Quizlet 2 Exam
5.0(2)Studied by 5 people
Card Sorting
1/52
Last updated 9:10 PM on 12/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
1
New cards
stem cells
undifferentiated cells, will in the future specialize, at one point in embryonic development you are just stem cells
tissues are groups of cells already differentiated
tissues are groups of cells already differentiated
2
New cards
the four tissue types
connective, muscular, epithelial, nervous
3
New cards
tissue
stem cells that have differentiated
group of cells that have similar structure and that function together as a unit
group of cells that have similar structure and that function together as a unit
4
New cards
epithelial tissue
surface cells, surfaces or linings or covering of organs, very thin, things can travel through, like bronchiole tissue, all your organs are covered in this
avascular, get oxygen and nutrients through diffusion
innervated
regenerative when they have proper nutrients
avascular, get oxygen and nutrients through diffusion
innervated
regenerative when they have proper nutrients
5
New cards
connective tissue
direct connections for tendons and ligaments, very thick tissue, example of achilles tendon, fat tissue, cartilage (nose, ears, joints), highly vascularized
6
New cards
muscle tissue
well vascularized
body movement
cells tightly packed together
possess myofilaments, actin and myosin
three different types:
skeletal muscle - striated and voluntary, attached to bones of skeleton, form flesh of body, body movement, precise alignment of myofilaments with obvious banded or striated appearance
smooth muscle - non-striated and involuntary, cells have no visible striation, spindle shaped, found mainly in walls of hollow organs other than heart, contracting and relaxing causes movement, digestive and urinary tract organs)
cardiac muscle - striated, involuntary, only in the heart, help propel blood through blood vessels to the rest of body, striated, cells only have one nucleus (uninucleate) and branching cells fit tightly together at unique junctions called intercalated discs
body movement
cells tightly packed together
possess myofilaments, actin and myosin
three different types:
skeletal muscle - striated and voluntary, attached to bones of skeleton, form flesh of body, body movement, precise alignment of myofilaments with obvious banded or striated appearance
smooth muscle - non-striated and involuntary, cells have no visible striation, spindle shaped, found mainly in walls of hollow organs other than heart, contracting and relaxing causes movement, digestive and urinary tract organs)
cardiac muscle - striated, involuntary, only in the heart, help propel blood through blood vessels to the rest of body, striated, cells only have one nucleus (uninucleate) and branching cells fit tightly together at unique junctions called intercalated discs
7
New cards
striated
muscle tissue classification, dark band stripes allowing contractile bonds, actin and myosin
The primary function of striated muscles is to generate force and contract in order to support respiration, locomotion, and posture (skeletal muscle) and to pump blood throughout the body (cardiac muscle)
The primary function of striated muscles is to generate force and contract in order to support respiration, locomotion, and posture (skeletal muscle) and to pump blood throughout the body (cardiac muscle)
8
New cards
nonstriated
muscle tissue classification
no stripes, Non-striated muscles are smooth and devoid of striations. Found in the hollows of internal organs such as the stomach, intestines, and urine bladder, among other places
no stripes, Non-striated muscles are smooth and devoid of striations. Found in the hollows of internal organs such as the stomach, intestines, and urine bladder, among other places
9
New cards
voluntary movement
muscle tissue classification
making yourself move the muscle, running, walking, etc
making yourself move the muscle, running, walking, etc
10
New cards
involuntary movement
muscle tissue classification
body just doing it - breathing, blinking
body just doing it - breathing, blinking
11
New cards
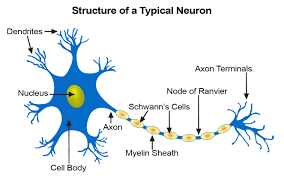
nervous tissue
nervous tissue is found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves it is responsible for coordinating and controlling many body activities
it stimulates muscle contraction, creates an awareness of the environment, and plays a major role in emotions, memory, and reasoning
contains, cell body, dendrites, axon, supporting cells
it stimulates muscle contraction, creates an awareness of the environment, and plays a major role in emotions, memory, and reasoning
contains, cell body, dendrites, axon, supporting cells
12
New cards
excitable
cardiac and muscle, tissue that can be stimulated and a response can happen
13
New cards
totipotent
(of an __immature__ or stem cell) capable of giving rise to any cell type or (of a __blastomere__) a complete __embryo__
These stem cells are the most powerful that exist. They can differentiate into embryonic, as well as extra-embryonic tissues, such as chorion, yolk sac, amnion, and the allantois. In humans and other placental animals, these tissues form the placenta
really strong and versatile stem cells
These stem cells are the most powerful that exist. They can differentiate into embryonic, as well as extra-embryonic tissues, such as chorion, yolk sac, amnion, and the allantois. In humans and other placental animals, these tissues form the placenta
really strong and versatile stem cells
14
New cards
endoderm
the innermost of the three basic layers of an embryo that forms the epithelium of the digestive tract and the parts of the body formed from it
inner lining of digestive system
inner lining of digestive system
15
New cards
ectoderm
the ectoderm is one of the primary layers of cells that exists in an embryo
the ectoderm cells differentiate into cells that form a number of external structures such as skin, sweat glands, skin sensor receptors, and hair follicles
nervous tissue
the ectoderm cells differentiate into cells that form a number of external structures such as skin, sweat glands, skin sensor receptors, and hair follicles
nervous tissue
16
New cards
mesoderm
the middle of the three primary germ layers of an embryo that is the source of many bodily tissues and structures (such as bone, muscle, connective tissue, and dermis) broadly : tissue derived from this germ layer. mesodermal)
17
New cards
mesoderm, ectoderm, and endoderm
The ectoderm gives rise to the skin and the nervous system. The mesoderm specifies the development of several cell types such as bone, muscle, and connective tissue. Cells in the endoderm layer become the linings of the digestive and respiratory system, and form organs such as the liver and pancreas
these primary germ layers specialize to form the four primary tissues
all three form epithelium
these primary germ layers specialize to form the four primary tissues
all three form epithelium
18
New cards
omnipotent
not as strong of stem cells as totipotent, but still very versatile
19
New cards
nervous tissue
main component of nervous system (brain, spinal chord, nerves)
two major cell types:
**neurons** - highly specialized nerve cells that generate and conduct nerve impulses, branching cells with cytoplasmic extensions (respond to stimuli, transmit electrical impulses within body)
**supporting cells** (neuralgia)- nonconducting cells, they support, insulate, and protect delicate neurons
two major cell types:
**neurons** - highly specialized nerve cells that generate and conduct nerve impulses, branching cells with cytoplasmic extensions (respond to stimuli, transmit electrical impulses within body)
**supporting cells** (neuralgia)- nonconducting cells, they support, insulate, and protect delicate neurons
20
New cards
mechanical barriers - 3 defenses at body’s external boundaries
skin, mucosae (cilia of epithelial cells lining respiratory tract), and strong cid produced by stomach glands
21
New cards
what happens when tissues are injured/boundaries penetrated
the inflammation (nonspecific) and immune response (specific) are triggered
22
New cards
Tissue repair basic
requires cells to divide and migrate (initiated by growth factors released by injured cells)
repair occurs in…
regeneration
fibrosis
which one occurs depends on the type of tissue damaged and severity of injury
repair occurs in…
regeneration
fibrosis
which one occurs depends on the type of tissue damaged and severity of injury
23
New cards
regeneration (tissue repair)
replaces destroyed tissue with the same kind of tissue
24
New cards
fibrosis
replaced destroyed tissue with scar tissue (dense connective tissue - fibrous connective tissue because fibers are the primary element)
25
New cards
1. inflammation
first step of tissue repair
trauma causes the injured tissue cells and masts to release inflammatory chemicals
these make local blood vessels leaky so that white blood cells, fluid, clotting proteins, and other plasma proteins to seep into the injured area
clotting prevents bacteria and other harmful substances from spreading
surface of clot exposed to air forms scab
trauma causes the injured tissue cells and masts to release inflammatory chemicals
these make local blood vessels leaky so that white blood cells, fluid, clotting proteins, and other plasma proteins to seep into the injured area
clotting prevents bacteria and other harmful substances from spreading
surface of clot exposed to air forms scab
26
New cards
2. organization restored blood supply
clot is replaced by ingrowth of fragile capillaries (**granulation tissue**) which restores vascular supply
fibroblasts multiple, produce growth factors and collagen fibers that bridge gap
when healing complete, these fibroblasts revert to resting stage or undergo apoptosis (cell suicide)
macrophages phagocytize dead and dying cells/other debris
surface epithelial cells multiply and begin to migrate over granulation tissue
fibroblasts multiple, produce growth factors and collagen fibers that bridge gap
when healing complete, these fibroblasts revert to resting stage or undergo apoptosis (cell suicide)
macrophages phagocytize dead and dying cells/other debris
surface epithelial cells multiply and begin to migrate over granulation tissue
27
New cards
granulation tissue
special tissue formed in initial part of wound healing, delicate pink tissue that contains capillaries that grow in from nearby areas and lay down on capillary bed, fragile and bleed freely
28
New cards
apoptosis
cell suicide
happens during tissue repair process when the fibroblasts commit apoptosis after healing is complete
happens during tissue repair process when the fibroblasts commit apoptosis after healing is complete
29
New cards
3. regeneration and fibrosis effect permanent repair
the fibroses area matures and contracts, pulling ends of wound together
as it regenerates, epithelial thickens under scab, which detaches
fully regenerated epithelium with underlying scar tissue results
scar could be visible as white line depending on severity of wound
as it regenerates, epithelial thickens under scab, which detaches
fully regenerated epithelium with underlying scar tissue results
scar could be visible as white line depending on severity of wound
30
New cards
what tissues regenerate well?
epithelial
bone
areolar loose connective tissue
dense irregular connective
blood-forming tissue
bone
areolar loose connective tissue
dense irregular connective
blood-forming tissue
31
New cards
regenerate moderately well
smooth muscle, dense regular connective tissue
32
New cards
weak ability to regenerate
skeletal muscle
cartilage
cartilage
33
New cards
no ability to regenerate
nervous tissue in brain and spinal chord, replaced by scar tissue
34
New cards
in the non regenerating tissue…
fibrosis replaces the tissue, but it cannot perform the function of the tissue it replaces, scar tissue is NOT flexible
35
New cards
cancer
cancers are malignant neoplasms
changes normal cell into a killer
cells multiply excessively
**neoplasm** results - abnormal mass of proliferating cells
neoplasms have two classifications:
benign - grow slowly, local, seldom kill hosts
malignant - metastasis and invasiveness
changes normal cell into a killer
cells multiply excessively
**neoplasm** results - abnormal mass of proliferating cells
neoplasms have two classifications:
benign - grow slowly, local, seldom kill hosts
malignant - metastasis and invasiveness
36
New cards
secondary neoplasms
non-encapsulated masses that grow relentlessly, invade surroundings, break away from primary tumor and travel (by blood or lymph) to other organs
37
New cards
metastasis
tumor cell ability to travel to other parts of the body
38
New cards
carcinogens
cause mutations in cells, or changes in DNA that alter the expression of certain genes
defenses against carcinogens:
liver deactivates many, cells have intrinsic DNA repair, immune cells continuously scan for cancer cells
defenses against carcinogens:
liver deactivates many, cells have intrinsic DNA repair, immune cells continuously scan for cancer cells
39
New cards
oncogenes
cancer-causing genes
40
New cards
protooncogenes
benign forms of oncogenes in normal cells
code for proteins that are essential in cell division, growth, cellular adhesion, etc
have fragile sites that carcinogens can break to form oncogenes
code for proteins that are essential in cell division, growth, cellular adhesion, etc
have fragile sites that carcinogens can break to form oncogenes
41
New cards
tumor suppressor gene
inhibit cell growth to try and slow growth of cancer cells
42
New cards
where are cancers most common
skin, colon, lung, breast, and prostate
usually preceded by lumps or structural changes in tissue
usually preceded by lumps or structural changes in tissue
43
New cards
WHAT IS THE CONNECTION BETWEEN CANCER AND TISSUE - explain cancer as it relates to tissue
cancer is uncontrolled cell growth
44
New cards
necrosis
death or disintegration of a cell or tissues caused by disease or injury - leads to tissue repair process
45
New cards
vasodilation
relaxation of the smooth muscle of the blood vessels, producing dilation, histamine is the messenger or neurotransmitter that causes vasodilation
46
New cards
histamine
causes blood vessels to dilate, chemical messenger, Causes vasodilation and increased capillary permeability; it is in the stomach and causes acid secretion
47
New cards
atrophy
reduction in size or the wasting away of an organ or cell regulating from disease or lack of use
inactivity in a muscle leading to this wasting away while on the other hand constant load and use makes it stronger and larger
inactivity in a muscle leading to this wasting away while on the other hand constant load and use makes it stronger and larger
48
New cards
endocrine gland
ductless glands that empty their hormonal products directly into the blood
49
New cards
exocrine gland
glands that have ducts through which their secretions are carried to a particular site
50
New cards
merocrine glands
term used to classify exocrine glands and their secretions secretions of that cell are excreted via exocytosis from secretory cells into an epithelial-walled duct or ducts and then onto a bodily surface or into the lumen
sweat glands abundant on palms, soles of feet, and forehead
sweat glands abundant on palms, soles of feet, and forehead
51
New cards
holocrine glands
glands that accumulate their secretions within their cells and secretions are only discharged upon rupture or death
releases sebum - made up of lipids to protect and hydrate skin
releases sebum - made up of lipids to protect and hydrate skin
52
New cards
aprocrine secretions
less numerous type of sweat gland produces a secretion containing water, salt, protein, and fatty acid
armpits, groin, breast
odor
armpits, groin, breast
odor
53
New cards
aging and signs of aging in tissue
lost of elasticity, loss of flexibility, dehydration of cells, neurological connections, digestion is slower