Collision Theory and Factors affecting Rates
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is rate?
Rate of reaction is the change in concentration of a reactant or product per unit time.
State the factors that affect the rate of a reaction.
Surface area
Concentration (solutions)
Pressure (gases)
Catalyst
Light (applies to certain reactions only)
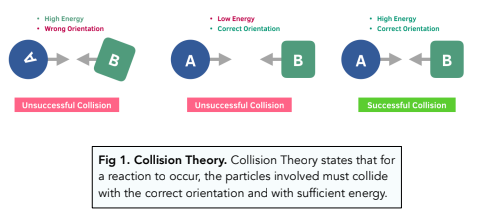
Summarise collision theory.
In order for a reaction to take place, particles must collide.
Reactant particles must collide with enough energy so that the bonds are broken between the reactants- this is the activation energy.
The particles involved must collide with the correct orientation.
Explain what is meant by: “Particles must collide with the correct orientation.”
For a reaction to be successful, the particles need to collide in the correct orientation so that the correct bonds are broken or formed.
The particles need to be moving towards in each other and facing each other so that the particles do not simply bounce off each other resulting in an unsuccessful collision.
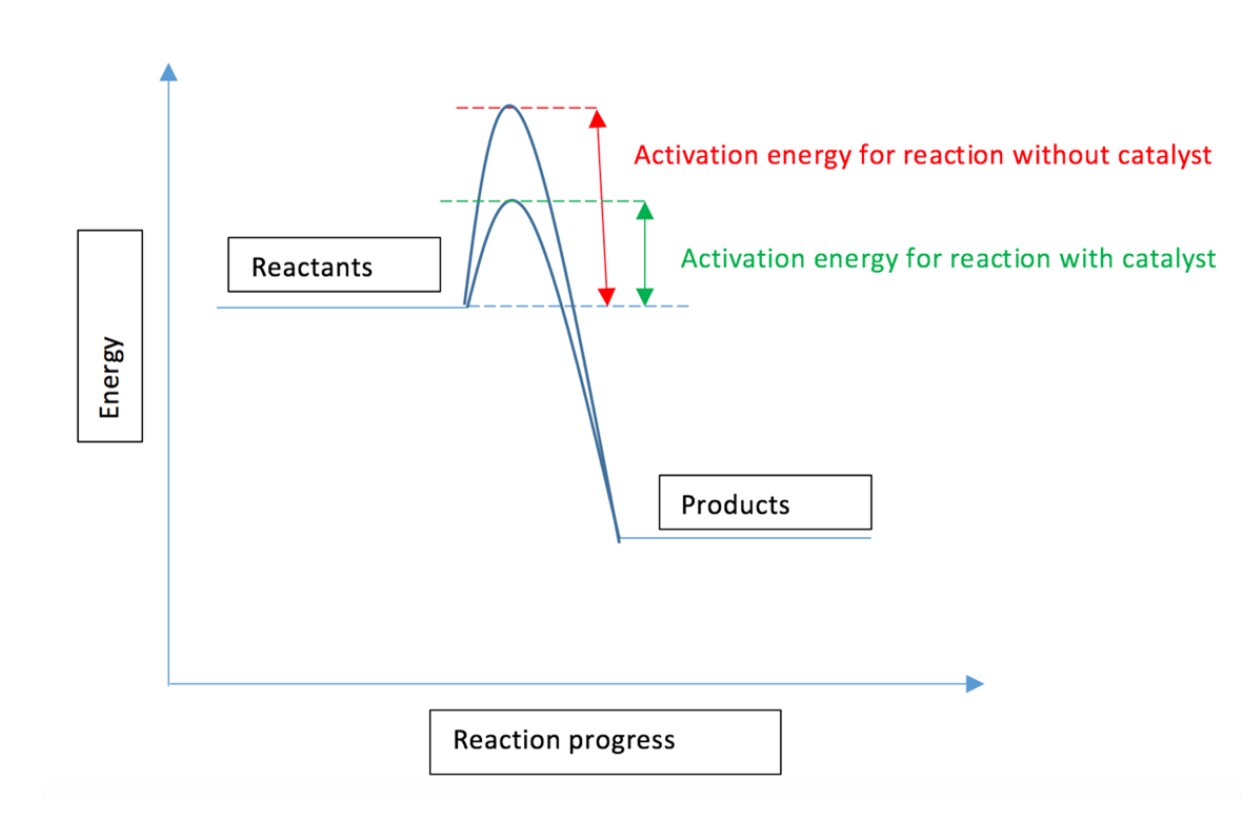
What is the activation energy?
The minimum amount of energy required for a successful collision to occur which will cause a reaction to happen.
According to collision theory, how do you increase the reaction rate?
To increase rate, you need to have:
More frequent collisions
More successful collisions
How can you increase the frequency of collisions?
Increase the speed of the particles
Increase the amount of particles present
How can you increase the chance of successful collisions?
Increase the energy of the particles
Lower the activitation energy
Explain how increasing the reaction temperature will lead to an increased reaction rate.
Particles have more kinetic energy and move faster.
Increased movement of molecules means collisions occur more often and with greater energy.
As a result, more collisions have energy greater than the activation energy and result in a reaction.
Increasing the reaction temperature will increase the rate of the reaction as more collisions of greater energy occur in a given time.
Explain how increasing the concentration of reactants will lead to an increased reaction rate.
Increasing the concentration increases the number of reactant particles in a given volume.
Particles are packed more closely together. This means particles react more frequently.
This increases the chance of successful collisions ∴ rate of reaction increases.
Explain how increasing the gas pressure will lead to an increased reaction rate.
Increasing the pressure increases the number of reactant particles in a given volume.
This means the particles are packed closer together in the reaction and the distance between them is small.
As there is a smaller distance between the particles, they collide more frequently.
There is an increase in the rate of reaction as there is an increase in the number of successful collisions per second.
Explain how increasing the surface area of a solid reactant will lead to an increased reaction rate.
Increasing the surface area of a solid reactant means more solid is exposed to other particles to be reacted with.
This means more possible collisions occur per second.
The rate of reaction increases.
What is a catalyst?
A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up in the process.
How does a catalyst affect the rate of a reaction?
A catalyst provides an alternative route for lower activation energy.
If the activation energy is lower, more particles will have that activation energy, so that the reaction will be faster.