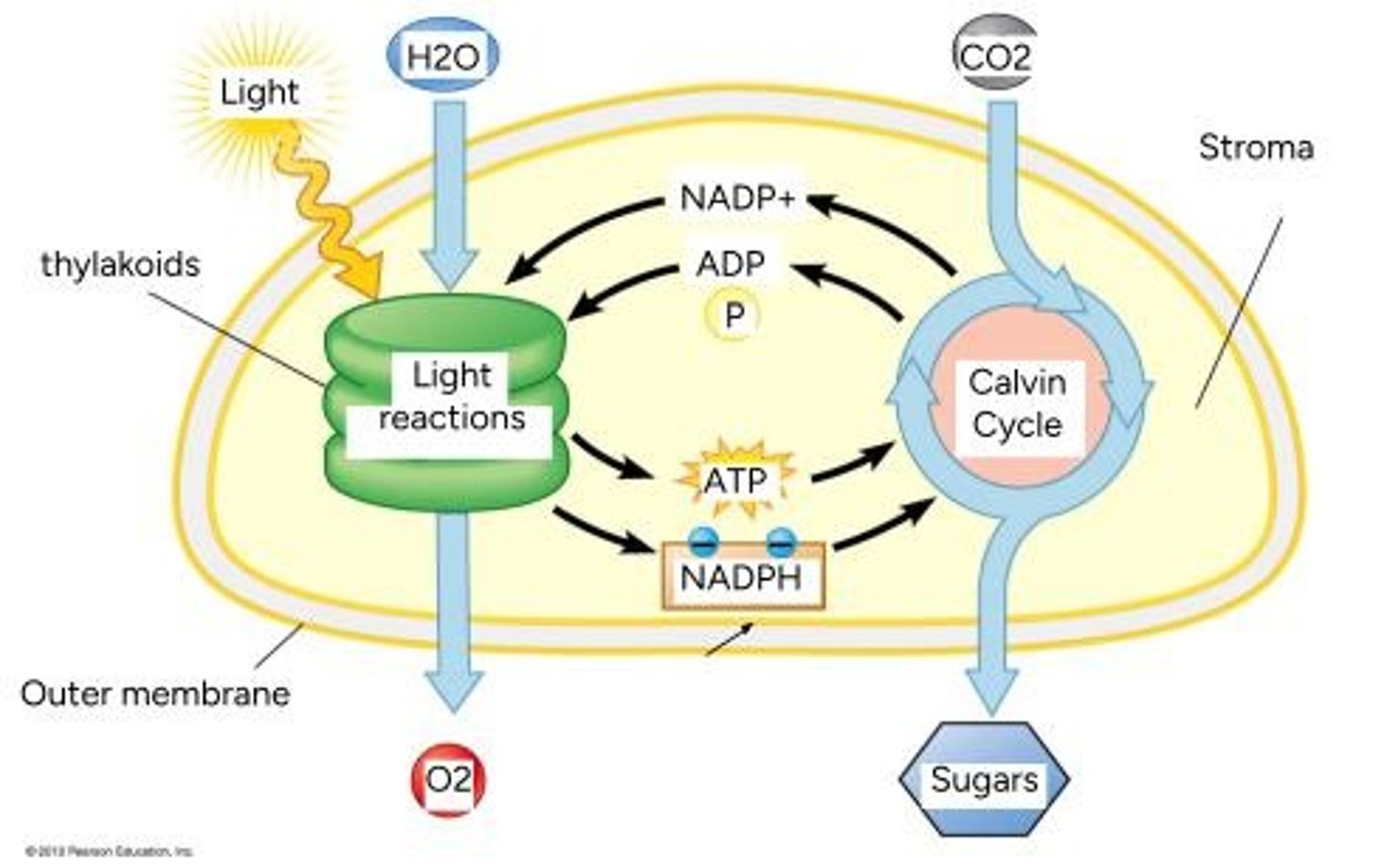
What is the overall chemical equation for photosynthesis?
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Light Energy -> C6H12O6 + 6 O2.
Where does photosynthesis occur?
In chloroplasts.
What are autotrophs?
Organisms that produce organic molecules from CO2, such as plants.
What are heterotrophs?
Organisms that cannot make their own food and rely on compounds produced by other organisms.
What are thylakoids?
Disk-like structures in the stroma of chloroplasts, stacked in grana.
What is the role of chlorophyll?
Pigment molecules located in the thylakoid membrane that give plants their green color.
What are the two steps of photosynthesis?
1. Light Reactions (requires light), 2. Calvin Cycle (synthesizes sugars, no light required).