a & p 1 final
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
regions of arm
brachial, antebrachial, carpals
anatomy
study of body structures
physiology
study of body functions
simplest level of organization
chemical
most complex level of organization
organ
first living thing within levels of organization
cells
anatomical position
standing upright, facing forward, hands at side facing outward
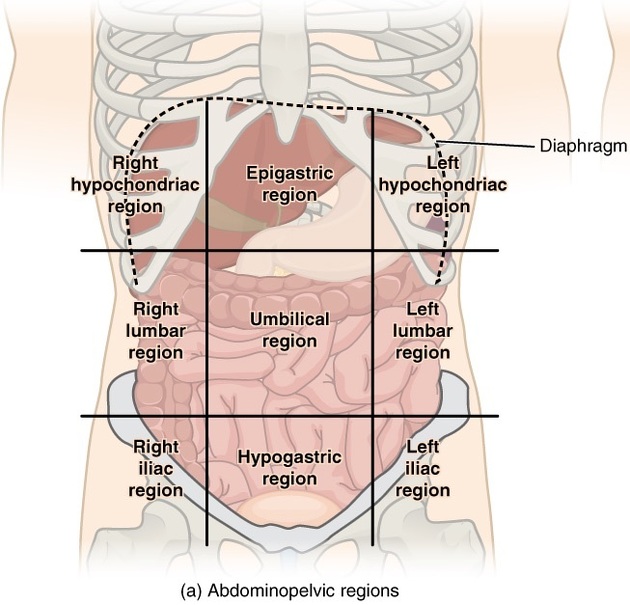
9 abdominal regions
epigastric: right hypochondriac, left hypochondriac
umbilical: right lumbar, left lumbar
hypogastric: right iliac, left iliac
what are proteins made of
20 amino acids
there are how many essential amino acids
9
what are carbohydrates made of
sugar
what is the pH of blood
7.35 to 7.45
3 types of passive transport
diffusion, osmosis, facilitated
where do i find skeletal muscle
through the body attached to bones via tendons
where do i find cardiac muscle
in the heart, has intercalated discs
where do i find smooth muscle
within hollow organs
what pigment causes tans
melanin
what pigment is orange
carotene
bones of the foot
calcaneus, talus, navicular, cuboid, cuneiforms
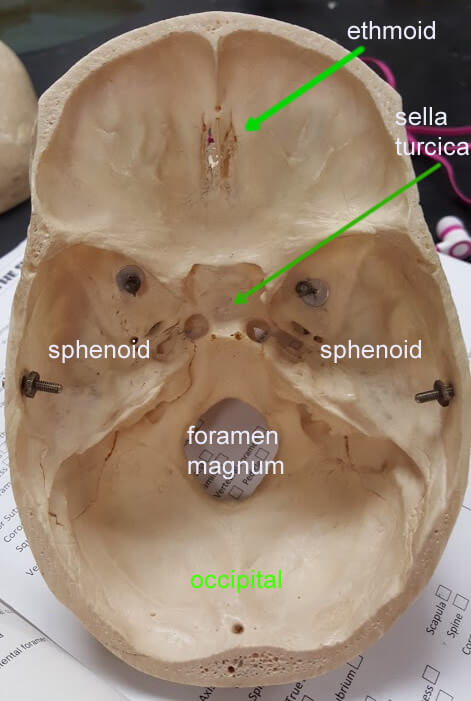
what bone has sella turcica
sphenoid bone
what is the function of the epiphyseal plate
bone growth during adolescence
osteoblasts
bone-building cells that create new bone tissue
osteoclasts
bone-resorbing cells that break down old or damaged bone
what muscles abduct the arm
deltoid
what muscle closes the mouth
masseter
sarcomere
contractile unit of a muscle fiber
sarcolemma
cell membrane of a muscle fiber
part of female reproductive system that is similar to male prepuce
clitoris
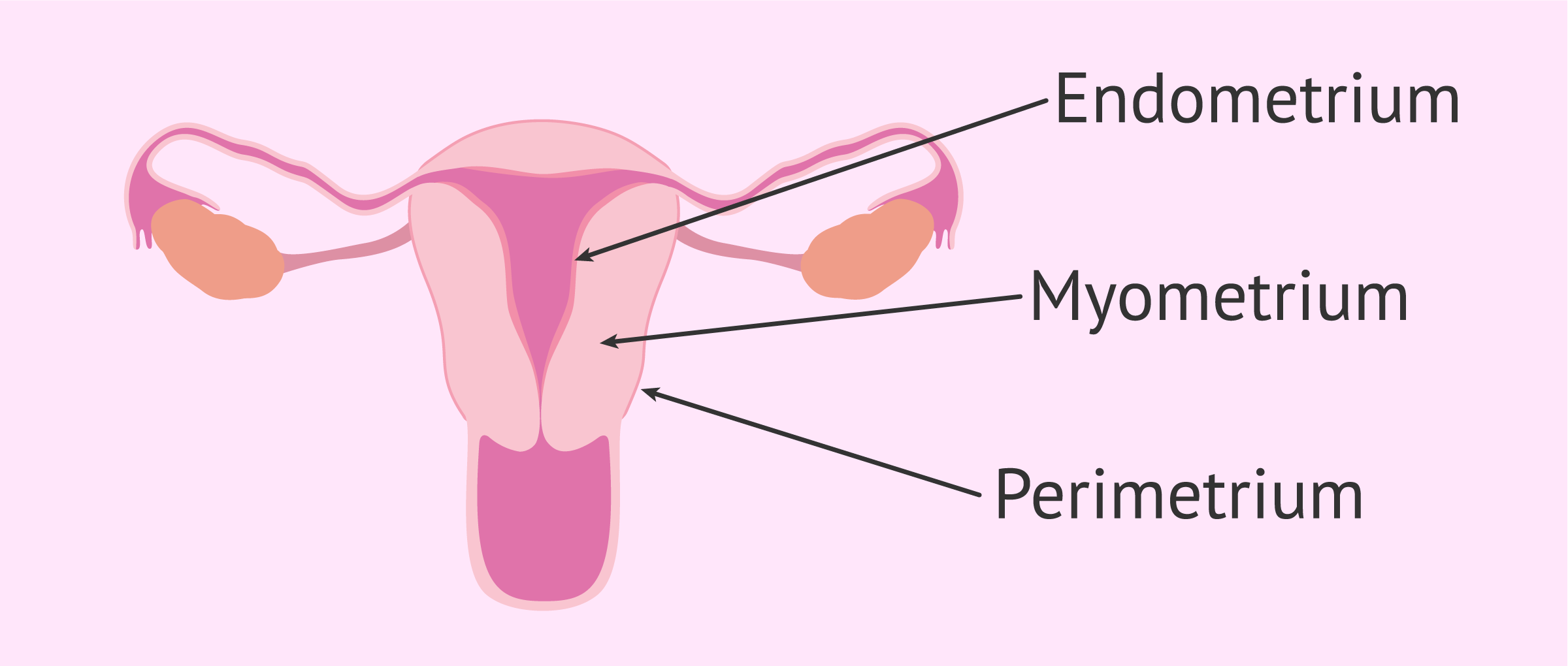
layers lining the uterus
perimetrium: covers posterior surface
endometrium: inner lining to support growing fetus
myometrium: thickest portion, provides force to move fetus outward
which organ makes gametes
reproductive organs called gonads, testes (male), ovaries (female)
what kind of joints are between cranial bones
fibrous joints known as sutures
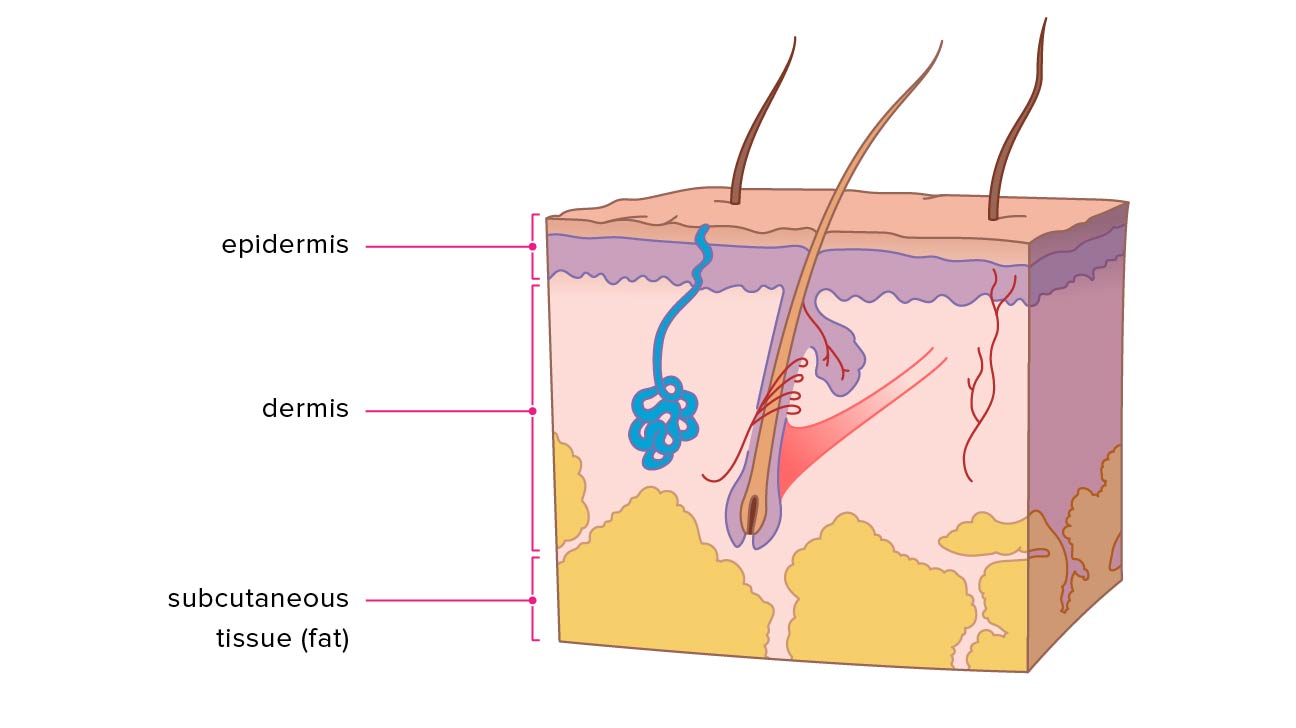
layers of the skin
epithelial, dermis, subcutaneous
where is sperm produced
seminiferous tubules within testes
where is sperm stored and matured
epididymis back of testes
epithelial skin with 1 layer of cells
simple squamous
epithelial skin with more than one layer of cells
stratified squamous
what kind of muscle has intercalated disc
cardiac muscle
atrophy vs hypertrophy
atrophy is decrease/ breakdown in muscle size due to lack of usage
hypertrophy is muscle growth
homeostasis
keeping the body in equilibrium
what is metabolism
chemical reactions (catabolic and anabolic)
catabolic reaction
take apart
anabolic reaction
put together
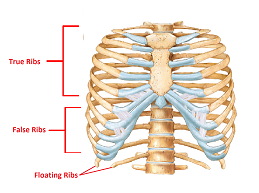
3 types of ribs
true, false, floating
what is the fluid inside of a cell
cytosol
what is the liquid outside of a cell
extracellular fluid
internal parts of female genitalia
vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries
external parts of female genitalia
mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibule, and associated glands
3 parts of the sternum
manubrium, body, xiphoid process
pH levels
acidic: 0-7
neutral: 7
basic: 7-14
most moveable joints in the body
synovial joints
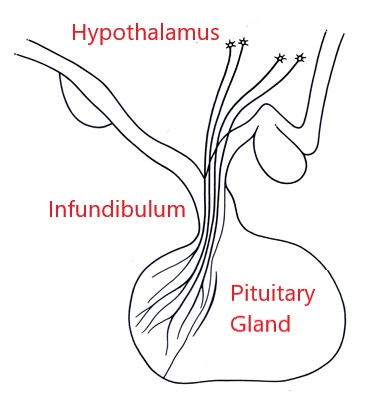
where does the antidiuretic hormone come from
posterior pituitary
what is the target of the antidiuretic hormone
the kidneys
where does the growth hormone (GH) come from
anterior pituitary gland
what is the master gland of the body
pituitary gland
what element is needed to make thyroid hormone
iodine
where does adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) come from
anterior pituitary gland
where does oxytocin (OXT) come from
posterior pituitary
what is the stalk between the hypothalamus and pituitary gland
infundibulum
purpose of antidiuretic hormone
make less urine
types of chemical bonds
covalent, ionic, hydrogen
covalent bonds
electrons are equally shared
ionic bonds
attraction between oppositely charged ions, give and take
purpose of mitochondria
produce ATP (energy)
order of mitosis
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase (PMAT)
functions of skin
insulation, protection, vitamin d absorption
axial skeleton
80 bones
skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage
appendicular skeleton
126 bones
pectoral girdle, upper limbs, lower limbs, pelvic girdle
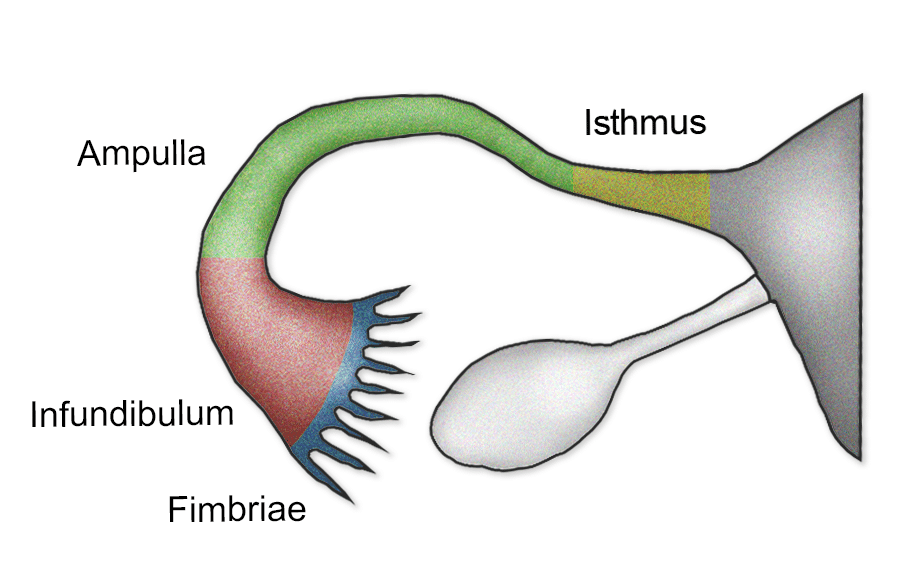
parts of a fallopian tube (oviduct)
isthmus, ampulla, infundibulum, fimbriae
what happens to RBC if they’re in a hypertonic solution
shrinkage