aice marine ynit 6
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
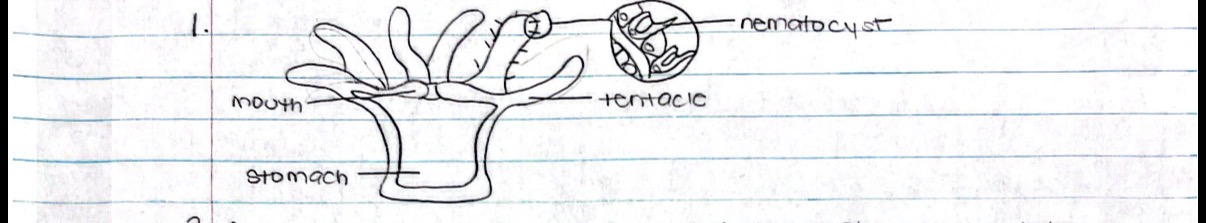
1. Draw a coral polyp and label the following parts: nematocyst, mouth, stomach, tentacle
Explain how organisms are classified using a taxonomic hierarchy. List all taxonomic levels from the most general to the most specific…………7 points
A taxonomic hierarchy is used to sort species into series of similar groups of organisms. The hierarchy starts from a very large group to the smallest, or most general to most specific. The levels, from most general to most specific, are: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species.
Outline the rules of naming organisms. Name the system that is used…..4points
Organisms are named using the Binomial Nomenclature system. Under this system, a species has a two-part name in Latin, composed of its Genus, which is capitalized, and its species, which is lowercase . When typed, the name is italicized, while it is underlined when handwritten.
Define and explain the use of a DICHOTOMOUS KEY…………………………………………………5 POINTS
A dichotomous key is an identification tool that utilizes a series of choices between different characteristics with directions to another stage in the key until the species is identified. These keys are used to identify which species an organism belongs to.
Define what is a keystone species and cite 3examples……………………………………………….5 points
A keystone species is a consumer that plays a crucial role in an ecosystem. They control other species by grazing, predation, and competition, and without them, the ecosystem would change drastically or fall to survive
Ex: blue shark, COTS, Kelp (seagrass)
List 2 characteristics of plankton…………………………………………………………………………………2 points
Plankton are microscopic free-floating organisms who are unable to propel themselves against a current, so they
float with currents. Plankton are keystone species.
List 3 characteristics of phytoplankton and provide 1 example………………………………………4 points
Phytoplankton are found at the surface to absorb sunlight. They absorb nutrients from their environment by completing photosynthesis. They are also important in removing CO2 from the atmosphere. Ex: diatoms, dinoflagellates
List 3 characteristics of zooplankton and provide 1 example………………………………………….4 points
Zooplankton are important consumers. They move vertically in the water column to feed on phytoplankton in the photic zone, and are very sensitive to environmental change. Pollution, ocean acidification, and water temp. increase can kill them. Ex: jelly fish, copepod, Krill
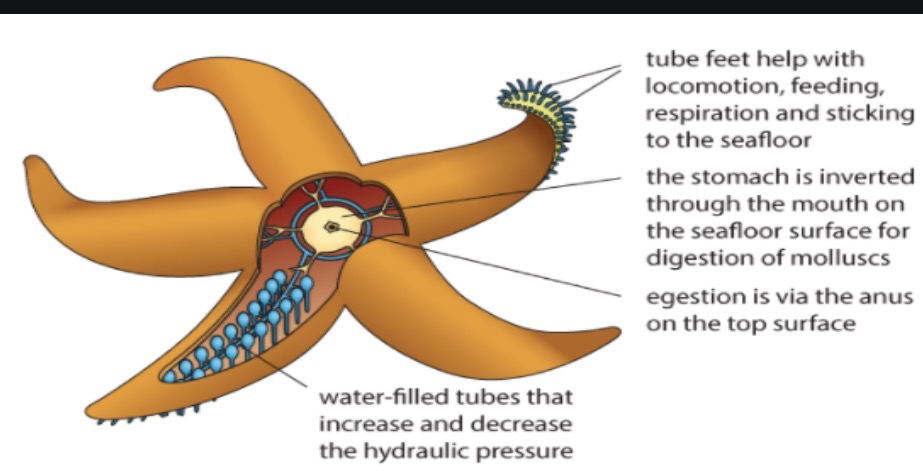
DISSCUSS 2 characteristics of echinoderms…………………………………………………………………..4 points
Echinoderms have penta radial symmetry: 5 arms radiate from a central body cavity. They also have tube feet, a system of water filled tubes under each arm that regulate hydraulic pressure. These are used for movement , feeding, and respiration.
Explain how echinoderms are important ecological in coral reefs, kelp forests, sandy shores……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..6 points.
In coral reef communities, echinodemes like COTS increase biodiversty by feeding on fast growing coral to make space for slow growing coral. In Kelp forests, echinoderms like sea urchins feed on the Kelp, while also being prey to sea otters. This predator-prey relationship is important to control kelp populations. In sandy shores, echinoderms like sea cucumbers filter seawater, produce nitrogenous waste used for coral growth, and contribute to the food chain (larvae).
11. list positive and negative economic importance or echinoderms………………………..…4 points
Echinoderms positively impact the economy as sea cucumbers and urchins are sources of income in the agriculture,fishing, food, and scientific industries. Their negative impacts include damage of ecotourism industries by COTS when they destroy coral reefs and Kelp forests.
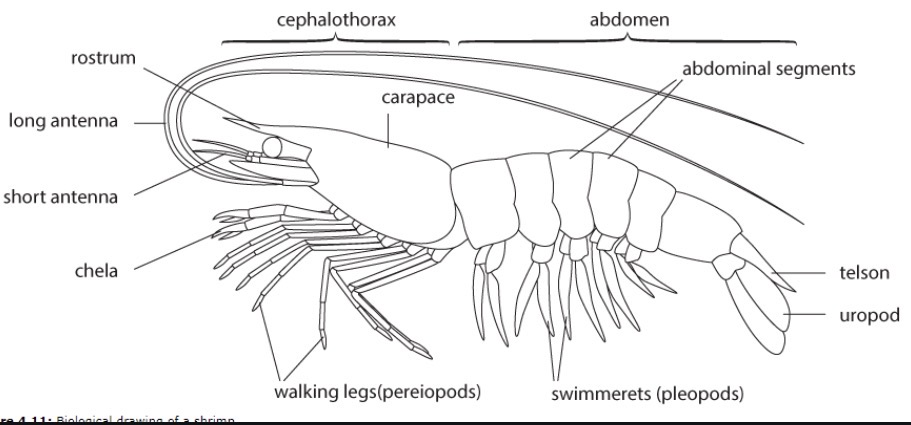
12. Outline 3 main features of crustaceans……………………………………………………………….….3 points
Crustaceans can survire in almost all aquatic habitats, Their starting stage is called a nauplius, & they have a hard exoskeleton that provides protection from predators and Water loss.
13. Discuss the parts of the crustacean’s cephalothorax…………………………………………….….6 points
A crustaceans cephalothorax is made up of its head and thorax. It has a carapace at the top, used for protection, two pairs of antennae (short/long), and jointed legs used to gather food (at least 5 pairs).
14. discuss the parts of the crustacean’s abdomen……………………………………………………..…3 points
A crustacean's abdomen is split into abdominal segments, contains swimmerets (used to assist with reproduction), and ends with a fan-shaped tail.
15. Discuss some ecological importance of crustaceans…………………………………………………5 points
Crustaceans are important for diff. ecosystems because some act as decomposers (break down decaying matter), many are important food sources, some shrimp eat algae (which stops algae from blocking sunlight for photosynthesis) and Krill! (→ important in polar waters → decreases because global warming → algal blooms).
16. list positive and negative economic importance of crustaceans…………………………….….4 points
Crustaceans' positive impacts on the economy include:
human consumption of large Crustaceans
Increase of the food web w/ smaller crustaceans
the creation of pharmaceutical supplements using Krill
Negative impacts
the effect on the growth of farm-raised marine organisms.
17. Describe the following features of a bony fish: operculum, lateral line, scales………….3 points
A bony fish's operculum, lateral line, and scales are all external features. The operculum is a bony flap of skin that covers and protects the gills; the lateral like is a canal that extends from the head along the body and contains sense organs, and the scales are bony features on the skin that protect and reduce drag.
18. List all 5 pairs of fins of fish and explain their location……………………………………………….10 points
Pectoral fins: Pairs on each side of the body behind the operculum
2 ) Caudal fin: Tail of the fish
3) Pelvic fins : Pairs at the bottom of the fish in front
4) Anal fin: Bottom of fish in the back
5) Dorsal fins: top of the fish (up to 3)
19. List the functions of the gills and the swim bladder on the bony fish………………………….4 points
The gills and swim bladder of a bony fish are internal structures. Gills are used for gas exchange, & the swim bladder is a buoyancy organ that allows the fish to stay afloat midwater without continuously swimming.
20 Discuss some ecological importance of bony fish……………………………………………………….6 points
-Bony fish are important to diff. ecosystems because they provide nutrients to primary producers when they excrete, they provide food for bears & freshwater species, during the summer they link nutrient cycles of diff. habitats through migration, feeding, and reproduction, and salmon are keystone species.
21. Discuss some economic importance of bony fish…………………………………………………….4 points
Bony fish positively impact the economy by providing nutrition for humans, providing nutritional supplements, providing income + jobs through fisheries, contributing to the production of fish feed and fertilizer, acting as pets, and contributing to scientific research.
22. Describe the following features from a cartilaginous fish: fins, gills, lateral line, scales, gill slits…..8 points.
Cartilaginous fish have fins & gills that act the same as those of bony fish. The lateral line of cartilaginous fish is found internally. They also have denticles, tooth-like scales, and gill slits, external openings from the gills.
List and explain 5 ecological importance of cartilaginous fish………………………………………….10 points
Blue sharks, a cartilaginous fish, are leystone species. This means they play an important role in food webs and can control invasive species through predation or competition. Sharks are a top predator, allowing them to regulate the populations of smaller organisms. They also promote biodiversity by helping maintain a balance between the predator and prey species.
list and explain some economic importance of cartilaginous fish …………………………………..4 points
Cartilaginous fish positively impact the economy by leading to tourism through commercial fishing and contributing to the production of goods with their parts. For example, jewelry, belts, wallets, boots, and cosmetics have shark parts.
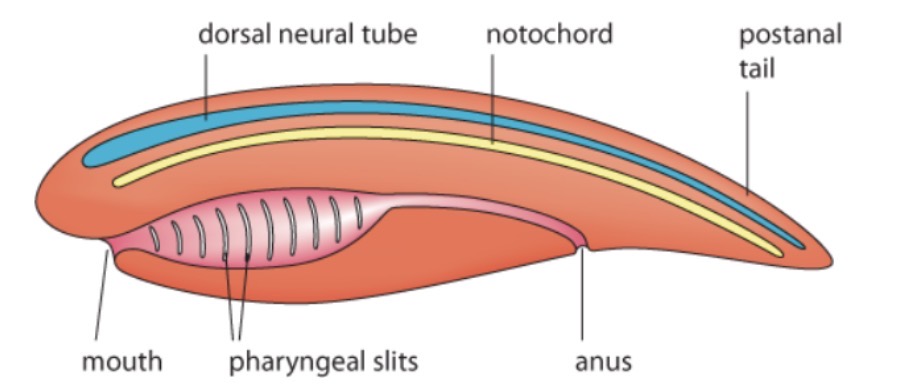
list and explain the function of the following features of a chordate: notochord, dorsal neural tube, pharyngeal slits, post anal tails…………………………………………………………………………………………8 points
A chordates notochord is a flexible, rod-shaped organ that allows the body to bend during muscle contractions. The dorsal neural tube is a tube-shaped organ that extends the length of the body a develops into the brain + spinal cord. Pharyngeal slits link to the mouth cavity & digestive system, allowing for filter feeding, ventilation, or the development into jaw/inner ear bones.The post - anal tail is used for swimming, located to the rear of the fish
26.Suggest 2 characteristics of macroalgae…………………………………………………………………………2 points
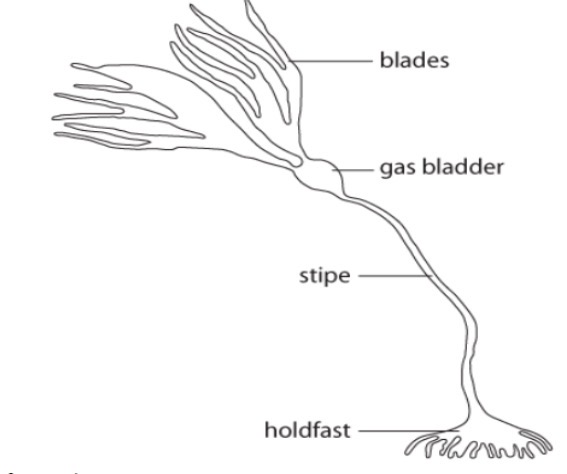
2 characteristics of macro algae include: blades and the holdfast. Macro-algae are large marine producers that go through photosynthesis + Live in shallow seas
Discuss the following macroalgae features: thallus, holdfast, stipe, blades, gas bladders…………8 points
The thallus of macroalgae is its main body, which has 3 main parts. The hold fast is a root-like structure that anchors the kelp to the seabed. The stipe is a stem-like structure that is vertical, long, and strong to prevent breakage. The blades are leaf-like structures that absorb light & minerals . Macro algae also have gas bladders, which keep them afloat in the photic zone to increase photosynthesis.
28. list and explain 4 economic importance of macroalgae…………………………………………………….8 points.
Macro algae, like seaweed, are used for cooking (since it is rich in protein), for medicine( it is put i n skin creams and herbal remedies), for aquaculture (it is processed into pellets for feed), in the food industry (as an emulsifier).
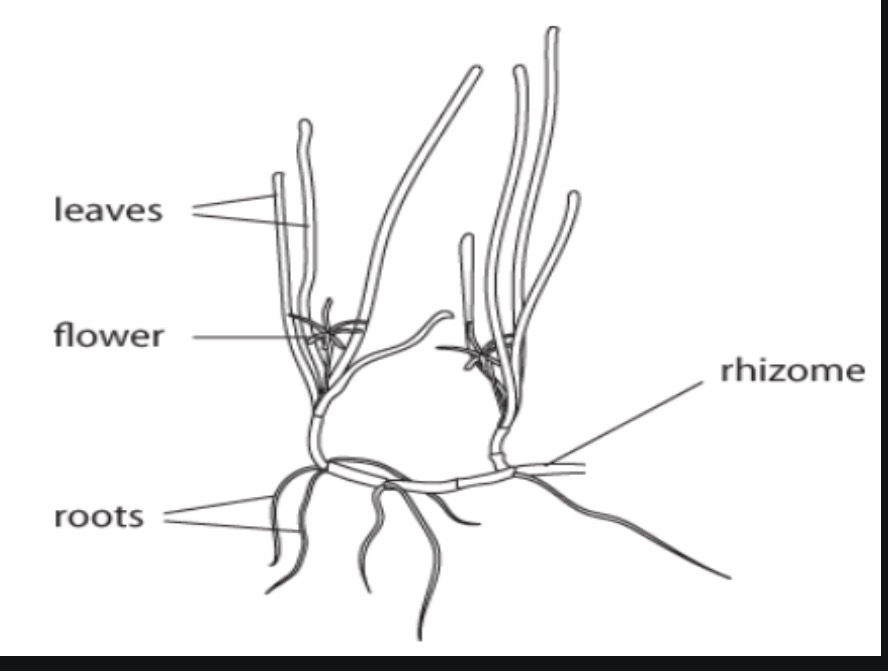
29. Discuss the 3 types of plants…………………………………………………………………………………….6 points
Marine plants are flowering marine producers. The 3 types include:
floating plants,
emergent plants rooted but projected abovesurface),
a submergent plants (rooted and remain underwater).
30. List and discuss the 4 adaptations marine plants have to live on the continental shelf……..8 points.
To live on the continental shelf, marine plants have roots (to anchor down), rhizomes (enables plant to reproduce asexually), leaves (with chloroplasts t o increase photosynthesis), + flowers (which
release pollen to grow population)
31. Discuss 5 ecological importance of marine plants…………………………………………………………10 points
Marine plants are important to diff. ecosystems because they are the foundation of aquatic communities w/ high biodiversity, they are dominant producers in estuarine habitats, they provide energy for organisms when they die, they provide nurseries, they increase the dissolved oxygen concentration in water.
32. Discuss 4 economic importance of marine plants…………………………………………………………8 points.
Marine plants hold economic importance be they are rarely used for food sources + cant be harvested easily, they provide economic support to coastal communities by being a form of protection, they increase tourism, and they provide wood for fires + building (mangroves)
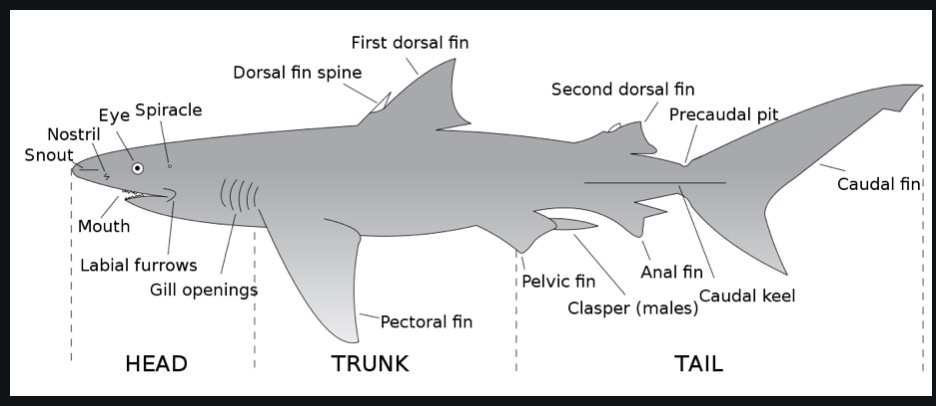
33. label all features of a shark
34 label all features of a lobster
35 label all features of a star fish
36 label all features of a marine plant
37 label all features of a macroalgae.
38 label all features of shrimp
label all features of chordates
38. KNOW ALL RULES OF DRAWING.
39. FORMULA TO REMEMBER: MAGNIFICATION= IMAGE SIZE / ACUAL SIZE