Hydrocarbons and Isomerism
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Similarities and Difference Between Alkenes and Cycloalkanes
Both have the same molecular formula. Alkenes have at least one double bond in their structure while cycloalkanes have only single bonds.
Another name for Alkanes
Paraffin
Chemical Property of Alkanes
Least reactivity and the chemical process is mainly combustion
Reacts with oxygen to produce heat, carbon dioxide and water (combustion reaction)
They undergo substitution reaction
Substitution reaction
Reaction in which an atom is replaced with another
Addition reaction
Reaction in which an atom is added to the molecule
Chemical Reactions of Alkenes nd Alkynes
Hydrogenation
Halogenation
Hydrohalogenation
Hydration
Physical properties of Hydrocarbons
they are non polar
they are odourless and colourless
Their boiling and melting points increases with increasing molecular weight
Factor that affect boiling melting points of hydrocarbons
The branching in organic compounds reduces the melting and boiling point.
Least dense Hydrocarbon
Alkane
Isomerism
The concept where compounds with different structures have the same molecular formula
Types of Isomerism
Constitutional/ structural Isomerism
Stereoisomerism
Constitutional/ Structural Isomers
These compounds have the same molecular formula but different atomic arrangements
They have different IUPAC names
The compounds may have the same or different functional groups
They have different chemical and physical properties
Some types of Constitutional Isomerism
Positional Isomerism
Functional Isomerism
Chain or skeletal Isomerism
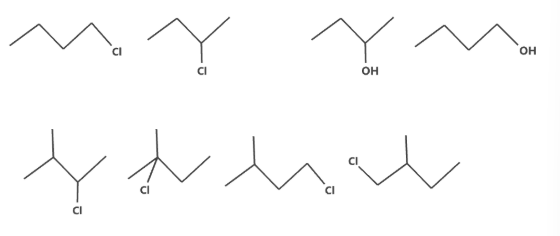
Positional Isomerism
These are the isomers with the same functional groups but at different positions in the molecular structure
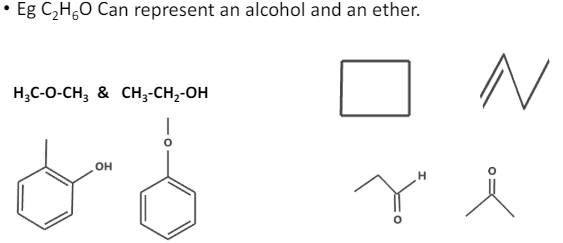
Functional group isomerism
these are the isomers with different functional groups
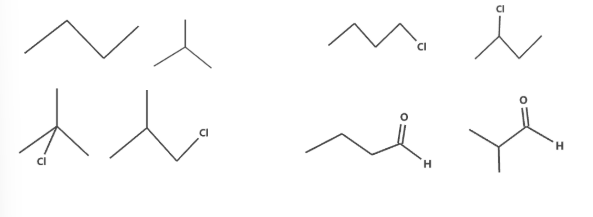
Chain or skeletal isomerism
These are isomers that have the same functional groups, molecular formula but different carbon structures
Stereoisomerism
This refers to compounds that have the same molecular formula and connectivity but have different arrangements of atoms in three dimensional space
Types of Stereoisomerism
Conformational Isomerism
Optical Isomerism
Geometric Isomerism
Conformational isomerism
This type of isomerism arises due to the rotation of a single carbon-carbon bond
Types of Conformational Isomerism
staggered conformation, eclipsed conformation
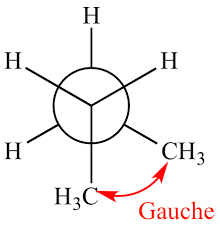
Staggered conformational Isomerism
This is the most stable type of conformation
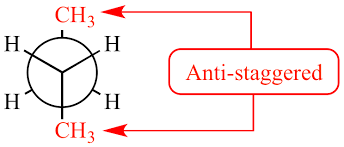
Anti Staggered conformational Isomerism
In this staggered conformation bulky groups such as methyl and halogens are placed 180 degrees apart from each other.
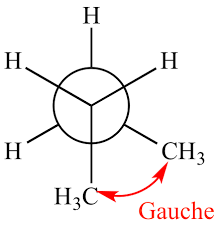
Gauche staggered conformation
In this staggered conformation bulky groups such as methyl and halogens are placed 60 degrees apart from each other.

Eclipse conformation
this is the least stable conformation isomerism
Geometric Isomerism
This is the type of isomerism where the order of atom bonds in the isomers are the same but different in a three dimensional plane
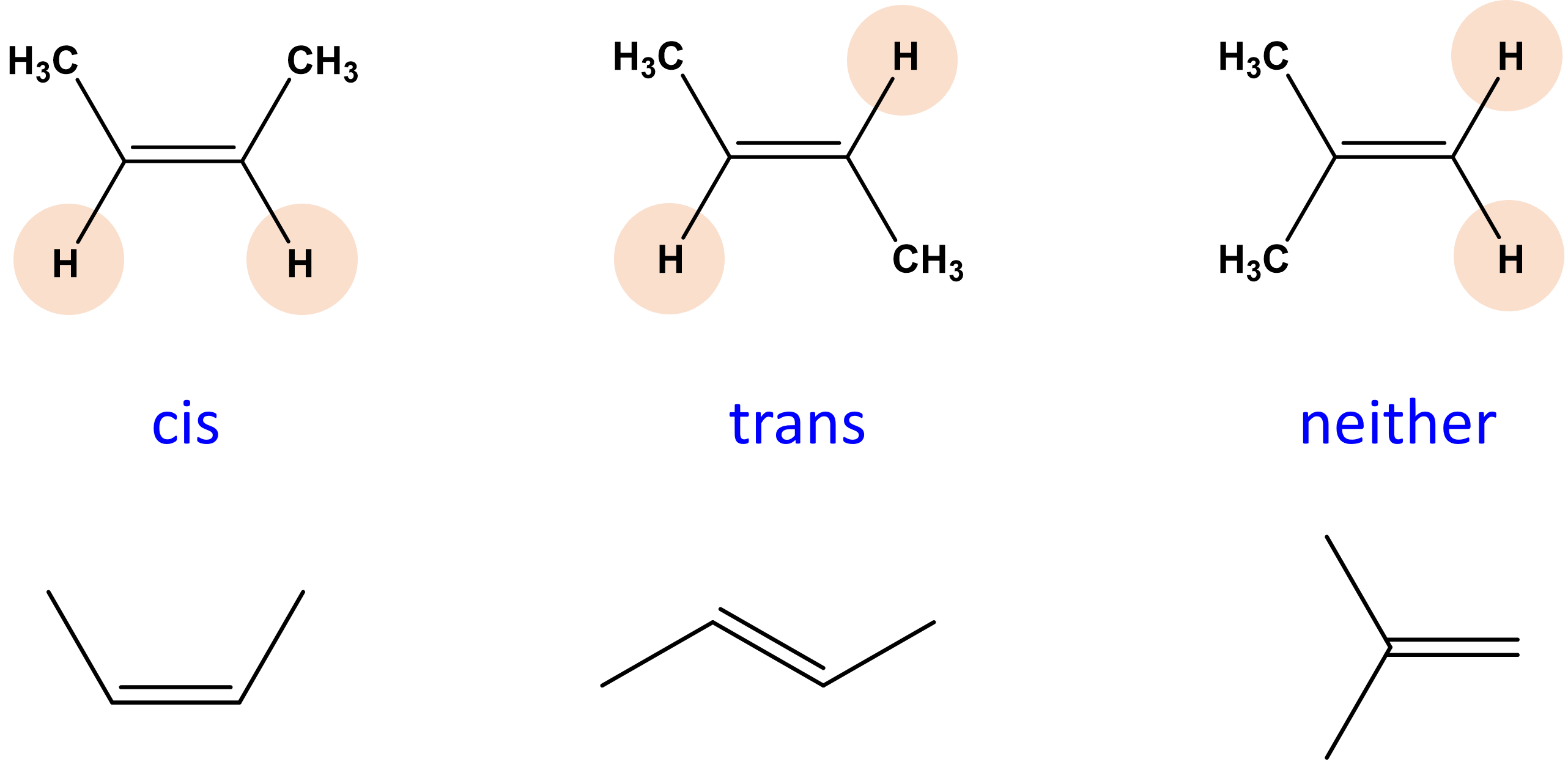
Cis Isomer
polar molecules of the same atoms that are on the same side of double bonds.
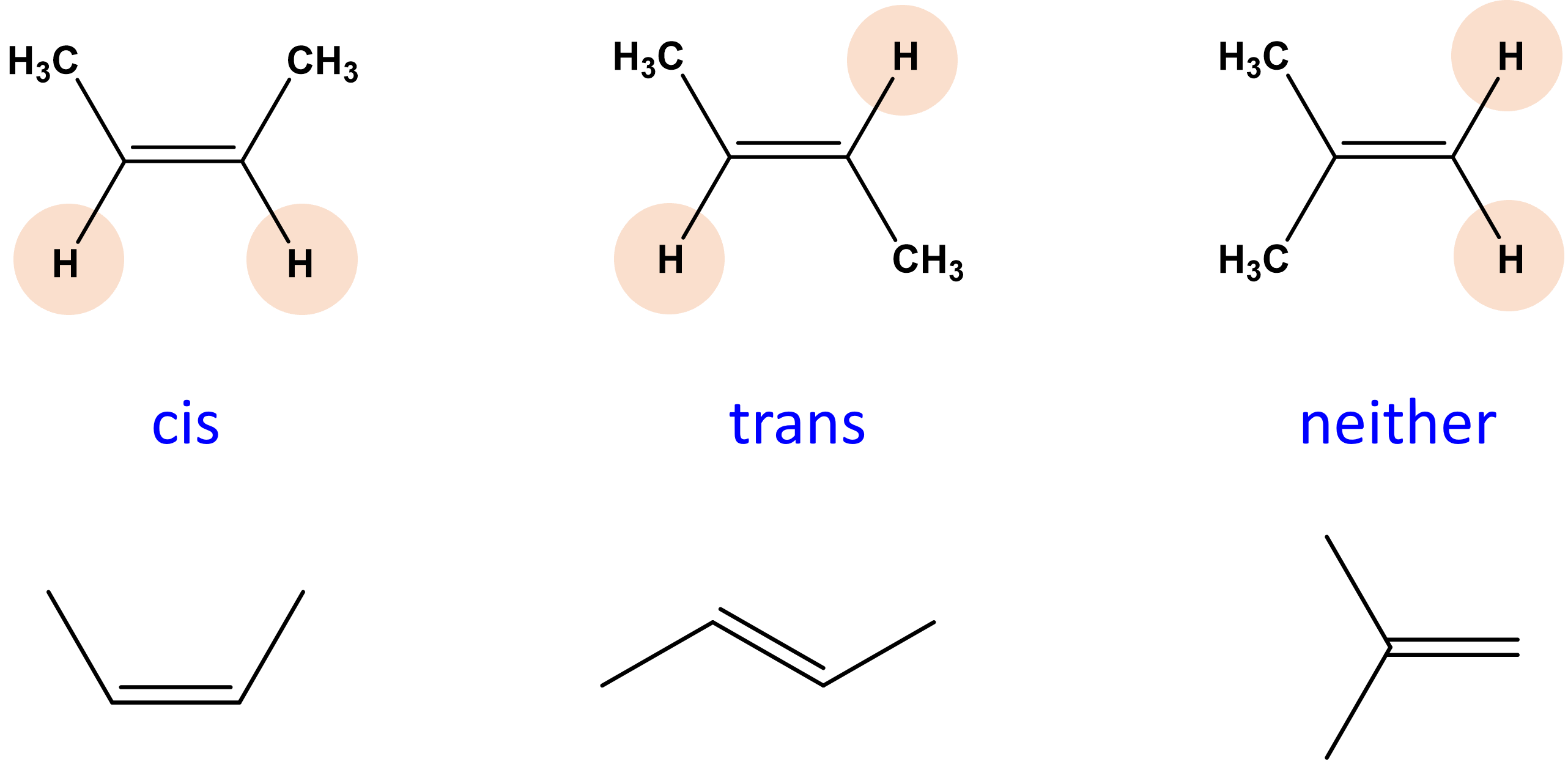
Trans isomer
a non polar isomer in which the functional groups are located on the other sides of the double bond
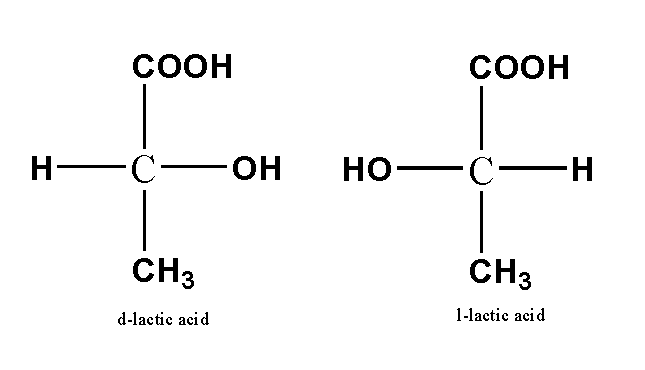
Optical Isomerism
This is the type of isomerism where two stereoisomers are related to each other by a reflection
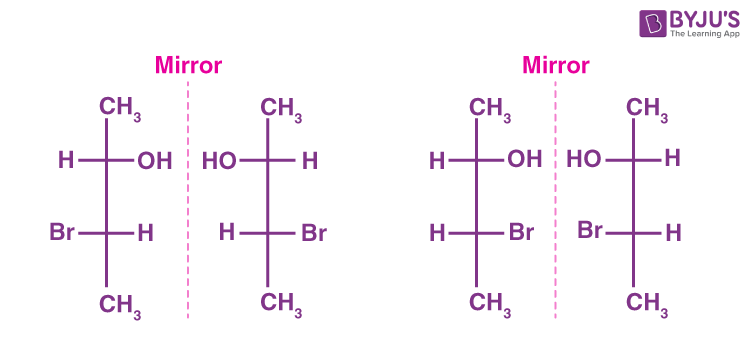
Enantiomers
Two compounds with the exact same connectivity, that are mirror images of each other but that are not identical to each other
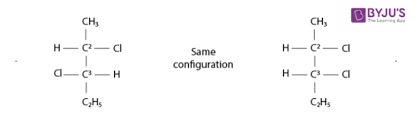
Diastereomers
wo molecules which are stereoisomers (same molecular formula, same connectivity, different arrangement of atoms in space) but are not enantiomers