EDEXCEL SNAB BIOLOGY Photosynthesis
1/36
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Where do the light dependent reactions take place?
Thylakoid membrane
State the 7 main components of the light dependent reactions? (some stages repeated)
electron excitement
photolysis
electron transport chain
chemiosmosis
PS I excitement
chemiosmosis
production
Initial electron excitement
light energy hits photosystem II
two electrons are excited to a higher energy level
The electrons leave photosystem II
Photolysis
one molecule of water is split
Useful products: 2H+ and 2e-
Waste: oxygen (one atom)
What are the waste products of the Light Dependent Reactions?
oxygen
What are the electrons in photolysis used for?
They replace the electrons lost from PS II.
Electron Transport Chain
Energy is released as electrons pass down the electron transport chain → used to pump protons into thylakoid space
Chemiosmosis
H+ ions are pumped from a high to low concentration from the stroma to the thylakoid membrane
a protein gradient is formed
ATP synthase facilitates the diffusion of H+ ions back into the stoma
the movement of H+ ions causes ATP synthase enzyme to catalyse the production of ATP.
Second Excitement of Electrons
At the end of the ETC, electrons are passed onto PS I.
light energy hits PS I.
a pair of electrons are excited to a higher energy level
the two electrons leave PS I and pass along the ETC
chemiosmosis takes place here
Production
These two electrons react with the hydrogen ions from the photolysis of water and the coenzyme NADP to produce NADPH (or reduced NADP)
Equation for Light Dependent Reactions
H+ + 2e- + NADP+ → NADPH
Cyclic Phosphorylation
Light hits Photosystem I
electrons are excited to a higher energy level
energy is released as the electrons pass through ETC
chemiomosis takes place
At the end of ETC, electrons rejoin PS I
no NADPH produced
When is cyclic phosphorylation used?
when higher volumes of ATP are required.
where do the light Independent Reactions take place?
Stroma
RuBP
ribulose bisphosphate
State the three main components of Light Independent Reactions
CO2 and RuBP react (carbon fixation)
Reduction of glycerate 3-phosphate
Regeneration of RuBP
carbon fixation
carbon dioxide reacts with a 5C sugar RuBP
this is catalysed by the enzyme rubisco
an unstable 6C carbon compound is formed which immediately splits
2 GP are produced
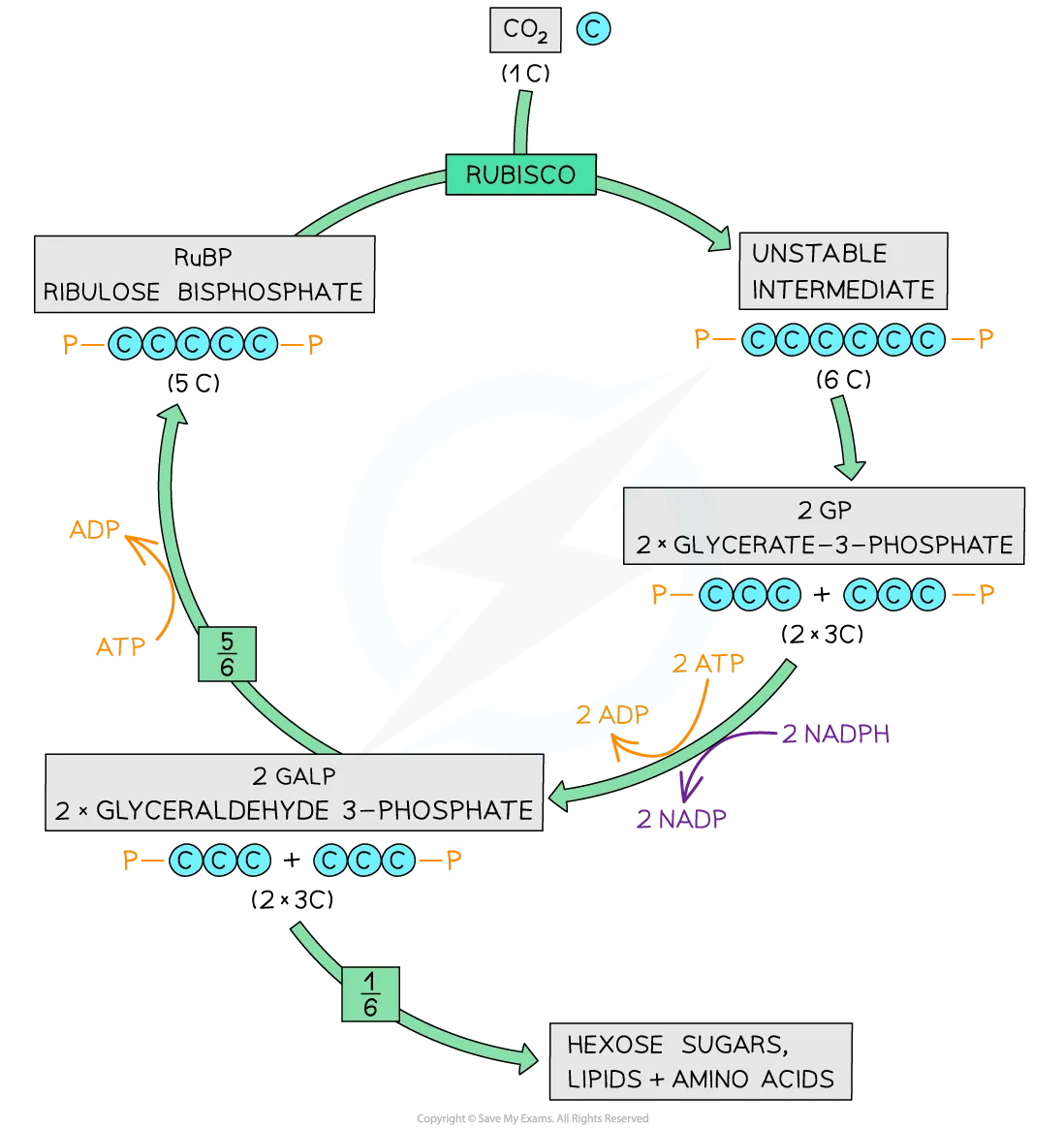
Reduction of glycerate 3-phosphate
Energy from ATP and hydrogen from NADPH
→ reduce 2GP → 2GALP
ADP and NADP are left
Regeneration of RuBP
energy from ATP facilitates:
5 carbons regenerate RuBP
1 carbon is used to form glucose
6 turns of the Calvin cycle produce one mole of glucose
GALP
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
GP
glycerate 3-phosphate
light intensity as a limiting factor
high rate of light independent reactions
high levels of ATP and reduced NADP
high rate of light independent reactions
until CO2 becomes limiting factor
Temperature as a limiting factor
rubisco enzyme functions at a low rate
low rate of light independent reactions
low rate of photosynthesis
until light intensity becomes limiting factor
NOW limited by light dependent reactions
Water as a limiting factor
stomata close - to prevent water loss by transcription
less CO2 diffuses into leaves
CO2 becomes limiting factor

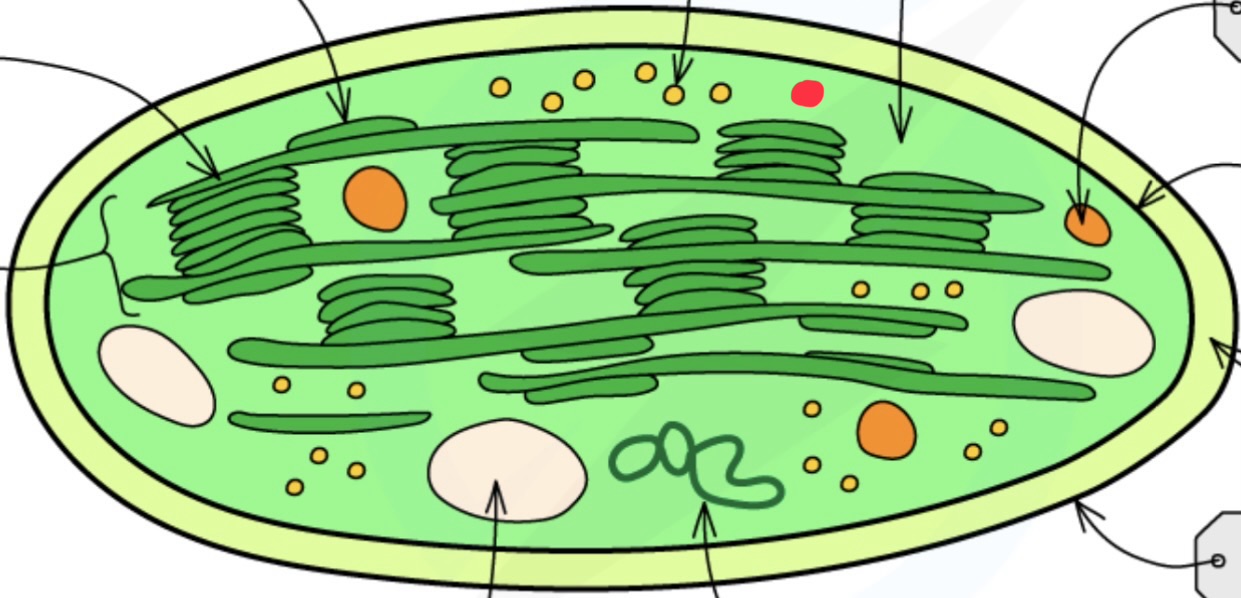
Stroma
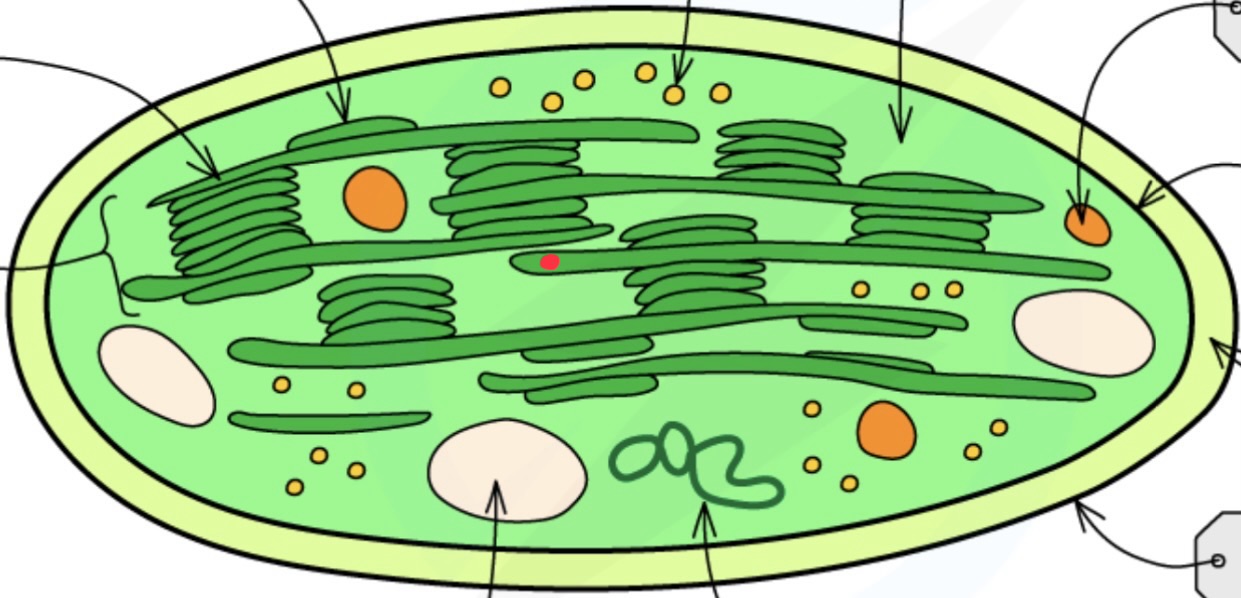
Thylakoid membrane

Grana grannum
What does the thylakoid membrane contain?
chlorophyll
ATP synthase
What size are the chloroplast ribosomes?
70S
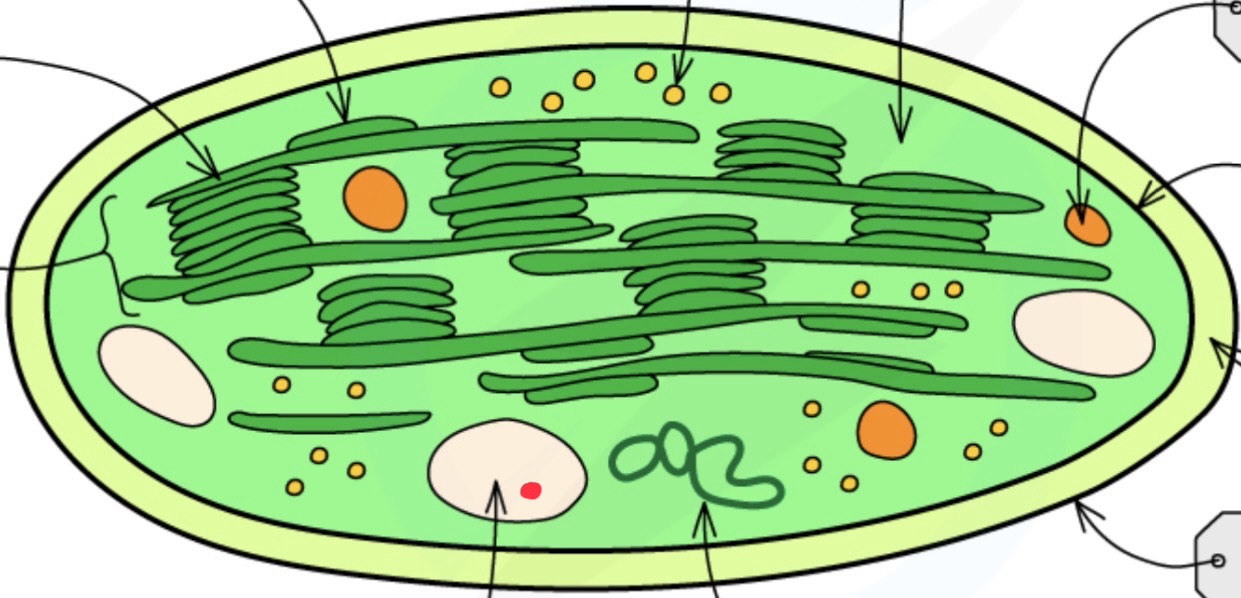
Starch grains

Ribosomes
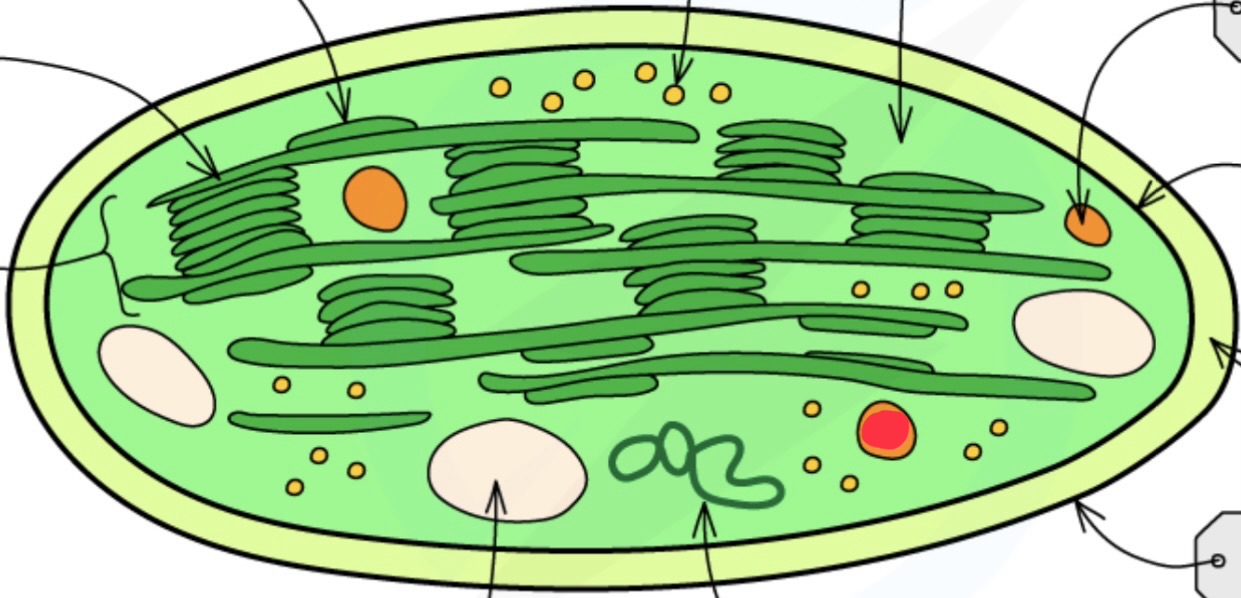
Drops of lipid
Chloroplast envelope function
controls transport of molecules between stromatolites and cytoplasm
Stroma function
contains enzymes that catalyse light independent reactions
Chloroplast DNA function
contains genes that code for proteins used in photosynthesis
Chloroplast ribosomes function
enable translation of proteins cod by chloroplast DNA