B9 - respiration
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
respiration
cellular respiration is an exothermic reaction which is continuously occurring in living cells
the chemical process of cellular respiration releases energy
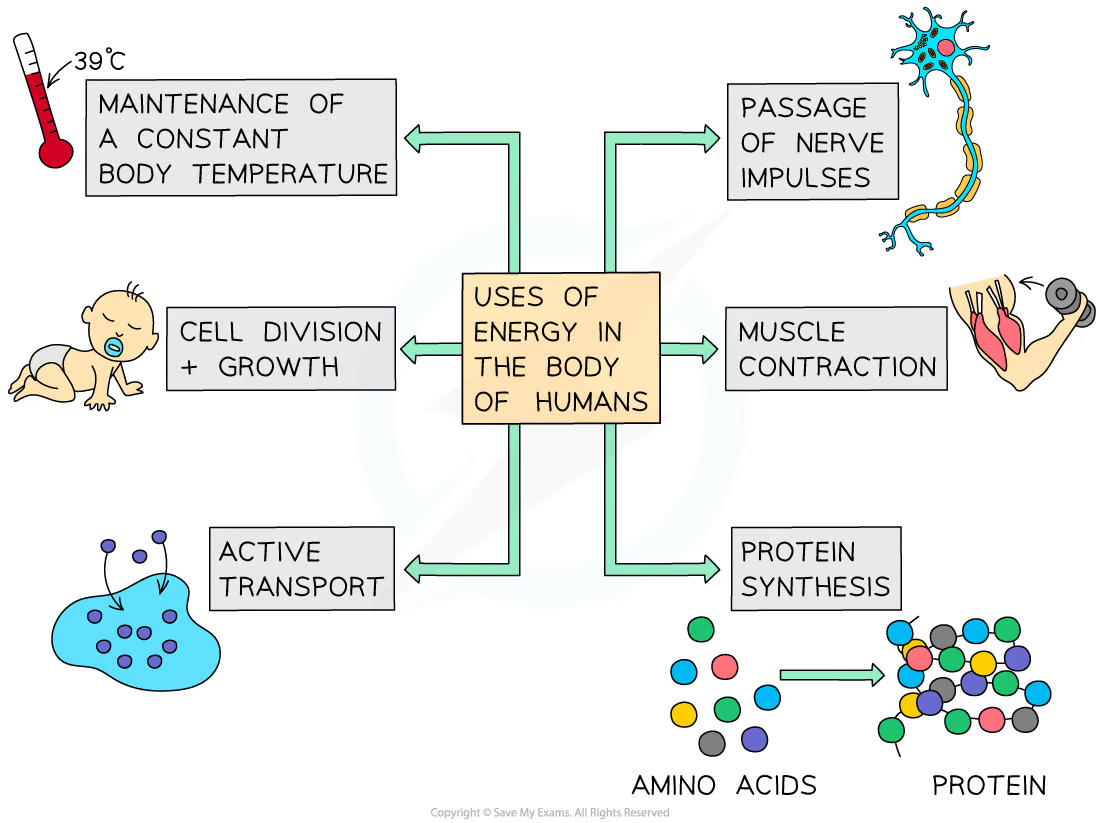
uses of energy
organisms need energy for:
chemical reactions to build larger molecules from smaller molecules
muscle contraction to allow movement
keeping warm (to maintain a constant temperature suitable for enzyme activity)
aerobic respiration
respiration in cells can take place aerobically (using oxygen) to transfer energy
glucose is reacted with oxygen in this process
word equation of aerobic respiration
glucose + oxygen ----→ water + carbon dioxide
symbol equation for aerobic respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
anaerobic respiration in animals
respiration in cells can take place anaerobically (without oxygen), to transfer energy; it involves the incomplete breakdown of glucose into lactic acid
this occurs when the body can’t supply enough oxygen for aerobic respiration, during exercise
word equation of anaerobic respiration
glucose ----→ lactic acid
symbol equation for anaerobic respiration
C6H12O6 ----→ 2C3H6O3
anaerobic respiration in plants n yeast
plants n yeast can respire without oxygen, breaking down glucose in the absence of oxygen to produce ethanol n carbon dioxide
anaerobic respiration in yeast cells is called fermentation
fermentation is economically important in the manufacture of bread (where the production of carbon dioxide makes dough rise) n alcoholic drinks (as ethanol is a type of alcohol)
anaerobic respiration in plants and yeast equation
glucose ---→ alcohol + carbon dioxide
body’s response to exercise
increase in heart rate, breathing rate n in breath volume
glycogen stores in the muscles are converted to glucose for cellular respiration
flow of oxygenated blood increases
oxygen debt
the amount of oxygen required to remove the lactic acid, n replace the body's reserves of oxygen
use of metabolites
Conversion of glucose to cellulose in plants to build n strengthen cell walls
conversion of glucose into glycogen in animals n starch in plants for storage
the formation of lipid molecules from a molecule of glycerol n three molecules of fatty acids to form triglycerides which are used for energy storage n as insulation in animals
In plants:
the use of glucose and nitrate ions to form amino acids which in turn are used to synthesise proteins required by cells (such as enzymes)
glucose is broken down in the process of respiration to release energy in all cells
in animals, the breakdown of excess proteins to form urea for excretion
metabolism
metabolism is the sum of all the reactions in the body.