Exam #1 Plant Sciences
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Nucleus
contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA) and controls the cell’s activities, (like the brain of the cell)
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Path along where molecules, especially proteins, move from one part of the cell to another.
Ribosomes
amino acids hook together to make proteins here
Lysosomes
filled with digestive enzymes that can break down certain materials and help get rid of unwanted waste in the cell
Vacuoles
stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates
Golgi apparatus
helps make and package materials from the Endoplasmic reticulum to be transported out of the cell (like a post office)
Mitochondria
POWERHOUSE OF THE CELL!!! breaks down food to release energy through cellular respiration
Plastids
double membrane organelles which are found in the cells of plants and algae (chloroplast, chromoplast, amyoplast)
Chloroplast
captures energy from sunlight and uses it to make its own food
Chromoplast
colored plastid other than a chloroplast, typically containing yellow or orange pigment. does not perform photosynthesis, but is vital for attracting pollinators and aiding in seed dispersal.
Amyloplast
colorless plant cell organelle, responsible for synthesizing and storing starch, converts glucose into starch.
Cell wall
strong supporting layer around cell membrane in plants, algae, and some bacteria
Cell membrane
thin flexible barrier around a cell; controls what enters and exits the cell
Cytosol
fluid component of the cytoplasm, exluding mitochondrial and microsomal fractions.
Cytoplasm
gel like material inside the cell that surrounds and protects organelles.
Mitosis
Cell division that results in duplicates of the parent cell. It produces two cells when complete. The cells maintain the same number of chromosomes. This process is for growth.
Meiosis
Cell division that results in four cells that have ½ the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. The process starts with one diploid cell and results in 4 haploid cells; each haploid cell is a gamete. Gametes that are different are called egg and sperm. This process is for sexual reproduction.
is water organic?
NO.
water is a polar molecule. what does this mean?
it has a positive side and a negative side.
what is the purpose of water being a polar molecule?
the separation of negative and positive charges gives water special properties that allow life on earth to exist, such as adhesion, cohesion, capillarity.
adhesion
the property of water molecules to attract and stick to molecules of different substances
cohesion
the ability of water molecules to be attracted to and stick to one another due to hydrogen bonding
capillarity
waters ability to be held in interconnected pore spaces of a material, such as soil, by the surface tension and capillary forces that arise from adhesion and cohesion.
What is the proper term for farming?
Production Agriculture
What are the major careers in plant business?
Production, processing, marketing, and research
Production
To bring crops to a point at which they will command a price
Processing
to convert an agricultural commodity into marketable form by a special series of special steps
Marketing
the total of activities involved in the transfer of goods from the producer or seller to the consumer or buyer, including advertising, shipping, storing, and selling
Research
All efforts directed toward increased knowledge of natural phenomena and the environment and toward the solution of in all fields of science.This includes basic and applied research. Much of the agricultural productivity of the United States is directly the result of applying research
What is agronomy? What are possible career options?
The specialization of agriculture concerned with the theory and
practice of field-crop production and soil management. The
scientific management of land.Career examples: Farm equipment dealer,crop consultant, agronomist, seed sales representative.
What is arboriculture? What are possible career options?
The cultivation and management of trees, shrubs, and other woody plants for landscape and environmental purposes. Career examples include arborist, tree care specialist, tree surgeon, entomologist, and tree trimmer.
What is botany? What are possible career options?
The scientific study of plants, including their physiology, structure, growth, and taxonomy. Career options include botanist, plant pathologist, and taxonimist.
What is floriculture? What are possible career options?
The cultivation of plants for their flowers and ornamental purposes, focusing on flower production, breeding, and marketing. Career options include floral designer and advertising manager
What is forestry? What are possible career options?
The sciences, arts, and business practices of crating, conserving,
and managing natural resources on lands designated as forests. Career options include Us Forest Service Manager, national park ranger, or lumber grader.
What is horticulture? What are possible career options?
The science of agriculture that relates to the cultivation of gardens or orchards, including the growing of vegetables, fruits, flowers, and ornamental shrubs and trees. Career options include horticulture journalist and garden center manager/employee.
What is Landscape Management? What are possible career options?
To beautify terrain as with plantings of trees, shrubs, and
flowering herbs; with ornamental features, such as terraces, rock
gardens, bog gardens, pools, walks, drives, etc. Career options include landscape designer, sports turf manager, and interiorscape artistry.
What is a nursery? What are possible career options?
Any place where plants, shrubs, and trees are grown either for transplanting or as grafting stocks. Possible career options are greenhouse manager or soil scientist.
What is an orchard ? What are possible career options?
A piece of land dedicated to the cultivation of fruit or nut trees. Career options include orchard manager, aerial spray service technician, and fruit production specialist.
What are careers in environmental research?
Product development chemist, DNA technician, or plant geneticist
What do we use plants for ?
Medicine, Aesthetics, Biofuels, Fibers, and FOOD
What are examples of plants as medicine?
Plants like willow bark, used for pain relief, and digitalis, derived from foxglove for heart conditions, are notable examples.
What are examples of aesthetics derived from plants?
Aesthetics derived from plants include the use of flowers and greenery in landscaping, botanical art, and floral arrangements, like ferns, succulents, flowers, and wreaths.
What are examples of biofuel products from plants?
Examples of biofuel products from plants include ethanol produced from corn, biodiesel made from vegetable oils, and biogas obtained from organic plant materials.
What are examples of fiber products from plants?
Examples of fiber products from plants include cotton used in clothing, hemp for textiles, and jute for ropes and mats.
What are examples of food products from plants?
Examples of food products from plants include fruits like apples and bananas, vegetables such as carrots and spinach, and grains like rice and wheat.
How do you know that a molecule is an “organic molecule”?
A molecule is considered an if it contains carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen atoms.
What are the four major classes of organic molecules?
Carbohydrates - CHO, sugars and starches and cellulose, quick energy source, glucose is C6H12O6
Lipid - CHO, fats oils waxes, long term energy storage,
Protein - CHO and Nitrogen, made of amino acids, structural material and functional material (enzymes)
Nucleic Acids - DNA and RNA
What is the chemical formula for water?
H2O, consisting of two hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to one oxygen atom.
What four components make up the whole soil?
Mineral particles (45%), organic matter (5%), water (25%), and air (25%)
What are characteristics of sand and it’s attributes to soil?
Size : 0.05 – 2.00 mm
• Round shape
• Feels gritty
Attributes to Soil
• Adds porosity
• Reduces water holding capacity
What are characteristics of silt and it’s attributes to soil?
Size: 0.002 – 0.05 mm
• Round shape – but very small to detect
• Feel smooth but does not stick together very
well
Attributes to Soil
• Moderately good for porosity
• Helps water holding capacity
What are characteristics of clay and it’s attributes to soil?
Size: Less than .002 mm
• Flat or platy
• Sticky when wet – ribbon test
Attributes to soil
• Bad for porosity
• Ties up water so plants can’t use it
What is loam, and how does it perform growing plants?
A soil that is a mixture of sand, silt, and clay is
called “ .”
- Loam soils are optimal soils for growing plants.
What two principles define soil and water relationships?
Permeability rate – how quickly water moves
through soilWater holding capacity – how much water is
retained by soil particles
What does permeability depend on ?
Texture, Structure, Organic Matter (Porosity)
What is the relationship of Soil & Water and what two principles define this relationship?
Permeability rate – how quickly water moves
through soil
Water holding capacity – how much water is
retained by soil particles
What does porosity depend on ?
Pores in the soil are created by:
Roots and other organic matter (i.e., decaying
substances)Animals, such as worms and rodents
Soil particle size and “fit”
Permeability Rate

Water Holding Capacity
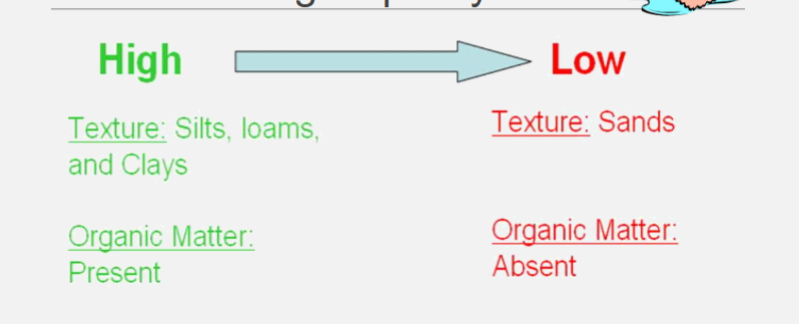
Types of Soil Water
Available water is free to plants for use.
Unavailable water is held too tightly by clay
particles and surface tension.Saturated soils have excess water that will run
off increasing erosion concerns.
What are the essential elements in soil?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
What are the macronutrients of soil?
Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulfur, which are essential for plant growth.
What are the micronutrients (trace) of Soil?
Boron, Chlorine, Copper, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, and Zinc
What are essential atmospheric elements for soil?
Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 )
Water (H2 O)
Glucose (C6 H126 )
What are the subcategories of Plant Nutrients?
Primary- required in the highest levels
Secondary - required in lower levels
What are the primary Macronutrients?
Nitrogen (N)
Phosphorus (P)
Potassium (K)
Make up the first values of a fertilizer analysis,
expressed as N-P-K
How does Nitrogen impact plants?
Present in chlorophyll
Increases vegetative growth
Deficiency symptoms:
Stunted growth
Pale yellow color
Yellow color “fires” from the bottom
of the plant to the top
How does Phosphorous impact plants?
Responsible for early plant growth’
Reproduction
Deficiency symptoms:
• Reddish coloring on the underside
of leaves
• Low quantity flowers and fruits
• Weak and spindly growth
How does Potassium impact plants ?
Involved with photosynthesis, primarily sugar
transformation
Deficiency symptoms:
• Slow growth
• Brown leaf tips and leaf margins
• Poor fruit and seed quality
What are the secondary macronutrients in soil?
• Calcium (Ca)
• Magnesium (Mg)
• Sulfur (S)
Required in smaller amounts than primary nutrients,
but still needed in ample quantities
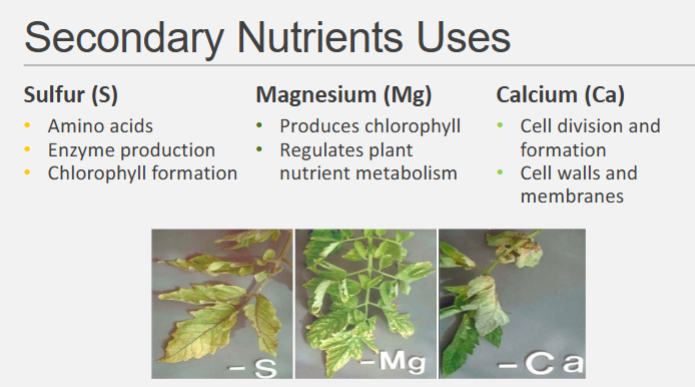
What are secondary nutrients uses?
Sulfur
Amino acids
enzyme production
chlorophyll formation
Magnesium
Produces chlorophyll
Regulates plant nutrient metabolism
Calcium
Cell division and formation
Cell walls and membranes
What are some sources of plant nutrients?
Organic substances
Legumes
Examples: peanuts, soybeans, and vetch
Legumes “fix” nitrogen.
• Improve nitrogen content of the soil.
• Most other crops deplete nitrogen.
• Often rotated with nitrogen-depleting crops.
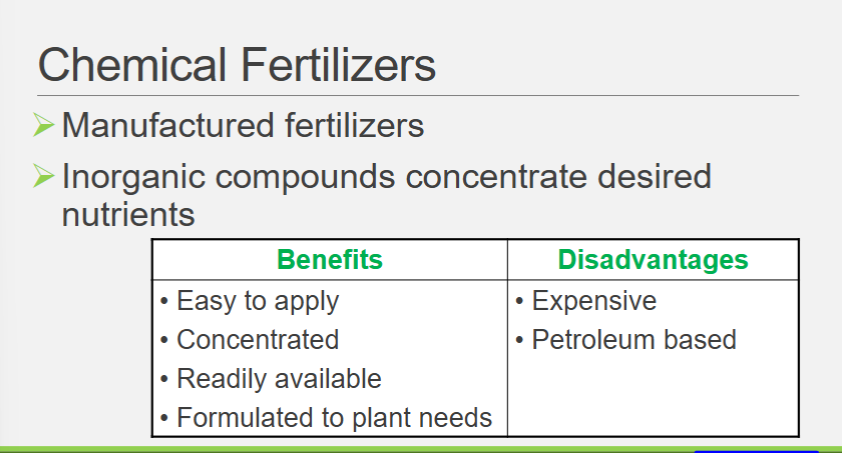
Chemical fertilizers
Manufactured fertilizers (come in forms like dry, liquid, water soluble)
Inorganic compounds concentrate desired nutrients
Organic substances come in forms such as ?
Examples: manure, sludge, and compost
• Manure contains nutrients in varying amounts.
• Sludge is processed human waste.
• Composting raises organic matter content and
destroys pathogens.
What do the numbers on a bag of fertilizer mean (ex. 10-20-10)?
• 10% elemental nitrogen
• 20% phosphate (P 2 O 5 )
• 10% potash (K 2 O)
How much nitrogen is in a 100 lb. bag of 15-16-
17 fertilizer?
15% x 100 = .15 x 100 = 15 lbs.This means there are 15 pounds of nitrogen in a 100 lb. bag of 15-16-17 fertilizer.
How many pounds of fertilizer do you need to
apply in order to get enough nutrients for a plant? (Formula)

You want to add fertilizer to a family member’s yard.
They have 1000 square feet of lawn
Recommended nitrogen application is 1 lb /1000 sq. ft.
You have 16-16-16 fertilizer
How much nitrogen fertilizer should you apply?

How are dry fertilizers expressed vs. liquid or water-soluble fertilizers?
Dry fertilizers are expressed in weight
measurementsLiquid or water-soluble fertilizers are expressed
in parts per million (ppm)
Why does a 100 lb bag of 20-20-20 cost twice as much as a
100 lb bag of 10-10-10?
Nutrient content is based on percentage, 20-20-20 has twice as
much nutrient value as 10-10-10.
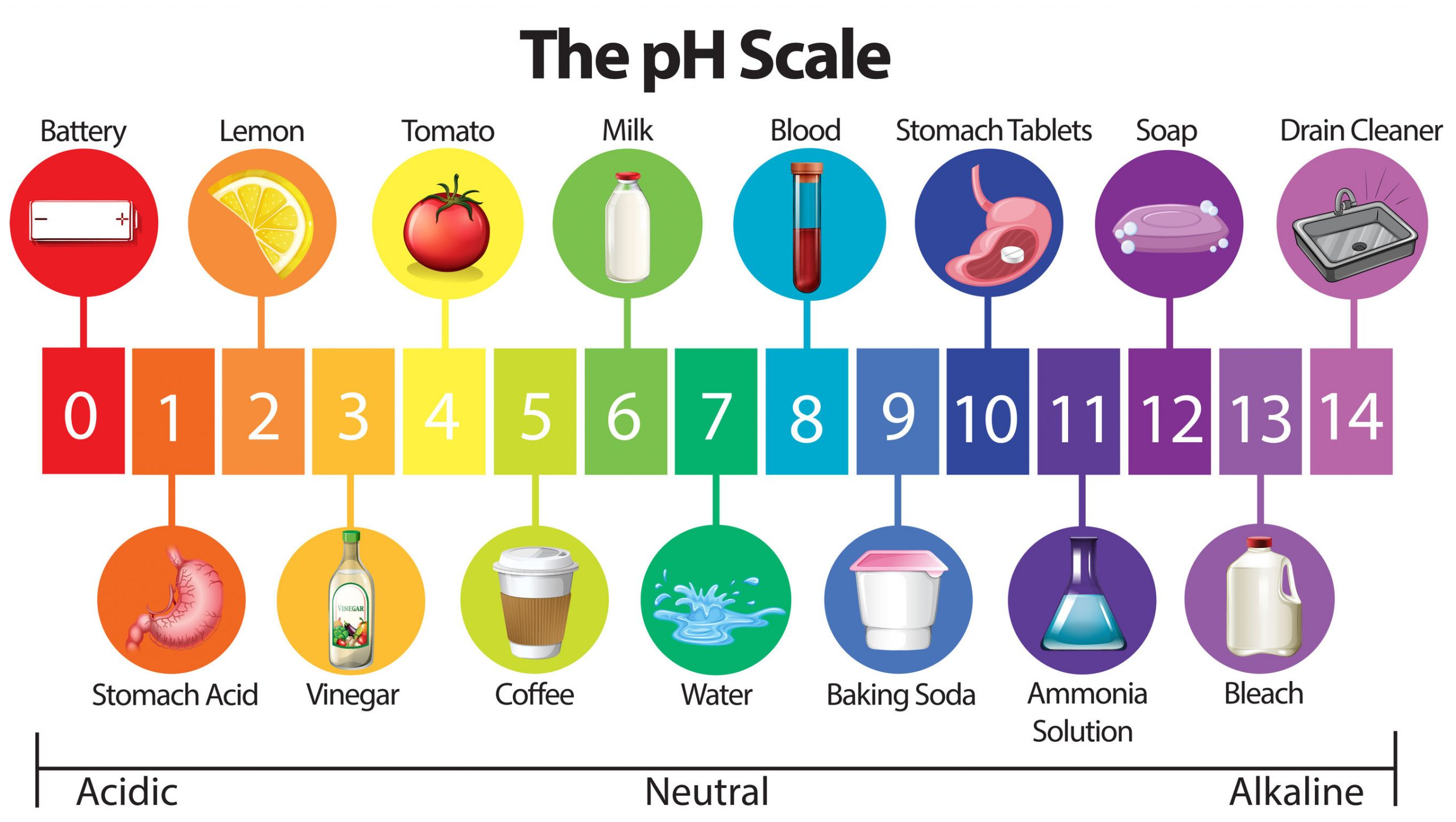
What is pH?
the measure of acidity or alkalinity in a soil, based on
the balance of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxyl ions (OH-)
What is acid?
A substance with a pH value less than 7.0; caused by a
higher concentration of hydrogen ions (H+)
What is alkaline?
substance with a pH value greater than 7.0; caused
by a higher concentration of hydroxyl ions (OH-).
How do you identify pH on a pH scale?
Measured on a scale of 0 - 14.
7.0 is neutral.
Each pH point multiplies the pH
factor by 10.
For example a pH of 5.0 is:
• 10 times more acidic than pH 6.0
• 100 times more acidic than pH 7.0.
Why does soil pH matter?
Soil pH is important to horticulturalists and crop
producers because of its influence of nutrient
availability in the soil.
• At the ideal soil pH level, plants can uptake soil
nutrients required for growth and health.
• Certain soil nutrients become unavailable at different
pH levels.
(The wider the bar the more available the
nutrient is to the plant)
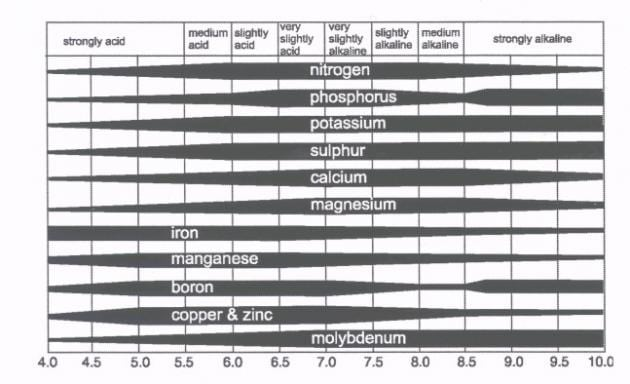
What are some ways soil pH be altered?
Low pH levels in soil can be changed by adding a buffer, such as lime to the soil. Lime raises soil pH to a more acceptable level.
Soil pH can also be lowered by adding sulfur compounds to the soil.
What trace nutrients play a role in photosynthesis?
• Copper
• Iron
• Manganese
• Zinc
What trace nutrients play a role in photosynthesis?
The following micronutrients influence the reaction of
enzymes needed for plant metabolism and function.
• Copper
• Manganese
• Molybdenum
• Nickel
• Zinc
What trace nutrients affect cell development in cells?
Boron
Iron
Zinc
What micronutrients aid in the translocation of
substances within plants?
Boron – sugar translocation
Iron – oxygen translocation
Some micronutrients are responsible for interaction with
metabolism and use of other elements
• Boron – nitrogen
• Chlorine – phosphorus uptake
• Manganese – phosphorus & calcium availability
• Molybdenum – nitrogen & phosphorus uptake
• Nickel – nitrogen metabolism and fixation
What micronutrients effect the maturity rate of plants?
Boron
Chlorine
Copper
What are other functions of Boron, Copper, and Nickel?
What are some soil-less growing medias?
Perlite: white hard material with many air holes. Helps aeration.
Vermiculite: mined material that is in many layers, helps with water retention and some nutrients. Looks silvery in light.
Peat (sphagnum) moss: organic material made from a dead moss. Very good for water retention. Looks brown in color.
Potting mix or potting ‘soil’ - not a mineral soil but is composed of perlite, vermiculite and peat moss.