unit 7 chemistry
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Equilibrium
Physical is a reversible change of state.
Chemical is a reversible chemical reaction that can go in the direction to create products or to create reactants.
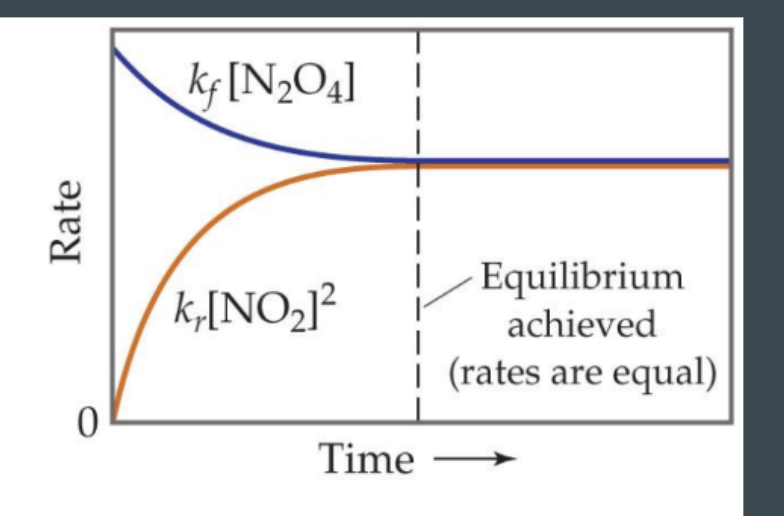
rate of the forward reaction is the same as the rate of the reverse reaction.
Key info
Only achieved in closed systems
Only possible in reversible reactions
dynamic because because the forward and reverse reactions are continuously happening at the same time and the same rate.
NOT same amount of products and reactants
No net change in reactants and products when reaching
Concentration graph at equilibrium
amount of product and reactant remains constant
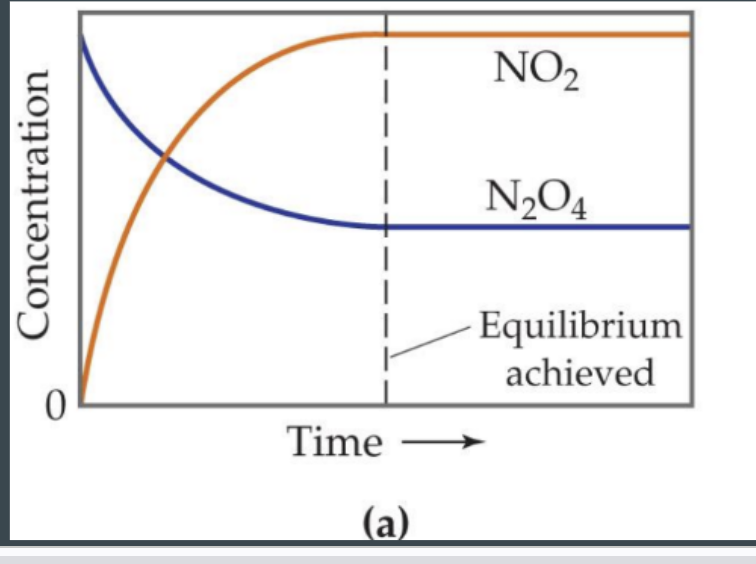
reaction graph at equilibrium
Proceed at same rate (foward and reverse)
Reaction Quotient (Q)
relative concentration/pressure of the reaction species at any time
Equilibrium Constant (K)
relative concentration/pressure of reaction species at equilibrium.
Equilibrium Expressions
Keq= [Concentration products] / [reactants] (no solids or liquids)
Reverse: More reactants formed
Foward: More products formed
When Keq> 1, reaction is product favored
When Keq< 1, reactant favored
When Keq very small, heavily reactant favored
When Keq very large, heavily product favored
Aqueous (concetration)
Qc + Kc
Gases (pressure)
Qp + Kp
A + B - C + D
Increase in concentration: shift AWAY from the side of the reaction where the substance is found
Decrease in concentration: shift TOWARDS the side of the reaction where the substance is found
Increase temperature: Shift away from the heat source
Decreased temperature: Shift rowards the heat
Increased pressure: Shift away from the side with the largest cumulative number of molecules found (coefficients)
Decreased pressure: Shift towards the side with the largest cumulative number of molecules found (coefficients)
Endothermic: Heat is a reactant
Exothermic: Heat is a product
When a stress is applied to a system in dynamic equilibrium, Q is no longer equal to K.
A shift occurs so Q is again equal to K.
Calculating K with multistep
When flipping the reaction, take the inverse
When doubling the reaction, square it
ICE
Initial, concentration, equilibrium
Ksp Calculations
Ksp is not the same as solubility.
Solubility is the quantity of a substance that dissolves to form a saturated solution
Molar solubility (s): The moles of solute that can dissolve in 1L of solvent
Units mol/L or M
Common units for solubility: Grams per liter (g/L) or Moles per liter (mol/L)