Chapter 6: Electronic Structure of Atoms
Electronic Structure
Electronic structure: the arrangement and energy of electrons.
Waves
Electromagnetic radiation moves as waves through space at the speed of light.
Wavelength (\lambda): the distance between corresponding points on adjacent waves.
Frequency (v): the number of waves passing a given point per unit of time.
The longer the wavelength, the smaller the frequency.
Example:
Top wave = low frequency, long wavelength
Bottom wave = high frequency, short wavelength
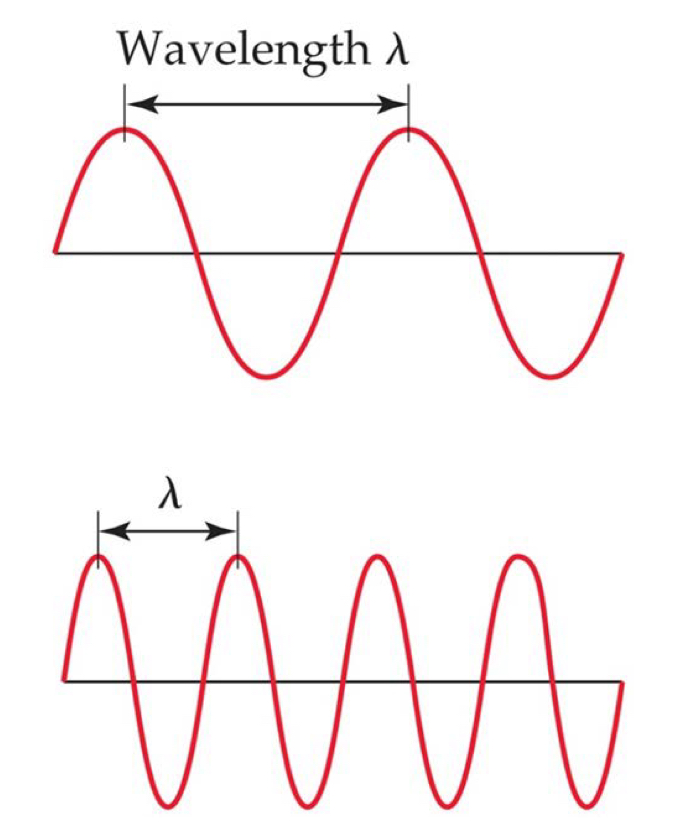
Electromagnetic Radiation
All electromagnetic radiation travels at the same velocity.
The speed of light (\:c\:) is 3.00\times 10^{8} m/s
c=\lambda v
3.00\times 10^{8} m/s = (wavelength)(frequency)
The Photoelectric Effect
Each metal has a different energy at which it ejects electrons.
Are lower energy, electrons are not emitted.
Energy is proportional to frequency
E=hv
Plank’s constant (h) is 6.626\times 10^{-34} J\sdot s
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics: describes the movement of electrons.
The square of the wave function gives the electron density, or probability of where an electron is likely to be at any given time.
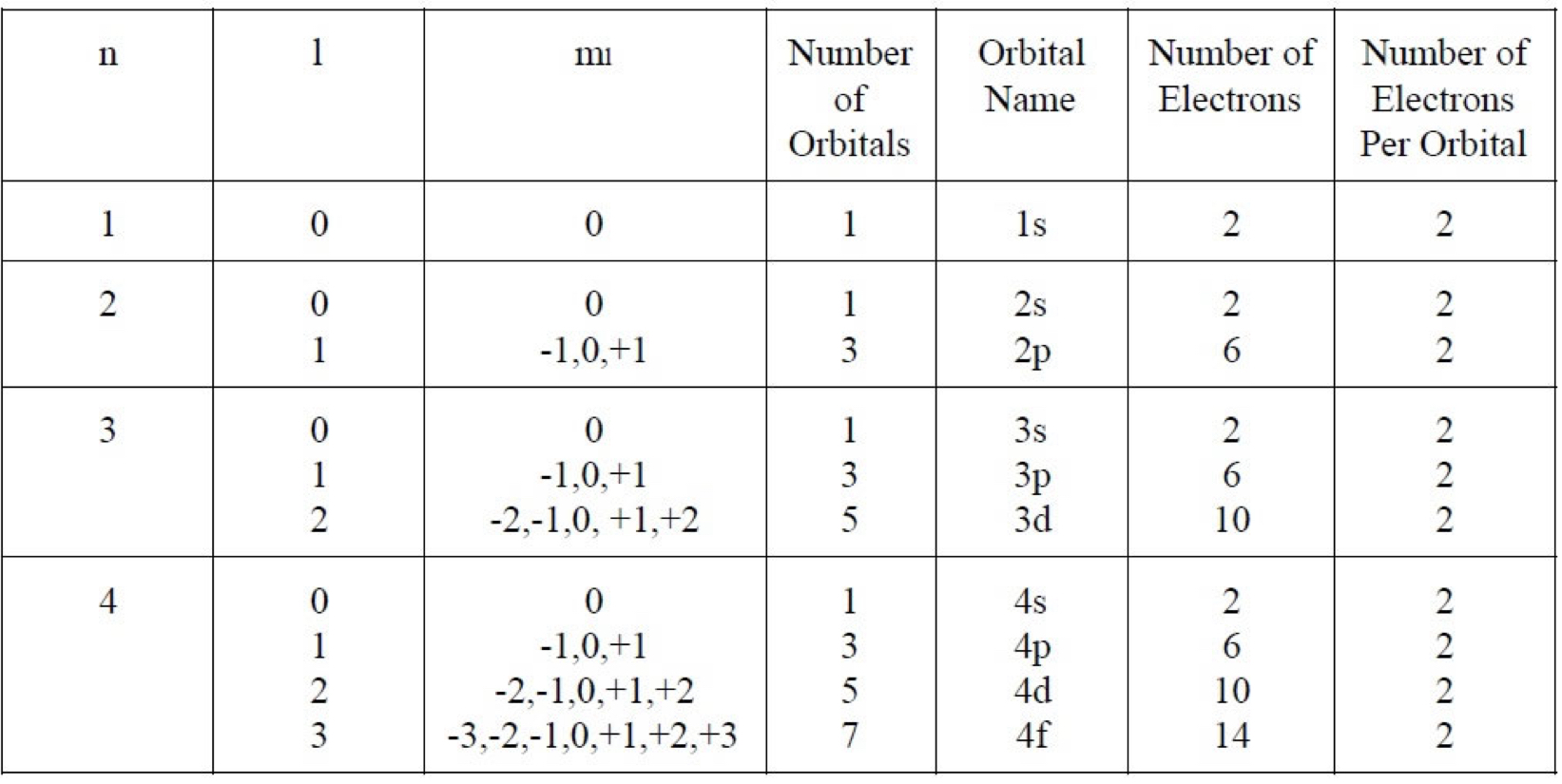
Quantum Numbers
Orbitals: describes a spatial distribution of electron density.
An orbital is described by a set of four quantum numbers.
Principal Quantum Number (n)
The principle quantum number, n, describes the energy level on which the orbital resides.
n provides the size
The values of n are integers greater or equal to 1.
n = 1, 2, 3, … \infty \geq 1
These correspond to the values in the Bohr model.
Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers (l)
This quantum number defines the shape of the orbital.
Allowed values of l are integers ranging from 0 to n-1
Letter designate the different values of l.
Value of l
Orbital letter used
0
s
1
p
2
d
3
f
Magnetic Quantum Number (ml)
The magnetic quantum numbers described the three-dimensional orientation of the orbital.
Allowed values of ml are integers ranging from -l to l including 0.
-l\leq m_{l}\leq l
There can be up to 1 s orbital, 3 p orbitals, 5 d orbitals, and 7 f orbitals.
Orbitals with the same value of n form an electron shell.
Different orbitals types within a shell are subshells.
Orbital orientations (ml)
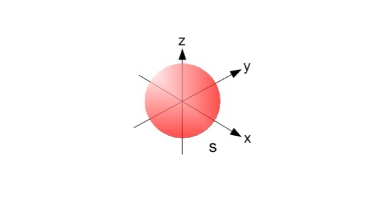
s Orbitals
The value of l for s orbitals is 0.
Spherical in shape.
Radius of sphere increase with the value n.
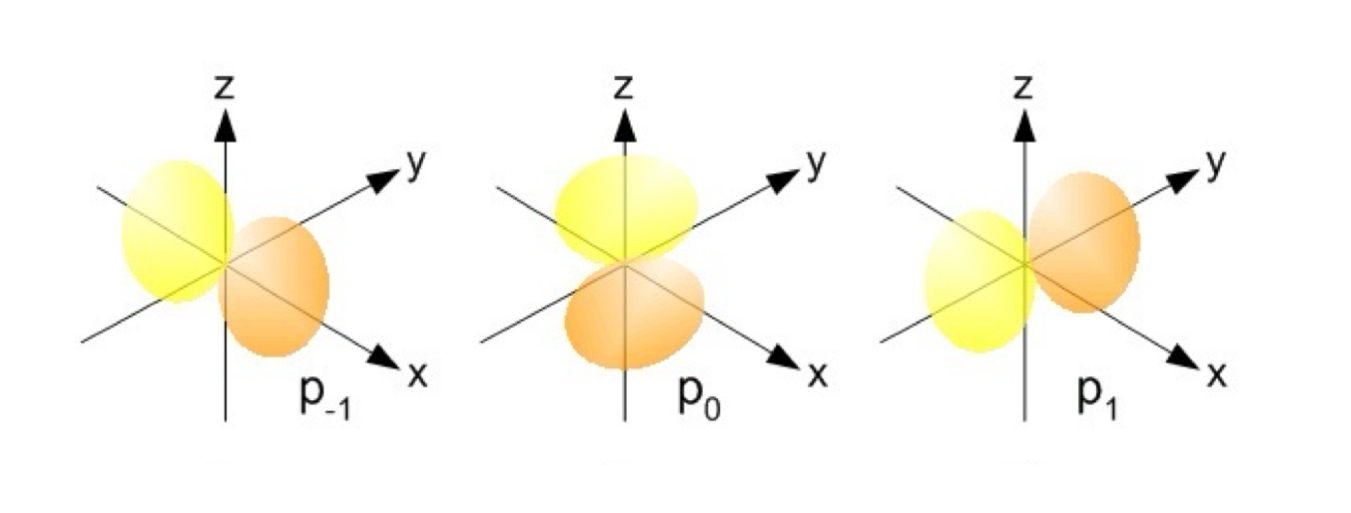
p Orbitals
The value of l for p orbitals is 1.
They have two lobes with a node between them.
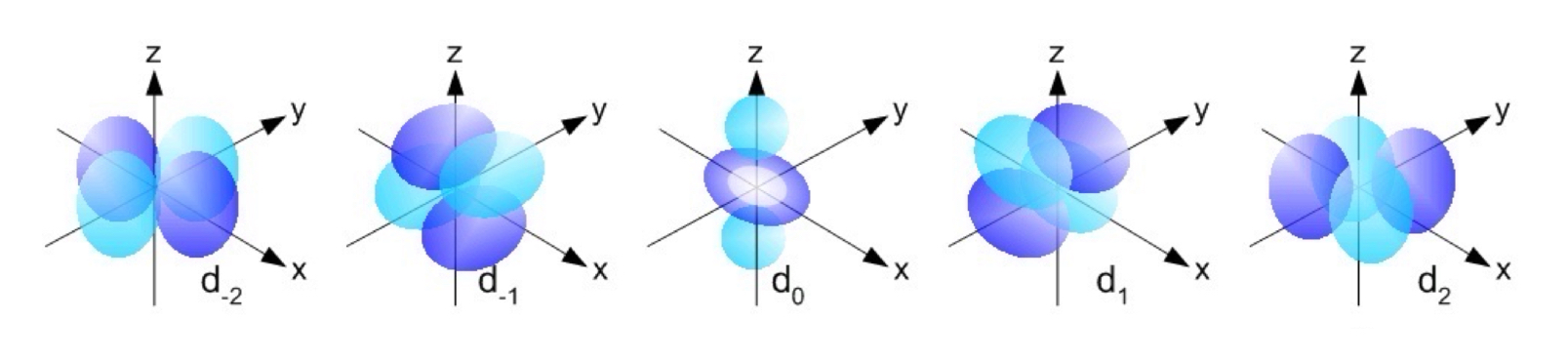
d Orbitals
The value of l for a d orbital is 2.
Four of five d orbitals have four orbitals; the other resembles a p orbital with a doughnut around the center.
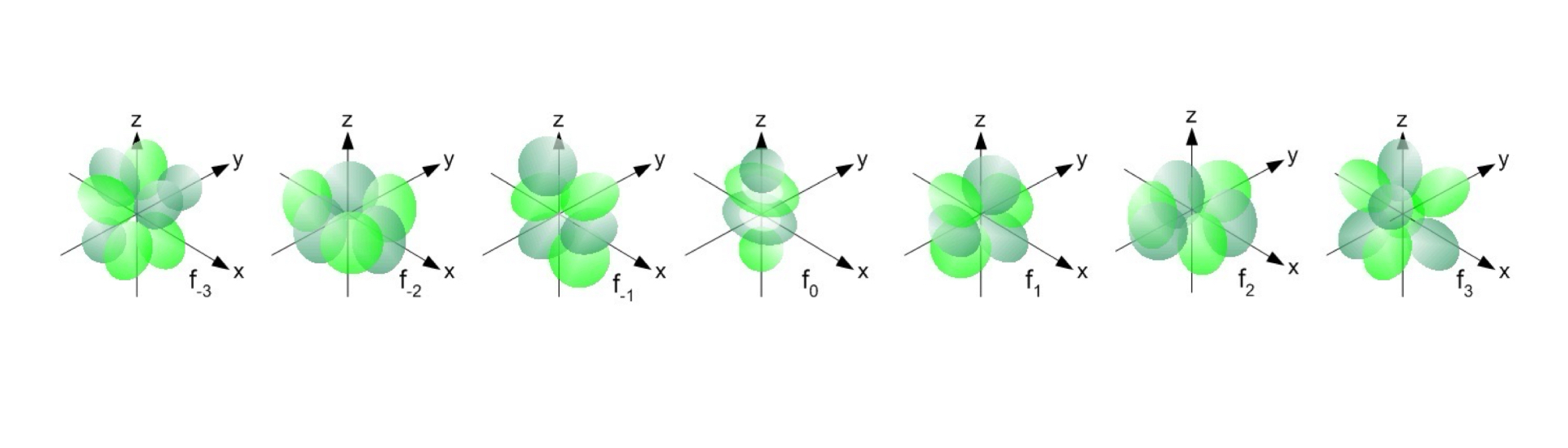
f Orbitals
The value of l for f orbitals is 3.
Complex shape.
Spin Quantum Number (ms)
Two electrons in the same orbital do not have exactly the same energy.
The “spin” of an electron describes its magnetic field, which affects its energy.
The spin of the quantum number has only two allowed values: +1/2 and -1/2
Only one can spin up, other other spins down.
Summary
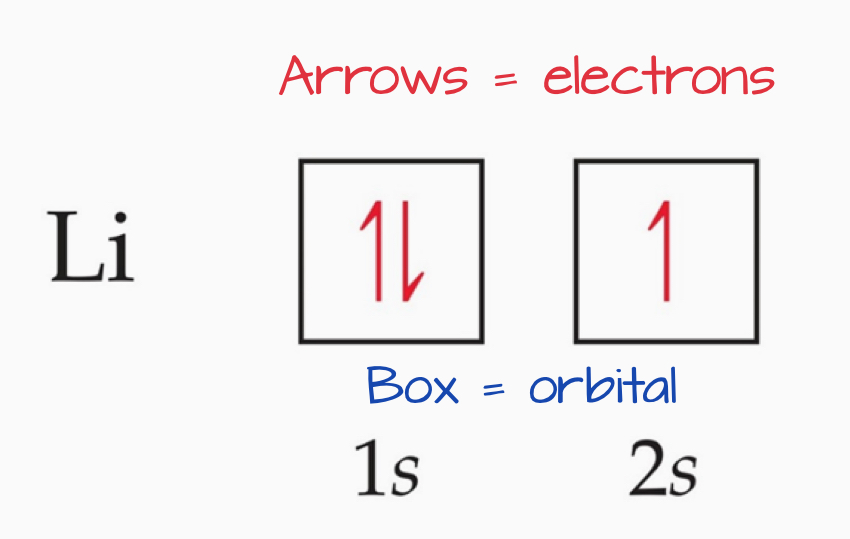
Orbital Diagrams
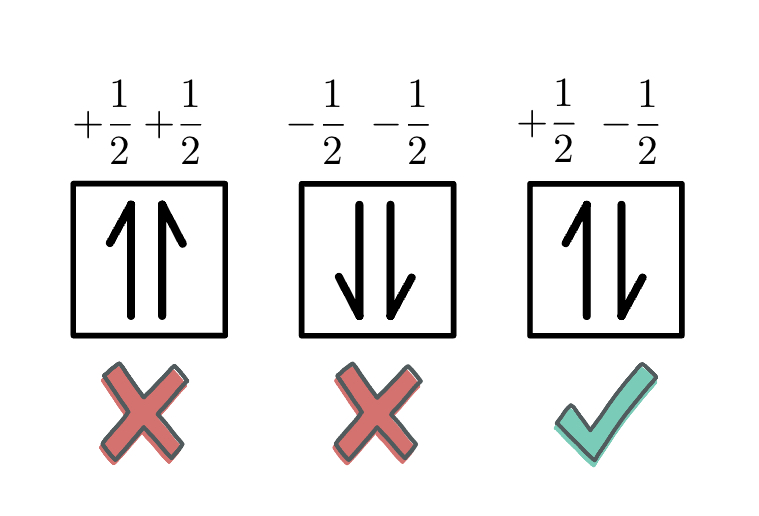
Each box in the diagram represents one orbital.
Half arrows represent the electrons.
The direction of the arrow represents the relative spin of an electron.
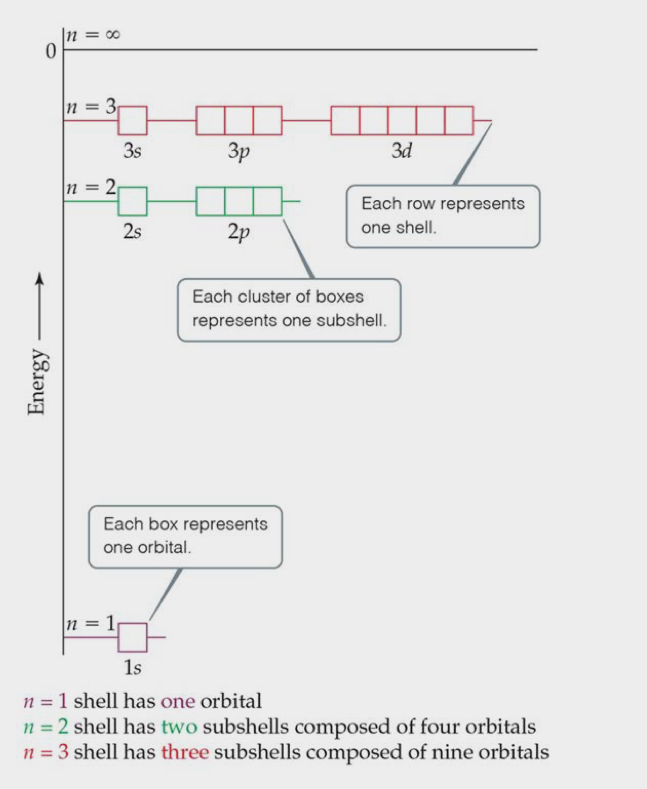
Energies of Orbitals
Degenerates: systems or orbitals that have the same energy.
As the number of electrons increases, so does the repulsion.
In atoms with more than one electron, not all orbitals on the same energy level are degenerate.
Energy levels start to overlap in energy (ex: 4s must be filled before 3p because its lower.
Hund’s Rule: For a set of orbitals in the same sublevel, there must be one electron in each orbital before pairing and the electrons have the same spin.
Pauli Exclusion Principle: No two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers.
Therefore, no two electrons in the same atom can have the exact same energy.
This means that every electron in an atom must differ by at least one of the four quantum number values. They will have OPPOSITE SPINS.
Electron Configurations
Electron configuration: the way electrons are distributed in an atom.
Ground state: the most stable organization is the lowest possible energy.
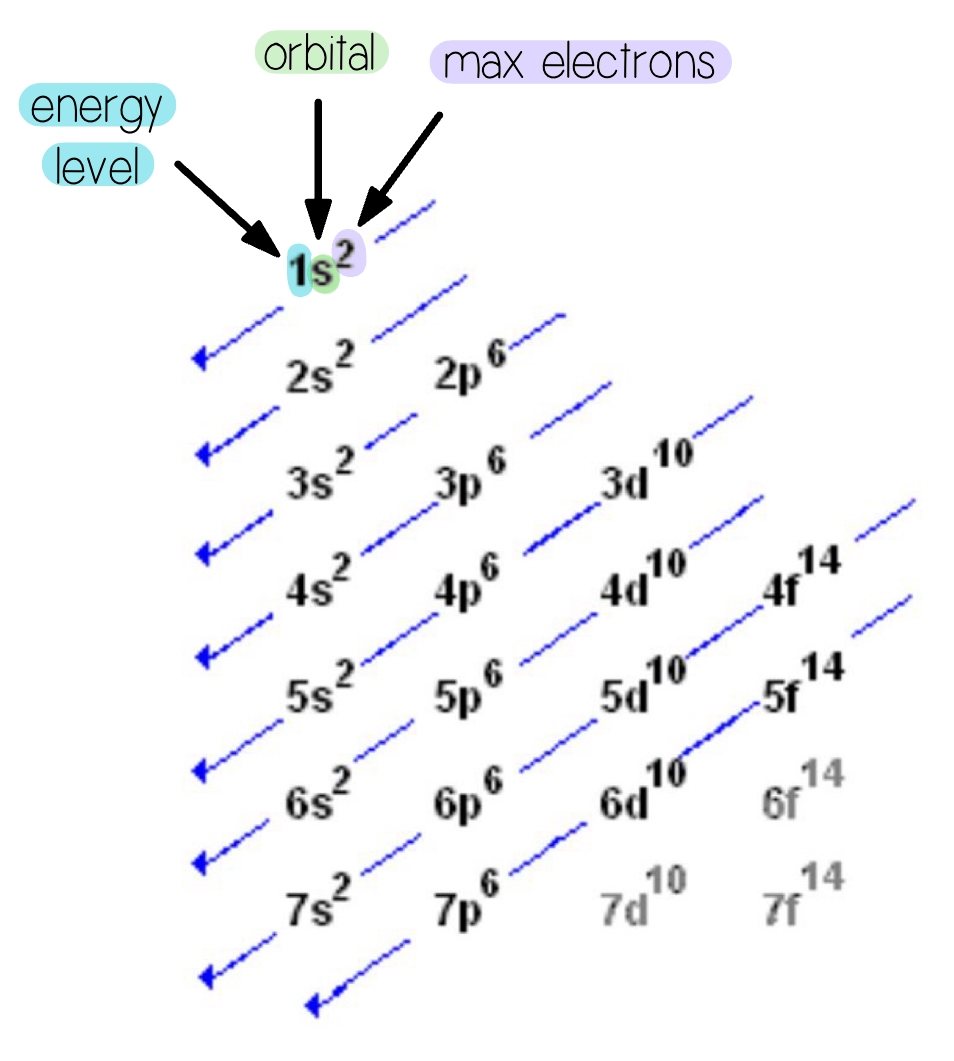
Each component consists of:
a number denoting the energy level
a letter denoting the type of orbital
a superscript denoting the number of electrons in those orbitals
Describes where electrons are located around the nucleus of an atom.
Moves diagonally
1s2 → 2s2 → 2p6 → 3s2 → 3p6 → 4s2 → 3d10 → 4p6 → 5s2 → 4d10 → and so on
Electron Configuration Examples
H: 1s1
Has 1 total electron
He: 1s2
Has 2 total electrons
Li: 1s22s1
Has 3 total electrons
Be: 1s22s2
Has 4 total electrons
B: 1s22s22p1
Has 5 total electrons
C: 1s22s22p2
Has 6 total electrons
N: 1s22s22p3
Has 7 total electrons
O: 1s22s22p4
Has 8 total electrons
F: 1s22s22p5
Has 9 total electrons
Ne: 1s22s22p6
Has 10 total electrons
Row and Energy Levels
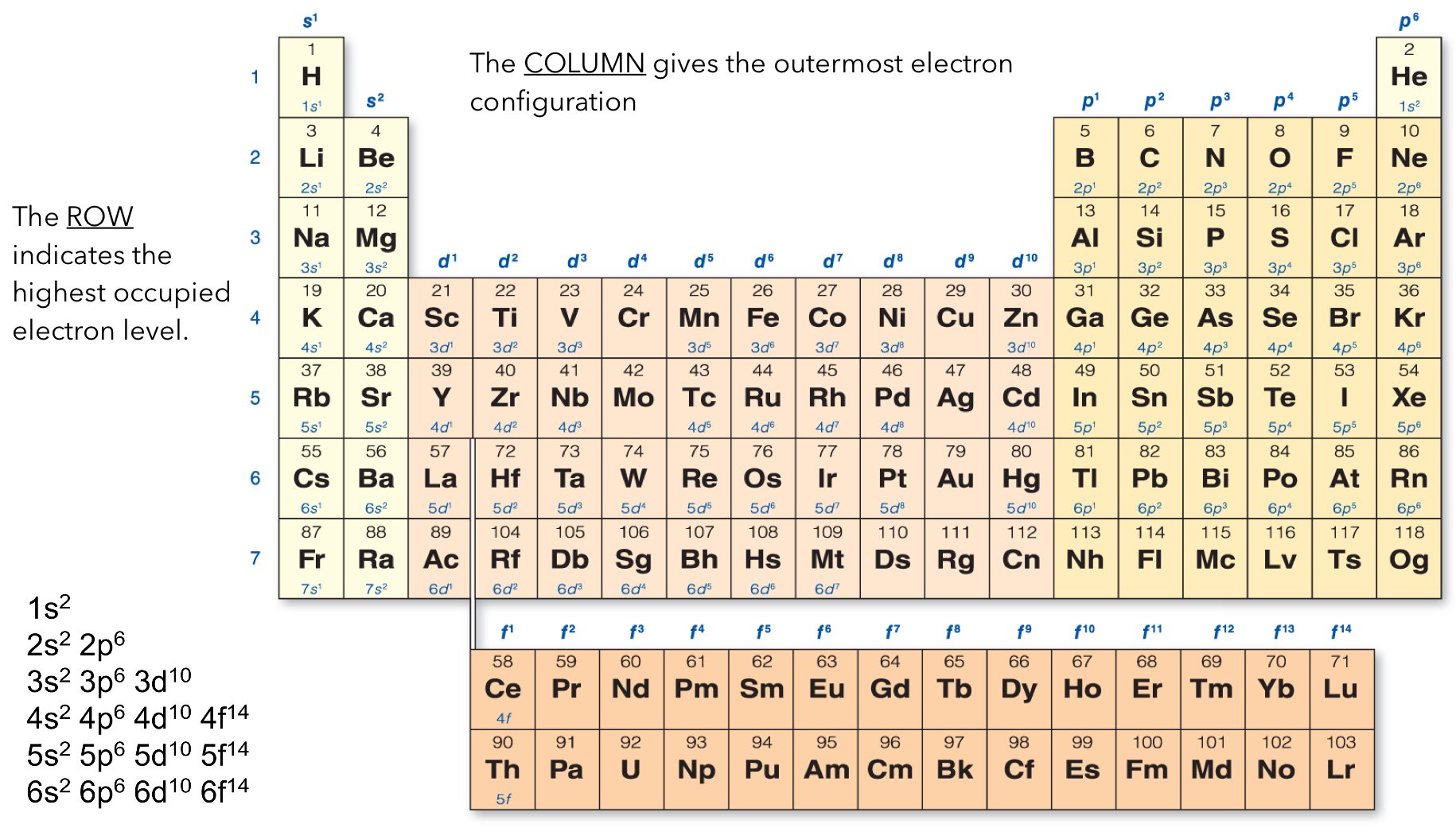
The periodic table is broken up into four blocks: s, p, d, and f.
Columns 1-2 and He are a part of the s block
The transition metals (columns 3-12) are the d block
Columns 13-18 make up the p block
The lower elements are part of the f block
The row indicates the highest occupied electron level.
The columns gives the outermost electron configuration (the superscript)
Condensed Electron Configurations
Elements in the same group of the periodic table have the same number of electrons in the outer most shell. These are the valence electrons.
The filled inner shell electrons are called core electrons.
The shortened version is written by using brackets around a noble gas symbol and listing only valence electrons.
Condensed Electron Configuration Examples:
Na = [Ne]3s1
Ne = [He]2s22p6
Cl = [Ne]3s23p5
O = [He]2s22p4
Ca = [Ar]4s2
Reference: Chemistry The Central Science (14th Edition)