1.0 Neurobiology
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Neurobiology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Physiology is the study of
Biological processes occurring in the body.
Study of functions within the body & how they work.
Anatomy is the study of the
the size, shape & location of the different bodily structures
Physiological functioning of the body is connected to
Cognitive processes
Emotions
Behaviors
The biological perspective of physiology
how psychological issues are impacted by biological processes
Physiology help psychologists to
Identifying physiological components of mental health disorders.
Understand the mechanism of action of psychiatric & recreative drugs.
Incorporating neuroscience findings into evidence- based practice.
Neurodiciplinar reserach
BIOfeedback
Machine that gives feedback of their own mental processes → to later help them to maintain physiological processes
Homeostasis
body’s attempt to maintain a constant internal environment, which requires constant monitoring &
adjustments as the conditions change.
Homeostatic regulation always requires
Receptor,
Control/integration centre
Effector
Components of homoestasis
Receptor
Control center
Effector
Receptor
Control center
Effector
Basic operational mechanism of the components in the homoestasis
Feedback loop
Homeostasis generally operates
Bidirectionally
Homeostasis generally operates bidirectionally
Respond to deviations in physiological parameters in both directions
When they rise or fall, ensuring that they are maintained relatively constant.
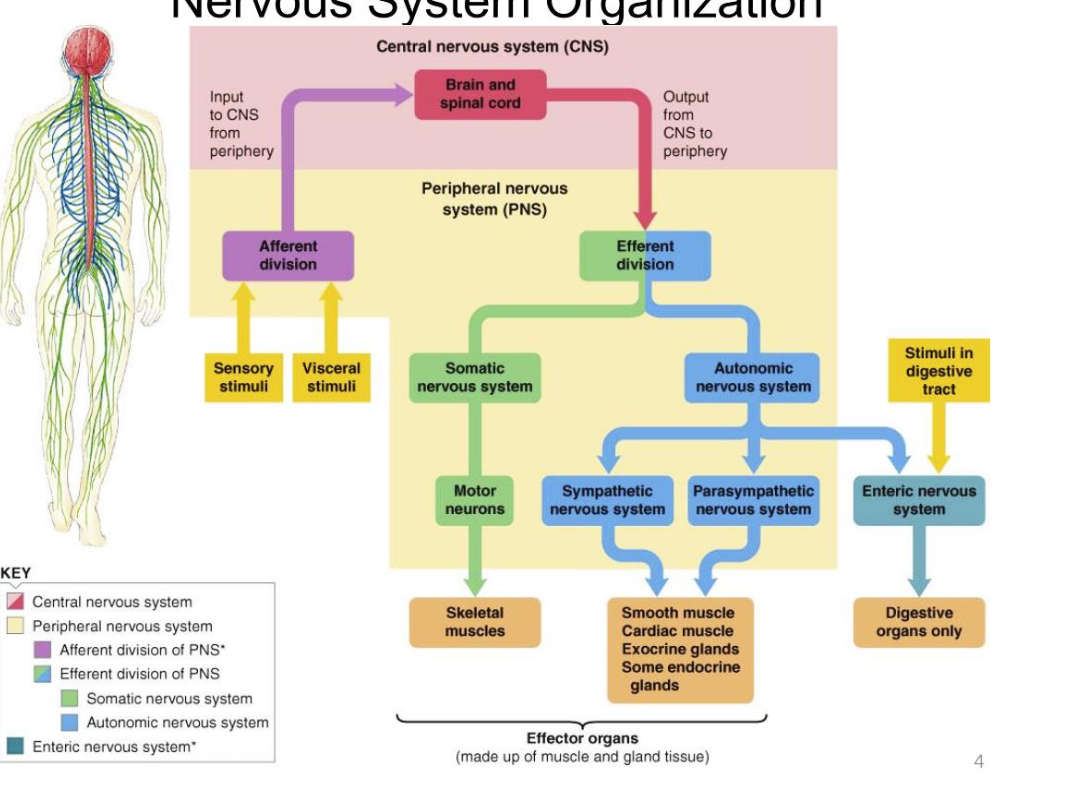
CNS anatomical
Spinal cord
Brain
PNS anatomical
Ganglia
Nerves (cranial / spinal)
Functions of NS
afferent (input from the CNS) & efferent (output from CNS)
The nervous & endocrine systems are the main
Responsible for regulating & maintaining homeostasis.
Functional division of the NS
The PNS neurons can be divided according to the direction of the information
Afferent / Sensory (neuron)
Peripheral sensory neuron
Efferent / Motor (neuron)
Motor neuron
Sensory or afferent neurons
information input to the CNS
Motor or efferent neuron
information output from the CNS
Somatic
Neurons that connect the brain and spinal cord to the skeletal muscle.
In charge of mostly voluntary movement but also skeletal muscle reflexes.
Autonomic
Neurons that connect the brain and spinal cord to involuntary effectors →
glands, cardiac muscle, & smooth muscle
Two branches in the (autonomic ns)
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Sympathetic
Emergency / alert state (fight or flight)
Parasympathetic
Relaxation/ recovery state (rest and digest)
Enteric system
Targets the digestive tract.
Sensory division
Afferent division
Motor divison
Efferent division
Effectors can be
muscles
glands
NS organization
Neurons
Cells that process & transmit information through electrical (impulse) & chemical signals (neurotransmitters)
Neuroglia / glial cells
Cells that provide support to neurons
Physical support (scaffolding)
Supply of nutrients
Regulate neuronal communication (synapse)
Defense
Information can only travel from
Dendrites to axon
Dendrites
Receives the information
Polar nervous cells
Each side of the cell is different & has a specific funtion.
Polarity ensures
Transmission of the electric impulse in one single direction
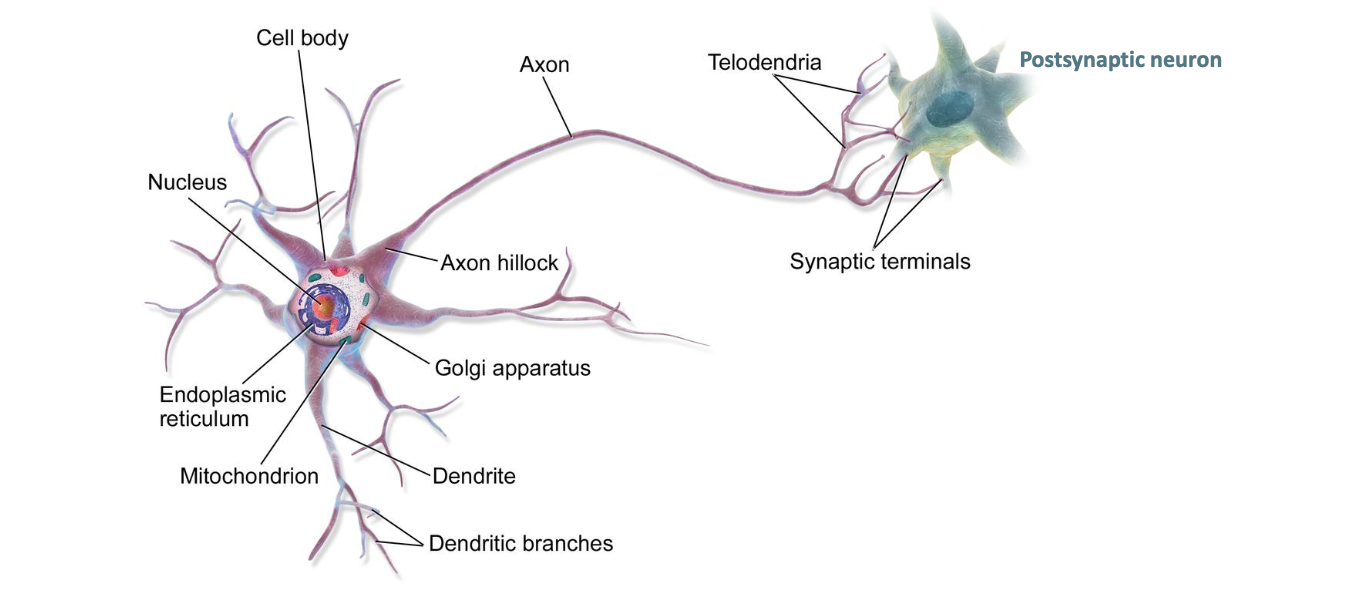
NEURONS: Celular structure
Dendrites
Soma
Axon
Dendrites
Branched expansion of the cytoplasm.
Area that receive the signals from pre-synaptic neurons.
Body of the neurons, containing the nucleus & most of the cytoplasm.
Axon
Main projection from the soma
Transmits the impulse.
Variable length (from mm to m (1m)).
Classification according to morphology is based on the
Number of neurites.
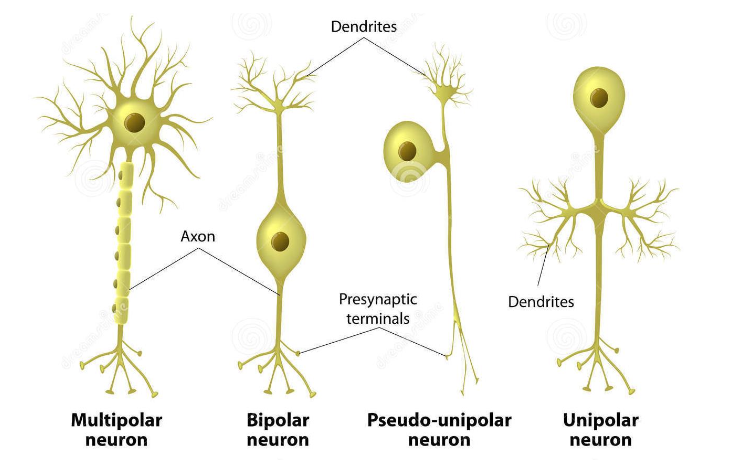
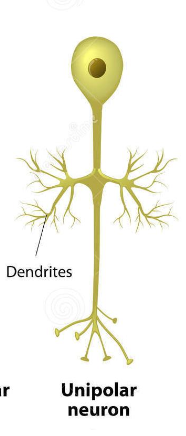
Unipolar
Sensory neuron
Only one projection emerges from the soma
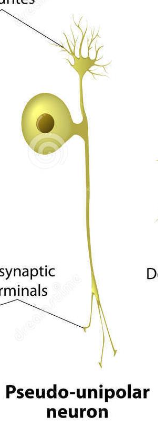
Pseudounipolar
One projection then divides in two branches.
Primary sensory neurons
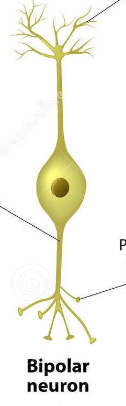
Bipolar
Two projections emerge from the soma in opposite directions → one axon & one dendrite.
Retinal cells.
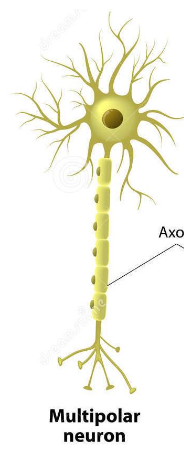
Multipolar
Projection of one axon & multiple dendrites from the soma
Most abundant in the brain
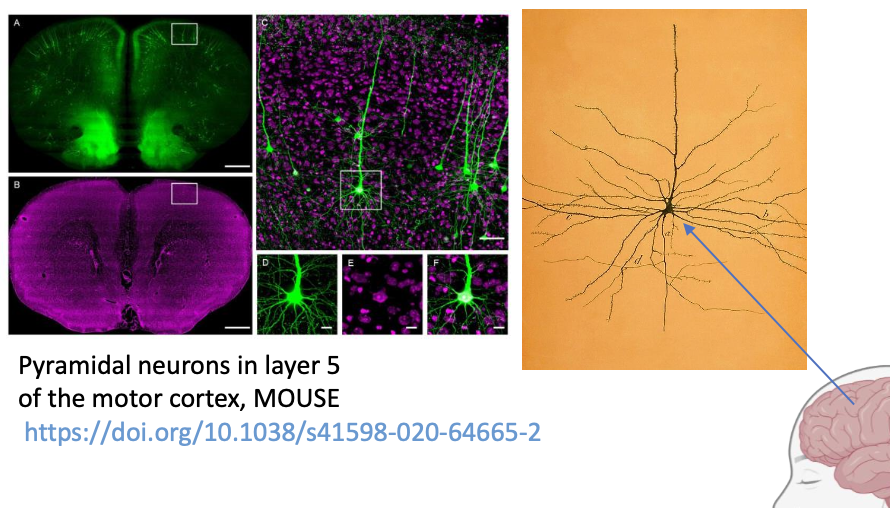
Two types of multipolar neurons
Pyramidal cells.
Purkinje Cells.
Pyramidal cells
Multipolar neuron typical of the cortex
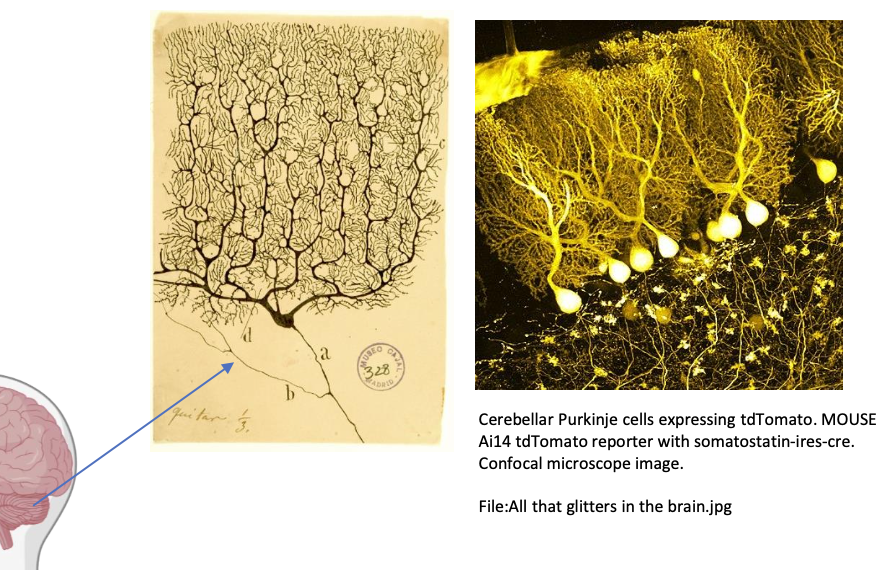
Purkinje Cells
Multipolar neuron typical of the cerebellum
Different functions of NEURONS
Sensory neurons / Afferent neurons
Interneurons
Motoneurons / Efferent nuerons
Sensory neurons / Afferent neurons
Neurons with sensory receptors (i.e. temperature) in their dendrites.
Usually are pseudounipolar, with the soma located in the peripheral ganglia
Transmit information (impulse) from the PNS to the CNS
Interneurons
Neurons from the CNS that receive information from sensory neurons (at the dendrites) and connect with another interneuron or with a motor neuron.
Usually multipolar.
Integrate & relay information
Motoneurons / Efferent nuerons
Neurons that conduct information (impulse) away from the CNS toward the target effectors.
Usually are multipolar.
Tracing of axonal projection from 1 single interneuron
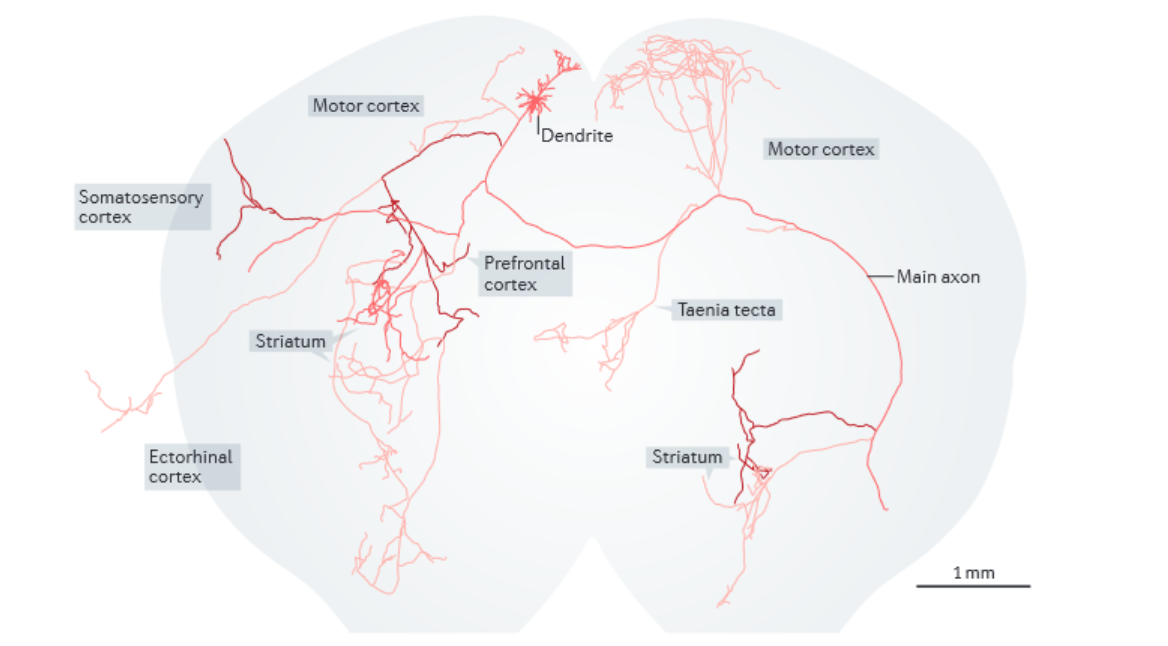
Multipolar neurons / Interneurons (two types)
Pyramidal cells
Purkinje cells
Parts of a neuron
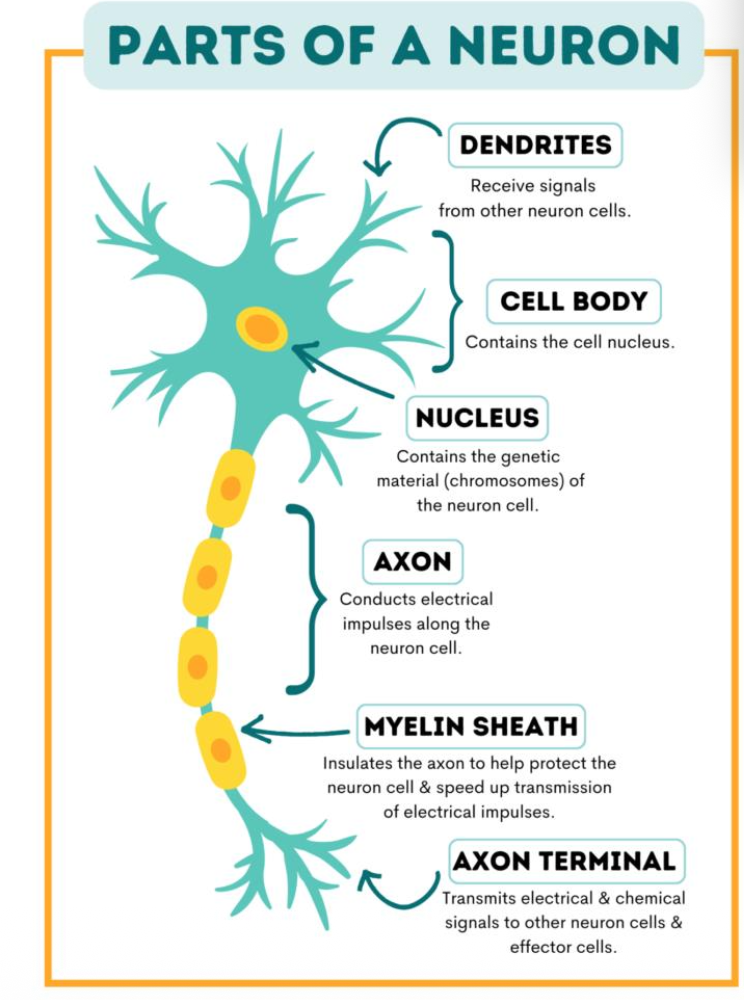
Dendrites
Receives signals from other neuron cells
Cell body
Contains the cell nucleus
Nucleus
contains the genetic material (chromosome) of the neuron cell
Axon
conducts electrical impulses along the neuron cell
Myeline sheet
Insulates the axon
Help to protect the neuron cell & speed up transmission of electrical signals
Axon terminal
Transmits electrical & chemical signals to other neuron cells & effector cells