Neuro Study guide WEEKS 0-3? (unfinished)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
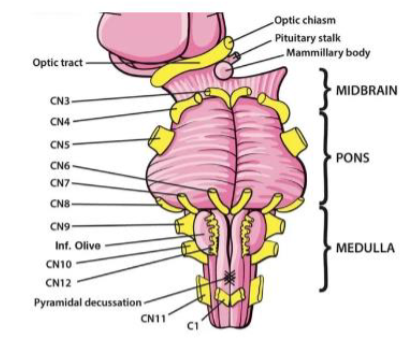
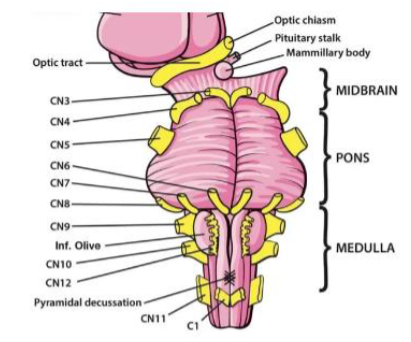
I (1) Olfactory
Smell — Sensory
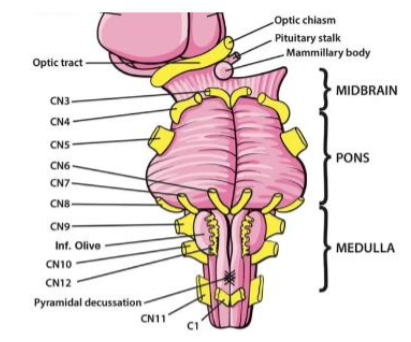
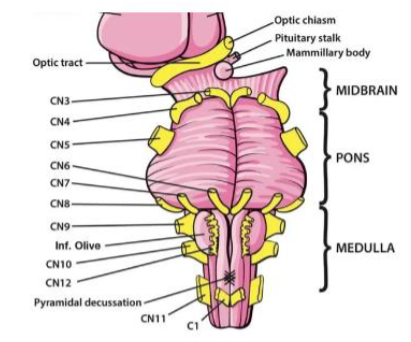
II (2) Optic
Vision — Sensory
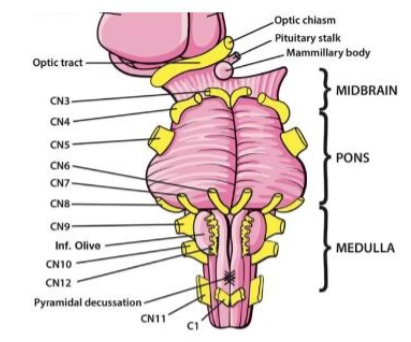
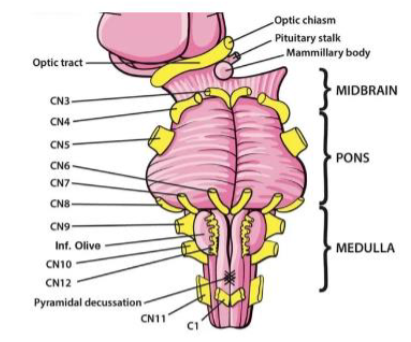
III (3) Oculomotor
Moves eye up, down and inward
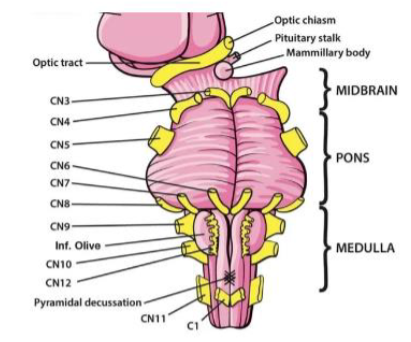
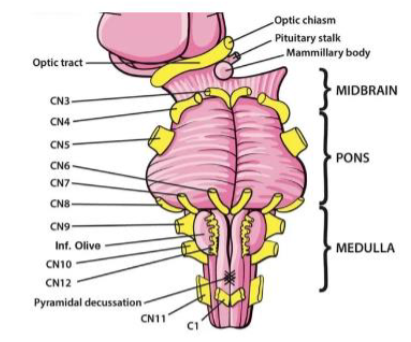
IV (4) Trochlear
Moves eye medially and down — Motor
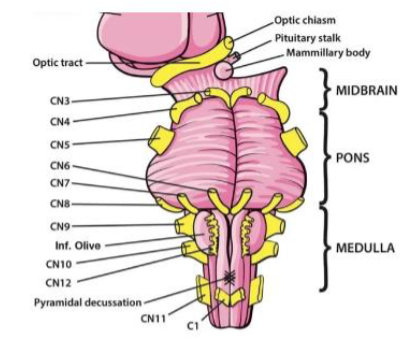
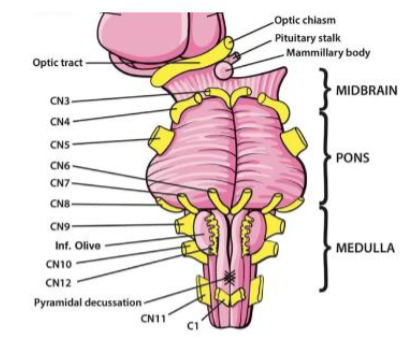
V (5) Trigeminal
Facial sensation; chewing — Both
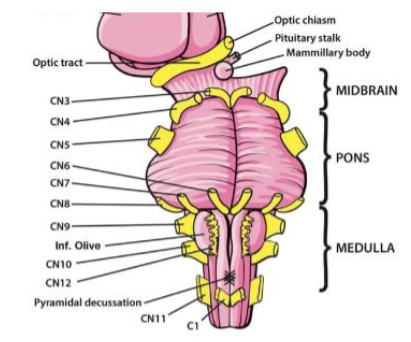
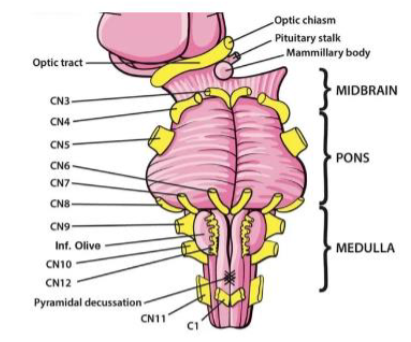
VI (6) Abducens
Abducts eye (moves eye laterally) — Motor
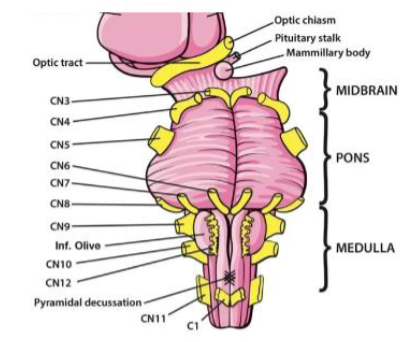
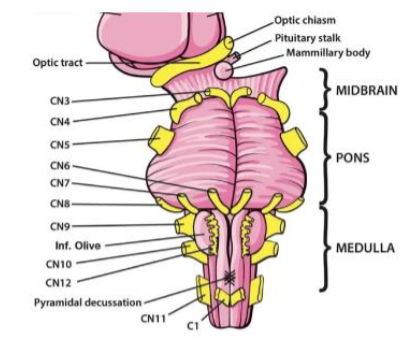
VII (7) Facial
Facial expression; taste (anterior tongue); tears; salivation — Both
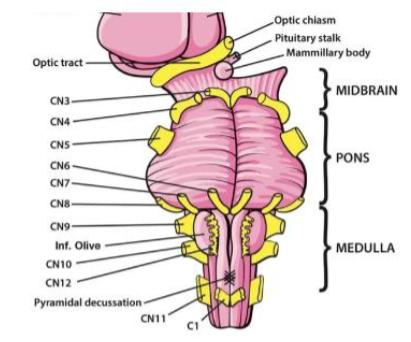
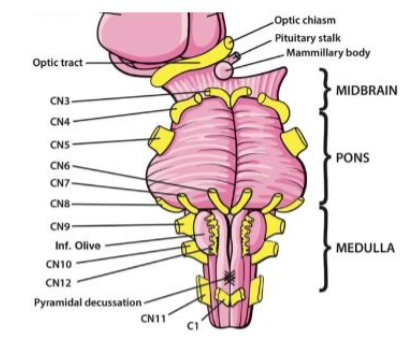
VIII (8) Vestibulocochlear
Hearing; balance (head position & movement) — Sensory
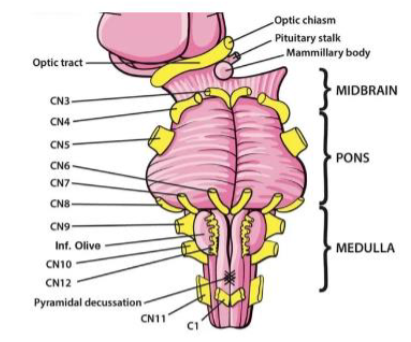
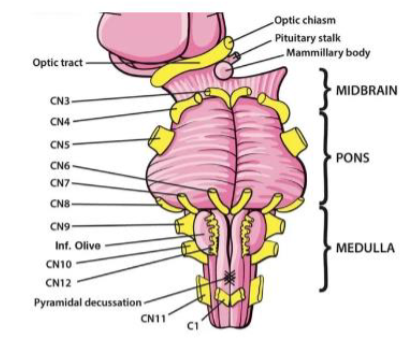
IX (9) Glossopharyngeal
Taste (posterior tongue); salivation; monitors BP from carotid; constricts pharynx, gag reflex, inner ear sensation — Both
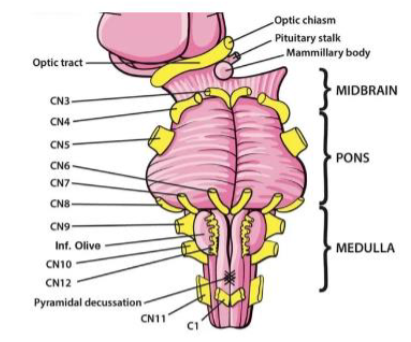
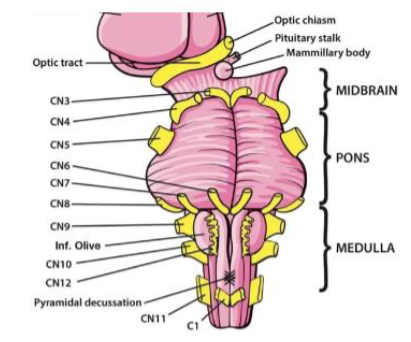
X (10) Vagus
Regulates swallowing & speech; taste; sensation from pharynx & larynx; regulates viscera, heartrate organs — Both
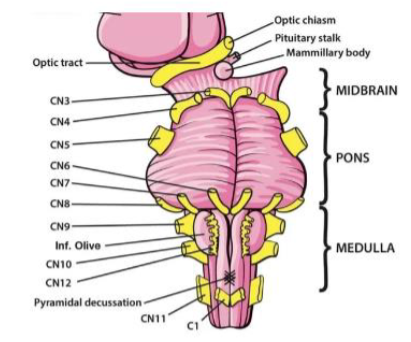
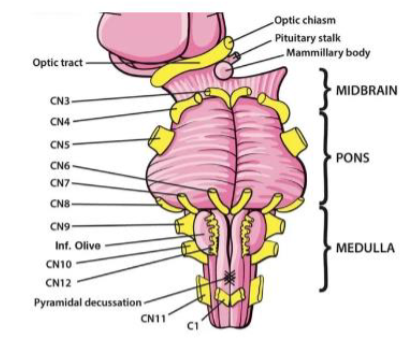
XI (11) Accessory
Elevates shoulders; turns head — Motor
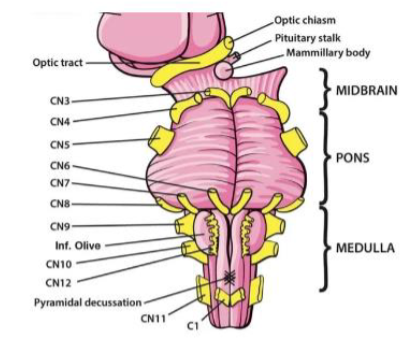
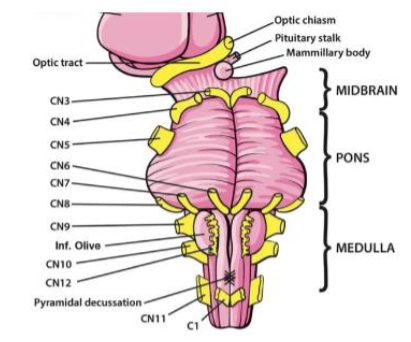
XII (12) Hypoglossal
Moves tongue — Motor
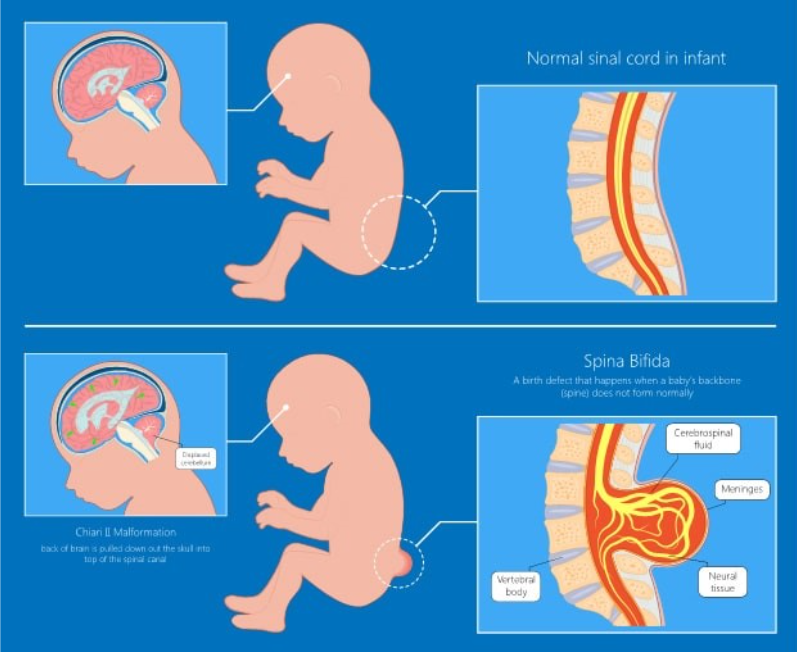
Descibe Spina Bifida
Spina bifida is a congenital neural tube defect where the spinal column does not close completely, resulting in varying degrees of disability and complications, depending on the location and severity of the defect.
mobility issues like difficulty walking, orthopedic problems such as hip dislocations and scoliosis, and sensory deficits in the legs and feet. Other complications are bladder and bowel dysfunction, increased risk of pressure sores and poor healing due to poor sensation, and reduced bone density
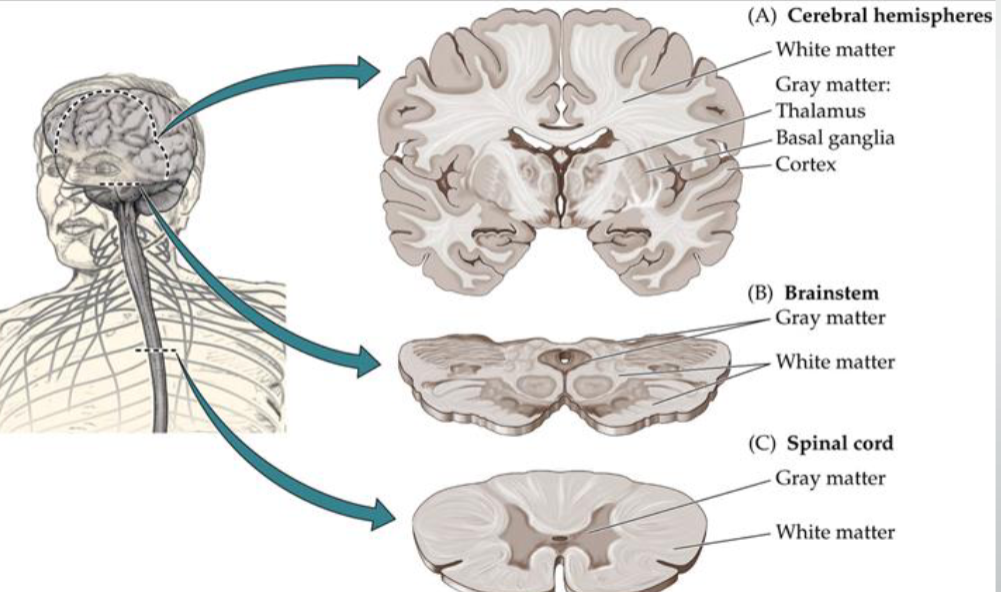
What is Grey Matter?
= Processing
It’s where the “thinking” parts of the nervous system live (cell bodies + dendrites).
If you group them in the CNS → called a nucleus.
If you group them in the PNS → called a ganglion.
If gray matter is spread out on the surface → called a cortex (like the cerebral cortex).
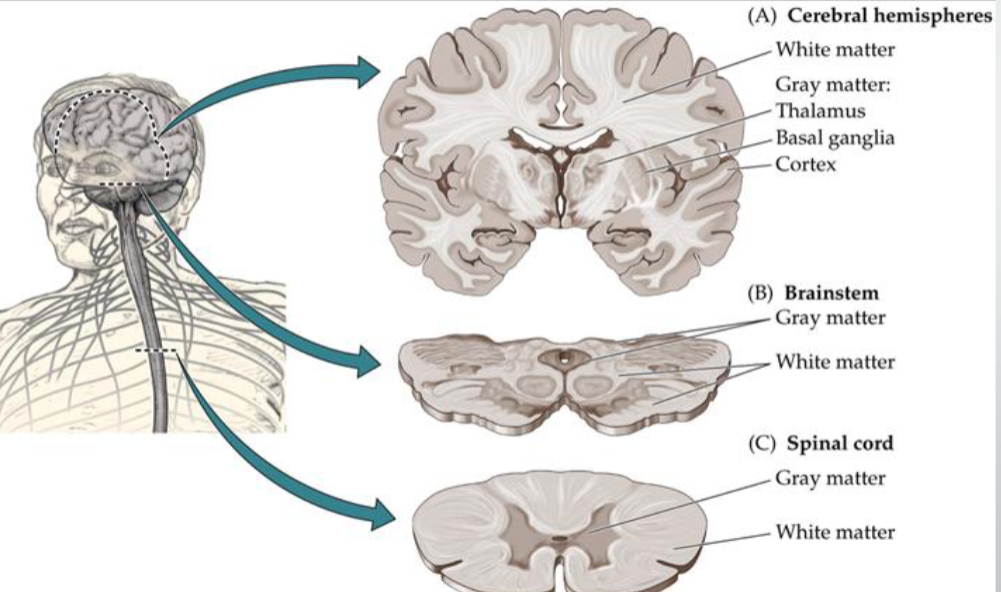
What is White matter?
= Signaling chanels or wiring
mostly axons, which are like wires that carry signals between different parts.
Depending on shape/location, bundles of axons get different names: tract, fasciculus, lemniscus, peduncle, bundle (all basically “cables”).
Two big special ones:
Corpus callosum = the giant bridge of axons that connects the left and right brain hemispheres.
Internal capsule = the “highway” that carries info up to the cortex and back down.
Descibe an Upper Mottor Neuron
originates in the cerebral cortex or brainstem and sends signals to lower motor neurons, thus controlling voluntary movements. They are involved in the direct control of movement by transmitting signals that influence muscle contraction and coordination.
If damaged:
Hyperreflexia when tested
Spastic (stiff) paralysis
Increased reflexes
Babinski sign
clonus (Muscle Jumping)
Describe a Lower Motor Neuron
A lower motor neuron is a type of neuron that originates in the spinal cord and directly innervates skeletal muscles. It is responsible for executing movements by transmitting signals from the central nervous system to the muscles.
If damaged:
flaccid paralysis,
muscle atrophy
decreased reflexes
Fasciulations under the skin (twitches)
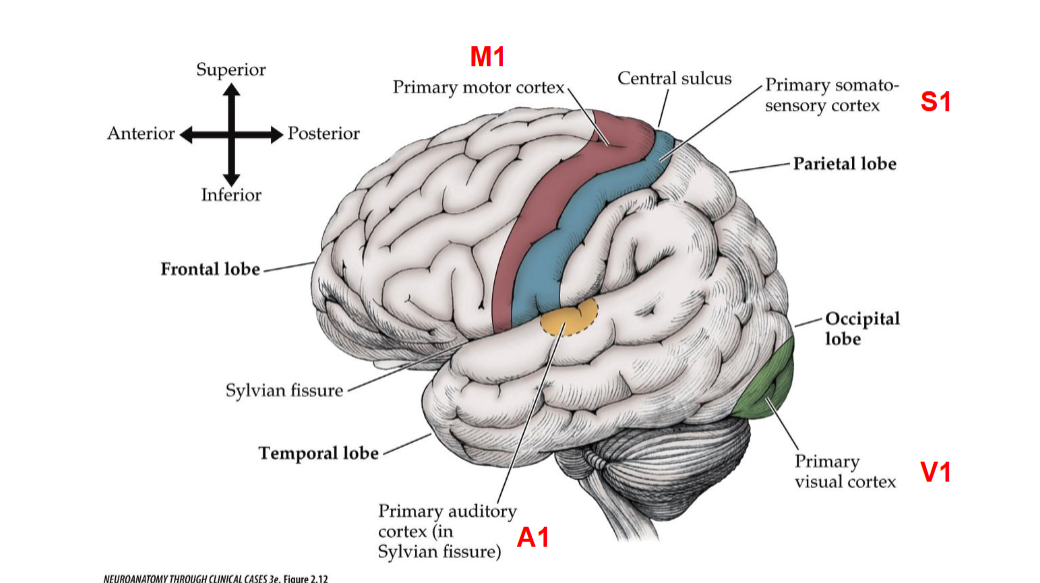
M1 Descibes what portion in the brain? Functions?
M1 refers to the primary motor cortex, located in the frontal lobe. It is responsible for initiating voluntary motor movements and coordinating motor functions.
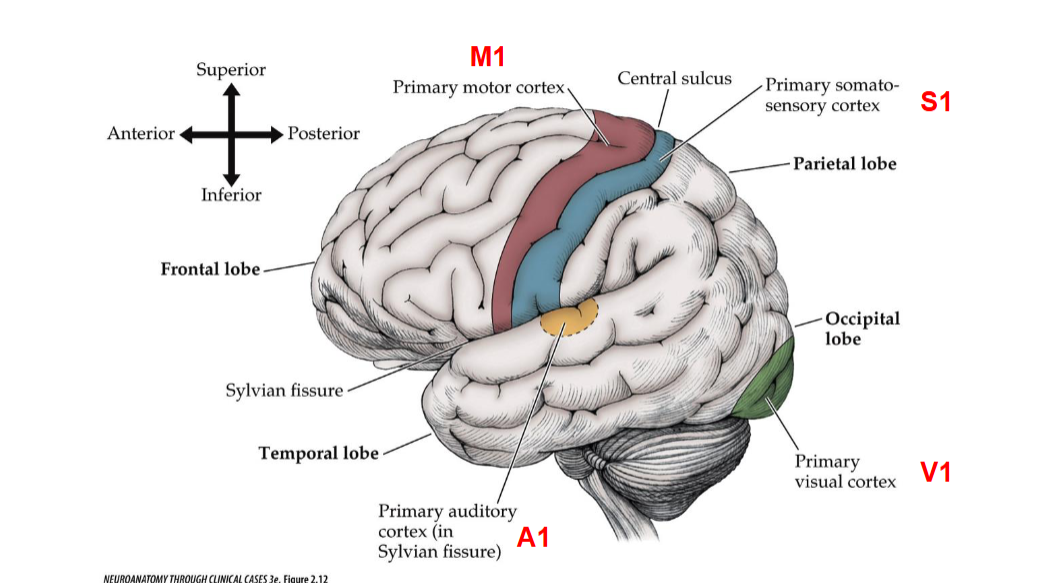
S1 Describes what portion in the brain? Functions?
S1 refers to the primary somatosensory cortex, located in the parietal lobe. It is responsible for processing sensory information from the body, such as touch, temperature, and pain.
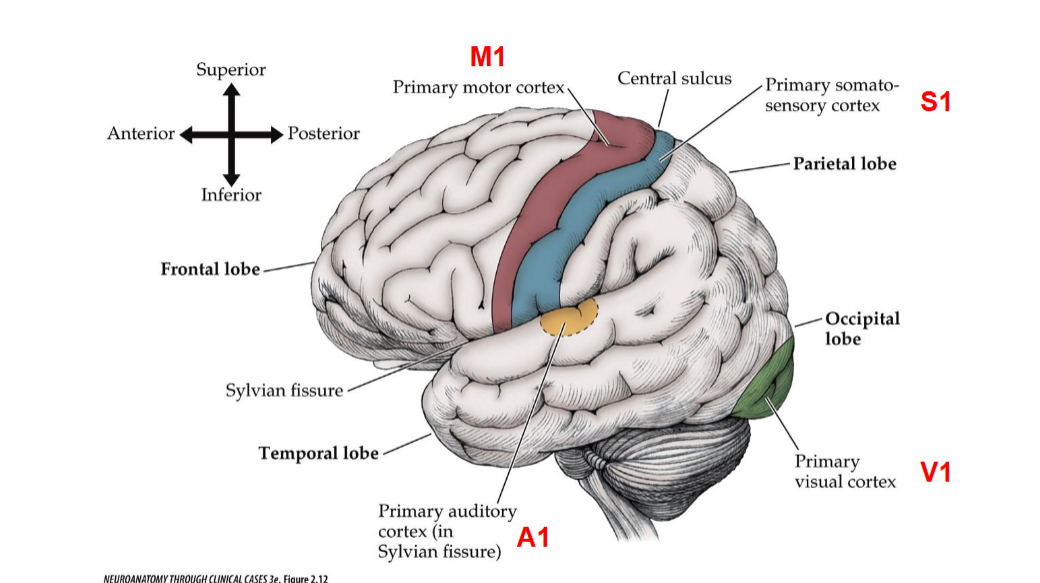
A1 Descibes which portion of the brain? Functions?
A1 refers to the primary auditory cortex, located in the temporal lobe. It is responsible for processing auditory information, including sound perception and language comprehension.
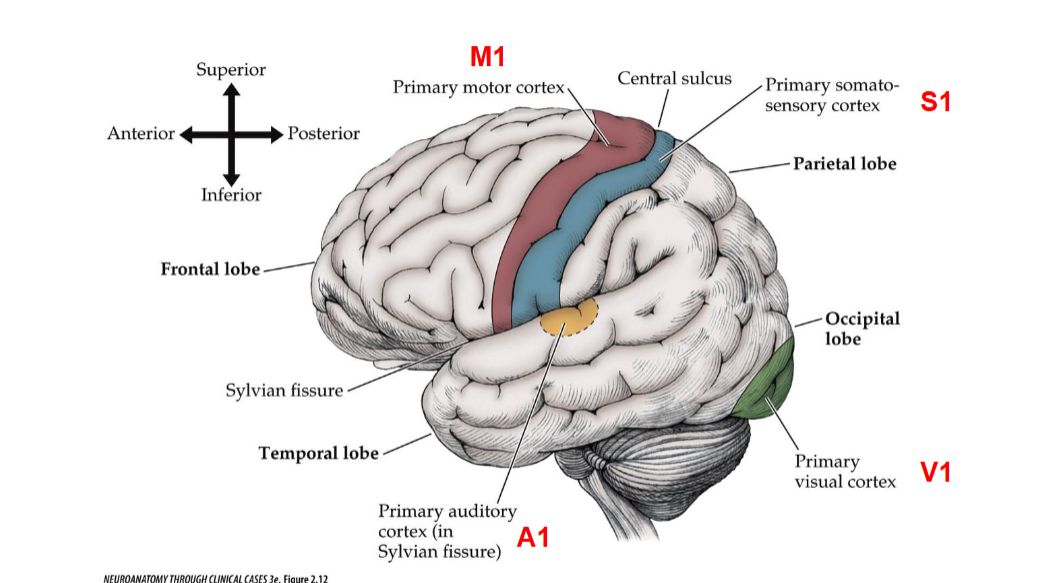
V1 Descibes which portion of the brain? Functions?
V1 refers to the primary visual cortex, located in the occipital lobe. It is responsible for processing visual information, including aspects such as color, motion, and depth perception.