Test 4 - Eyeball Parts and Functions
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
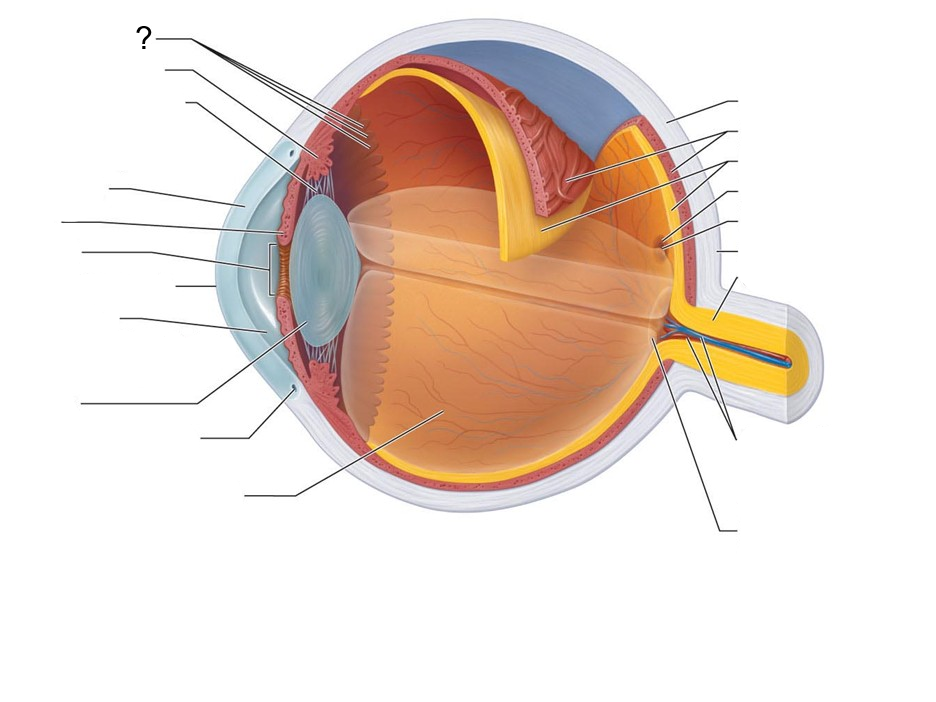
What structure is this?
Ora Serrata
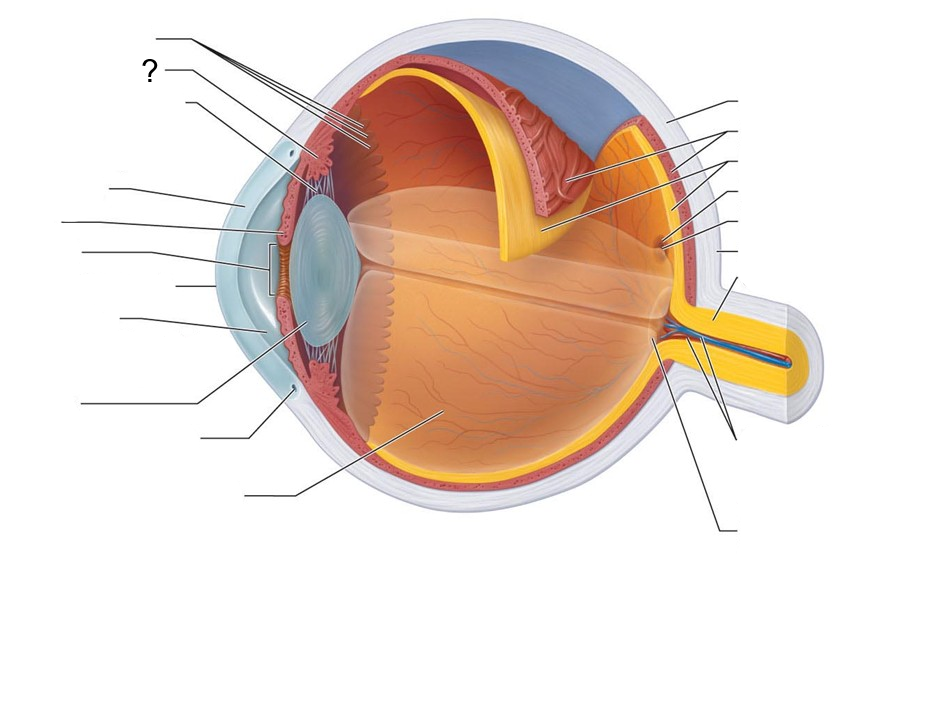
What structure is this?
Ciliary body
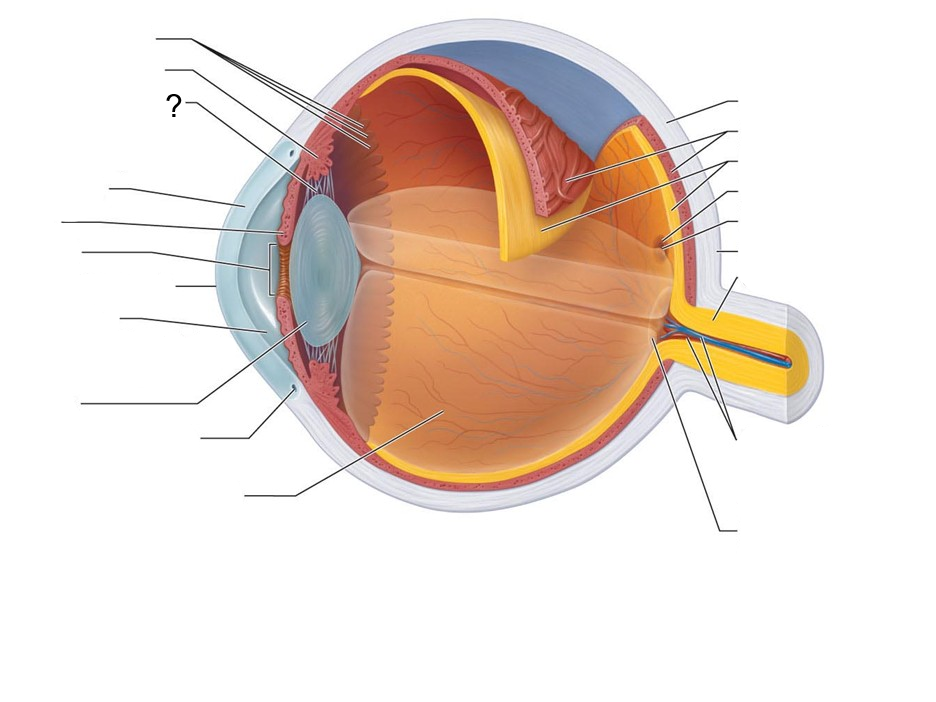
What structure is this?
Ciliary Zonule (suspensory ligament)
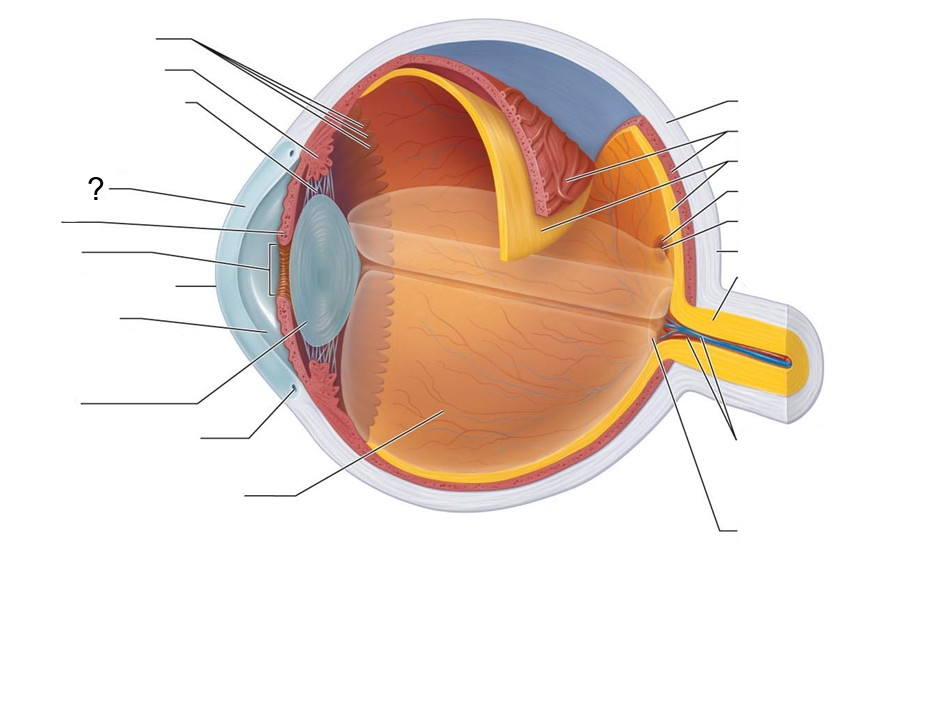
What structure is this?
Cornea
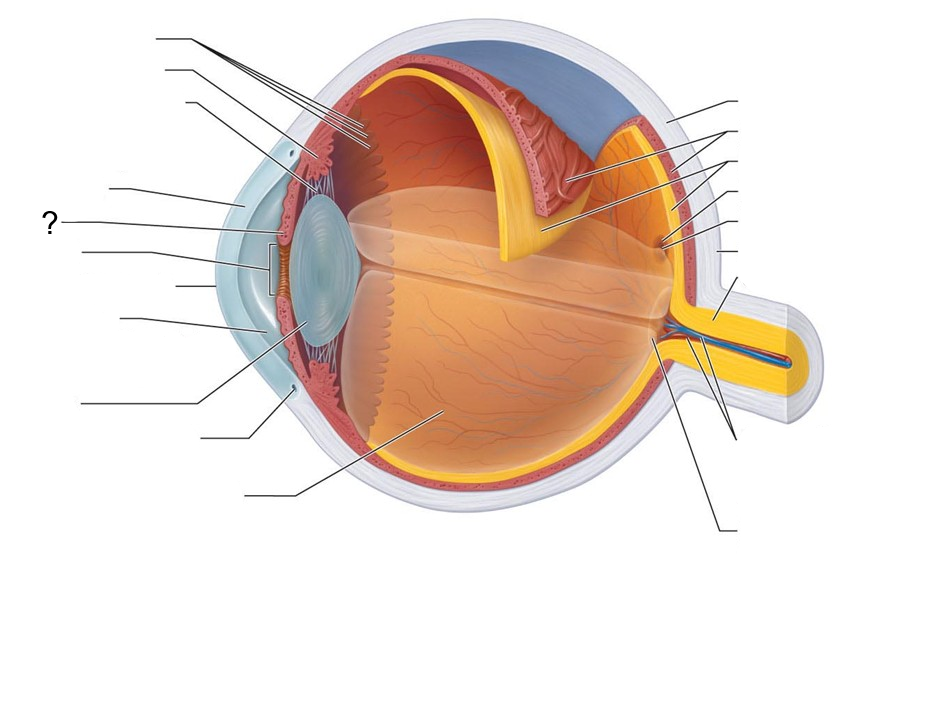
What structure is this?
Iris
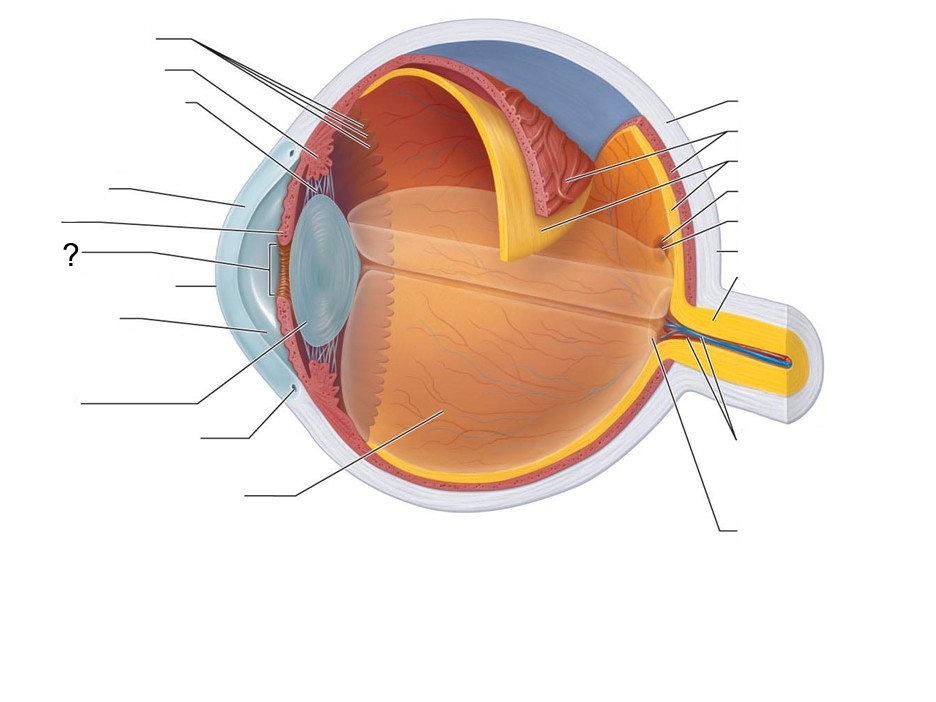
What structure is this?
Pupil
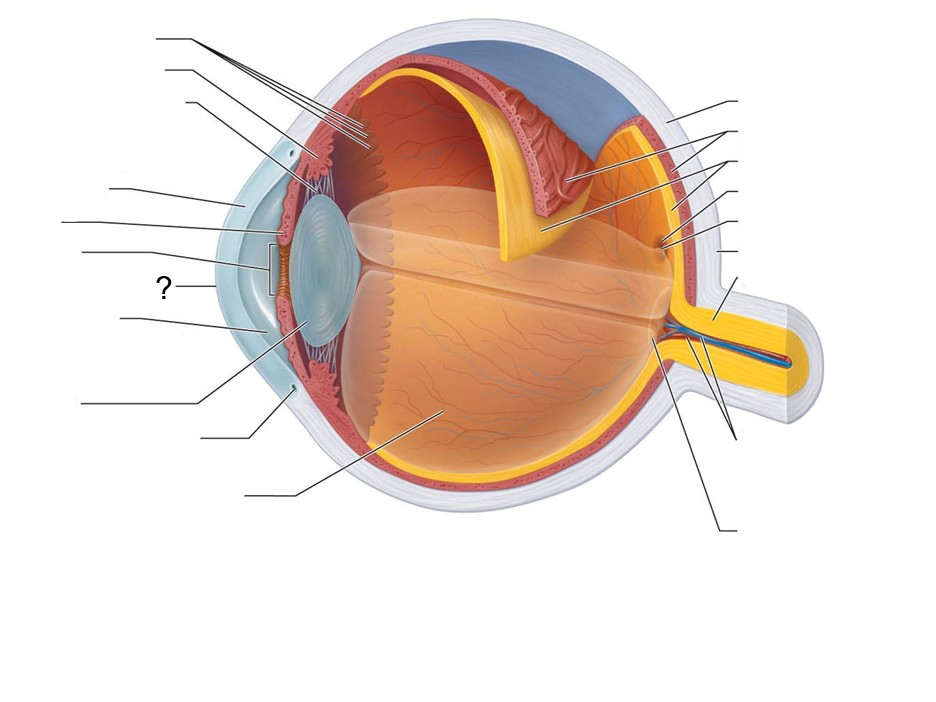
What structure is this?
Anterior Pole
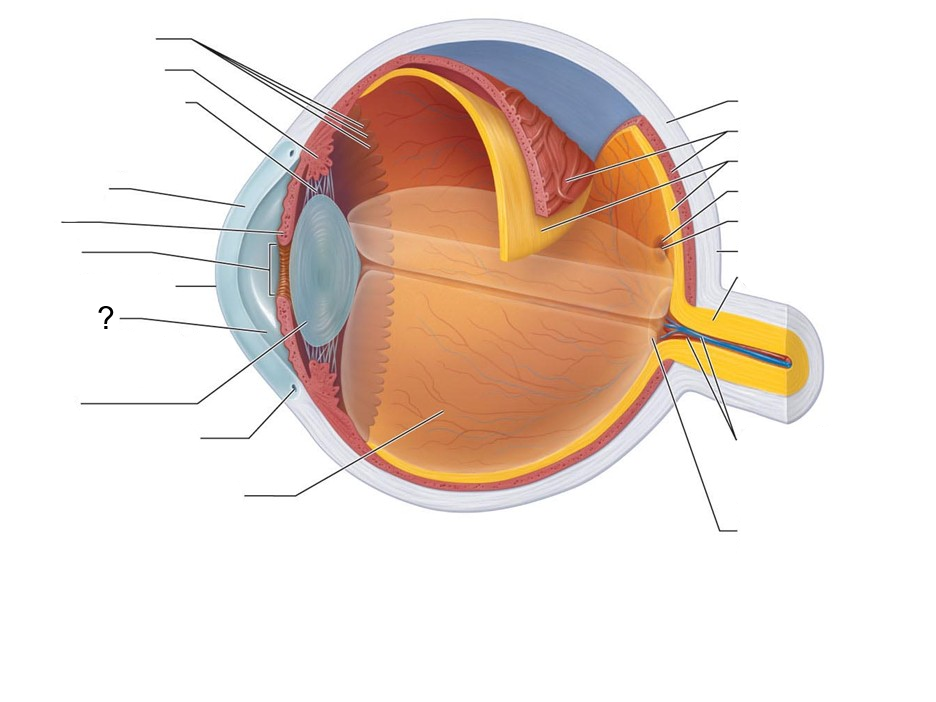
What structure is this?
Anterior Segment (contains aqueous humor)
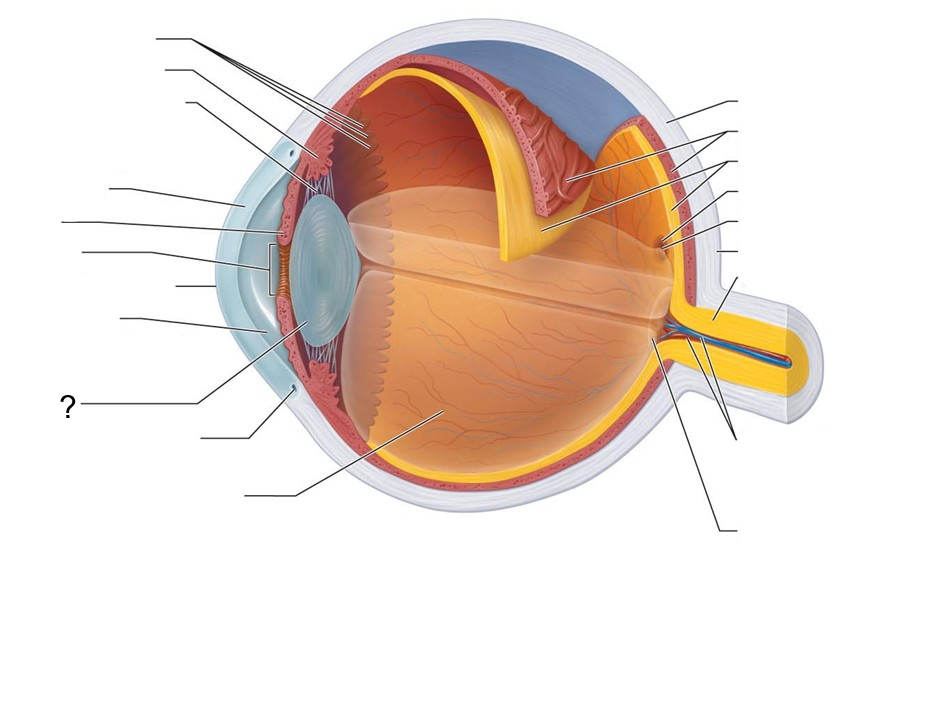
What structure is this?
Lens
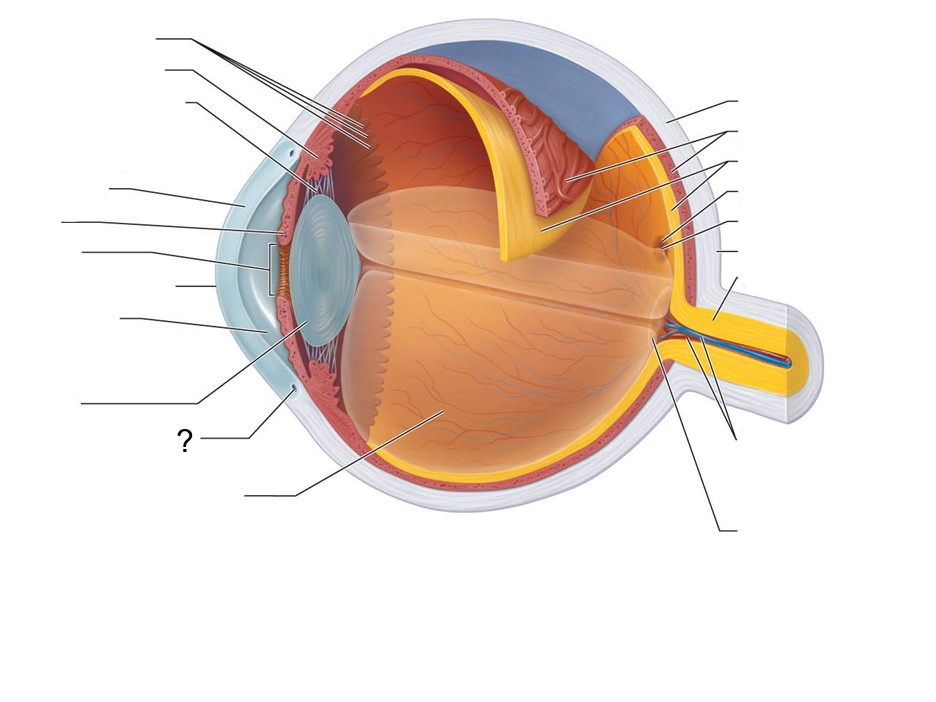
What structure is this?
Scleral Venous Sinus
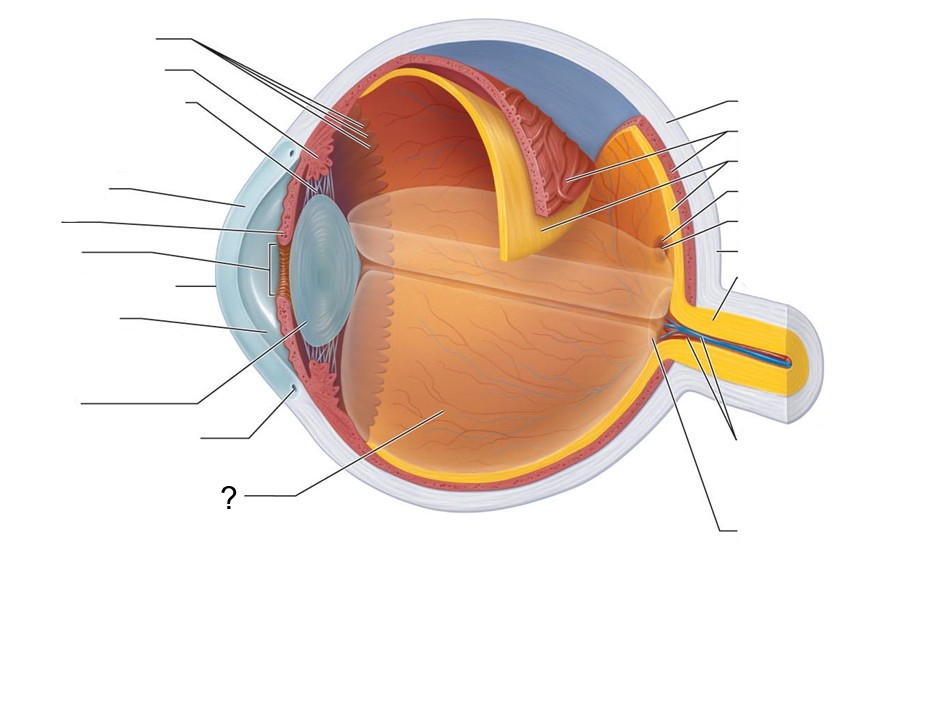
What structure is this?
Posterior Segment (contains Vitreous humor)
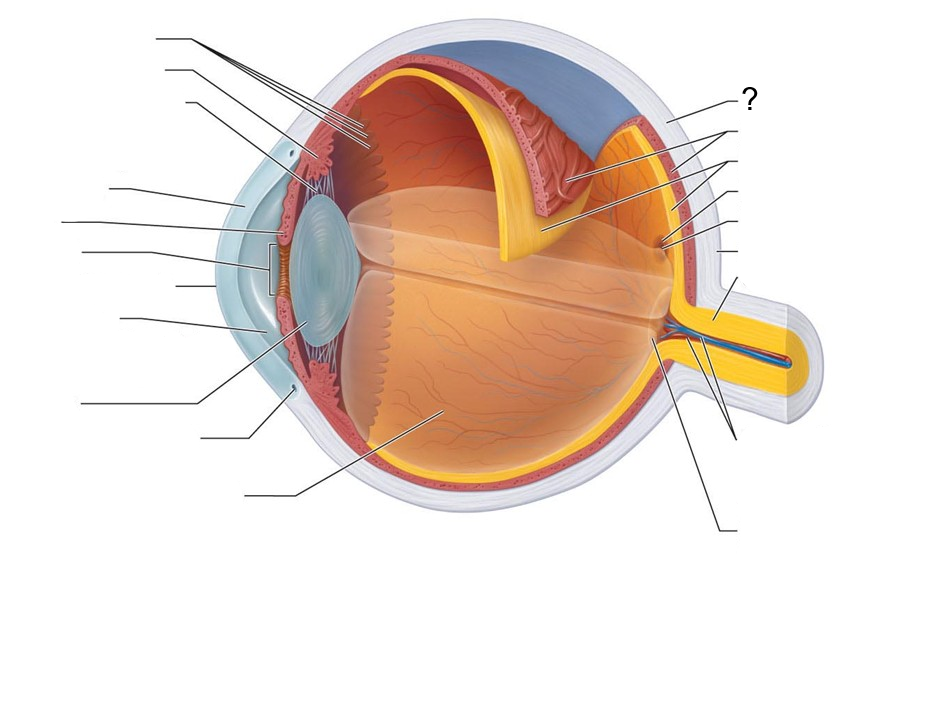
What structure is this?
Sclera
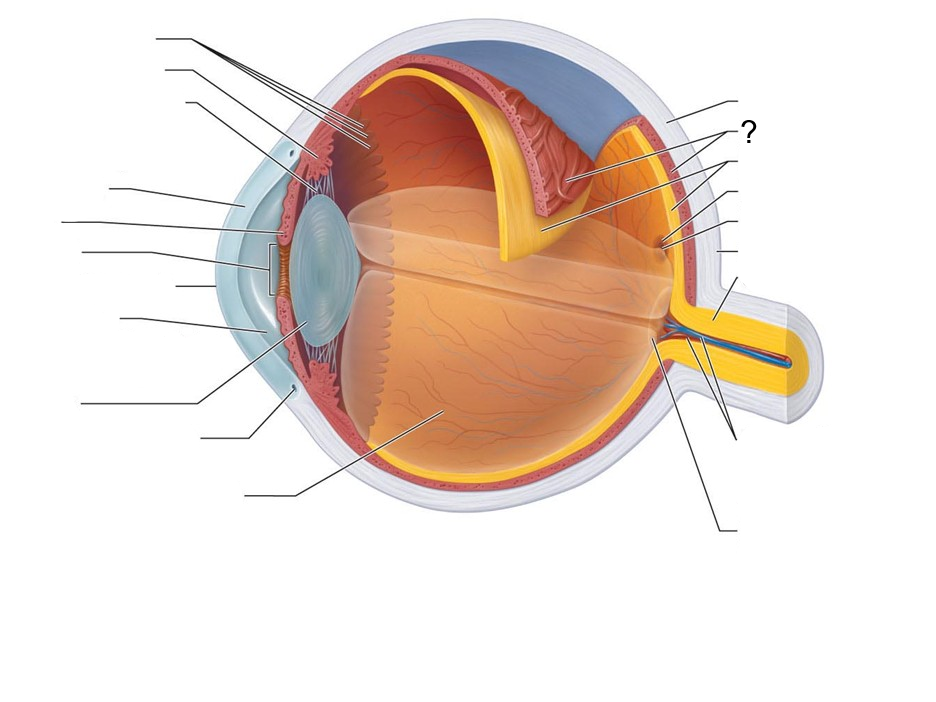
What structure is this?
Choroid
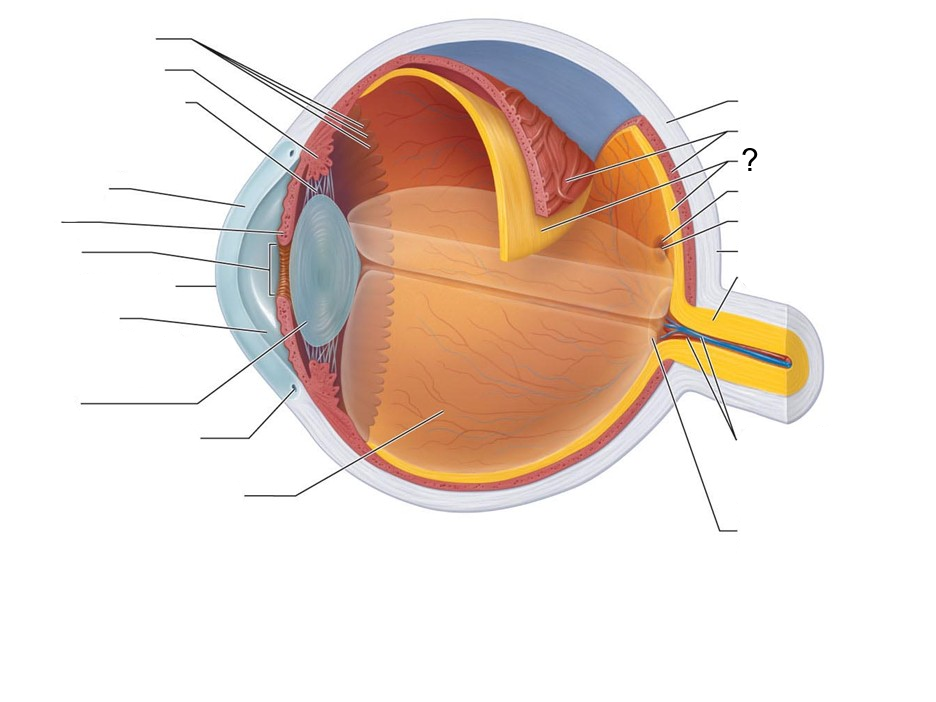
What structure is this?
Retina
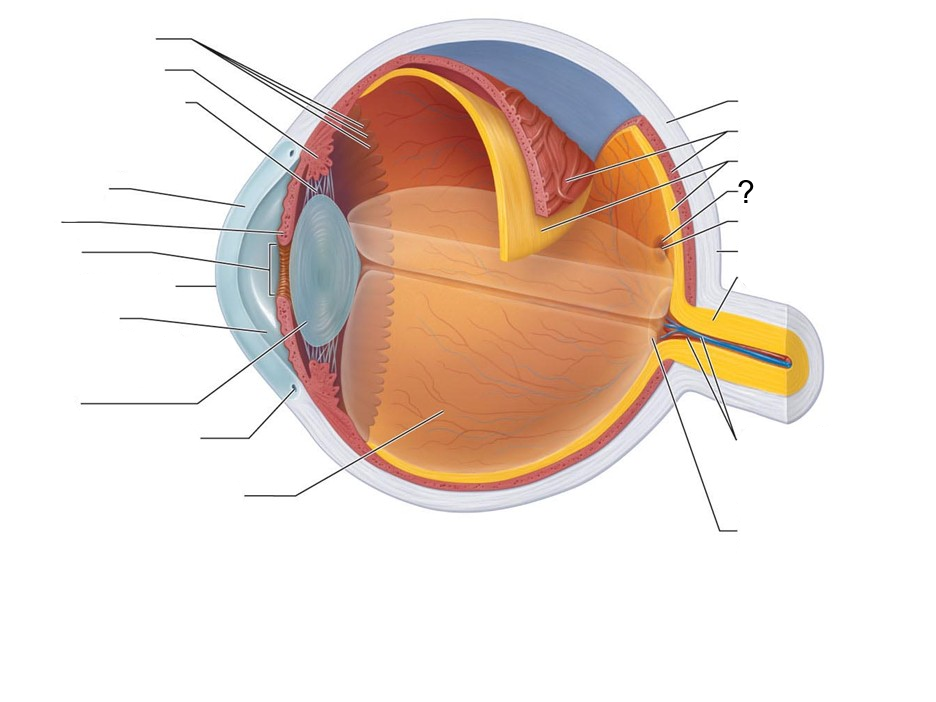
What structure is this?
Macula Lutea
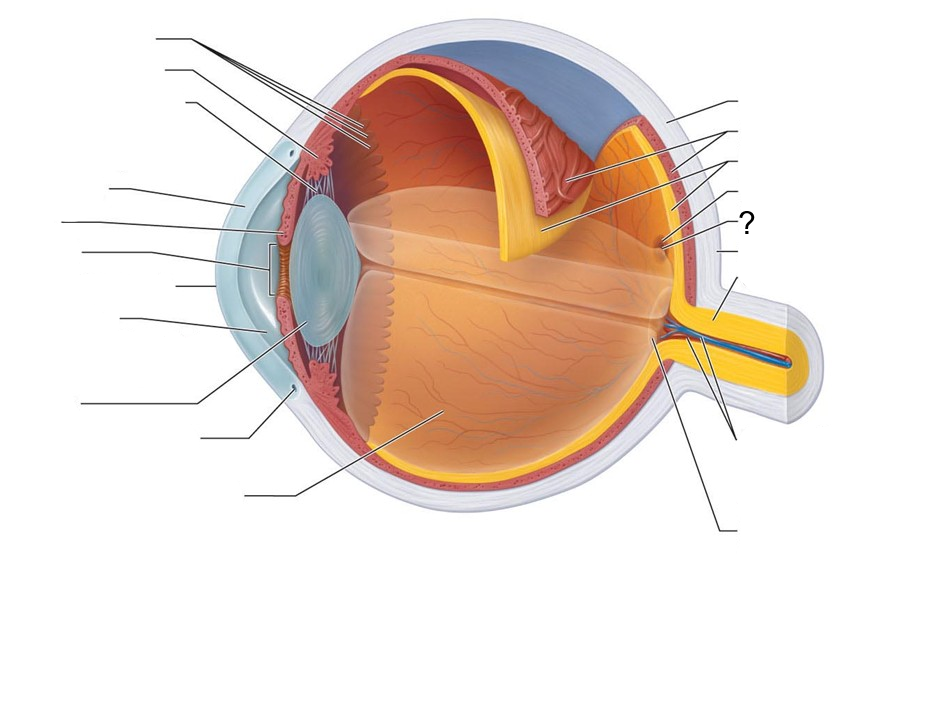
What structure is this?
Fovea Centralis
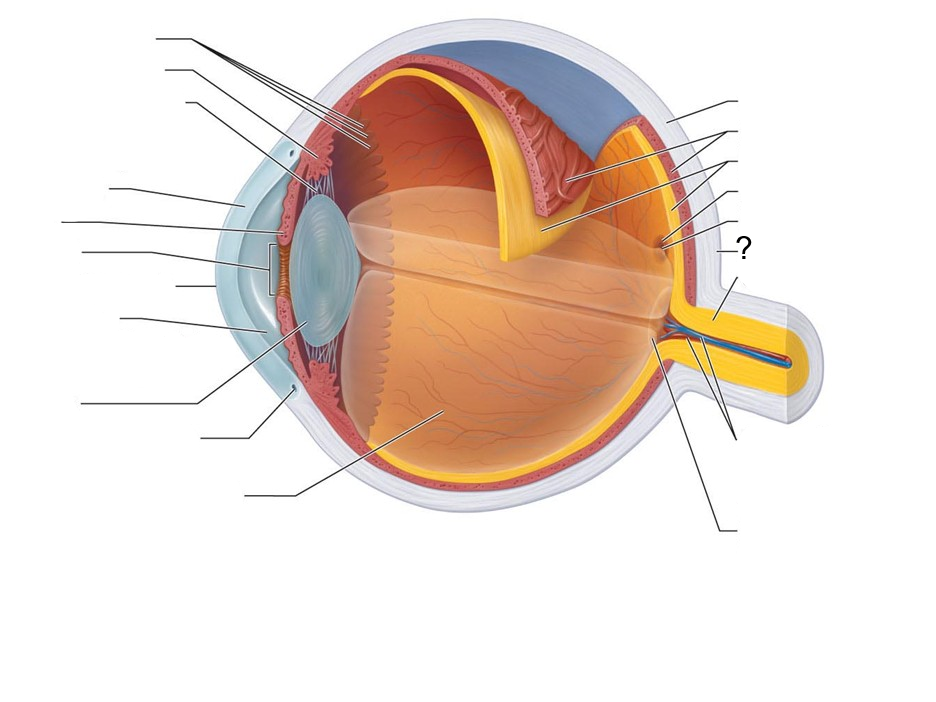
What structure is this?
Posterior Pole
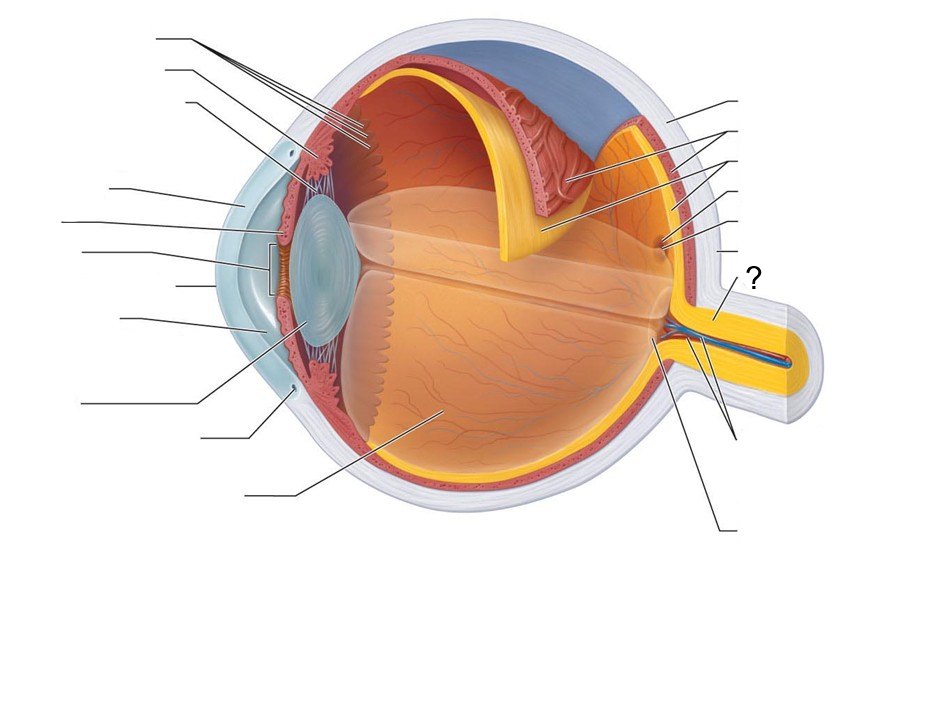
What structure is this?
Optic Nerve
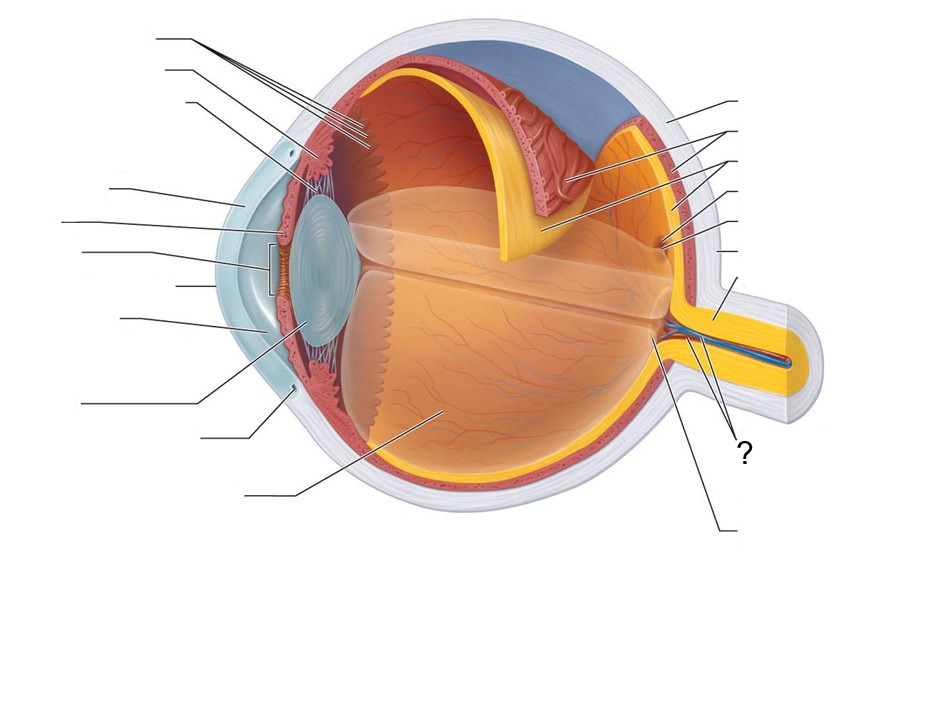
What structure is this?
Central Artery and Vein of the Retina
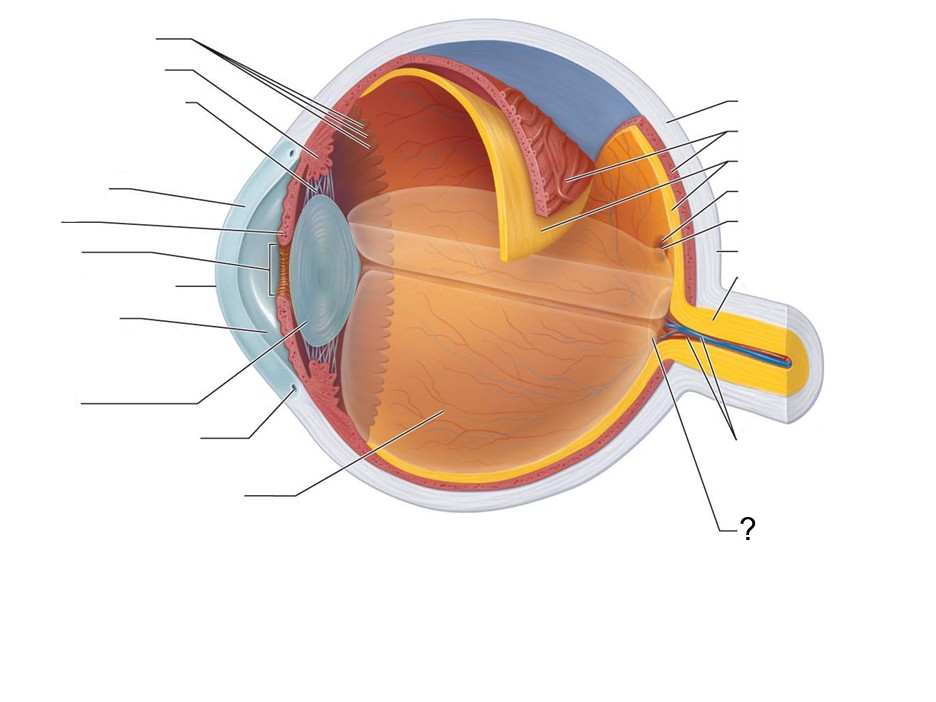
What structure is this?
Optic Disc (blind spot)
What is the function of the cornea?
It serves as a window to the eye and helps focus light rays
What is the function of the Sclera?
Serves as an attachment point for the eye muscles
White portion of the eye
What is the function of the Choroid coat?
Provides nourishment to the retina through the blood vessels it contains
covered in a dark brown pigment to absorb light
What is the function of the Ciliary body?
Suspend the lens had helps focus it
Muscular layer
What is the function of the lens?
Becomes rounder or flatter to focus light to different degrees
Supported by suspensory ligaments
What is the function of the Iris?
Regulates the amount of light entering the eye through the pupil
Muscular ring
Eye color is determined by the amount and location of brown pigment in the iris
What is the function of the Retina?
Action point of the eye
Contains the photoreceptors that detect light
Has two basic layers
What is the outer layer of the Retina?
It’s a thin, pigmented layer that is in contact with the choroids coat
What is the inner layer of the Retina?
Is the Visual, nervous layer composed of 3 principal layers of neurons:
Rods and cones - Initiate the electrical impulses (photoreceptors)
The impulses are then passed to bipolar neurons
the impulses are then passed to the ganglion neurons
Light has to go through the layers of ganglion neurons and bipolar neurons to reach the photoreceptors (rods and cones)