Chapter 3: Populations (copy) Recreated
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
1
New cards
Survivorship curves
It show age-distribution characteristics of species, reproductive strategies, and life history
2
New cards
Biotic potential
The maximum reproductive capacity of an organism under optimum environmental conditions
3
New cards
Environmental Resistance
Any factor that inhibits an increase in the number of organisms in the population
4
New cards
J-Curve
It represents a population growth occurs in a new environment when the population density of an organism increases rapidly in an exponential or logarithmic form, but then stops abruptly as environmental resistance or another factor suddenly impacts the population growth
5
New cards
S-Curve
It occurs when, in a new environment, the population density of an organism initially increases slowly but then stabilizes due to the finite amount of resources available
6
New cards
Limiting Factor
It can be any resource or environmental condition that limits the abundance, distribution, and/or growth of a population
7
New cards
Density-dependent limiting factors
These are factors whose effects on the size or growth of the population vary with the density of the population
8
New cards
Density-independent factors
These are factors that limit the size of a population, and their effects are not dependent on the number of individuals in the population
9
New cards
Rule of 70
It helps to explain the time periods involved in exponential population growth occurring at a constant rate
10
New cards
Doubling time
It is the amount of time it takes for a population to double in size
11
New cards
Age-structure diagrams
These are determined by birth rate, generation time, death rate, and sex ratios
12
New cards
Pyramid-shaped age-structure diagram
It indicates that the population has high birth rates and the majority of the population is in the reproductive age group
13
New cards
Bell shape age-structure diagram
It indicates that pre-reproductive and reproductive age groups are more nearly equal, with the post-reproductive group being smallest due to mortality
14
New cards
Urn-Shaped age-structure diagram
It indicates that the post-reproductive group is largest and the pre-reproductive group is smallest, a result of the birth rates falling below the death rate, and is characteristic of declining populations
15
New cards
Total fertility rate (TFR)
The average number of children that each woman will have during her lifetime
16
New cards
Demographic transition
It is the transition from high birth and death rates to lower birth and death rates as a country or region develops from a pre-industrial to an industrialized economic system
17
New cards
Stage 1
Pre-Industrial (High Stationary) (Low growth)
18
New cards
Stage 2
Transitional (Early Expanding) (Very High growth Rate)
19
New cards
Stage 3
Industrial (Late Expanding) (Slow growth)
20
New cards
Stage 4
Post-Industrial (Low Stationary) (No or negative growth)
21
New cards
Birth Rate Formula
Birth Rate (%) = \[(total births/total population)\] × 100
22
New cards
Crude Birth Rate Formula
CBR = \[(*b* ÷ *p*) × 1,000\]
23
New cards
Death Rate Formula
Death Rate (%) = \[(total deaths/total population)\]× 100
24
New cards
Crude Death Rate Formula
CDR = \[(*d* ÷ *p*) × 1,000\]
25
New cards
Doubling Time Formula
Doubling Time = 70/% growth rate
26
New cards
Percent Rate of Change Formula
Percent Rate of Change = \[(new # - old #)/old #\] × 100
27
New cards
Population Growth Rate Formula
\
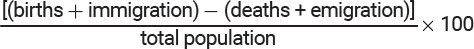
28
New cards
Based on _________, even if all other factors are favorable, the one that is least favorable will dictate the growth, abundance, or distribution of the population of a species.
Liebig’s law of the minimum
29
New cards
This type of population growth is termed “_________” since the growth rate depends on the number of organisms in the population.
density-dependent
30
New cards
This type of population growth rate is known as “_______,” a regulation of the growth rate is not tied to the population density until the resources are exhausted and the population growth crashes.
density-dependent
31
New cards
Type I Survivorship
Exhibit high survivorship through life
32
New cards
Type II Survivorship
Constant proportion of loss over time
33
New cards
Type III Survivorship
very high mortality rate
34
New cards
r-Strategists
small, many offspring, don’t invest in offspring, mature early, short lifespans, reproduce once, low resource competition
35
New cards
K-Strategists
larger, less offspring, lot of parental care, mature slowly, longer lifespan, reproduce more than once, high resource competition