psyc 60 steiner quiz 3
5.0(5)Studied by 199 people
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Last updated 8:50 PM on 2/4/26
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
central limit theorem
the theorem that specifies the nature of the sampling distribution of the mean
2
New cards
central limit theorem definition
given a population with a mean μ and a variance σ², the sampling distribution of the mean will have a mean equal to μ and a variance equal to σ²/N.
* The distribution will approach the normal distribution as N, the sample size, increases (this sentence is true regardless of the shape of the population distribution)
* The distribution will approach the normal distribution as N, the sample size, increases (this sentence is true regardless of the shape of the population distribution)
3
New cards
if you increase the sampling size,
the distribution becomes more normal (bell-shaped)
4
New cards
5 factors that affect whether the t-value will be statistically significant
1) the difference between X̄ and μ
2) N (sample size)
3) S (standard deviation)
4) α
5) one-tailed vs two-tailed tests
2) N (sample size)
3) S (standard deviation)
4) α
5) one-tailed vs two-tailed tests
5
New cards
the difference between X̄ and μ
the greater the difference, the more likely you'll have statistical significance
6
New cards
N
the greater the sample size, the more likely you'll have statistical significance
- critical value becomes smaller
- critical value becomes smaller
7
New cards
S
the greater the standard deviation, the less likely you'll have statistical significance
8
New cards
α
the greater the alpha (the larger the rejection region), the more likely you'll have statistical significance
9
New cards
one-tailed vs two tailed tests
- if you're using a one-tailed test and you're right about the
direction, you're more likely to have statistical significance
because you've doubled the area of the rejection region
- if you're using a one-tailed test and you're wrong about the direction, you'll never have statistical significance because the area of the rejection region is 0
direction, you're more likely to have statistical significance
because you've doubled the area of the rejection region
- if you're using a one-tailed test and you're wrong about the direction, you'll never have statistical significance because the area of the rejection region is 0
10
New cards
effect size
the difference between 2 populations divided by the standard deviation of either population
- it is sometimes presented in raw score units (and sometimes in standard deviations)
- it is sometimes presented in raw score units (and sometimes in standard deviations)
11
New cards
effect size in terms of standard deviations
d^\= X̄ - μ / S
12
New cards
guidelines for interpreting d^
trivial, small, medium, large effect size
13
New cards
< 0.2
trivial effect size
14
New cards
≥ 0.2 & < 0.5
small effect size
15
New cards
≥ 0.5 & < 0.8
medium effect size
16
New cards
≥ 0.8
large effect size
17
New cards
confidence interval
an interval, with limits at either end, having specified probability of including the parameter being estimated
18
New cards
Confidence Interval
X̄± t_df * S/√N
19
New cards
what makes a confidence interval wider?
- smaller α (0.05 to 0.01)
- larger s
- smaller N
- larger s
- smaller N
20
New cards
what makes a confidence interval narrower?
- bigger α
- smaller s
- bigger N
- smaller s
- bigger N
21
New cards
related samples
an experimental design in which the same subject is observed under more than one treatment
ex: comparing students' two sets of quiz scores (DV) after they used two different studying strategies
ex: comparing students' two sets of quiz scores (DV) after they used two different studying strategies
22
New cards
repeated measures
data in a study in which you have multiple measurements for the same participants
ex: measuring a person's cortisol level before and after a competition
ex: measuring a person's cortisol level before and after a competition
23
New cards
matched samples
an experimental design in which the same subject is observed under more than one treatment
ex: asking a husband and wife to each provide a score on marital satisfaction
ex: asking a husband and wife to each provide a score on marital satisfaction
24
New cards
d‾
the difference of the means
25
New cards
S_D
the standard deviation of the difference scores
26
New cards
difference scores (gain scores)
the set of scores representing the difference between the subjects' performance on two occasions
27
New cards
advantages of related samples
1) it avoids the problem of person-to-person variability
2) it controls for extraneous variables
3) it requires fewer participants than independent samples designs to have the same amount of power
2) it controls for extraneous variables
3) it requires fewer participants than independent samples designs to have the same amount of power
28
New cards
disadvantages of related samples
1) order effect
2) carry-over effect
2) carry-over effect
29
New cards
order effect
the effect on performance attributable to the order in which treatments were administered
ex: you want to know if stimulant A or B improves reaction time more
ex: you want to know if stimulant A or B improves reaction time more
30
New cards
carry-over effect
the effect of previous trials (conditions) on a subject's performance on subsequent trials
ex: you want to know if Drug A or B improves depression more
ex: you want to know if Drug A or B improves depression more
31
New cards
independent-sample t tests
are used to compare two samples whose scores are not related to each other, in contrast to related-samples t tests
ex: comparing male and female grades on a language verbal test
ex: comparing male and female grades on a language verbal test
32
New cards
two assumptions for an independent-samples t test
1) homogeneity of variance
2) the samples come from populations with normal distributions
2) the samples come from populations with normal distributions
33
New cards
homogeneity of variance
the situation in which two or more populations have equal variances
- the variance of a sample is similar to another
- the variance of a sample is similar to another
34
New cards
heterogeneity of variance
a situation in which samples are drawn from populations having different variances
35
New cards
homogeneity assumption is for
population variances, not sample variances
36
New cards
the samples come from populations with normal distributions
however, independent-samples t tests are robust to a violation of this assumption, especially with sample sizes less than 30
37
New cards
pooled variance
a weighted average of separate sample variances
38
New cards
standard error of difference between means
the standard deviation of the sampling distribution of differences between means
39
New cards
sampling distribution of differences between means
the distribution of the differences between means over repeated sampling from the same populations
40
New cards
degrees of freedom for one-sample t test
N-1
41
New cards
degrees of freedom for related-samples t test
N-1
42
New cards
degrees of freedom for independent-samples t test
n1+n2-2
or
N-1
or
N-1
43
New cards
formula for pooled variance
^
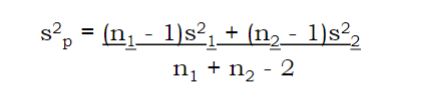
44
New cards
formula for independent-samples t test
^
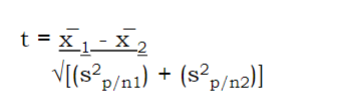
45
New cards
counterbalancing
how to solve the problems of order and carry-over effect (disadvantages)