Pharm Exam 1
1/221
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
222 Terms
Graded dose-response curve
a graph of increasing response to increasing drug concentration or dose
- 1 patient
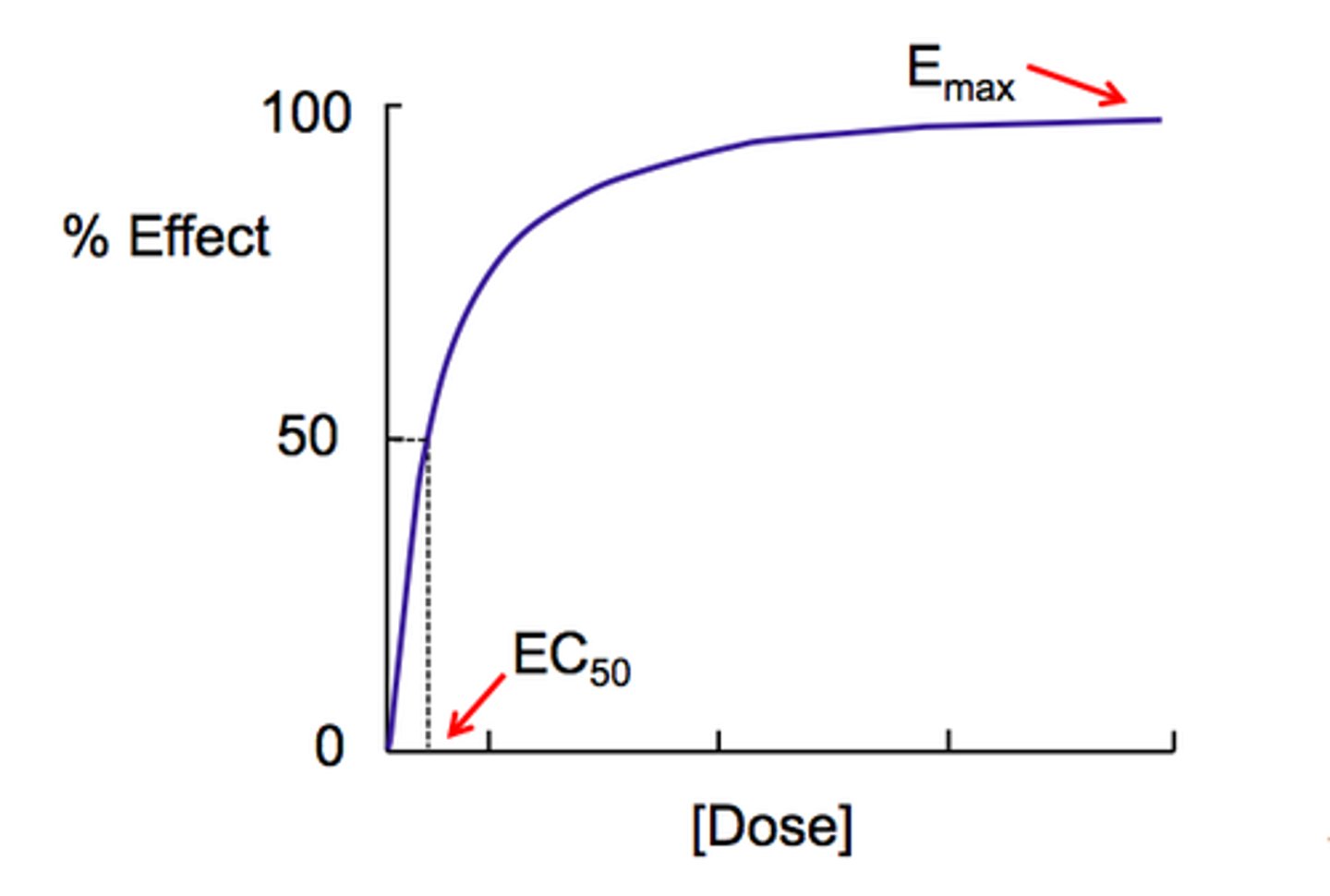
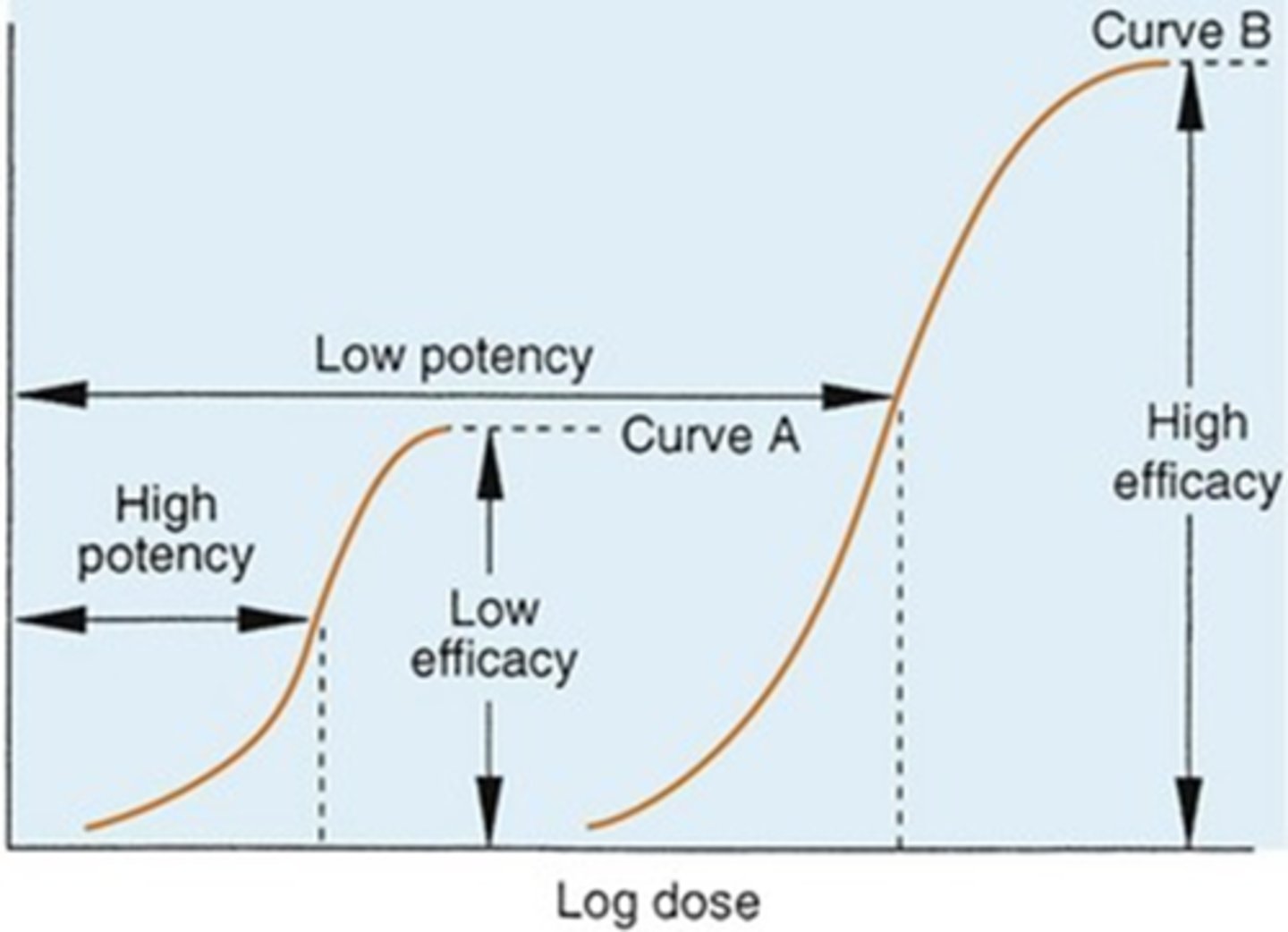
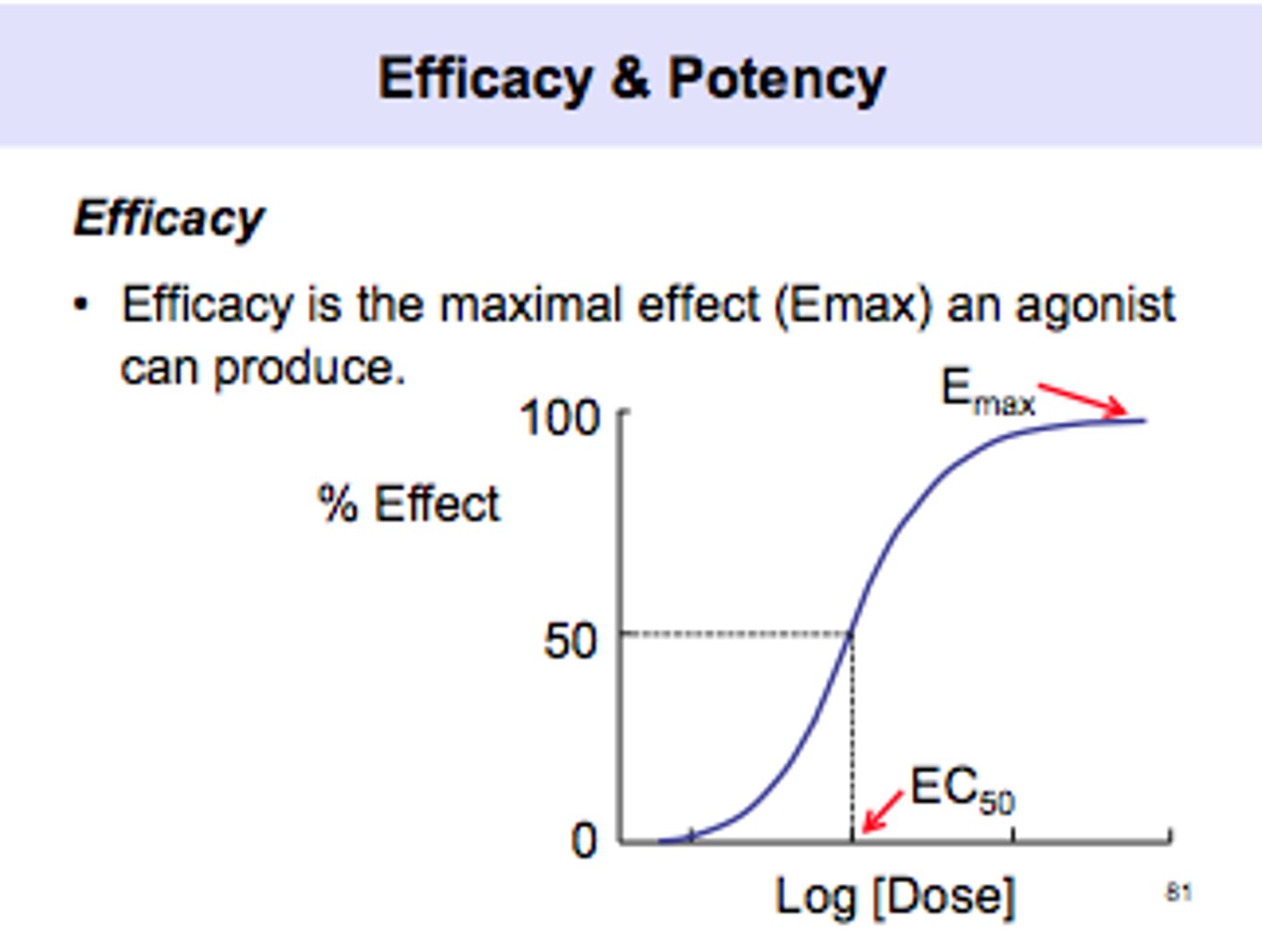
potency
the strength of a drug
- more potent = less dosage
- determined by affinity for its receptor and/or ability of the drug to reach its site of action
efficacy
the ability to produce a desired or intended result
determined by:
- type of interaction with the receptor (agonist vs antagonist)
- limitations on amount that can be administered
POTENCY DOES NOT EQUAL MAXIMUM EFFICACY
Emax
Maximum effect achievable by a drug
quantal dose response curve
represents dose response relationships in POPULATIONS
- Y-axis with end in "ing"
- represents variations in drug responses
hyporeactive
the intensity of a given dose of a drug is less than anticipated.
hyperreactive
intensity of a given dose of drug is greater than anticipated
tolerance
Time-related loss of response to a drug
- within weeks to months of being on a drug
idiosyncratic drug response
infrequently observed drug effect
tachyphylaxis
rapid decrease in response to a drug
- within minutes to hours of being on a drug
hypersensitivity
allergic reaction to a drug
therapeutic index
TD50/ED50 = TI
- indicator of a drug's safety
- greater the value of TI, the safer the drug is considered to be
- larger the TI, the larger the dose to evoke a toxic response
when the benefits outweigh the risks (cancer)
When is it acceptable to take a drug with a low TI?
Pharmacokinetics
Study of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion.
bioavailability
The extent to which the drug reaches systemic circulation
- Through IV = 100%
- Orally, first pass effect
volume of distribution
body space into which a drug can diffuse
clearance
amount of blood from which all of a drug is removed per unit of time
half life
predicts how long it takes the dosing regimen to achieve steady-state concentrations
- 4-5 half lives
pharmacodynamics
study of a drug at the site of action and the EFFECT ON THE BODY
affinity
refers to the attraction between a receptor and a ligand (drug)
efficacy
____ refers to the ability of a ligand to bind to the receptor, activate it, and lead to some physiological response
agonist
a drug that binds to the receptor and causes some type of response
- has both affinity and efficacy
antagonist
a drug that binds to the receptor without resulting in any response
- only has affinity
selectivity
Drug elicits only the response for which it is given
- no such thing because of side effects
first pass effect
a phenomenon in which drugs given orally are carried directly to the liver after absorption, where they may be largely inactivated by liver enzymes before they can enter the general circulation; oral drugs frequently are given in higher doses than drugs given by other routes because of this early breakdown
- 50% is active
ED50
median effective dose:
- dose at which 50% of population responds in specified manner
TD50
median toxic dose
- dose at which 50% of the population exhibits adverse effect
no (high abuse: LSD, heroin)
are schedule I drugs used medically?
IV
Schedule II-___ drugs are used medically but also have the potential for abuse
aspirin uses
- analgesic
- antipyretic
- anti-inflammatory
- anti-platelet
blood thinner
the advantage of aspirin having antiplatelet qualities is that it can act as a ____ ____ and reduce the risk of heart attack, however, it increases the risk of hemorrhage
aspirin
Irreversible inhibitor of COX
- effects persist until new COX generated
doan's
Magnesium Salicylate (NSAID)
- relieve's musculoskeletal pain and inflammation
ben-gay
topical salicylate
- external use for pain and inflammation
- think icy hot
inhibition of COX
these drugs all have a MOA of _____ ___ ____
- ibuprofen
- naproxen
- fenoprofen
- piroxicam
- indomethacin
ibuprofen
shorter duration of action than naproxen
- anti-inflammatory
- anti-pyretic
- analgesic
- safe to use with anticoagulants
naproxen
has a long half life so administered less frequently
- anti-inflammatory
- antipyretic
- analgesic
- decreases renal blood flow
- shows an increase in liver toxicity in marathon runners
fenoprofen
less intense GI side effects than those occurring with aspirin
- reversible inhibitor of COX
- anti-inflammatory
- antipyretic
- analgesic
- good for mild/moderate pain (cramps, dental pain, headaches)
- good for OA and RA
piroxicam
once a day dosing (half life= 50-60 hours)
- used for OA and RA- 9.5x higher risk for peptic ulcer and bleeding compared to other NSAIDS
- antiplatelet: more similar to aspirin
indomethacin
used for arthritis, bursitis, gouty arthritis, close DA in premies
- reduces pain and fever but not used for these effects
- antiplatelet effects
- high incidence of dose-related side effects (25-50%)
- INITIAL TREATMENT OF GOUT AND MOST OFTEN USED TODAY FOR GOUT
celecoxib
used for OA and RA
- NO platelet aggregation
- anti-inflammatory
- antipyretic
- analgesic
- works on COX-2 and not on COX-1, so leaves protective prostaglandins in stomach
- fewer GI ulcers than other NSAIDS
- may increase risk for serious CV events (MI/stroke)
acetaminophen
only inhibits prostaglandins in CNS
- weak inhibition of COX
- analgesic
- antipyretic
- NOT an anti-inflammatory agent
- categorized as an analgesic
-used in fever reduction in children
-liver toxicity is most serious side effect
methotrexate
- rapid acting DMARD (3-6 weeks)
- this is the drug given initially to treat, other agents if not working
sulfasalazine
treats IBD
- retards progression of joint deterioration
- GI problems and rash
- may produce serious hypersensitivity and blood dyscrasias
leflunomide
suppresses immune cell proliferation (reduces inflammation)
- slows formation of bone erosion
- well tolerated, benefits in 1 month
- side effects: GI distress, rash, liver function
etanercept
anti tumor necrosis factor (TNF) drug
- biologic
- injection under the skin weekly
- increased risk of infection especially if used with other immunosuppressants
- prevents release of cytokines (role in immune response and inflammation)
adalimumab
- biologic
- anti TNF alpha drug
- injection under the skin weekly or bi-weekly
- increased risk of infection especially if used with other immunosuppressants
Tofacitinib
- janus kinase inhibitor (which play a role in joint inflammation)
- possibly inhibits progression of structural damage
colchicine
- prophylaxis of recurrent episodes of gouty arthritis
- troublesome diarrhea
- grapefruit can elevate levels
probenecid
- decreases net reabsorption of uric acid by affecting transport sites
- large urine volume recommended to minimize possibility of kidney stones
allopurinol
- xanthine oxidase inhibitor
- long-term treatment to prevent gout attacks
- not used to treat acute gout attacks
morphine
- mu agonist
- does not reach the brain quickly, lasts 4-5 hours
- relieves pain
- side effects: orthostatic hypotension, constipation, pupil constriction, respiratory depression
Hydromorphone
- mu agonist
- more lipid soluble, able to cross BBB more rapidly, faster acting
- relieves severe pain, extended release capsules exist
- constipation and dizziness can occur
codeine
- mild to moderate pain reliever (never achieves morphine-like efficacy)
- often used in combination with aspirin or acetaminophen
oxycodone
- never achieves morphine-like efficacy
- schedule II drug (VERY addictive)
- Purdue Pharma scandal
methadone
- mu agonist
- equipotent with morphine
- longer duration of action
- used in treatment of opioid abuse (milder withdrawal symptoms, helps taper them off)
fentanyl
- mu agonist
- most widely used of synthetic opioids (legally and illegally)
- 100x more potent than morphine
- short acting (1-1.5 hours)
tramadol
- weak mu agonist
- mild to moderate pain
- may cause seizures (never give to epileptics)
- useful in chronic neuropathic pain
naloxone
- aka narcan
- mu antagonist
- used to treat opioid overdoses
naltrexone
- useful in treatment of alcoholism (blocks endogenous opioids that give feeling of euphoria)
cromolyn sodium
- stabilizes mast cells and prevents release of contents
- takes 2-3 weeks to be effective
- aerosol and nasal spray
- side effects: burning, itching, sneezing, coughing
H1 blockers
- classical type
- allergies
- first generation (drowsiness)
- second generation (non-sedating)
H2 blockers
inhibits gastric acid secretion
- relieves symptoms of ulcers
diphenhydramine
- first generation
- H1 blocker
- for allergies
- sedation in 50% of patients
dimenhydrinate
- aka dramamine
- H1 blocker
- 1st generation
- causes muscular weakness/drowsiness
fexofenadine
- 2nd generation
- H1 blocker
- for allergies
- causes less drowsiness
loratadine
- 2nd generation
- H1 blocker
- for allergies, less sedating
- once a day extended release formulas
cimetidine
- H2 blocker
- inhibits cytochrome p450 metabolism of other drugs
- causes headaches, breast tissue in males
famotidine
- H2 blocker
- heart burn and gastric acid relief
glucocorticoids
- influence carbohydrate metabolism
mineralcorticoids
- modulate salt and water balance
cortisol
____ is the most important endogenous glucocorticoid
ACTH
the synthesis of glucocorticoids is controlled by ____
aldosterone
____ is the most important endogenous mineralcorticoid
RAAS (renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system)
mineralcorticoids are regulated by the ____
hydrocortisone
- similar to cortisol
- also has mineralcorticoid properties
- replacement therapy
- also to treat allergic reactions, inflammation, cancer
- at low doses, generally safe
fludrocortisone
- mineralcorticoid available for replacement therapy
- also glucocorticoid activity
- treats Addison's disease, hypoaldosteronism, and congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- if dose is too high, salt and water retention= weight gain, HTN, hypokalemia, and edema
withdraw
you should never _____ someone abruptly from a corticosteroid as it is life-threatening
- may need to taper from 2 months-1 year
- need to allow recovery of normal pituitary-adrenal response to endogenous corticosteroids
false
T/F: corticosteroids decrease blood glucose levels
cortisone
- an inactive form of cortisol, or a synthetic, anti-inflammatory medication used in medical treatments
PSNS
Housekeeping (GI, bladder, eye)
- slows HR
- increased gastric secretion
- emptying of bladder
- emptying of bowel
- focusing of the eye for near vision
- constriction of pupil
- contraction of bronchial smooth muscle
SNS
Fight or flight
- increased HR and BP
- shunting of blood away from skin to muscles
- dilation of bronchi
- dilation of pupils
- mobilization of stored energy
Ach
what NT is binds to cholinergic receptors?
- Nicotinic N/M and muscarinic
NE and Epi
What NTs bind to adrenergic receptors
- Alpha 1/2, Beta 1/2/3, and dopamine
heart
Beta1 is dominate in the ____
lung
beta2 is dominate in the ____
life cycle of Ach
choline + acetylcoenzyme A
- stored
- destroyed by AchE
- uptake of choline
life cycle of NE
- precursors
- stored in vesicles
- reuptake
- converted to Epi
bethanechol
- muscarinic agonist
- relieves urinary retention
atropine
- muscarinic antagonist
- used for muscarinic poisoning
physostigmine
- inhibitor of AchE
- given for antimuscarinic poisoning (atropine poisoning)
neostigmine
- reversible cholinesterase inhibitor
- used for myasthenia gravis
- binds to cholinesterase preventing it from catalyzing breakdown of Ach
tubocurarine
- neuromuscular blocking agent (non-depolarizing)
- competes with Ach to bind to nicotinicM receptors
- Uses: muscle relaxation during surgery, mechanical ventilation, endotracheal intubation, and electroconvulsive therapy
succinylcholine
- neuromuscular blocking agent (depolarizing)
- binds to nicotinicM receptors and remains bound resulting in constant depolarization
- uses: endotracheal intubation, electroconvulsive therapy, endoscopy
epinephrine
- catecholamine (adrenergic agonist)
- alpha1, alpha2, beta1, beta2
- anaphylactic shock, delay absorption of anesthetics, hemostasis, reduce nasal congestion, overcome AV heart block, pupil dilation, asthma
norepinephrine
- catecholamine (adrenergic agonist)
- alpha1, alpha2, beta1
- used for hypotension and cardiac arrest
isoproterenol
- catecholamine (adrenergic agonist)
- beta1, beta2
- uses: AV heart block, asthma, bronchospasm
dopamine
- catecholamine (adrenergic agonist)
- dopamine, beta1, alpha1
- uses: shock, heart failure, acute renal failure
terbutaline
- noncatecholamine
- beta2
- uses: asthma and preterm labor
ephedrine
- noncatecholamine
- alpha1, alpha2, beta1, beta2
- uses: nasal congestion and narcolepsy