Chapter1-3 exam
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Anatomy
The study of the structure of the body or body parts.
Physiology
The study of the function of the body or body parts.
what does complementarity of Structure and Function mean?
The principle that function is dependent on structure .... and the structure of a body part implies its possible function.
Cellular Level
The smallest living unit, made up of molecules.
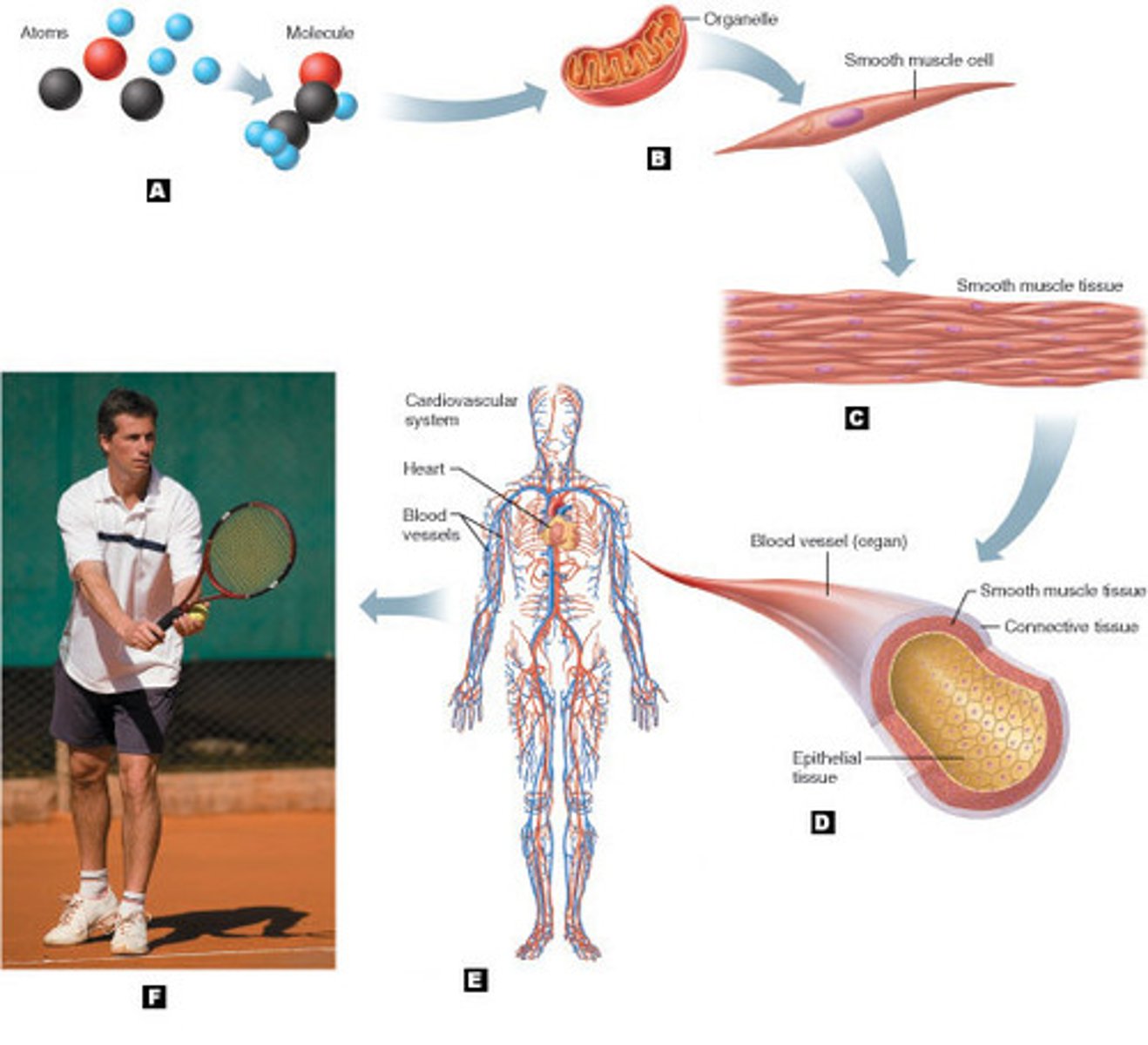
Tissue Level
Consists of similar types of cells.
Organ Level
Composed of different types of tissues.
Organ System Level
Groups of organs that work together closely.
Organismal Level
The highest level, representing the complete human organism made up of many organ systems.
whats the most abundant compound / molecular in the body?
water
Normal Body Temperature
A narrow range (35-37°C or 95-98.6°F) required for the body to function properly.
what do we need oxygen for?
high-yield ATP production
what is: the ability to maintain a stable internal environment in a changing external environment.
homeostasus
Negative Feedback
Mechanisms that work to reverse a change.
Positive Feedback
Mechanisms that amplify (make bigger) a change.
Anatomical Position
The standard reference position where the body is upright, directly facing the observer, with feet flat on the ground and arms at the sides with palms facing forward.
Superior (cranial)
Toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body; above.
Inferior (caudal)
Away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the body; below.
Anterior (ventral)
Toward or at the front of the body; in front of.
Posterior (dorsal)
Toward or at the back of the body; behind.
Medial
Toward or at the midline of the body; on the inner side of.
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body; on the outer side of.
Proximal
Closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk.
Distal
Farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk.
Superficial (external)
Toward or at the body surface.
Deep (internal)
Away from the body surface; more internal.
Dorsal Body Cavity
Houses the central nervous system, including the cranial and vertebral cavities.
Cranial Cavity
Houses the brain.
Vertebral/Spinal Cavity
Houses the spinal cord.
Ventral Body Cavity
Houses the visceral organs, subdivided into the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities.
Thoracic Cavity
Fills the chest and contains the heart and lungs.
Abdominal Cavity
Holds digestive organs and kidneys.
Pelvic Cavity
Holds reproductive organs and organs of excretion.
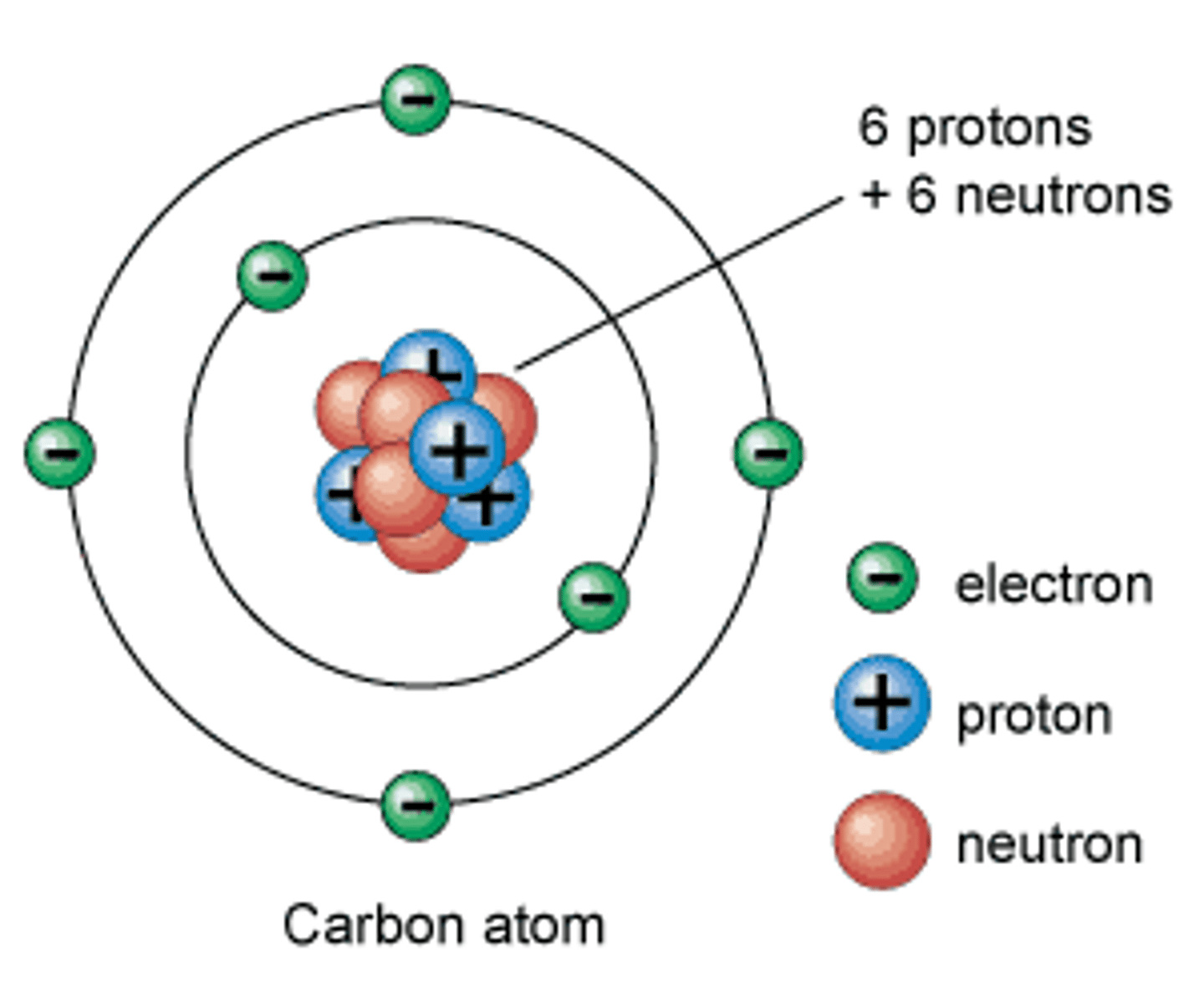
Atoms
The building blocks of matter, consisting of a central nucleus with positively charged protons and neutral neutrons, surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons.
Elements
Unique substances made of only one type of atom.
Ions
Atoms that have gained or lost electrons, giving them a net electrical charge.
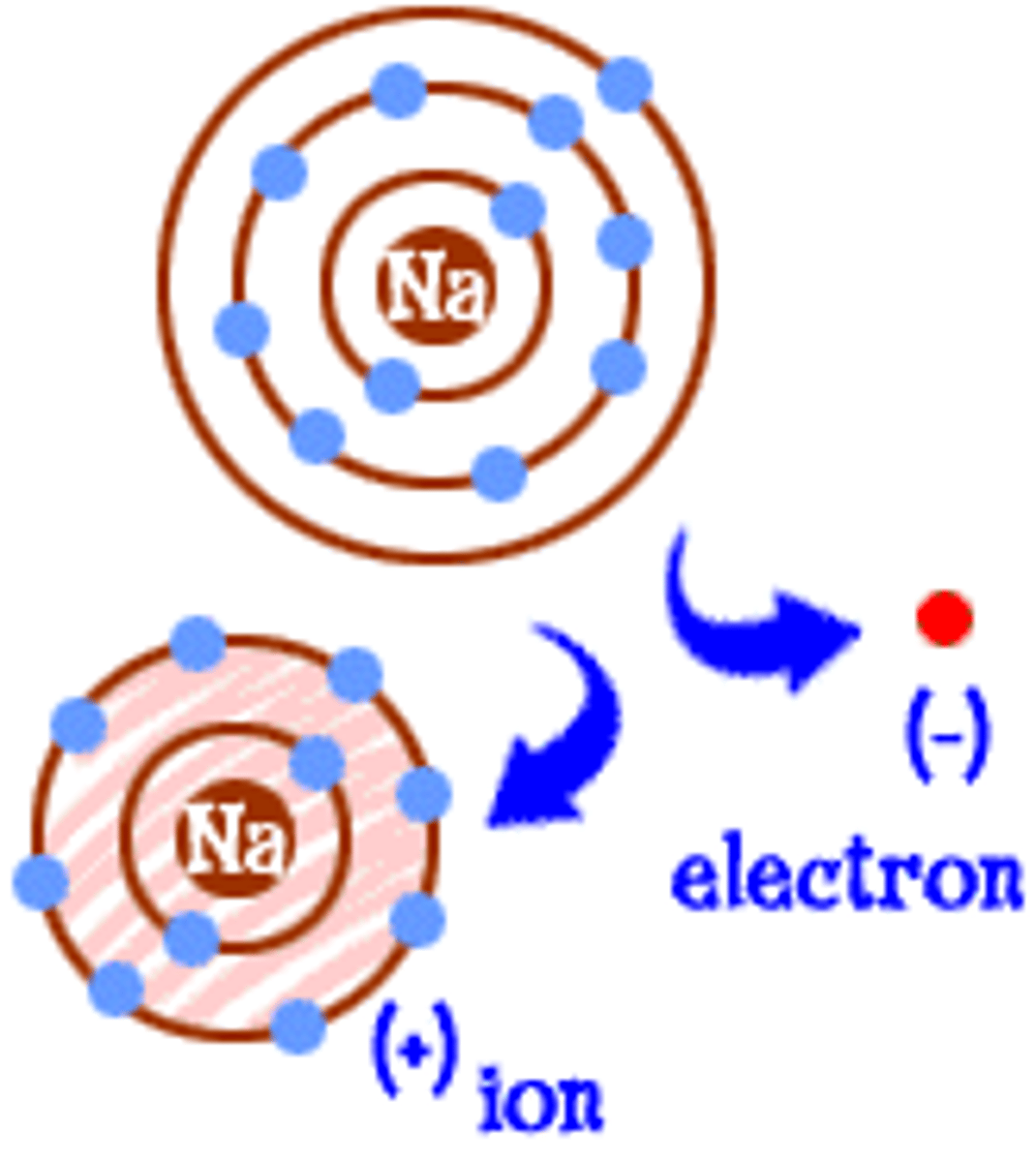
Cations
Positively charged ions (lost electrons).
Anions
Negatively charged ions (gained electrons).
Molecules
Two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds.
Mixtures
Two or more components that are physically intermixed but not chemically bonded.
Solutions
Homogeneous mixtures where a solute is dissolved in a solvent
solute particles are very tiny and do not settle out or scatter light
Suspensions
Mixtures where particles are very large and will settle out.
Concentration
The amount of substance per unit volume; Molarity (M) is moles per liter
moles of the substance/ L of water
Covalent Bonds
Formed when atoms share valence electrons; these are the strongest chemical bonds.
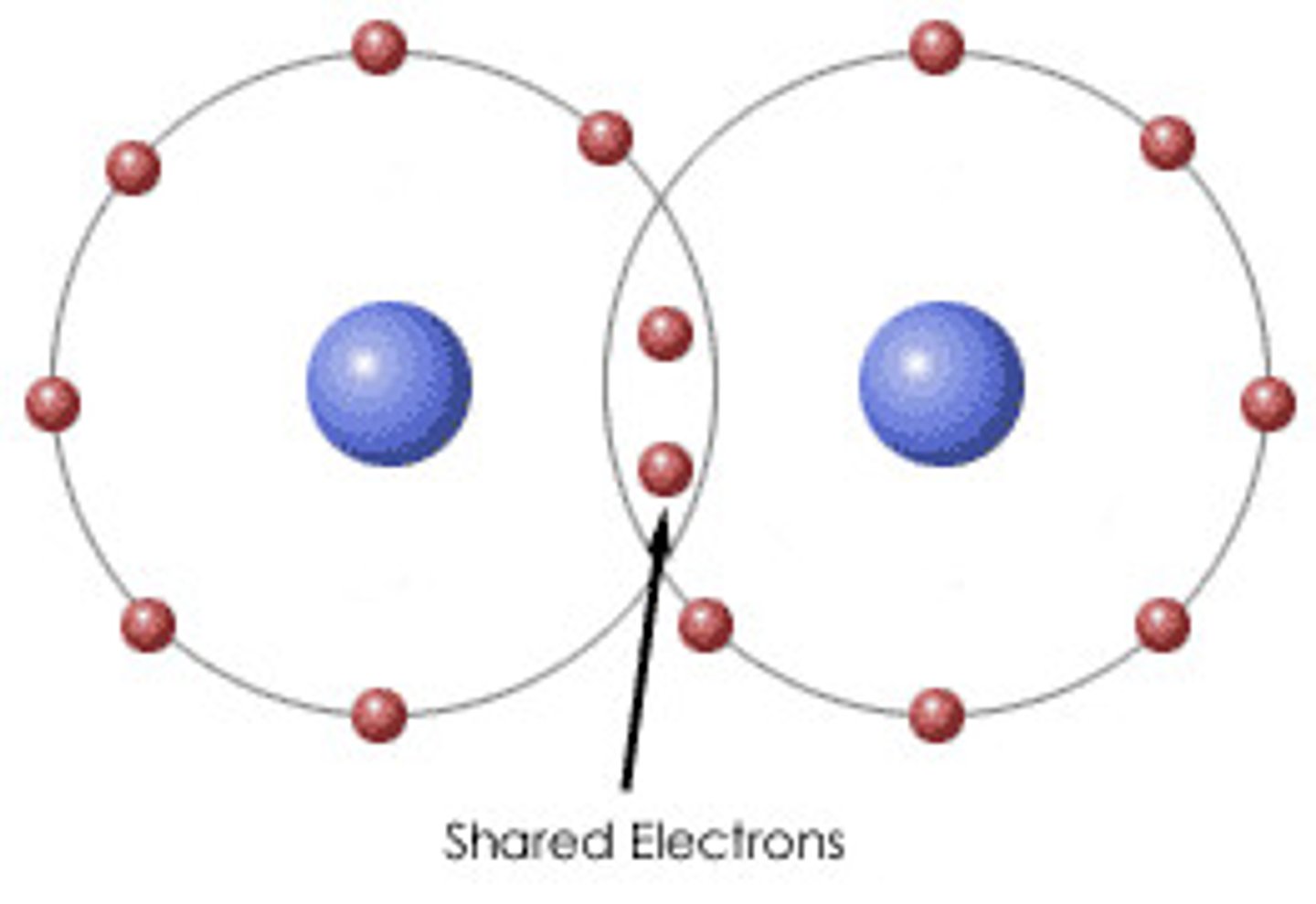
Ionic Bonds
The attraction between a cation and an anion. (have charges!)
They are relatively weak and can be broken by water.
Hydrophilic
"Water-loving" substances that dissolve in water and interact with it.
Hydrophobic
"Water-fearing" substances that do not dissolve in water.
Organic Compounds
Compounds containing carbon (and H usually)
Carbohydrates
Hydrophilic organic molecules (sugars) often used as an energy source.
the most basic unit is: monosaccharide
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars / 1 saccharide molecule
- 6 carbon ring
3 types : glucose, galactose, fructose
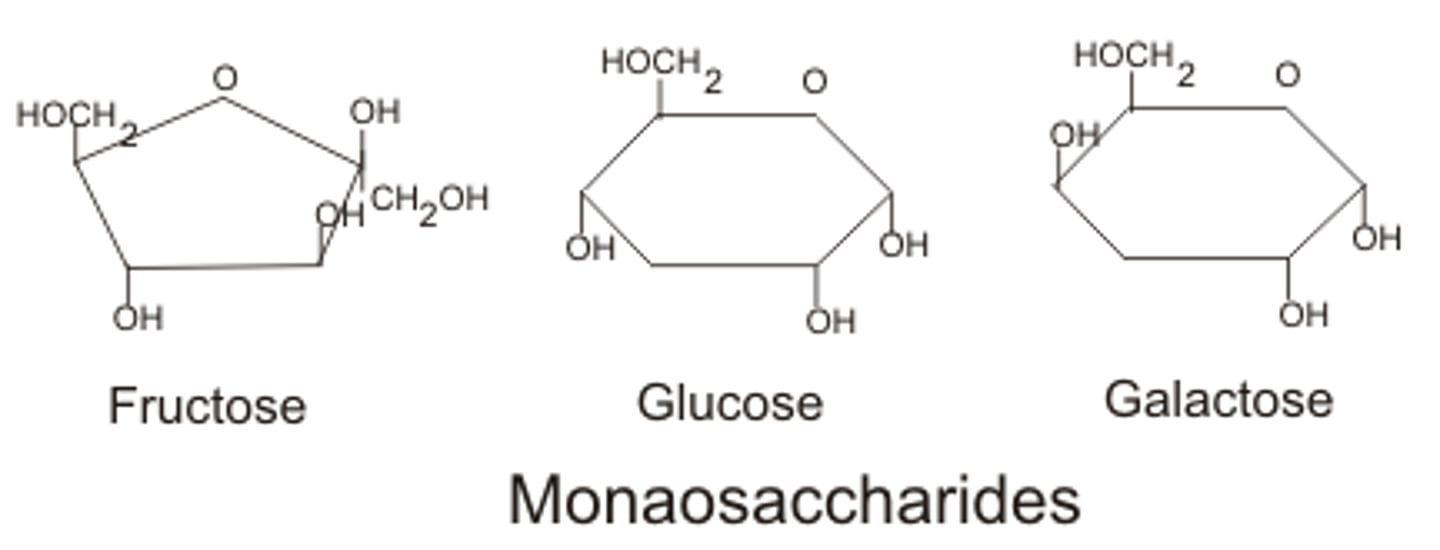
most basic unit of carbohydrate?
monosaccharide
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharides covalently bound.
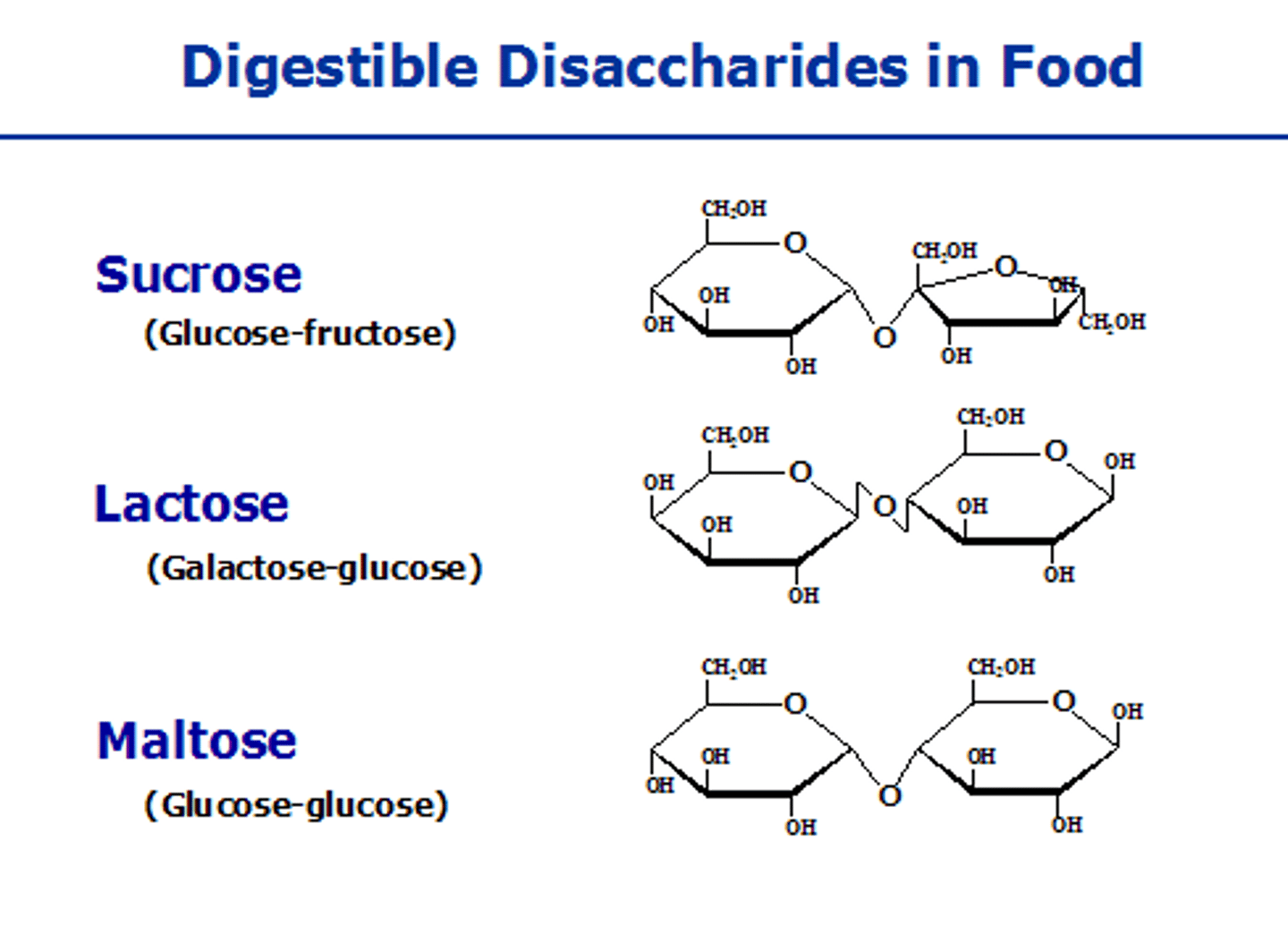
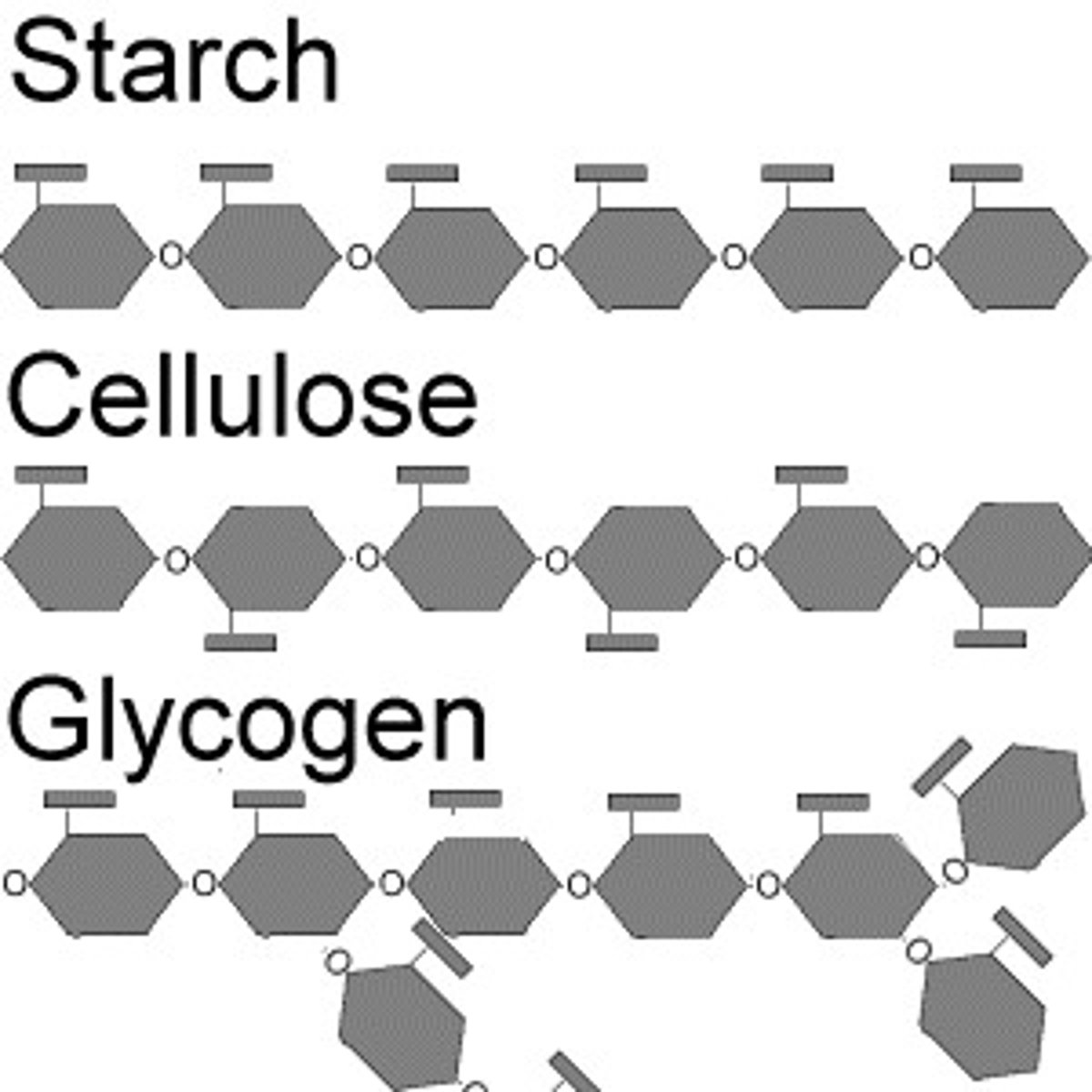
Polysaccharides
Long chains of sugar monomers used for carbohydrate storage in an organism:
- such as glycogen in animals,
- starch or cellulose in plants
Lipids
Hydrophobic organic molecules (fats).
what is the smallest unit of lipids?
fatty acids
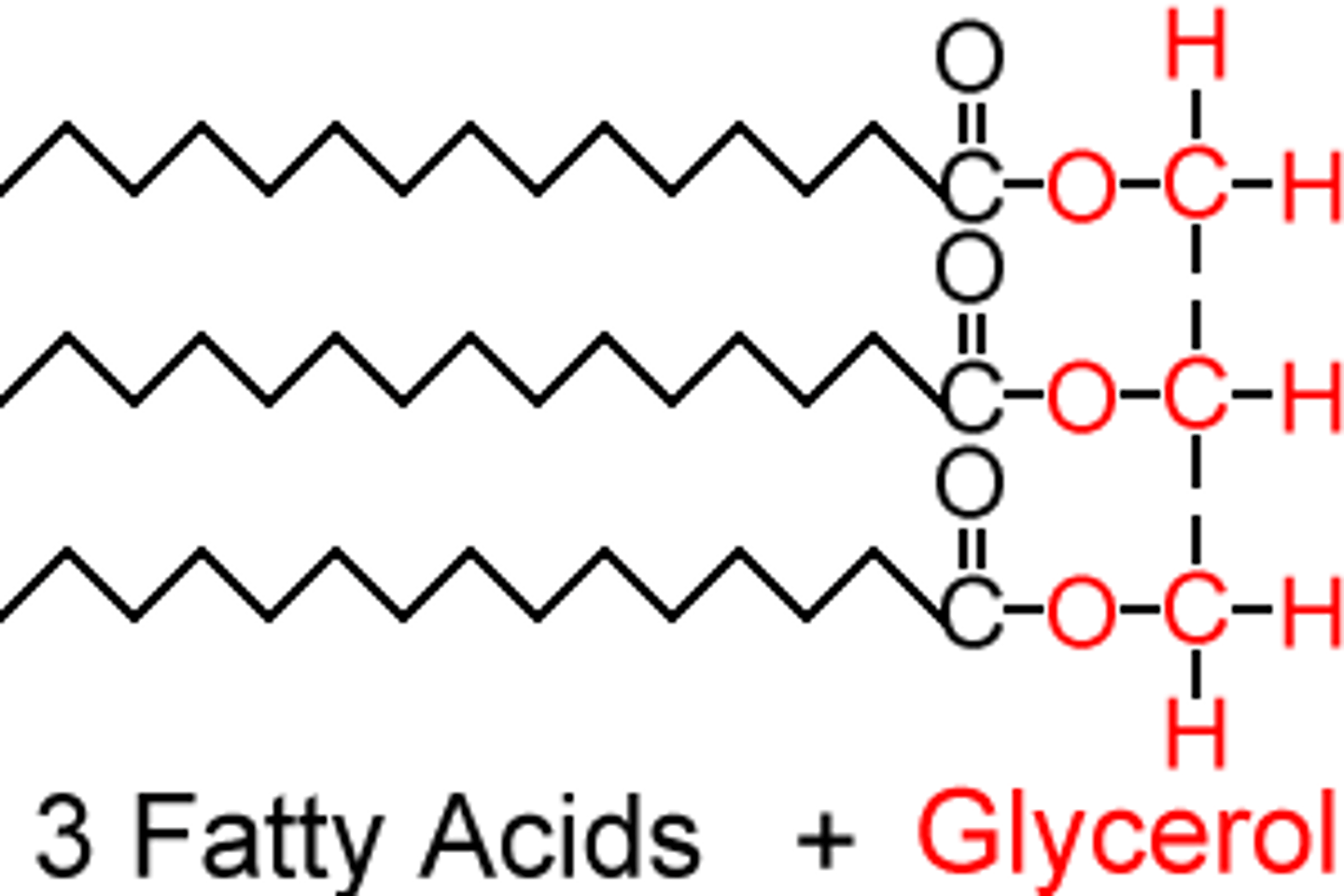
Triglycerides
3 fatty acids bound to glycerol, used for energy storage.
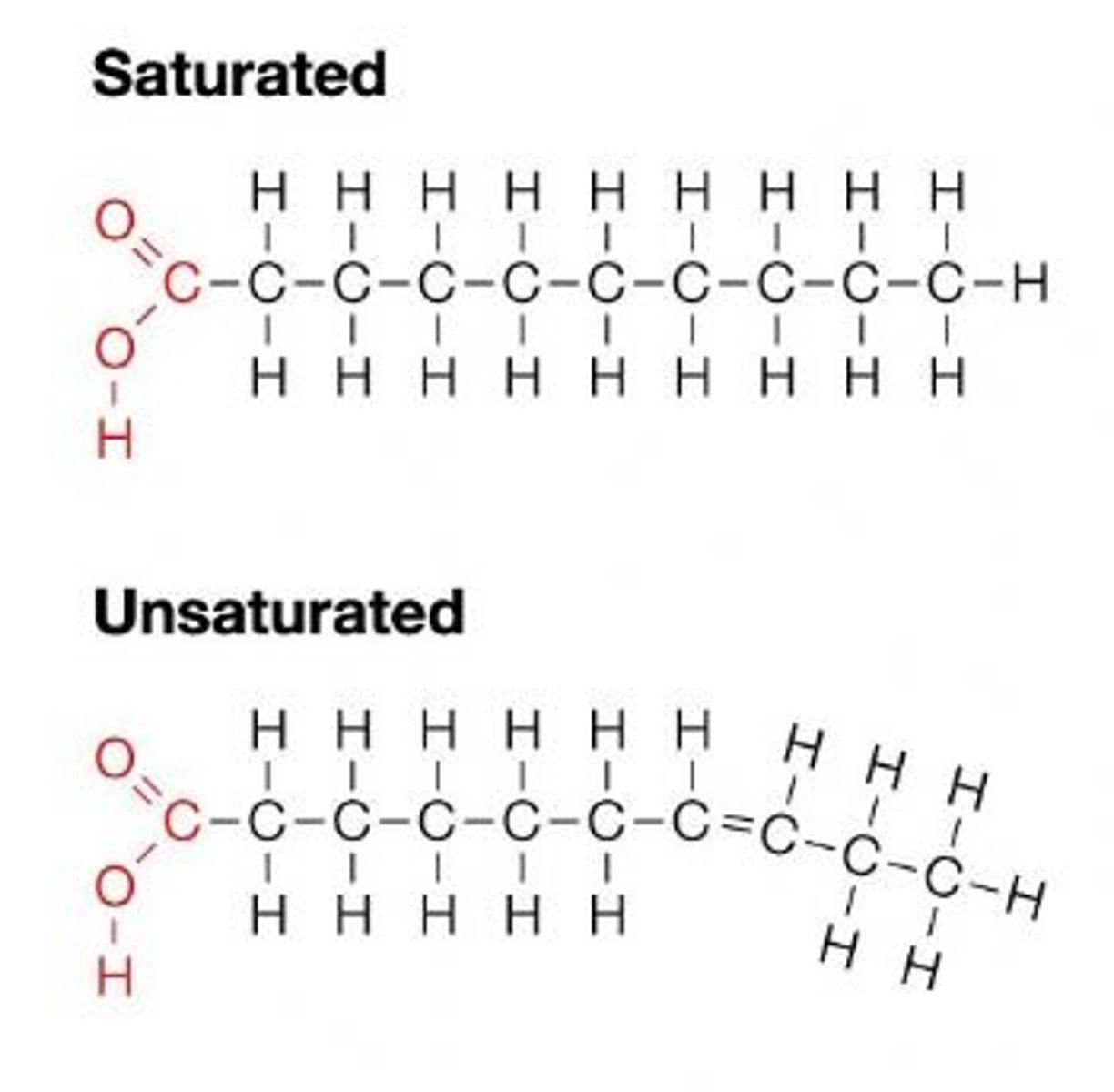
saturated fatty acid?
a long-chain hydrocarbon with single covalent bonds in the carbon chain (no C to C double bonds)
these are solid at room temperature - ex: butter - because they can pack more closely together
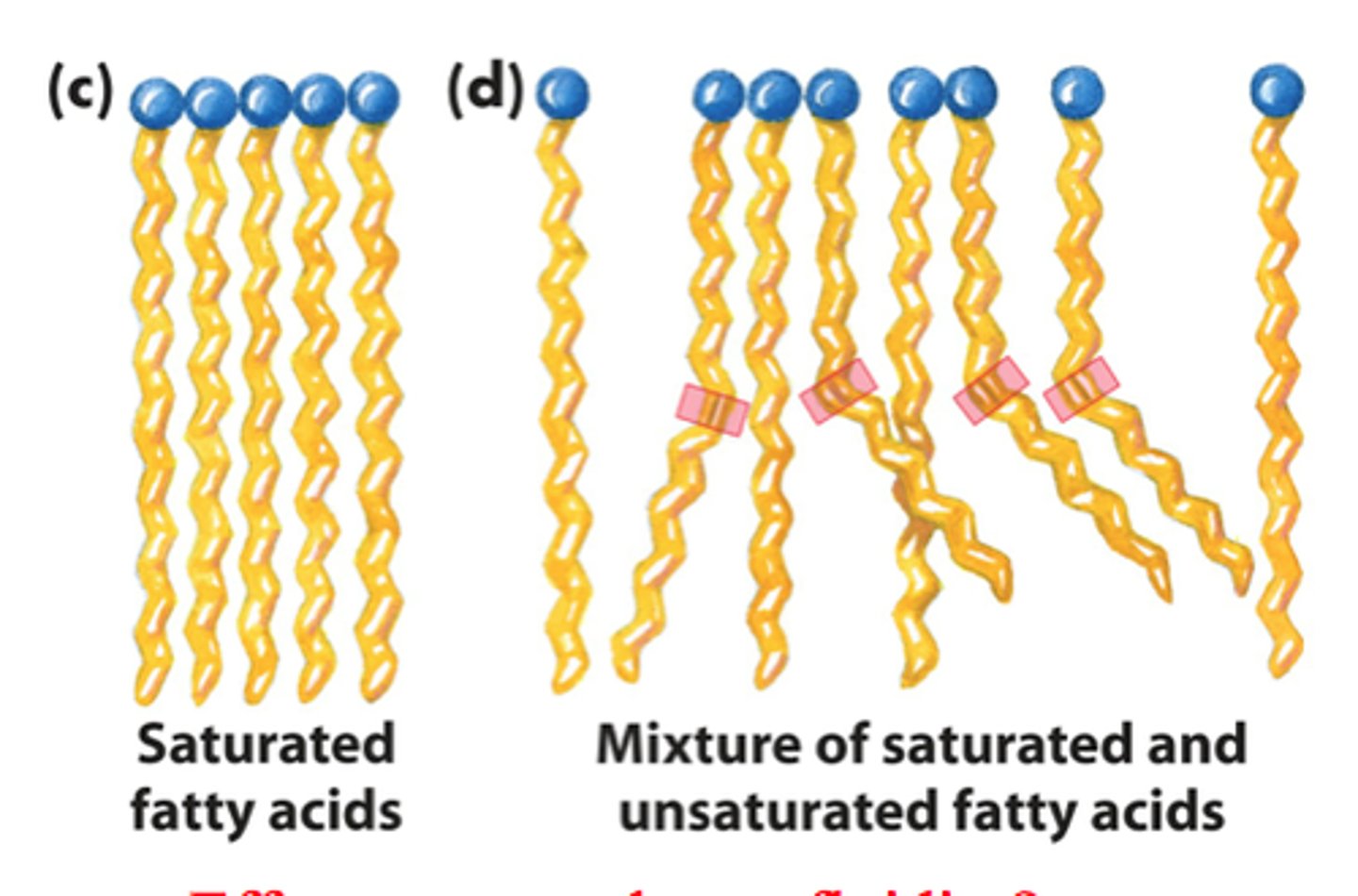
unsaturated fatty acid?
A fatty acid possessing one or more double bonds between the carbons in the hydrocarbon tail
these are liquid at room temperature
- ex: oil - because they kink/bend and cannot pack closely together
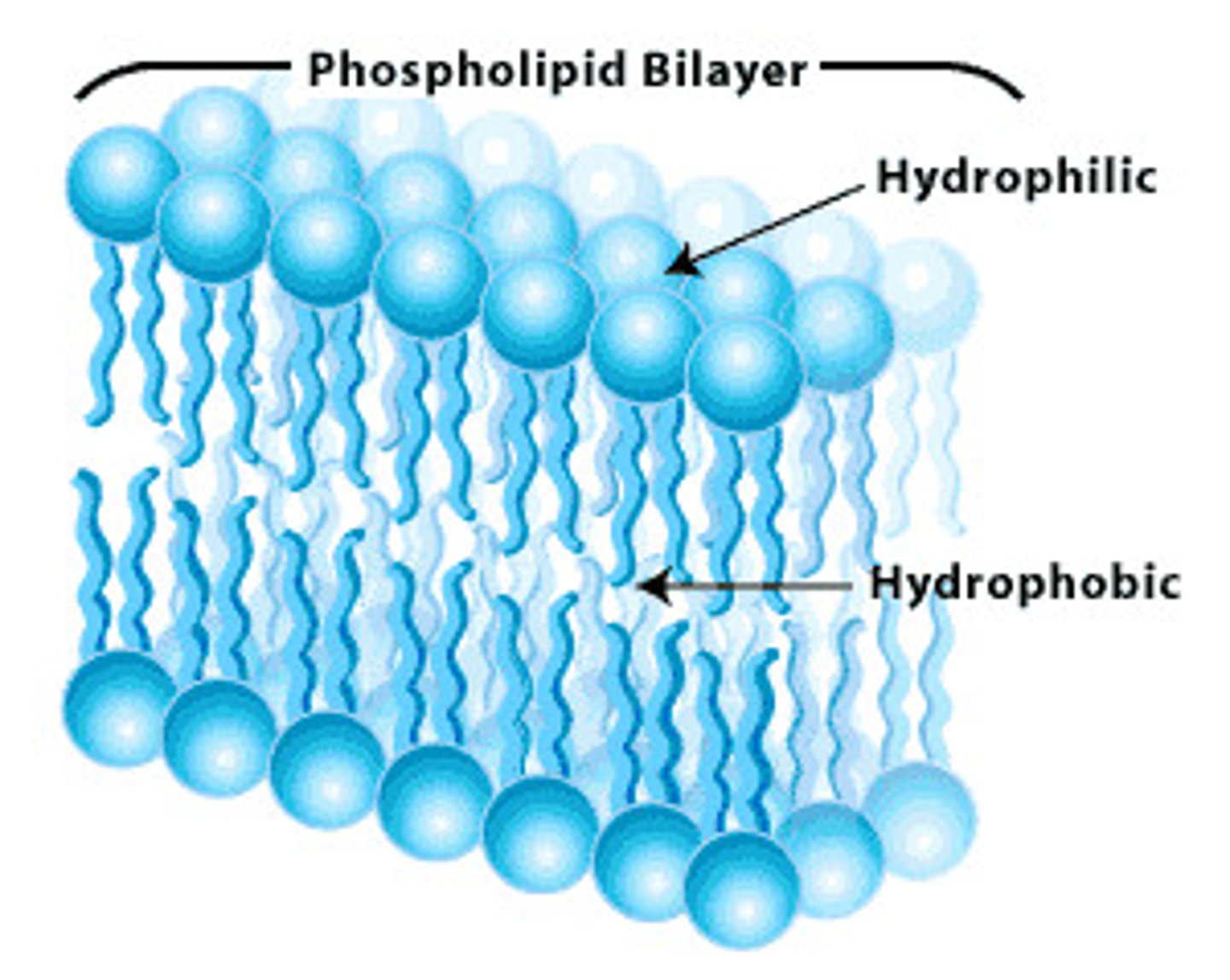
Phospholipids
2 fatty acids bound to glycerol plus a phosphate headgroup
- which is the structural foundation of cell membranes
- They have a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails.
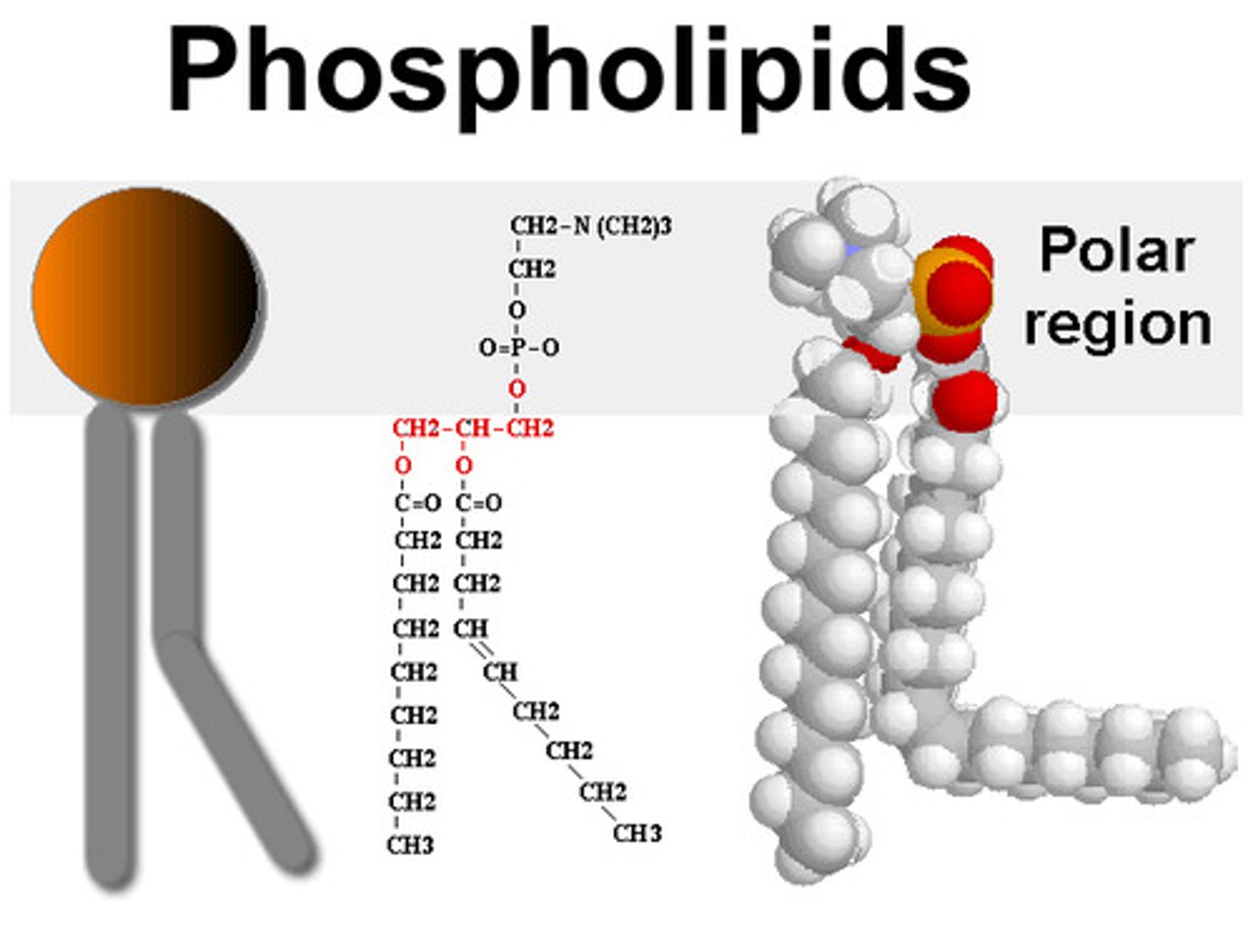
what part of a phospholipid is hydrophilic? head or tail?
phosphate head group
Steroids
Hormones made from cholesterol that are important signaling molecules and a component of animal cell membranes.
- made of fats/lipids
Proteins
Polymers (chains) of amino acids.
what are amino acids made of?
nucleic acids
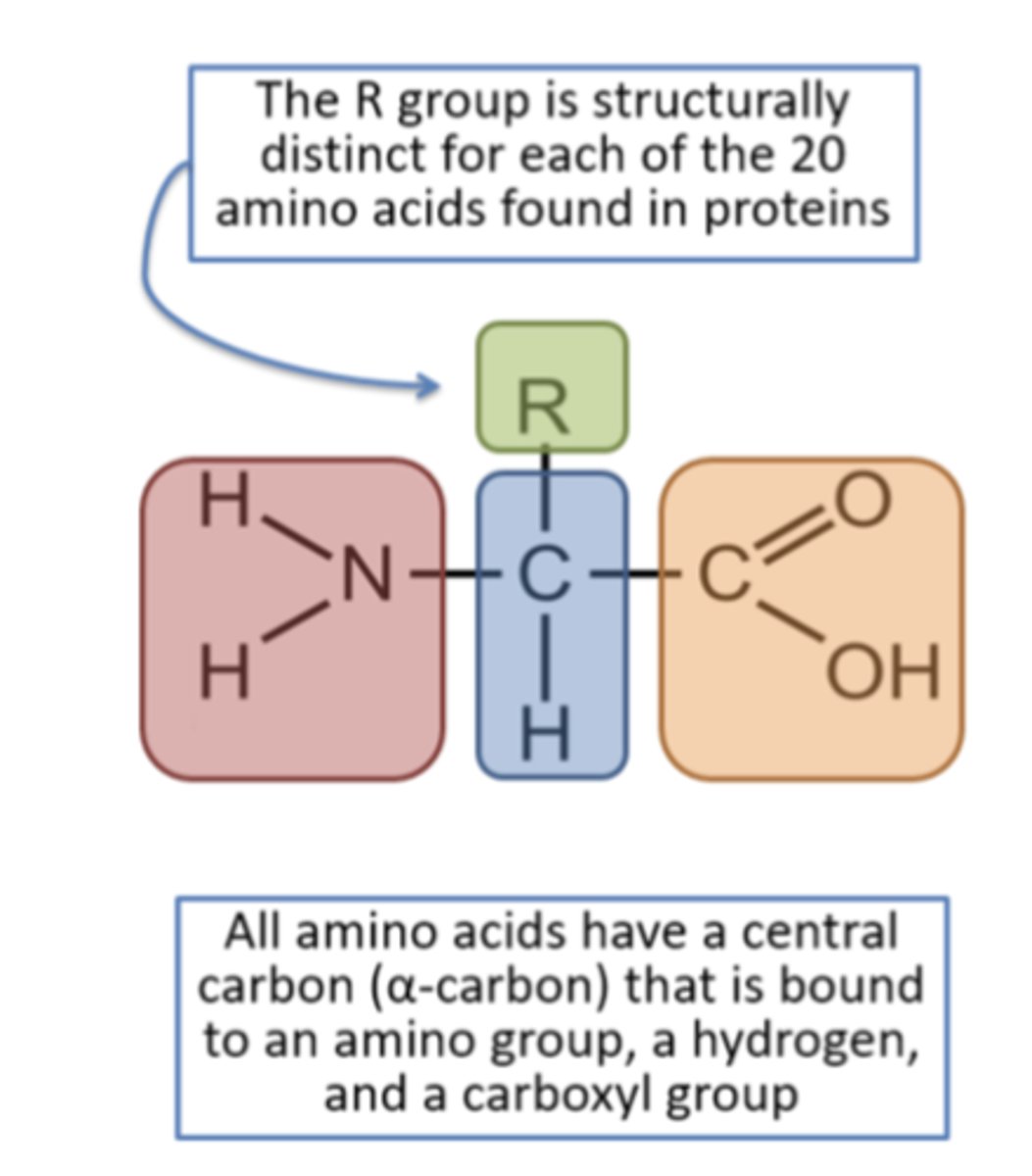
Peptide Bonds
Bonds linking amino acids to form proteins.
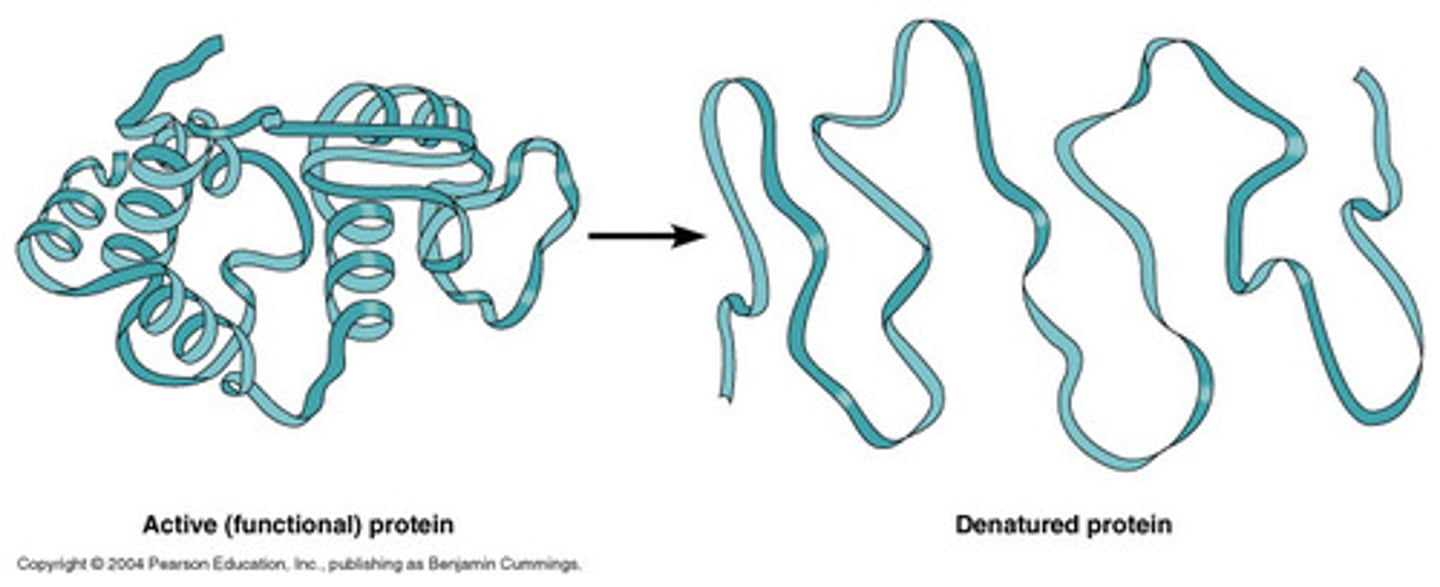
Denaturation
The partial or complete unfolding of a protein, which leads to a loss of its biological activity.
Nucleic Acids
Chains of nucleotide subunits that store and transfer genetic information.
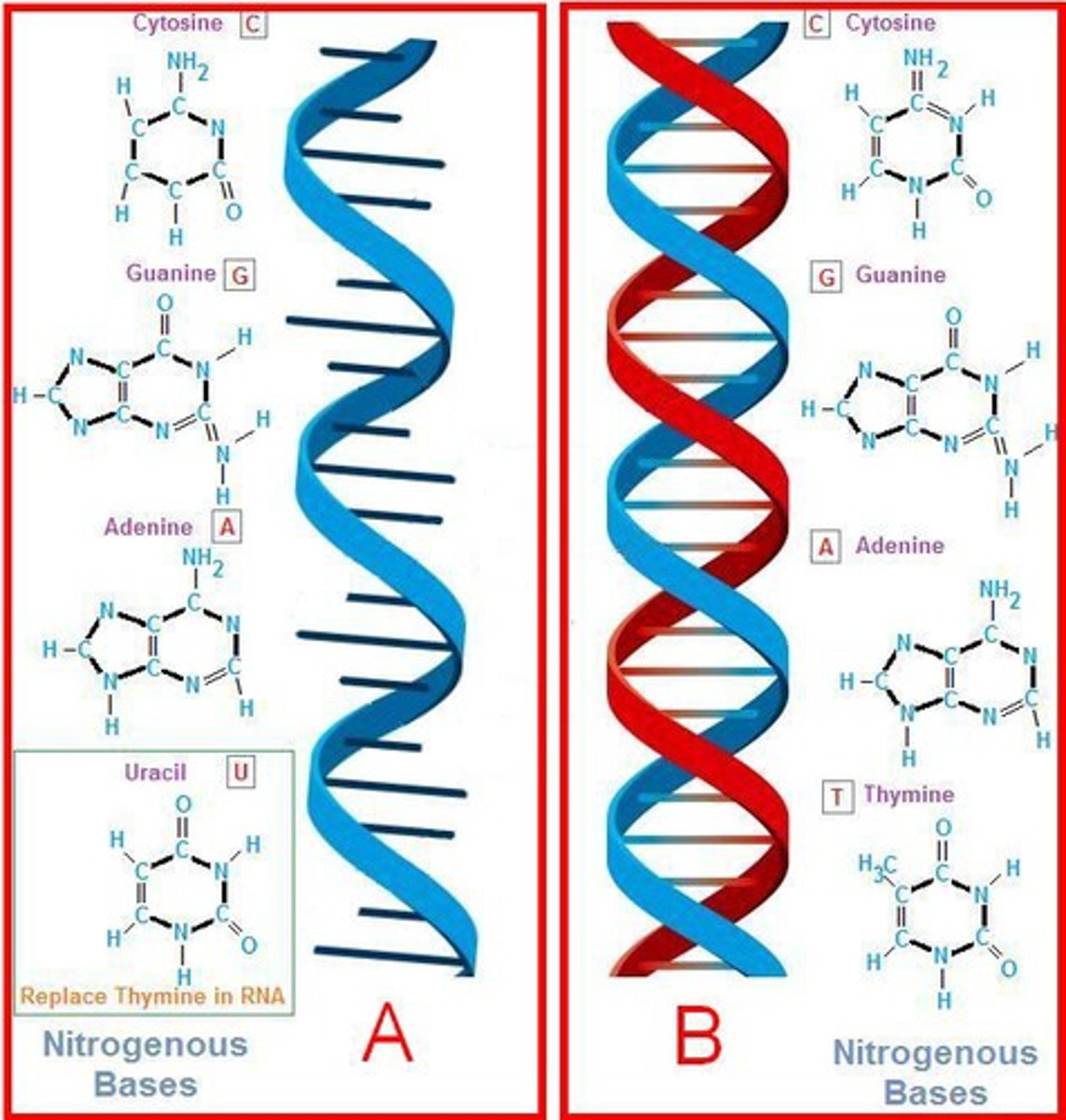
what are nucleic acids made of?
sugar phosphate backbone and a nitrogenous base (toward the middle)
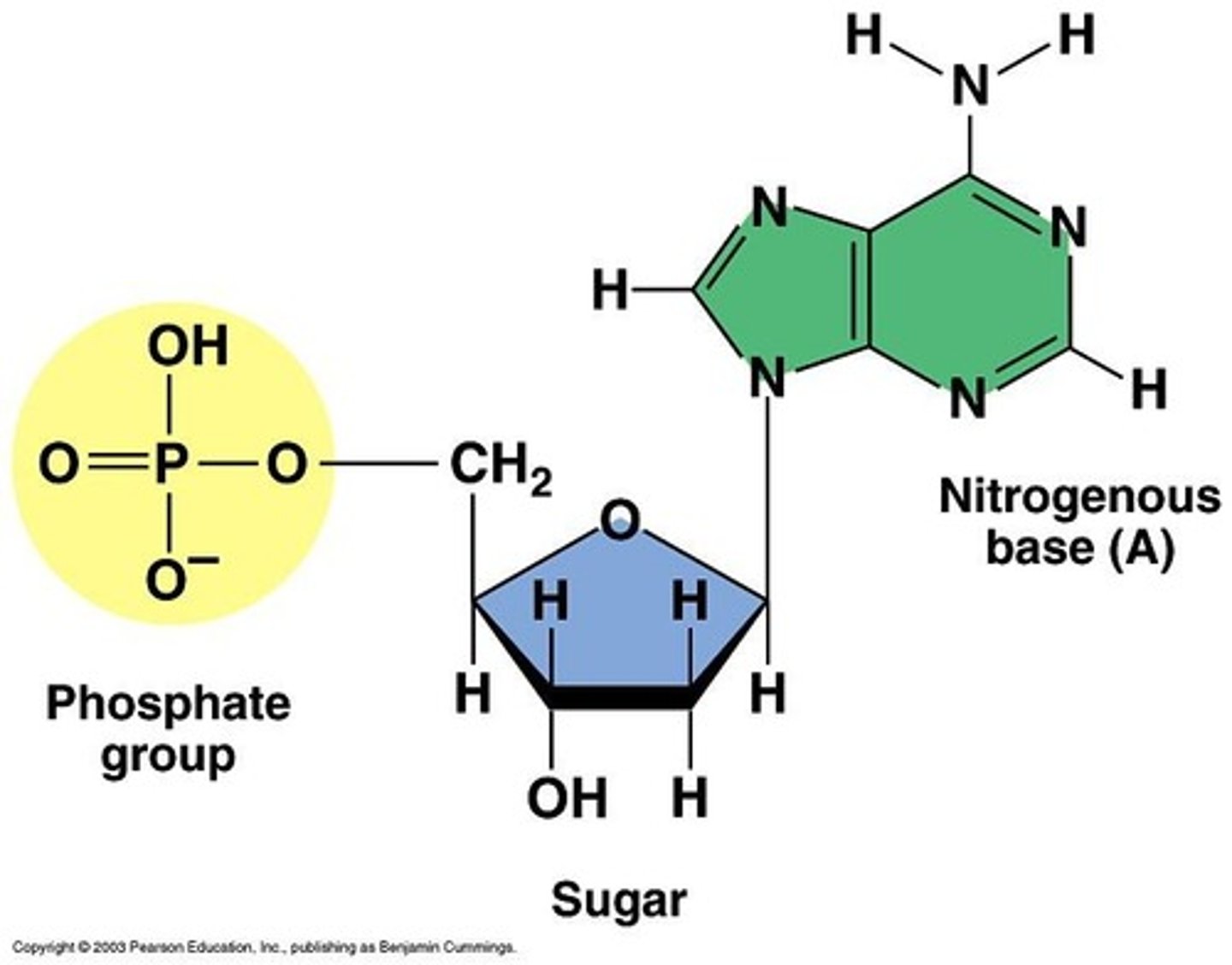
DNA
Contains the genetic information of a cell and determines what proteins it makes.
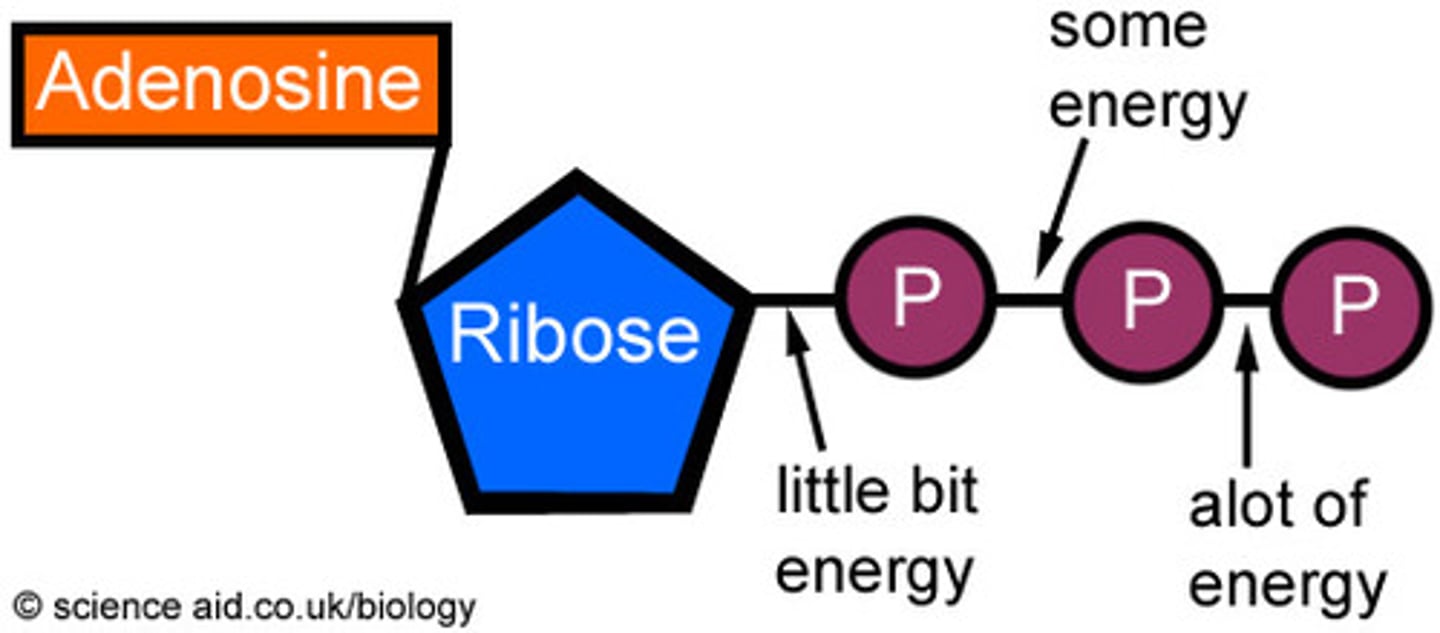
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
- the energy transfer molecule in the body.
- It releases energy when its high-energy phosphate bonds are broken.
Cell
The smallest living unit.
Plasma Membrane
The outer boundary of the cell, a bilayer of phospholipids, proteins, and cholesterol in animal cells.
Cytoplasm
The material within a cell, excluding the nucleus.
Nucleus
The organelle that contains the cell's genetic material.
Key Cell Functions
Include metabolism and energy use, synthesis of molecules for structure and function, communication, and reproduction and transmission of genetic information.
Bilayer
Flexible structure described as a fluid mosaic.
Selectively permeable
Allows some substances to pass through but not others.
Receptors
Bind extracellular ligands and transmit signals.
Enzymes
Catalyze chemical reactions at the membrane surface.
Channels
Allow solutes like ions in and out of the cell.
Carriers
Function to move things in and out of the cell.
Cell-identity markers
Allow the body to distinguish self from non-self.
Cell-adhesion proteins
Bind cells to one another.
Microvilli
Finger-like projections that increase the surface area of the plasma membrane for absorption or secretion.
Cilia
Hair-like projections with a whipping/wave motion to propel substances over the cell surface.
Passive Transport
Does not require energy; net movement is down the concentration gradient.
what is Filtration? is it active or passive?
Particles are forced across a barrier by hydrostatic pressure
passive!
Simple Diffusion? is it active or passive?
The net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration.
PASSIVE!
Osmosis? active or passive?
The diffusion of water down its concentration gradient.
PASSIVE!
Facilitated Diffusion
Movement of solutes down their concentration gradient with the help of a carrier or channel protein.
passive!
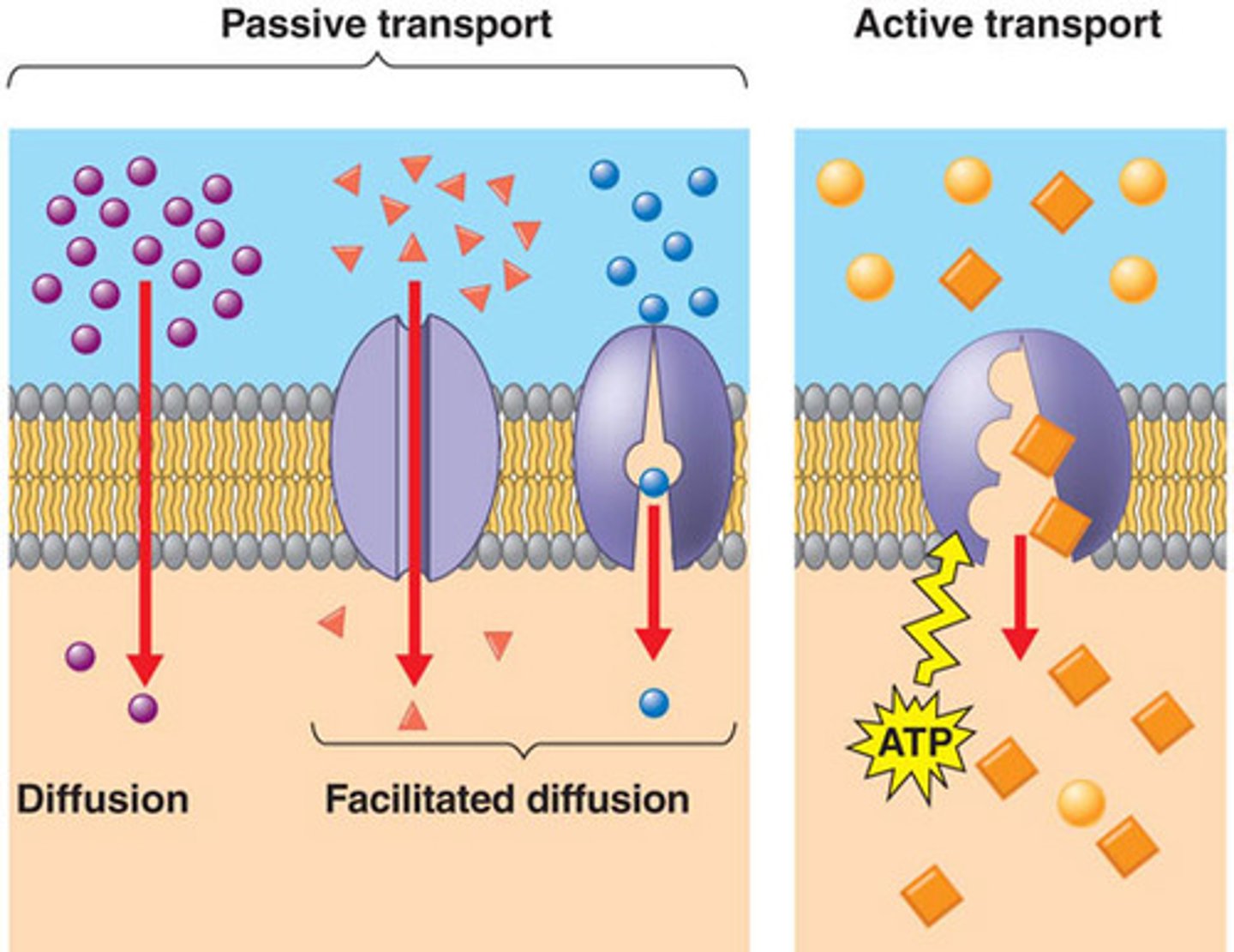
Active Transport
Requires energy (ATP) to move solutes against their concentration gradient.
Vesicular Transport
Movement of materials into and out from the cell by vesicles.
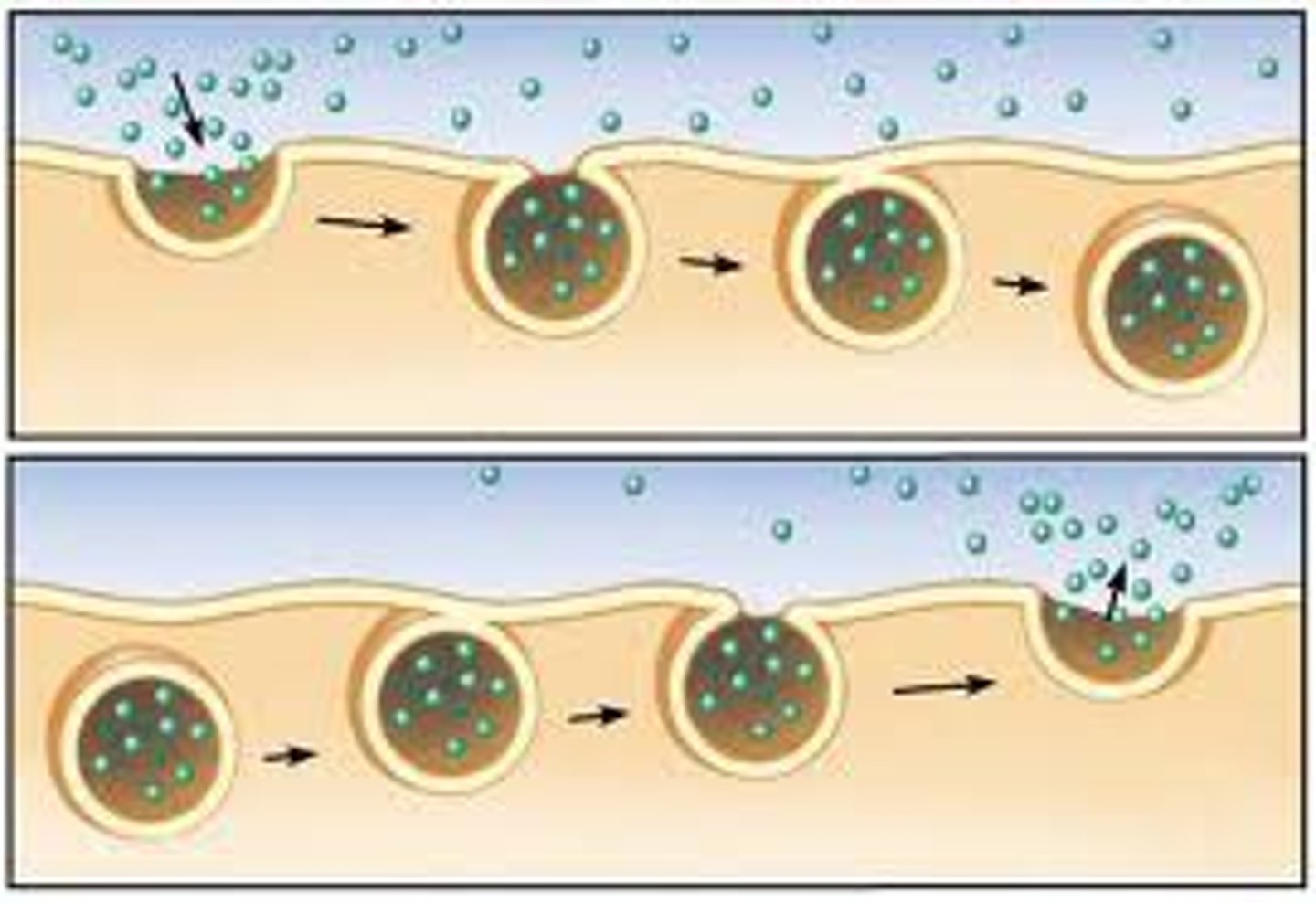
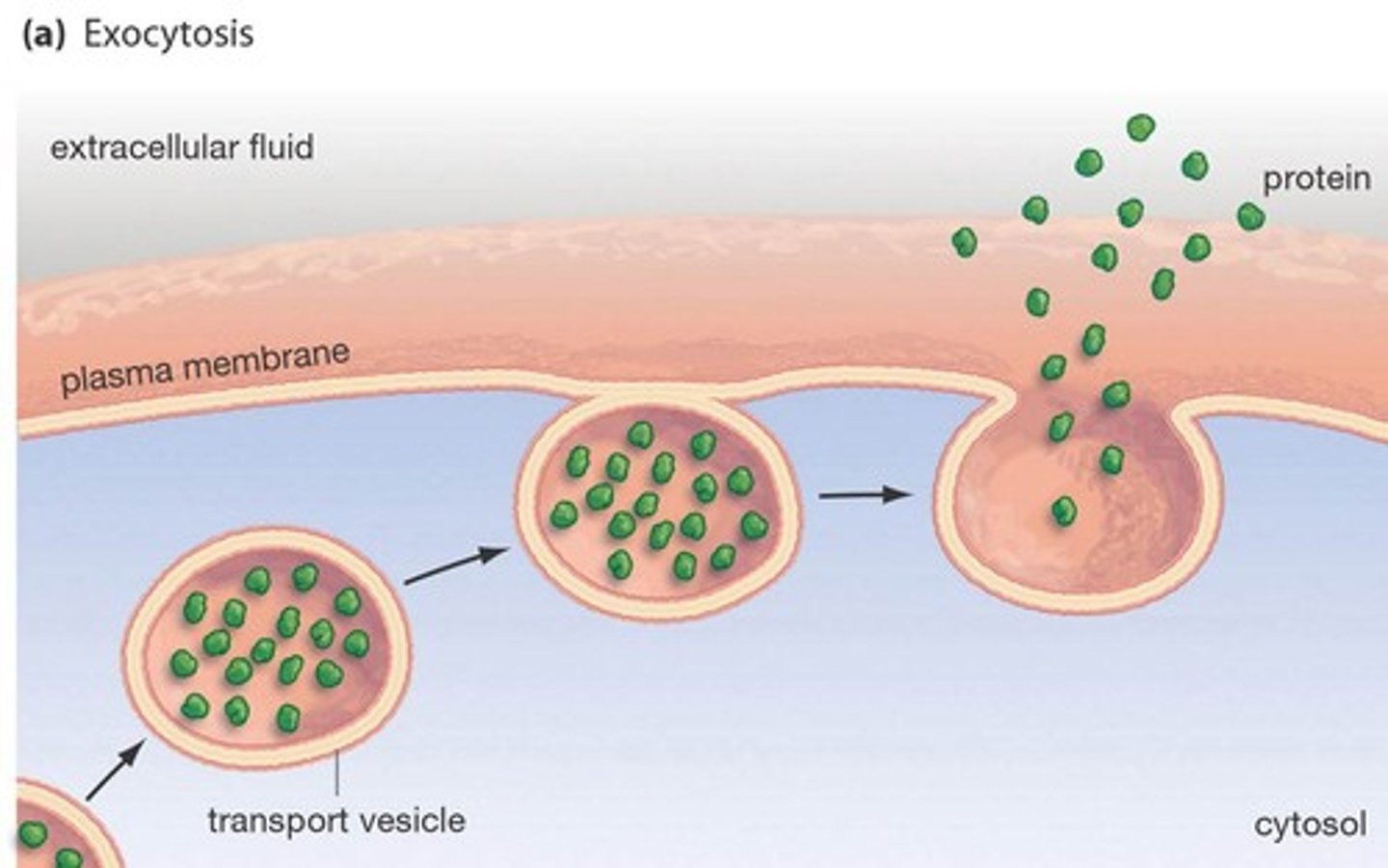
Exocytosis
Vesicular transport of materials out of the cell.
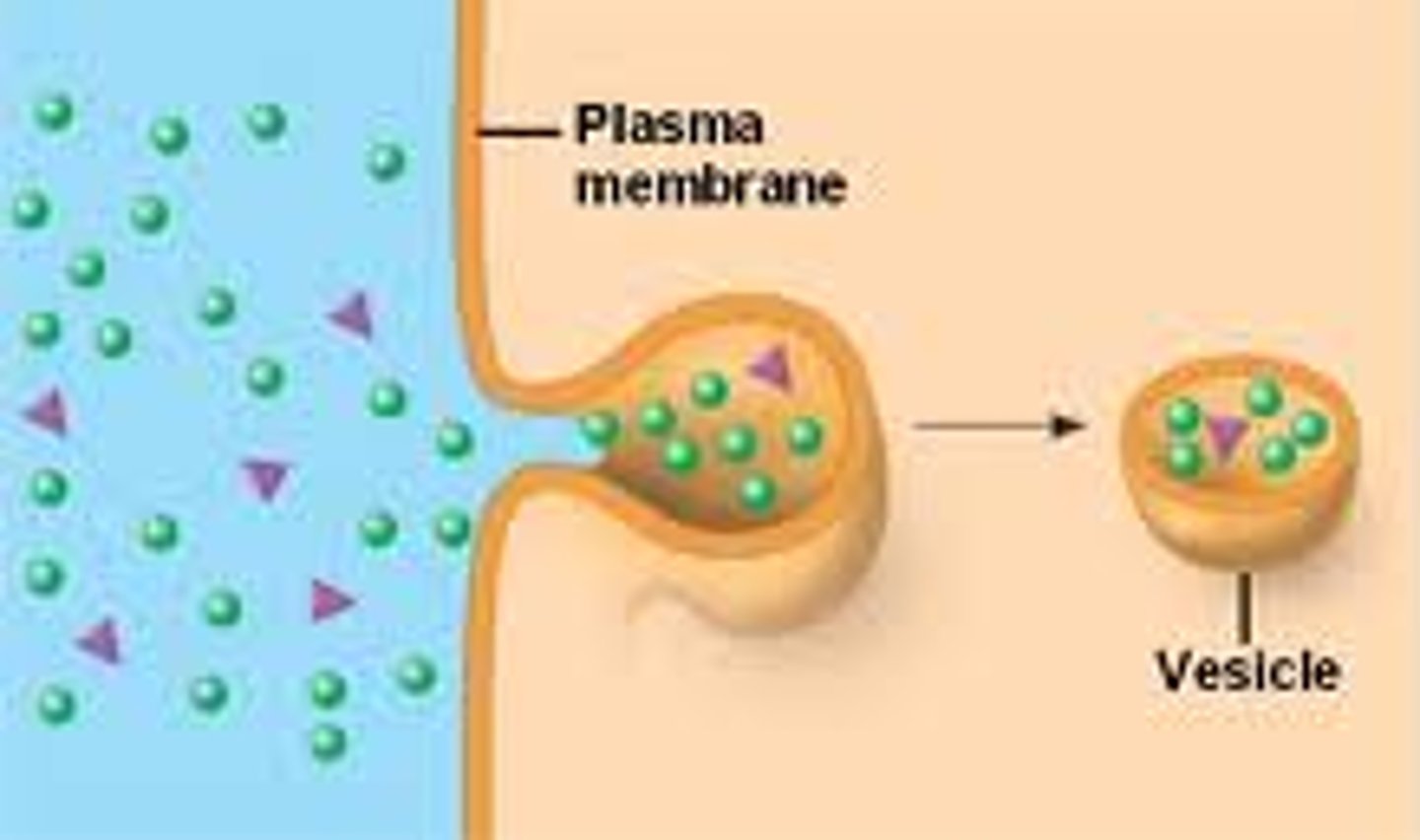
Endocytosis
Vesicular transport of materials into the cell.
Phagocytosis
"Cellular eating," where the cell extends its plasma membrane to engulf a foreign body.
large particles!
Pinocytosis
"Cellular drinking," where the cell engulfs extracellular fluid and solutes.
small particles!
Cytosol
The viscous, semi-transparent fluid in which other cytoplasmic components are suspended.
Organelles
"Little organs" that are specialized cellular compartments that serve a specific function for the cell.
What is the function of rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)?
Protein synthesis via ribosomes
What is the function of smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)?
Lipid synthesis and Calcium storage - no ribosomes
Golgi Apparatus
Stacks of membrane-bound sacs that modify, package, and distribute proteins and lipids.
Mitochondria
The "powerhouses" of the cell; they produce ATP.