aging horses by teeth
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
describe the standard system
categorizes teeth based on their type and location, incisors, canines, premolars, molars
describe the cheek teeth system
highlights function and location, premolars, molars
describe the triadan system
numerical system that divides the mouth into four quadrants: right maxillary, left maxillary, left mandibular, right mandibular
hypsodont teeth
continually erupting, slowly erupt over most of life, long crown (body), little root
hypsodont animals
horses, cows, deer
brachydont teeth
permanent teeth fully erupt before maturity, normally survive for life of animal
brachydont animals
dog and cat
what is cementum and where is it found
bone-like tissue that covers tooth root (comes off when floated)
what does floating mean
leveling the teeth
what is enamel and where is it found
coating of the crown, gives it hardness, protecting underneath, found in complex folds or ridges on the occlusal
what is dentin and where is it found
makes up bulk of tooth, surrounds pulp cavity, less mineralized than enamel but harder than bone
what is the pulp cavity of an equine incisor tooth?
soft tissue where the blood and nerve supplies of tooth come through tooth. incisor can have single pulp, cheek teeth complex compartmentalization of pulp cavities, 5 compartments
how does the pulp cavity relate to the dental star
dental star is visible mark that appears on the occlusal surface of tooth as pulp cavity gets filled with dentin due to wear and aging
why can we generally age younger horses (<5 yrs) more accurately?
when under 5 yrs, we can use eruptions as a guide and it is very consistent and predictable whereas over 5 yrs you use shape and wear of occlusal teeth which does happen consistently and is more of an educated guess. wide ranges of wear and shape exist
deciduous teeth
baby teeth, smooth no ridges, distinct neck, round
permanent teeth
adult teeth, grooved, less white, not distinct neck, more square in shape
describe canine teeth, where are they?
between upper and lower corner incisors and the first cheek teeth, called the bridle path
when do canine teeth erupt
typically erupt around 4-5 yrs of age
do females have canines?
typically no, but if they do, they are to a much smaller scale. Canines are testosterone driven teeth.
true or false: The canines, molars, and wolf teeth are not preceded by deciduous teeth.
true, only incisors and premolars are preceded by deciduous teeth
The permanent cheek teeth all have deciduous caps that fall off.
false, don’t have caps and aren’t precede by deciduous teeth
Molars begin to erupt at 8 years of age
false, begin to erupt around 6 yrs
All the permanent incisors are erupted and in wear for the first time at 3 ½ years.
false, typically in wear at 5 yrs
Galvayne’s groove is on the lower I3 teeth (303/403).
no, UCI, upper corner incisor
dental star
appears when tooth is worn to the pulp space; pulp space filled in with dentin. appears on labial (lip) side of tooth, rostral to enamel spot
enamel spot
appears after the cup has worn down to the bottom
cup (infundibulum)
physical indentions/ depression you can see in tooth
full mouthed meaning
all permanent incisors erupted and in wear (by 5 yrs)
smooth mouthed meaning
they have no cups left on their teeth, at least 11 yrs
what are caps, which teeth have them?
caps refer to retained baby teeth specifically deciduous premolars, that haven’t shed naturally as permanent teeth erupt.
what problems can caps cause?
uneven tooth growth, pain, difficulty eating or biting
what are wolf teeth? why remove them?
vestigial teeth, premolar 1, typically get removed because they can cause interference and irritation with the bridle/bit
what does in wear mean
two permanent teeth erupt fully from gemlike and are in wear/ are touching. erupt > 6 months> in wear. in wear is at least 5 yr
permanent dental formula. explain and include why there is a variable number of teeth in adult horses
2(I 3/3 C (0-1)/(0-1) P (3-4)/(3-4) M 3/3) = 36-44 total
Incisors-canines(varies, male horse has one or some mares)-premolar (varies due to wolf tooth)-molar. variation is due to the variability of presence of first premolars (wolf teeth) in males and females and variability of canines in females
on what tooth/teeth and surface is Galvayne’s groove potentially visible?
Groove on lateral (labial) surface of upper I3: UCI (upper corner incisor)
how is Galvayne’s groove useful in determining age of horse
10yrs- groove appears
15 yrs- groove ½ down
20 yrs- groove all the way down (reaches occlusal surface)
25 yrs- absent from upper ½
30 yrs- grooves disappears
who was Dr. Galvayne?
a well known horse tamer and author who created a “perfect” system for horse aging by looking at their teeth
how is UCI and upper central incisors used to “ball park” horses into age category?
through shape and wear
5-9 yrs: wider than tall
10-14 yrs: UCI was about as wide as tall, square
15-20 yrs: UCI was taller than wide
Rule of 8’s
1-8days: I1 erupts
4-8 weeks: I2 erupts
6-8 months: I3 erupts
occlusal surface
touching, grinding surfaces
buccal surface
surface against cheek
lingual surface
surface against tongue
labial surface
surface against lip
shapes in relation to age
young-oval transversely
9-10 yrs- round
16-17 yrs- triangular
20yrs- oval rostrocaudally
impacted wolf tooth
lack of eruption
over bite
parrot mouth
under bite
monkey mouth
examining for aging steps
1. Look at incisor profile
2. determine number of deciduous and/or permanent incisors
3. shape of upper i3. Look for galvaynes upper i3
4. examine occlusal surface of lower incisors (cups)
aging
Rule of 8”: if under 2 ½
2 ½ to 5 yrs: i1 2 ½ yrs i2 3 ½ yrs i3 4 ½ yrs in wear at 5 years canines 4-5 yrs
Over 5: shape of UCI- wider vs taller: 5-9 square: 10-14 taller vs wider: 15-20
Lower: i1 cup gone 6 yrs i2 cup gone 7 yrs(hook on upper i3) i3 cup 8 yrs
Upper: i1 cup gone 9 yrs i2 cup gone 10 yrs i3 cup gone:11 yrs (smooth mouthed) by 11 yrs
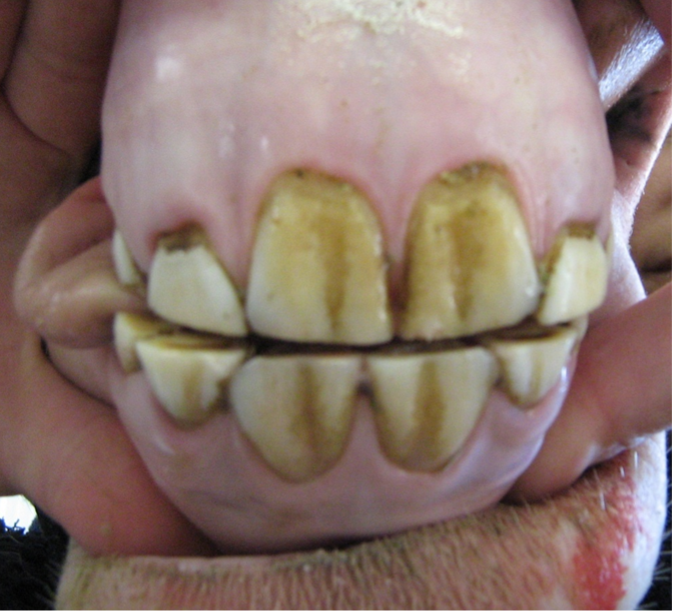
Age this horse (within 6 months), and state 3 specific reasons why you chose that age
it has its I1 permanent teeth which puts it at least at 2 1/2 , it can be seen that the horses I2 are starting to come in so it is a little under 3 ½ but since the i1 are in use, 6 months can be added. This horse is most likely 3 yrs
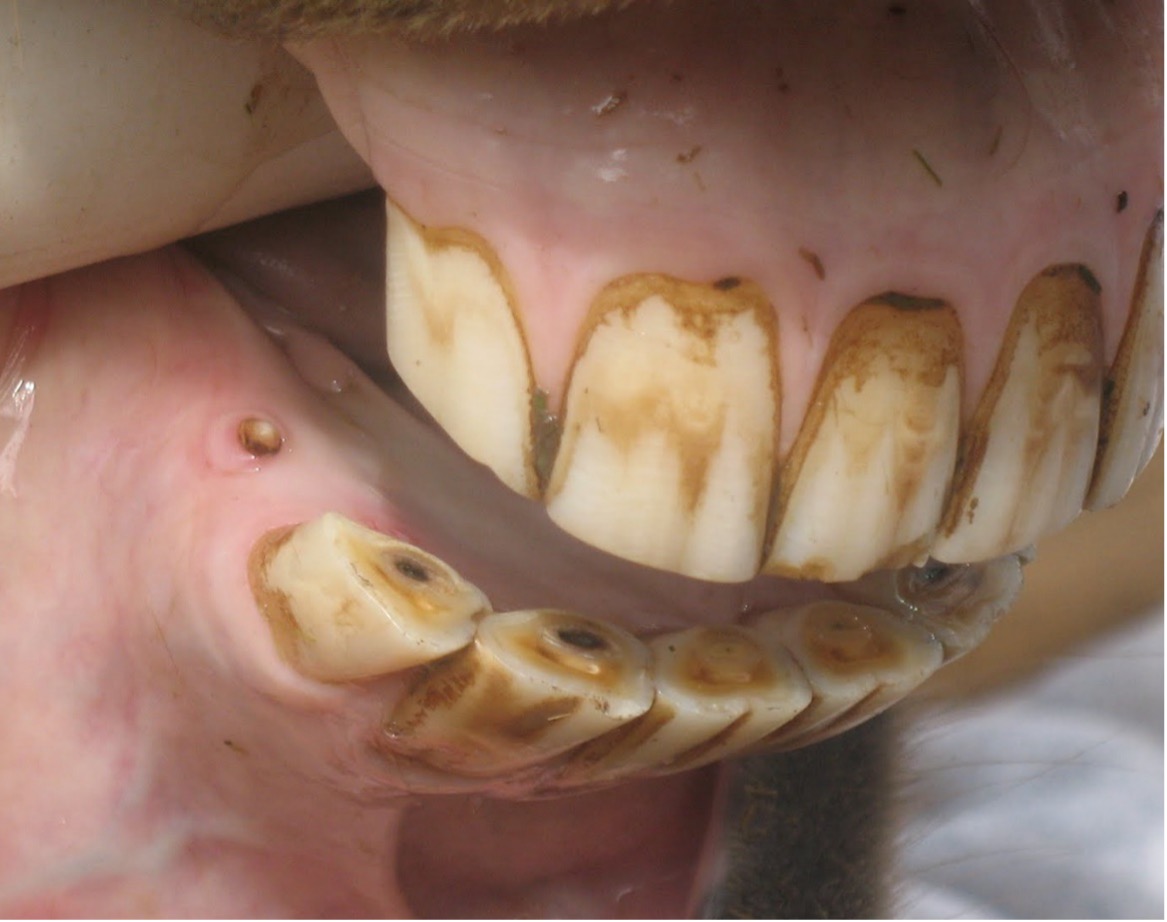
Age this mare (within 1 year), and state 3 specific reasons why you chose that age
It has all of its permanent teeth and they are in wear so at least 5 years, it also has the canine teeth, so at least 4-5 yrs, it also is missing cups on I1 so it is at least 6 years. My guess is 6 years
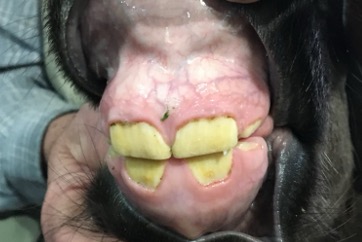
Age this foal and state 3 specific reasons why you chose that age range.
over 4 weeks because the I1 has erupted so it is at least over 8 days and the I2 is beginning to erupt so that puts it in the 4-8 week range and these are deciduous teeth
stage permanent
I1: 2 ½ I2: 3 ½ I3: 4 ½
stage cup gone
I1: 6 yr I2: 7 yr I3: 8 yr
stage dental star
I1: 8 yr I2: 9 yr I3: 10 yr
stage cup gone upper
I1 9 yr I2 10 yr I3 11 yr
stage enamel spot gone
I1 12 yr I2 13 yr I3 15 yr