autonomic nervous system
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
roles of the ANS
involuntary branch of the efferent division of the peripheral nervous system (PNS)
controls the body’s internal environment in a coordinated manner
regulates contraction/relaxation of cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, glands
heart rate, circulation, respiration, digestion
internal organs controlled by ANS: heart, lungs, stomach etc.
CNS control of ANS
spinal cord
integrates autonomic reflexes not subject to higher control e.g. urination, defecation
medulla and pons
regulate cardiovascular, respiratory and digestive tracts
hypothalamus
heart rate, blood pressure, respiration (via medulla)
hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA) (hormone secretion)
ANS control of sympathetic nervous system
dilates pupils (distance vision)
increases heart rate and contractility, blood pressure rises
dilates airways (bronchi, bronchioles)
inhibits digestive activity
closes sphincters
ANS control of parasympathetic nervous system
constricts pupils
slows heart rate and contractility
constricts airways (bronchi, bronchioles)
stimulates digestive activity
opens sphincters
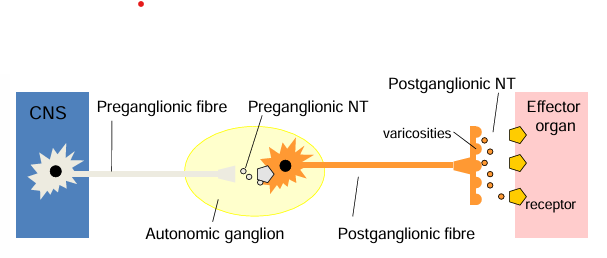
nerve pathways in the ANS
every ANS pathways from the CNS to the effector organ/tissue is a chain of 2 neurons
CNS → preganglionic neuron → ganglion → postganglionic neuron → effector organ
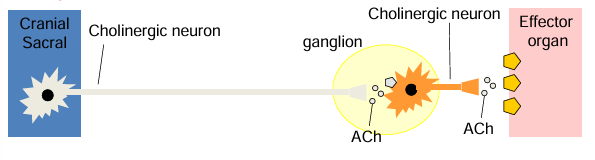
parasympathetic nerve path
pre ganglionic nerves originate from cranial (X-vagus nerve) and sacral (lower spinal cord) regions of spinal cord
pre ganglionic nerves are long
pre ganglionic nerves release ACh and nicotinic receptors
post ganglionic nerves are short
post ganglionic nerves release ACh and muscarinic receptors
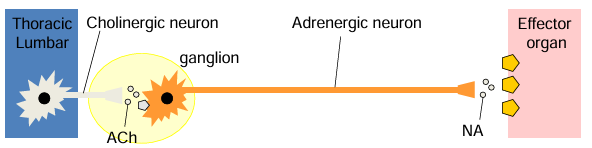
sympathetic nerve paths
pre ganglionic nerves originate from thoracic and lumbar regions of spinal cord (T1-L3)
pre ganglionic nerves are short
pre ganglionic nerves release ACh and nicotinic receptors
post ganglionic nerves are long
post ganglionic nerves release Noradrenaline and alpha and beta receptors
ANS NT receptors
all the effects of the ANS are carried out by ACh and noradrenaline (and adrenaline)
neurotransmitters can stimulate or inhibit in the target organs/tissues - the responses are determined by the type of receptors present
acetylcholine: cholinergic receptors
nicotinic
muscarinic (effector organs)
noradrenaline/adrenaline: adrenergic receptors
Alpha
Beta
adrenergic receptors
found at effector organs in sympathetic system
two major classes alpha and beta
alpha 1: excitatory e.g. increases contraction of arterioles → raises blood pressure
alpha 2: inhibitory e.g. decreases smooth muscle contraction in digestive system → reduces GIT motility
beta 1: excitatory e.g. increases contraction of cardiac muscle → increases rate and force of contractions
beta: inhibitory e.g. relaxes smooth muscle in respiratory tract → dilation of bronchioles
all are metabotropic
adrenal medulla
adrenal medulla is a modified part of the sympathetic nervous system
no post ganglionic fibers
pre ganglionic fibers release ACh which directly stimulates the adrenal medulla
adrenal medulla secretes NT (hormones) into blood
sympathetic and parasympathetic systems
dual reciprocal innervation
most organs innervated by both systems
systems mostly exert opposing effects
enable rapid and precise control
enables rapid transitions from rest state to fight or flight
under most circumstances there is partial activation of both systems (tonic activity)
sympathetic dominates in emergency or stressful situations
parasympathetic dominates in quiet, relaxed situations
dual reciprocal effects of ANS on various organs
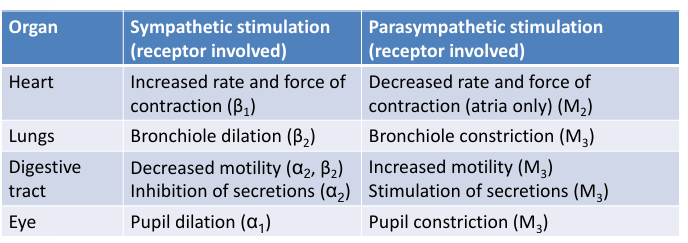
ANS control of heart
sino-atrial (SA) node regulates heart rate
myocytes regulate force of contraction
these are innervates by both sympathetic and parasympathetic NS
both systems are active at rest - your heart rate and the force of contraction are determined by the balance of both systems
exceptions
most arterioles and veins are only innervated by sympathetic nerves
most sweat glands are only innervated by sympathetic nerves
in some cases, other NTs or signaling molecules are involved in the ANS e.g. GABA, serotonin, dopamine