A level Physics Electricity
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
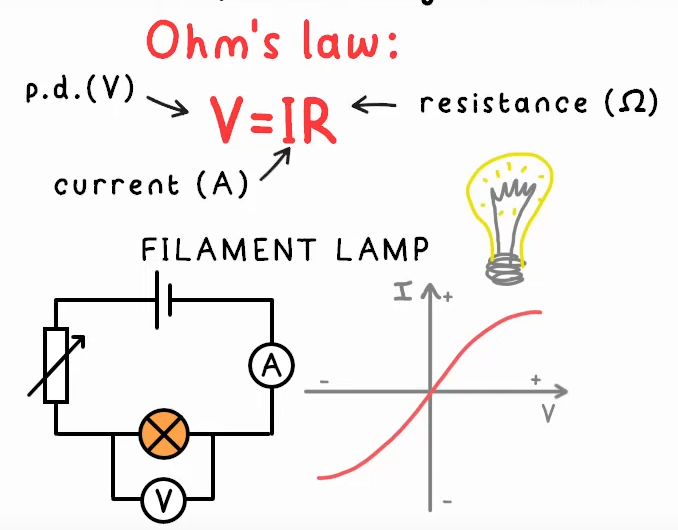
why is resistance for a filament lamp not constant?
The lamp is made from metal. Metal is an ionic lattice with a sea of delocalised electrons. A greater current means the electrons move faster and collide with ions more. (increases the temp.) The ions vibrate and make it harder for electrons to pass through. Higher Resistance.
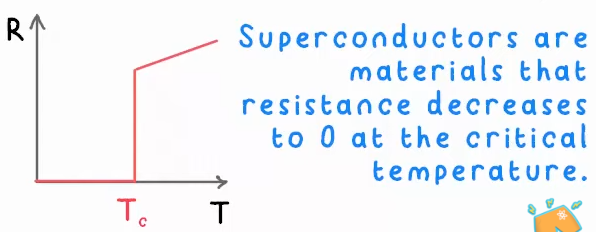
What is a super conductor?
Material where the resistance is 0. Super conductors must be cooled to reach a “critical temperature” where it resistance becomes 0.
define resistivity
the resistance of a cube of unit length sides.
OR
ρ=(RA)/L ρ(rho) is resistivity, R is resistance, A is cross-sectional area, L is length
what happens to p.d., current, and resistance in a series circuit?
-p.d. is split between all components
-current is the same across all components
-total resistance is the sum of all resistances
what happens to p.d., current, and resistance in a parallel circuit?
-p.d. is the same across all components
-current is split between all components
-total resistance= 1/R1+1/R2+1/R3
-adding more resistors in parallel REDUCES the total R
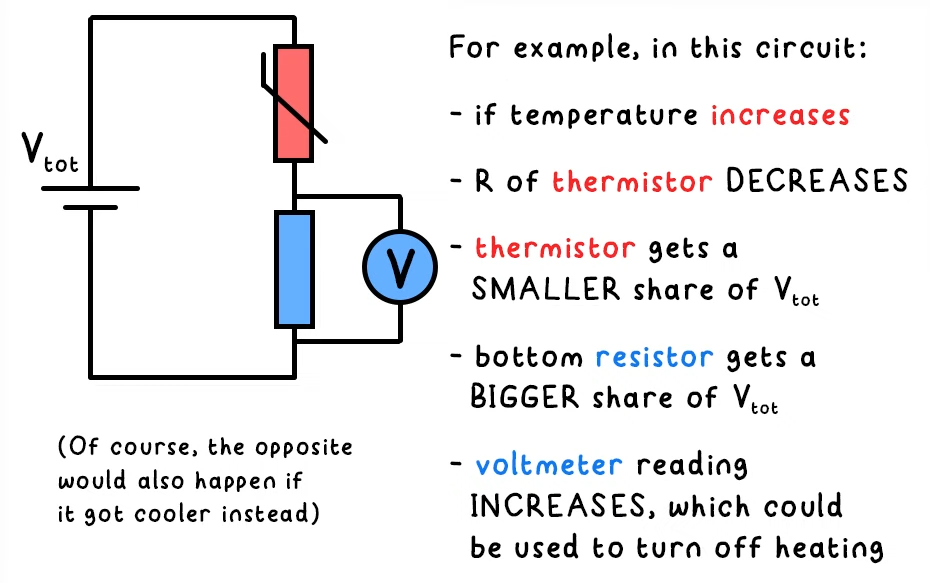
How does a potential divider circuit with a thermistor work?
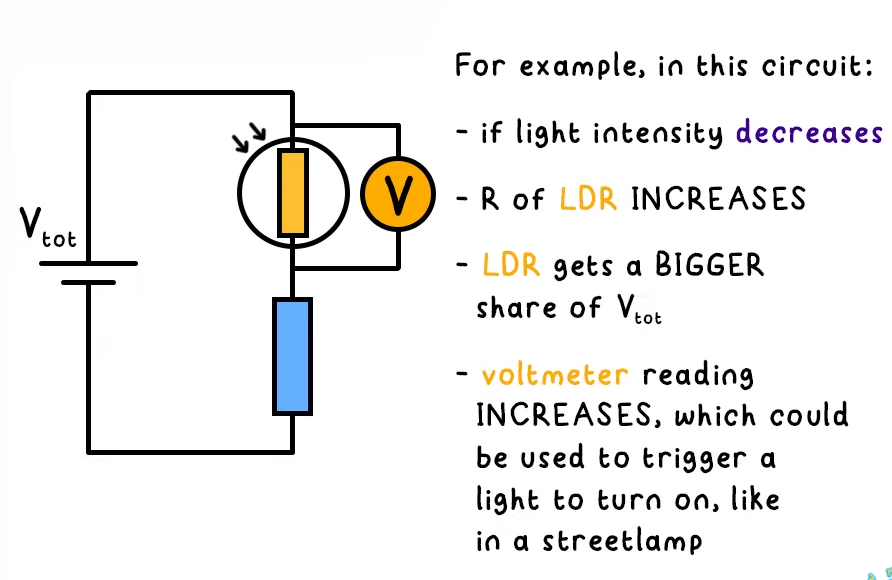
How does a potential divider circuit with a LDR work?
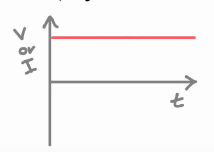
what is a direct current (D.C)?
a p.d./ voltage that only acts in one direction (it’s direct) results in a direct current (e.g. from a battery, electronics use D.C. to work)
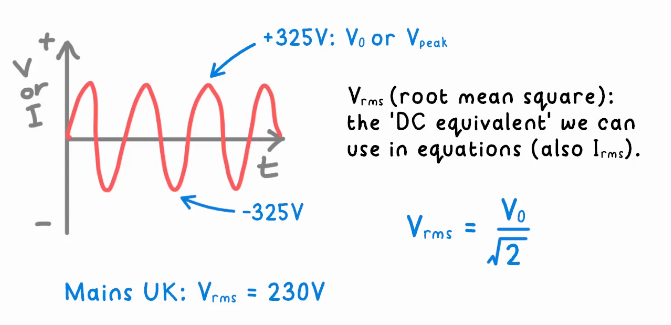
What is an alternating current (A.C.)?
used to transmit electricity long distances (e.g. through the national grid) alternating p.d./ voltage which leads to alternating current. To use A.C. in equations it must be converted to it’s D.C. equivalent. To get to the D.C. equivalent the A.C. value must be divided by root 2