HESI - Skeletal Images
1/205
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
206 Terms
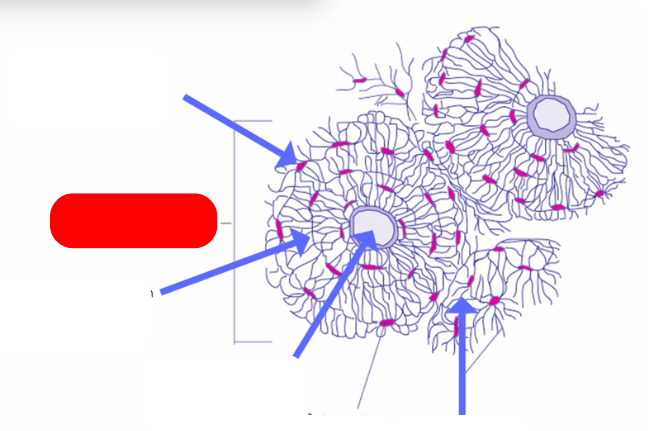
Osteon - aka haversian systems. on the lines of force. form interconnected matrix for structure ans support. makes up compact bone
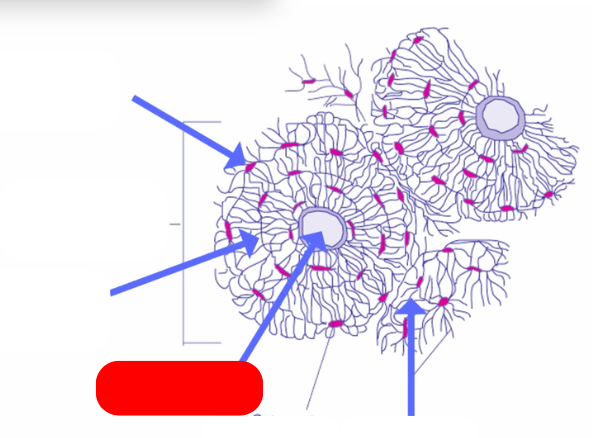
haversian canal - pathway for blood vessels and nerves`
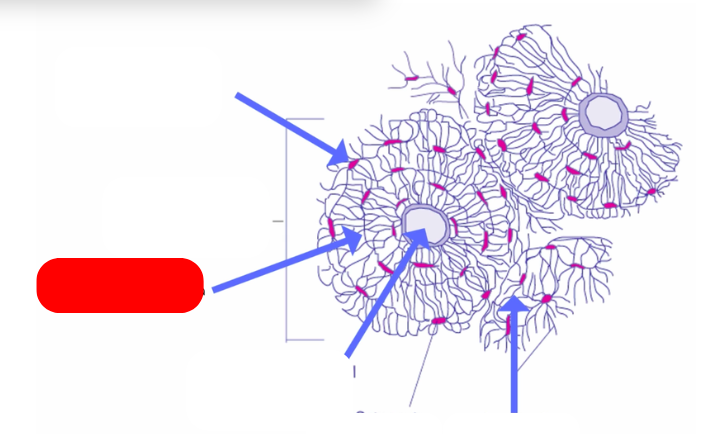
lamellae: bone deposited in concentric circles
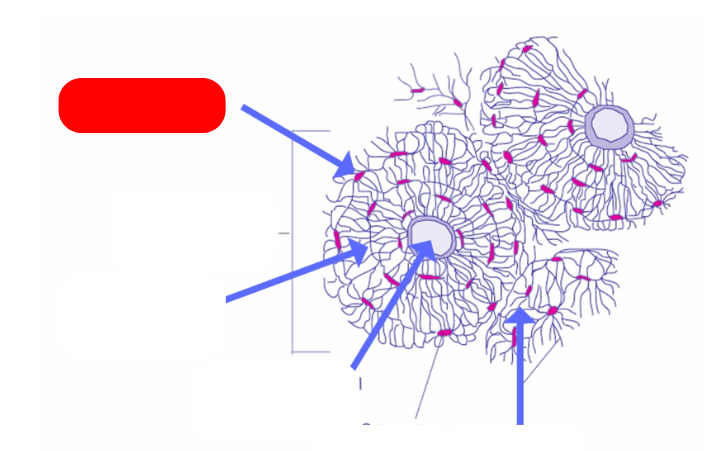
lacunae: openings in the lamellae for osteocytes and fluid
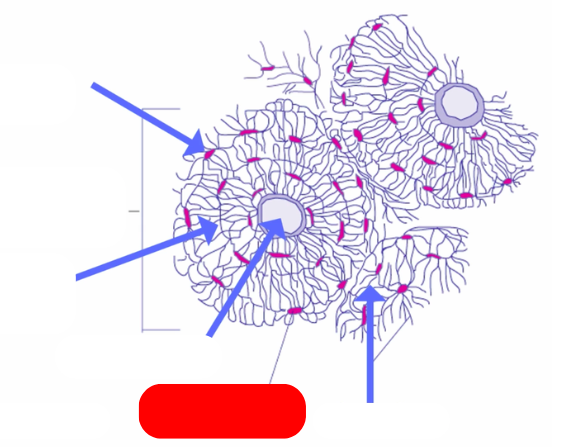
osteocyte: mature osteoblast that no longer divides in the lacunae
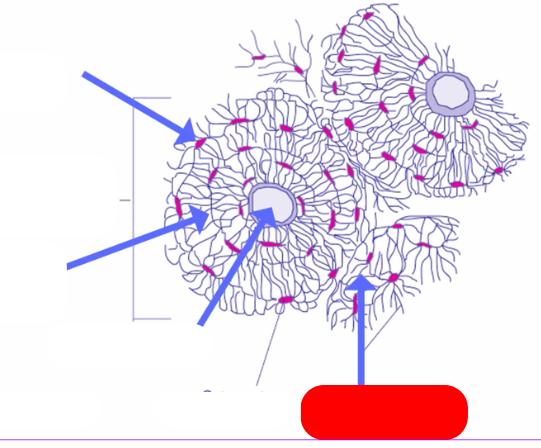
caniculi: radiate out from lacunae form small canals
compared to villsmanns/perforating canals that connect osteons
describe this bone formation process
INTRAMEMBANOUS OSSIFICATION
-for flat bones
-forms in sheet like layers of connective tissue
-layers have vascular supply and osteoblasts
-osteoblasts secrete bony matrix in all directions (osteoid)
-matrix from multiple osteoblasts unites to form bone
-osteoblasts are eventually walled off by bone —> then officially osteocytes
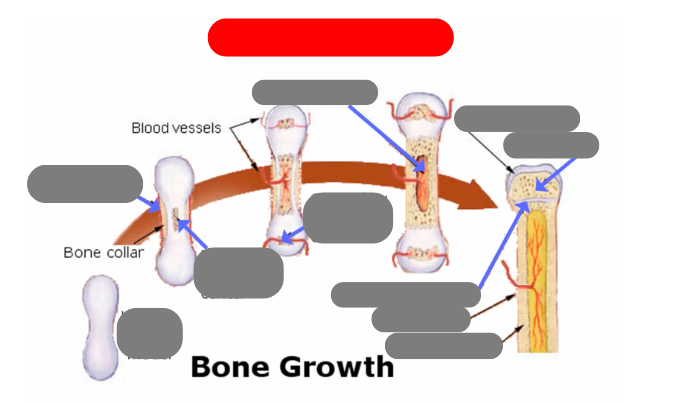
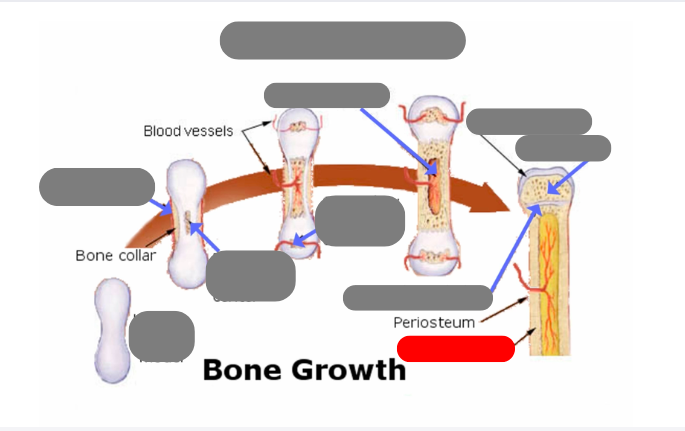
endochondrial ossification: for tubular bones based off a cartilage model
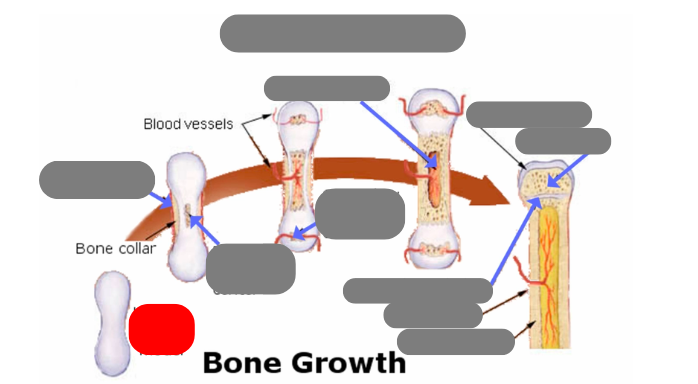
hyaline cartilage model
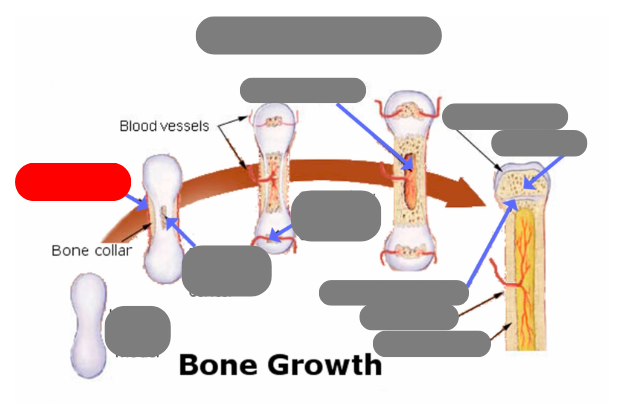
1st step: formation of periosteum
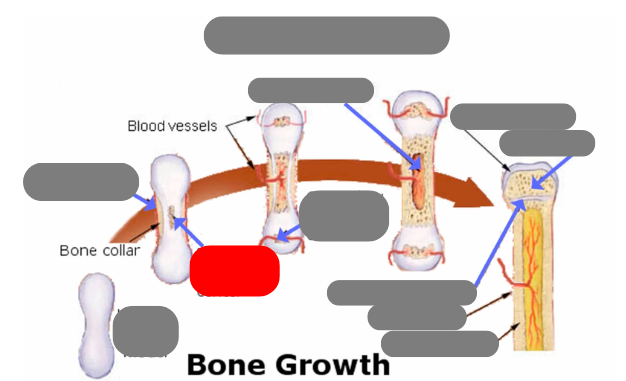
2nd step: formation of primary ossification center in the now calcified matrix in the center. still uncalcified on the ends
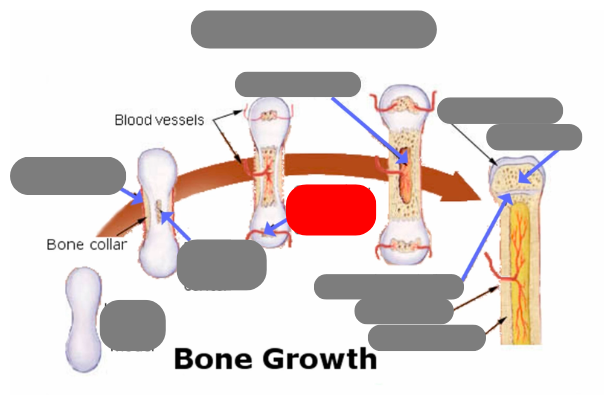
3rd step: formation of secondary ossification center in the ends when they get blood flow. still some uncalcified areas on the top and bottom
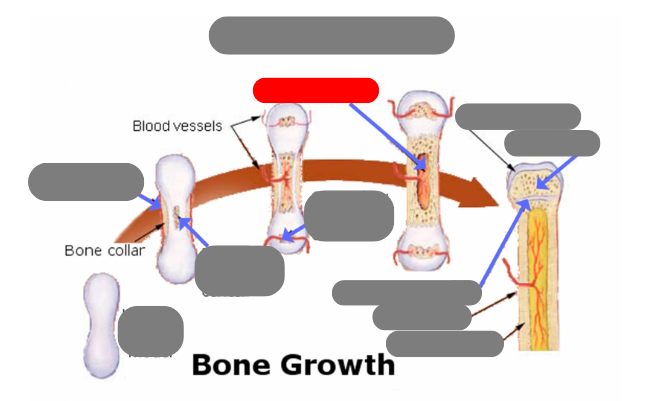
4th step: formation of medullary cavity in the middle
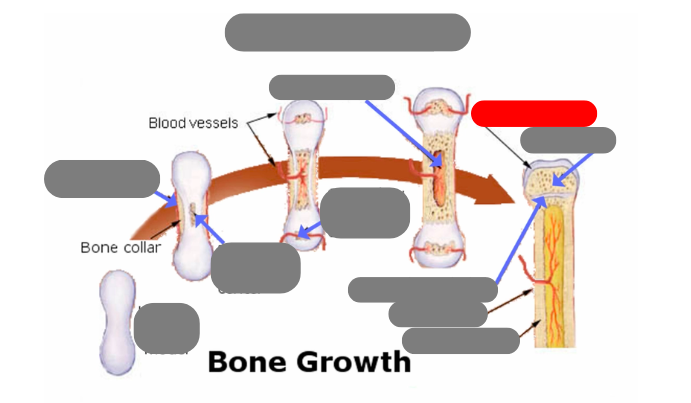
5th step: formation of the epiphysis - articulate cartilage on the ends
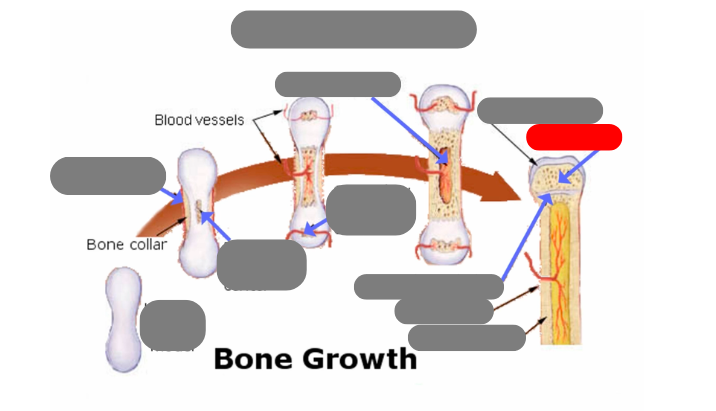
5th step: formation of the epiphysis - spongy bone now in the epiphysis vs compact in the diaphysis
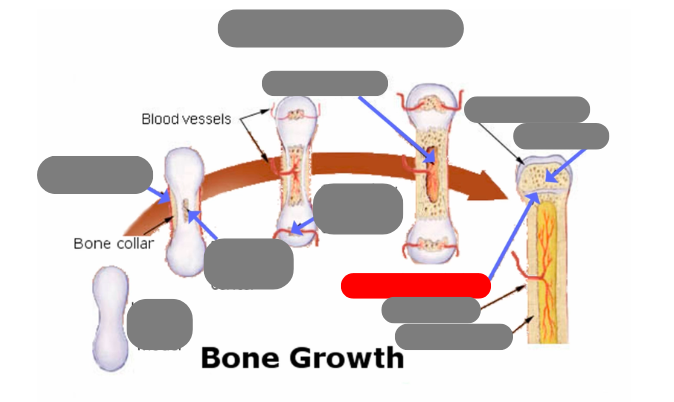
5th step: formation of the epiphysis - formation of epiphyseal plate aka growth plate
compact bone now in the diaphysis
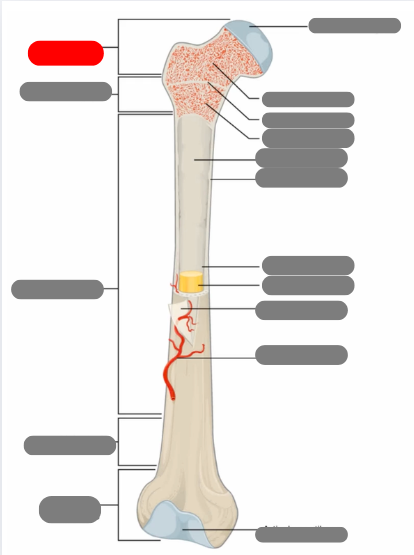
proximal epiphysis
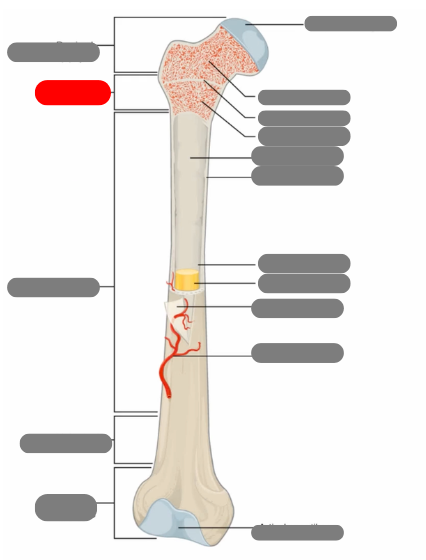
metaphysis
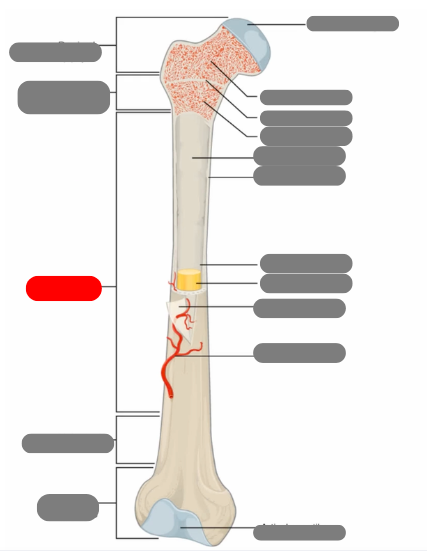
diaphysis
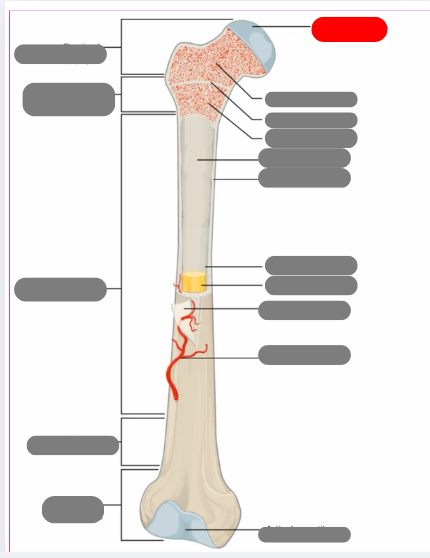
articulate cartilage
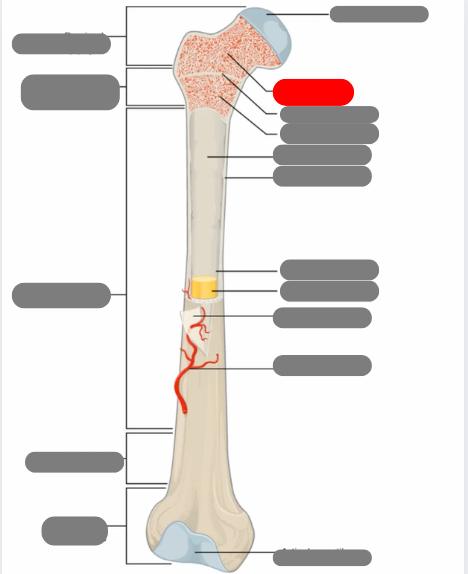
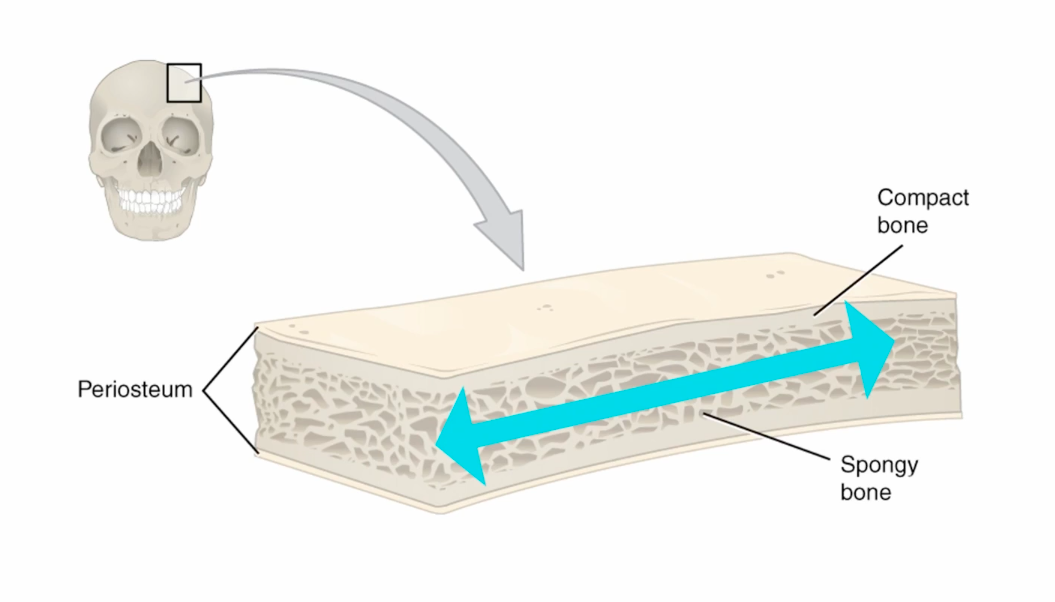
spongy bone
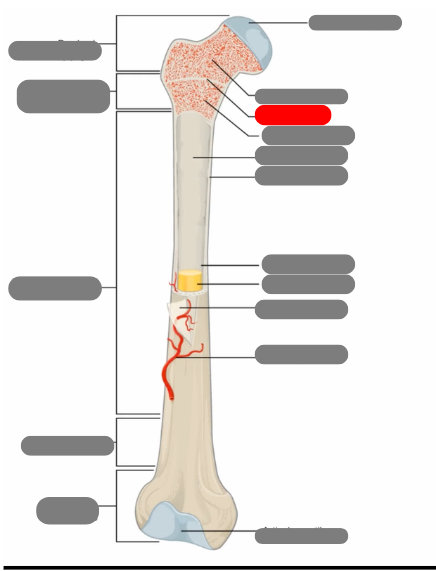
epiphyseal line
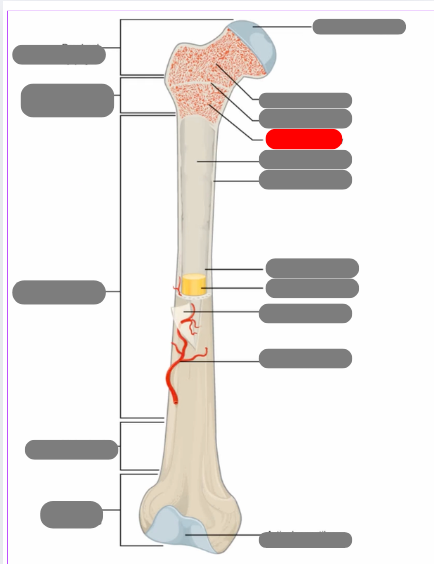
red bone marrow
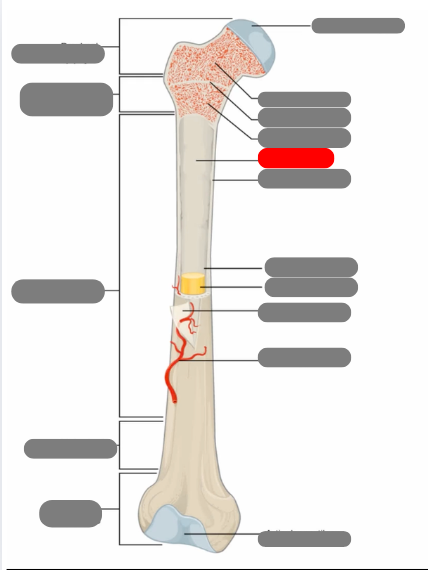
endosteum
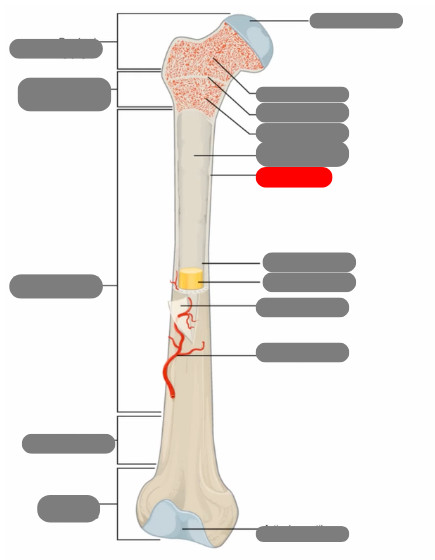
compact bone
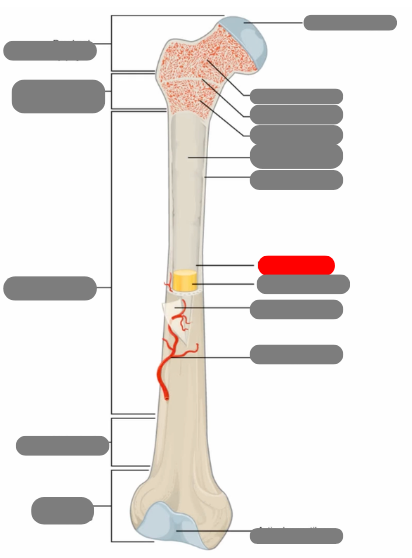
medullary cavity
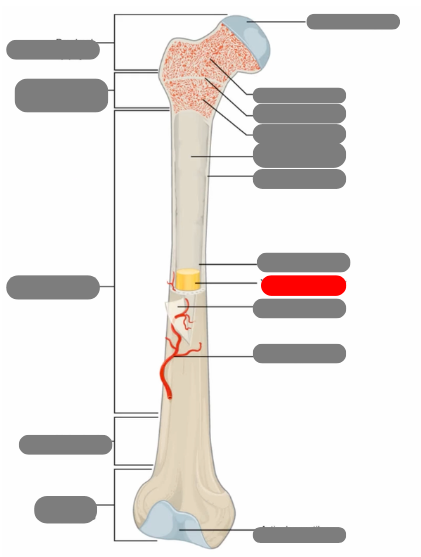
yellow bone marrow
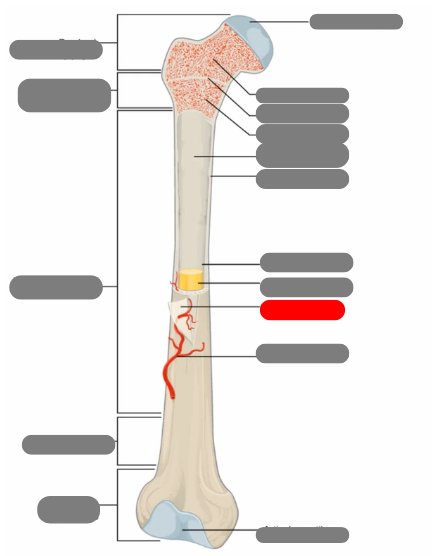
periosteum
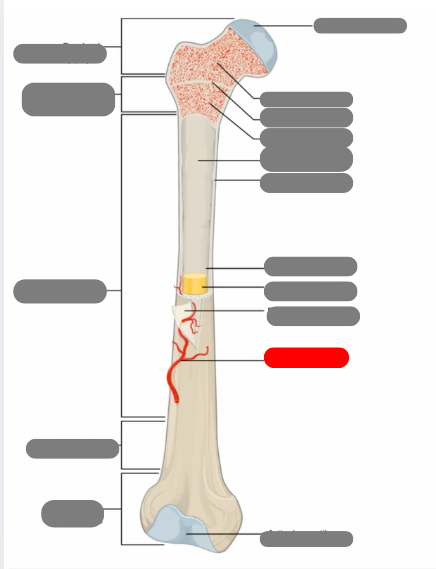
nutrient artery
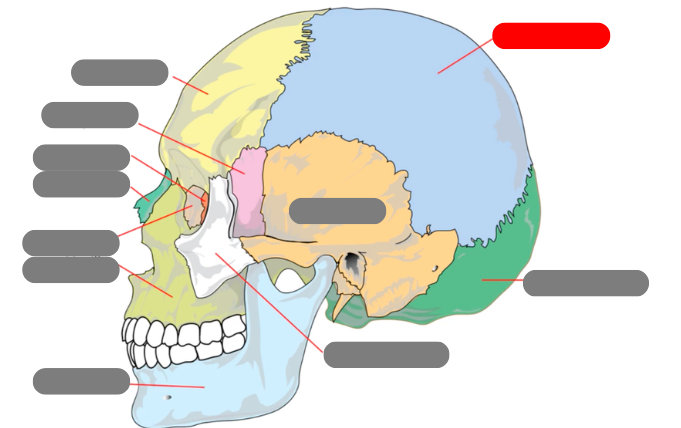
parietal
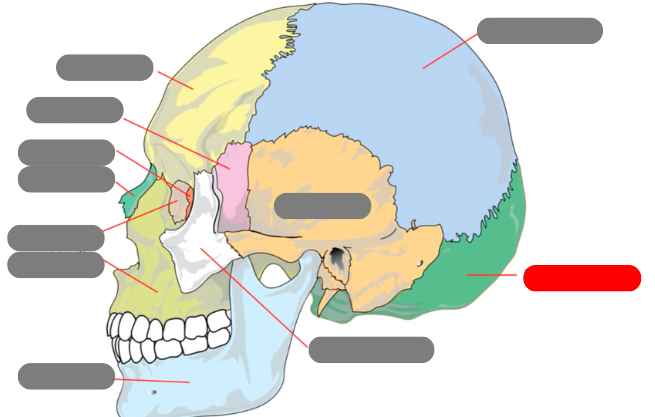
occipital
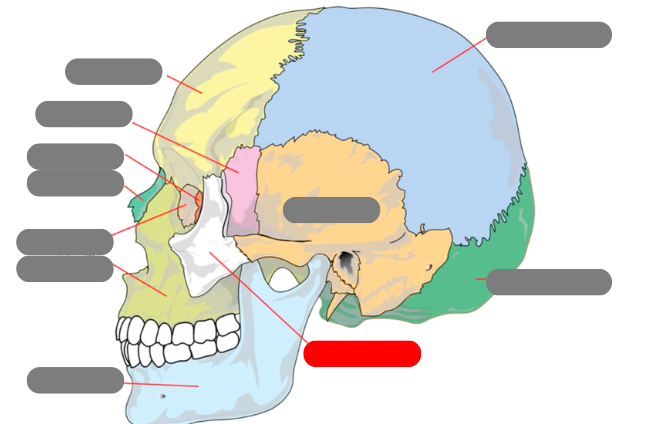
zygomatic
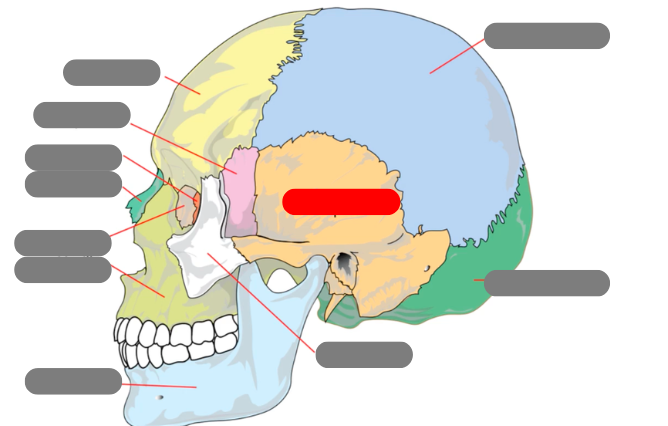
temporal
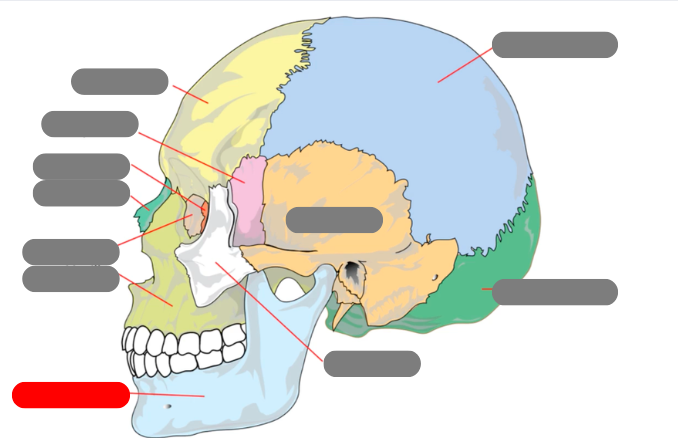
mandible - has condlyles that connect to the temporal bone forms TMJ - temporalmandibular joint
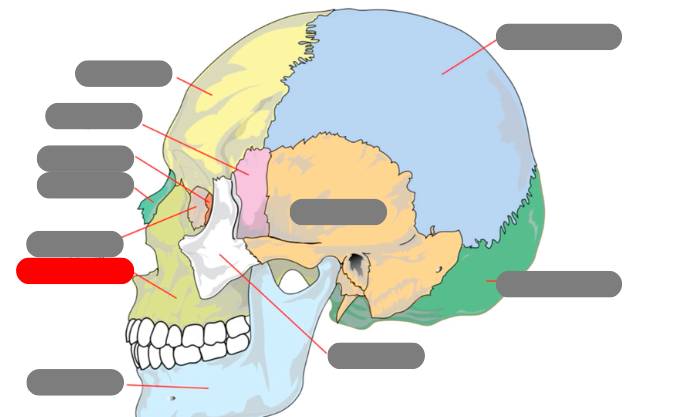
maxilla
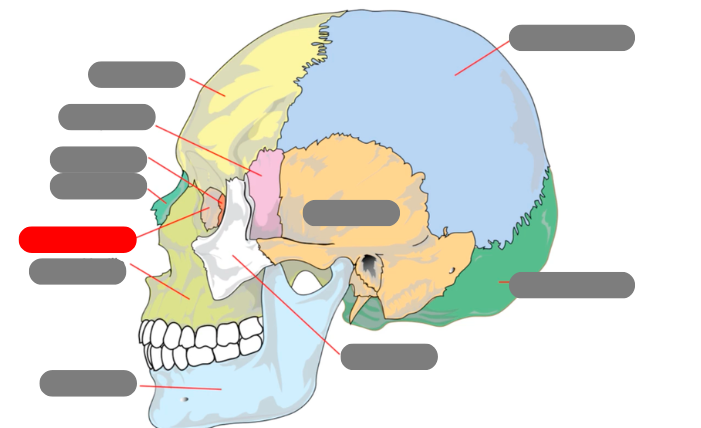
lacrimal
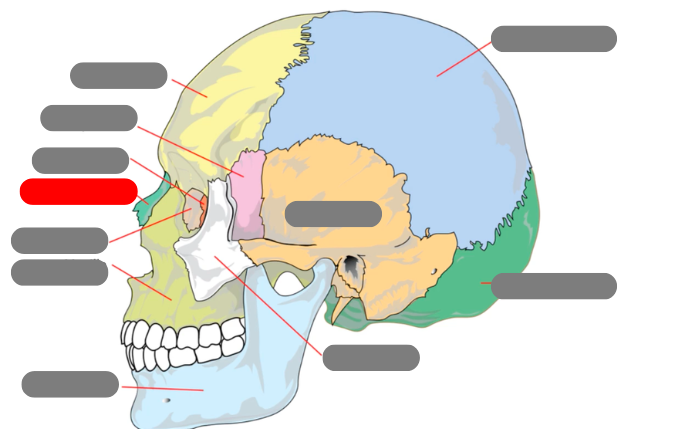
nasal
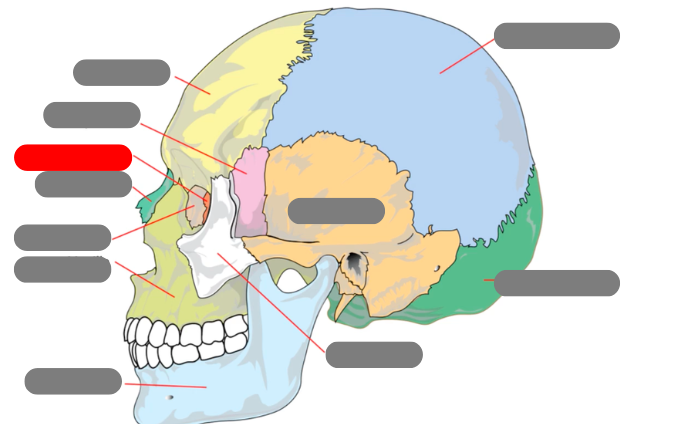
ethmoid
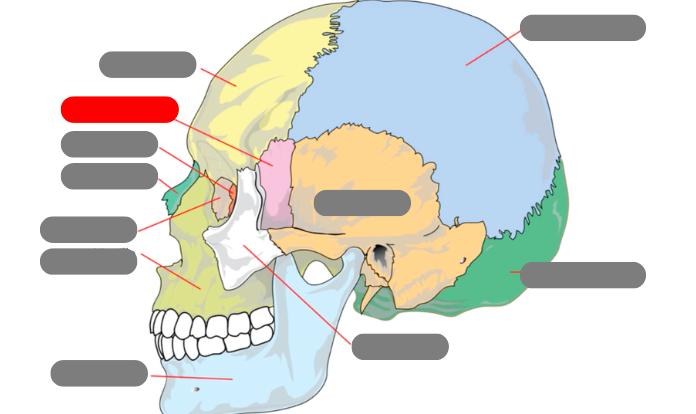
sphenoid
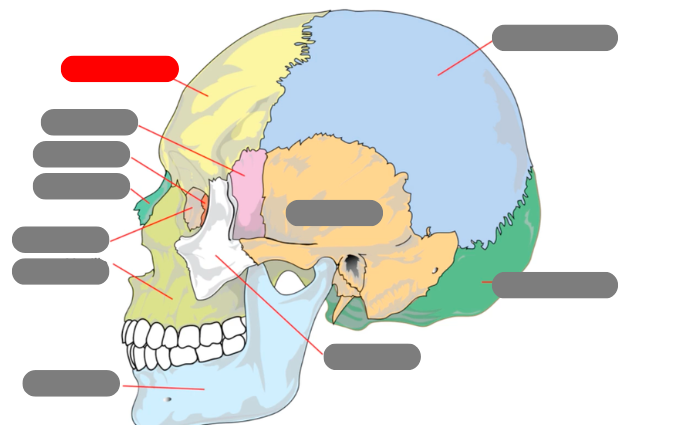
frontal
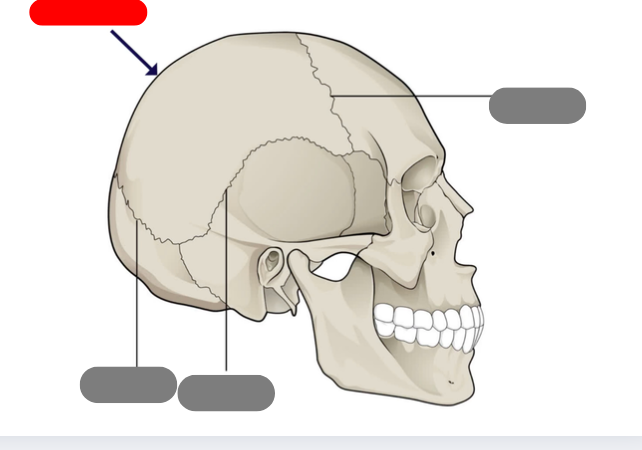
sagittal suture
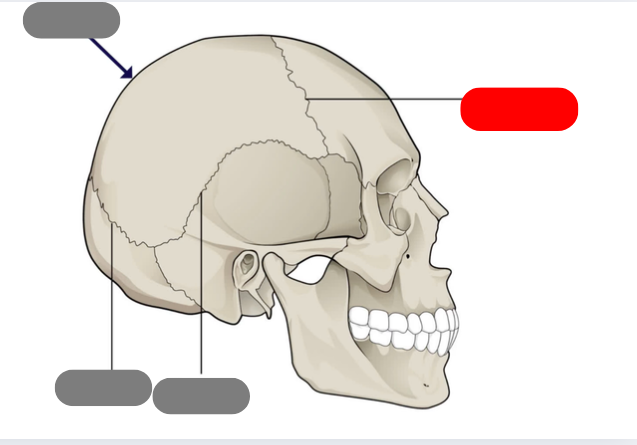
coronal suture
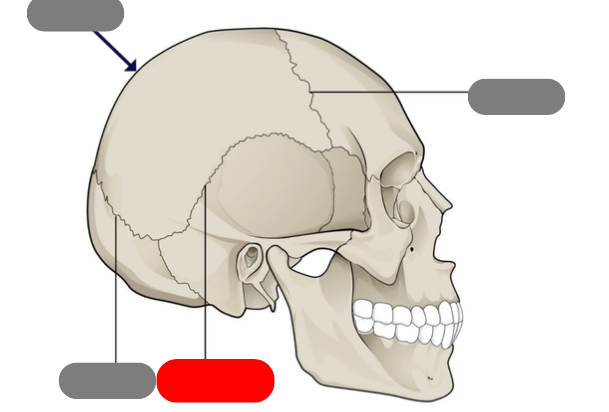
squamous suture
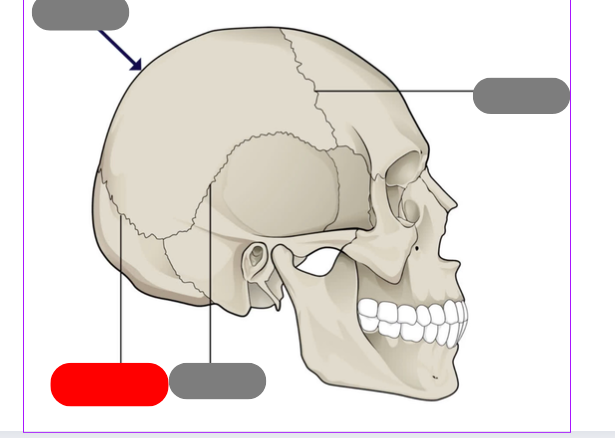
lambdoid suture
tubercle
rounded bump
tuberosity
rounded bump with gradual slope
styloid process
pointy shape
trochanter
large process found on femur bones
condyle
large rounded process
foramen
hole in bone for blood vessels and nerves
sinus
hollow cavity in a bone
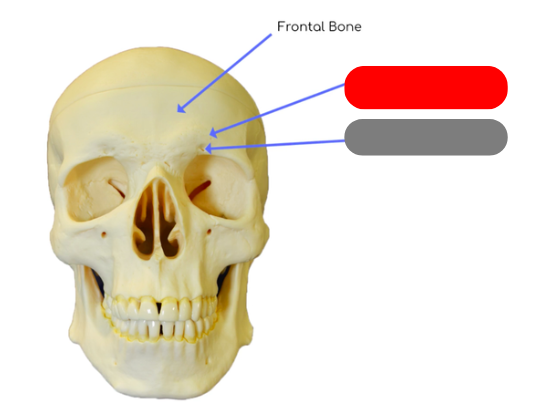
supraorbital margin: thickened process above orbits to protect eye
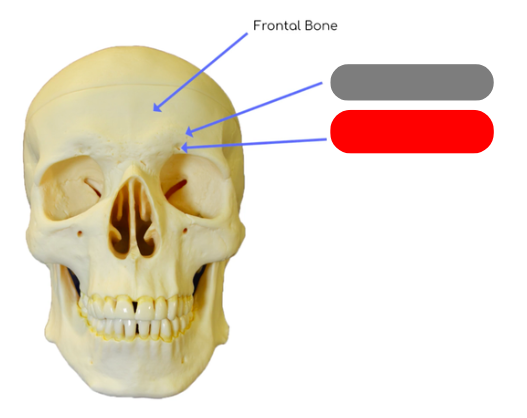
supraorbital foramen: passageway for blood vessels supplying the frontal sinus, eye brow and eye lid
landmarks fo the frontal bone
frontal sinus behind it (creates mucus to flush nasal cavity), supraorbital margin, supraorbital foramen
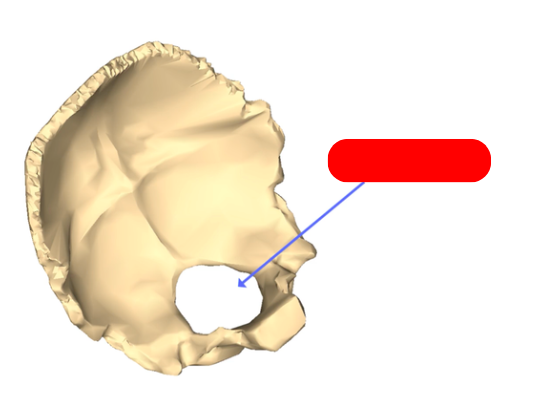
foramen magnum - in occipital bone. passageway for spinal cord
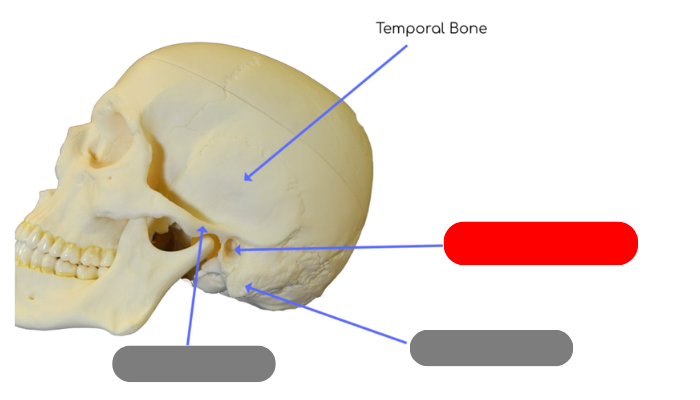
external auditory canal in temporal bone - tube like structure that houses structures for external and middle ear
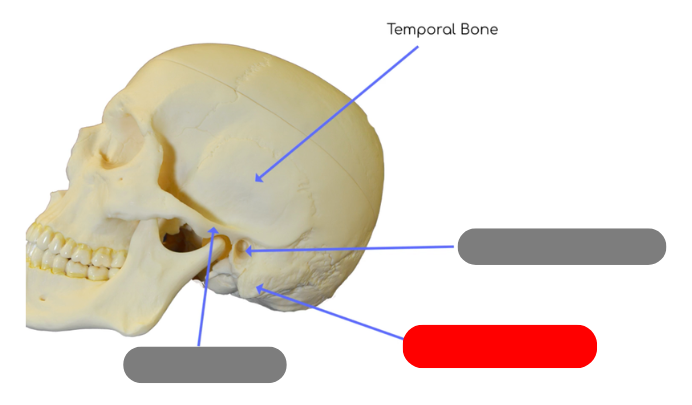
mastoid process - site of muscle attachment for some neck muscles, contains small cavities called air cells that connect with middle ear
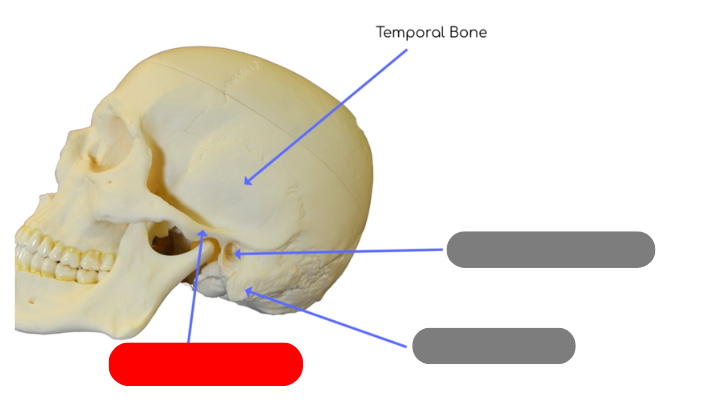
zygomatic process - posterior portion of zygomatic arch, articulates with temporaral process of zygomatic bone
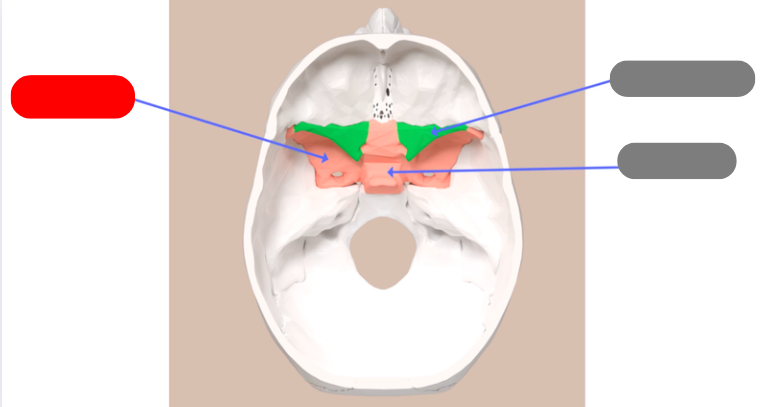
greater wings of the sphenoid bone, form part of the floor of the cranium
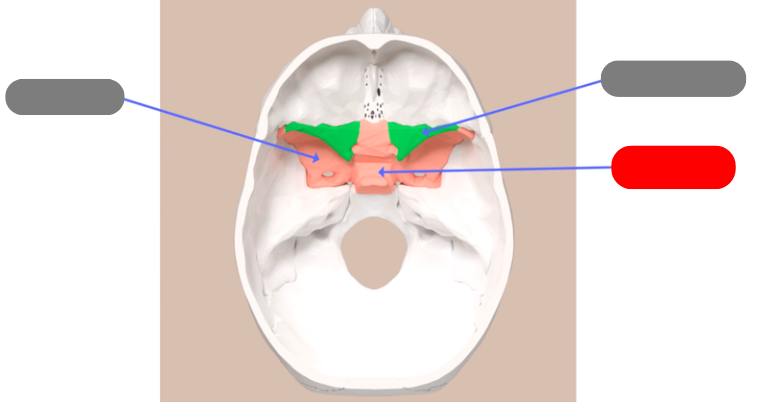
sella turcica - aka turkish saddle. groove in the middle of the sphenoid bone. pituitary gland sits in it
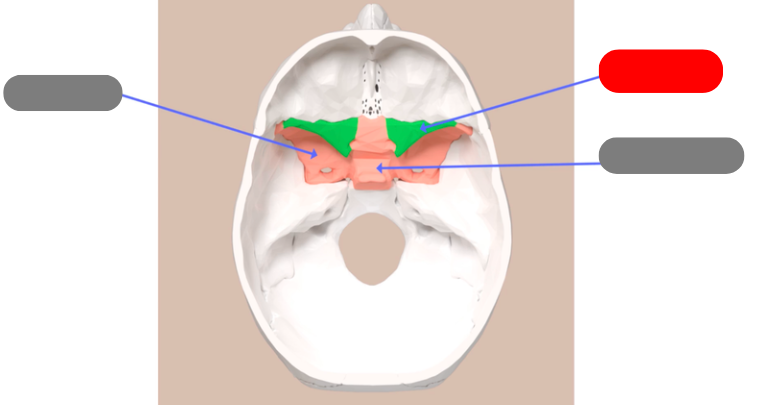
lesser wings of the sphenoid bone
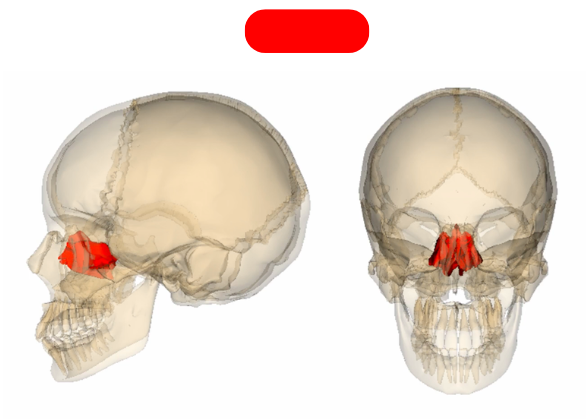
ethmoid bone - forms roof of nasal cavity and superior portion of nasal septum. has sinuses that create mucus to flush the nasal cavity
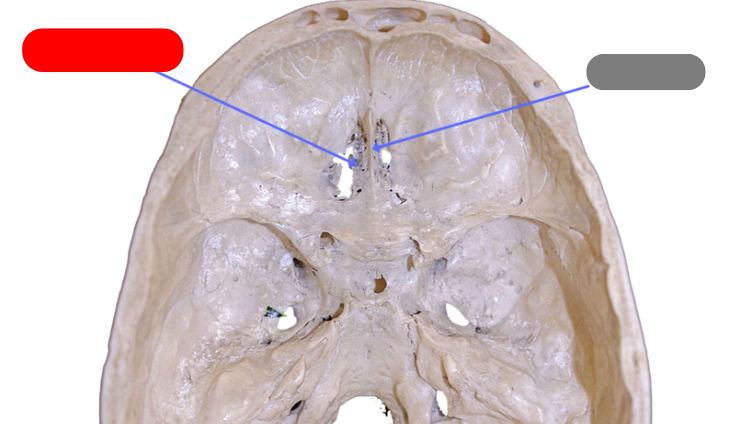
cribiform plate - perforated section, fibers from the olfactory bone pass through holes on their way to the frontal lobe
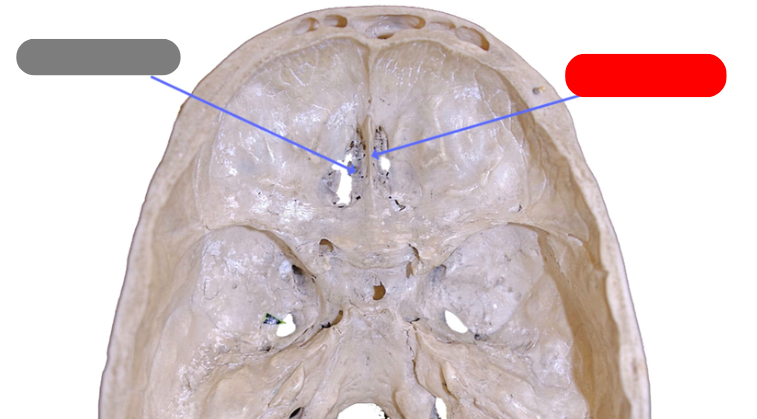
crista galli - ridge that a portion of the dura mater attaches to
perpendicular plate - forms superior portion of nasal septum
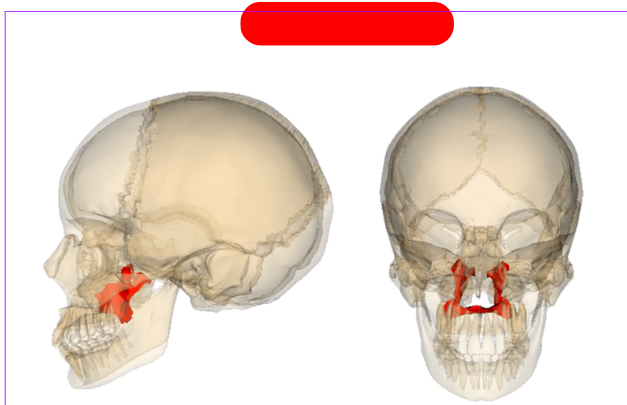
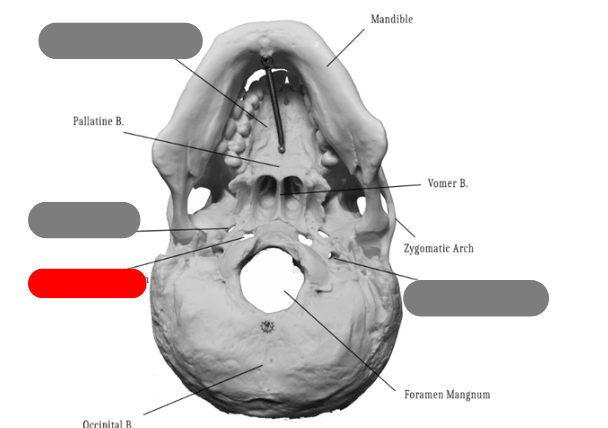
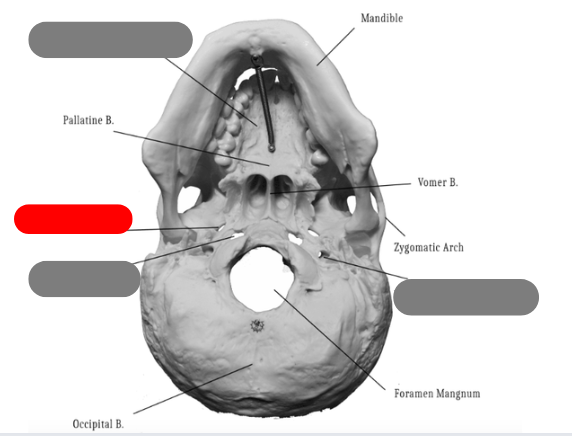
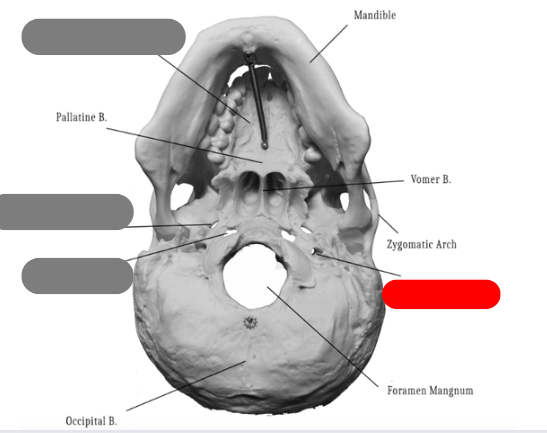
palatine bone - one of the bones that forms the hard palate, connects with palatine process of maxilla. between maxilla and sphenoid
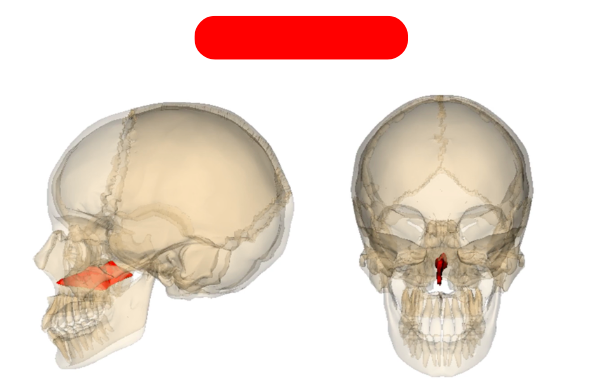
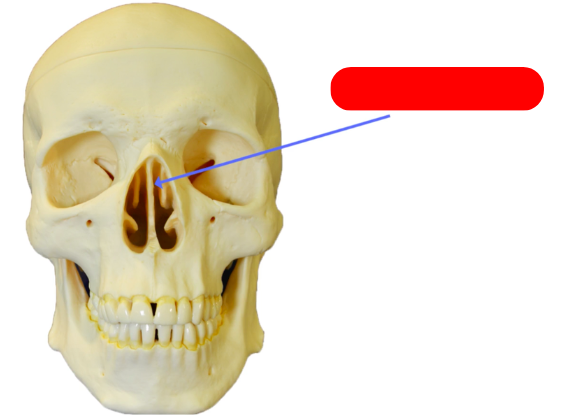
vomer bone - forms inferior aspect of nasal septum, connects to ethmoid, sphenoid, maxilla, palatine
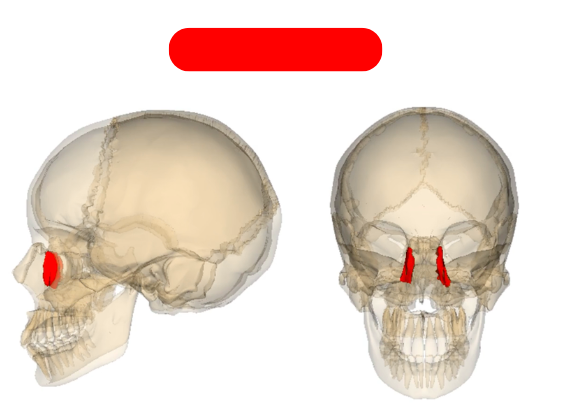
lacrimal bones
foramen lacerum
foramen ovale
foramen spinosum
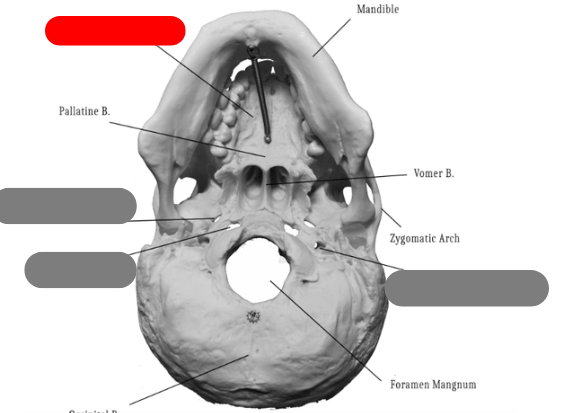
pallatine process of maxilla
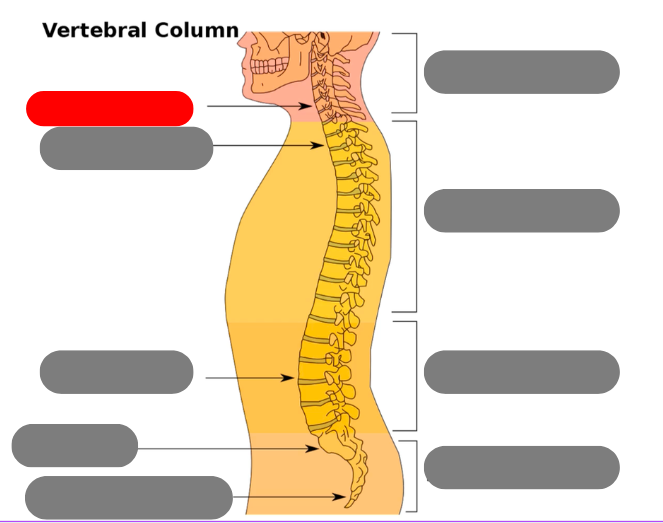
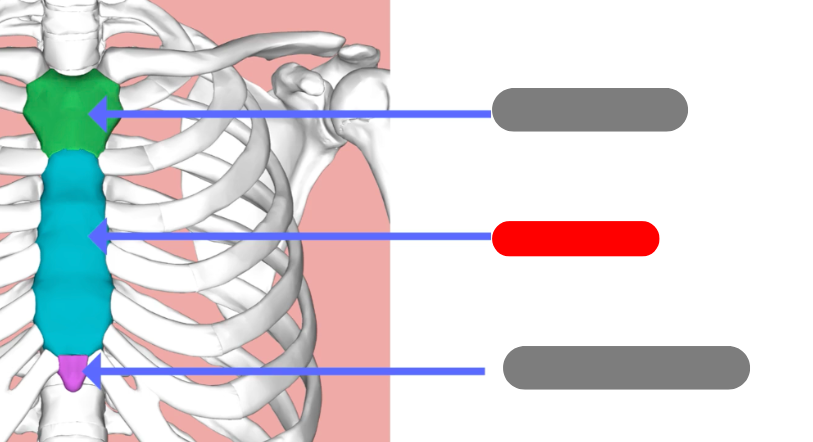
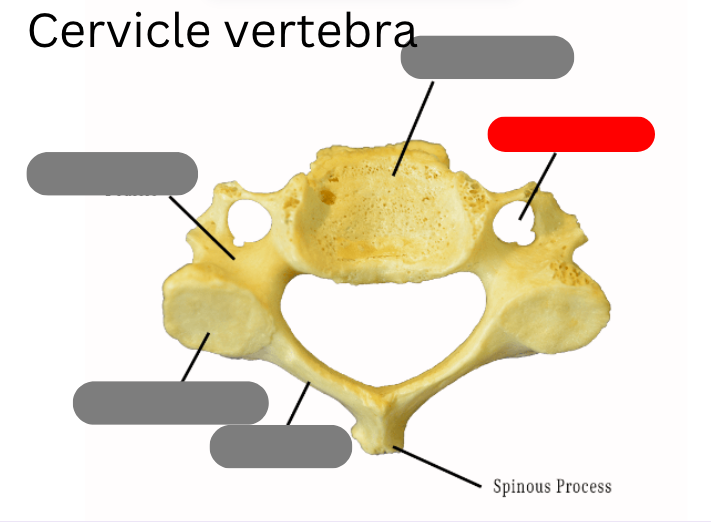
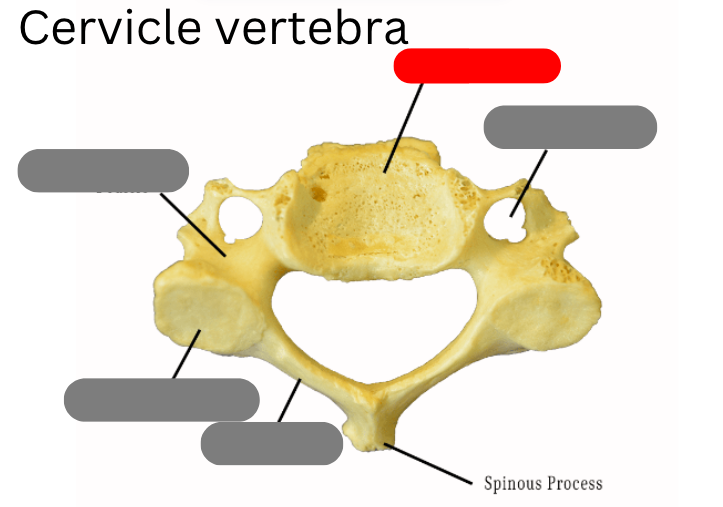
cervical vertebrae - 7 of them including the atlas (1) and axis (2)
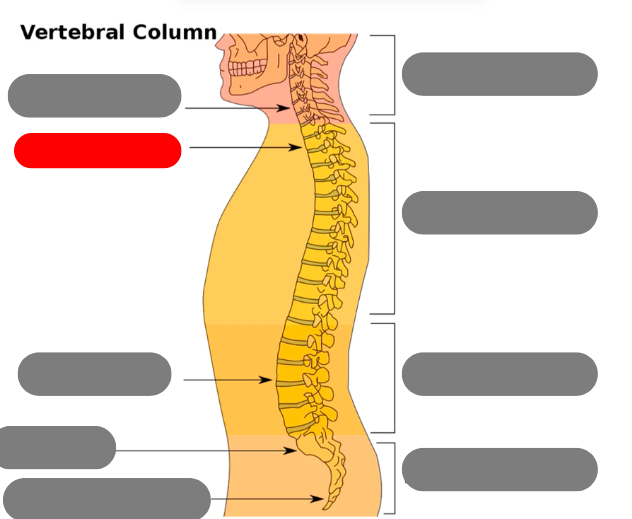
thoracic vertebrae - 12 of them that connect to the ribs
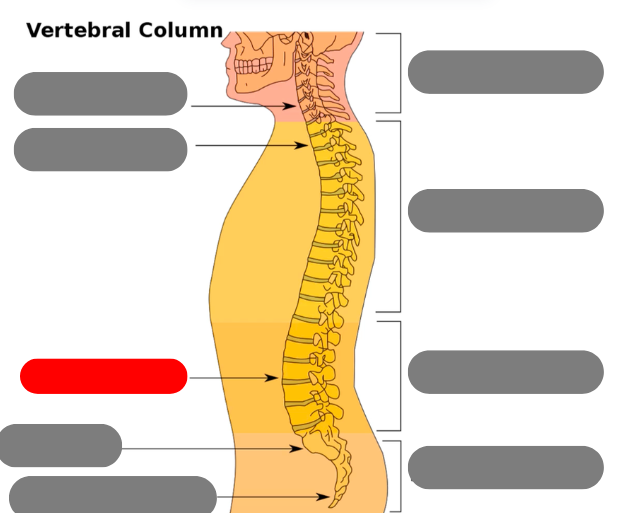
lumbar vertebrae - 5 of them
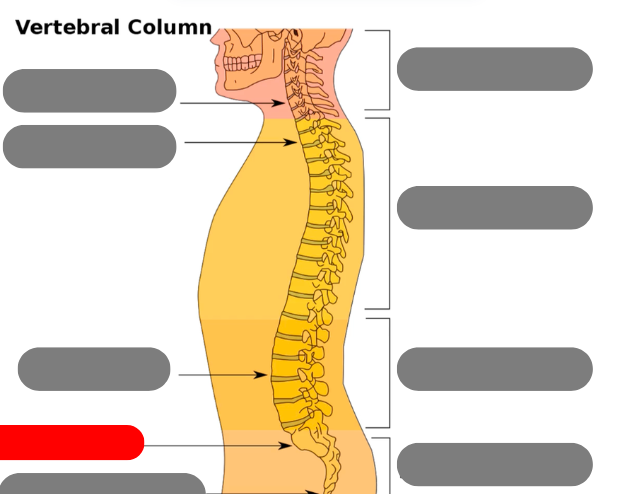
sacrum - triangular bone consisting of 5 fused vertebrae
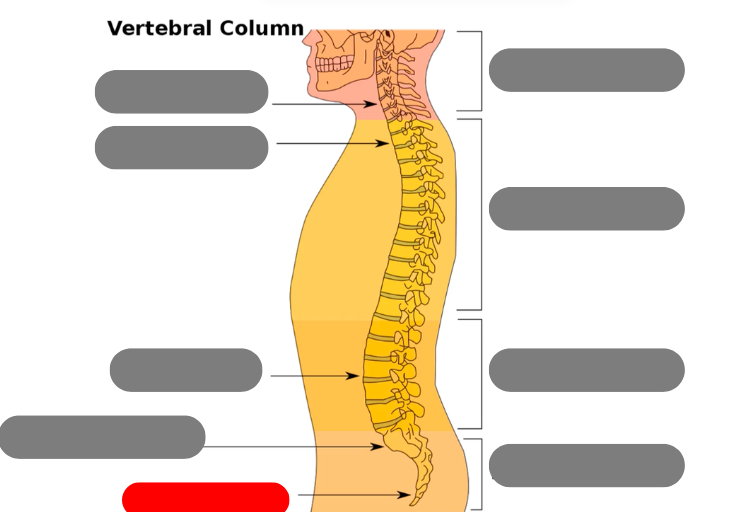
coccygeal vertebrae / coccyx - 3-5 very small fused vertebrae
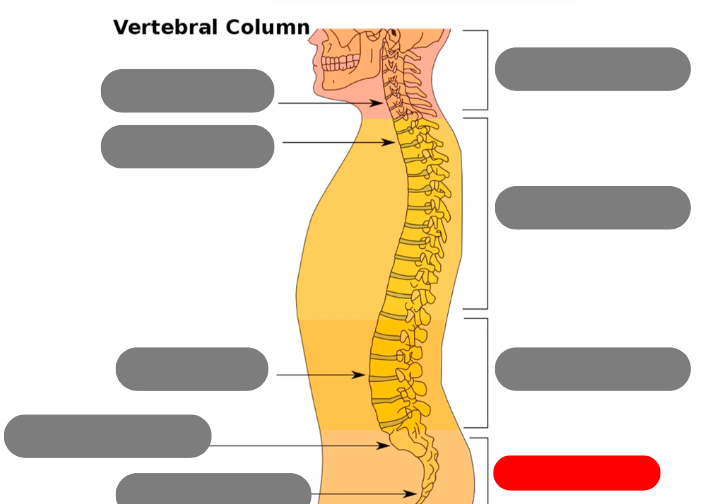
pelvic curve - kyphotic. concave anteriorly. primary curve b/c present at birth
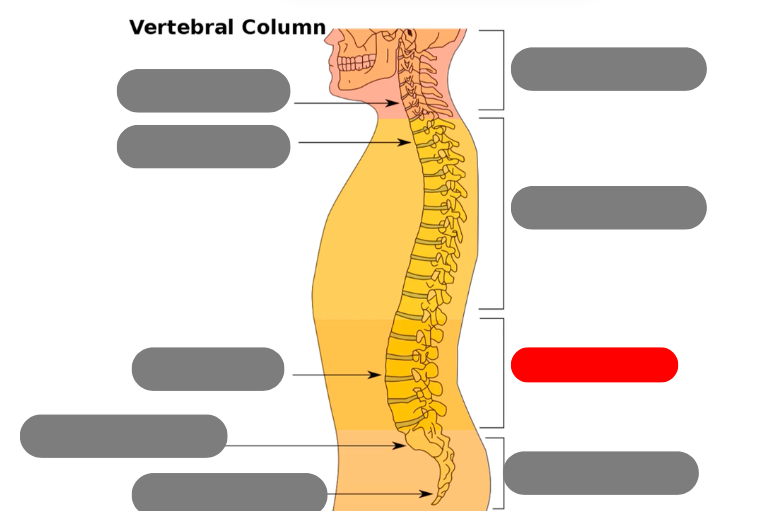
lumbar curve - lordotic/lordoses. anteriorly confex. secondary because developed after birth
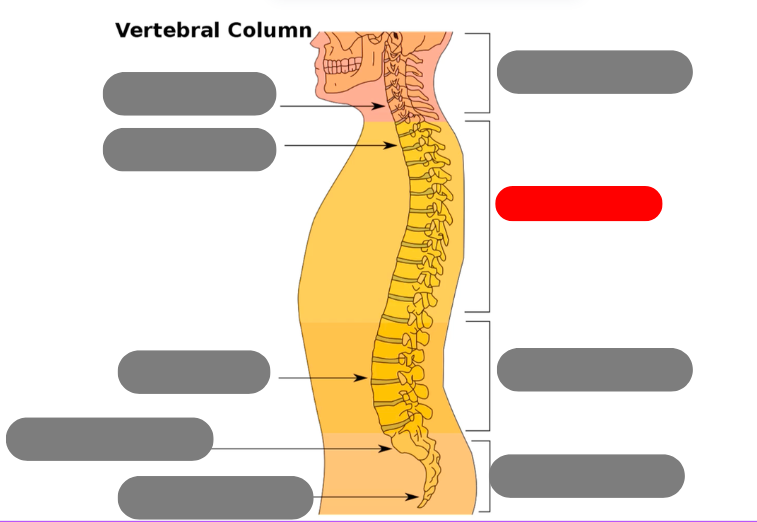
thoracic curve - kyphotic. concave anteriorly. primary because present at birth
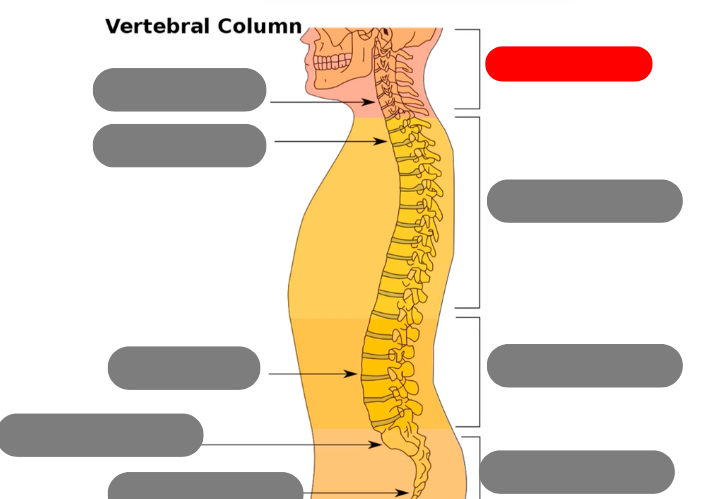
cervical curve - lordotic/lordoses, secondary developes after birth. convex anteriorly
hyperlorosis
increased curvature of the cervical or lumbar curves
hypolordosis
decreased curvature of the cervical or lumbar spine
3 types of ribs
true ribs: ribs 1-7 b/c they attach directly to sternum with costochondral cartilage
false ribs: ribs 8-10 b/c they don’t attach to the sternum but to the cartilage of the true ribs
floating ribs: ribs 11 and 12 b/c no connection to other ribs or sternum
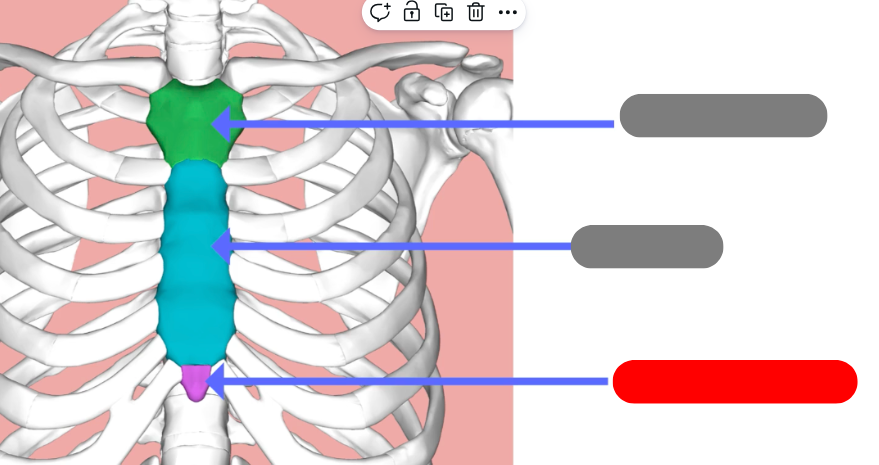
xiphoid process
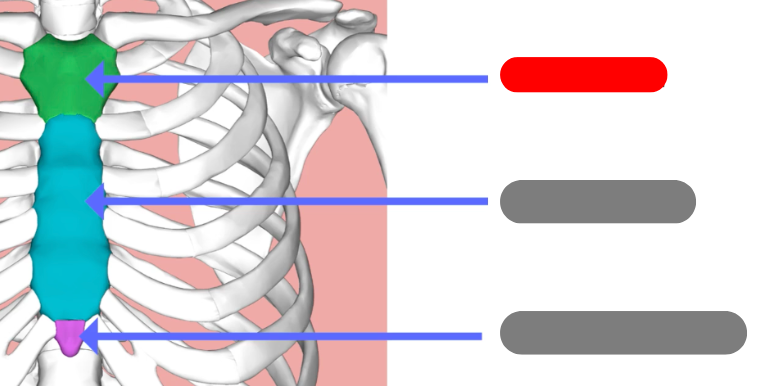
manubrium
body
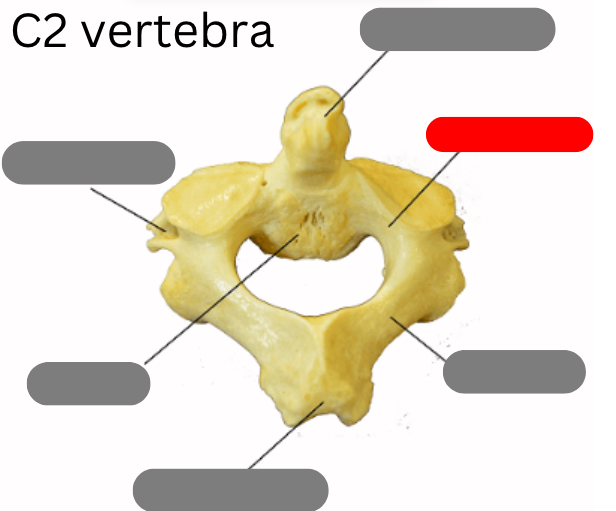
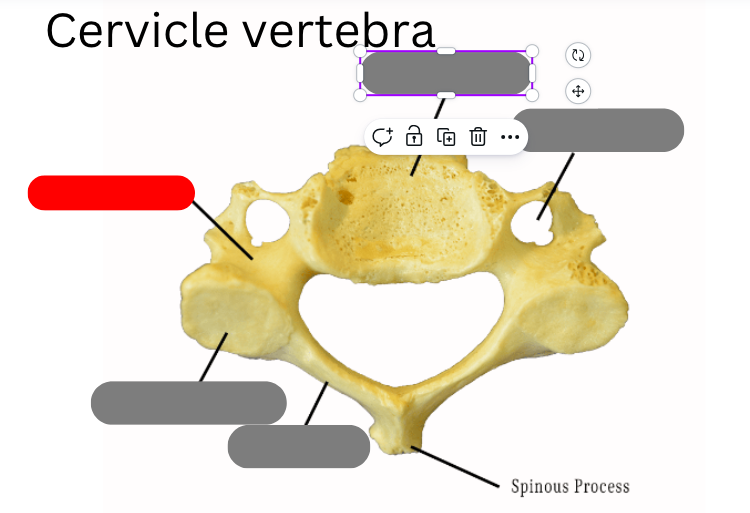
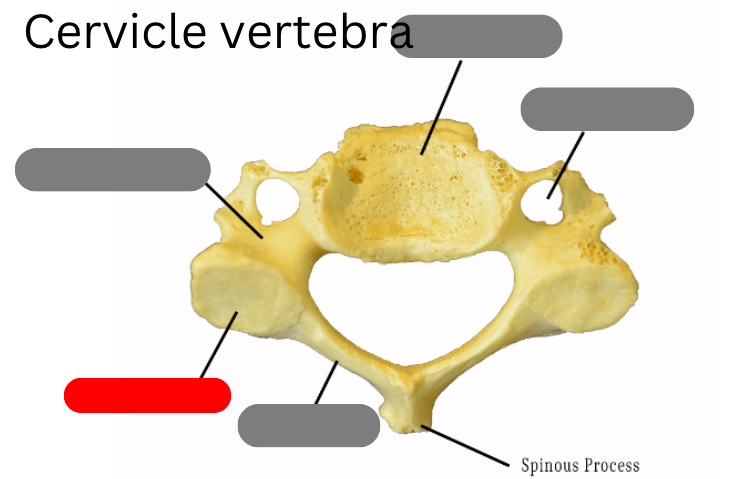
pedicle
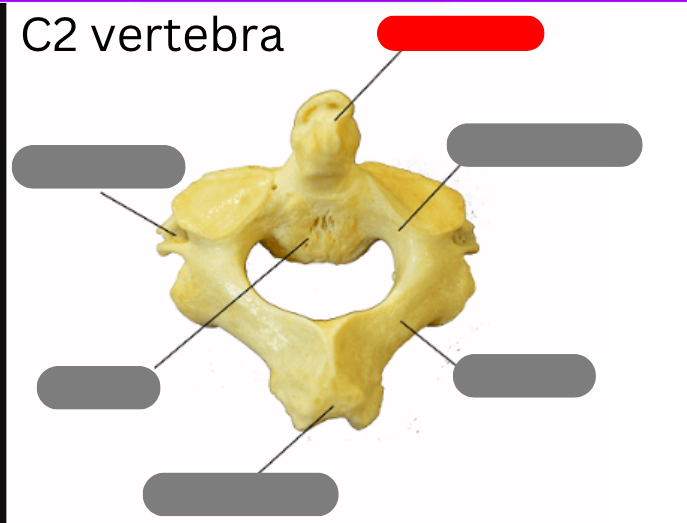
Dens
transverse foramen
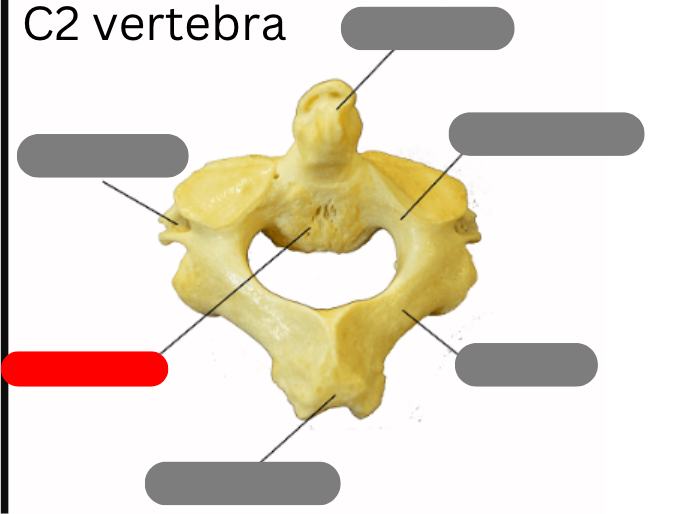
body
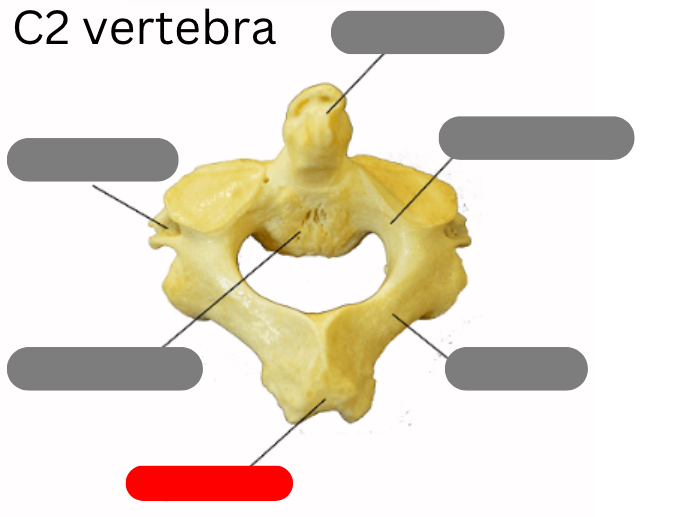
spinous process
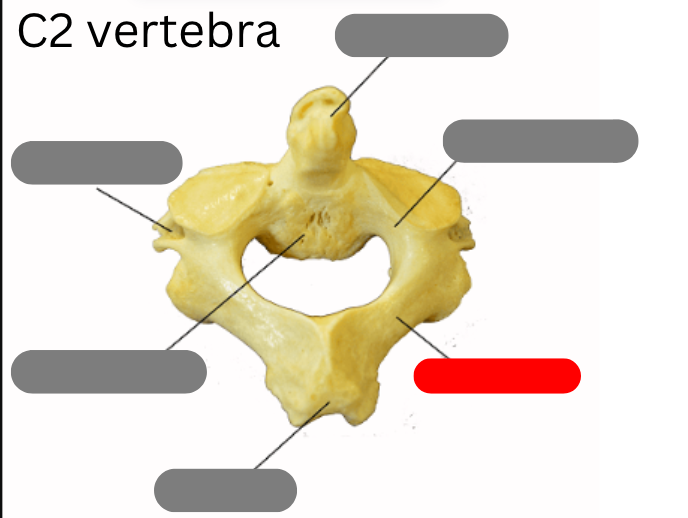
lamina
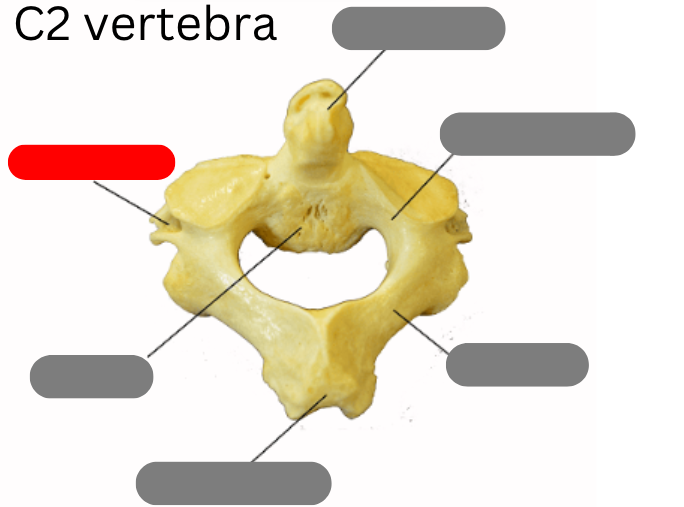
transverse foramen
body
pedicle
facet
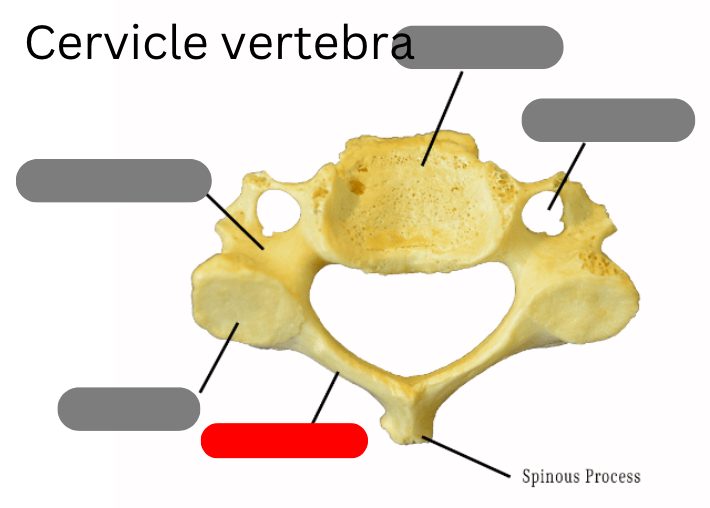
lamina
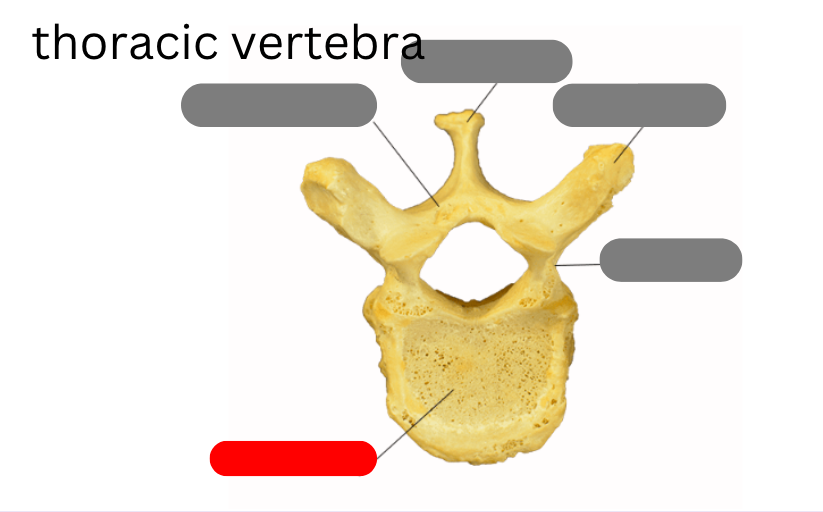
body