Intro to Research Design- Krysiak
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
IF it says FYI- not on the exam... I just thought it would be good info to look at if you haven't looked at the powerpoints like me.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is a research design?
FYI
Overall plan that allows researchers to seek answers to study questions and test study
hypotheses
In simpler terms... answer a research question
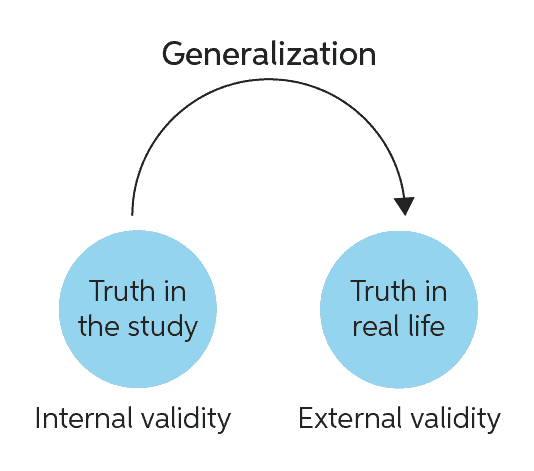
Internal Validity Definition:
reflects the extent to which the clinical outcome of interest (dependent variable) in a study is caused by the treatment (independent variable)
BASICALLY: did the study measure what it was supposed to? did the independent variable cause the change in the dependent variable?
External Validity Definition:
refers to the extent to which the results of a study can be generalized to other settings
Basically: can we use this study and apply it in real life?
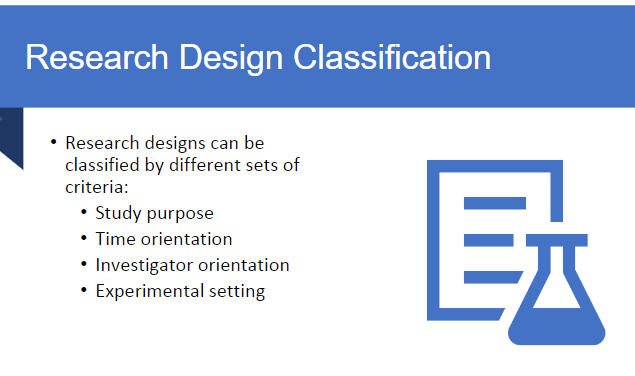
Research Designs can be classified based on what types of criteria?
FYI
study purpose
time orientation
investigator orientation
experimental setting
What type of study describes or summarizes info about diseases, events or characteristics of study subjects w/out making causal inferences?
descriptive study
What type of study is aimed at understanding the relationship and/or causal mechanism that may exist between 2 or more variables?
Analytical study
If you are classifying a research design by time orientation, a ______________ approach collects data after study onset by following individuals over a period of time.
AKA forward in time
(prospective/retrospective)
prospective
If you are classifying a research design by time orientation, a ______________ approach evaluates data from past events or existing data like medicals records.
AKA event has already occurred
(prospective/retrospective)
retrospective
What type of outcomes are prior to initiating the study, and researchers have one main outcome or “purpose” or the study?
(primary, secondary, tertiary)
primary outcomes
What type of outcomes are not the primary purpose of the study, but usually still important and may change how a study is conducted?
(primary, secondary, tertiary)
secondary outcomes
What type of outcomes are deemed not important and are more exploratory in nature and should not pose any risk or put patients through any discomfort?
(primary, secondary, tertiary)
tertiary outcomes
Definition of a superiority study:
one intervention is “better” than the other, usually compared to a placebo
Ex: If I give this drug will it be better than this placebo
Definition of an equivalency study:
usually used to establish therapeutic equivalence of a generic drug and brand name
A non-inferiority study tests if…
one intervention is not “meaningfully worse” than a comparator that has already been shown to have a positive impact
What randomization technique is similar to a coin toss where groups are assigned based on outcome of the toss?
simple randomization
What randomization technique attempts to balance groups based on characteristics and subjects are randomized in blocks based on known and unknown baseline characteristics or confounding disease states?
stratified randomization
What randomization technique ensures about equal number of subjects throughout the enrollment period and is most commonly used when enrollment must be extended over long periods of time, like rare diseases?
blocked randomization
What type of blinding involves matching different dosage forms within a clinical trial to help with blinding?
(double-dummy, single, double, triple)
double-dummy
What type of blinding ensures ALL personnel involved with the conduct of the trial and data analysis are unaware of treatment assignment?
(double-dummy, single, double, triple)
triple-blind
What type of blinding conceals treatment assignments from BOTH the investigators and subjects?
(double-dummy, single, double, triple)
double-blind
What type of blinding has either the subject or investigator unaware of the treatment?
(double-dummy, single, double, triple)
single-blind
What are the two types of analytical studies and the studies that belong to each of those two types?
FYI
observational- cohort, case-control studies
interventional- randomized controlled studies
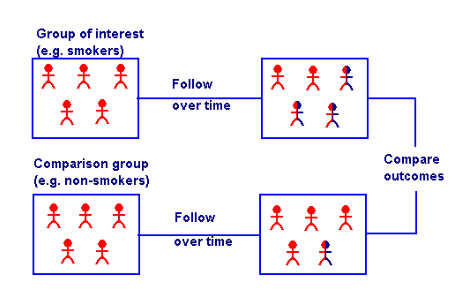
Describe a cohort study:
who’s followed over time
at baseline what happens?
groups are defined based on…
determines what?
considered the strongest what?
exposed and unexposed groups are followed over time to see if they develop an outcome
at baseline, neither group has the outcome
two groups defined on exposure status
exposed v unexposed
determines the incidence of outcome and provides measure of relative risk
considered the STRONGEST FORM OF OBSERVATIONAL DESIGN
but STILL NO RANDOMIZATION
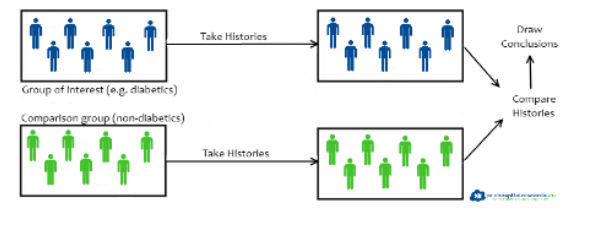
Describe a case-control study:
compares what?
researches have to determine what?
design of choice for…
comparison of exposure status among pts w/ the disease (cases) and those without (controls
researchers determine exposure HISTORY (retrospectively)
design of choice for RARE OUTCOMES
What type of trial is considered the GOLD STANDARD in evaluating safety and efficacy of an intervention?
randomized controlled trials (RCT)
Randomized controlled trials have what 2 essential elements? and are always ______________.
randomization
intervention (experimental) and no intervention (control)
always prospective
___________________________ is systematically reviewing the literature and combining trials to answer a question that may have conflicting answers.
systematic review
__________________ is application of statistical analyses to a combo of trial results.
Meta-analysis