SDL 8: tumors of thyroid gland
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
a result of metastasis
secondary thyroid tumors are
Follicular adenomas outnumber thyroid carcinomas by a ratio of nearly 10:1
most common type of thyroid tumor
thyroid cancer
diagnosed at a younger age in women than most other adult cancers
-external radiation to the cervical region and iodine deficiency
most significant risk factors for thyroid neoplasm
follicular and anaplastic adenomas
iodine deficiency is an especially associated risk factor for what thyroid tumors?
follicular cells
-C cells (parafollicular cells)
two cell types that give rise to thyroid carcinomas:
-papillary, follicular, and anaplastic carcinomas
follicular cells give rise to what thyroid cancers
MTC
C cells give rise to what thyroid carcinoma
increase
serum TSH levels ________ when thyroid nodule is malignant
-ultrasound provide more anatomic detail than physical exam
-need FNA to check malignancy
imaging used to assess thyroid noddules
mostly solid, hyperechoic nodules
US findings of malignant thyroid nodules
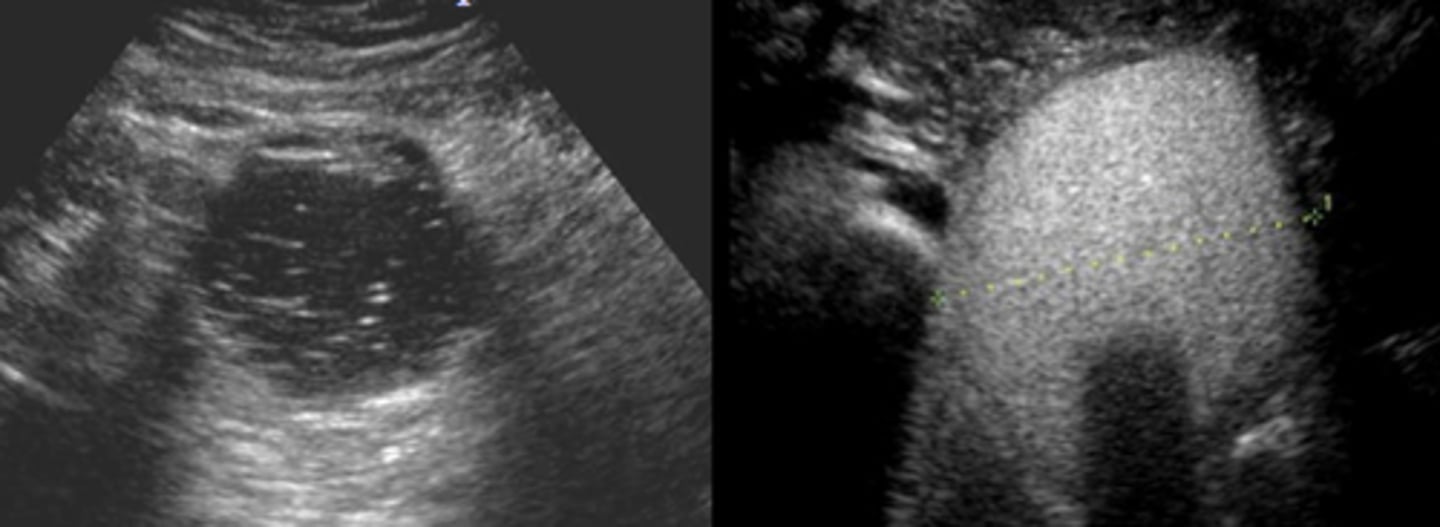
follicular adenoma and follicular carcinoma
what thyroid cancers can FNA not diagnose?
follicular adenoma
benign encapsulated tumor with follicular cell differentiation
-seen surrounded by a thin fibrous capsule
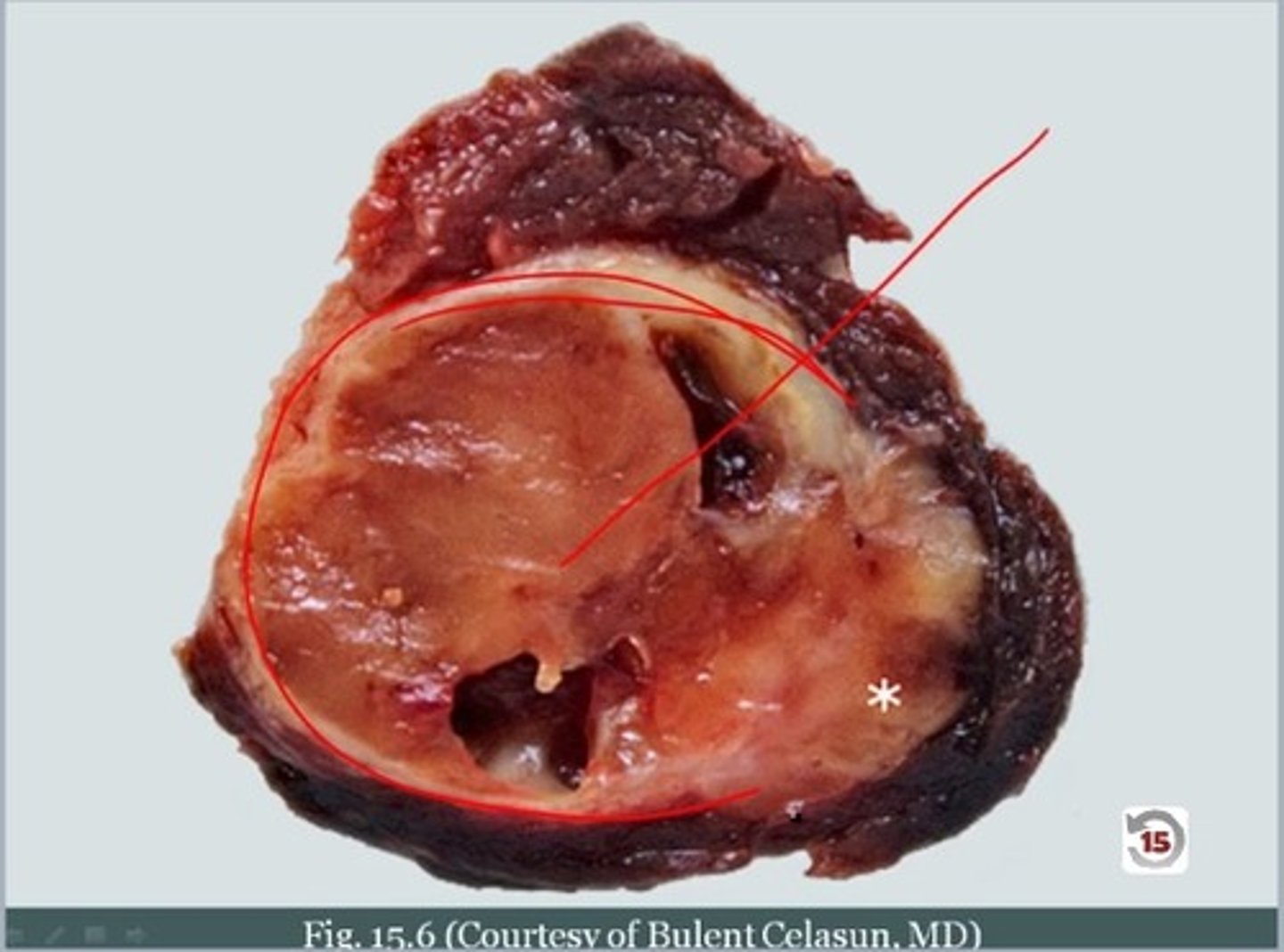
presence of an intact, well formed capsule encircling the tumor
hallmark of follicular adenoma
normofollicular adenoma
most common subtype of follicular adenoma
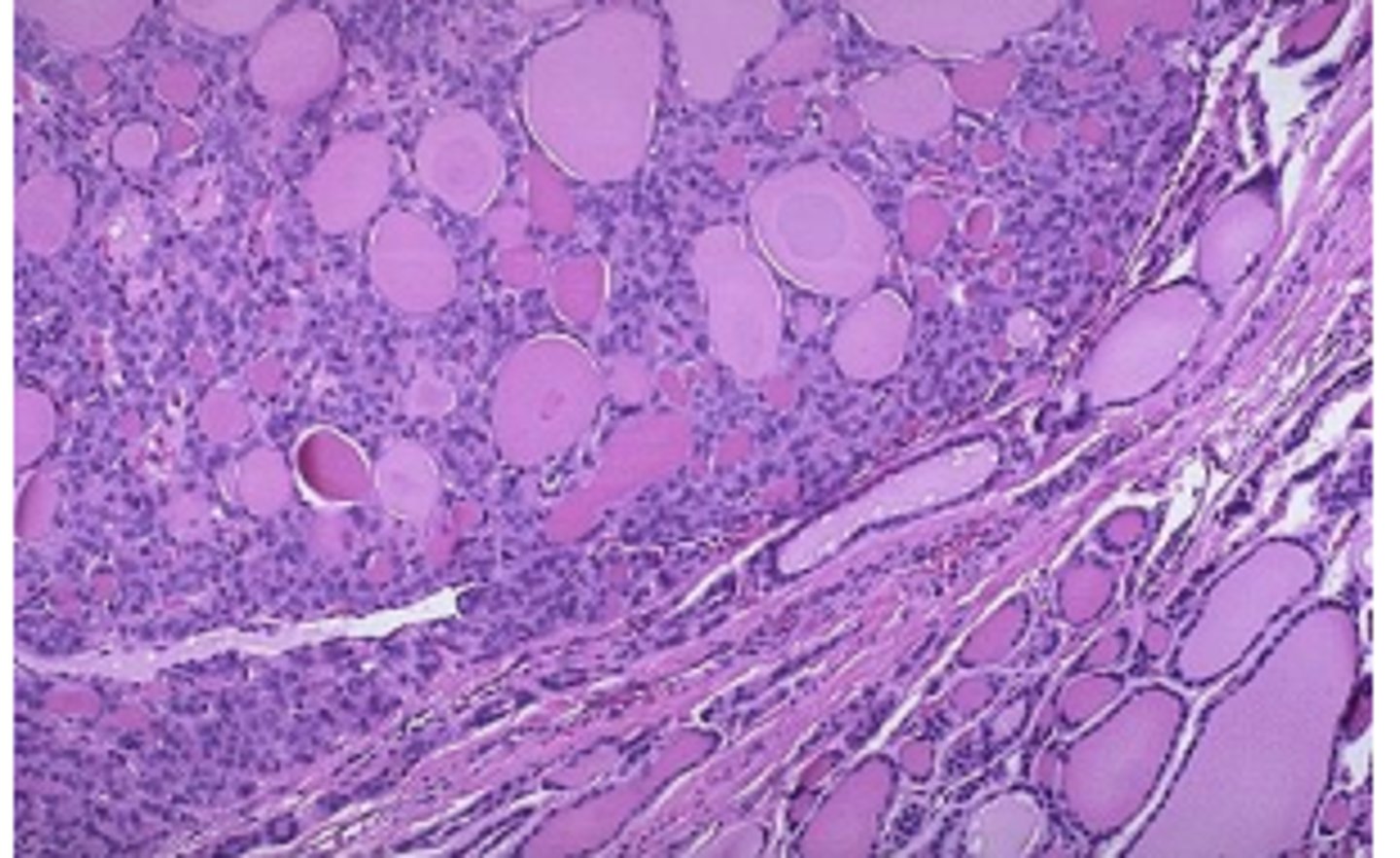
microfollicular adenoma
smalll, closelly packed follicles
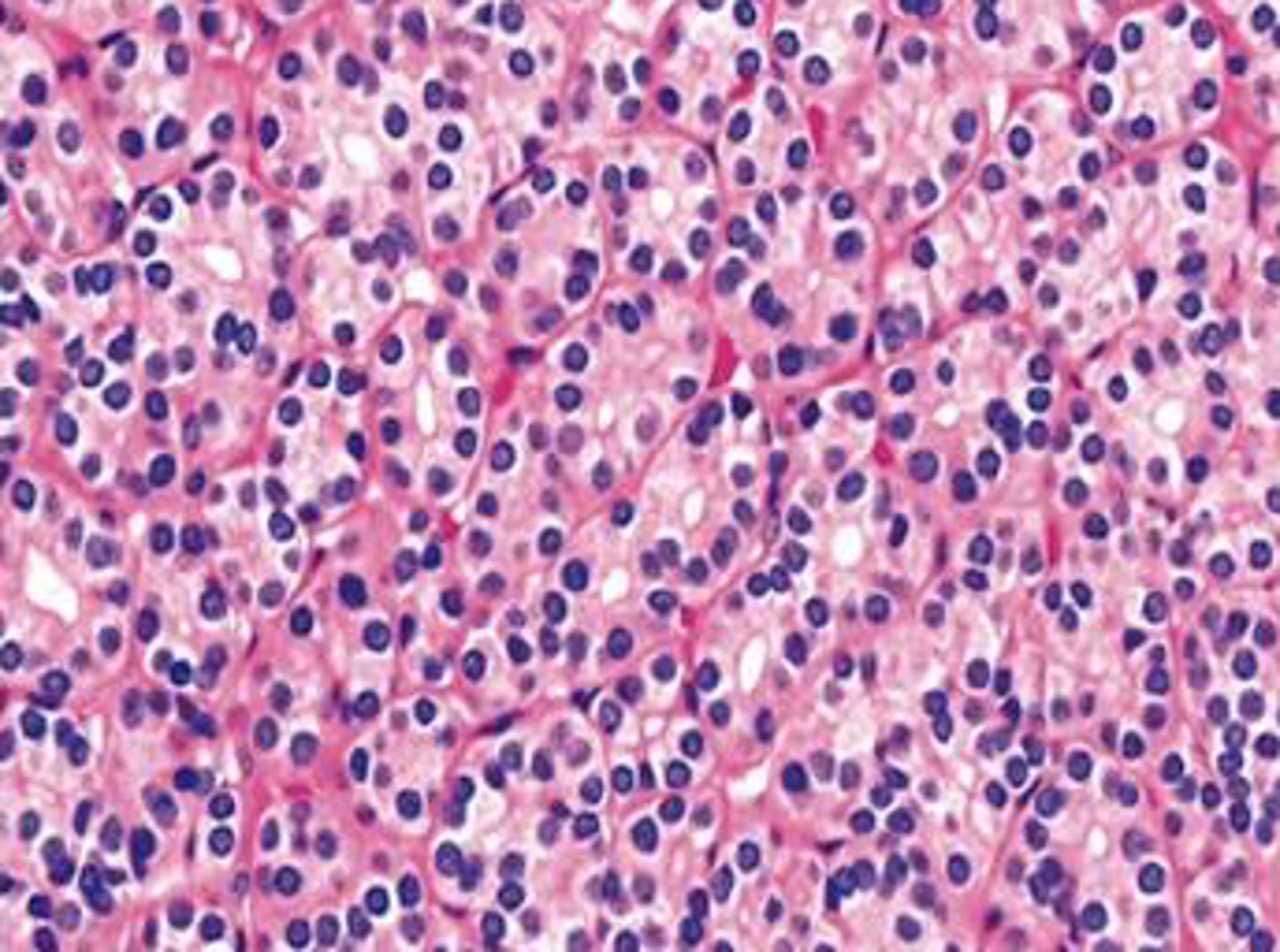
trabecular adenoma
subtype of follicular adenoma with cords or trabeculae with few follicles
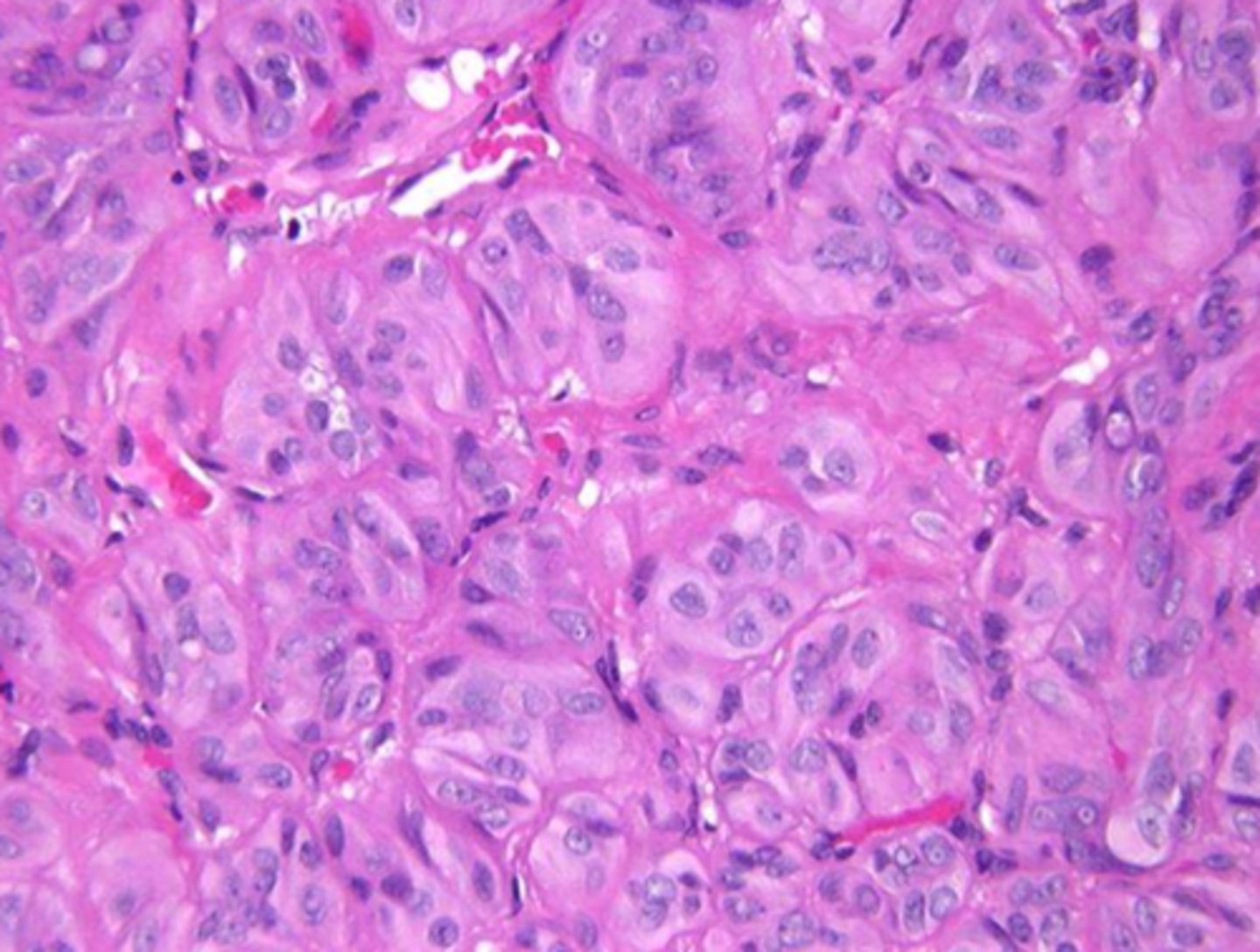
solid (embryonal) adenoma
follilcular adenoma composed of solid sheets
no
are toxic adenomas and toxic multinodular goiters precursors to folllicular carcinoma?
follicular adenoma
-US shows solitary nodule
-most are euthhyroid
-RAIU shows a cold nodule (hot if bigger)
papillary thyroid carcinoma
slow growing tumor characterized by papillary pattern with distinctive nulcar features
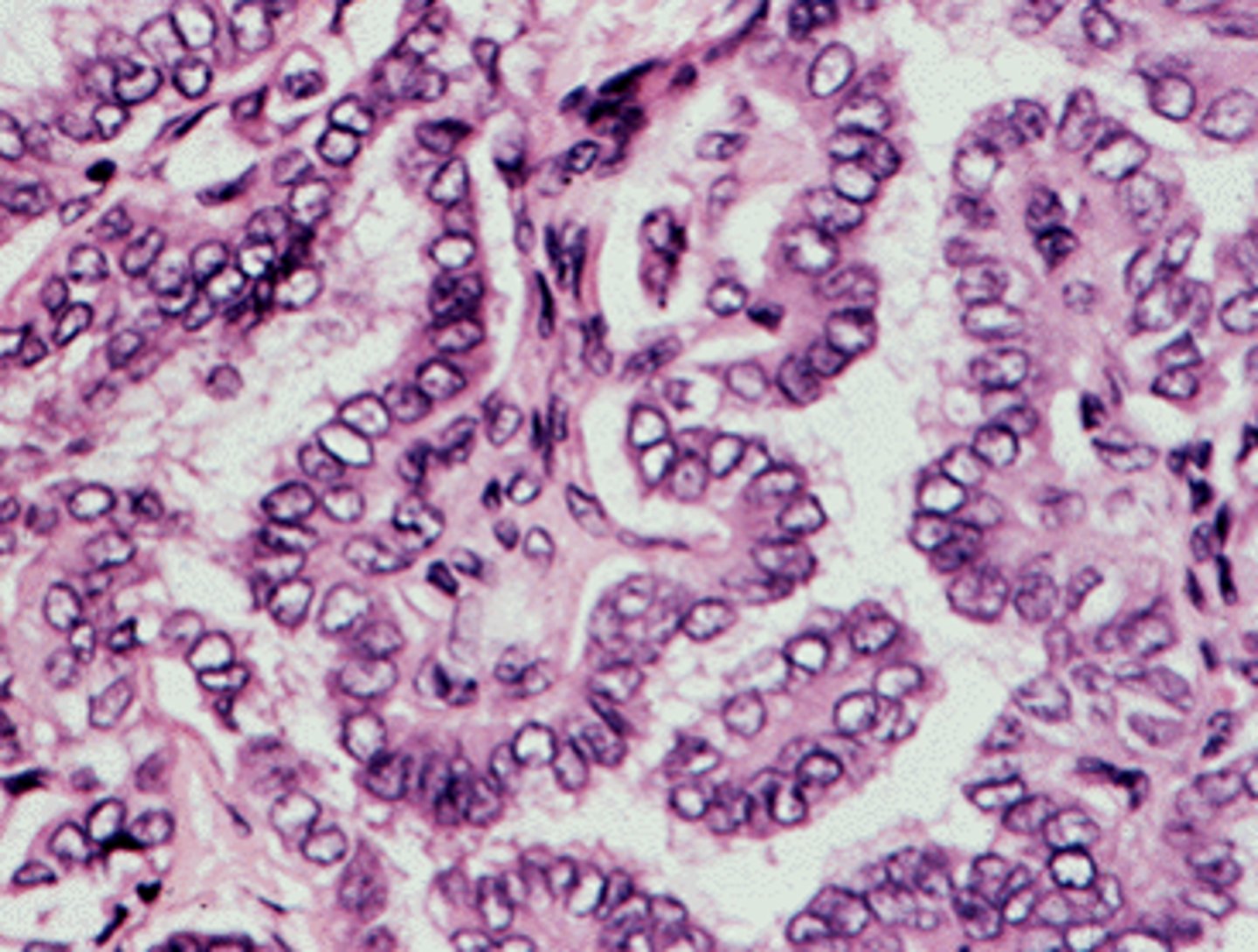
papillary thyroid carcinoma
tumor is pale white with cystic degeneration
-clear/empty appearance---> ground glass or orphan annie eye nuclei
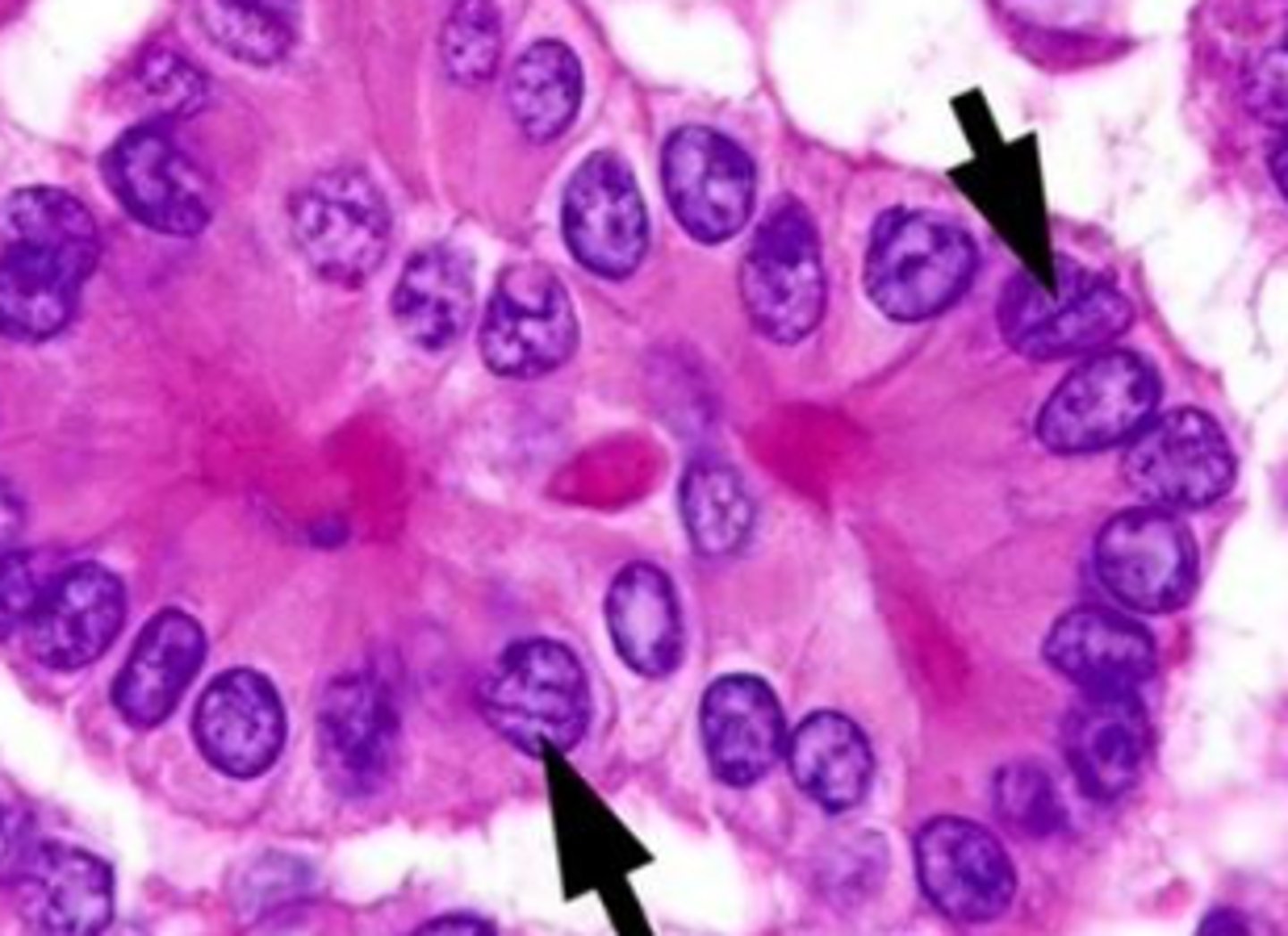
nuclear morphology of pappillary carcinoma
orphan annie eye nuclei
Seen in Papillary Carcinoma of the Thyroid. Enlarged thyroid cells with ground glass nuclei
intranuclear "pseudo-inclusion"
intranuclear grooves of papilllary carcinoma
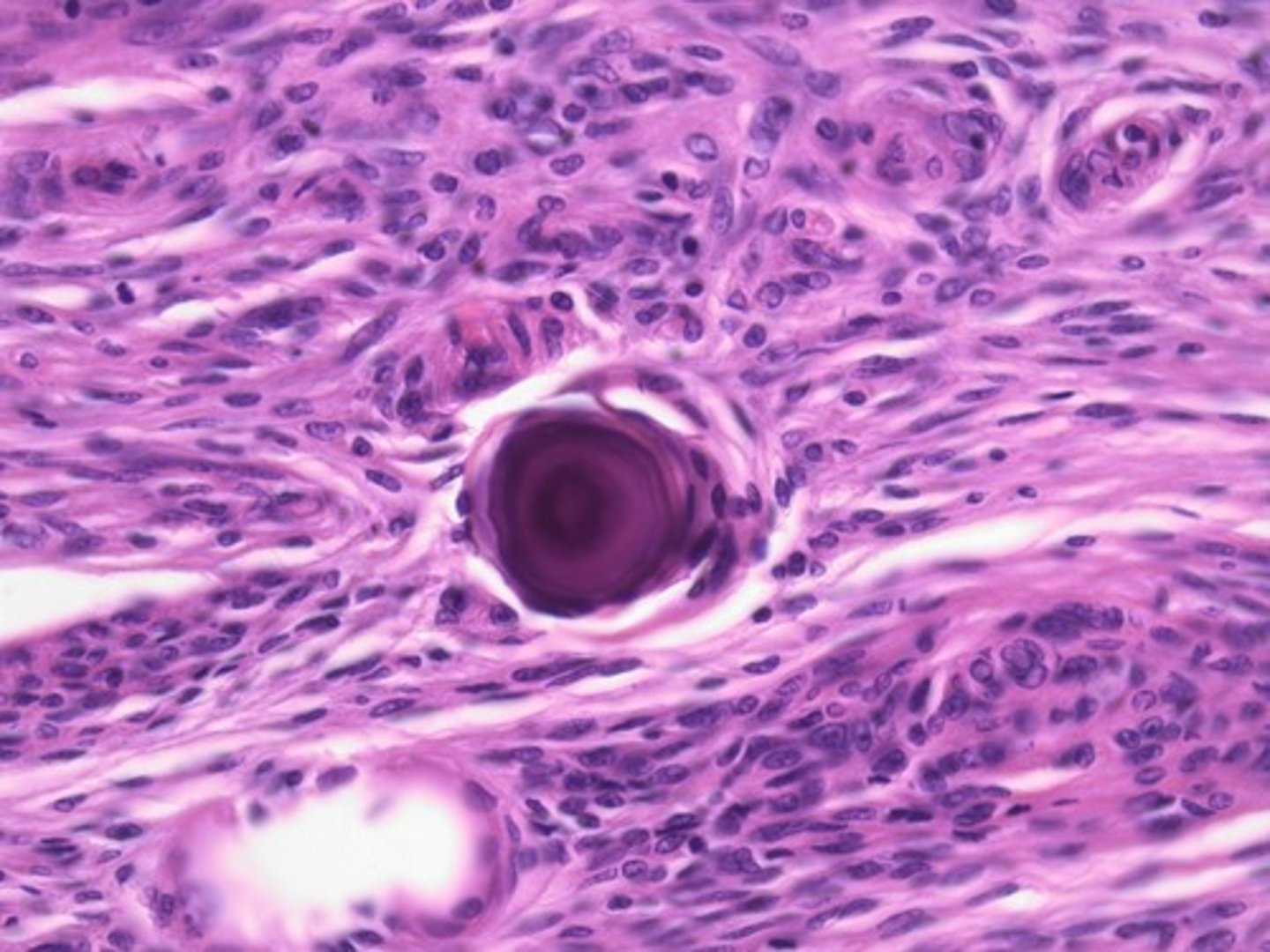
Psammoma bodies
calcified struuctures in papilllary carcinoma
-indicates lymphatic invasion
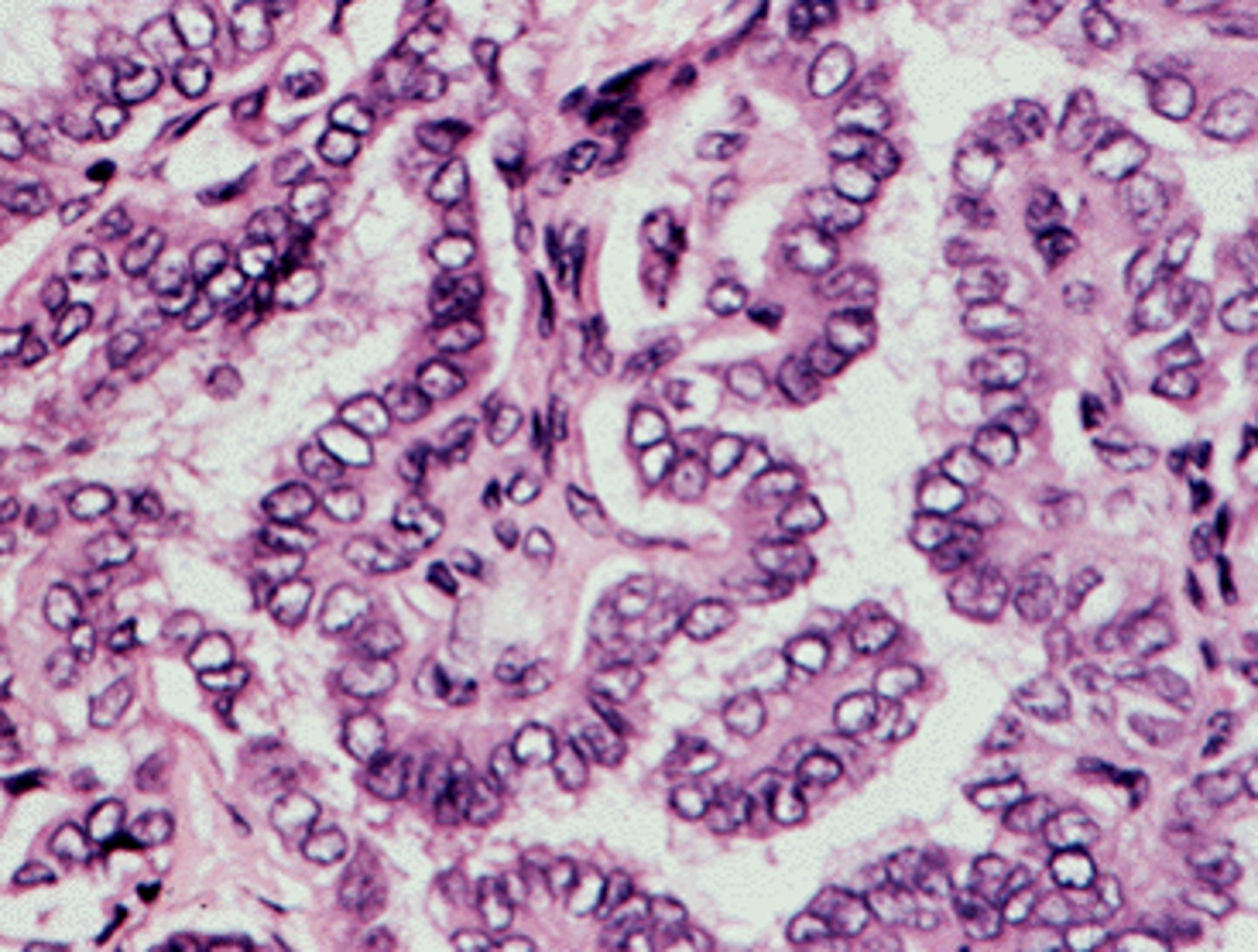
follicular variant
most common variant of papillary carcinoma
-has characteristic nuclei, but totally follicullar architecture
BAY 43-9006 (Sorafenib)
-kinase inhibitor with activity against BRAF--> papillary carcinoma
papillary carcinoma
BRAF mutations, RET rearrangement indicates
Sunitinib
oral, multitargeted RET tyrosine kinase inhibitor that has been developed as targeted therapy for papillary thyroid carcinomas
asymptomatic thyroid mass or an enlarged lymph nodule
-no signs of hypo or hyper thyroidism
presentation of papillary carcinoma
solid and hypoechoic
malignant nodules on sonography appear
cold
hot or cold masses in pap carcinoma?
excellent
prognosis of papillary carcinoma
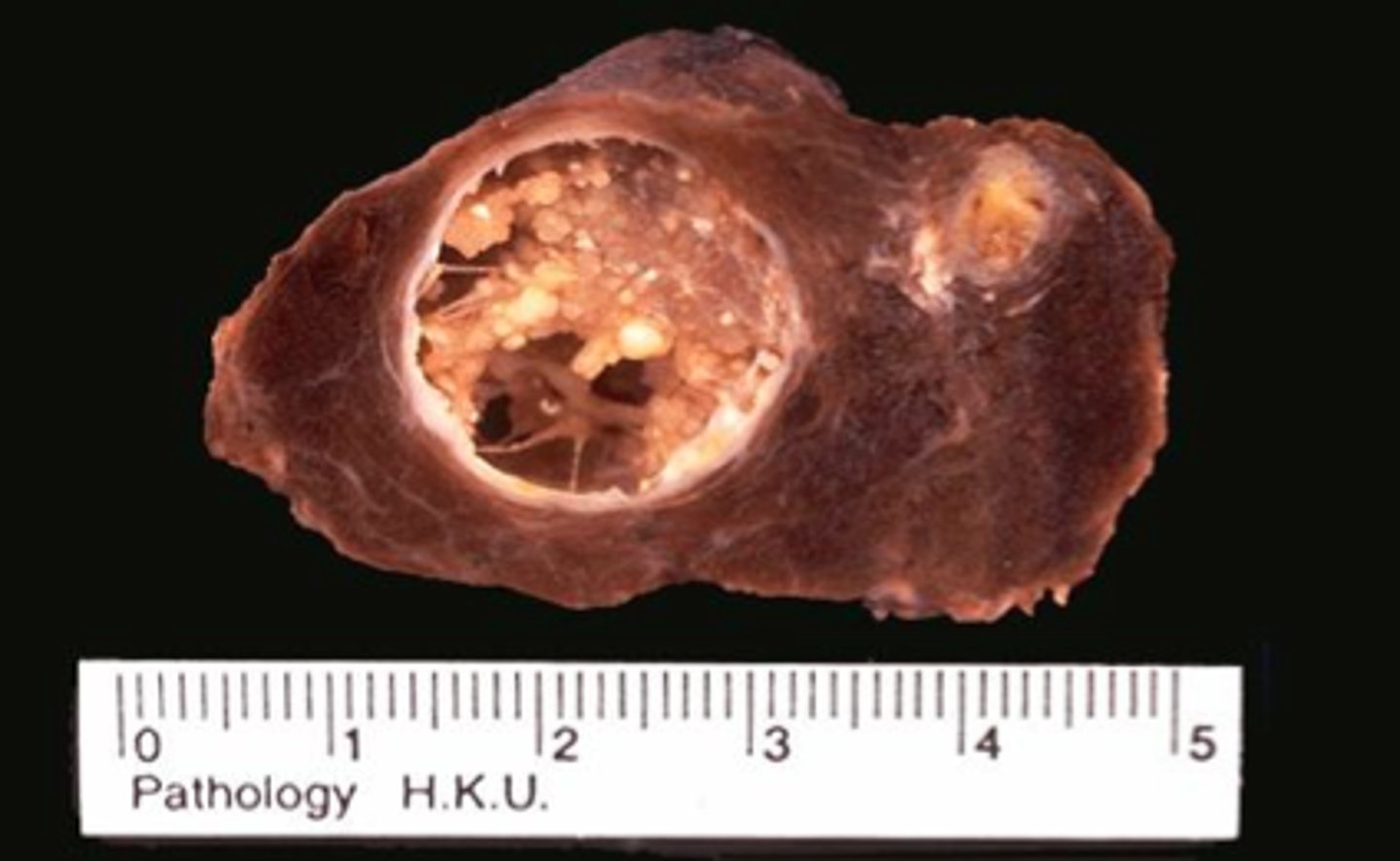
follicular thyroid carcinoma
second most common malignant thyroid tumor
follicular thyroid
gross pathology: solitary nodules well circumscribed with thick white fibrous capsule
-nodules are yellow tan on cut section
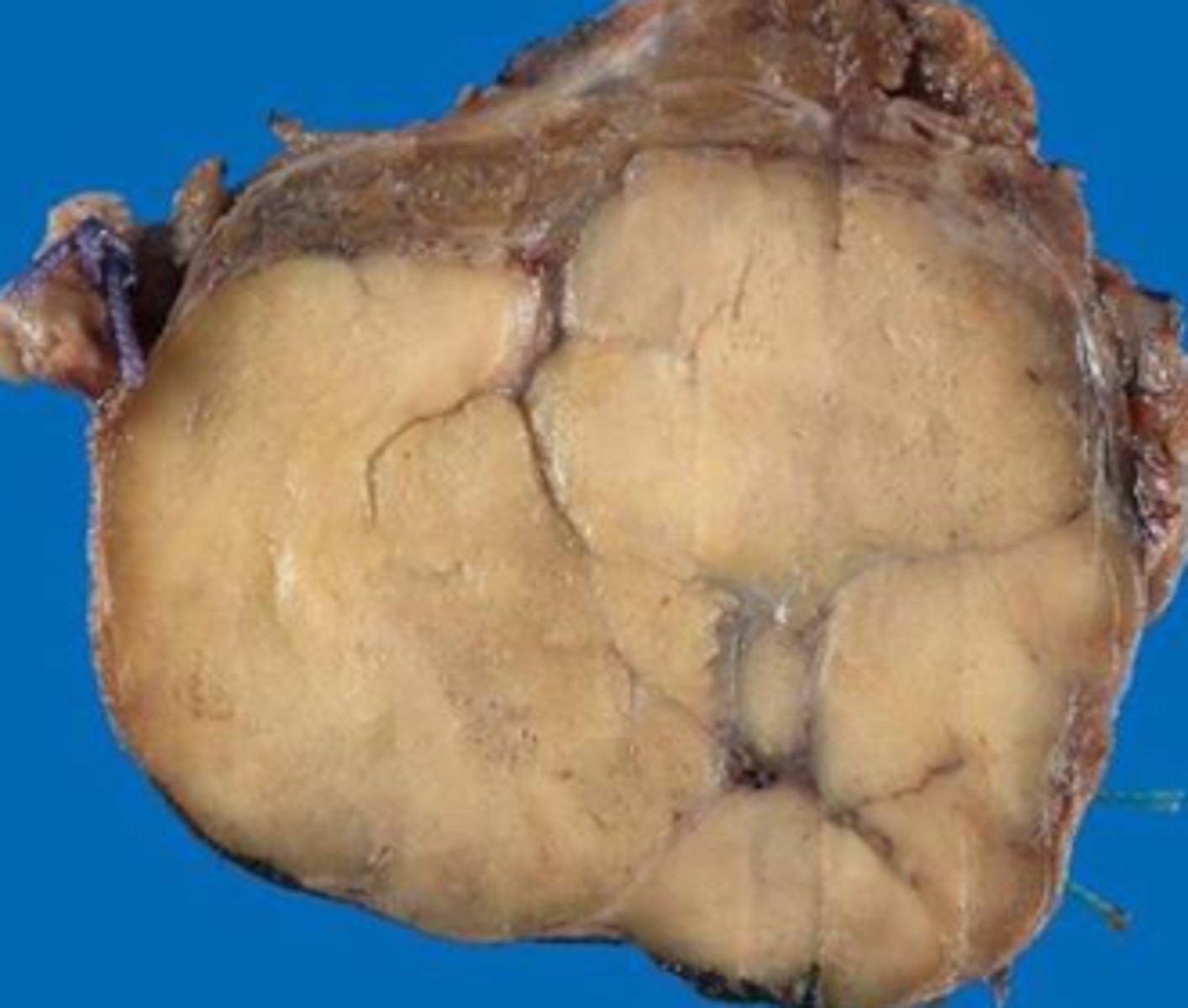
FTCs are differentiated from benign follicular adenomas by tumor capsule invasion and/or vascular invasion
how is follicular carcinoma differentiated from follicular adenoma on groww pathology?
indicates follicular carcinoma
-PI3K/AKT pathway mutations
-RAS mutations
PTEN mutations
PTEN
Inactivating somatic mutations of ____ gene are found in 27% of follicular carcinomas
PAX8-PPAR rearrangement
fusion transcript associated with follicular carcinoma
asymptomatic, painless solitary thyroid nodule
-nodule is fixed to surrounding tissue
presentation of follicular carcinoma
cold nodule
RAIU finding on follicular carcinoma

-FTC metastases are hematogenous, not lymphatic, and are direct to the bones, shoulder, pelvic girdles, sternum, and skull
how does follicular carcinoma differ from papillary carcinoma?
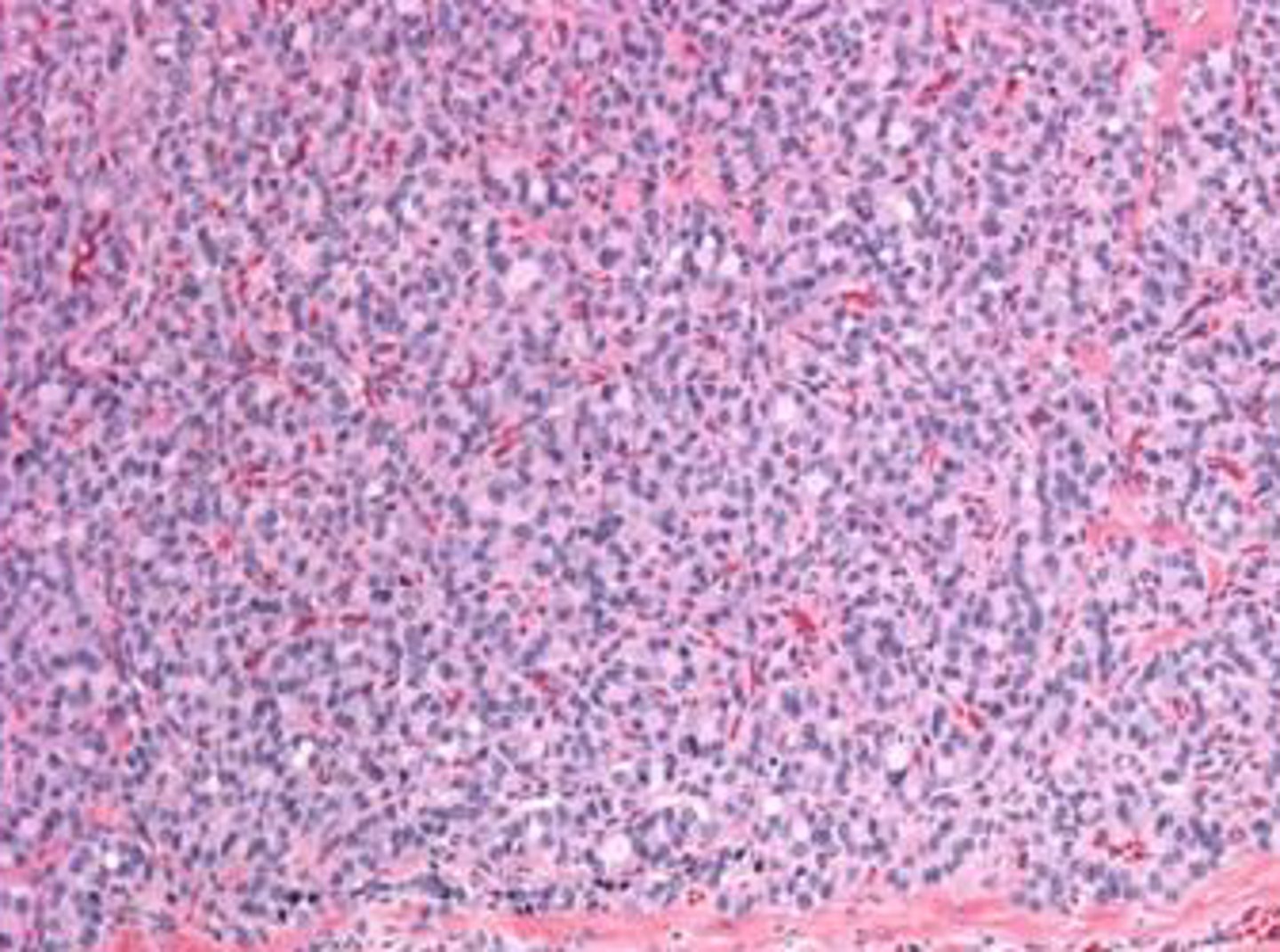
anaplastic thyroid carcinoma
the most aggrressive thyroid malignancy?
anaplastic carcinoma
cancer may derive from papillary or follicular types; peak incidence in 6th and 7th decade of life
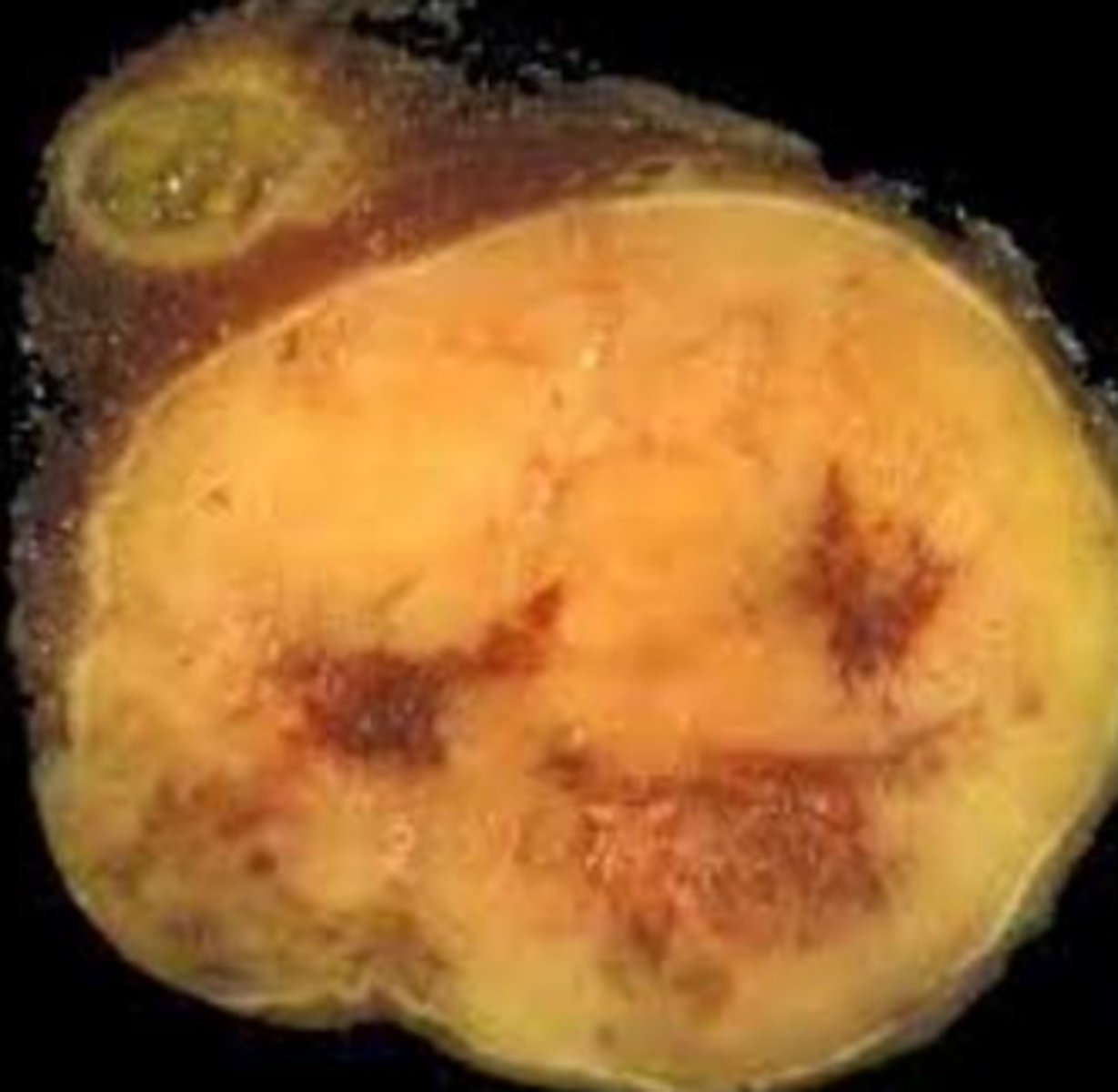
anaplastic carcinoma gross pathology
highly necrotic and hemorrhagic solid mass; tan to brown cut
HUGE
squamous pattern, spindle pattern, giant cell type
what are the three histologic patterns of aanaplastic thyroid carcinoma?
anaplastic carcinoma
presentation: rapidly enlarging neck mass, rapidly lethal clinical course
medullary thyroid carcinoma
neuroendocrine neoplasms derived form the parafollicular (C cells)
calcitonin
medullary thyroid carcinomas secrete
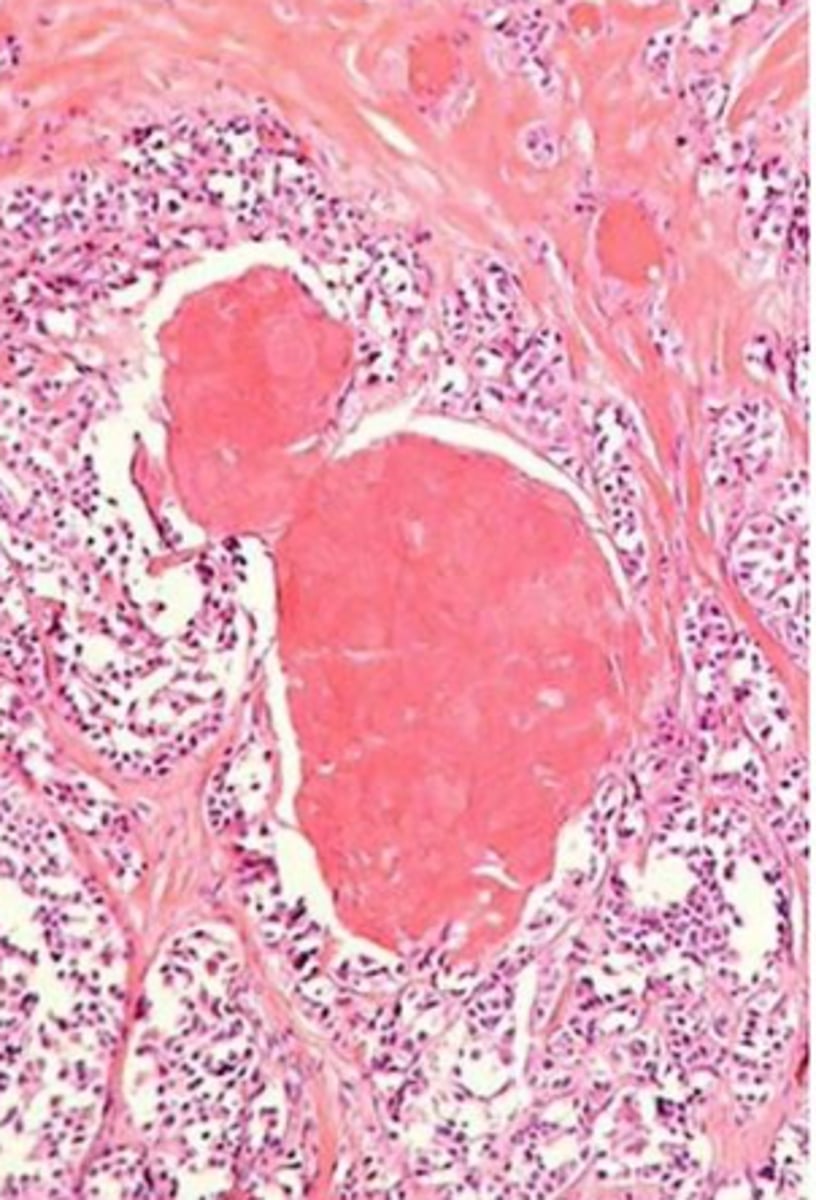
medullary thyroid carcinoma
amyloid stains positively with calcitonin immunostains
RET protooncogene
key molecule associated with the development of MTC
RET oncogene
in mosst pts with MEN2A or MEN 2b have activatinng point mutations in
Sunitinib
RET kinase inhibitor currently in clinicla trails for treatment of MTC
asymptomatic thyroid nodule
-larger ones cause difficulty swallowing
-may cause hoarseness
-flushing and diarrhea from increased electrolyte secretion secondary to high calictonin
presentation of medullary thyroid carcinoma
elevated basal serum calcitonin levels
diagnostic lab values of MTC
thyroglobulins
primary biochemical marker for pts with differentiated thyroid cancers
predicts te absencce of recurrence during long term follow up!
undetectable postoperative Tg predicts what prognosis of thyroid cancer?