Acute Pulmonary Edema
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Pulmonary Edema: Definition
Abnormal accumulation of fluid in the interstitial spaces and alveoli of the lung
•Life-threatening condition
•Associated with acute decompensated HF
Pulmonary edema Results from
•left ventricular failure
•AMI or acute exacerbation of CHF
•Non- cardiac disorders (renal failure)
Left ventricle fails
-=> blood backs up into left atrium=>
-Rapid increase in atrial pressure=> increased pulmonary venous pressure=> interstitial edema
-"flash pulmonary edema"
left sided HF
-affects the lungs
-crackles
-SOB
-dyspnea
-orthopnea
-pink frothy sputum
-paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
-pulmonary edema
-hypoxia
-change LOC
-IMPAIRED gas exchange
-cough
for left sided HF
-pulmonary artery wedge pressure (4-12)
Right sided HF
-JVD
-ascites
-hypervolemia
-anorexia
-hepatomegaly
-weight gain
-peripheral edema
-hypertension
-nausea
-weakness
for r sided HF what do we look at
CVP
Right sided HF interventions
-I/O
-daily weight (same time each day)
-educate
-diuretics
-LOW NA/ fluid restriction diet
-restrictive clothing
L sided HF interventions
-elevate HOB
-OXYGEN
-diuretics
-pulse ox continuous
-ABG
can HF be acute
yes
Chronic congestive failure can have acute episode
they stop taking meds/ have a trigger
-have their sx coming out at that moment
fluid builds from the
bases
-important to listen for breath sounds, if their is fluid in the lungs patients cannot exchange gasses
how will pulmonary edema patients look
-dusky
-pale
-no gas exchange
-drowning from within
Clinical Manifestations of pulmonary edema
•Decreased cerebral oxygenation
•Confusion, anxious, restless→stuporous
•Sudden dyspnea
•Sense of suffocation
•Cold, moist, pale
•Weak, rapid pulse
•Cyanosis/ashen (Skin/nail beds)
•Neck vein distention
•Cough
•Breathing is rapid, noisy
•"Drowning in secretions"
•Decreased oxygen saturations
•Sputum→ pink, frothy sputum (Fluid within alveoli mixes with air)
physical assessment for pulmonary edema
•ABC evaluation
•Vital signs
•Cardiac monitor
•IV access
diagnostic tests for pulmonary edema
•Electrolytes
•BUN/Creatinine
•CBC
•CXR
•Right vs. Left
pulmonary edema on an xray
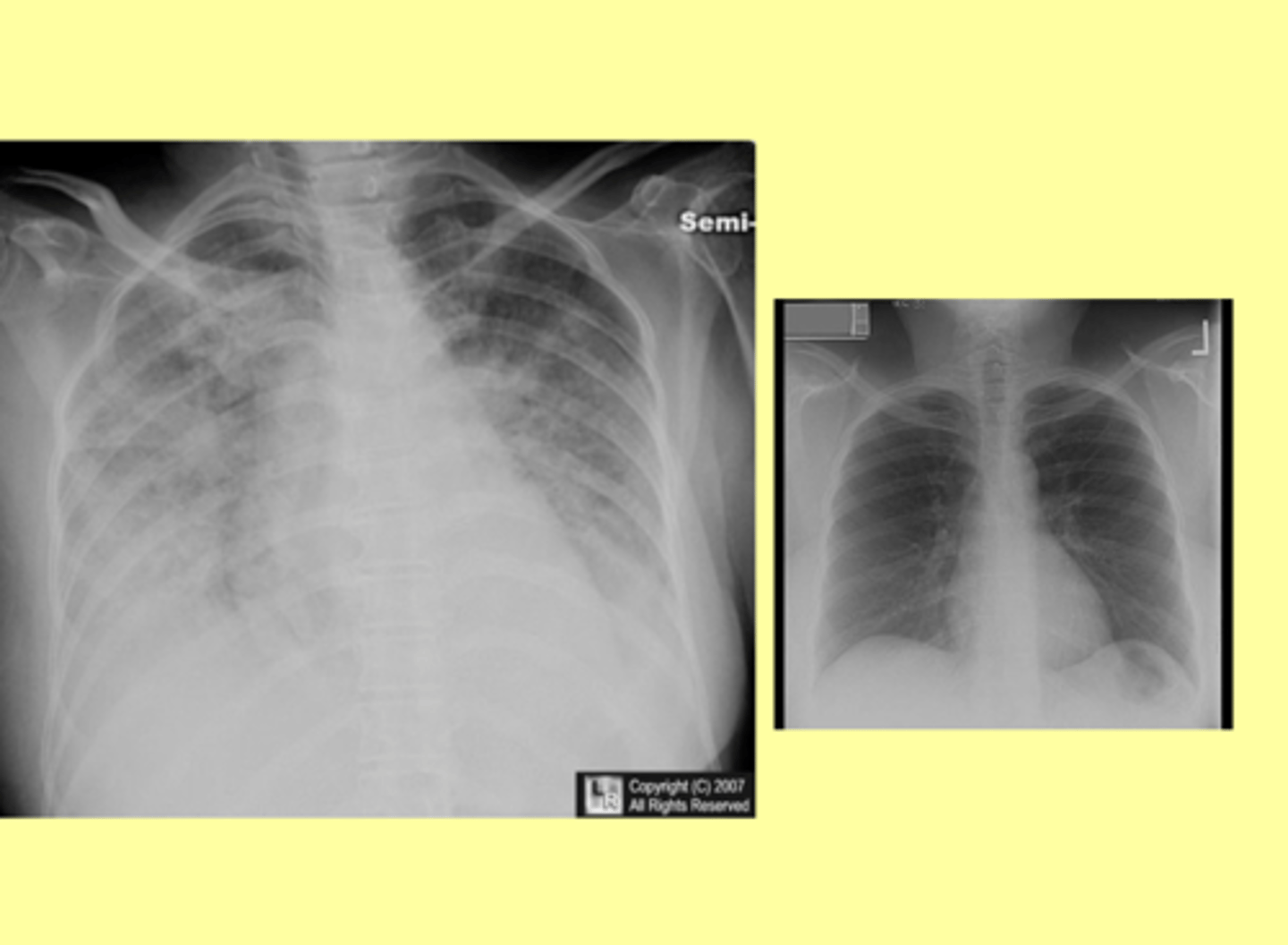
prevention of pulmonary edema
•Easier to prevent than treat
•Assess for early indicators
early stages of pulmonary edema you need to
•Upright position
•Legs dependent
•Eliminate overexertion
•Minimize stress
Patient education
pulmonary edema medical management
•Correct the underlying disorder
goals for medical management
•Reduce volume overload
•Improve ventricular function
•Increase respiratory exchange
what interventions do you do
-oxygen
-diuretics
-Vasodilators
-nursing actions
Oxygen Therapy
•Relieve hypoxemia and dyspnea
•NRB
•NIPPV
•Endotracheal intubation
•Mechanical ventilation
Diuretics
•Loop diuretic (IV)
•BP monitoring
•U/O monitoring
•I/O
•Daily weights
•Electrolytes
Vasodilators
•IV nitroglycerin
•IV nitroprusside
•Monitor BP
Nursing Management
•Upright
•Legs dangling
•Psychological support
•Monitoring medications
nursing management pt 2
•Assisting with intubation
•Administer oxygen/monitor hypoxia
•Administer and monitor response to medication
•I/O
•VS
•N/V
•EKG monitoring
•Electrolytes
•Position to promote optimal circulation
•Provide psychological support