Unit 3 -- Elasticities
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Elasticity
a measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded or quantity supplied to a change in one of its determinants
PED (Price Elasticity of Demand)
The % change in Qd given a 1% change in the price.
Determinants of PED
1. Availability of close substitutes.
2. Necessities versus luxuries.
3. Proportion of income devoted to the product
.4. Time horizon.
Demand tends to be more elastic when...
1. the larger the number of close substitutes.
2. if the good is a luxury.
3. the more narrowly defined the market.
4. the longer the time period.
PED Equation
% change in QD / % change in price
Midpoint method
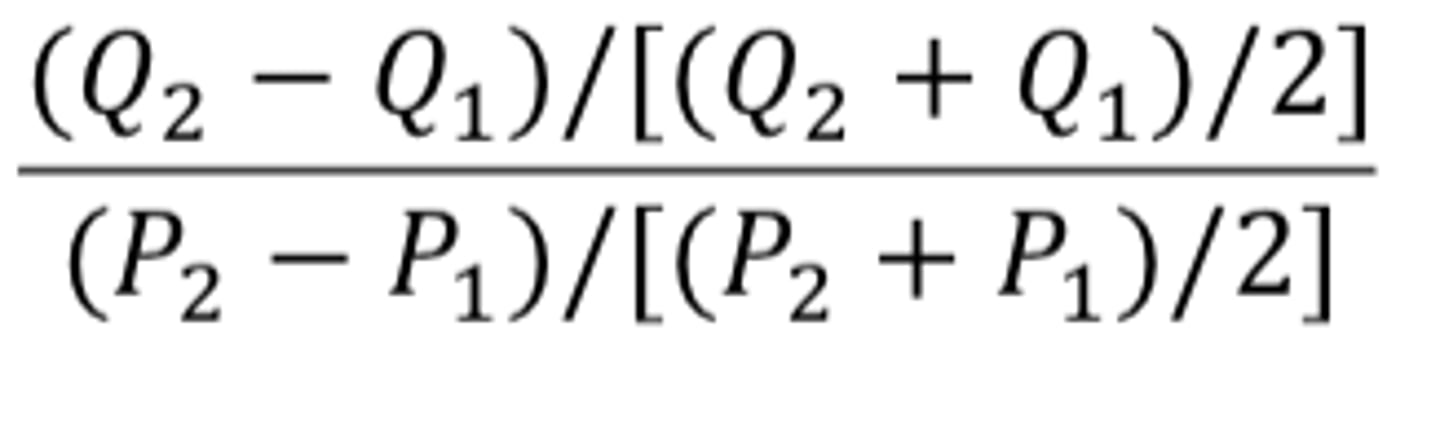
Price Inelastic Demand (PED > 1)
- Quantity demanded does not respond strongly to price changes.
- Price elasticity of demand is less than one.
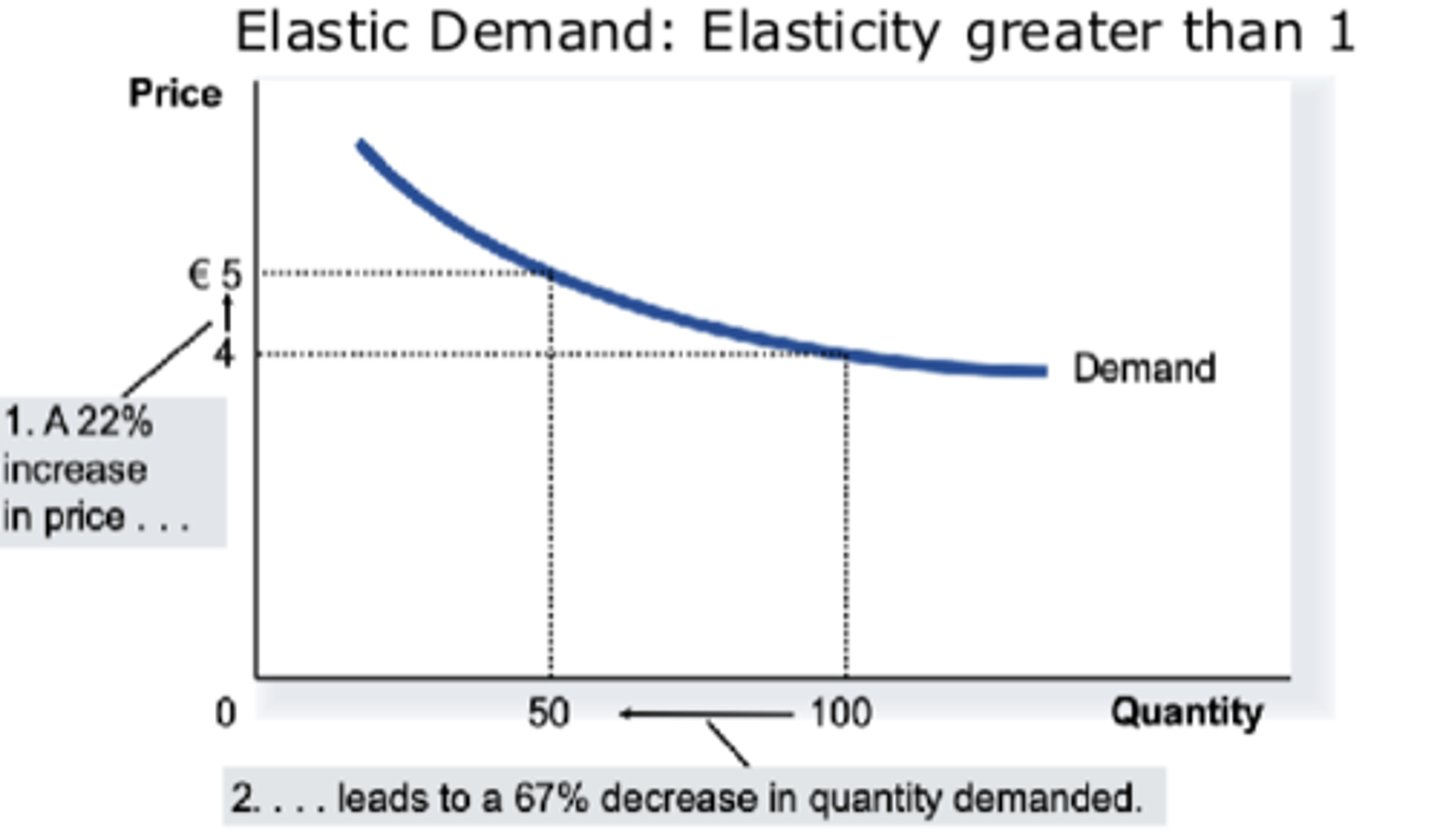
Price Elastic Demand (PED < 1)
- Quantity demanded responds strongly to changes in price.
- Price elasticity of demand is greater than one.
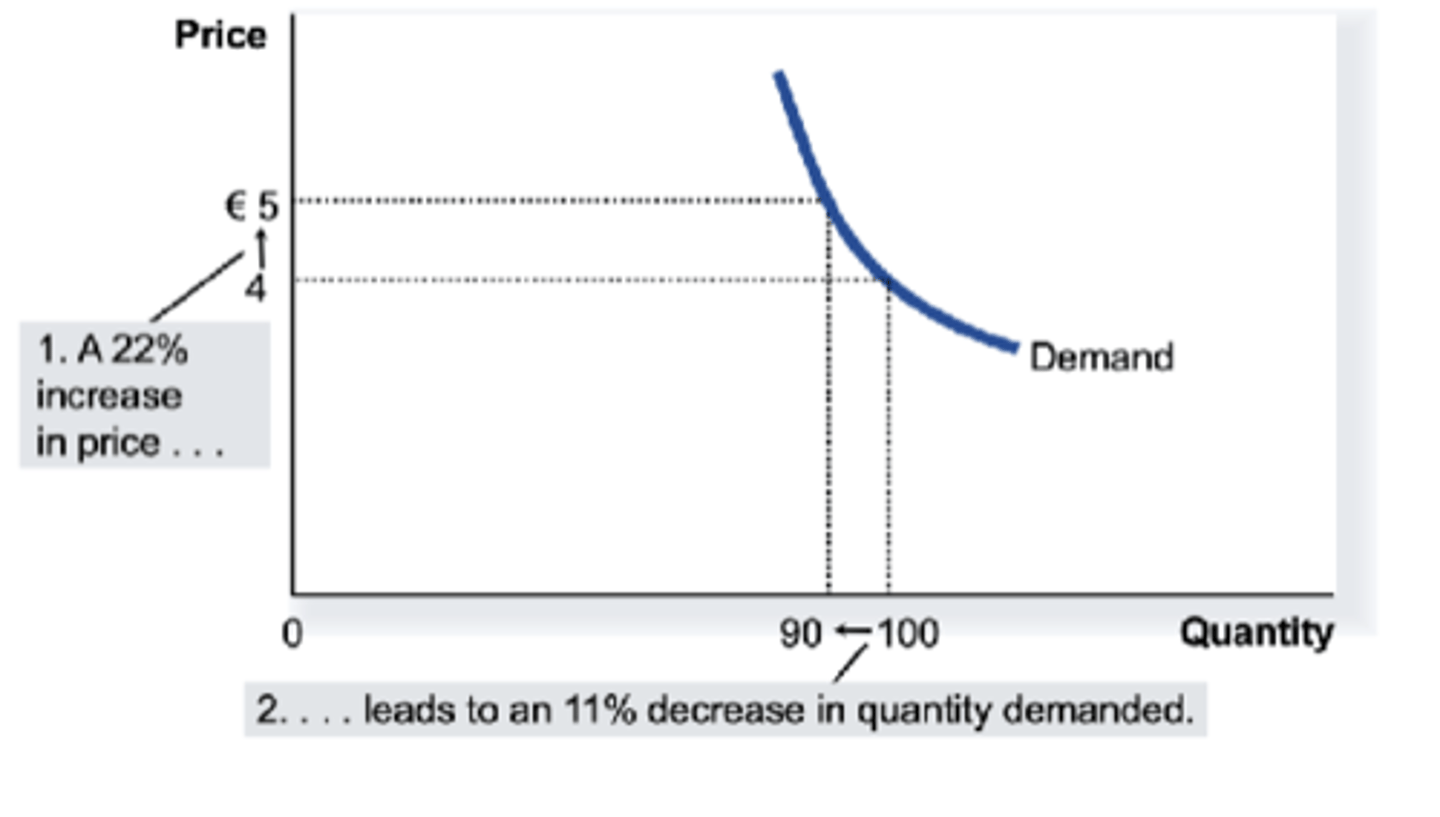
What does inelastic demand (lower than 1) look like?
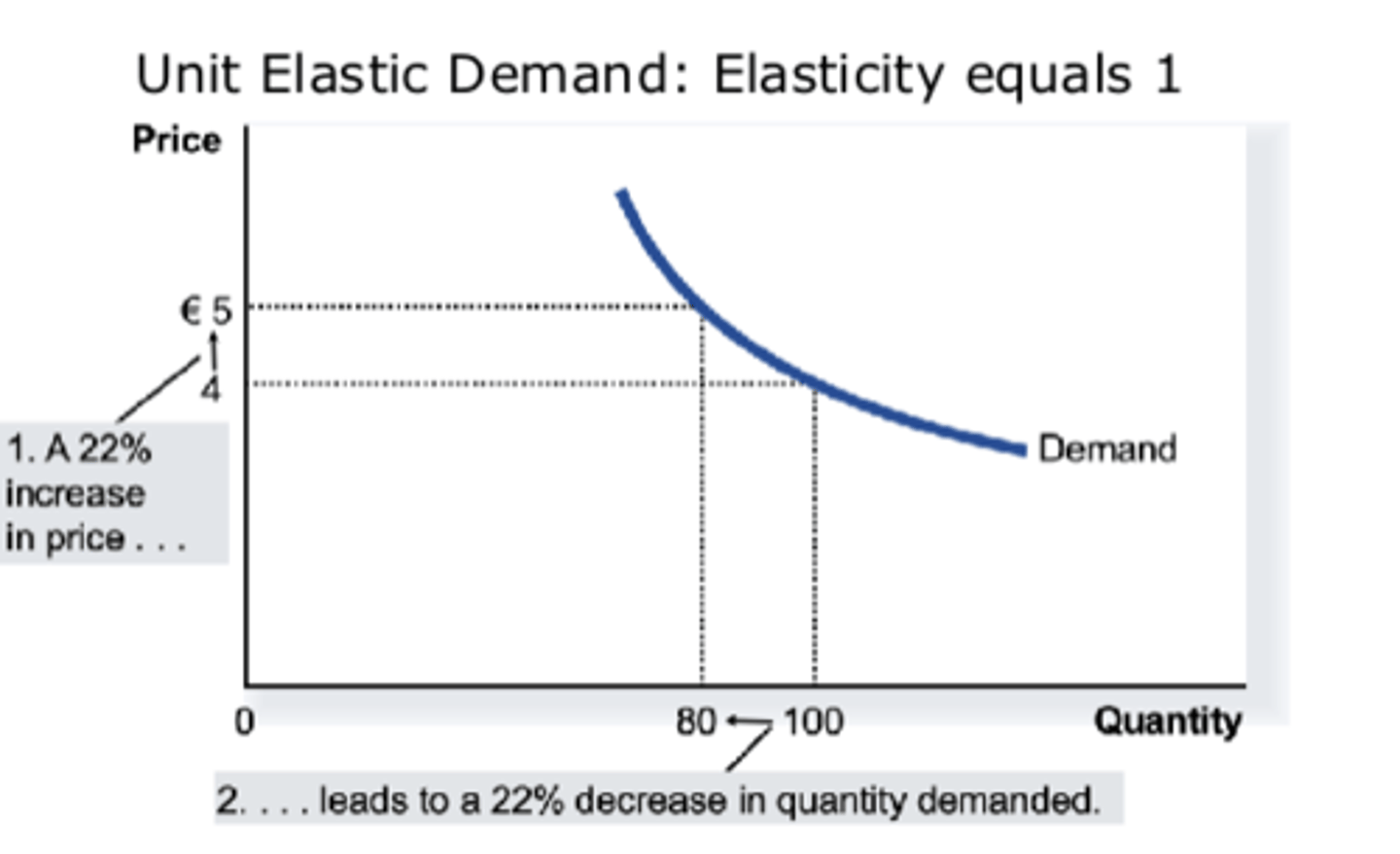
What does unit elastic demand (equals 1)?
What does elastic demand look like (greater than 1)?
What does perfectly elastic demand look like (= infinity)?
perfect elastic graph
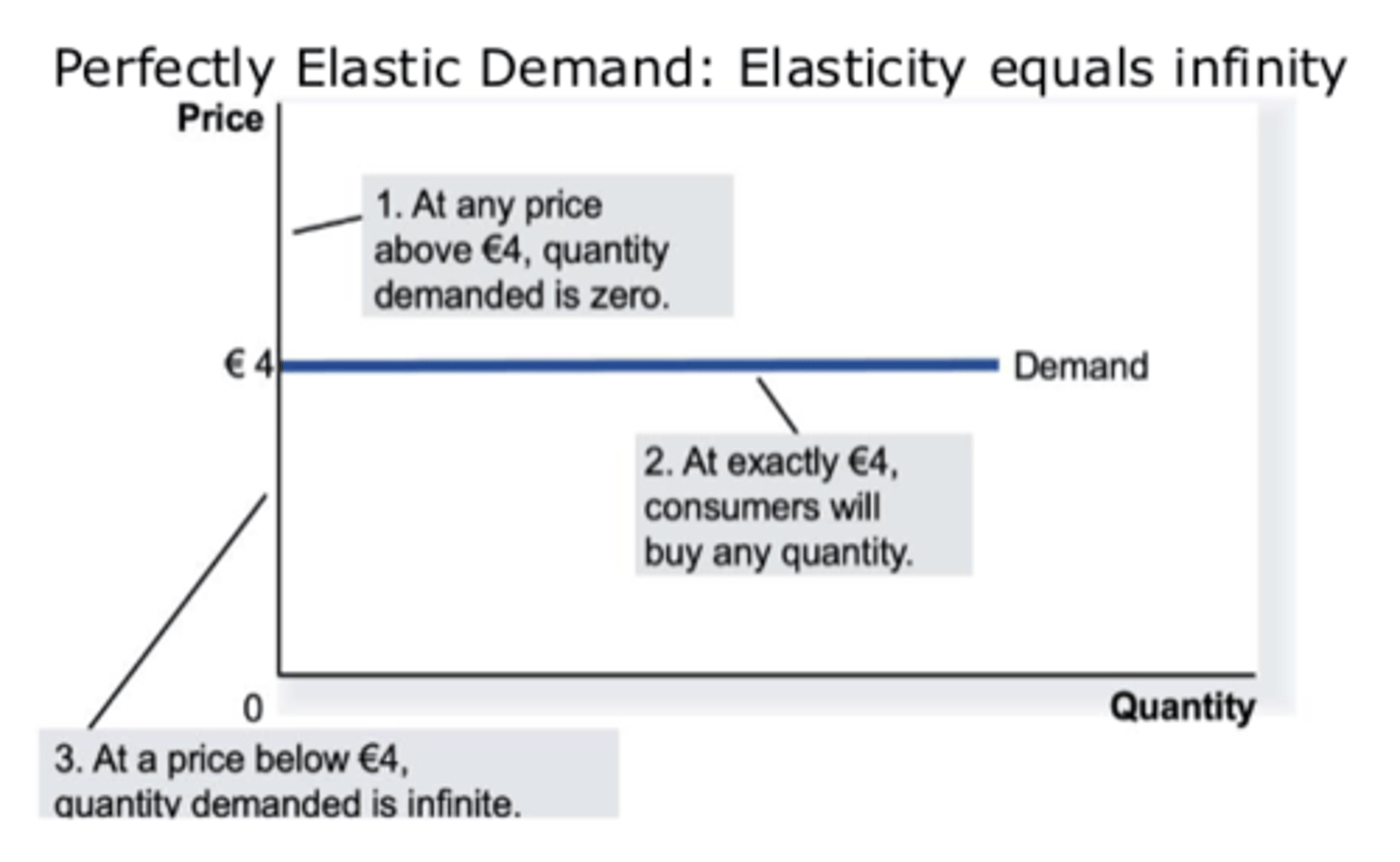
Total Revenue
the amount paid by buyers and received by sellers of a good, computed as the price of the good times the quantity sold (P x Q)
When demand is price inelastic...
price and total expenditure move in the same direction.
When demand is price elastic...
price and total expenditure move in opposite directions
If demand is unit price elastic...
total expenditure remains constant when the price changes
Income elasticity
sensitivity of demand for a product relative to changes in income
Income elasticity eqn.
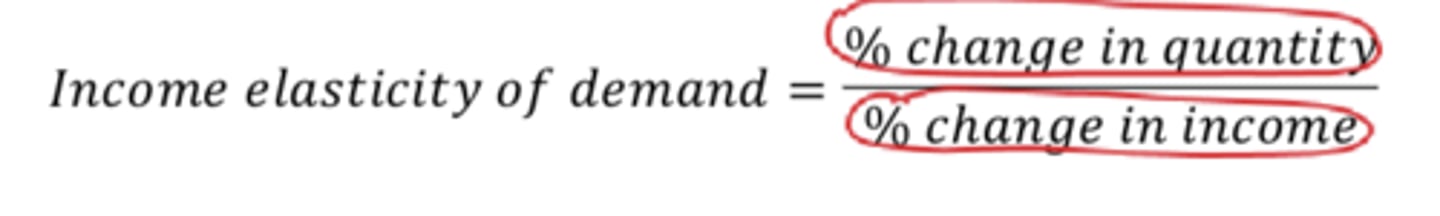
Normal goods (positive income elasticity)
Higher income raises the Qd for normal goods
Inferior goods (negative income elasticity)
Lower income highers Qd for inferior goods
Within normal goods, demand for goods consumers regard as necessities tends to be...
income inelastic (food, fuel, clothing, etc)
Within normal goods, demand for goods consumers regard as luxuries tends to be...
income elastic (furs, expensive foods, sports cars, etc)
Cross elasticity
Measures the responsiveness of demand for a product following the change in the price of another product
Cross price elasticity equation
% change in quantity of A demanded / % change in price of B
Substitutes have ___ cross price elasticities
positive
Complements have ___ cross price elasticities
negative
PES (Price Elasticity of Supply)
a measure of how much the quantity supplied of agood responds to a change in the price of that good
PES Equation
% change in quantity supplied / % change in price
PES Determinants
1. Time period. Supply is more price elastic in the long run.
2. Productive capacity and the ability of sellers to change the amount of the good they produce. The higher the capacity the more elastic the supply will be.
3. Size of the firm or industry. The larger the size the more elastic.
4. Mobility of the factors of production. The higher the mobility the more elastic.