BIO130: Week 7 - Cell Membrane Structure
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What are the 2 components unique to animal cells?
1. Extracellular Matrix
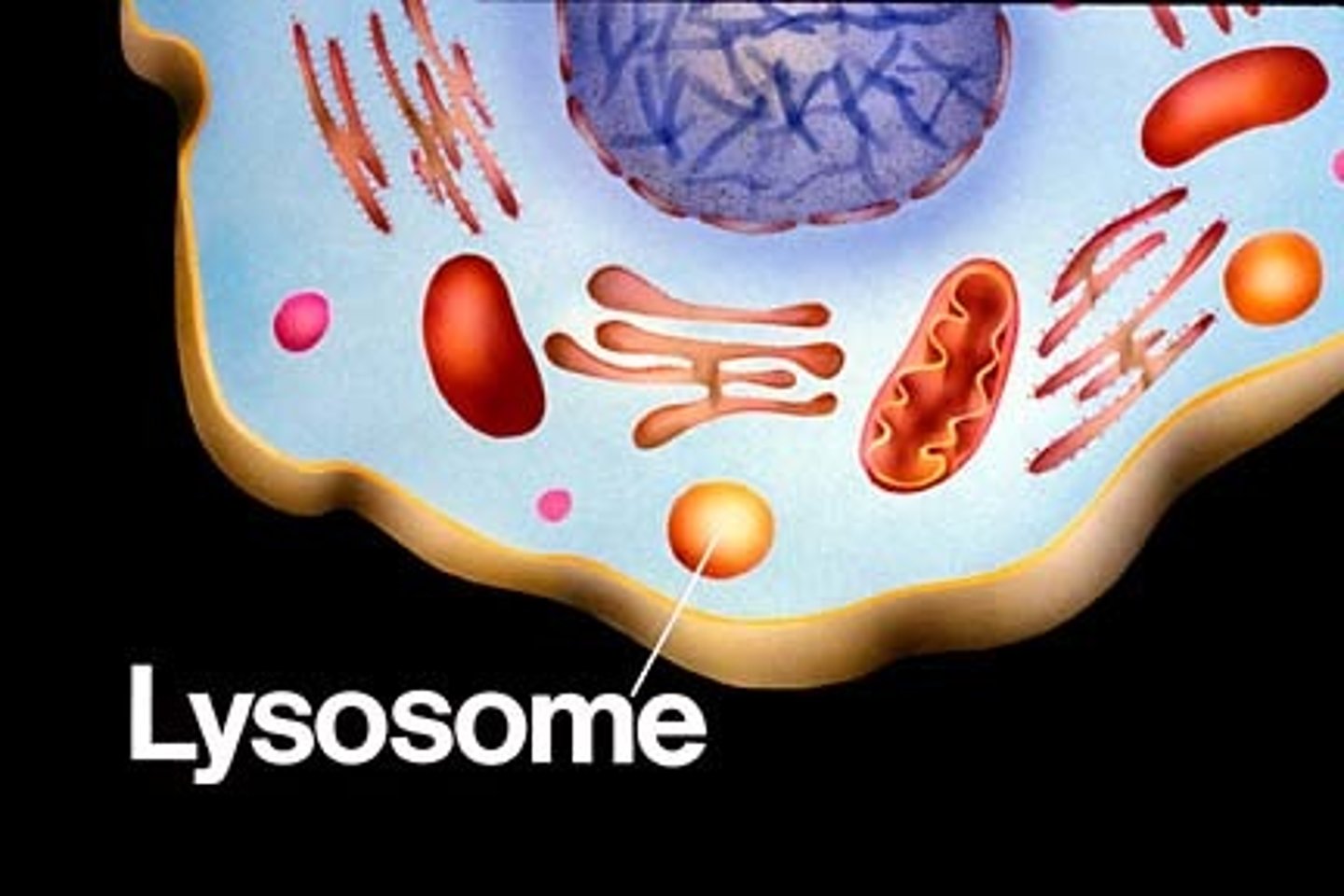
2. Lysosome
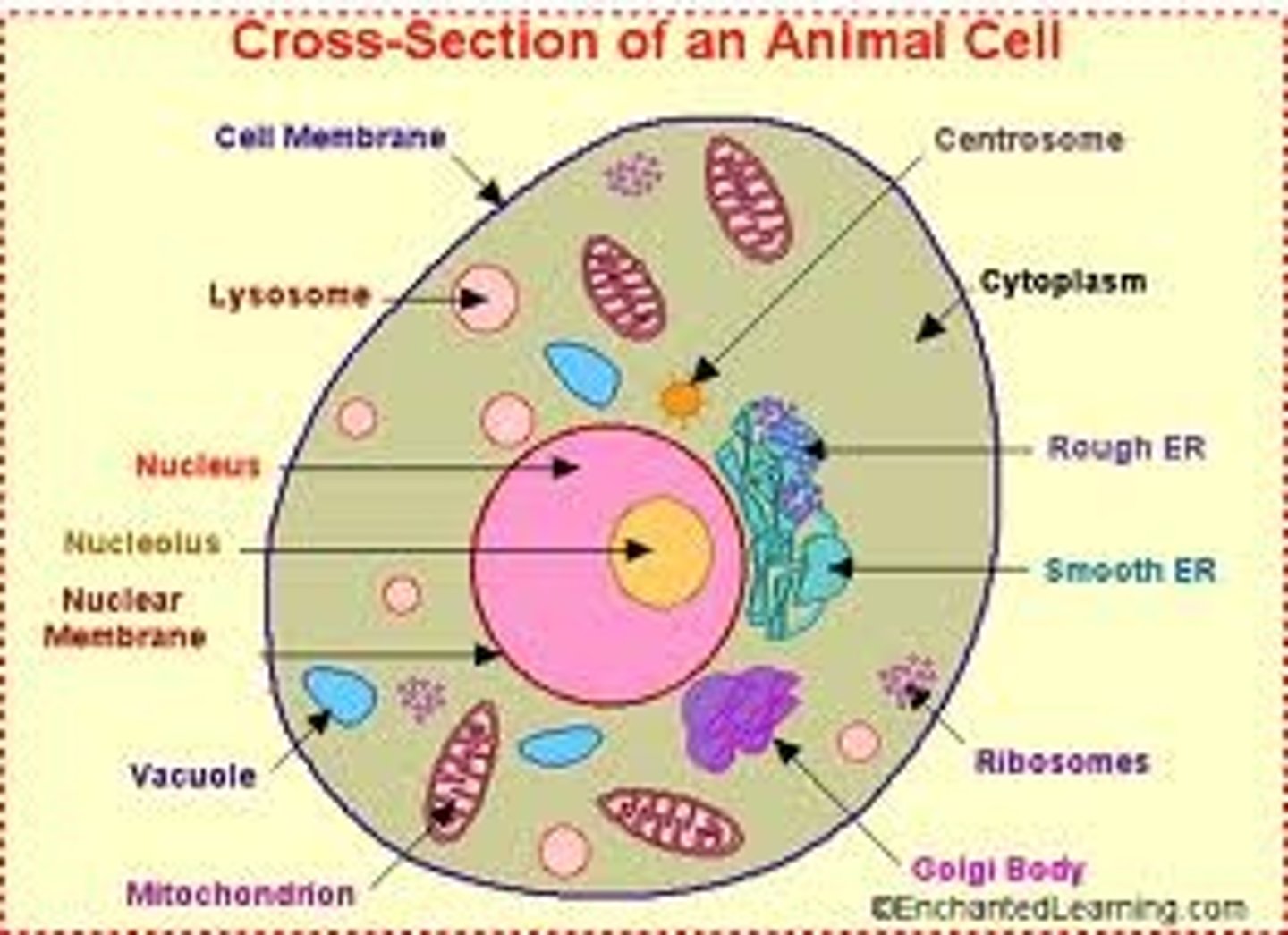
What is the extracellular matrix used for?
specialized material outside of the cell = safe space

What is the lysosome used for?
degrading cellular components no longer needed
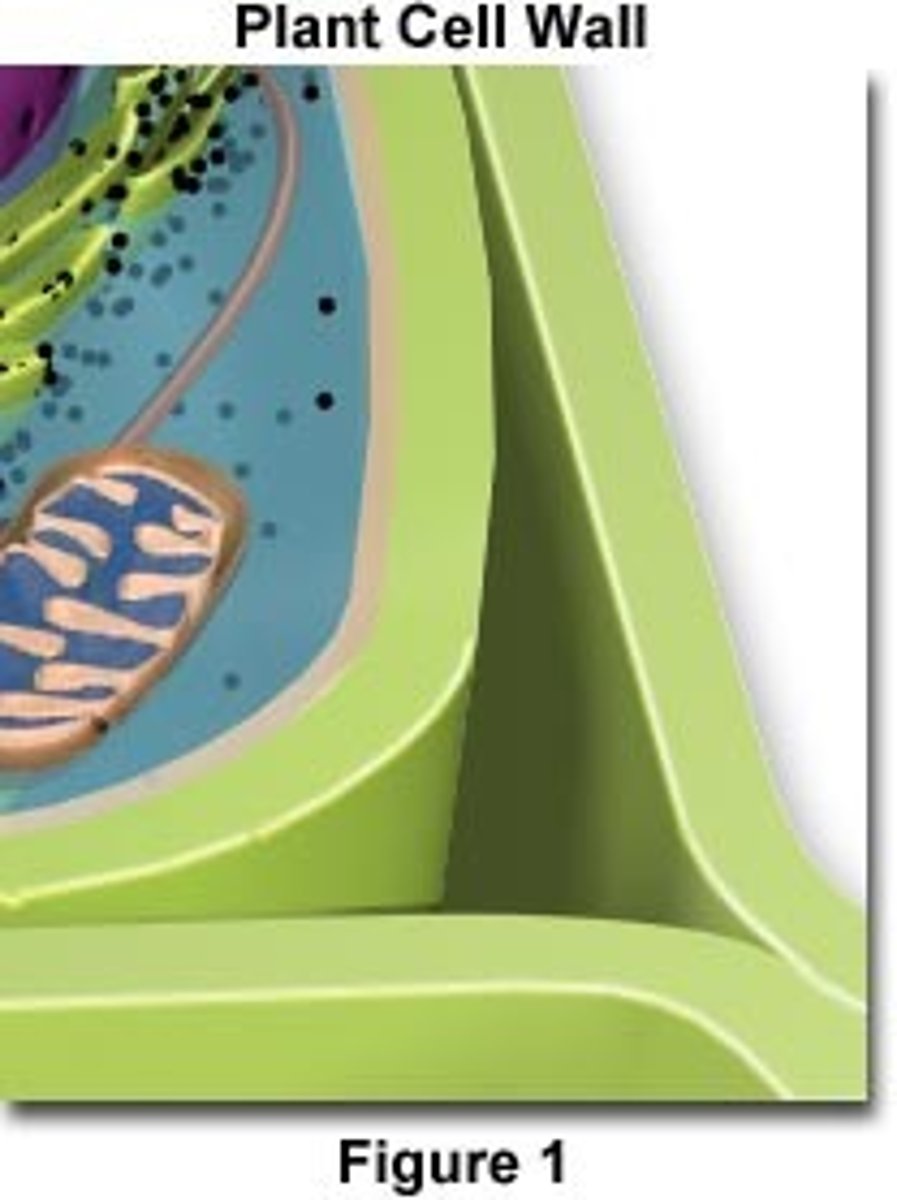
What are the 3 components unique to plant cells?
1. Cell Wall
2. Vacuoles
3. Chloroplast
What does the cell wall do?
supports and protects the cell
What are the 2 functions of vacuoles?
1. Degradation (similar to lysosome in animal cells!)
2. Storage of small molecules + proteins
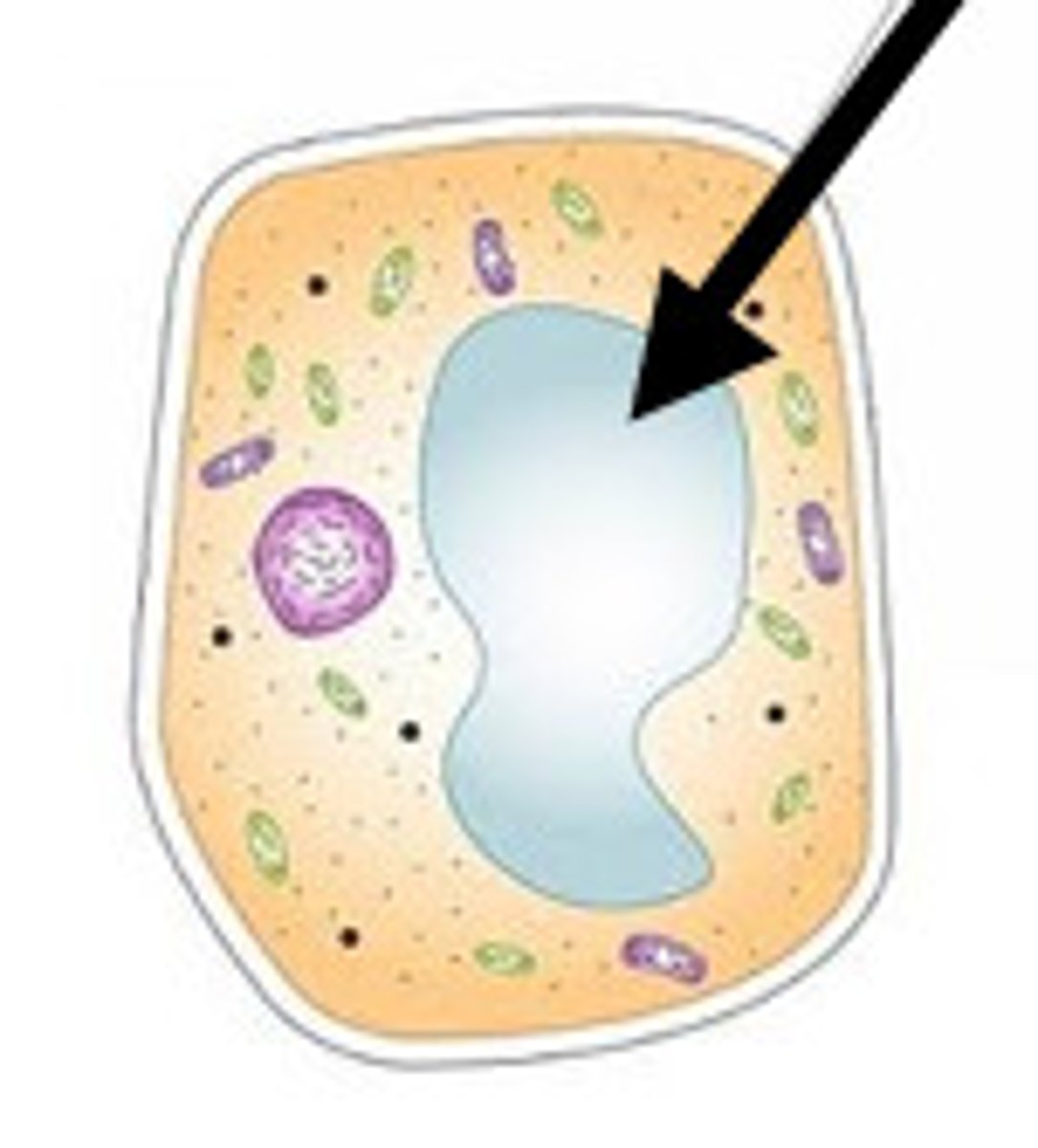
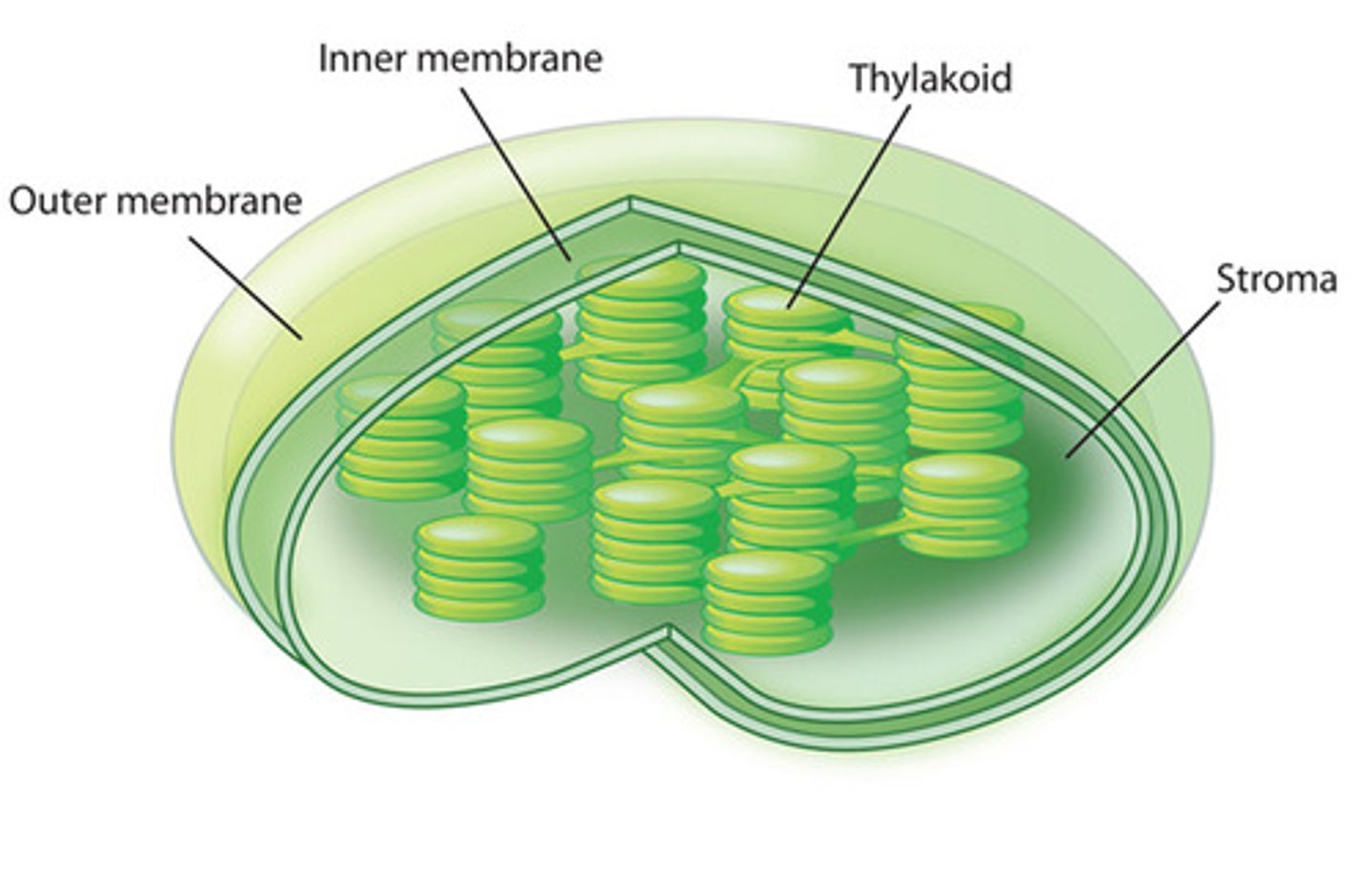
What does the chloroplast do?
site for photosynthesis
What are the 3 eukaryotic organelles with membranes?
1. Cytoplasm
2. Cytosol
3. Lumen
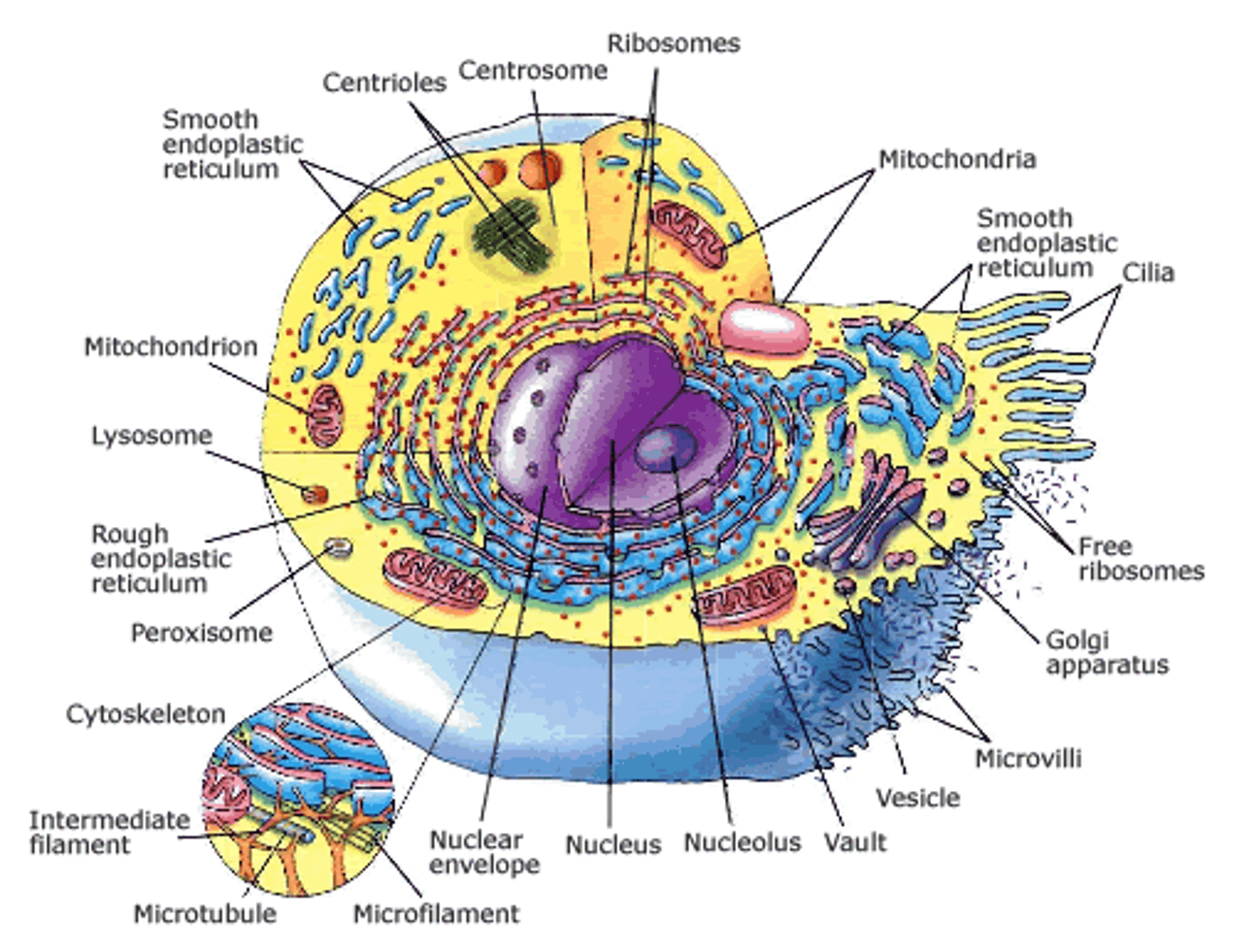
What is the cytoplasm made of?
everything OUTSIDE the nucleus (including cytosol)
What is the cytosol made of?
aqueous part of the CYTOPLASM
- proteins, solutes (dissolved ions and molecules)
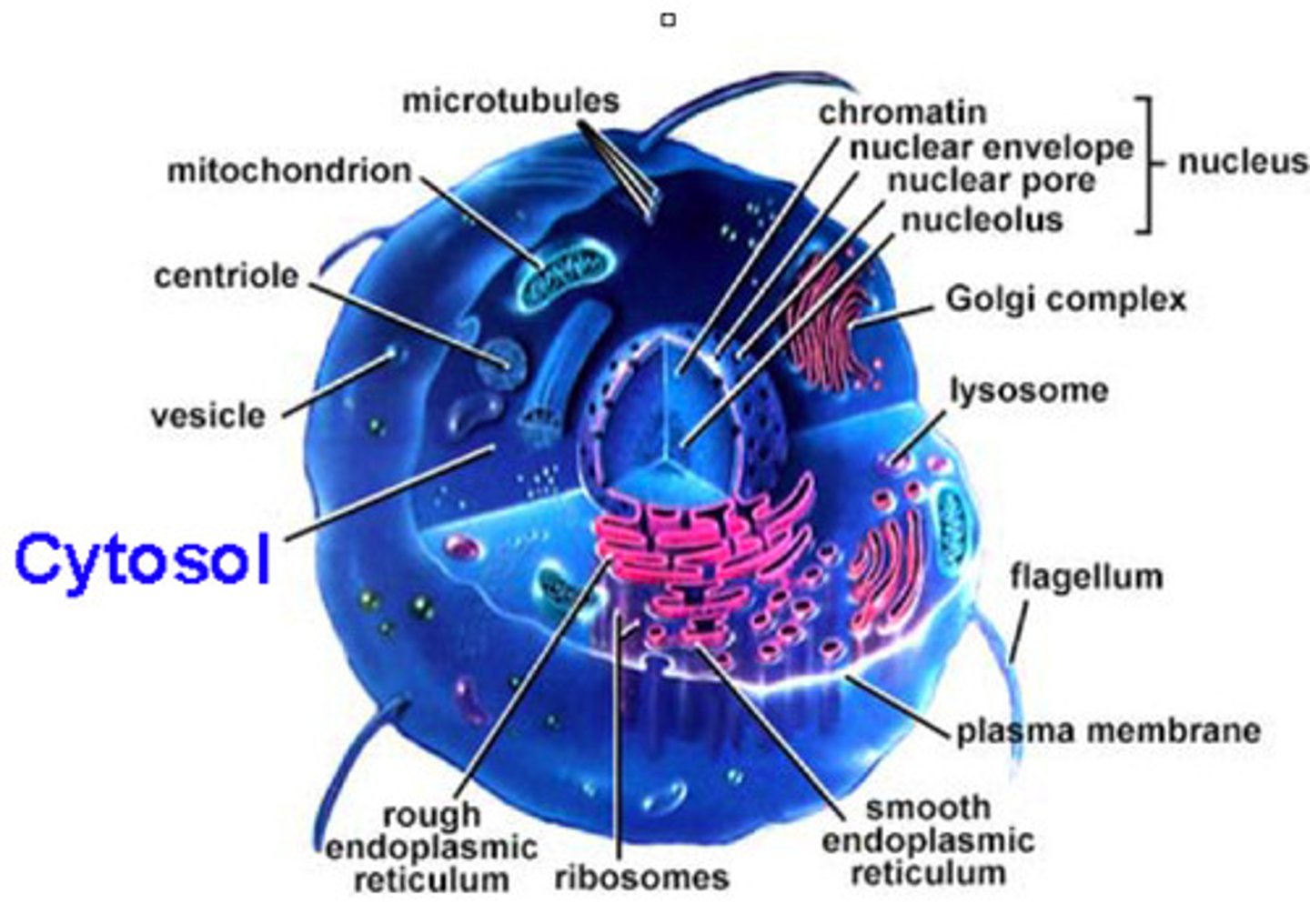
What is the lumen made of?
INSIDE of organelles
- ex. "golgi lumen, lysosome lumen"
What are the 6 functions of membranes?
1. Compartmentalization
2. Biochemical activities (ex. ATP production)
3. Selectively permeable
4. Transport of solutes (ions, molecules)
5. Response to signals
6. Cell-cell interaction
What are the 3 components of membrane bilayers?
1. Lipid molecules (ex. phospholipids)
2. Protein molecules
3. 2 leaflets/layers
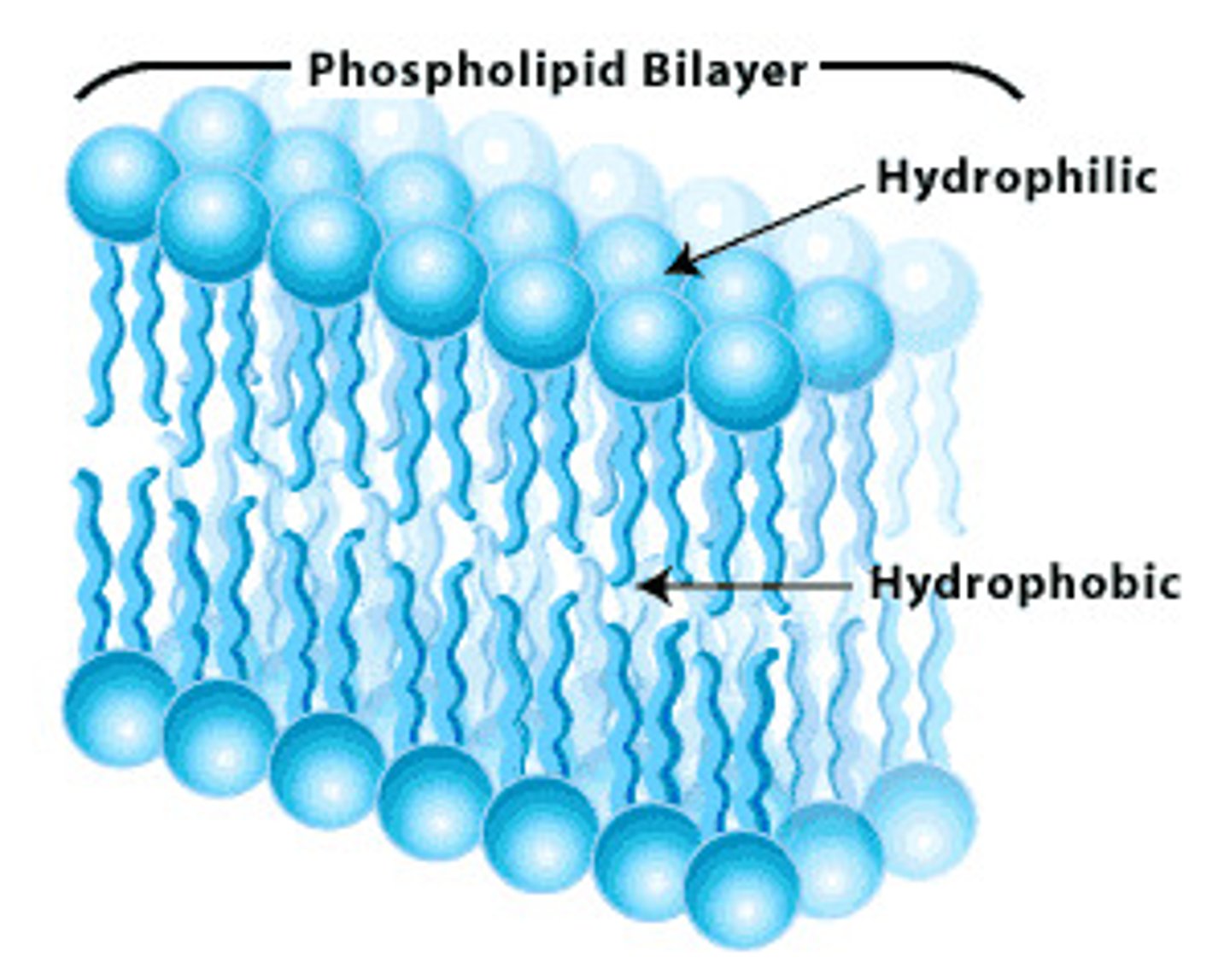
What is the energetically favourable orientation for a lipid?
amphipathic: has hydrophilic + hydrophobic parts
- hydrophilic head facing aq. environment
- hydrophobic tail facing other tails
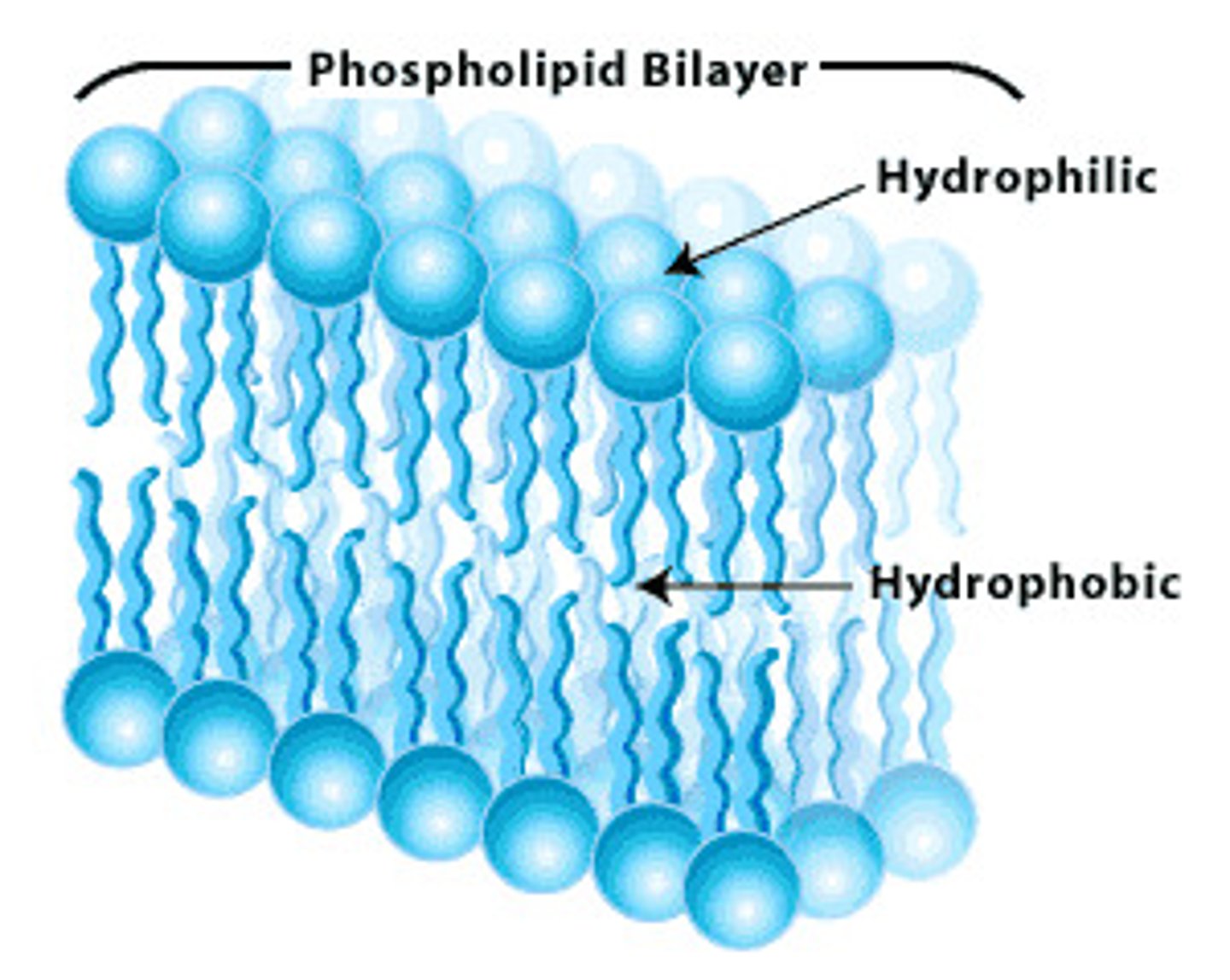
What are phosphoglycerides?
lipids w/ GLYCEROL group
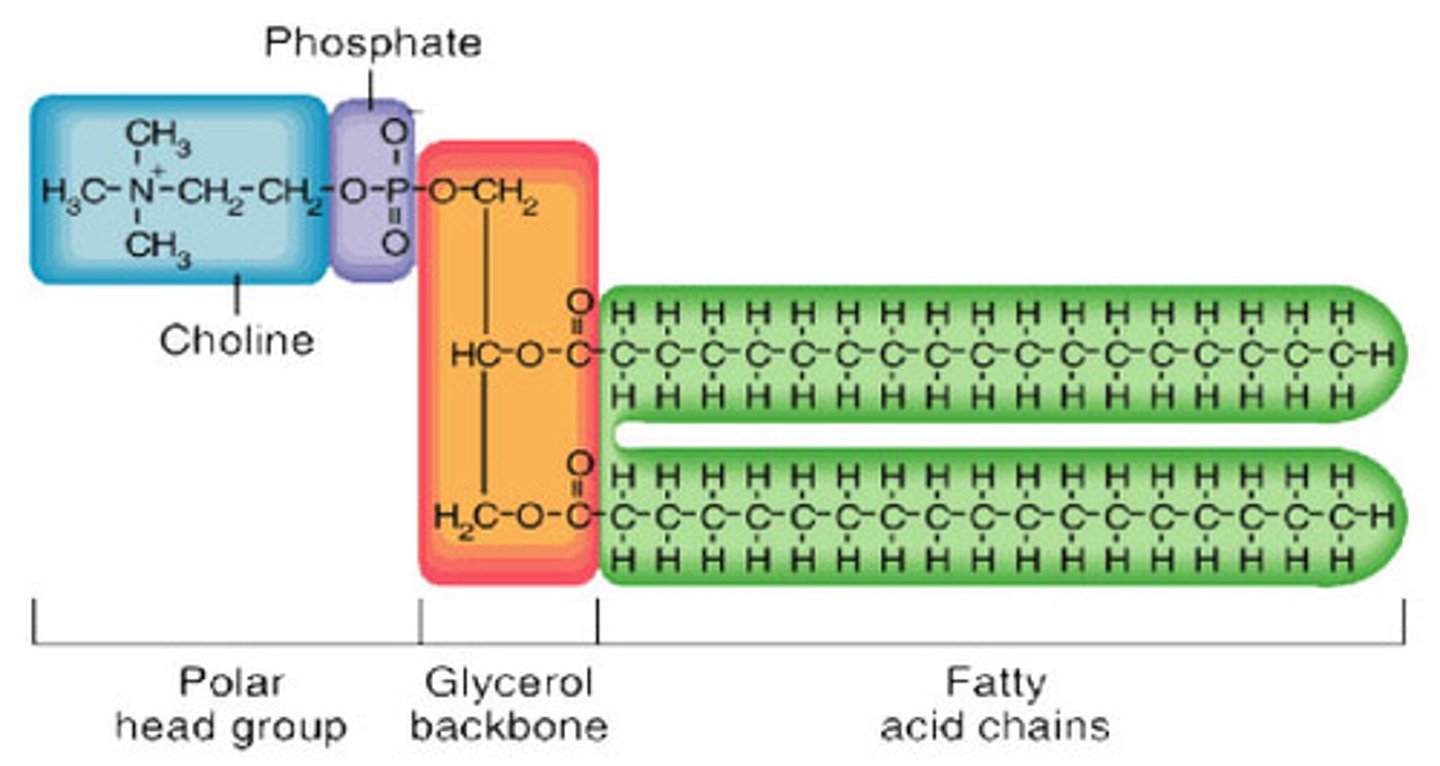
What makes up the hydrophilic head of a phosphoglyceride?
diff. groups + phosphate
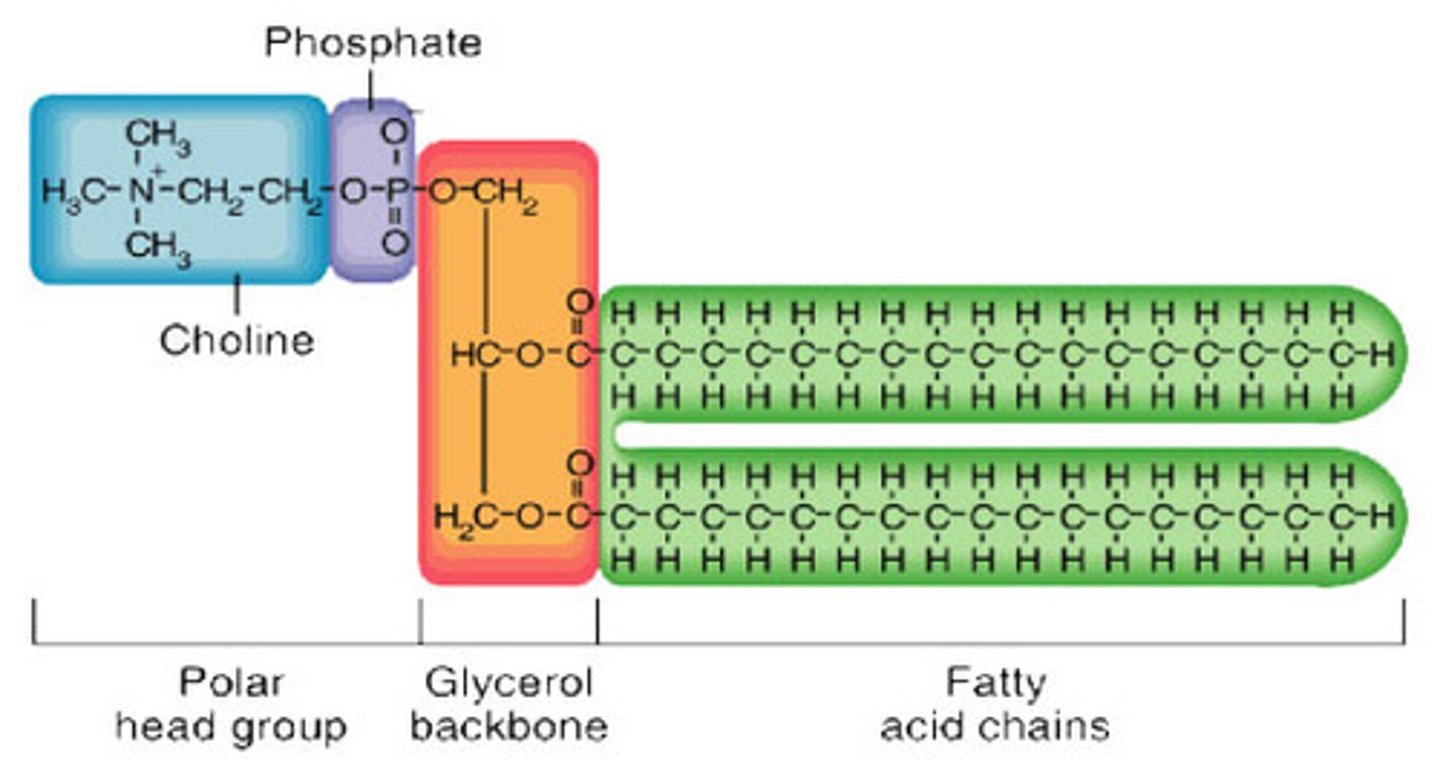
How long are hydrocarbon tails?
14-24 carbon atoms
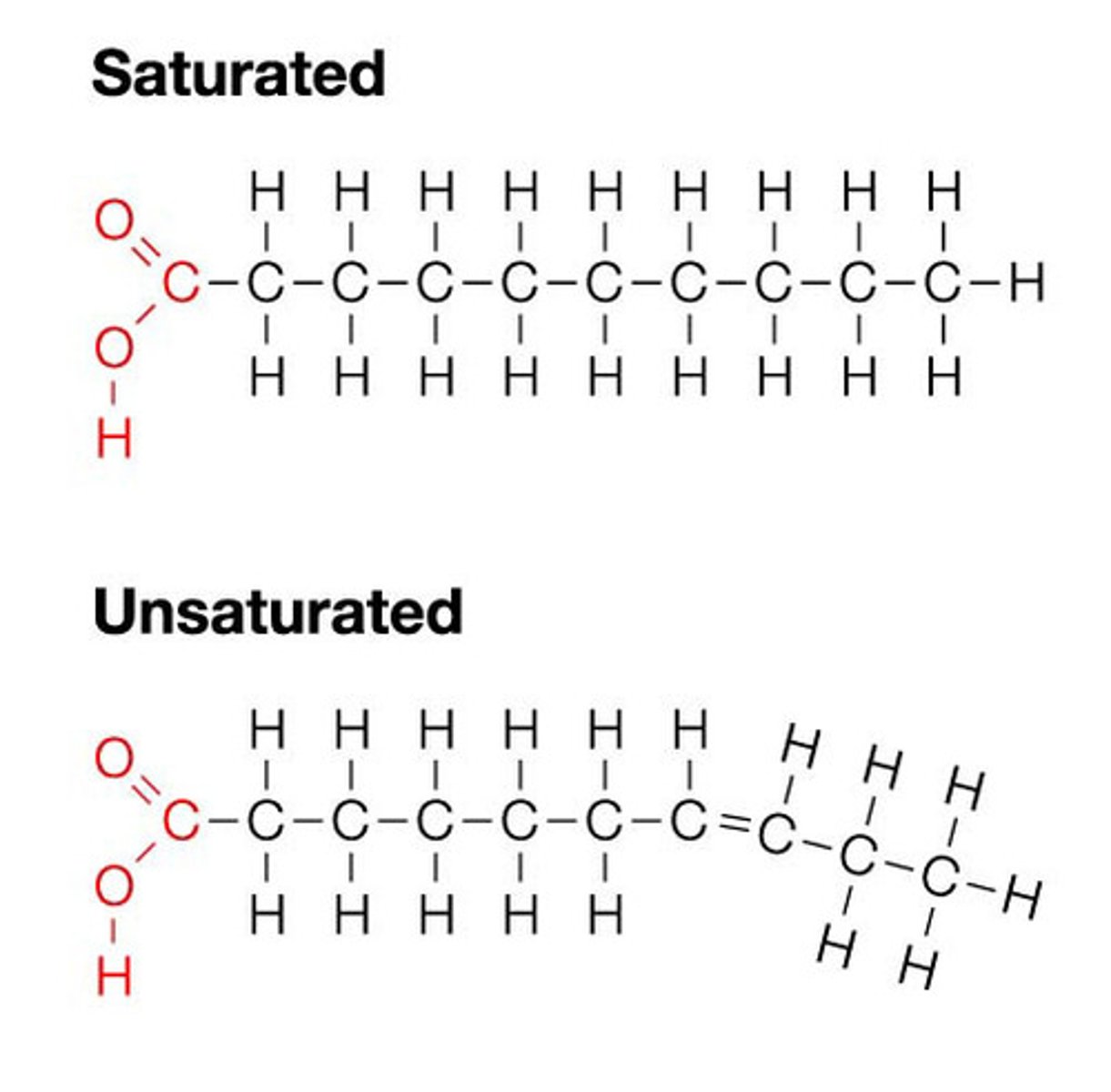
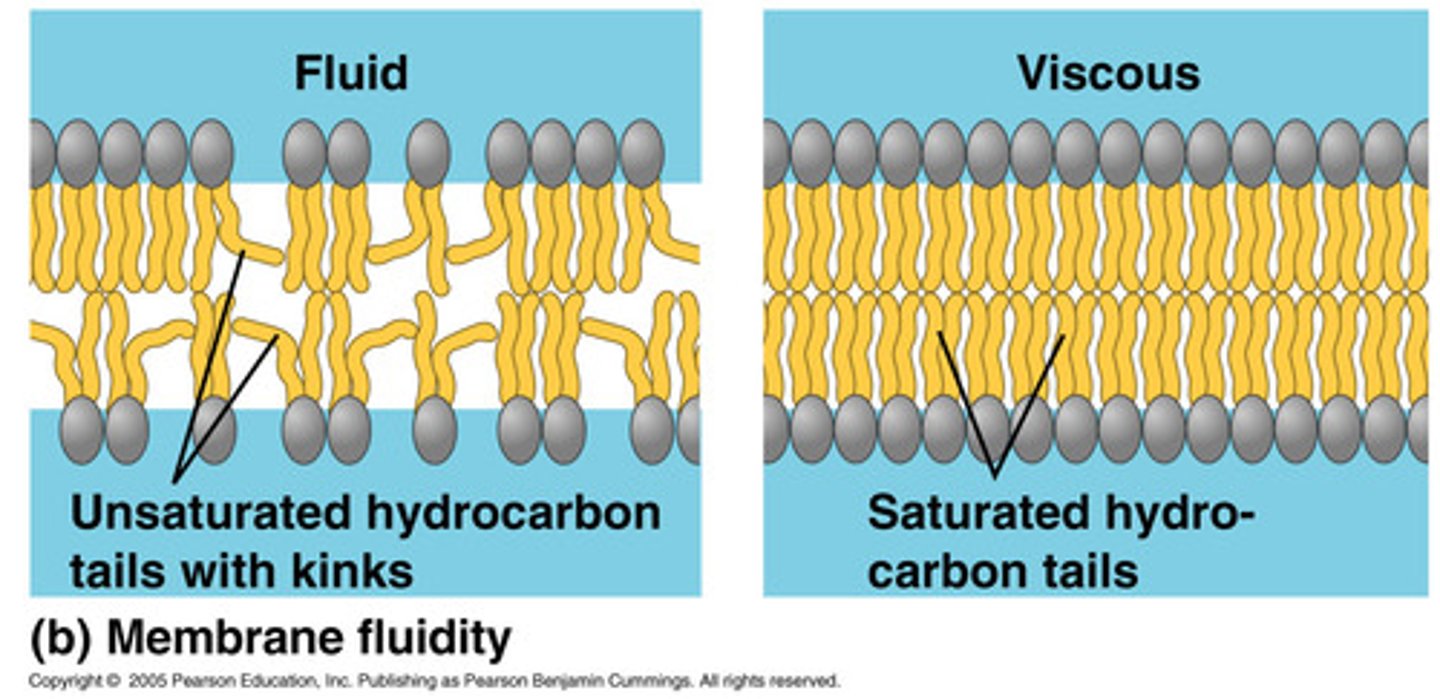
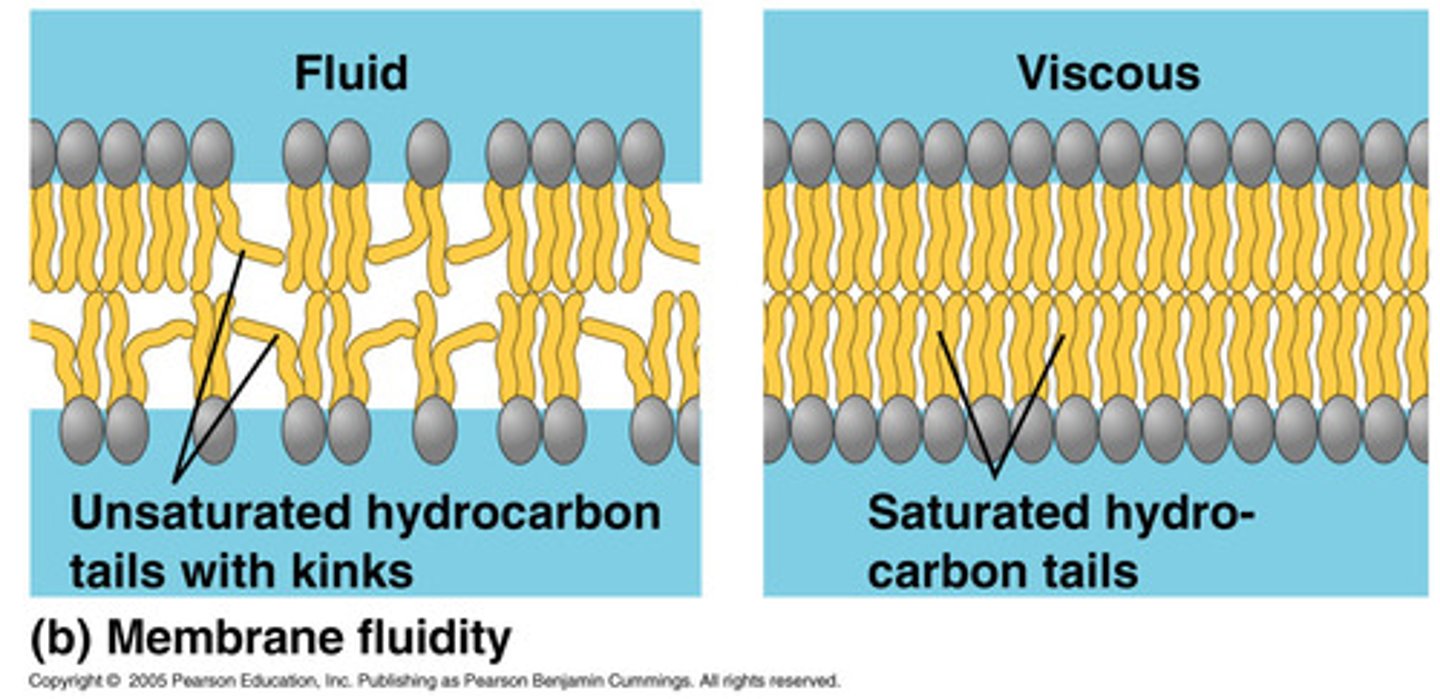
What is the difference btwn. saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbon tails?
saturated = straight
unsaturated = kink
- cis double bond creates a BEND
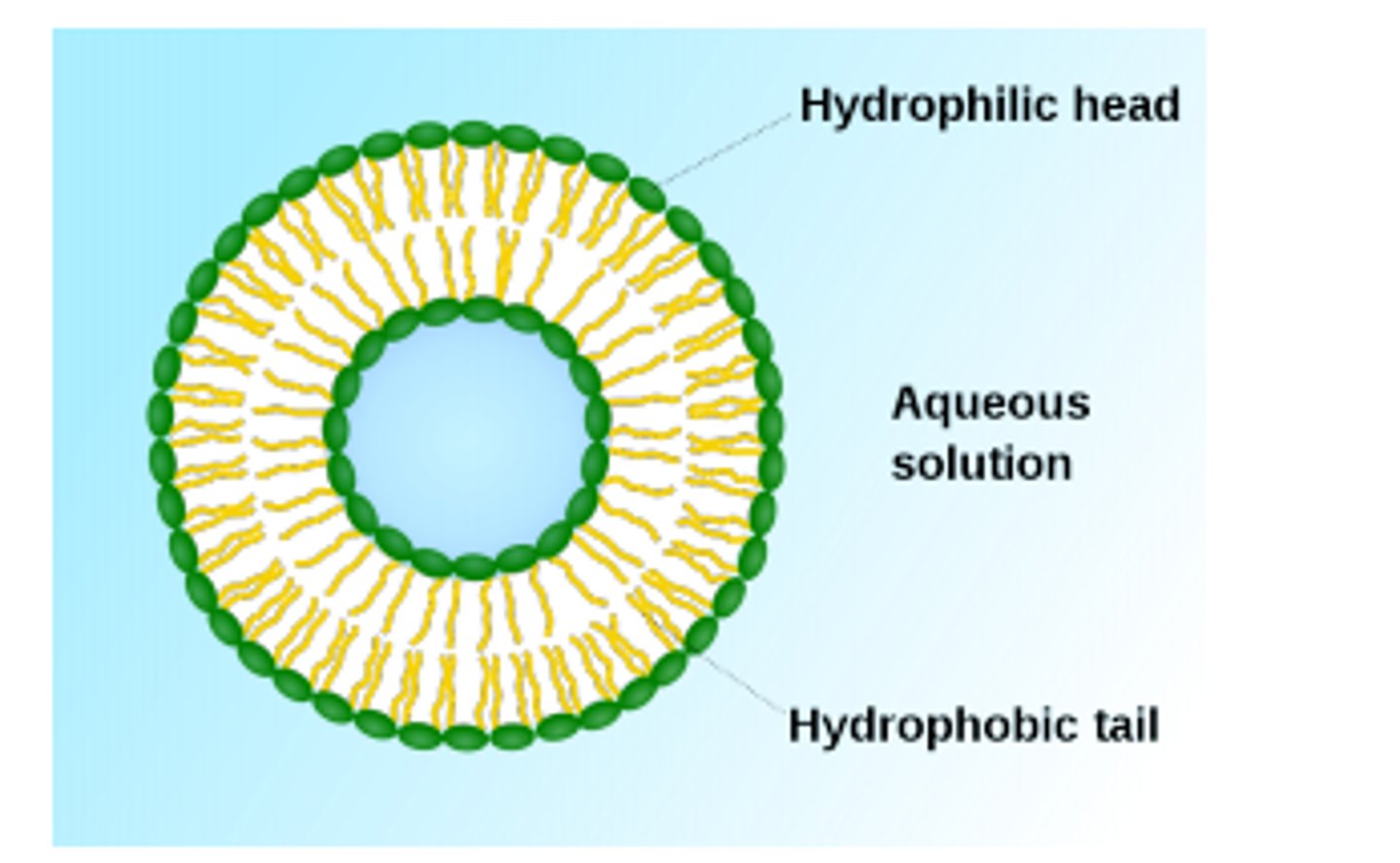
What are liposomes?
artificial closed-lipid bilayer circles for favourable composition (tails hiding)
- for when the aq. environment is inside and outside
What are the 3 functions of liposomes?
1. Studying diff. lipid fn's.
2. Studying diff. protein fn's.
3. Drug delivery through membrane
What is live cell imaging?
studying cells by using laser tweezers to move the membrane
- membrane is flexible = no damage
What are the 4 ways a phospholipid can move?
1. Lateral diffusion (moving sideways)
2. Rotating (left & right)
3. Flexing (wiggling tails)
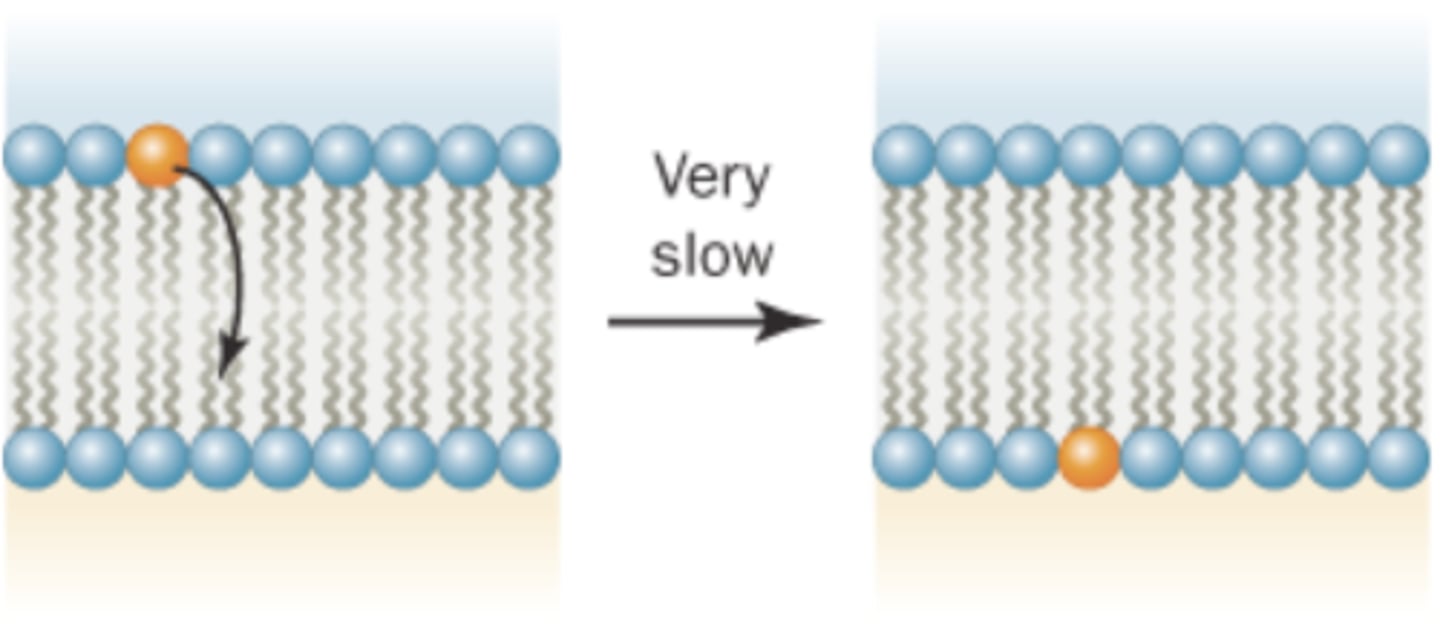
4. Flip-flop (moving to another leaflet)
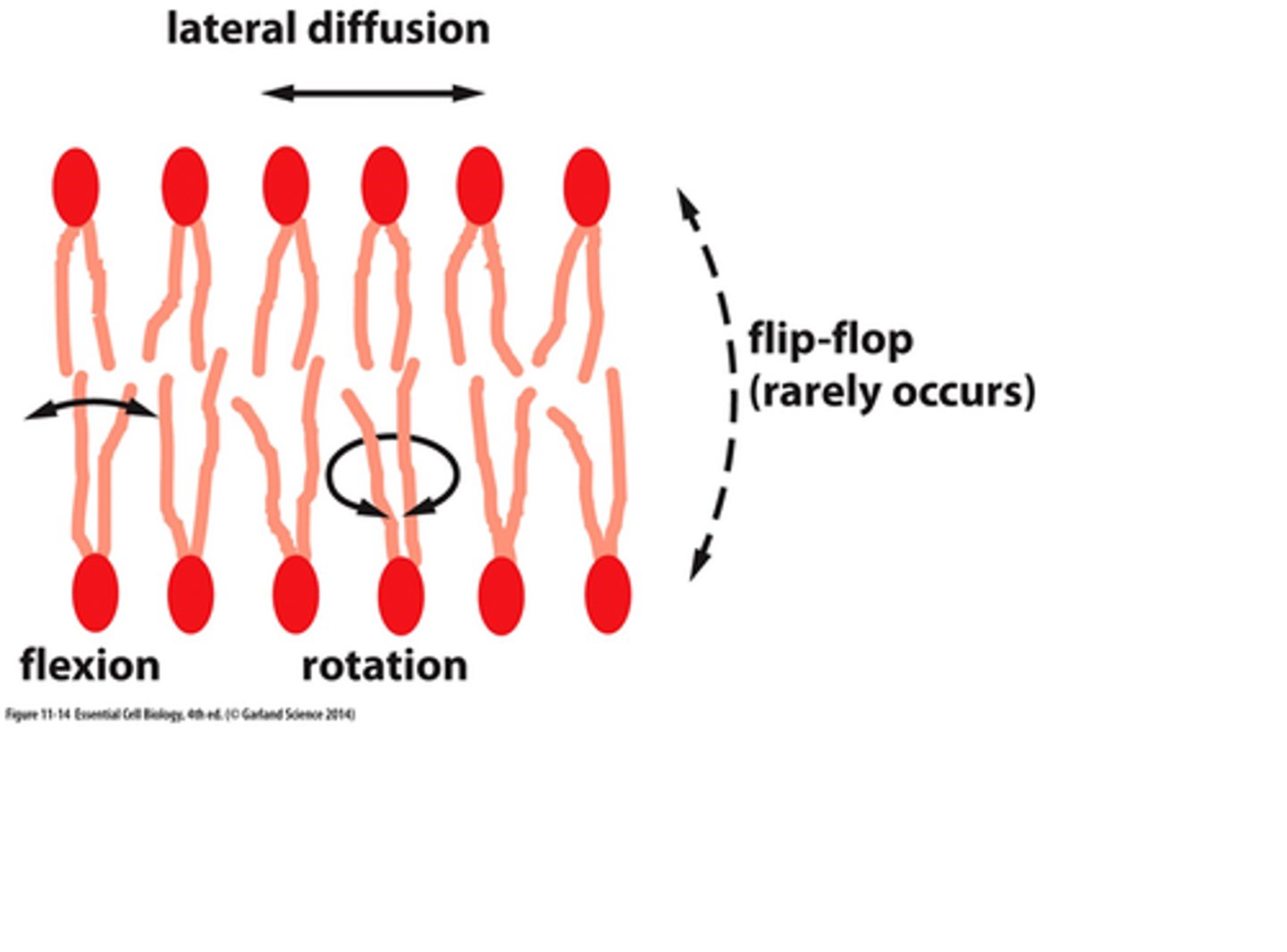
Why does flip-flop rarely occur?
head has to move through unfavourable conditions (hydrophobic core) to switch to the other leaflet
What are the 2 factors affecting membrane fluidity/flexibility?
1. Temperature
2. Composition
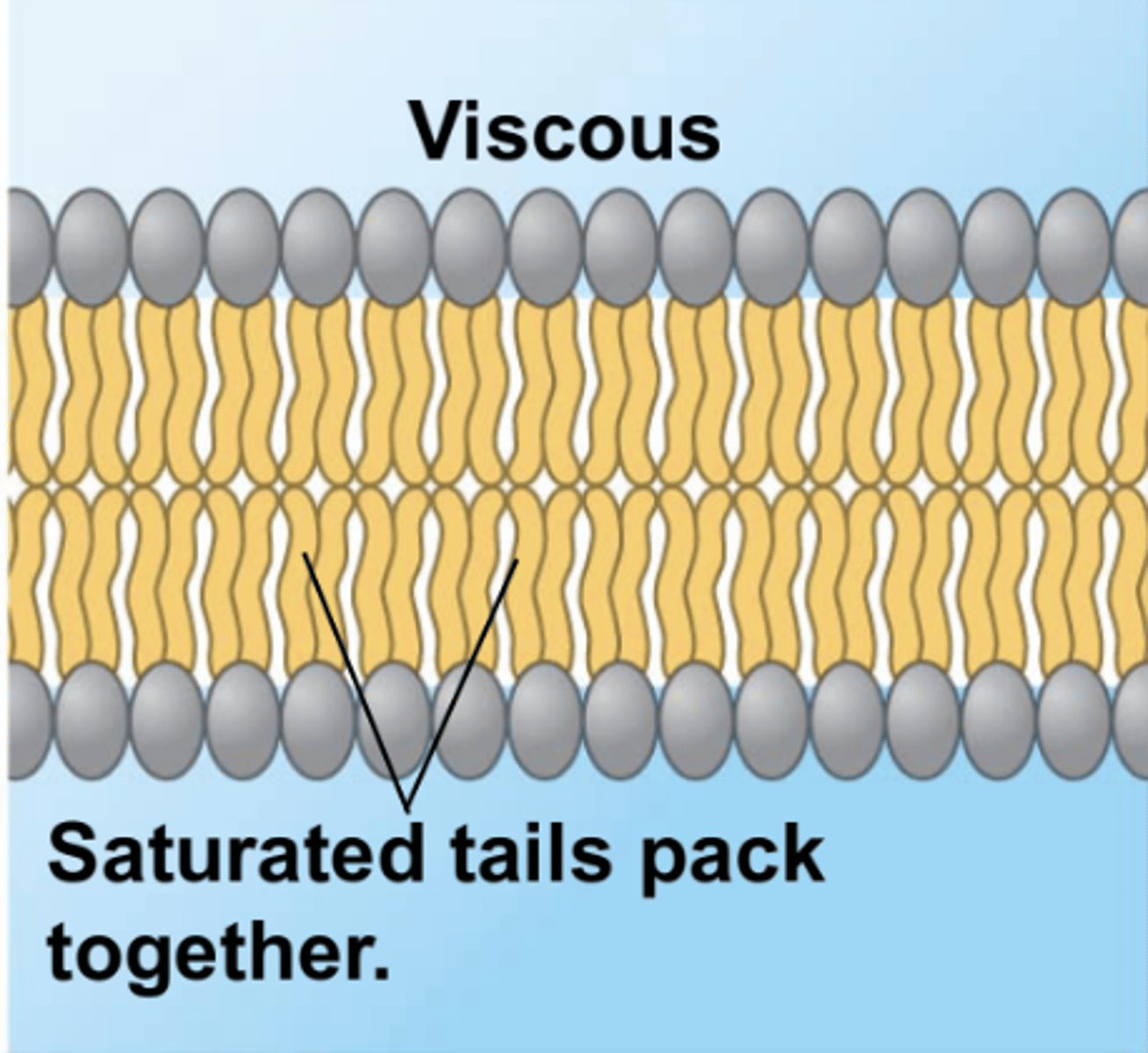
How do lower temperatures affect a membrane?
too cold = stiff (viscous)
- less fluid!
What are the 3 compositions that affect membrane fluidity?
1. Saturation
2. Tail length
3. Lipid composition
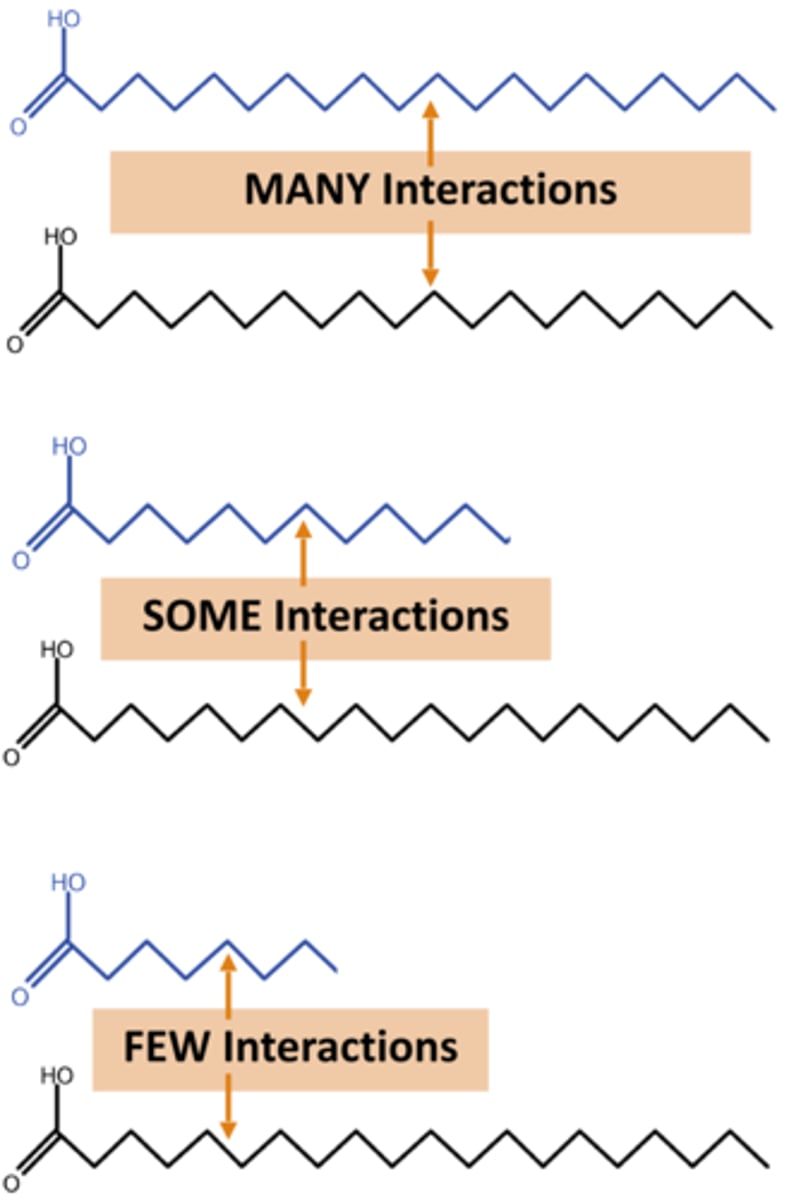
How does saturation affect a membrane?
unsaturation with KINKS increases fluidity
- helps w lower temp!
saturation with more hydrophobic interaction decreases fluidity
How does tail length affect a membrane?
short tails = less tail interaction
- more fluidity!
How does lipid composition affect a membrane?
hydrophobic CHOLESTEROL added fills in empty spaces btwn. lipids = decreased fluidity
- great for stability!
- membrane becomes less permeable to polar molecules
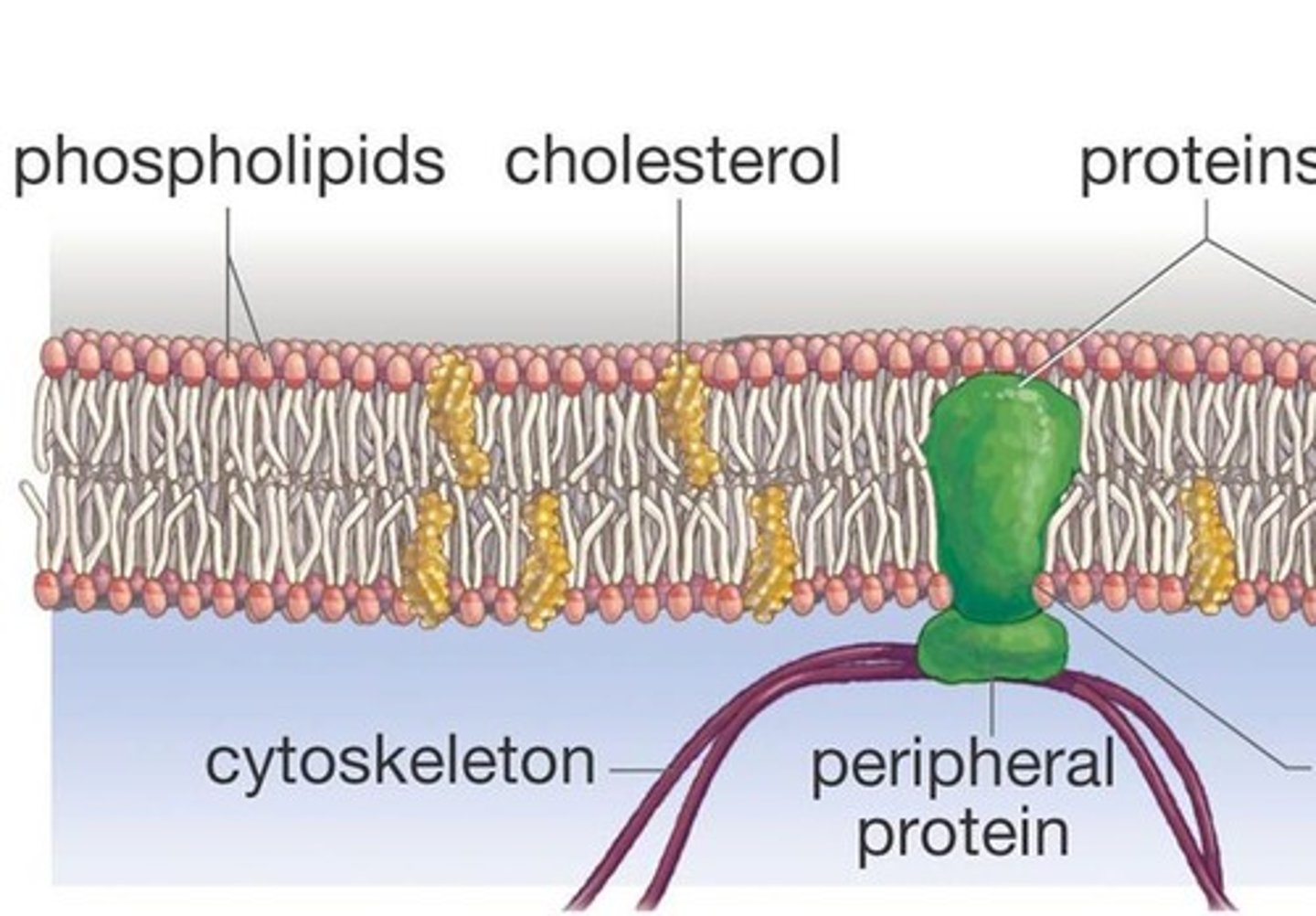
What ratio of cholesterol and phospholipids can there be?
1:1
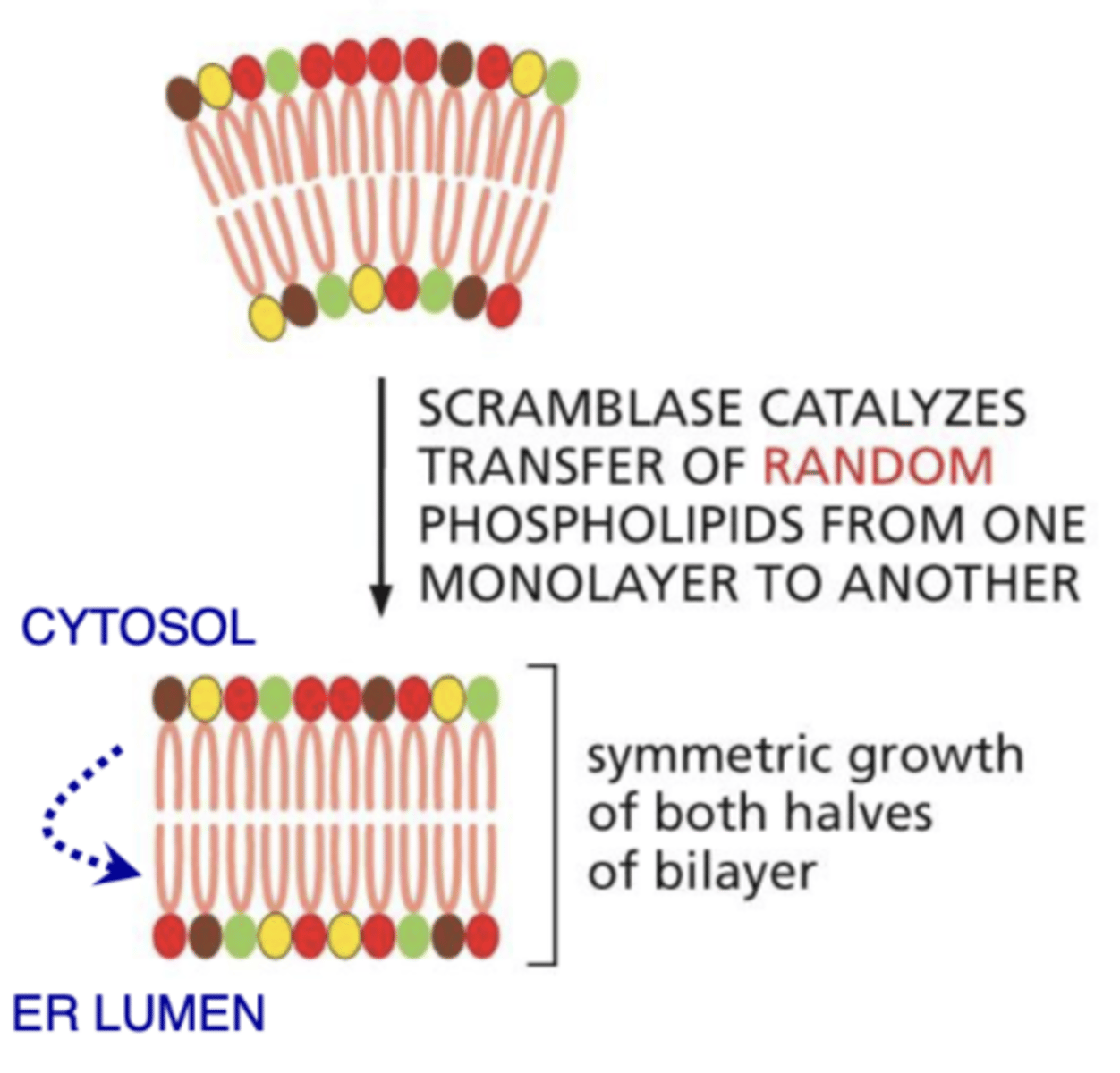
What is the enzyme in the ER membrane needed for flip-flop?
Scramblase
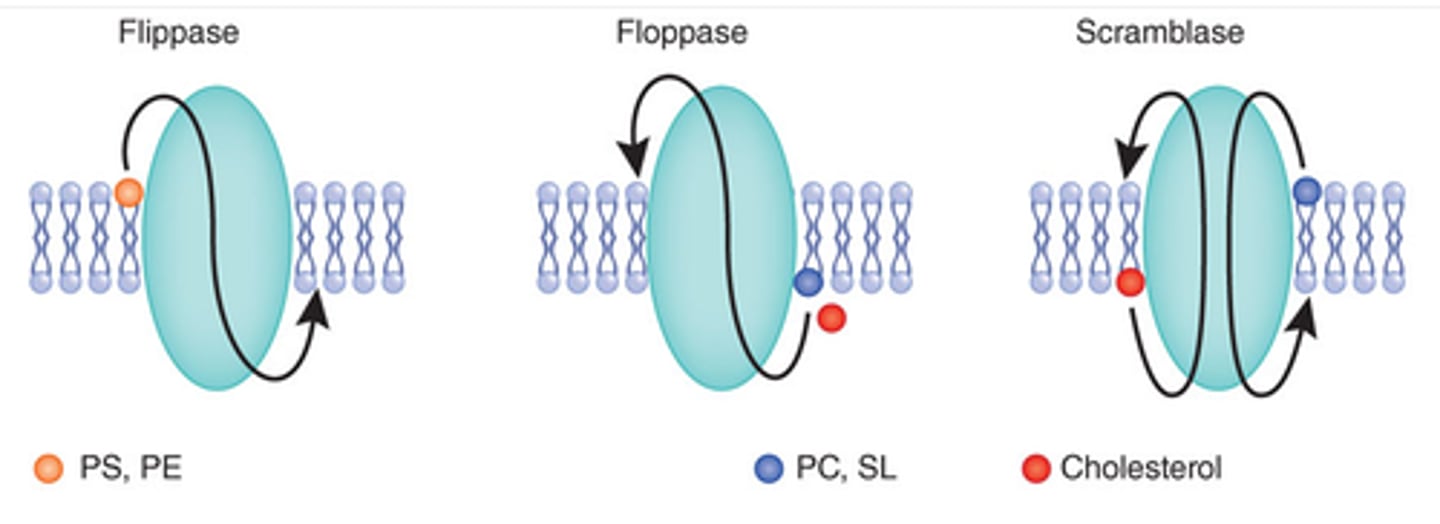
What does scramblase do?
RANDOMLY moves lipids from one leaflet to the other
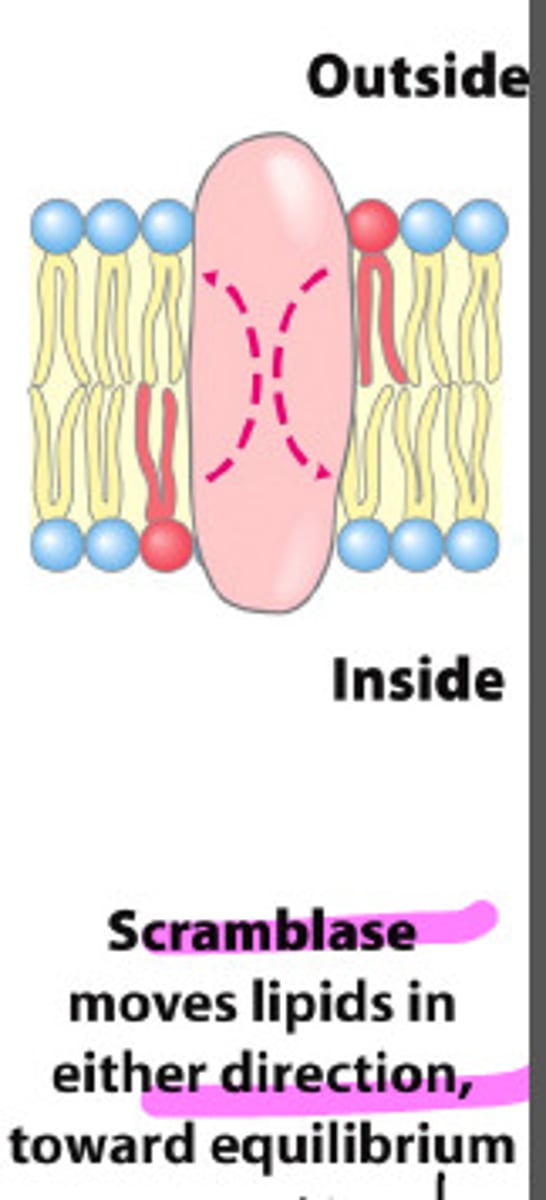
Why is scramblase needed?
phospholipids are made in cytosolic side of ER = imbalance
- scramblase balances halves!
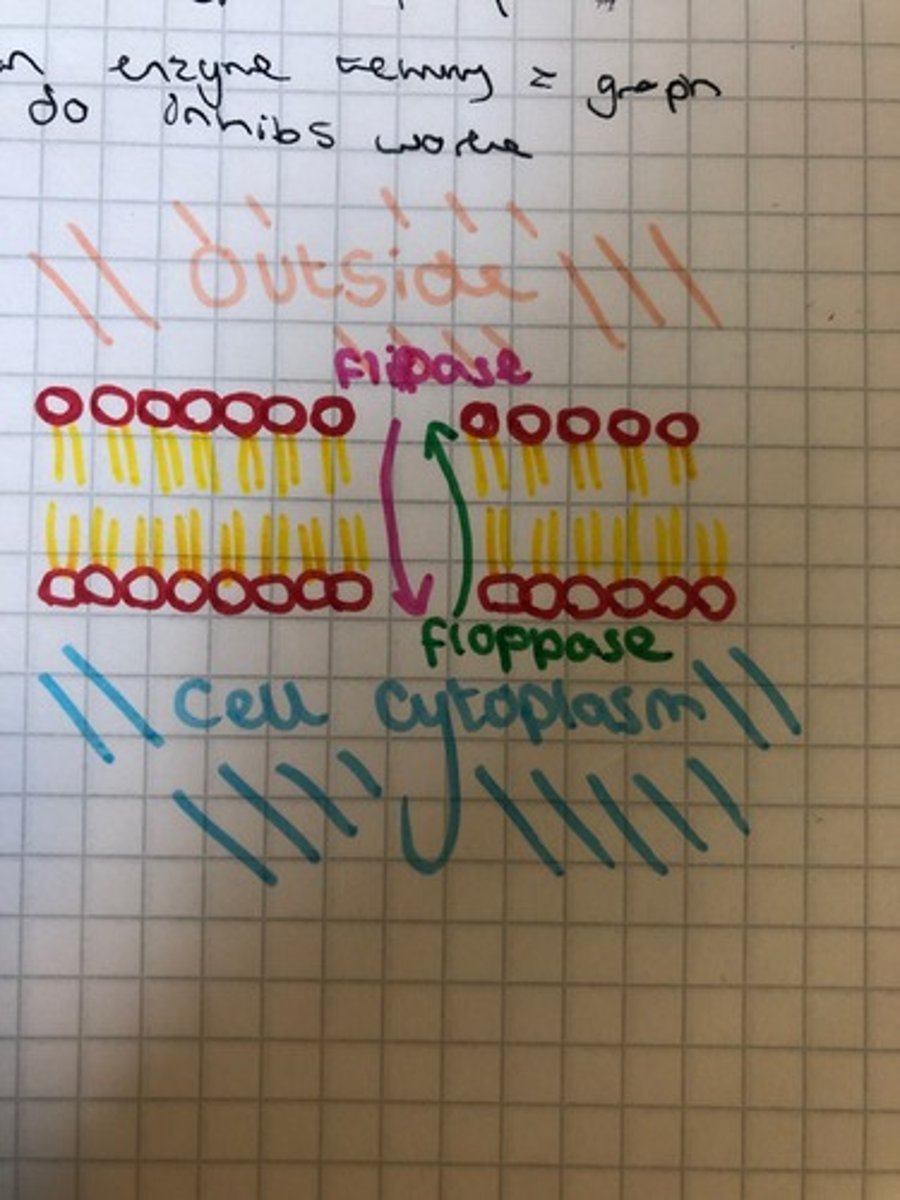
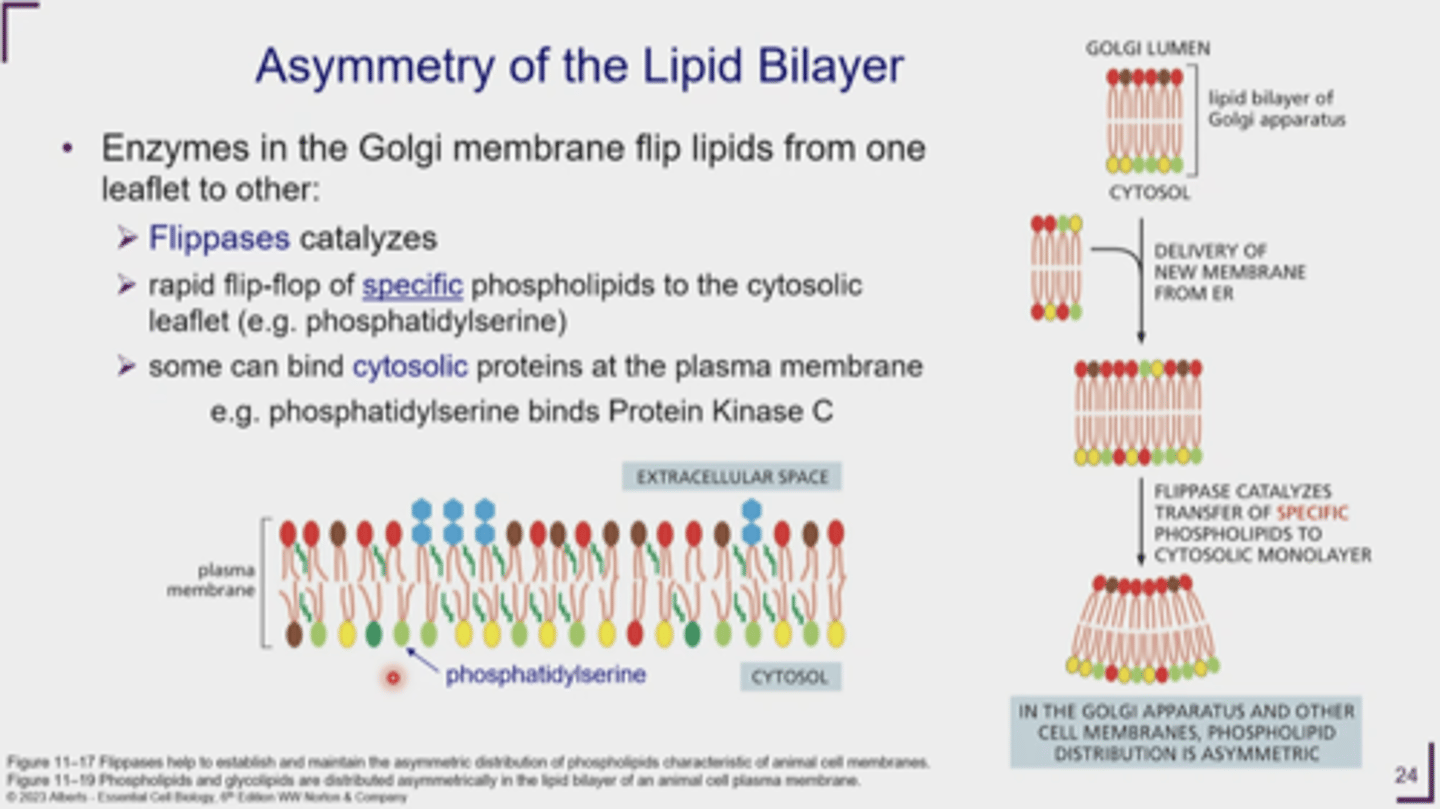
What is the enzyme in the Golgi membrane needed for flip-flop?
Flippase
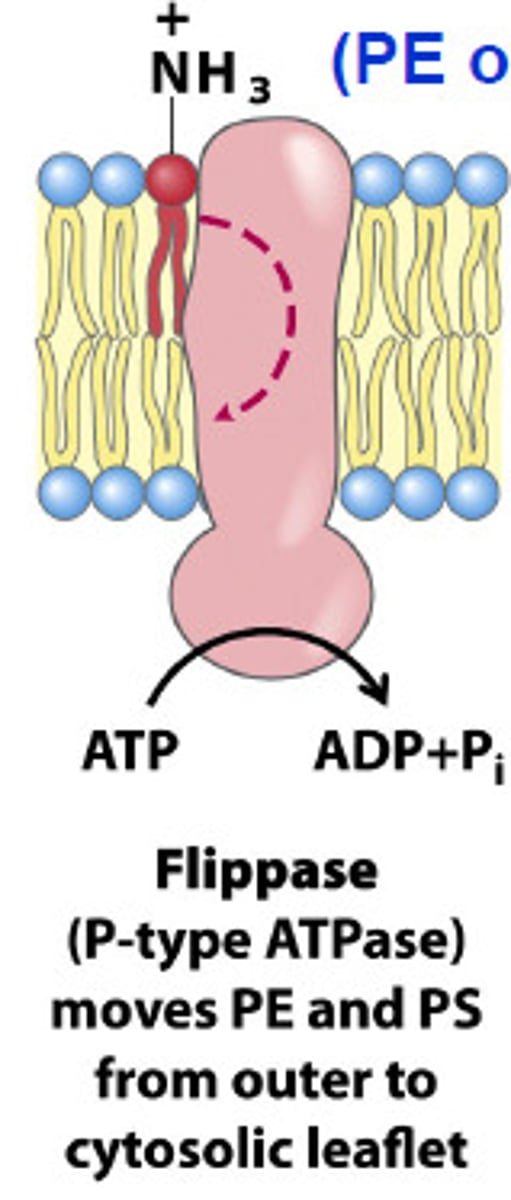
What does flippase do?
SELECTS lipids to move to the CYTOSOLIC leaflet
- ex. phosphatidylserine
Why is flippase needed?
new membranes from the ER are added to membrane = lipids must be organized to correct leaflet
Why should phosphatidylserine be in the cytosolic leaflet?
binds to Protein Kinase C
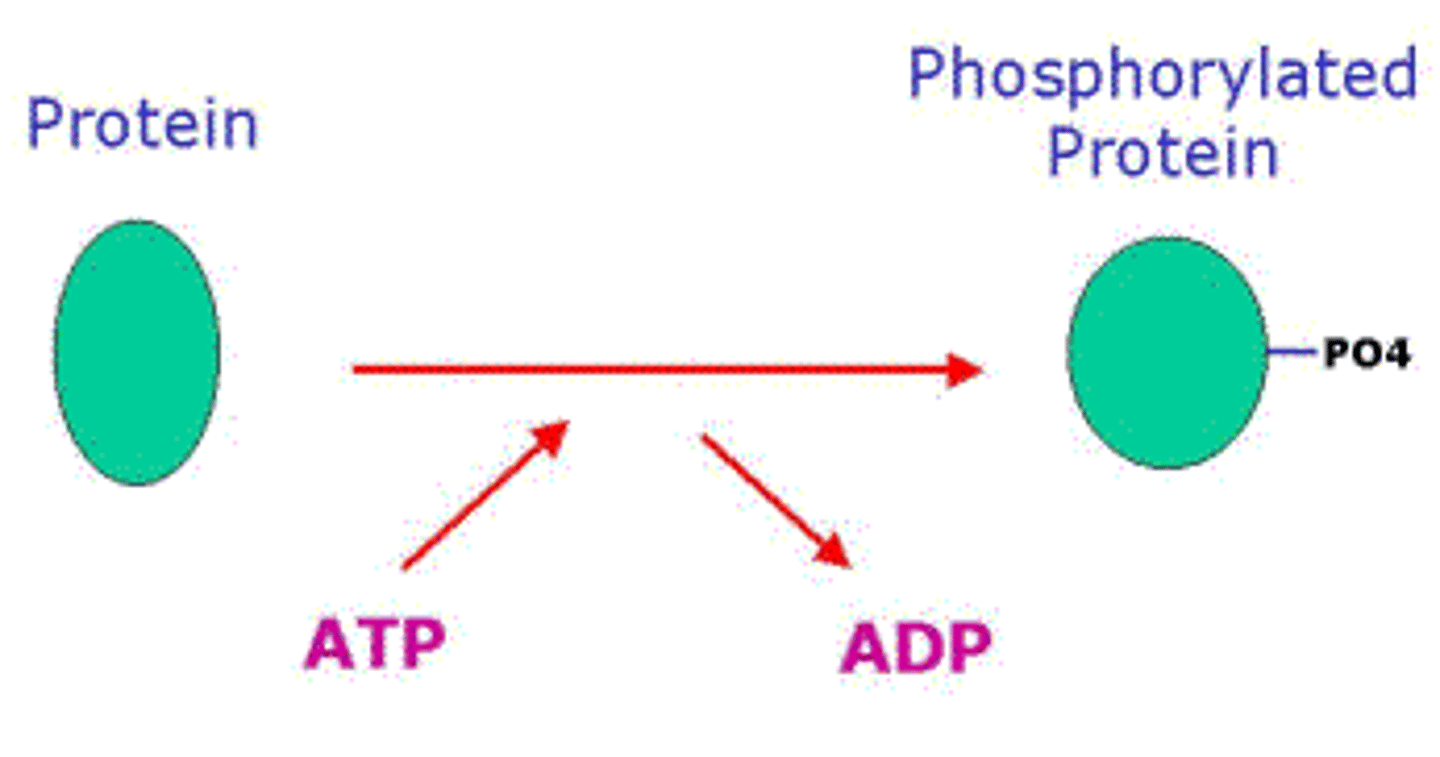
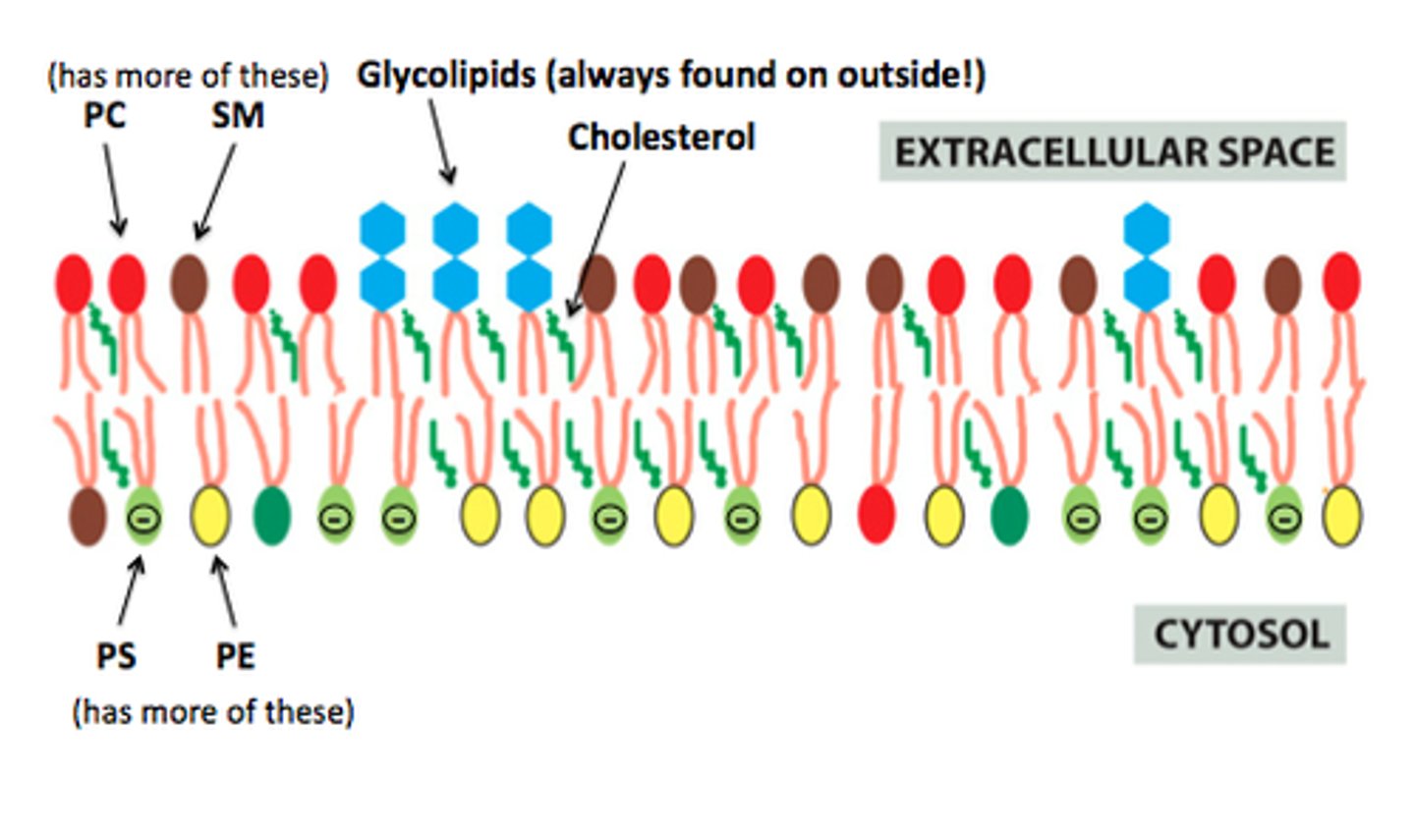
What orientation is phospholipid distribution and the lipid bilayer itself?
asymmetric
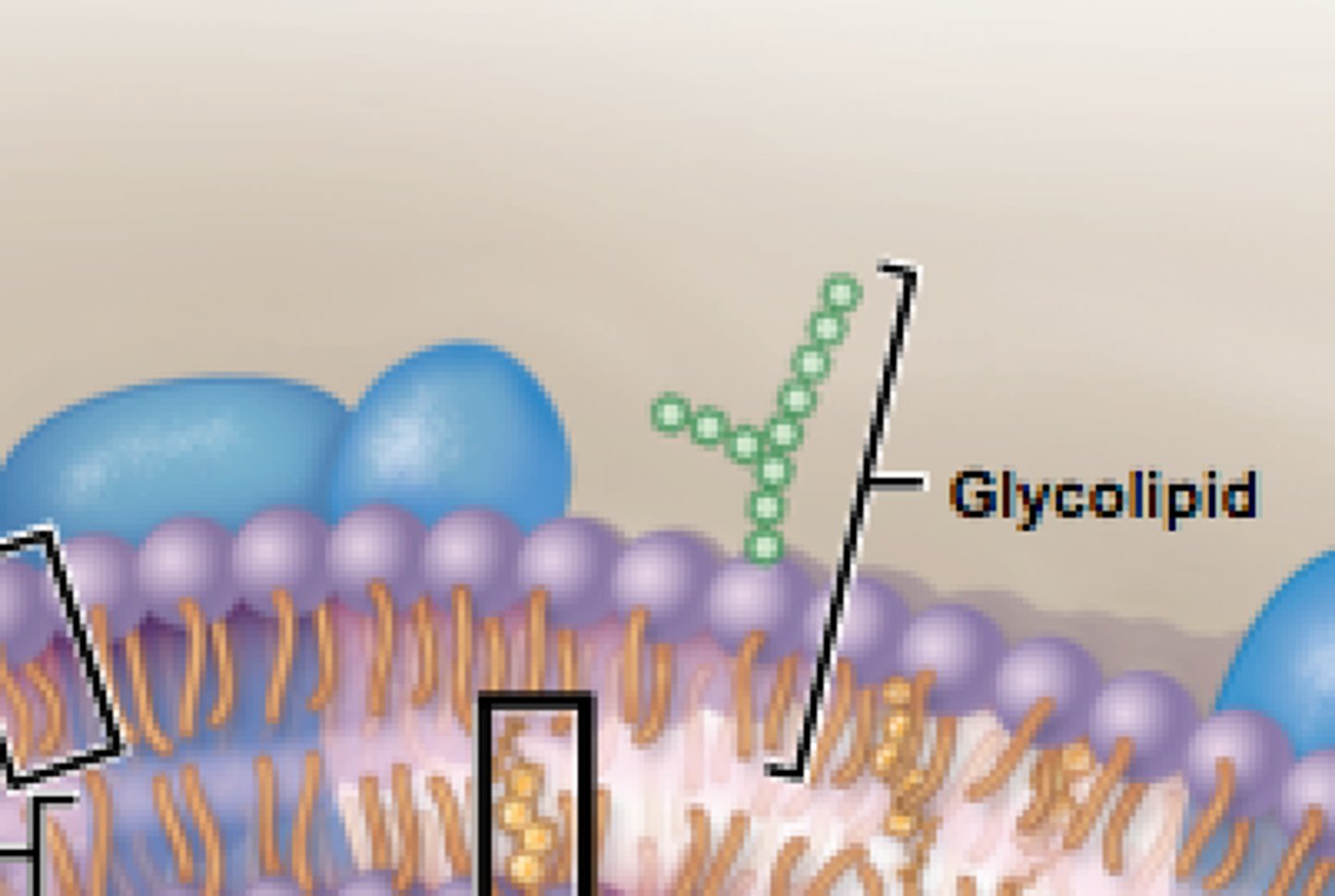
How are glycolipids and glycoproteins formed?
adding sugar groups to lipids/proteins on LUMEN-facing leaflet of GOLGI membrane
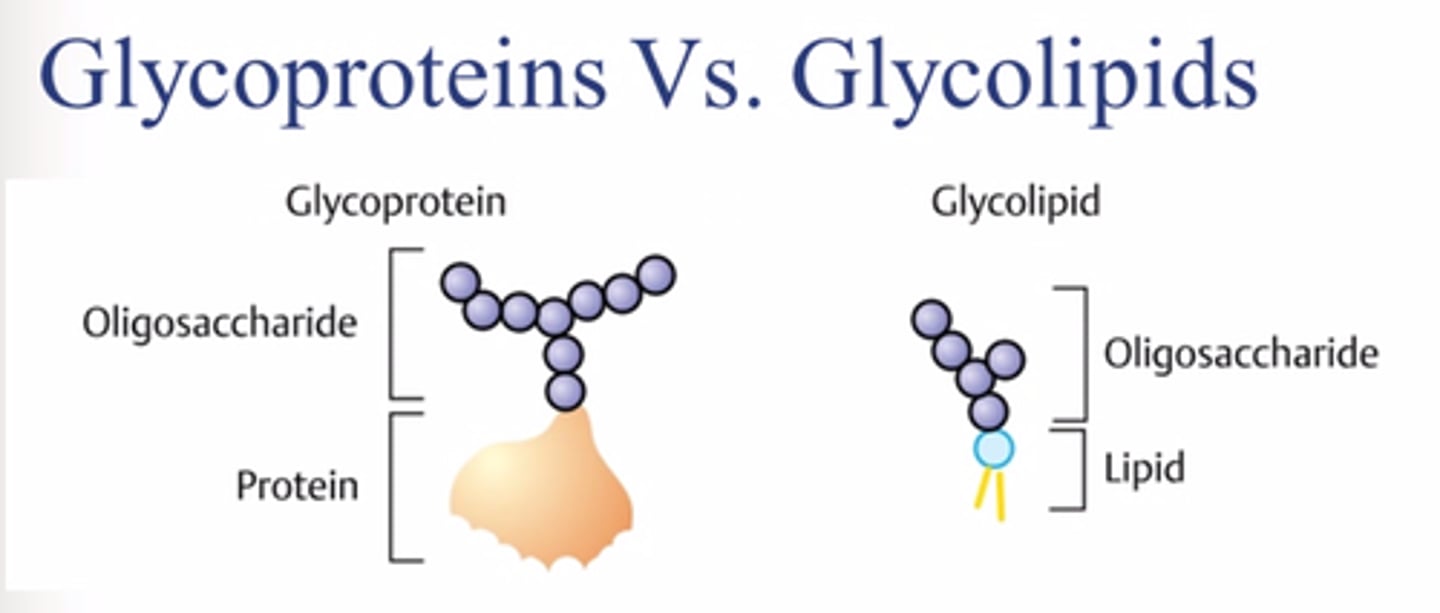
Where are the 2 places glycolipids/glycoproteins end up in?
1. Plasma membrane (outside facing extracellular fluid)
2. Inside organelles (facing lumen)