Binomial Trees
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What does the one-step binomial model describe?
It describes how a stock price moves over one time step, assuming it can either go up or down.
What are the key assumptions of the one-step binomial model?

How do you calculate the percentage change in stock price?
If the stock moves up: u−1.
If the stock moves down: 1−d.
What happens if the stock price moves up in the binomial model?
The stock price increases to S0u, and the option's payoff is fu.
What happens if the stock price moves down in the binomial model?
The stock price decreases to S0d, and the option's payoff is fd.
What does the diagram in the binomial model represent?
It shows the two possible movements of the stock price:
Upward movement to S0u with option value fu.
Downward movement to S0d with option value fd.
What does a riskless portfolio consist of in the binomial model?
A long position in Δ shares and a short position in one option.
How is the portfolio value calculated if the stock price moves up?
The value is S0uΔ −fu.
How is the portfolio value calculated if the stock price moves down?
The value is S0dΔ − fd.
What equation ensures the portfolio remains riskless?
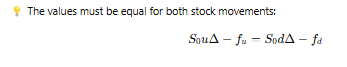
What is Δ (hedge ratio) and how do you calculate?
The sensitivity of an option's price to changes in the underlying asset's price.
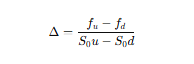
Why must the portfolio earn the risk-free rate r?
Because if it earned more or less, arbitrage opportunities would exist, violating the no-arbitrage principle.
What is the present value of the portfolio in the one-step binomial model?

What is the cost of setting up the portfolio at time t=0?
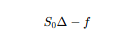
What equation follows from setting up the portfolio?
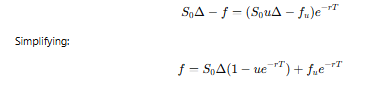
What is the formula for the option price f?
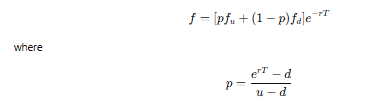
What does p represent in the binomial model?
p is the risk-neutral probability of an upward movement in the stock price.
What is the expected payoff of the option in the risk-neutral world after one period of time?
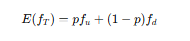
What is the expected return of the stock in the binomial model?
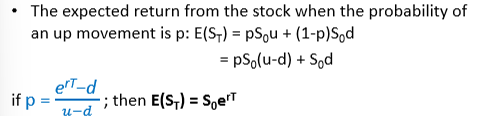
What happens when using risk-neutral probability p?
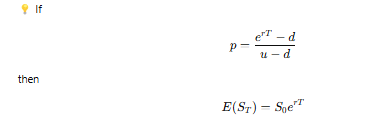
What is the key assumption in risk-neutral valuation?
The stock return equals the risk-free return, meaning we assume a risk-neutral world.
Why is risk-neutral valuation different from real-world valuation?
Because in the real world, investors demand extra return for risk, but in the risk-neutral world, we assume no risk premium.
What are the 4 key steps in one step binomial to compute actual option price today?
Compute possible future stock prices Su and Sd.
Compute option payoffs fu and fd.
Compute risk-neutral probability p.
Compute present value of the option using risk-neutral pricing.
What is a two-step binomial tree?
A model where a stock price evolves over two time steps, allowing for multiple possible outcomes.
What are the possible final stock prices in a two-step binomial tree?
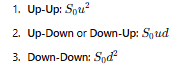
How is the option value at each node calculated?
Using backward induction, starting from the final payoffs:
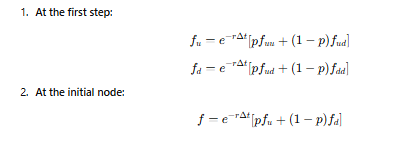
What are the 5 key steps in the two-step binomial to compute actual European option price today?
Construct the stock price tree.
Compute the payoffs at expiry.
Compute the risk-neutral probability p.
Compute option value at first step.
Compute the pv of the option.
What is the alternative method for American options?
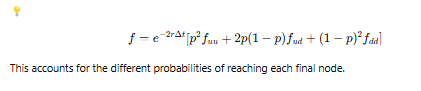
What are the probabilities of reaching different final nodes in a two-step binomial tree?

How is an American option valued in a binomial tree?
The process works backward through the tree, checking at each node if early exercise is optimal.
How is the value of an American option determined at the final node?
The final value is the same as for a European option because there is no time left for early exercise.
How is the value of an American option determined at earlier nodes?
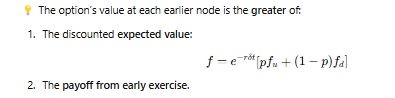
When should an American option be exercised early?
When the early exercise value is greater than the expected value from holding the option.
What is the Cox-Ross-Rubinstein (CRR) model used for in binomial trees?
It defines up (u) and down (d) factors to match stock price volatility.
What are the formulas for u and d in the CRR model?

How is the risk-neutral probability p calculated?
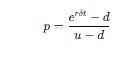
How does the formula change if the stock pays a dividend yield q?
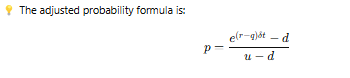
What assumption does the binomial model make for a dividend-paying stock?
The dollar amount of the dividend is known in advance, rather than the dividend yield.
How to Treat Dividends in a Binomial Tree - Case 1: Dividend is Paid at a Node
If the dividend is paid exactly at a node in the tree, it's simple:
Subtract the dividend from the stock price at that node.
Continue building the tree using the adjusted price.
How to Treat Dividends in a Binomial Tree - Case 2: Dividend is Paid Between Nodes (More Complicated)

Why is adjusting for dividends important in the binomial model?
Because dividends reduce stock price, affecting the option valuation.
How do stock prices evolve after the ex-dividend date?

How can the binomial model for a dividend-paying stock be simplified?
The stock price can be divided into two components:
Uncertain part: S∗
Present value of all future dividends during the option’s life.
When does the ex-dividend date (τ) occur in the binomial tree?
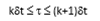
How is the uncertain component (S∗) of the stock price defined?
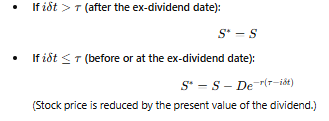
Why is the present value of dividends subtracted in the model?
Because when a stock pays dividends, its price drops by the dividend amount on the ex-dividend date.
How are stock prices in the binomial tree adjusted for dividends before the ex-dividend date (iδt≤τ)?
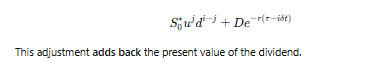
How are stock prices calculated after the ex-dividend date (iδt>τ)?
