3-zolliinger ellison syndrome
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pg 51-
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
zollinger ellison syndrome is characterised by the _________________ in ____________.
__________ releases excessive _______ → stimulates ___________ to release more _______ → causing __________.
features of ulcers → (2)
SX →
excessive HCL →
DX → (2)
presence of tumor(gastrinoma)…pancreas and duodenum
gastrinoma…gastrin…parietal cell of stomach…HCL…multiple ulcers
resistant to TX and abnormal localisation
abdominal pain, dyspepsia, weight loss, GI bleeding, chronic diarrhea
fasting gastrin test, secretin stimulation test
patient recently had full course h.pylori eradication. presents with burning retrosternal pain + endoscopy shows multiple ulcers in lower oesophagus, stomach and duodenum. investigation?
carbon 13 urea test
fasting gastrin test, secretin stimulation test
mesalazine drug class →
5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA)

perforated peptic ulcer
**upper GI endoscopy (primary diagnostics)
x-ray → free air under diaphragm
IV fluids, analgesic, AB, antiemetics → urgent surgery
hereditary haemochromatosis is autosomal _________.
it causes __________________ → ____________________
5 organs and its signs
triad : ________ + _________ + ___________
recessive
the increase in absorption of iron… ‘deposition’ in tissues
liver → hepatomegaly, cirrhosis → hepatoma/cancer
pancreas → DM
skin → bronze skin (hyperpigmentation)
joints → arthropathy
heart → cardiomyopathy
hepatomegaly + DM + bronze skin
persistent dyspepsia + severe epigastric pain (night esp) + no DX or TX before. next step →
h.pylori serology test (initial step)
to diagnose → endoscopy

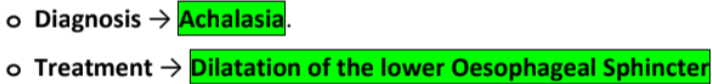
patient with hx of peptic ulcer is prone to get perforated peptic ulcer after surgery, why?
stress → high production of gastric acid
cholestatic hepatitis
→ ______ age, hx of use of _______________
SX → (6)
labs → (4)
old..co-amoziclav, amoxicillin, flucloxacillin
(drug induced hepatotoxicity)
dark urine, pruritus, fatigue, nausea, vomit, abd pain
high ALT, ALP, bilirubin and GGT
celiac disease
blistering rash on elbow →
shortening of the villi →
dermatitis hepetiformis
villous atrophy
pseudomembranous colitis is caused by
clostridium difficile
examples of AB that causes C. Difficile
manifestations
DX
TX
clindamycin | amoxicillin | ampicillin co-amoxiclav | broad spectrum cephalosporine | quinolones (eg ciprofloxacin)
hx of recent treatment with AB, diarrhea (maybe bloody), abd pain, fever, high WBCs and CRP
stool
1st line - vancomycin 2nd - metronidazole (ORAL)

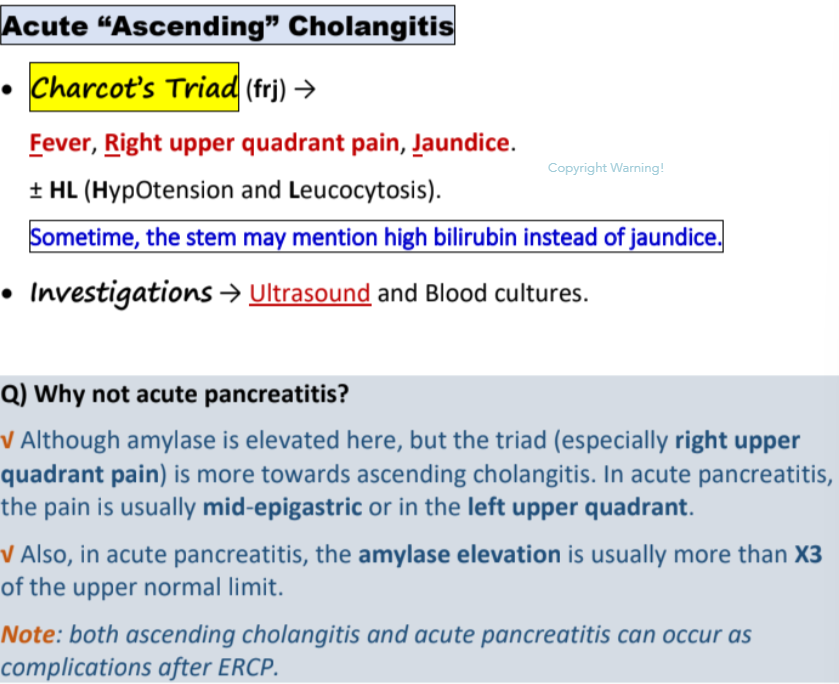
mediastinitis can be caused by ____________ during the ________.
X-ray shows ___________.
Prominent symptoms is _________.
Types are ________(_______ area) and ________ (________ region radiates to ________).
TX → __________ + ___________
(normal BP excludes ___________)
(clear lung fields exclude ________ and _________)
oesophageal perforation… endoscopy
mediastinal widening
chest pain
anterior (subcostal)…posterior (epigastric…interscapular region)
AB + repairment of perforation
vascular injury…pneumothorax…aspiration pneumonia