Pre-midterm highlights
1/211
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
212 Terms
4 types of mineralization throughout body
metastatic
dystrophic
idiopathic
neoplastic

what are the timelines for
lytic changes
productive changes
lytic - 5-7 days to see on rads
productive - 10-14 days to see on rads
what percent of bone loss present to see on rads
30-60%
6 criterial for eval non-agg vs agg lesion
location of # of lesion
pattern lysis
pattern new bone
cortical disruption
transition zone
change in appearance over time
osteoporosis
loss of bone mass
osteomalacia
loss of mineralization of bone matrix (quality of bone bad)
what tumors affect axial vs appendicular skeleton
primary bone tumors - appendicular
mets - axial (ribs and vertebrae)
what conditions can be seen epiphysis, metaphysis, diaphysis of bone
epiphysis - juvenile bacterial osteomyelitis
diaphyseal - metastatic tumor
metaphyseal - juvenile bacterial osteomyelitis, mets, primary bone tumors, fungal osteomyelitis
what types of lysis are benign vs agg
benign - geographical
agg - moth eaten, permeative
periosteal rxn in order from least to most agg
smooth - callus
lamellated - onion skin
columnar - palisading
spiculated/sunburst
amorphous -disorganized spikey
active vs inactive lesion
active = fuzzy
inactive = more sharp
how do we assess duration of lesion
opacity of rxn
immature - dull and bone like
mature - bright
which transition zone is agg vs benign
short transition - benign
long transition - agg
4 OCD lesion locations in the dog
cd humerus
medial humeral condyle (elbow)
lateral femoral condyle (knee)
medial trochlear ridge (ankle) - worst prognosis
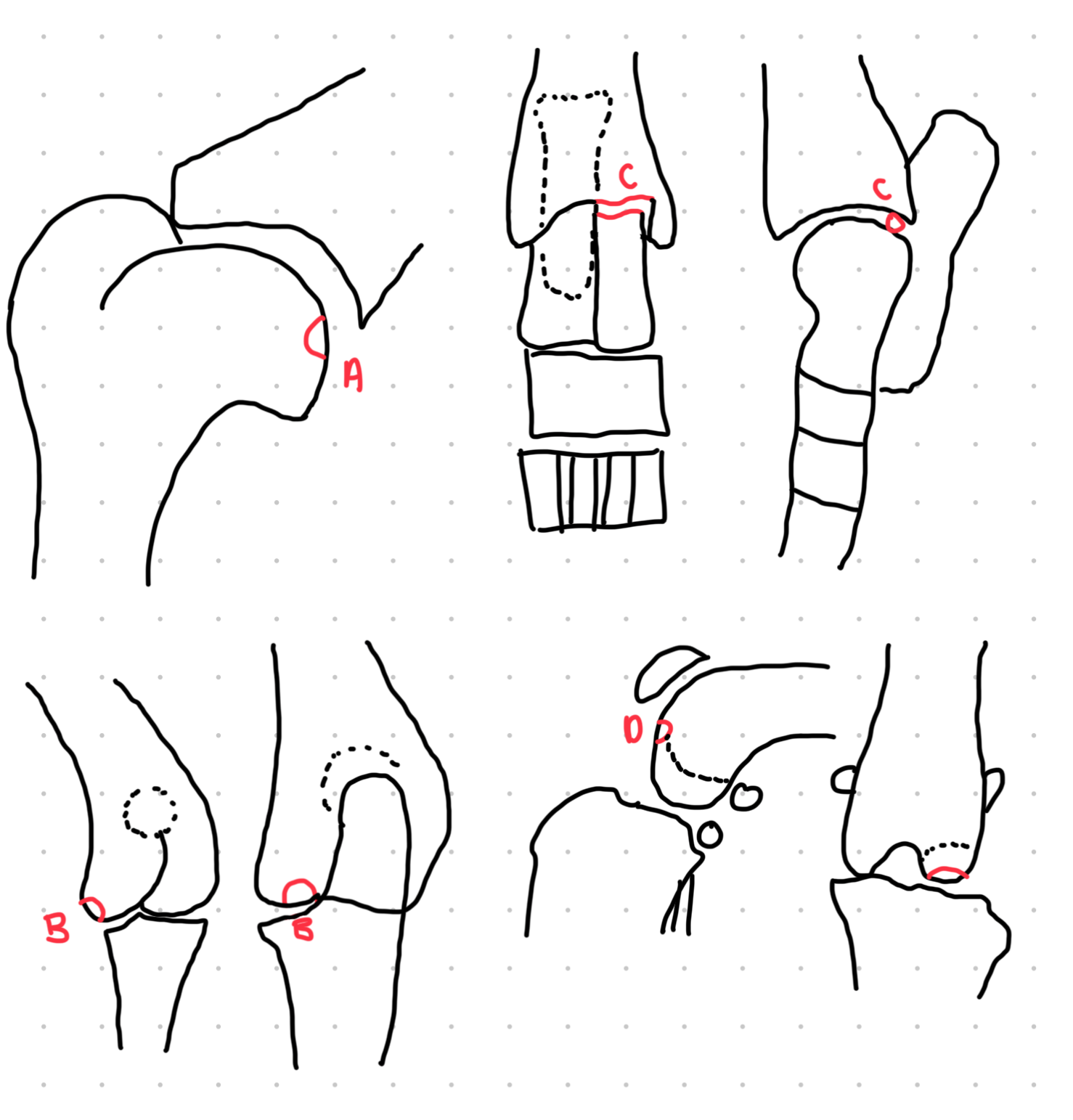
which OCD lesions are these in the dog
A = cd humerus
B = medial humeral condyle (elbow)
C = medial trochlear ridge (ankle)
D =lateral femoral condyle (knee)
Dog OCD signalment
young giant breed (6-9 mo age)
FCP signalment
young (5-12 mo) medium large breed, male
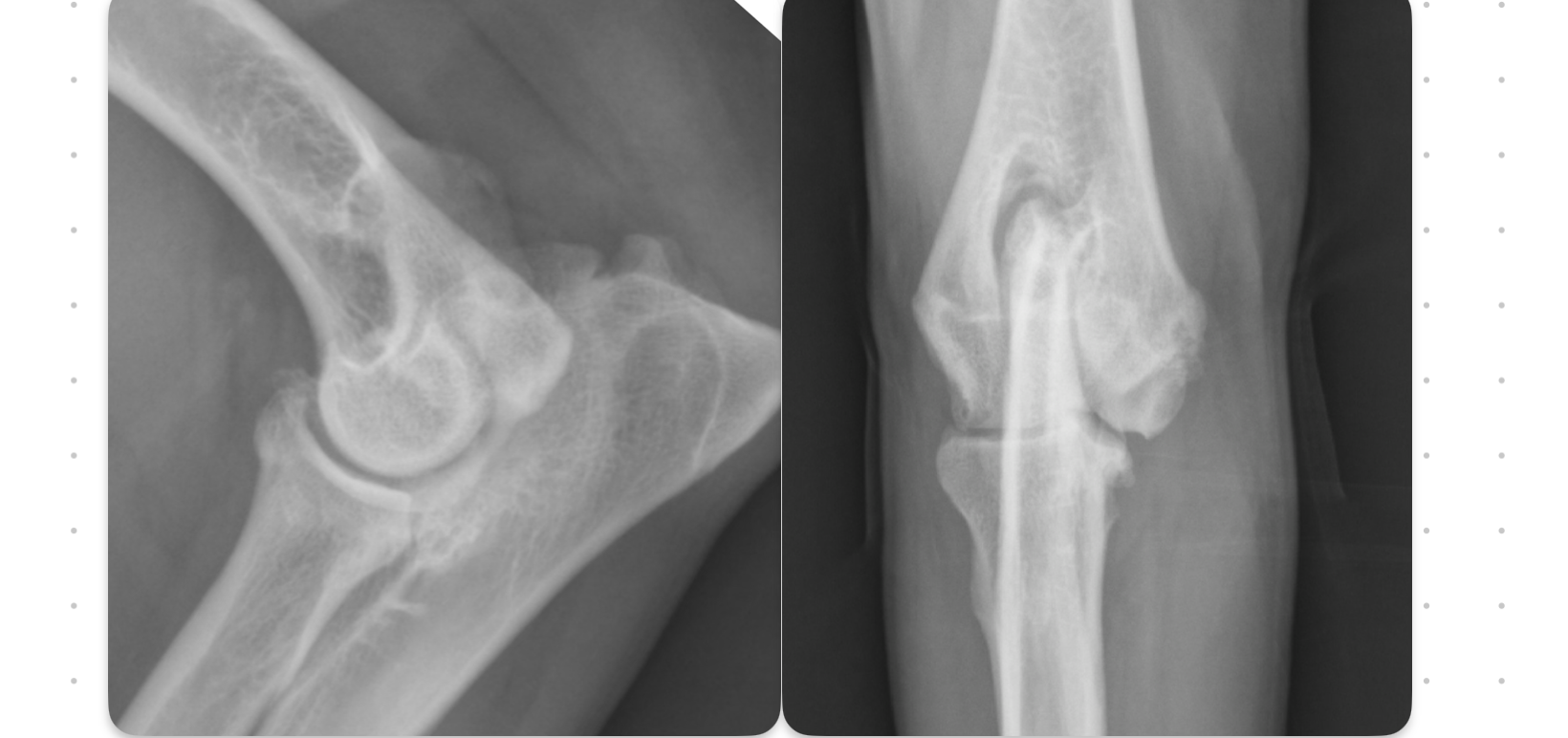
FCP
blunted wedge of medial coronoid
little bite taken out of condyle on cr/cd view
UAP signalment
GSD, large breeds, basset hound
5-12 mo age
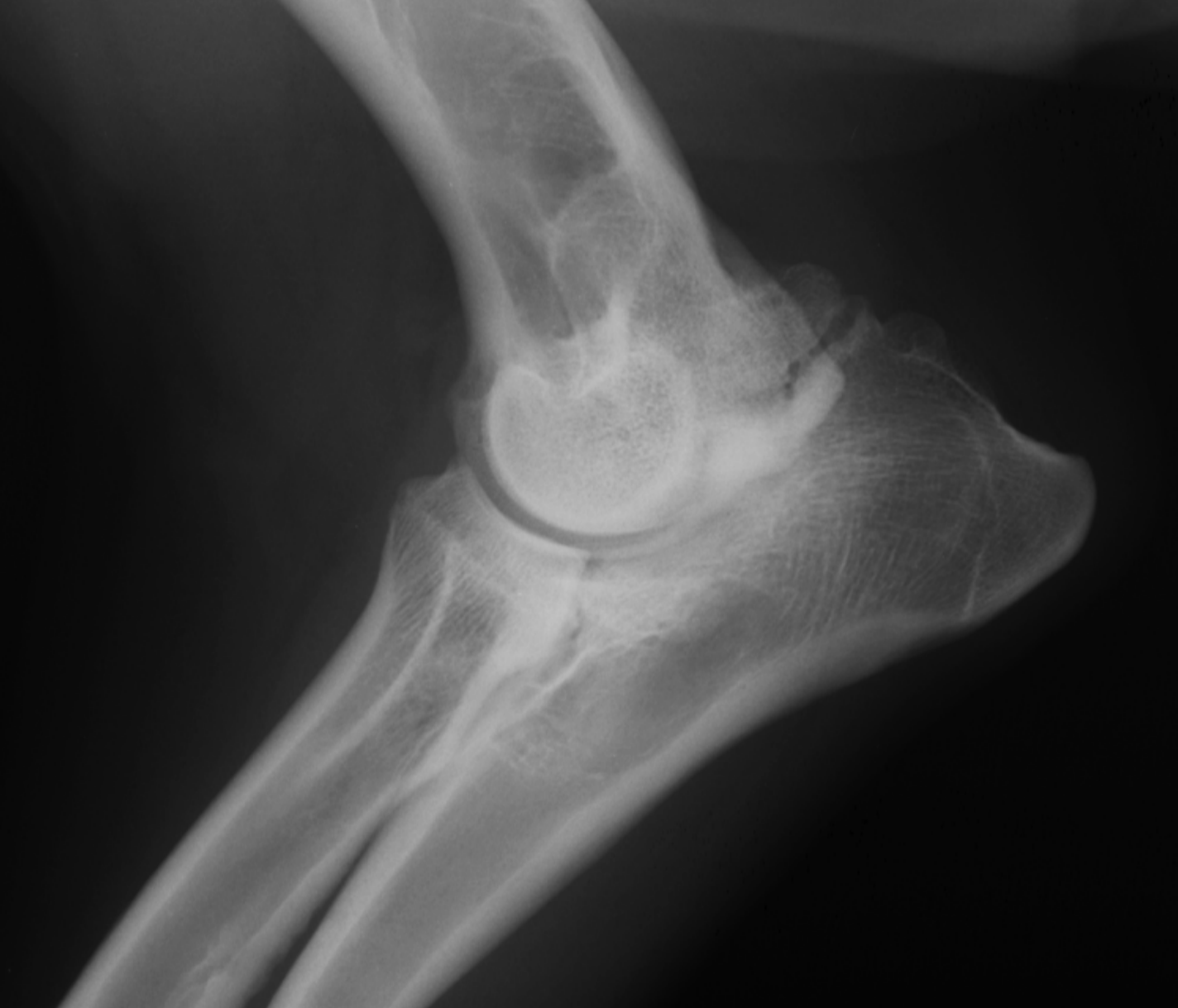
UAP - would see this better on a flexed view
UME signalment
Labradors, GSD, english setters
6 - 12 mo age
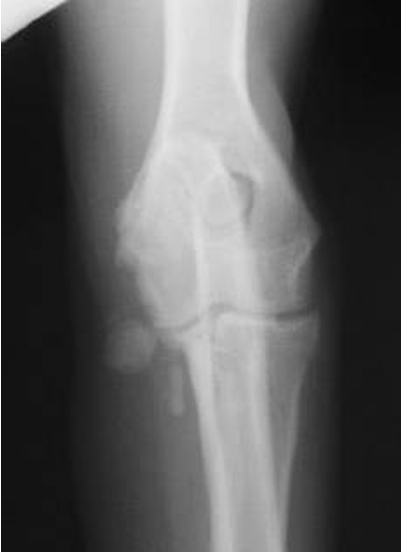
UME
look for thing off to the side of medial epicondyle
panosteitis signalment
5-18 mo → 7 yrs
large giant breeds - GSD, doberman, Retriever, basset hounds
shifting leg lameness and pain palpating long bones
NO lysis
cigarette smoke
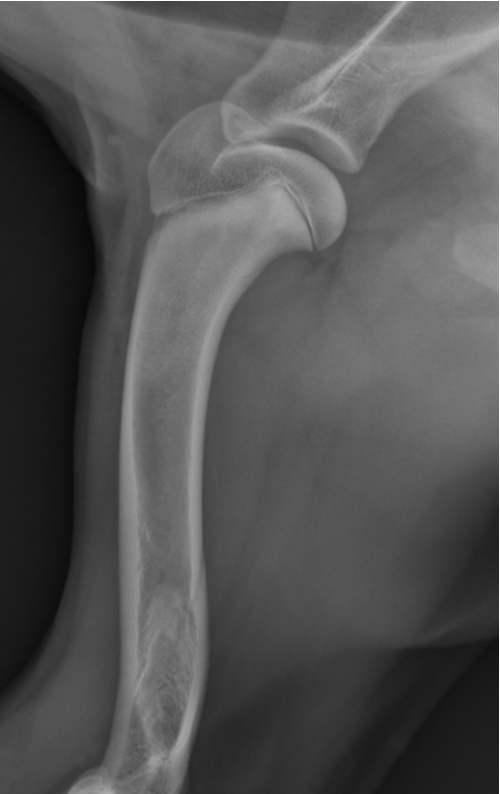
panosteitis
panosteitis
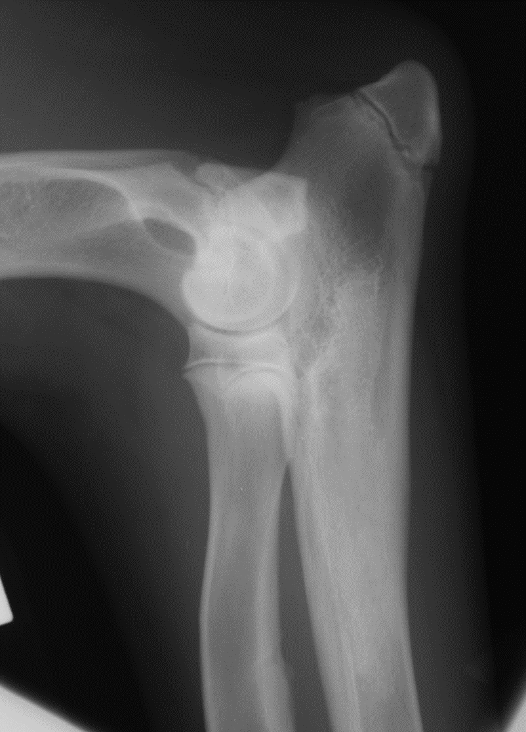
Metaphyseal osteopathy signalment
2-7 mo age
large giant breeds
systemically ill
bilateral/all 4 limbs
double physeal sign ± cuff
Metaphyseal osteopathy

Metaphyseal osteopathy
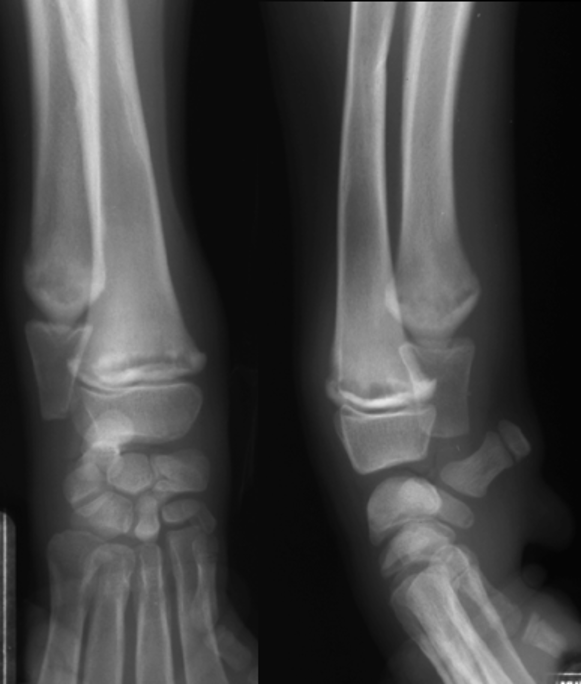
retained cartilaginous core signalment
6-12 mo age
large giant breeds, saint bernards
OC of distal ulnar metaphysis/physis
often bilateral and incidental
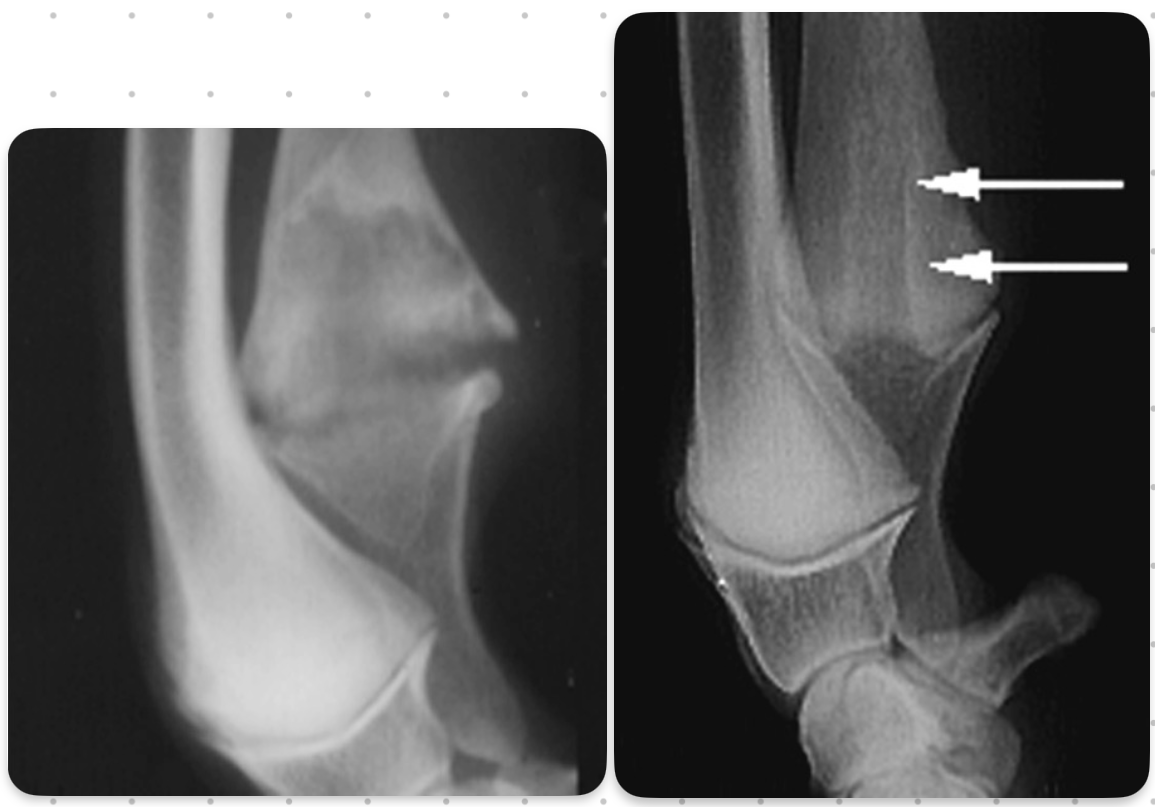
retained cartilaginous core
2 parallel lines with Lucent in the middle going towards the ulna
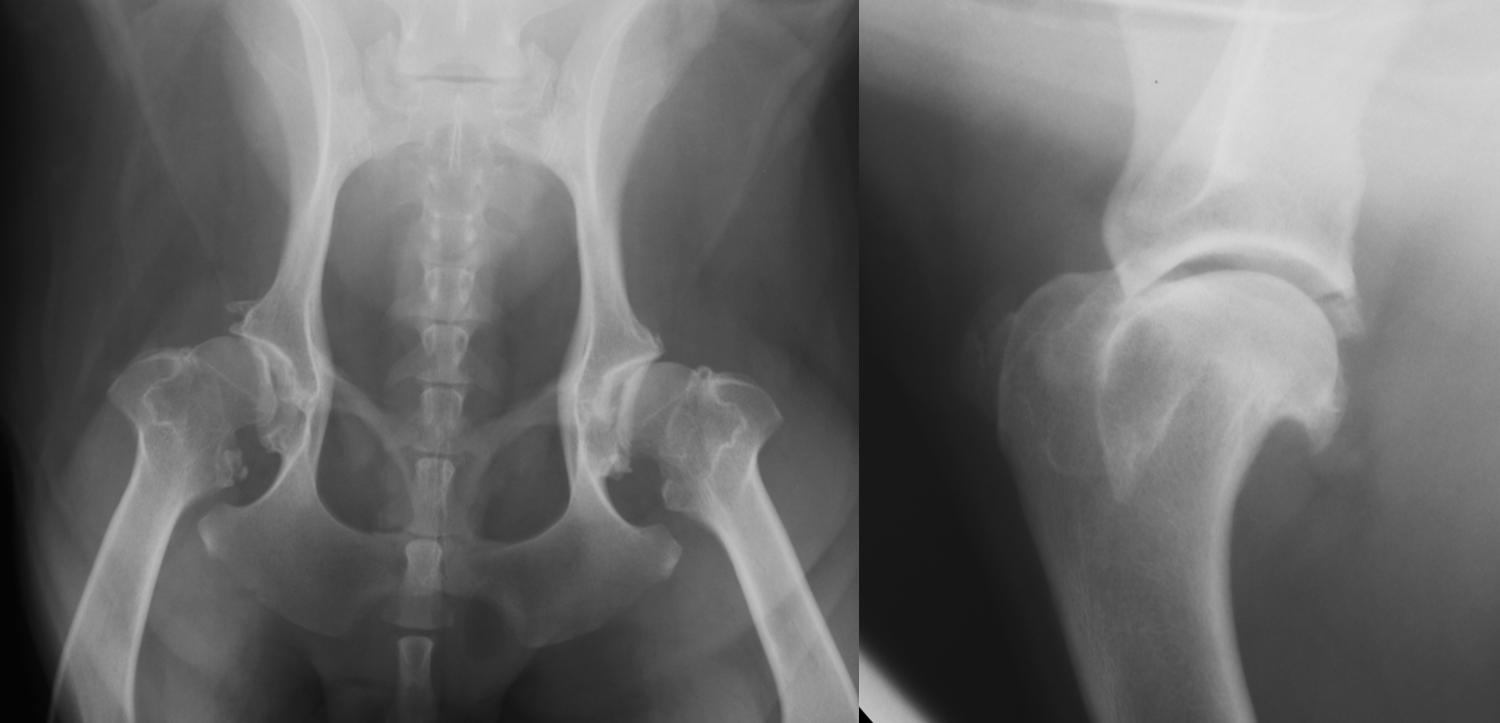
hip dysplasia signalment
large breed dogs
bilateral - inherited
flattened acetabulum, bad femoral head coverage, osteophytes along rim, morgans line
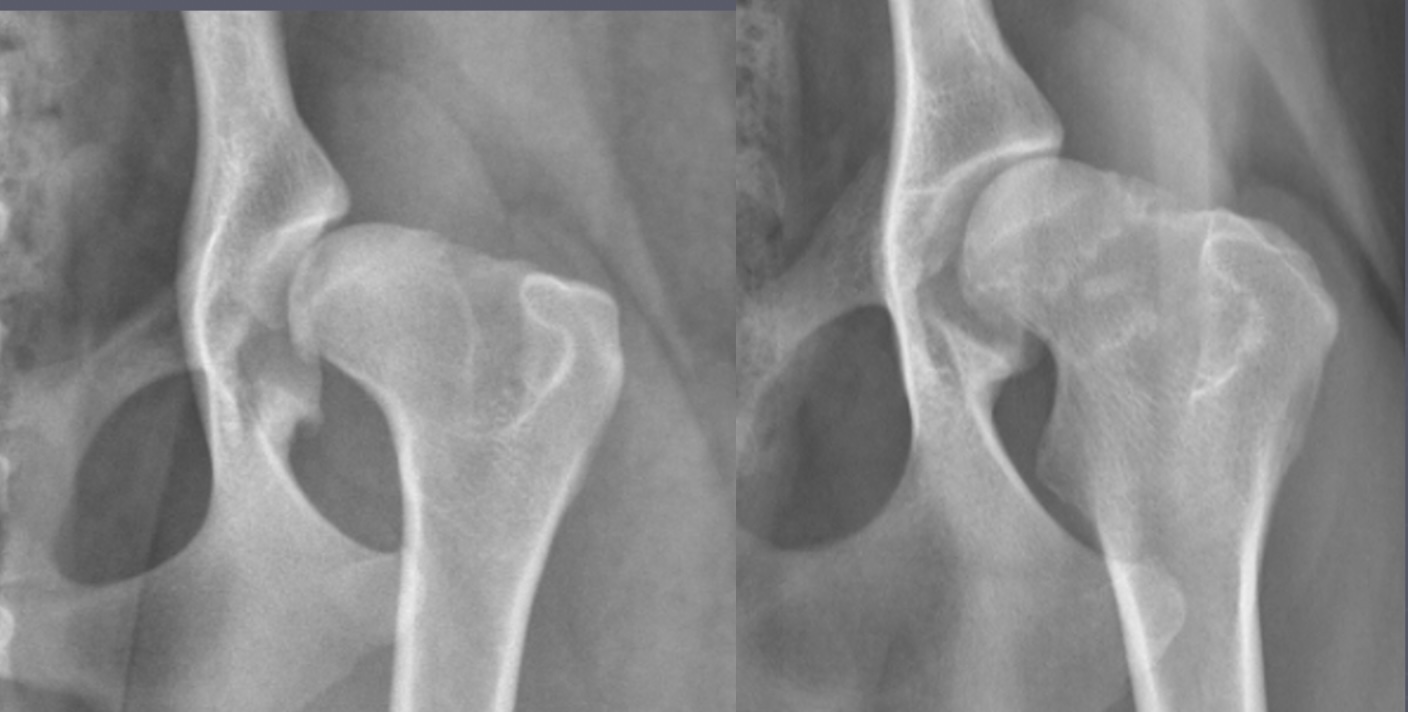
hip dysplasia

morgans line - early sign of DJD
what are the 3 views PennHip wants for hip dysplasia
extended leg VD
compression VD
distraction VD
calve legg perthes signalment
immature toy/small dogs
unilateral
increased joint space, irregular femoral head
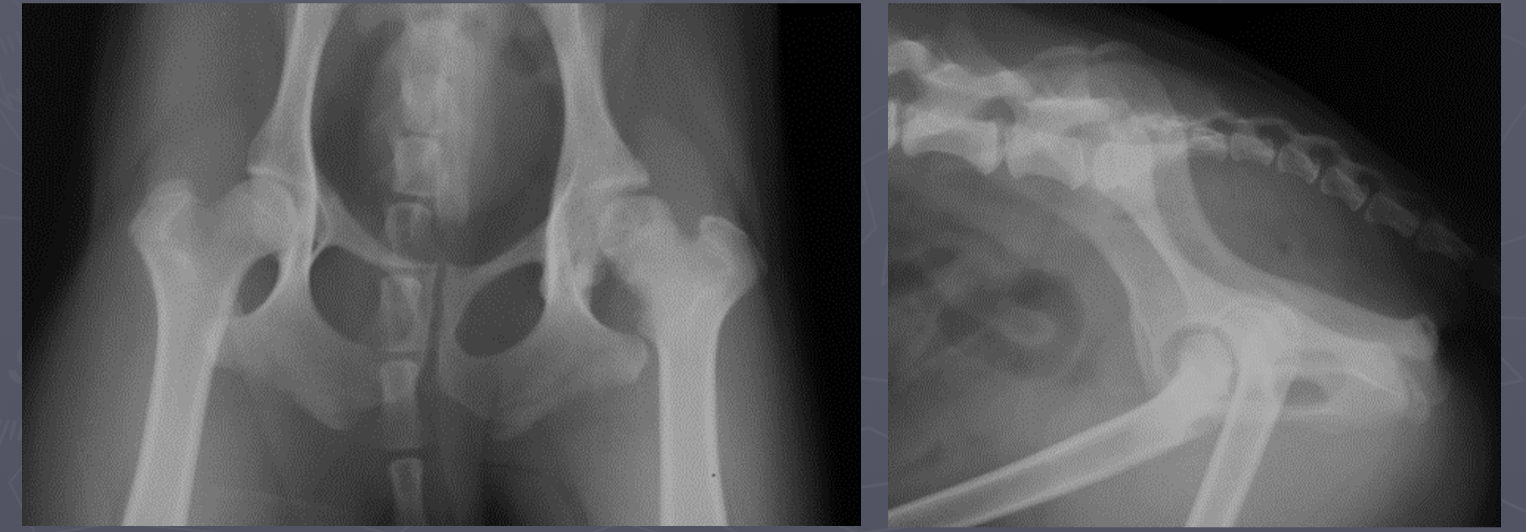
calve legg perthes
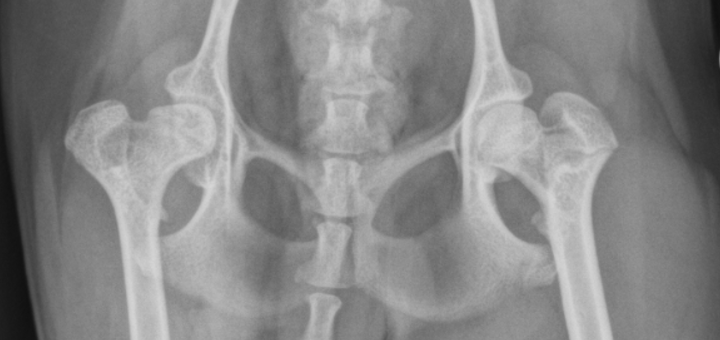
calve legg perthes
medial patellar luxation signalment
young small breed dogs
lateral is a large dog thing
congenital mostly from bow leg (coxa vara)
shallow trochlear groove
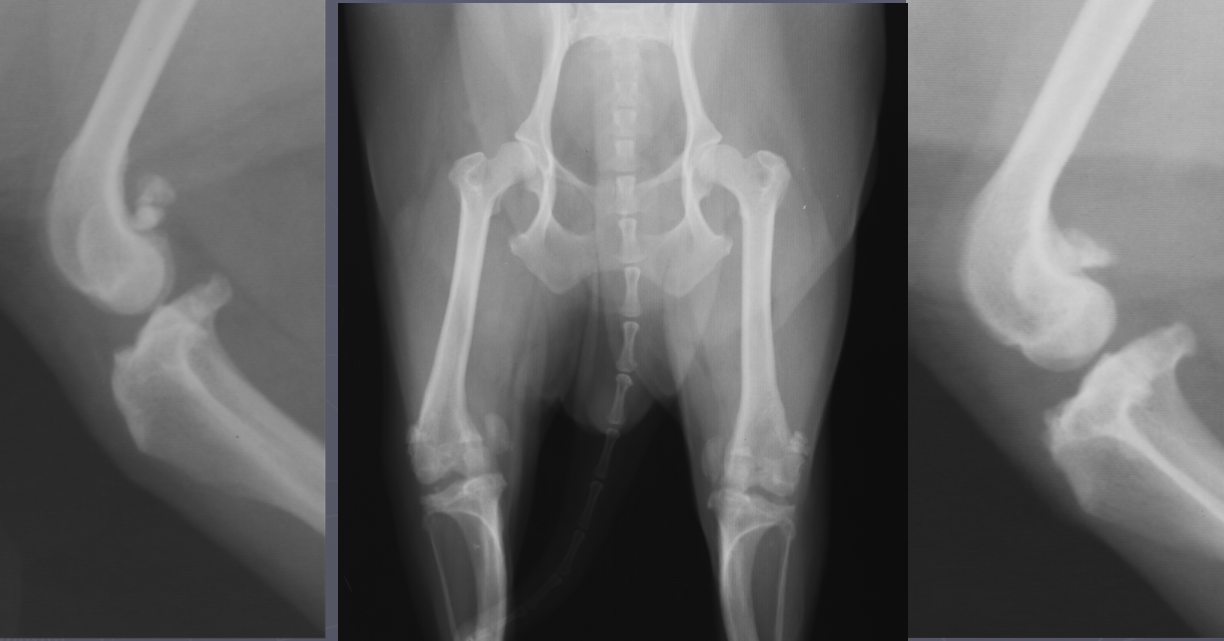
medial patellar lux
do luxating patellas contribute to DJD in the future
nope, happens outside the joint capsule
hypertrophic osteopathy signalment
middle to older dog
secondary to thoracic or abdominal dz/mass
spares small bones of carpus and tarsus
starts from MC/MT bones and goes up the leg symmetrically and bilateral
NO lysis but LOTs of periosteal rxn
AGG lesion
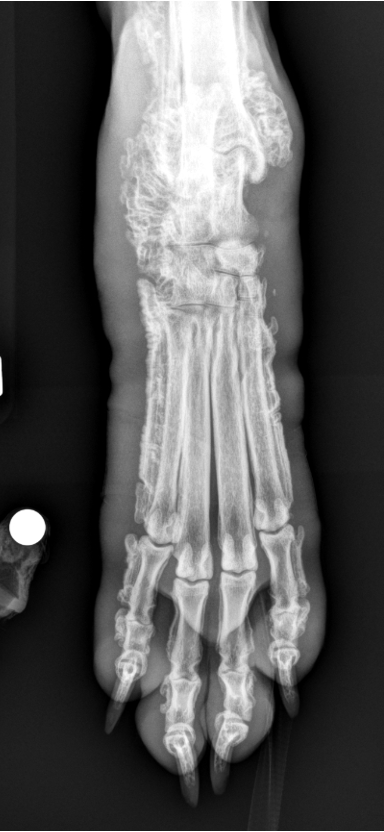
Hypertrophic Osteopathy
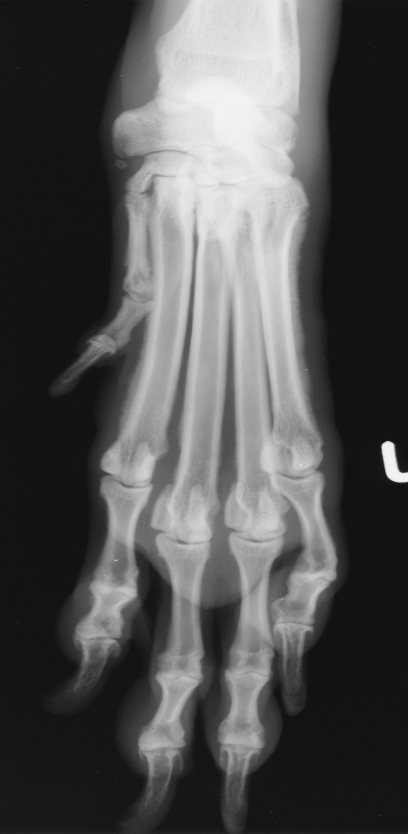
Hypertrophic Osteopathy
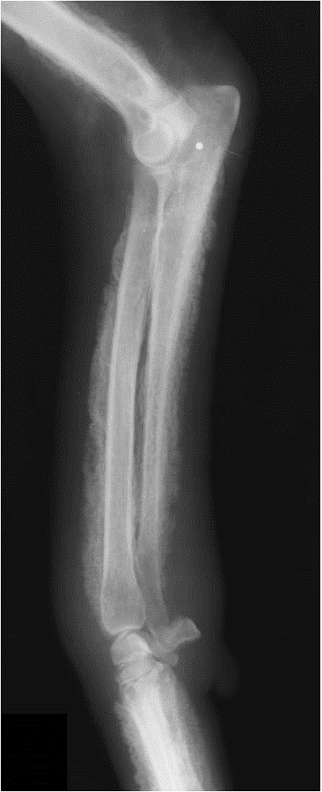
Hypertrophic Osteopathy
signalment for fungal osteomyelitis
systemically ill
young to middle age
large working/sporting breeds
polyostotic
lysis and production
metaphysis
AGG lesion

fungal osteomyelitis

fungal osteomyelitis
bacterial osteomyelitis signalment
hx of bite wound or soft tissue injury
adult animal
diaphysis
polyostotic
lysis and periosteal rxn
can be surrounding implant
AGG lesion
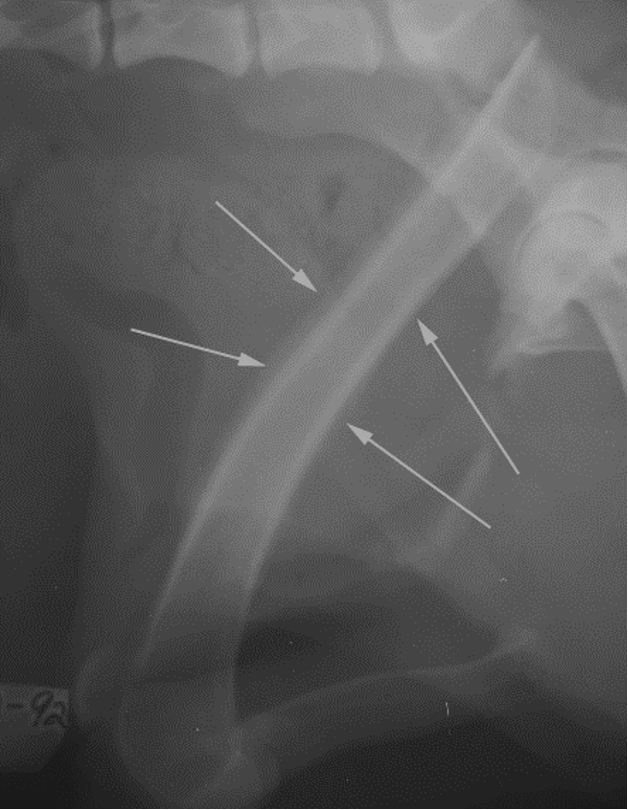
bacterial osteomyelitis
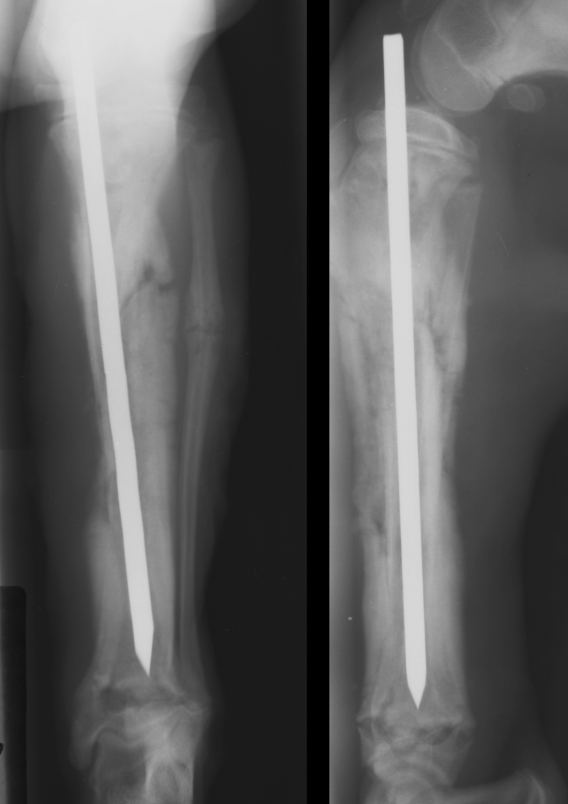
bacterial osteomyelitis
primary bone tumor signalment
large/giant dogs
bimodal age distribution
males
lung mets
monostotic - no cross joint
OSA - away from elbow, towards knee, distal tibia
AGG lesion
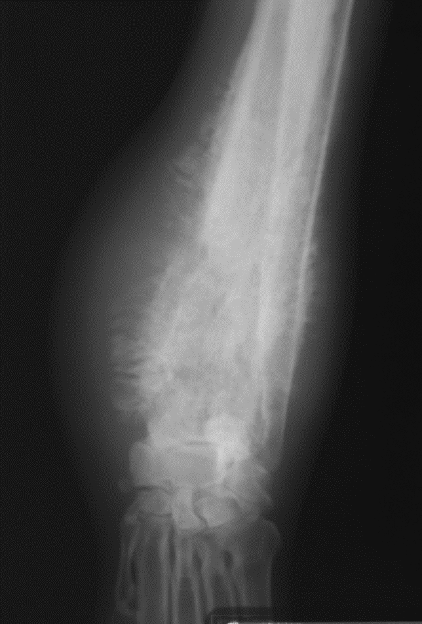
primary bone tumor
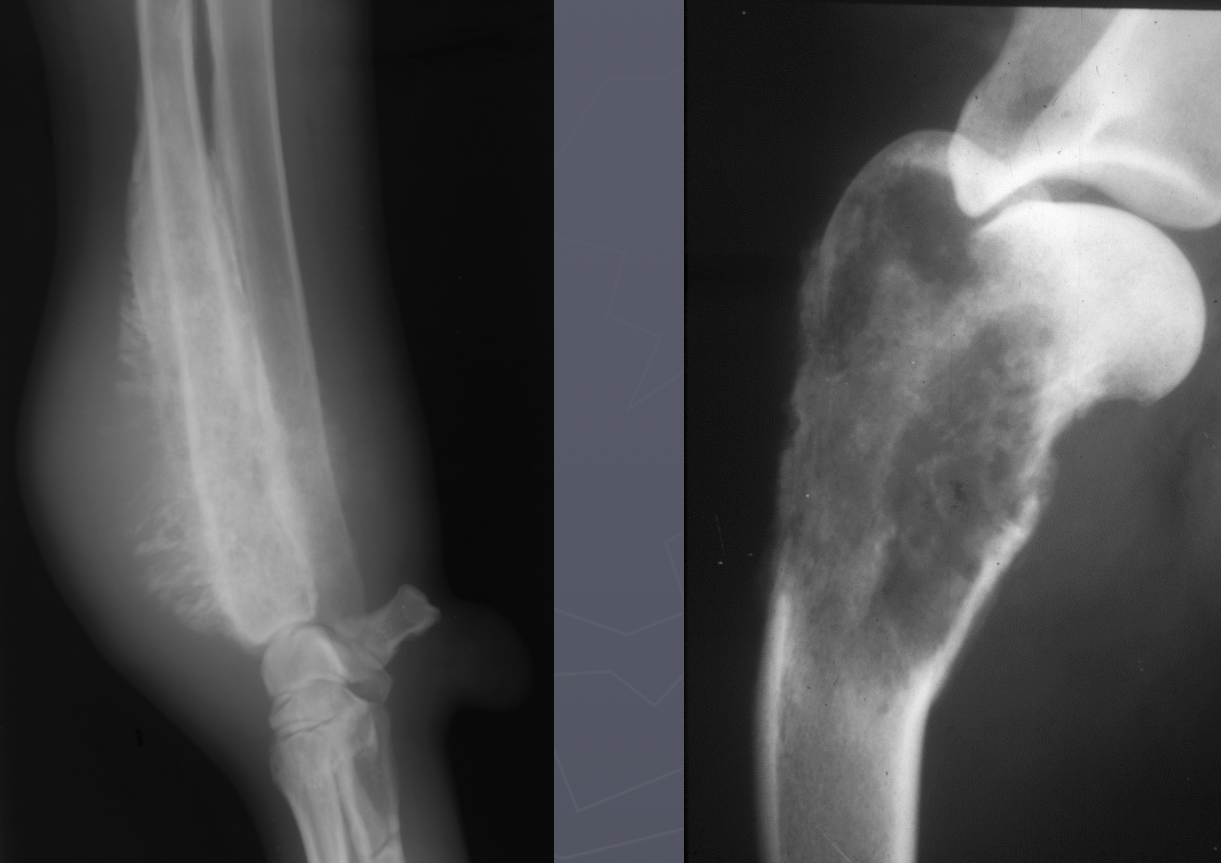
primary bone tumor
Salter harris fx classification
S - same
A - across
L - low
T - through
R - rammed/compressed
premature distal ulnar physis closure roentgen signs
gap - ulna and humerus, and gap at the bottom of ulna and carpus
cranial bowing of radius
premature distal radius physis closure roentgen signs
gap - radius and humerus, radius and carpus
no real ALD
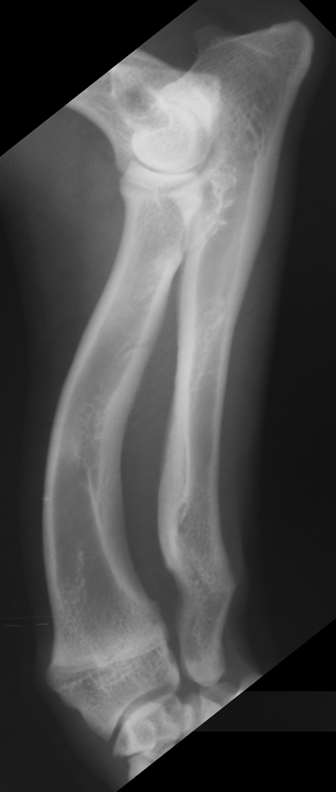
which physis closed early
ulna
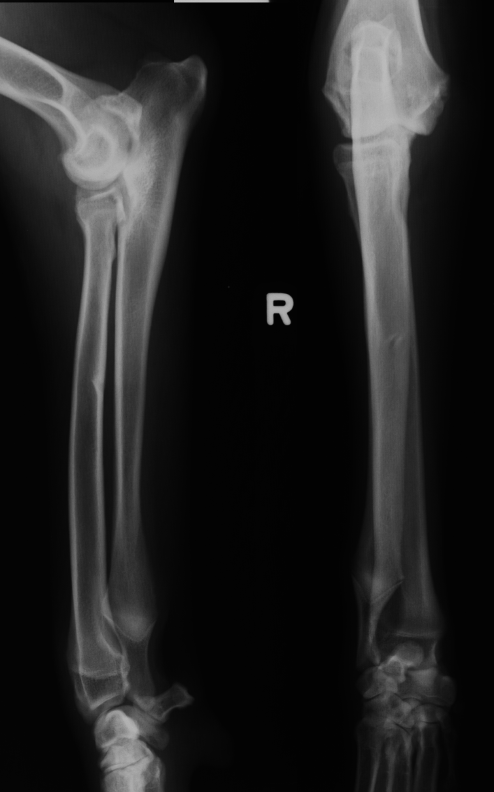
which physis closed early
radius
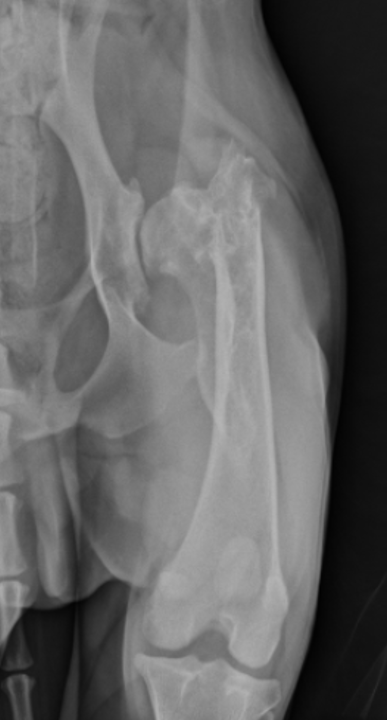
malunion
just looks wonky
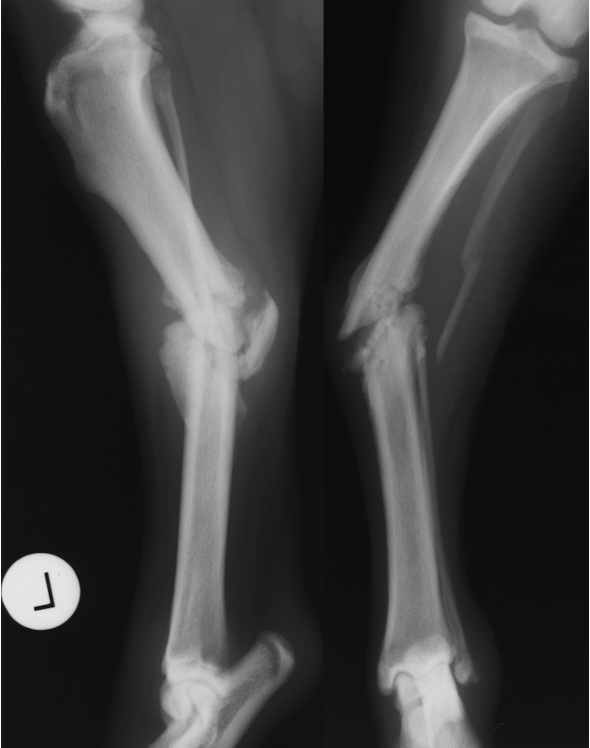
14 wks later
delayed union
taking longer than 12 wks
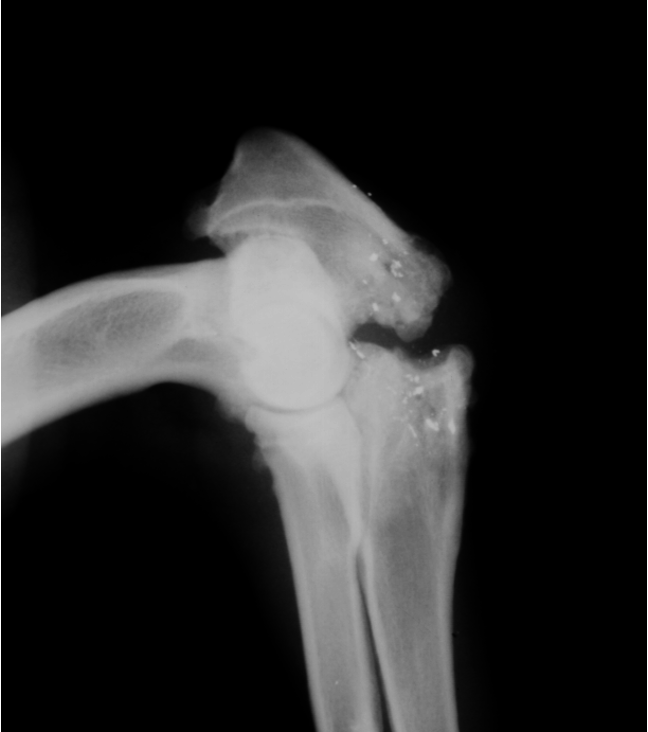
non-union
never got back together
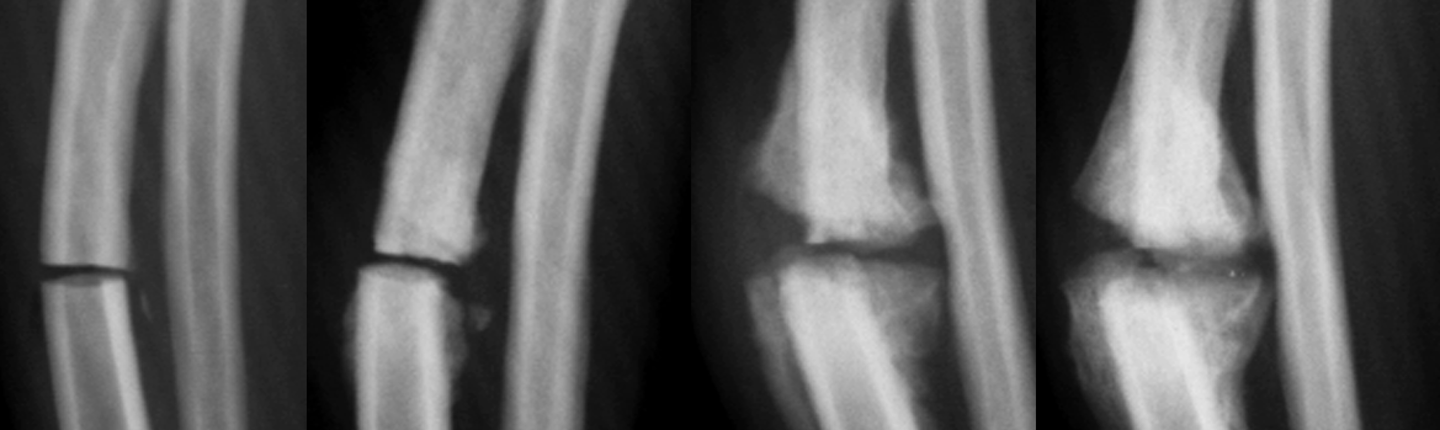
hypertrophic non-union
its trying but failing to close the gap
oligotrophic non-union
gave up closing the gap
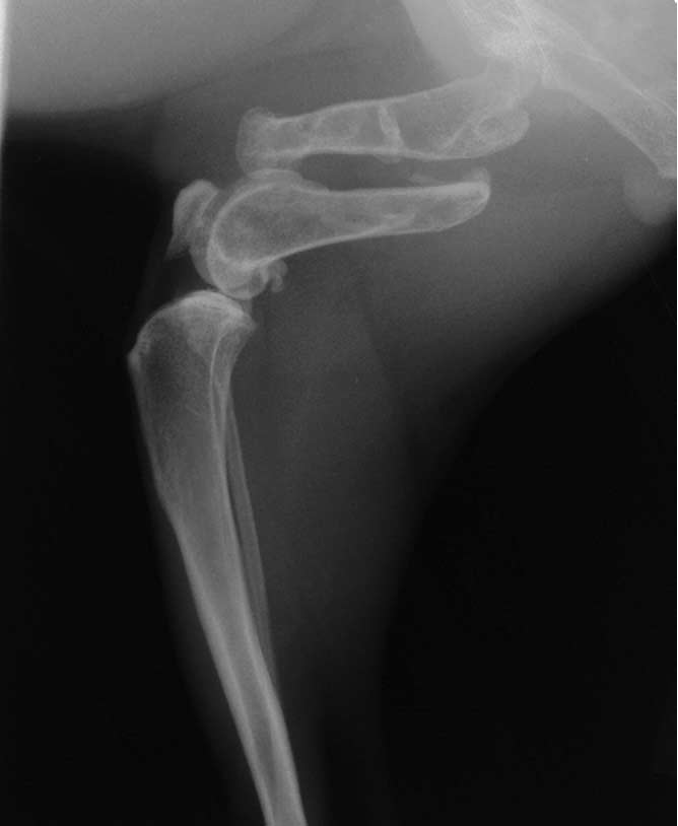
hallmark signs of DJD in dogs
intracapsular swelling
NON-aggressive changes
osteophytes
small joint space on weight bearing views

DJD
DJD
CCL rupture signalment
females
young athletic dogs and middle age overweight dogs
acute, non-wt bearing lameness or insidious onset
tibia displaced cr. , intracapsular swelling
displace fat pad
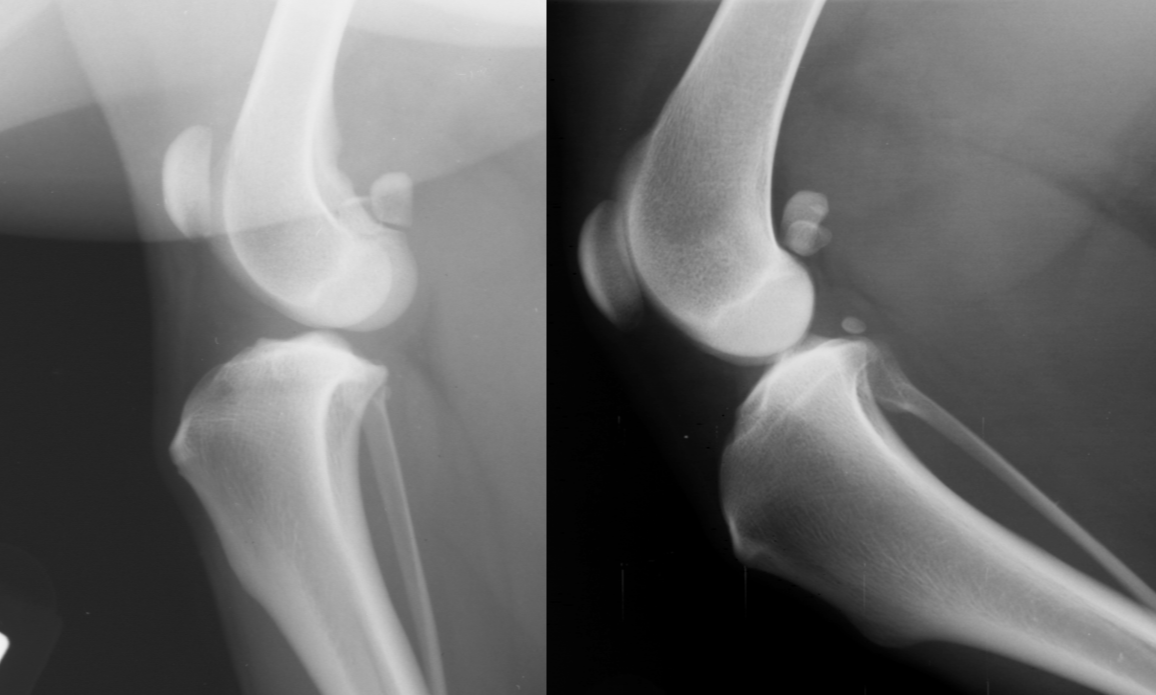
CCL rupture
septic arthritis signalment
systemic infected/ill or hx of direct injury
AGG lesion
soft tissue swelling
lysis with periosteal rxn
central on joint
multiple joint surfaces
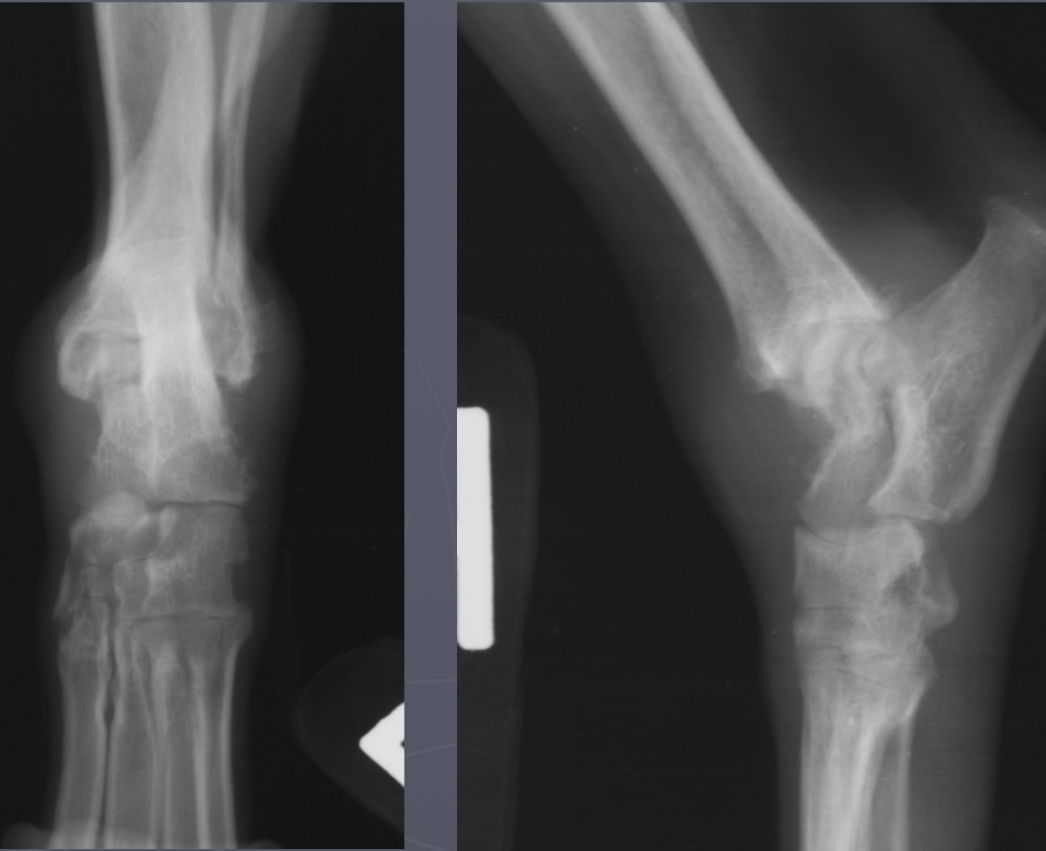
septic arthritis
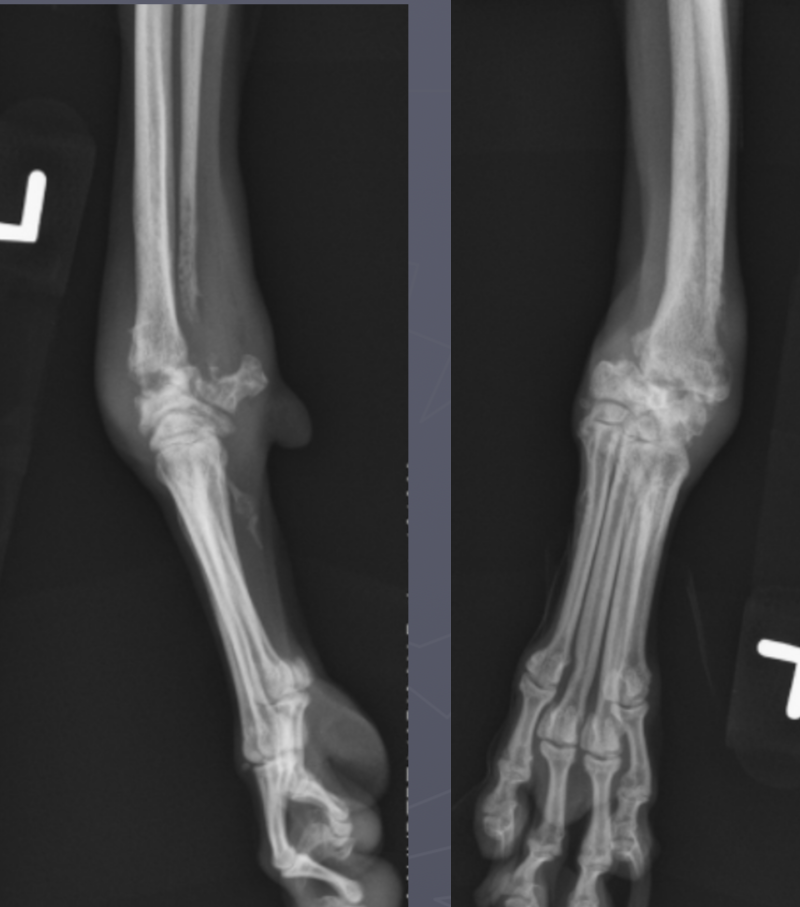
septic arthritis
erosive polyarthritis/rheumatoid arthritis signalment
AGG lesion
small breeds -shetland sheepdog and poodle
greyhounds
cats get a proliferative polyarthropathy
swelling, cyst like lucencies, destroyed joint surface
± multiple bones
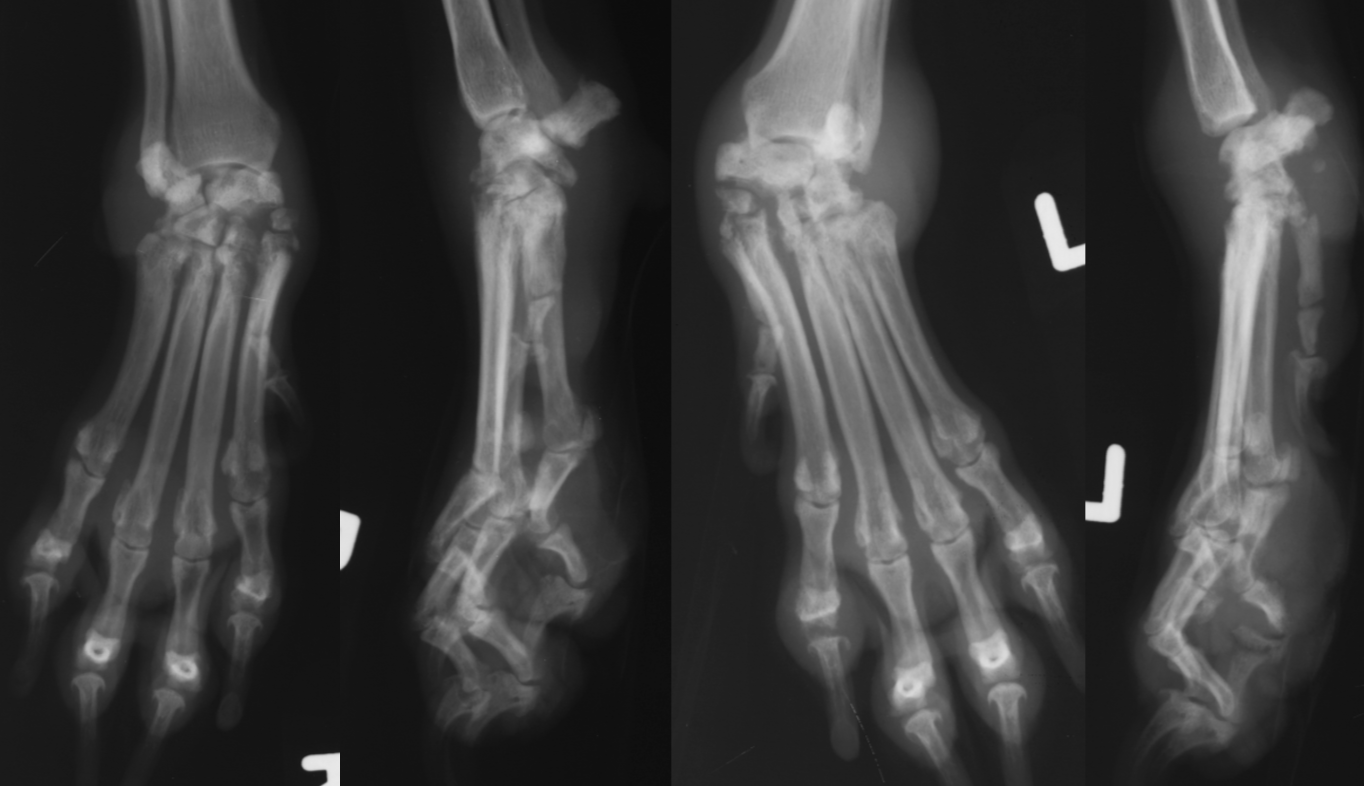
erosive polyarthritis
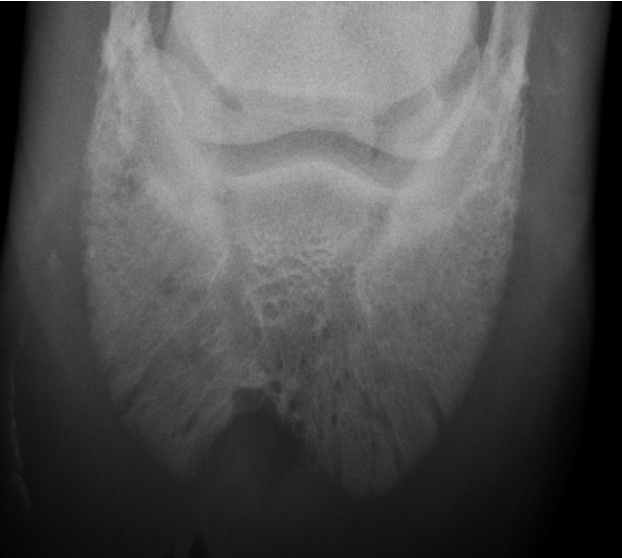
non-erosive polyarthritis signalment/lupus
just soft tissue swelling
multiple joints involved
NO lysis
non-erosive polyarthritis
joint tumor signalment
AGG lesion
middle/large breed dog
stifle and elbow joints
cross the joint
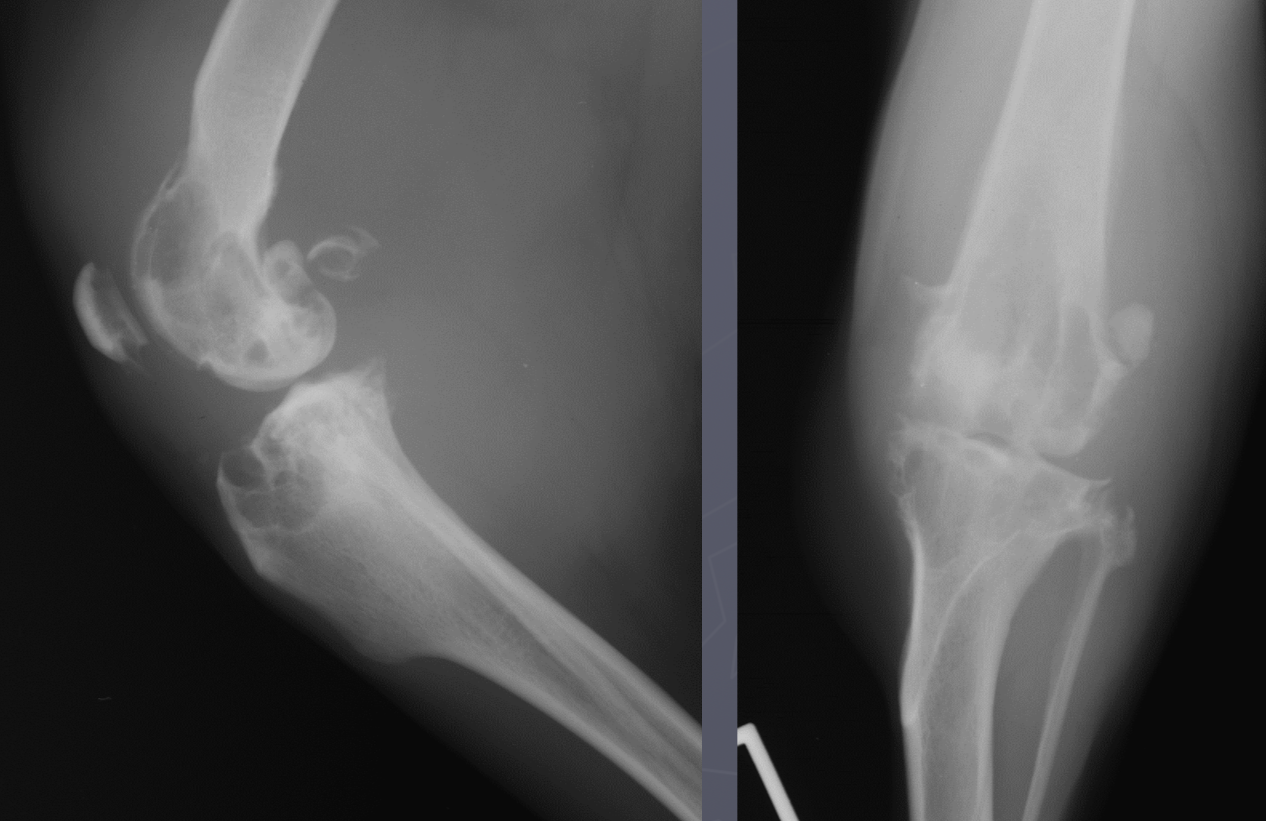
joint associated tumor

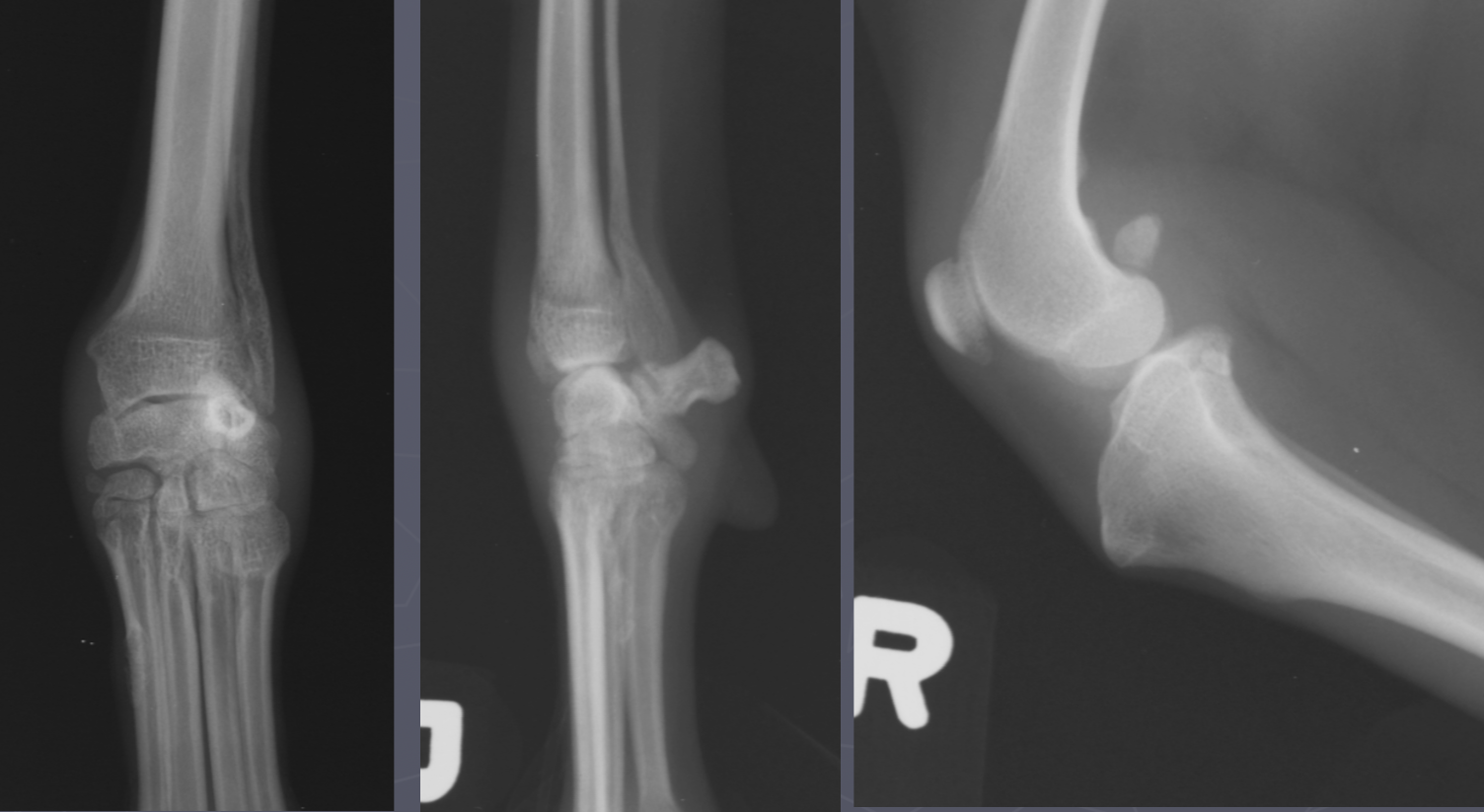
pedal osteitis
solar margin demineralizes
widening of vasc channels
septic osteitis
associated with solar abscesses and penetrating wounds
margin defect ± sequestrum
demineralized solar margin
what are 3 measurements for laminitis
palmar displacement of P3 - rotation/tipping
hoof wall: P3 ratio
coronary bad to extensor distance - sinking
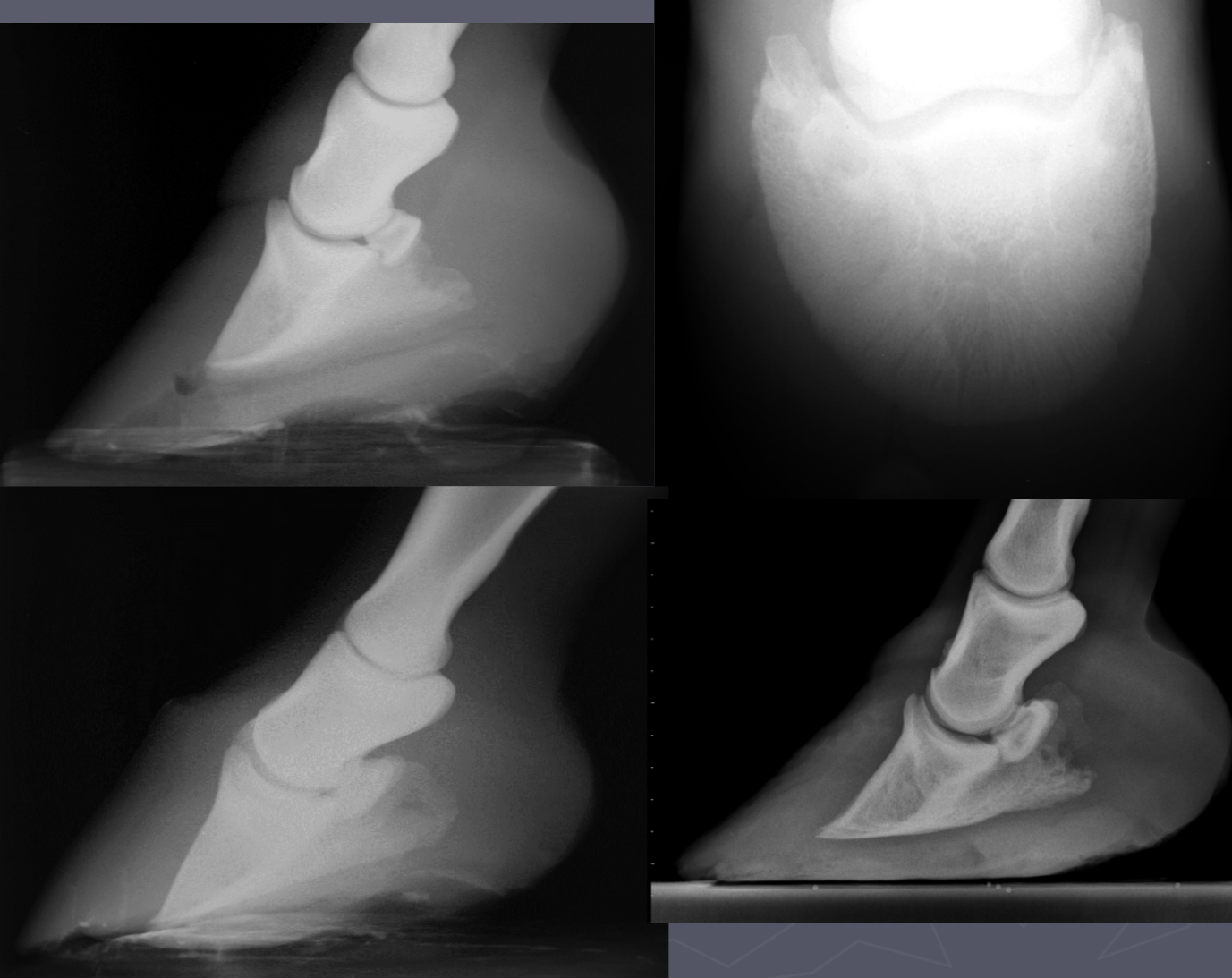
laminitis
DJD low ring bone signs
osteophytes P2-P3
NON-AGG lesion
incongruity of joint space on wt bearing rads
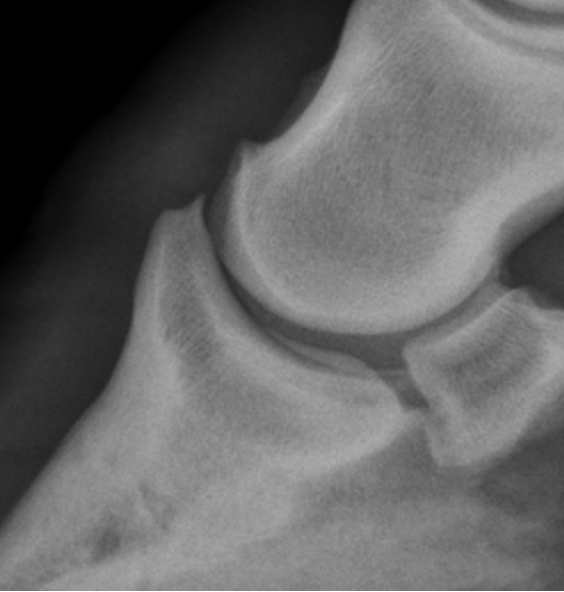
low ringbone DJD
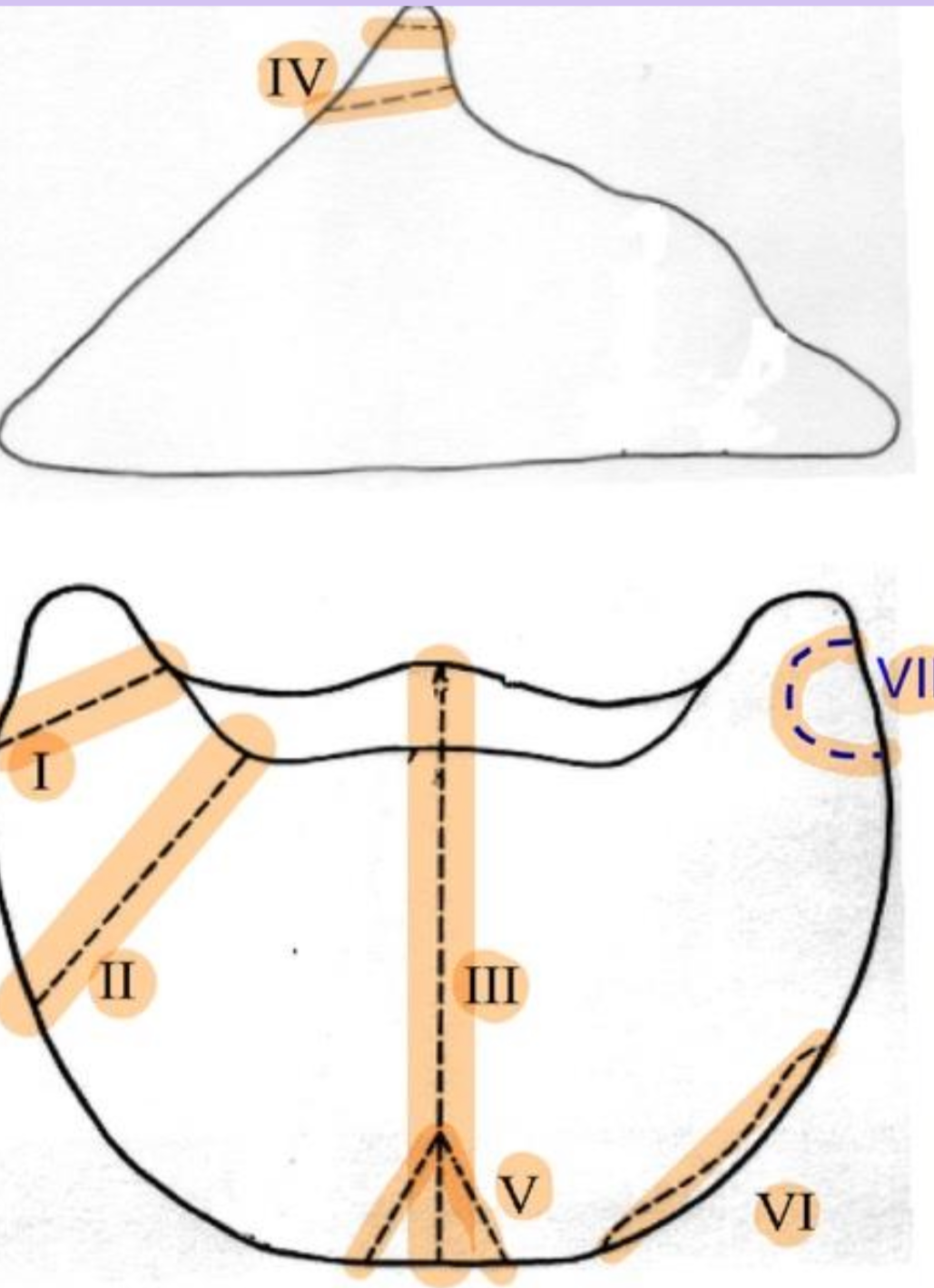
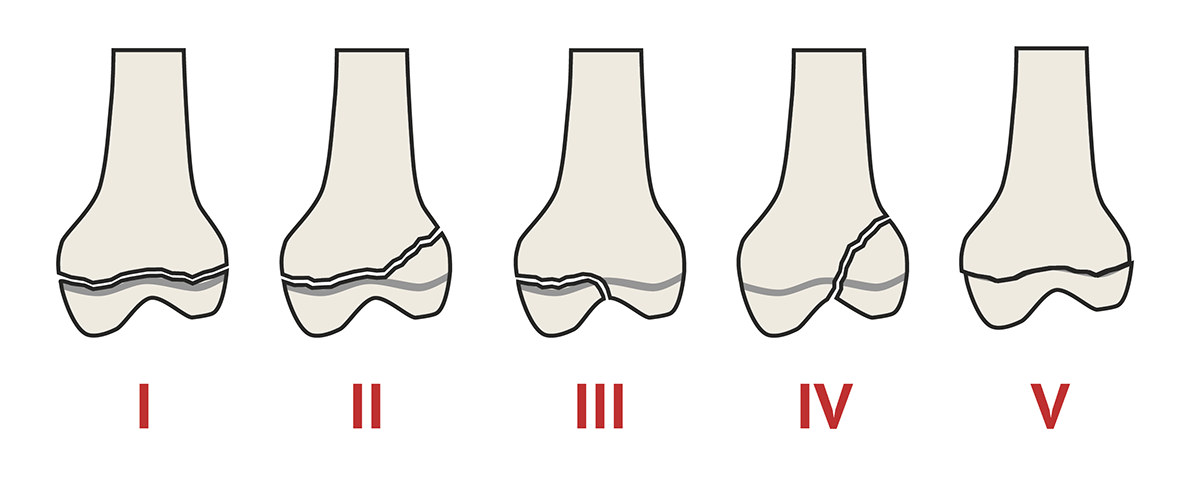
P3 fx
I.Non-articular fx of palmar/plantar processes
II. Larger fx of palmar/plantar processes extending into body
III.Split P3 into 2 pts of equal size
IV.Fx of extensor process
V.Comminuted fx of solar margin
VI.Marginal fx
VII.Non-articular fx of palmar/plantar process in foals -3-32 wks of age
Ossification of lateral cartilages signalment
side bones
draft horses
separate centers of ossification → look like horns

Ossification of lateral cartilages
navicular degeneration signs
synovial invaginations on distal border
abnormal margins
cyst like lesions
sclerotic
erosion of flexor surface
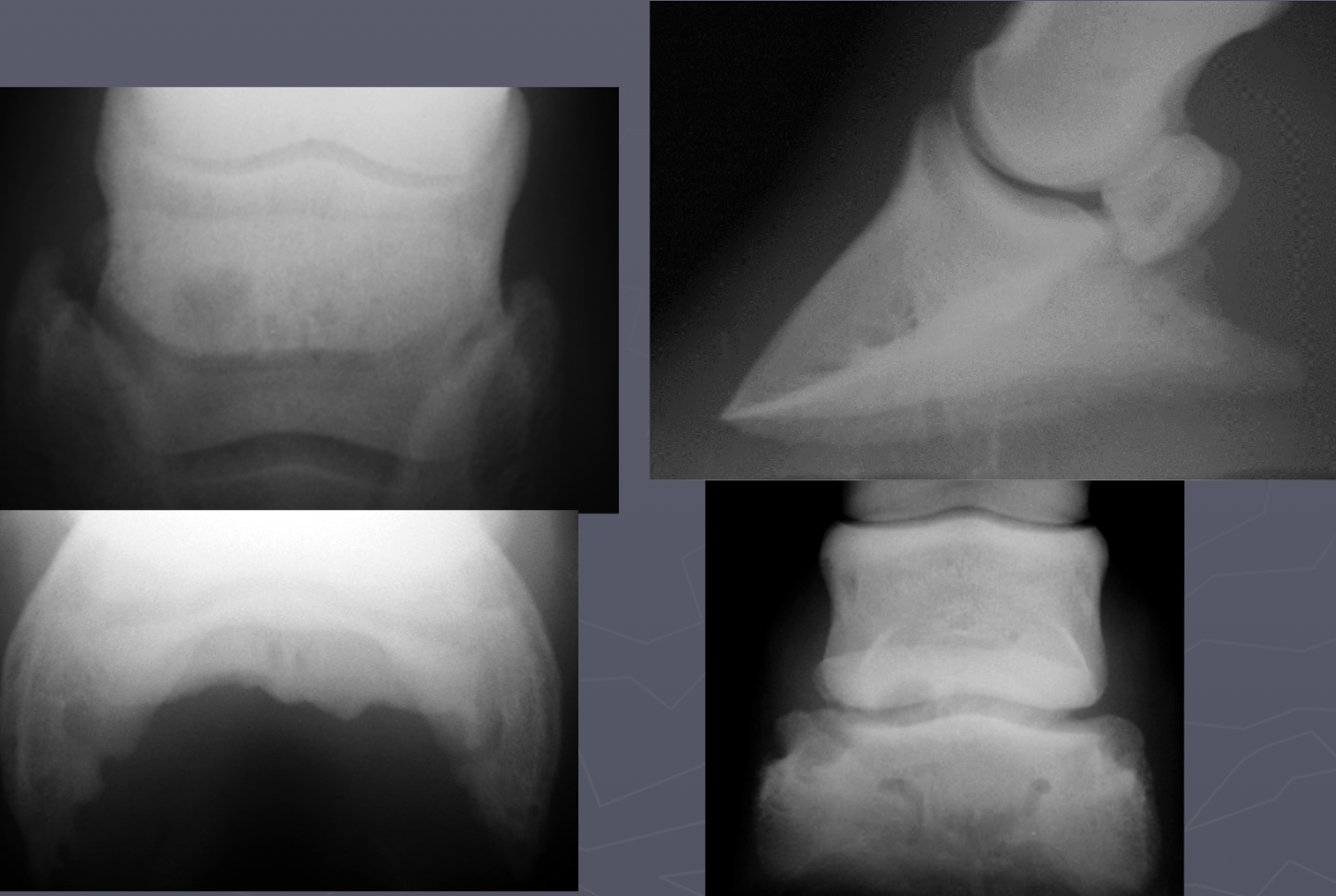
navicular degeneration
navicular osteomyelitis signs
penetrating wound
fistulography with draining tract
toe touching lame that is resolved with nerve block
lysis and sclerosis of flexor surface
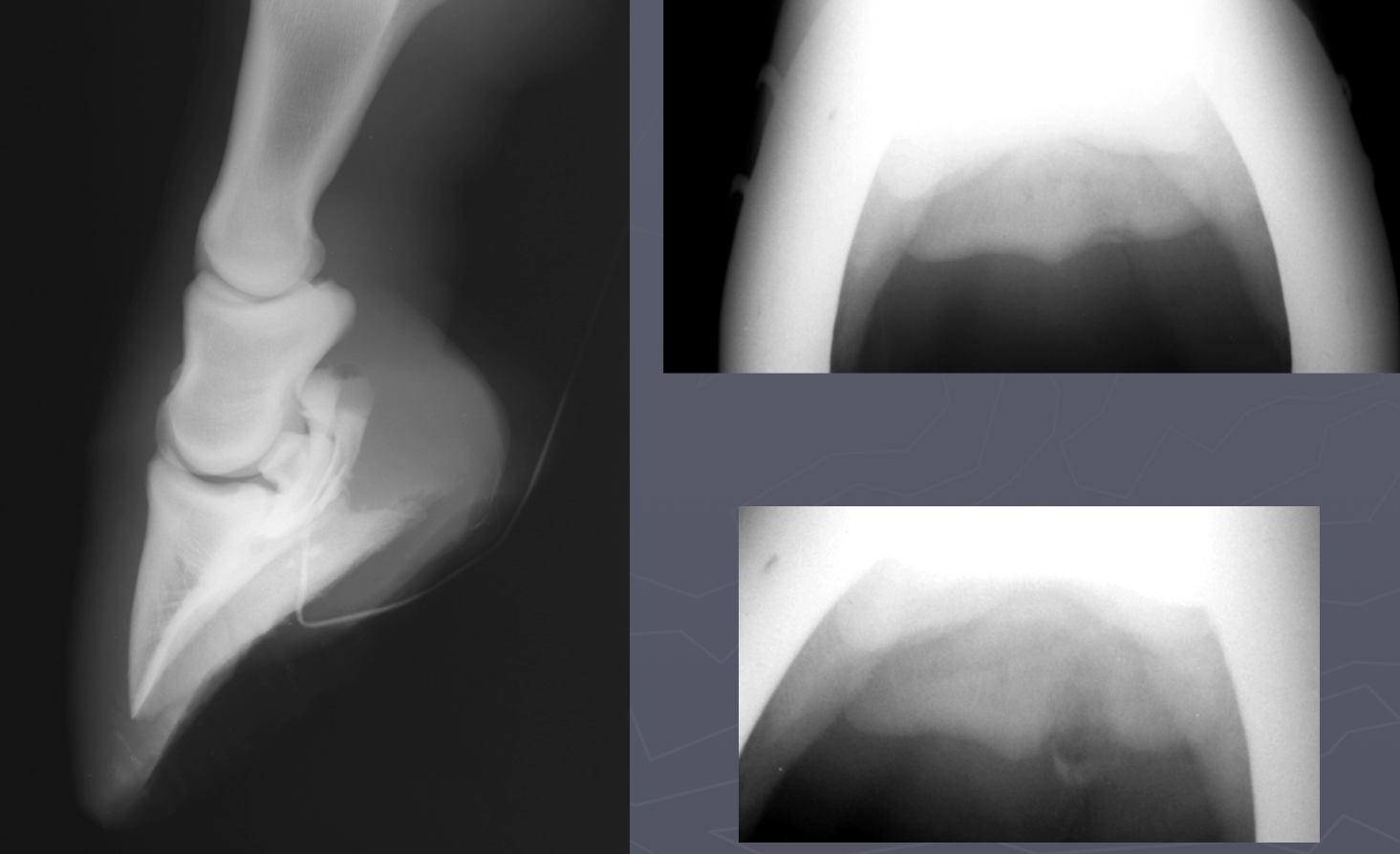
navicular osteomyelitis
Multipartite navicular bones signs
bilateral and symmetric
genetic
no lameness
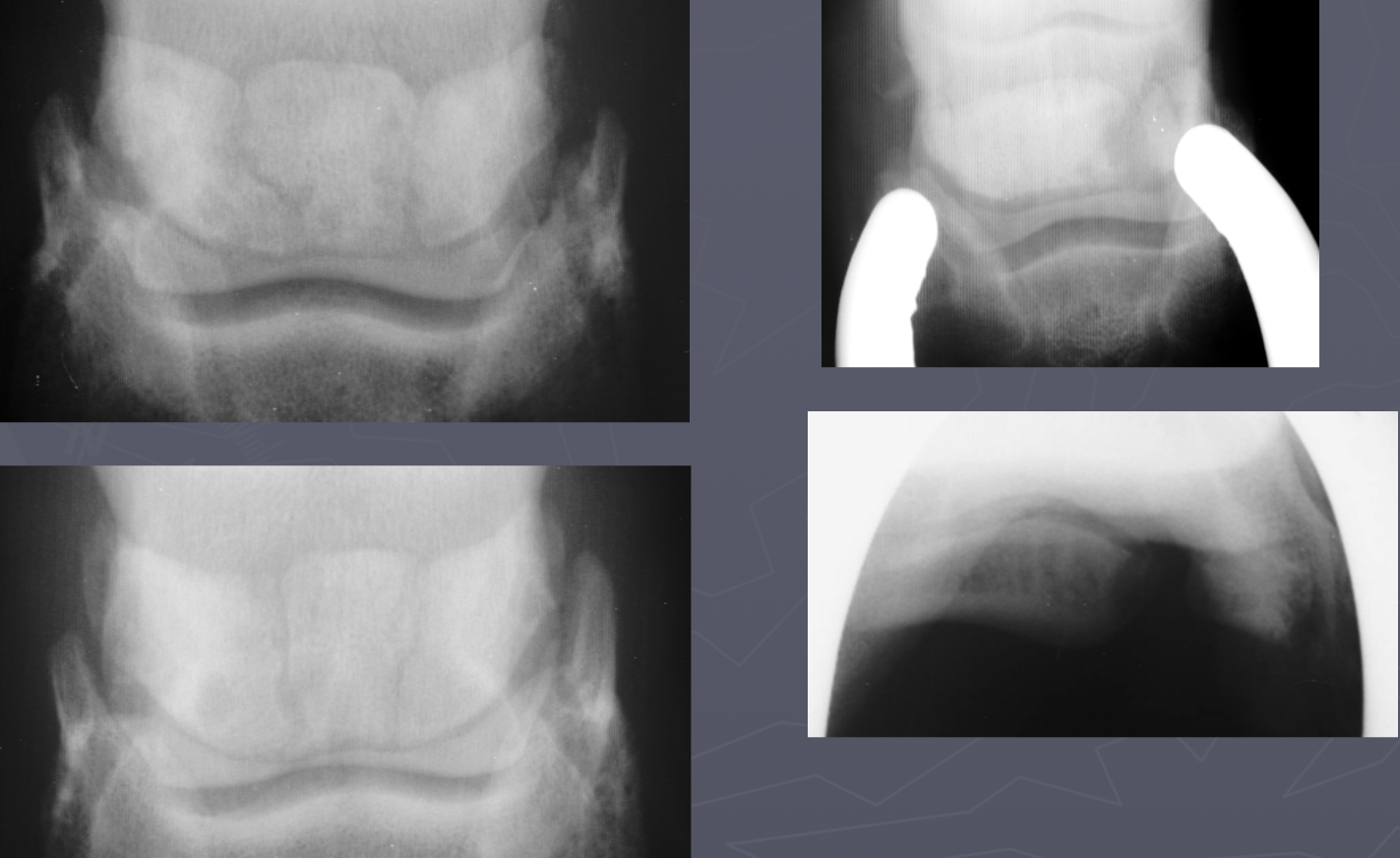
Multipartite navicular bones
high ring bone DJD
osteophytes and narrow joint space at P1
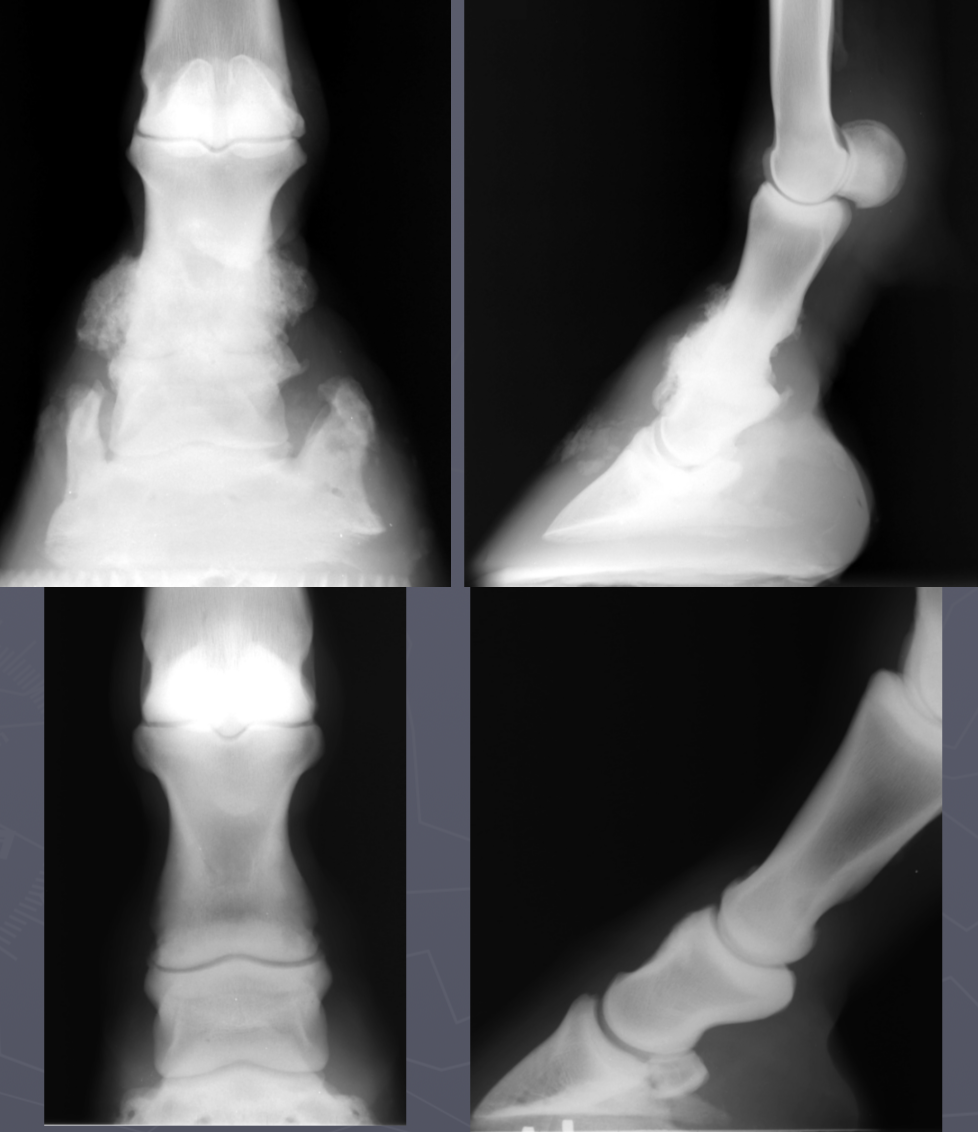
high ring bone DJD
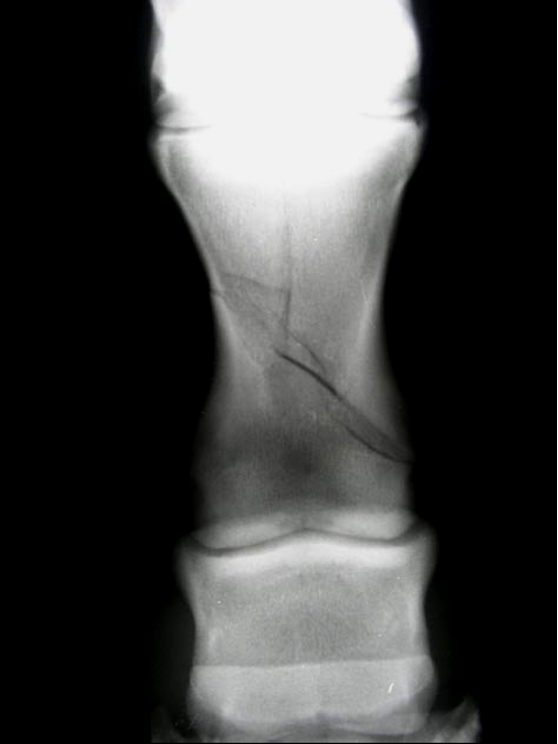
P1 fx
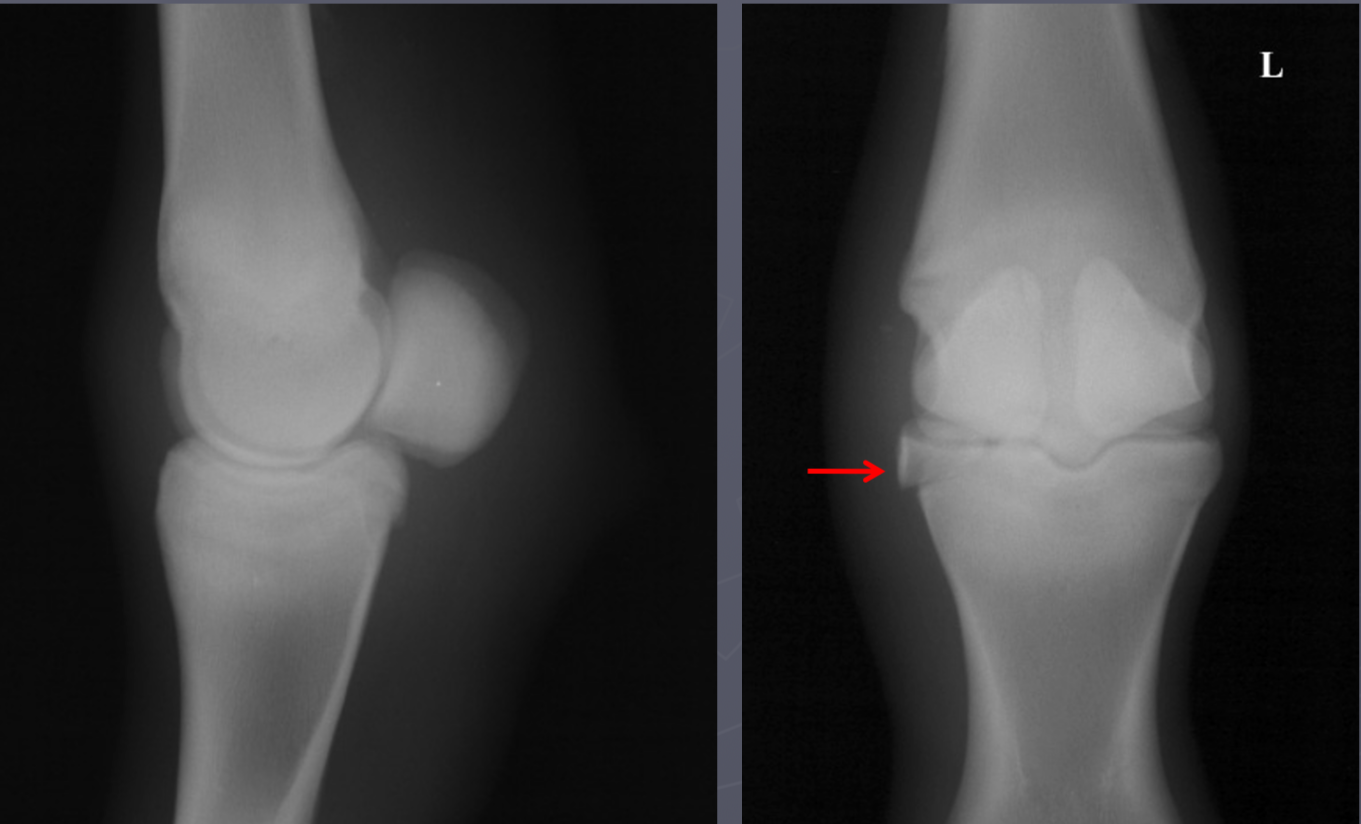
type III salter harris fx P1
physis close at 12 mo
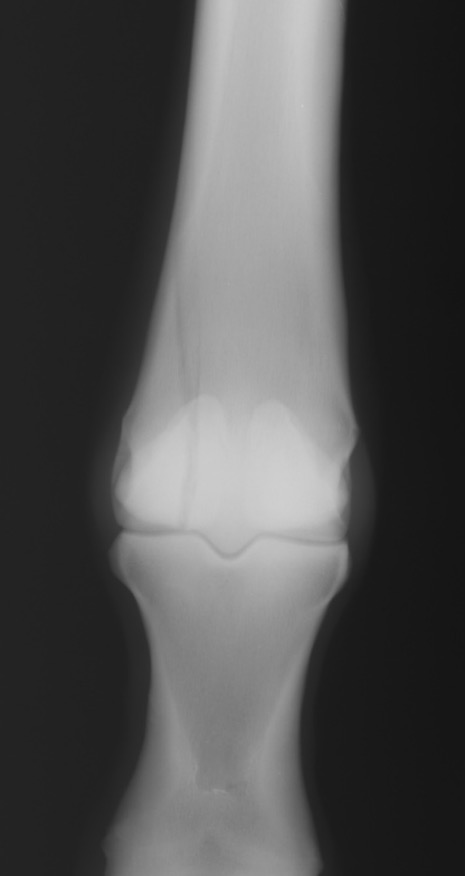
fetlock DJD
P1
MC/MT III
sesamoid bones
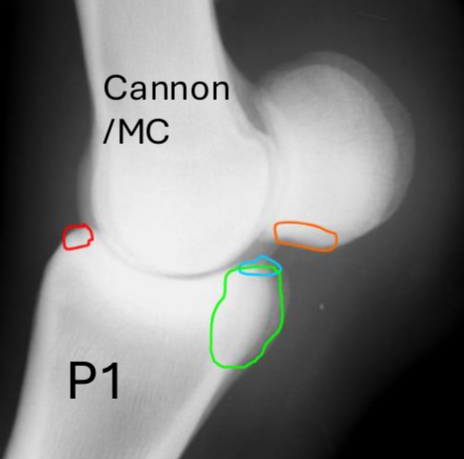
what are these fetlock fx’s
red = dorsopalmar
blue = type I prox P1 between saggital groove
green = type II wing of prox phalanx
orange = type III -basilar fx of sesamoid bones
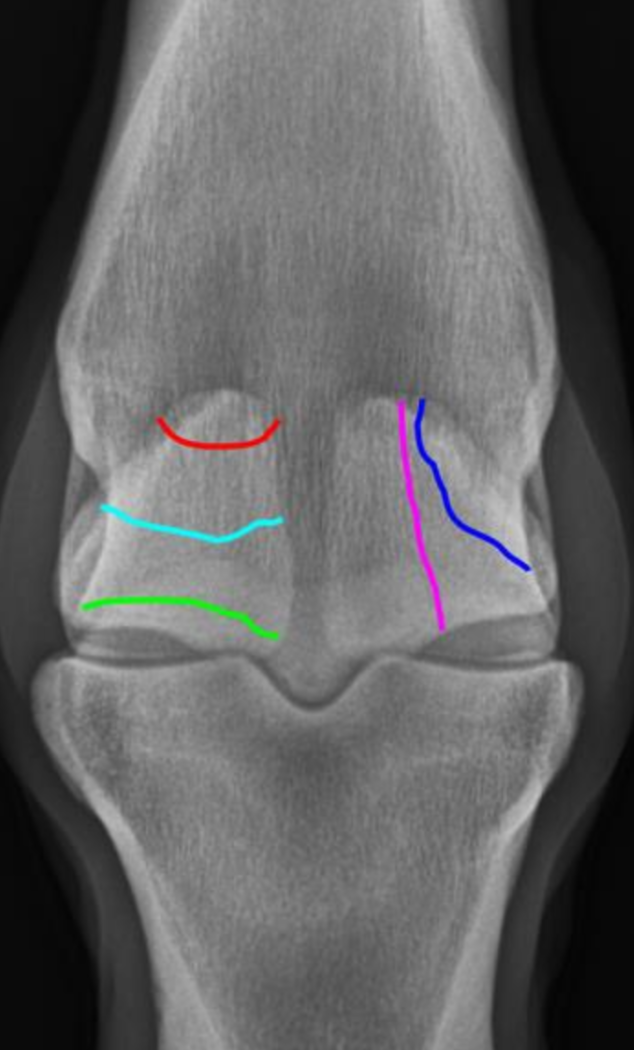
sesamoid fx’s
red = apical
light blue = mid body split
green = basilar
dark blue = abaxial - susp lig here
pink = sagittal
Fx of MC/MT III condyle
lateral > medial