Understanding the Cell Cycle and Mitosis
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
What is the continuity of life based on?
The reproduction of cells, or cell division.
What distinguishes living things from nonliving matter?
The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind.
What are the key roles of cell division in life?
Cell division allows for the reproduction of organisms, growth and development in multicellular eukaryotes, and renewal and repair in fully grown multicellular eukaryotes.
How do prokaryotic cells and unicellular eukaryotes reproduce?
They divide to give rise to a new organism (another cell).
What is a genome?
The complete collection of an organism's genetic material.
How do prokaryotes store their genome?
On a single, circular chromosome.
How do eukaryotes store their genetic material?
In multiple linear chromosomes.
What is chromatin?
Unpacked DNA that is accessible for use.
What are chromosomes?
Packaged DNA for cell division.
What are germ line cells?
Diploid progenitor cells that undergo meiosis to produce haploid gametes (reproductive cells).
What are somatic cells?
All other cells that are diploid, containing two copies of each chromosome.
What does polyploid mean?
Having more than two sets of chromosomes, mostly seen in plants.
What is the haploid number of chromosomes in humans?
23 (46 total, diploid).
What is the result of mitosis in somatic cells?
Genetically identical daughter cells (clones).
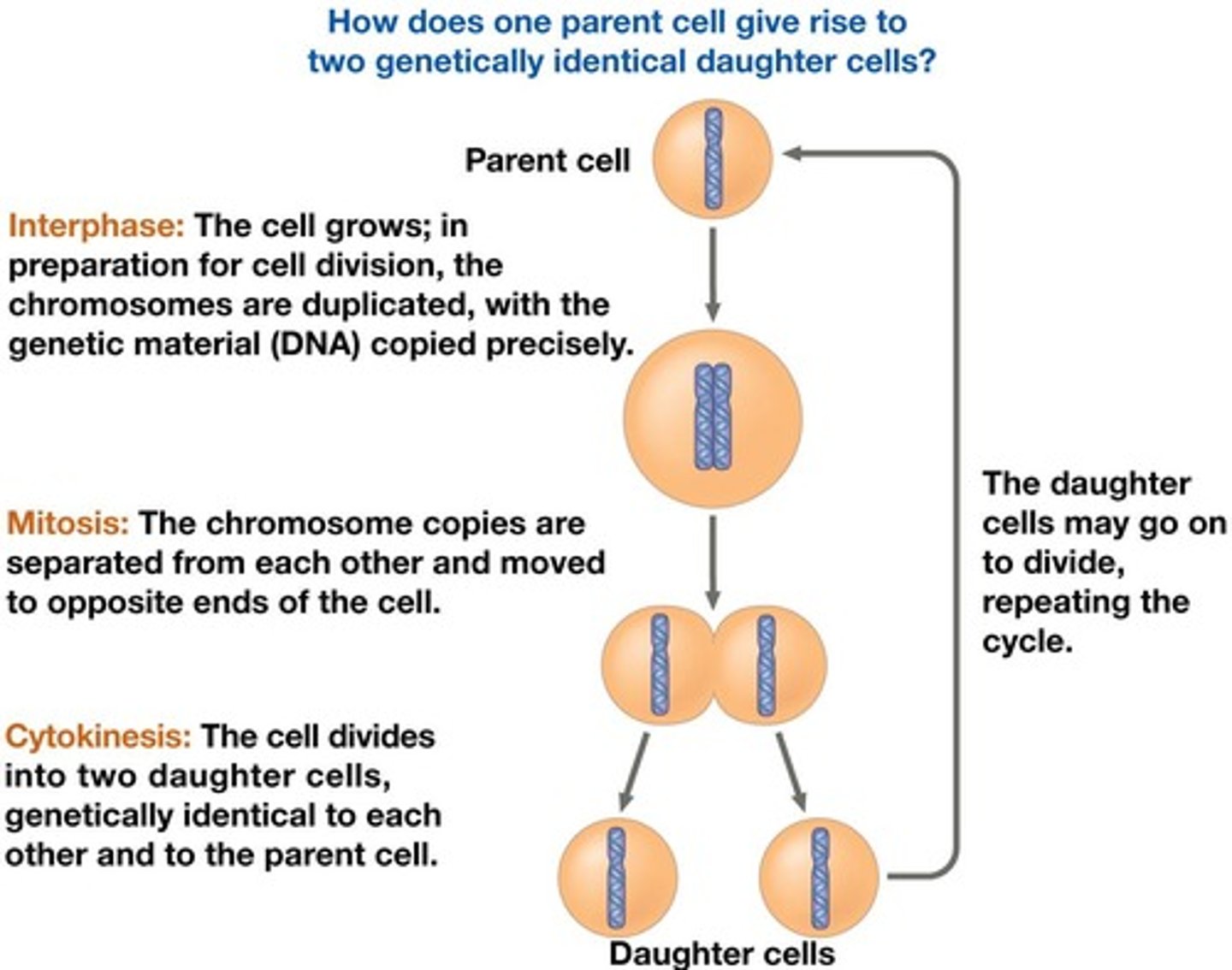
What does meiosis produce?
Nonidentical daughter cells (gametes, or sperm and egg cells).
What phases are included in the M Phase of the cell cycle?
Mitosis and cytokinesis.
What occurs during the G1 Phase of the cell cycle?
Growth after division and normal cell function, with the possibility of diverting into G0 phase.
What happens during the S Phase of the cell cycle?
DNA is copied in preparation for cell division.
What is the purpose of the G2 Phase?
Extra growth, replication of centrosomes, reproduction of organelles, and checking for DNA problems.
What are the five stages of mitosis?
Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
What is the role of the nuclear envelope during late G2 Phase?
It surrounds the nucleus.
What happens to centrosomes during late G2 Phase?
Centrosomes replicate from a single centrosome.
What occurs during prophase?
Chromatin fibers condense, nucleoli disappear, duplicated chromosomes take on an X shape, the mitotic spindle begins to form, and centrosomes migrate to opposite ends of the cell.
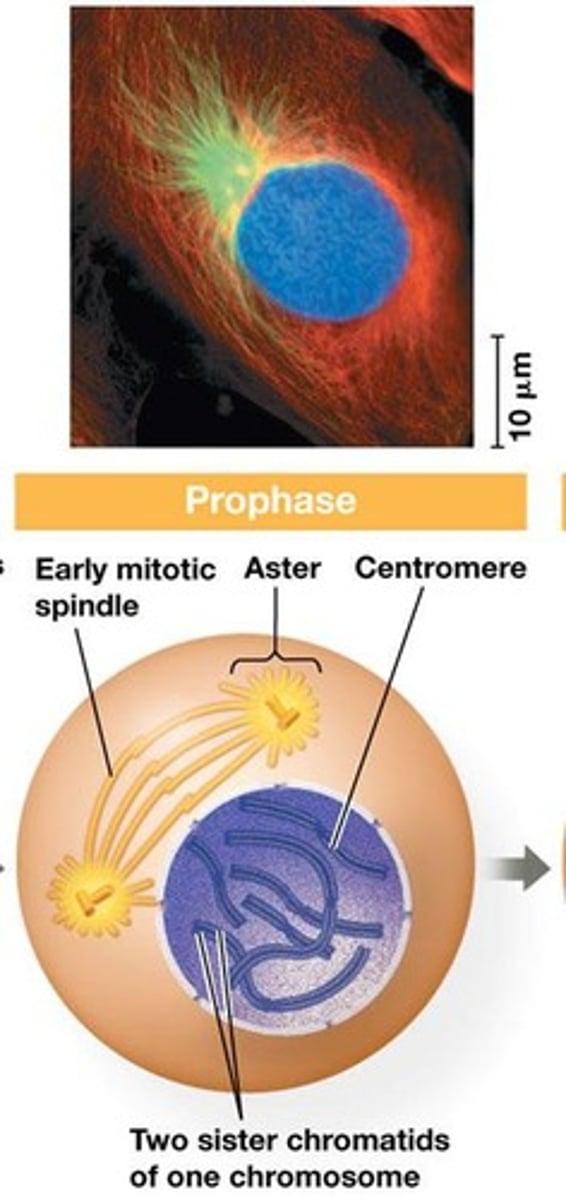
What happens to the nuclear envelope during prometaphase?
It fragments.
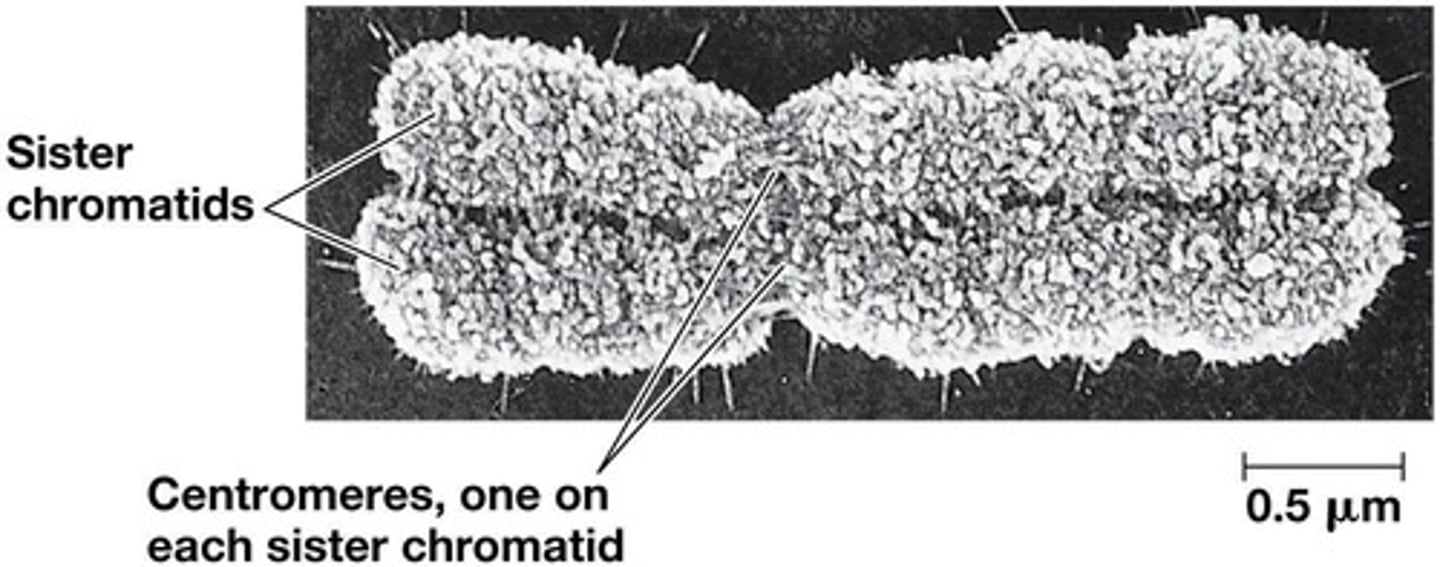
What forms on the centromeres during prometaphase?
Kinetochores.
What is the role of the mitotic spindle?
It controls chromosome movement during mitosis.
Where does the assembly of spindle microtubules begin?
In the centrosome.
What is the metaphase plate?
An imaginary line in the middle of the cell where chromosomes are lined up.
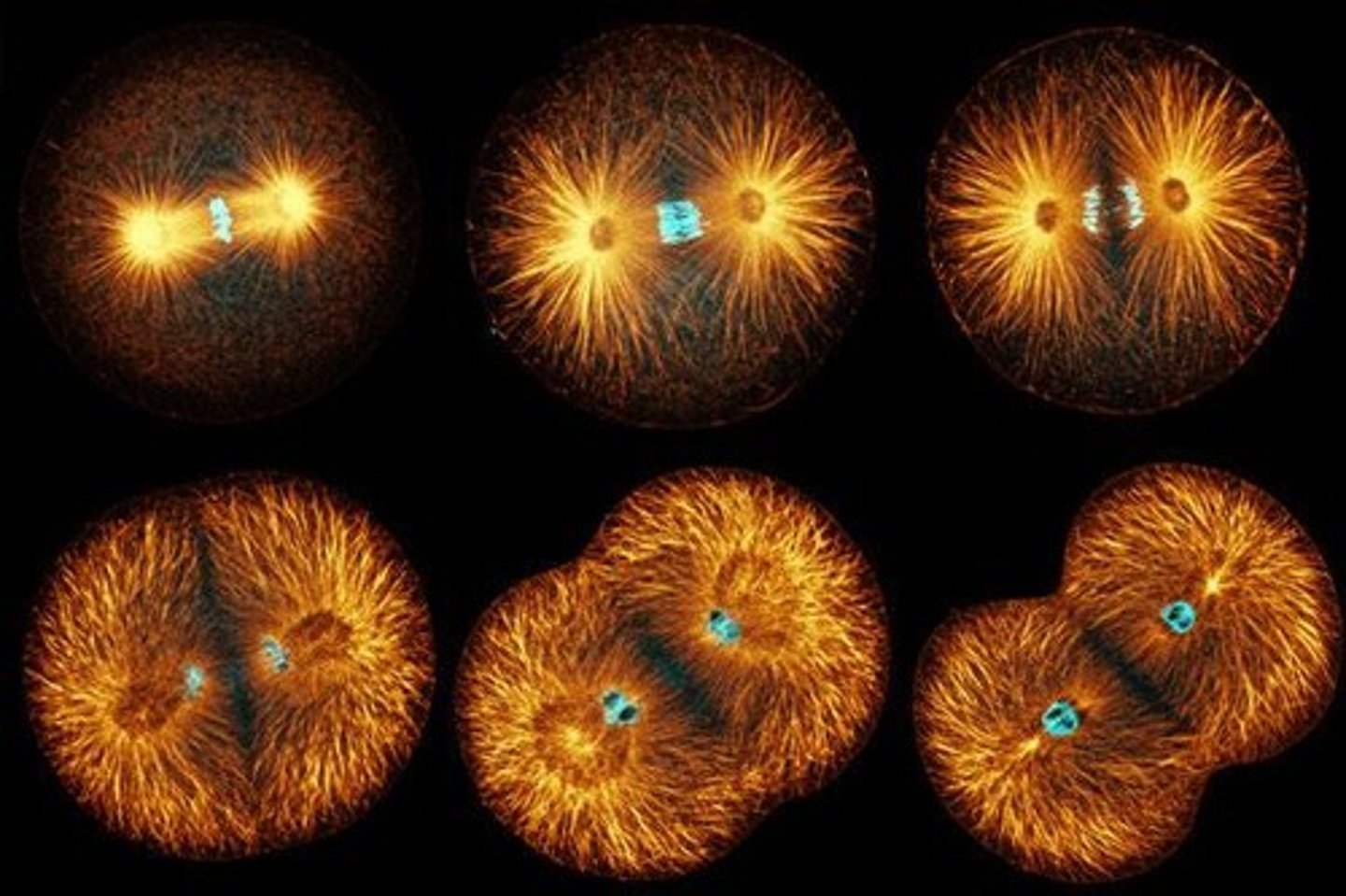
What occurs during anaphase?
Cohesin proteins are cleaved, sister chromatids separate, and are pulled towards opposite ends of the cell.
How do kinetochore microtubules behave during anaphase?
They get shorter.
What happens to non-kinetochore microtubules during anaphase?
They get longer, elongating the cell.
What reforms during telophase?
The nuclear envelope.
What begins during telophase?
Cytokinesis (cell division).
How does cytokinesis occur in animal cells?
A cleavage furrow forms and a contractile ring tightens to separate the daughter cells.
What structure forms during cytokinesis in plant cells?
A cell plate.
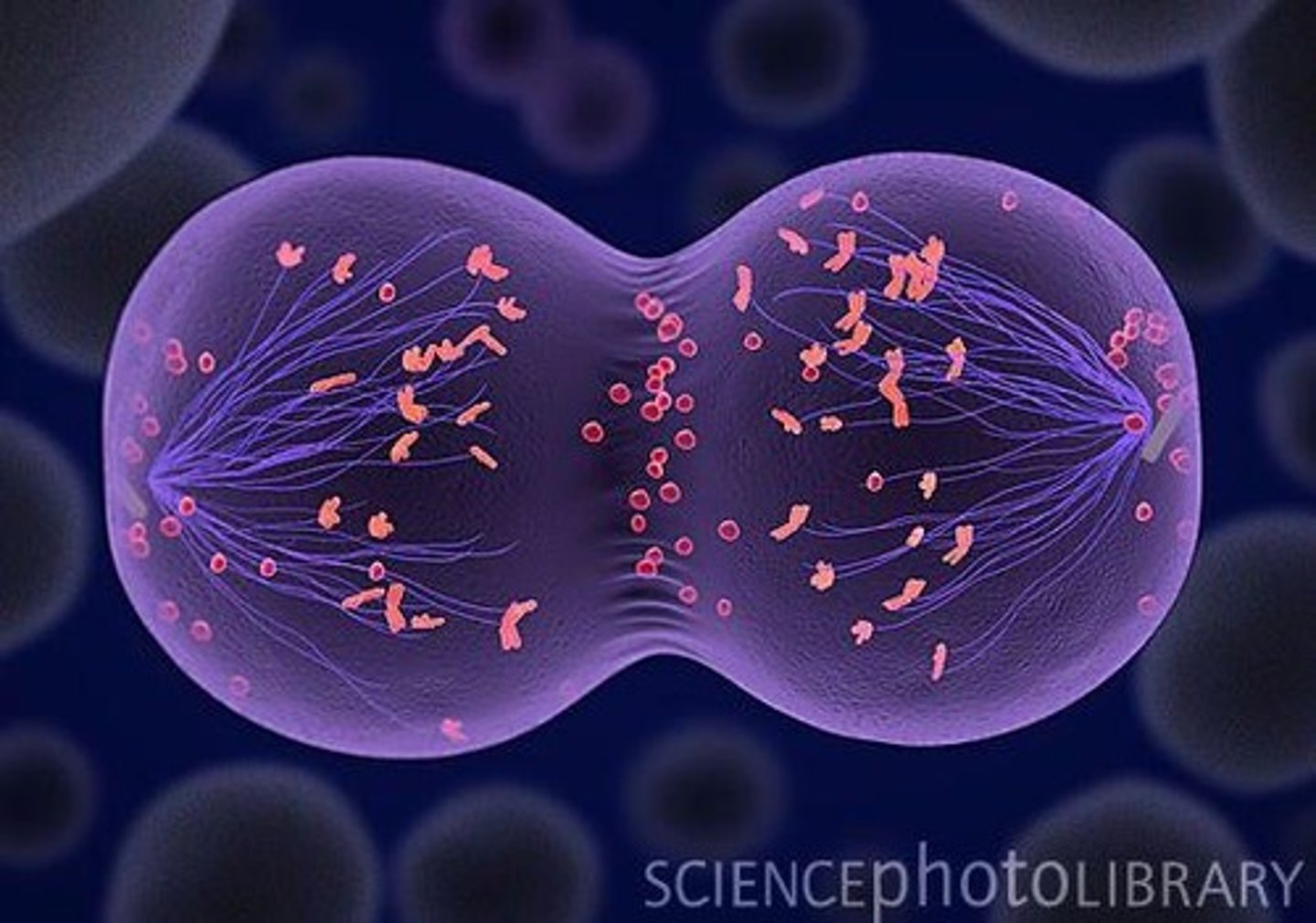
What is the function of kinetochores?
They are protein complexes that assemble on DNA at centromeres and attach to spindle microtubules.
What happens to the centrosomes during interphase?
They duplicate and migrate to opposite ends of the cell.
What is an aster in the context of the mitotic spindle?
A radial array of short microtubules extending from each centrosome.
What happens to microtubules during anaphase?
They shorten by depolymerizing at their kinetochore ends.
What is the role of motor proteins during anaphase?
They help reel in chromosomes at the spindle poles.
What is the significance of the spindle microtubules?
They attach to kinetochores and exert a pull on chromosomes.
What is the first stage of mitosis?
Prophase.
What occurs to chromosomes during prometaphase?
They condense even more.
What is the relationship between centrosomes and spindle microtubules?
Spindle microtubules grow out from the centrosomes.
What is the final outcome of cytokinesis?
Separation of the daughter cells.
What happens to microtubules during early anaphase?
They disassemble at the kinetochore end, not at the spindle pole.
What occurs at the end of anaphase in cell division?
Duplicate groups of chromosomes arrive at opposite ends of the elongated parent cell.
What initiates cytokinesis?
Cytokinesis begins during anaphase or telophase.
How do bacteria replicate?
Bacteria replicate by binary fission.
What is the first step in prokaryotic cell division by binary fission?
The single chromosome replicates, beginning at the origin of replication.
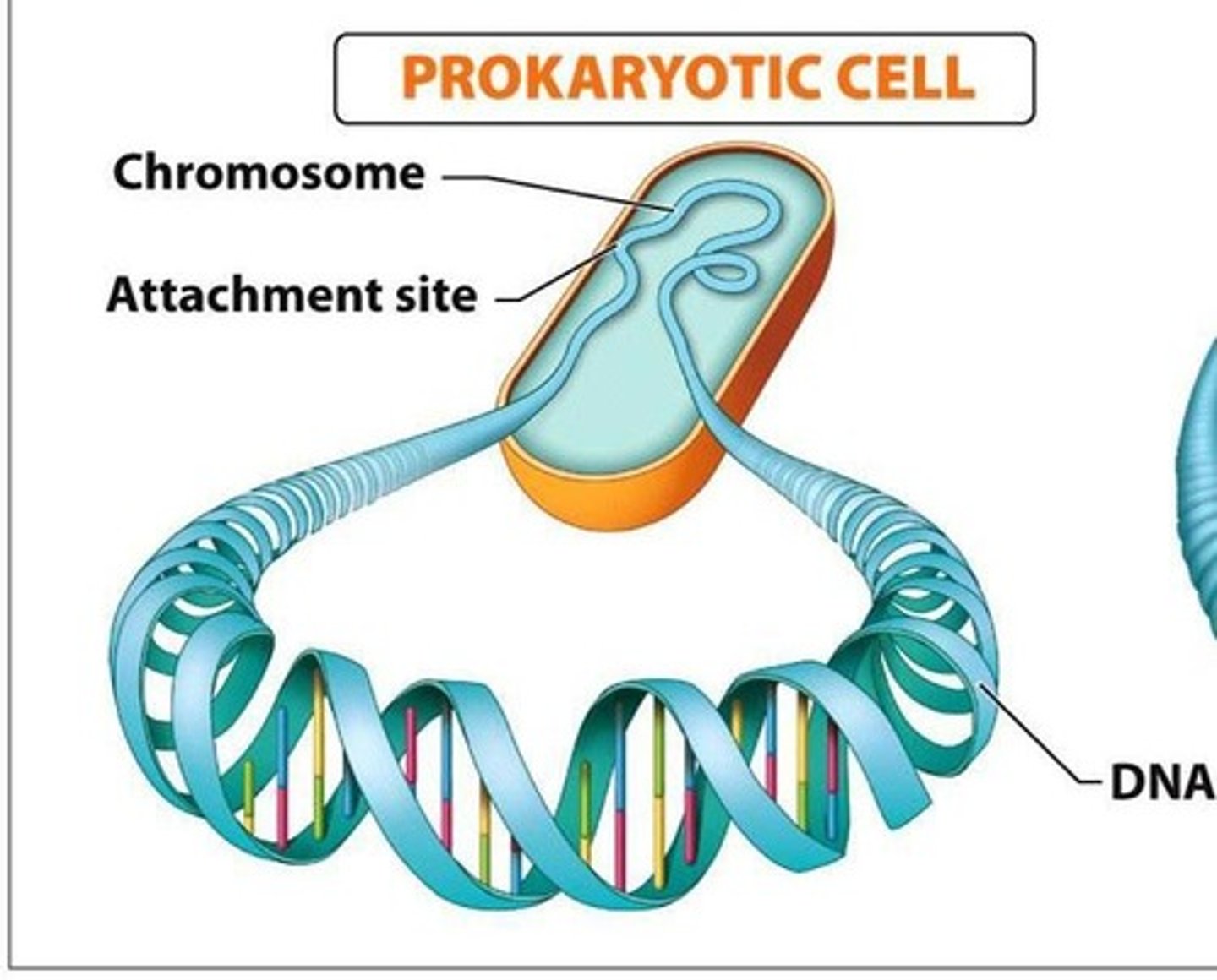
What happens to the plasma membrane during binary fission?
It pinches inward, dividing the cell into two, each containing one copy of the chromosome.
What is the role of growth factors in the cell cycle?
They can control the rate of cell division.
What is the function of checkpoints in the cell cycle?
They monitor and dictate the progression of the cell through different stages.
What is assessed at the G1 checkpoint?
Whether the DNA is damaged.
What happens if DNA is damaged at the G1 checkpoint?
The DNA is repaired or the cell undergoes apoptosis.
What is checked at the S checkpoint?
Whether DNA replication is proceeding correctly.
What occurs if DNA replication is not correct at the S checkpoint?
The DNA is repaired, and more nucleotides are made.
What is evaluated at the G2 checkpoint?
Whether DNA replication is complete and correct, and if the spindle is in place.
What happens if the spindle is not in place at the G2 checkpoint?
The cell undergoes apoptosis.
What is checked at the metaphase checkpoint?
Whether all chromosomes are aligned in the middle and each has two microtubules attached.
What characterizes cancer cells in relation to the cell cycle?
They disregard density signals, do not check DNA duplication, and have high mutation rates.
What are oncogenes?
Cancer-causing genes that are hyperactive.
What are tumor-suppressor genes?
Genes that inhibit cell growth and can cause cancer when turned off.
What is the role of proto-oncogenes?
They are normal cellular genes responsible for normal cell growth and division.
What can genetic changes do to proto-oncogenes?
They can convert proto-oncogenes into oncogenes.
What are benign tumors?
Slow-growing tumors that are contained and remain at the original site.
What are malignant tumors?
Tumors that metastasize, invade other tissues, and spread.
How are localized malignant tumors typically treated?
With radiation.
How are metastatic tumors typically treated?
With chemotherapy.
What can result from a loss of cell cycle controls?
The formation of cancer cells and tumors.