Discovering Design with Chemistry - Chapter 5 Review Questions
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Define the following terms:
a. Covalent bond
b. Homonuclear diatomic
c. Covalent compound
d. Atomic radius
e. Electronegativity
f. Polar covalent bond
g. Polar covalent molecule
h. Purely covalent bond
i. Purely covalent molecule
a. Covalent bond - A chemical bond that is made by sharing electrons
b. Homonuclear diatomic - A molecule consisting of two atoms of the same element.
c. Covalent compound - A compound whose elements are held together with covalent bonds.
d. Atomic radius - The distance from the center of the nucleus to the atom's valence electrons.
e. Electronegativity - A measure of how strongly atoms attract electrons in a covalent bond.
f. Polar covalent bond - A covalent bond in which the electrons are not shared equally.
g. Polar covalent molecule - A molecule that has an uneven distribution of electrons, resulting in slight changes within the molecule itself.
h. Purely covalent bond - A covalent bond in which the electrons are shared equally.
i. Purely covalent molecule - A molecule that has an even distribution of electrons, resulting in no charges within the molecule itself.
List the seven homonuclear diatomic elements you need to remember.
1. Hydrogen
2. Nitrogen
3. Oxygen
4. Fluorine
5. Chlorine
6. Bromine
7. Iodine
Draw the Lewis structures for the following molecules:
a. F₂
b. 0C1₂
c. NHI₂
d. S₂
e. CSI₂
f. N₂
g. HSiP
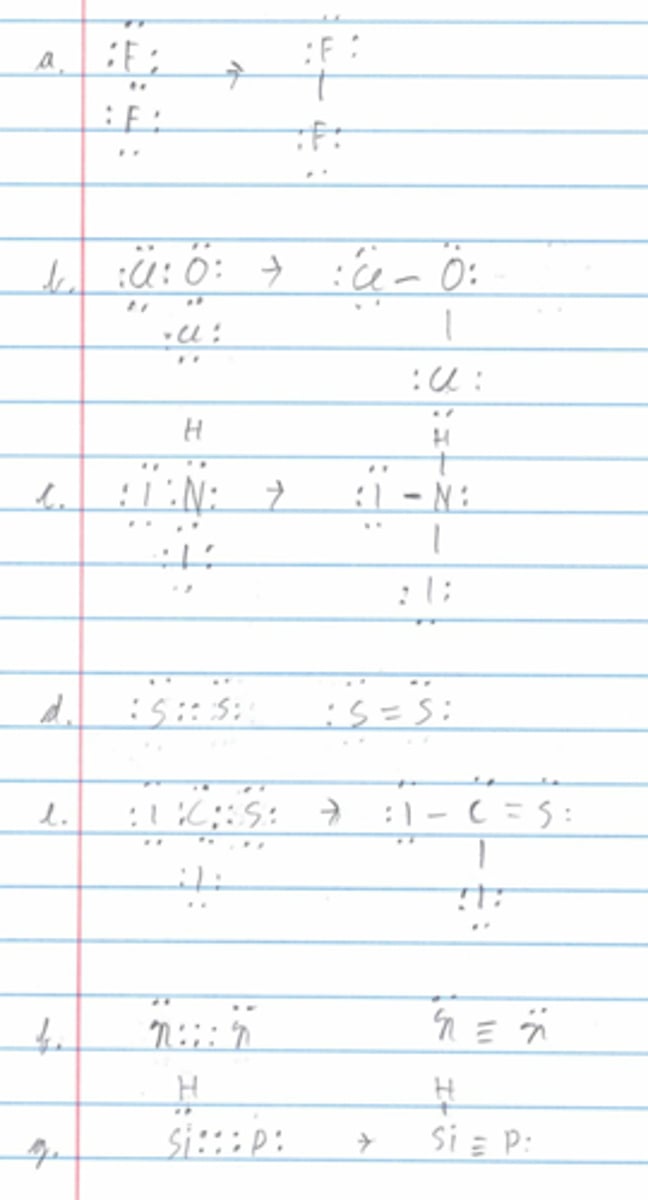
Name the following molecules:
a. SO₂
b. PH₃
c. K₂O
d. P₂O₅
e. N₂O₃
a. Sulfur dioxide
b. Phosphorus trihydride
c. potassium monoxide
d. Diphosphorus pentaoxide
e. Dinitrogen Trioxide
Which of the following atoms is the largest? Cu, Cs, Ca, Co
Cs
Which of the following atoms is the most electronegative? Ga, Ba, As, S, O
O
Which of the following molecules will have a purely covalent bond in it? HI, CF,, i2
I₂
Is it possible for a molecule to be composed of polar covalent bonds and still be a purely covalent
molecule?
Yes
Which kind of molecule (ionic, polar covalent, or purely covalent) has charges that are free to move
around?
An ionic molecule has charges that are free to move around.
Which kind of molecule (ionic, polar covalent, or purely covalent) has charges that are weaker than the
charges on a proton and electron?
A polar covalent molecule has charges that are weaker than the charges on a proton and electron.
Determine the shape and draw a stick figure for the following molecules:
a. SiC1₄
b. H₂S
c. GeSe₂
d. PF₃
e. H₂SiO
f. HBr
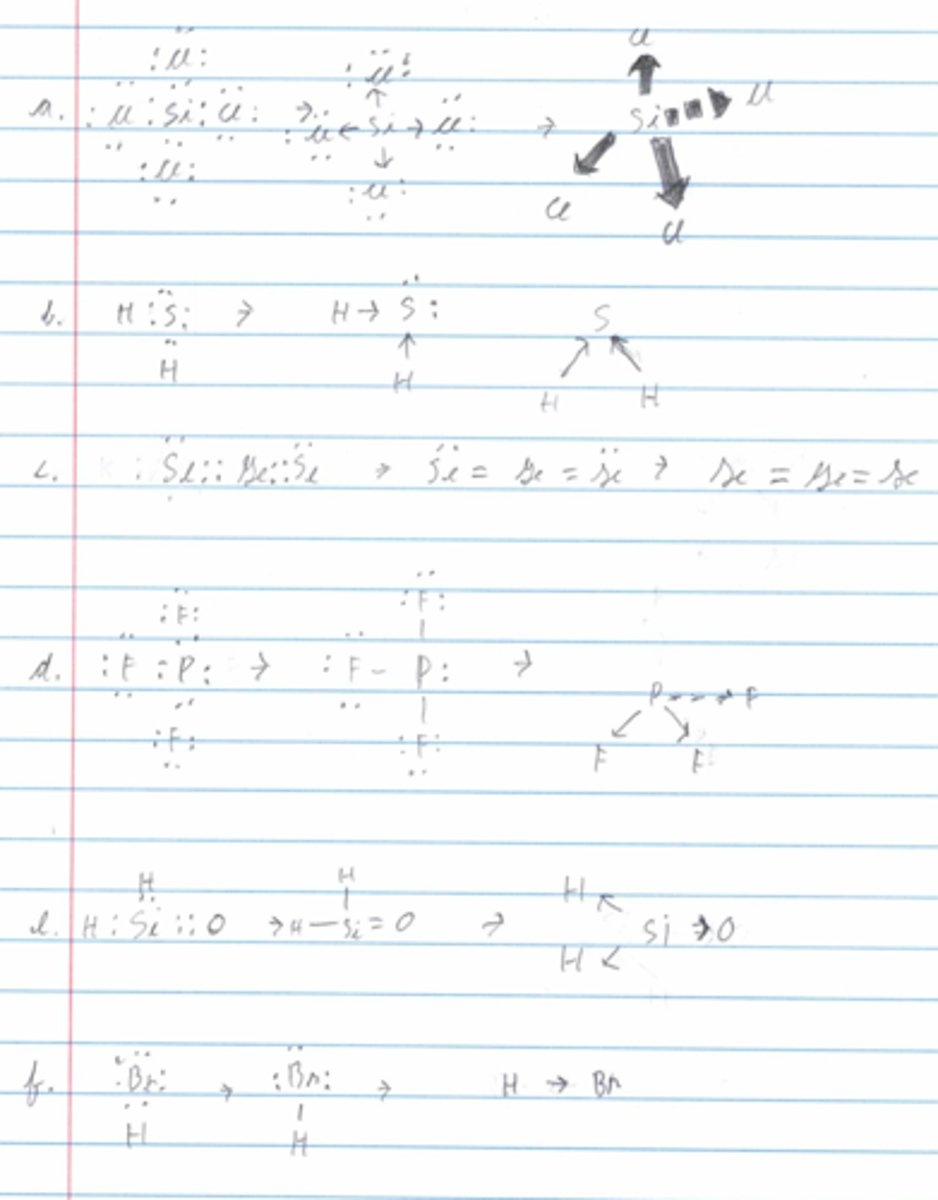
For each of the molecules above, indicate whether it is polar covalent or purely covalent.
a. SiC1₄ is Purely Covalent
b. H₂S is Polar Covalent
c. GeSe₂ is Purely Covalent
d. PF₃ is is Polar Covlent
e. H₂SiO is Polar Covalent
f. HBr is Polar Covalent
For each of the molecules in #11, indicate whether or not it is likely to dissolve in water.
a. SiC1₄ is not likely to dissolve in water.
b. H₂S is likely to dissolve in water.
c. GeSe₂ is not likely to dissolve in water.
d. PF₃ is likely to dissolve in water.
e. H₂SiO is likely to dissolve in water.
f. HBr is likely to dissolve in water.
Fill in the blank: The active ingredient in soap is a long molecule with one end that is ionic, and one
end that is
Nonpolar ( It has no charge )