Introduction to Inflammation
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Inflammation
Dynamic process by which living tissues react to injury
Complex reaction in the vascularized connective tissue
Reaction of blood vessels, leading to the accumulation of fluid and leukocytes in extravascular tissue
Repair
The inflammatory process is closely related to what process?
Inflammation is fundamentally a protective response with the goal of removing the cause of cell injury
True
Trauma
Heat
Radiation
Physical causes of inflammation
Simple chemical poisons
Organic poisons
Chemical causes of inflammation
Bacteria
Viruses
Parasites
Infective causes of inflammation
Antigen-antibody
Cell-mediated
Immunological causes of inflammation
Acute inflammation
Short duration
Characterized by exudation of plasma, proteins, and emigration of leukocytes
Chronic inflammation
Longer duration
Presence of lymphocytes and macrophages
Proliferation of blood vessels and connective tissue
Bacterial pathogens
Injured tissues
Causative agents of acute inflammation
Persistent acute inflammation due to non-degradable pathogens, viral infection, persistent foreign bodies, autoimmune reactions
Causative agent of chronic inflammation
Neutrophils
Basophils
Eosinophils
Major cells involved in acute inflammation
Mononuclear cells (monocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes, plasma cells)
Fibroblasts
Major cells involved in chronic inflammation
Vasoactive amines
Eicosanoids
Primary mediators of acute inflammation
IFN-γ and other cytokines
Growth factors
Reactive oxygen species
Hydrolytic enzymes
Primary mediators of chronic inflammation
Exudation
The escape of fluid, proteins, and blood cells from the vascular system in to interstitial tissue or body cavity
Exudate
Inflammatory extravascular fluid with high protein concentration
Signify alteration in normal permeability of blood vessels
Denotes an excess of fluid in the interstitial or serous cavities
Transudate
Fluid with low protein content
Essentially an ultrafiltrate of blood plasma and results from hydrostatic imbalance across the vascular endothelium
Pus
A purulent exudate
Inflammatory exudate rich in leukocytes (mostly neutrophils) and parenchymal cell debris
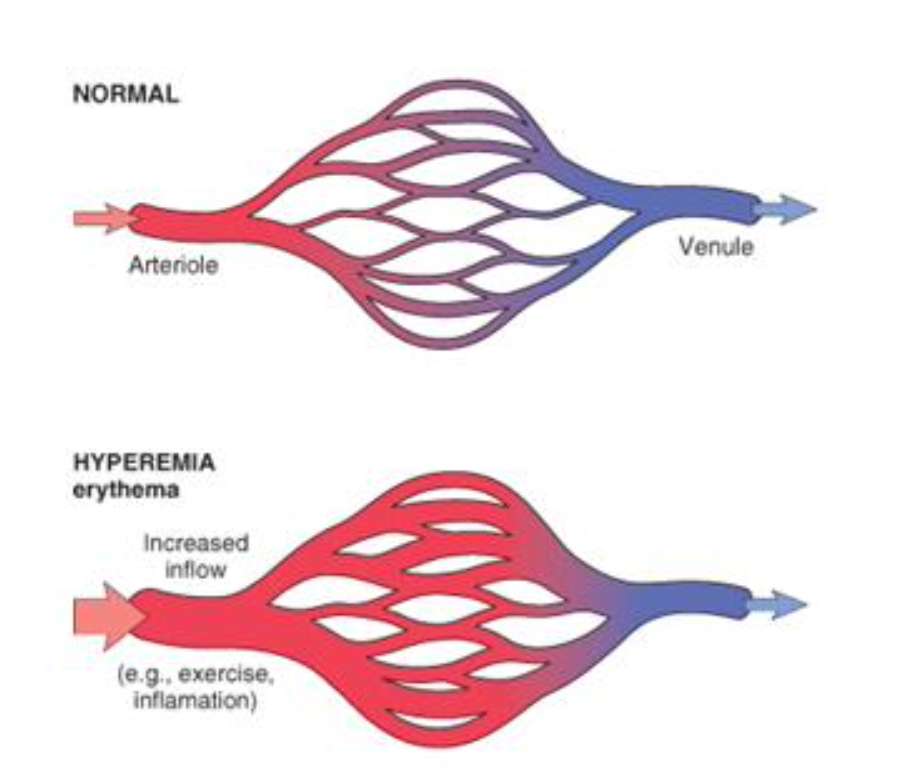
Hyperemia
Redness
Heat
“Flush and flare”
Ameboid
Neutrophils and mononuclears pass between the endothelial cell junctions by what movement?
Flush zone (redding)
Flare (spreading)
Wheal (elevation)
Lewis’ triple response
Vasoconstriction
(Lewis’ triple response) Blunt instrument stroke with marked white line
Capillary dilatation
(Lewis’ triple response) A dull red line immediately follows
Arteriolar dilatation
(Lewis’ triple response) A bright red irregular surrounding zone