Health, fitness and well-being
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Physical benefits of exercise
Improves heart function, improves the efficiency of the body's systems, improves fitness, and reduces the risk of obesity
Mental benefits of exercise
Reduced stress, release of serotonin, and helps to control emotions
Social benefits of exercise
Make friends, improved cooperation, and improved teamwork
Physical health and wellbeing
All body systems working well, free from illness and injury. Ability to carry out everyday tasks.
Mental health and wellbeing
State of wellbeing in which the individual realises his or her own abilities, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully, and is able to make a contribution to his or her community.
Social health and wellbeing
Basic human needs are being met (food, shelter and clothing). The individual has friendship and support, some value in society, is socially active and has little stress in social circumstances.
Fitness
The ability to meet the demands of the environment
Advantages of having good fitness levels
Helps you to remain healthy, reduces the chances of injury, and ensures you are physically able to work
sedentary lifestyle
A lifestyle with irregular or no physical activity.
Physical effects of exercise
improves heart function
• improves efficiency of the body systems
• reduces the risk of some illness
• able to do everyday tasks
• to avoid obesity
Mental effects of exercise
• reduces stress/tension
• release of feel good hormones (serotonin)
• able to control emotions.
Social effects of exercise
• opportunities to socialise/make friends
• cooperation
• teamwork
• have essential human needs (food, shelter, clothing)
Effects of increased fitness
• reduces the chances of injury
• can aid in the physical ability to work, eg on your feet all day/manual labour
Mental consequences of a sedentary life style
Lack of sleep, poor self esteem, lack of motivation, depression, stress
Physical consequences of a sedentary life style
Higher risk of: coronary heart disease, becoming obese, osteoporosis, hypertension and type 2 diabetes
Social consequences of a sedentary life style
Lose friends, not able to make new friends, become scared of socialising and lose social skills
Hypertension
high blood pressure
Obesity
The state of being grossly fat or overweight
Effects of obesity on sporting performance
• limits stamina/cardiovascular endurance
• limits flexibility
• limits agility
• limits speed/power
Mental effects of obesity
It can cause depression and loss of confidence
Physical effects of obesity
• cancer
• heart disease/heart attacks
• diabetes
• high cholesterol
Social effects of obesity
• inability to socialise
• inability to leave home.
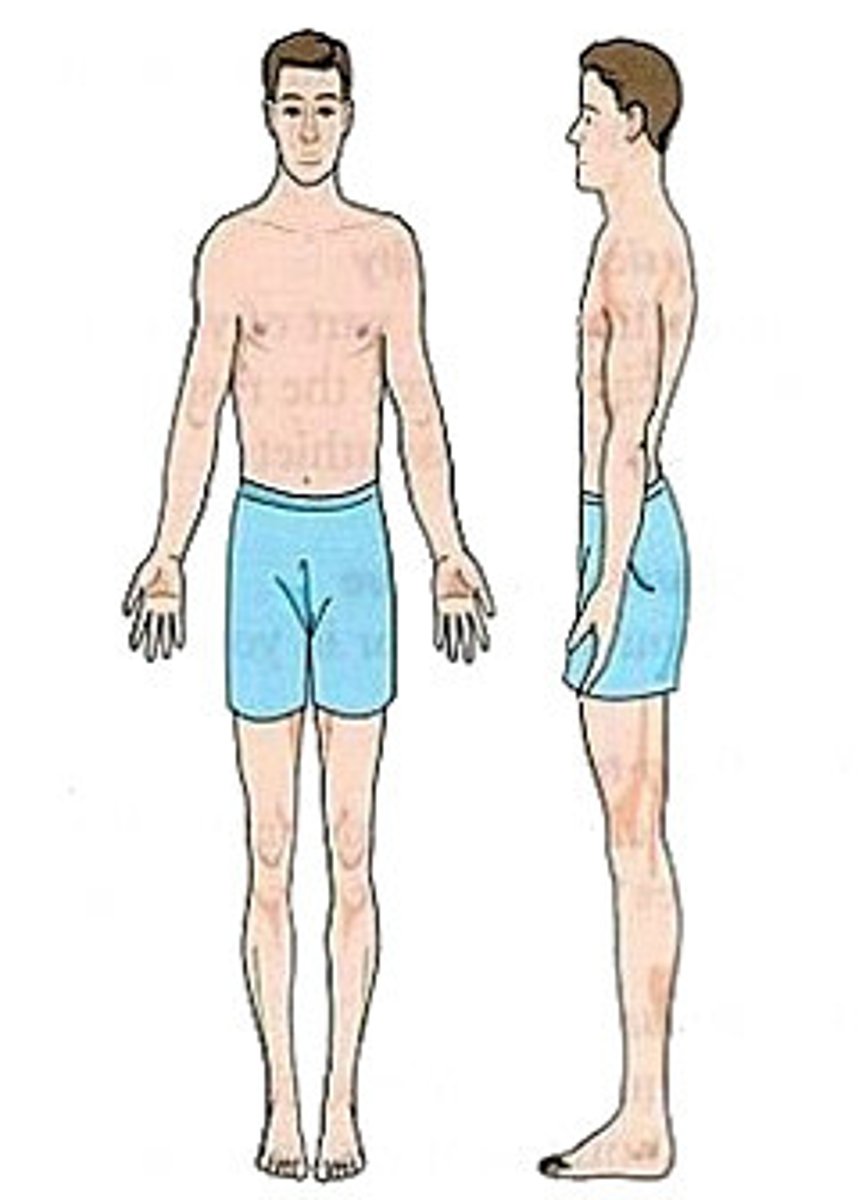
Ectomorph
Narrow shoulders and hips
not much muscle or fat
long, thin limbs
Good at high jump and marathon running
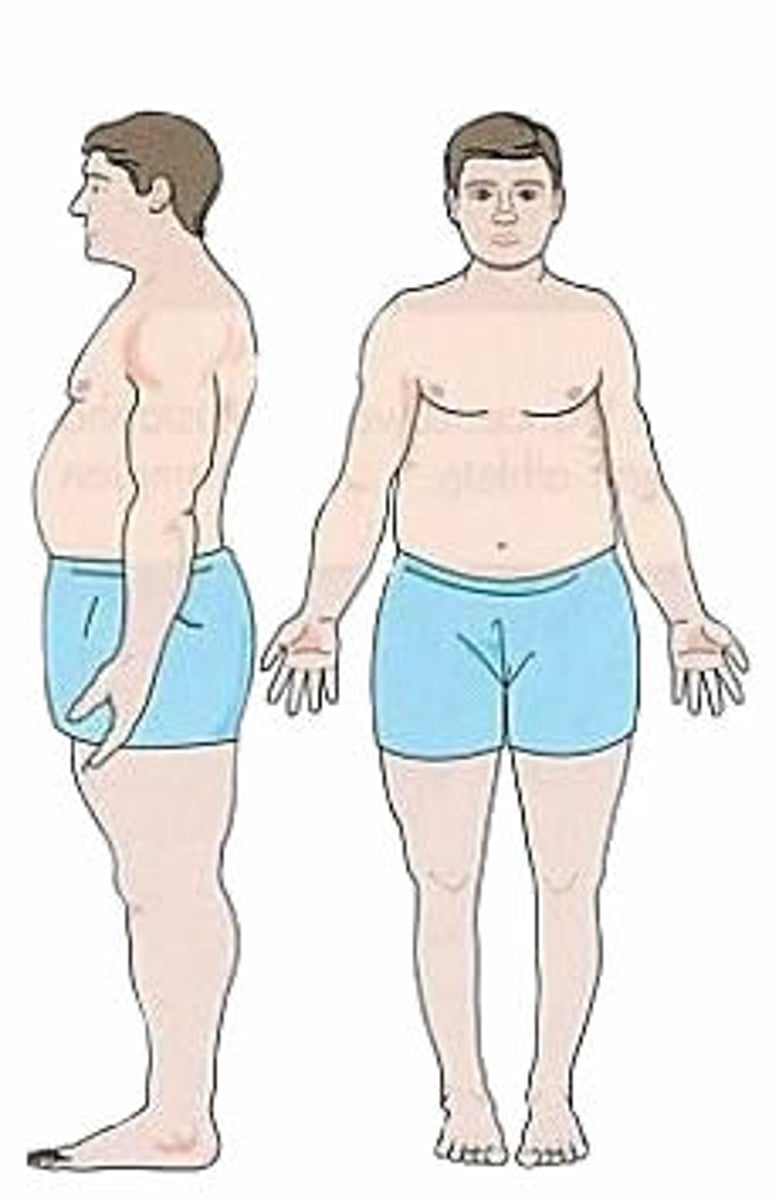
Endomorph
Wide hips,
Large amounts of body fat
shorter limbs
Thick ribcage
Good at rugby as a prop/forward
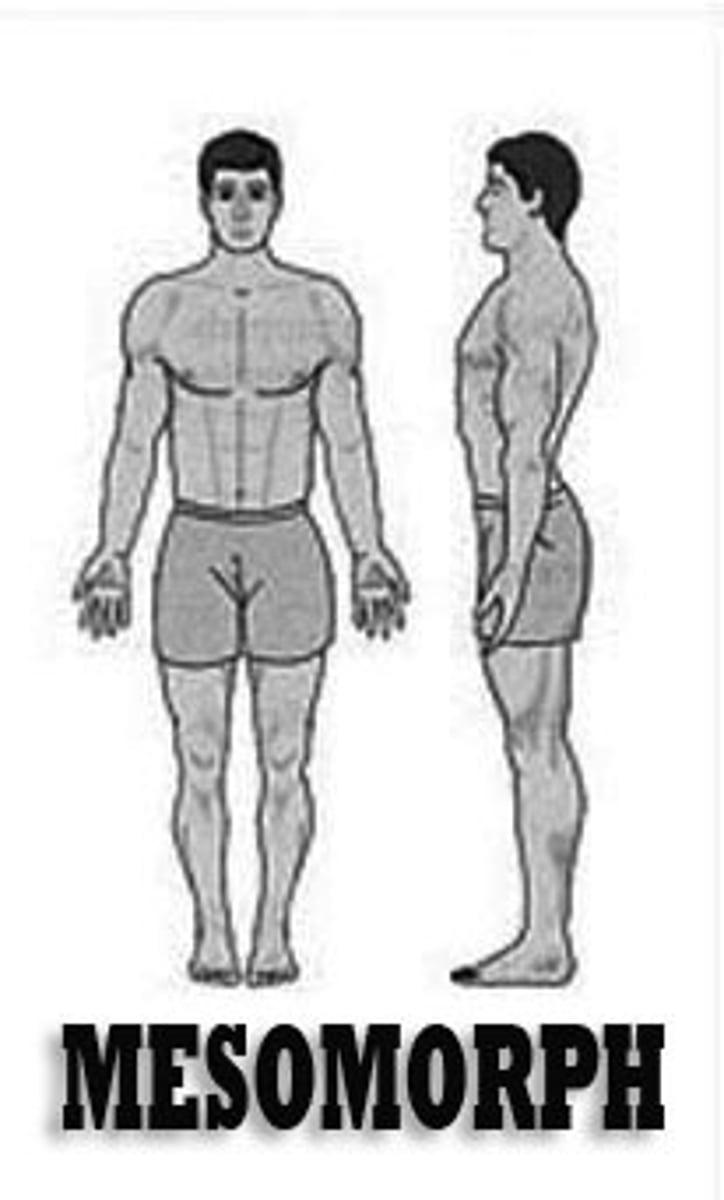
Mesomorph
Wide shoulders, flat stomach
Naturally strong and powerful
Builds muscle easily
Thick + dense muscles
Sprinter and weight lifters
Somatotype
Classification of body type
2,000
How many calories does the average woman require a day?
2,500
How many calories does the average man require a day?
Age, height, gender and energy expenditure
What does the recommended calorie intake depend on?
BMI
body mass index
Under 20
What is the BMI for underweight?
20-25
What is the BMI for a healthy weight?
26-30
What is the BMI for overweight?
30+
What is the BMI for obese?
muscle weighs more than fat
What is the problem with the BMI scale?
A balanced diet
A diet that contains the right amount of food, the correct amount of calories and a mix of food types so the body receives enough vitamins and minerals
Complex carbohydrates
starches found in grains, potatoes, and vegetables
simple carbohydrates (sugars)
Sugars found in fruit, cake and chocolate
Carbohydrates
Stored in the muscles and liver as glycogen, which can be converted quickly back into energy. It is the main and preferred energy source for all types of exercise, of all intensities
It will be turned into fat and stored in the body
What happens to unused energy?
55-60%
What percent of your diet should be made up of carbohydrates?
25-30%
What percentage of your diet should be fat?
15-20%
What percentage of your diet should be protein?
Fat
an energy source. It provides more energy than carbohydrates but only at low intensity
Protein
For growth and repair of muscle tissue.
Vitamins and Minerals
For maintaining the efficient working of the body systems and general health
Hydration
Having enough water to enable normal functioning of the body
Dehydration
Excessive loss of water from the body, interrupting the normal function of the body
Rehydration
Consuming water to restore hydration.
consequences of dehydration
• blood thickening (increased viscosity), which slows blood flow
• increases in heart rate/heart has to work harder/irregular heart rate (rhythm)
• increase in body temperature/overheat
• slowing of reactions/increased reaction time/ poorer decisions
• muscle fatigue/cramps