Human Biology I Lab: Skeletal Muscle and Joints
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
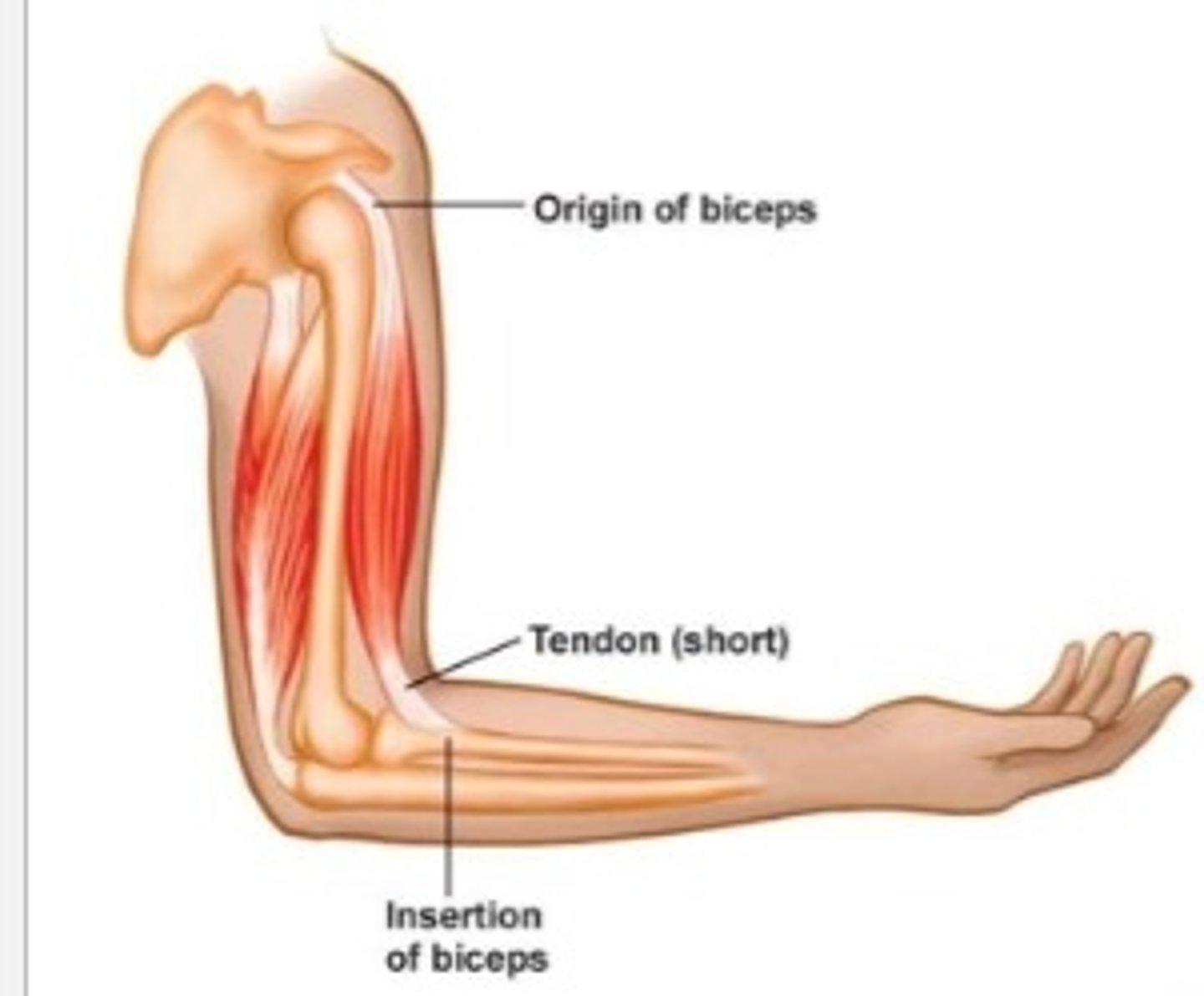
What is the origin of a muscle?
The fixed end of a muscle that remains stationary during contraction.
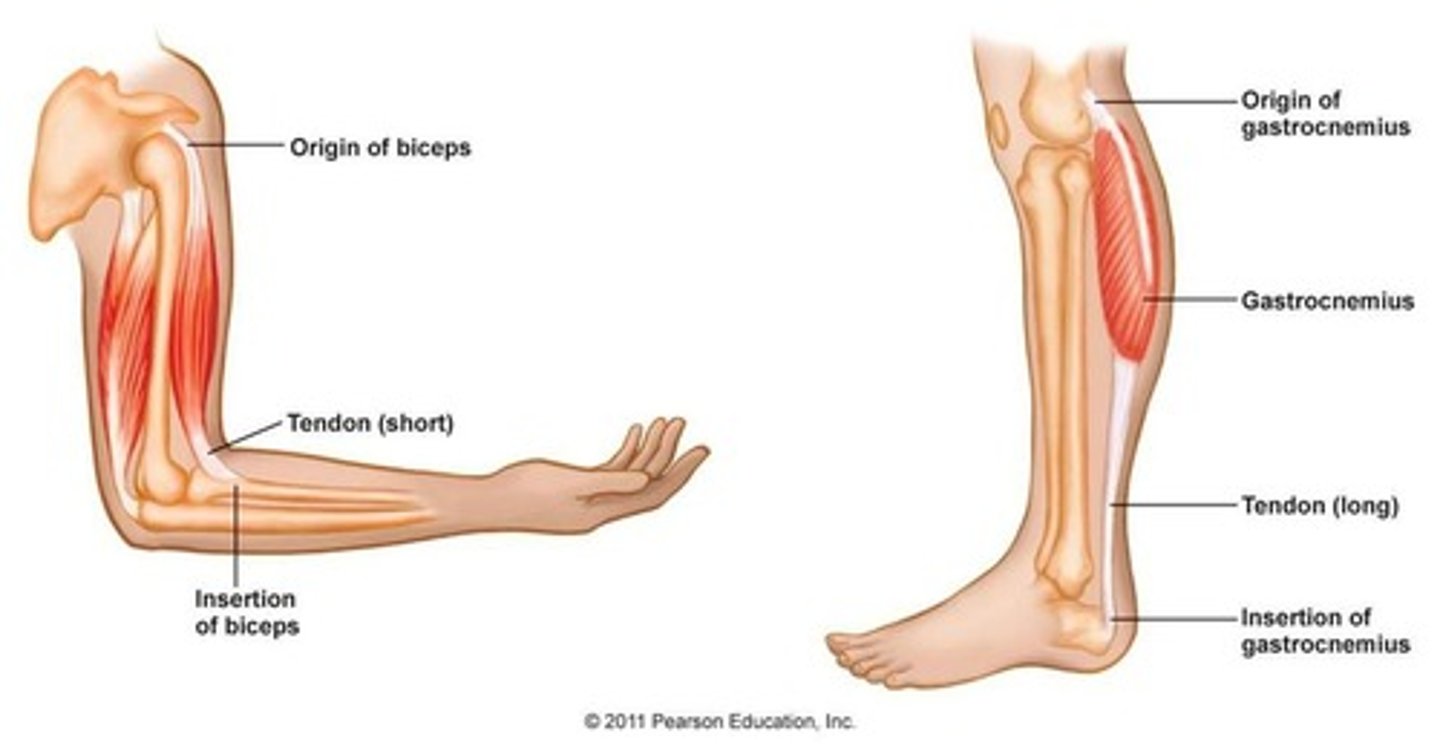
What is the insertion of a muscle?
The moveable end of a muscle that moves closer to the origin during contraction.
What type of joint is the glenohumeral joint?
Ball-and-socket joint.
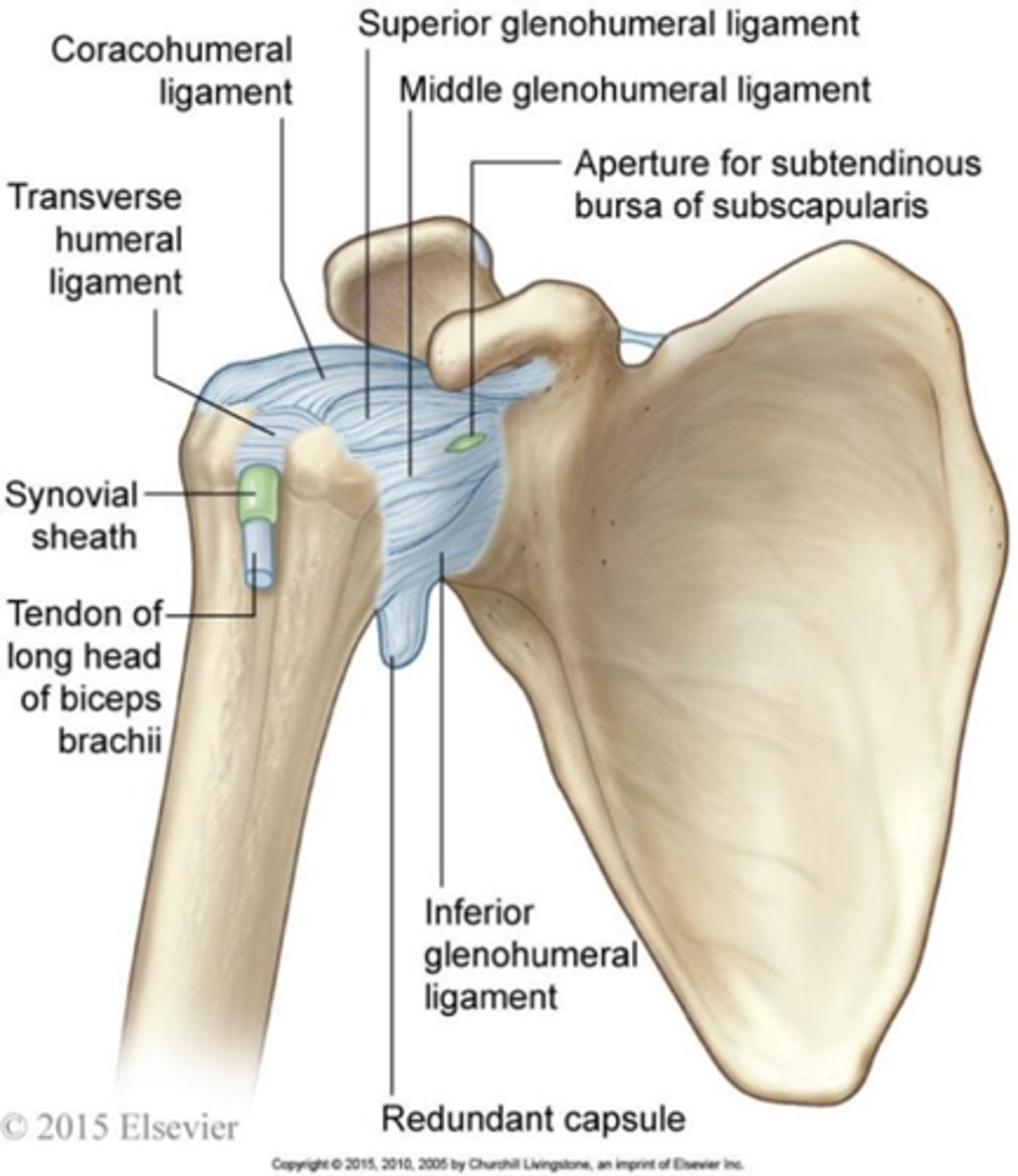
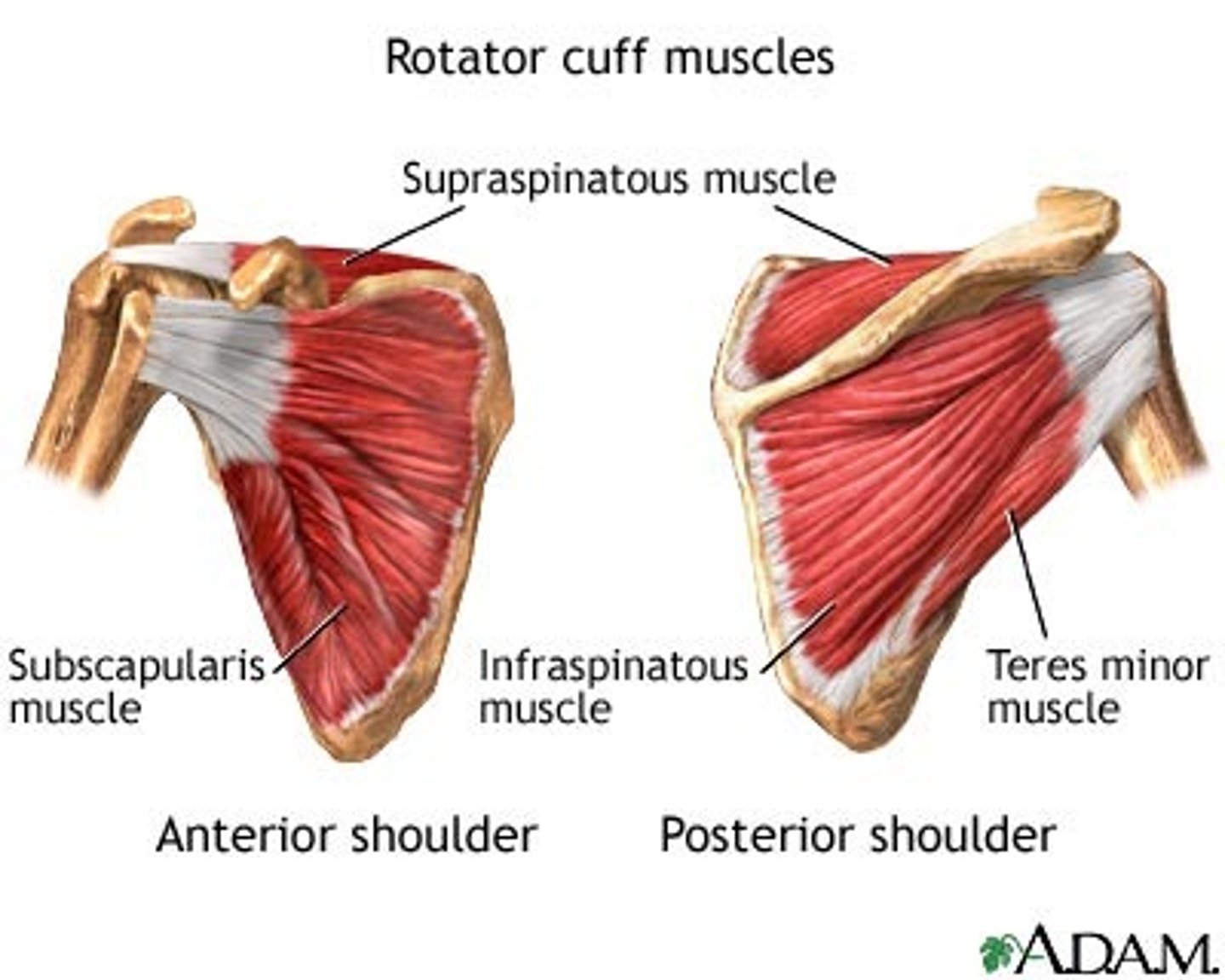
Name the four muscles that make up the rotator cuff.
Subscapularis, Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres Minor.
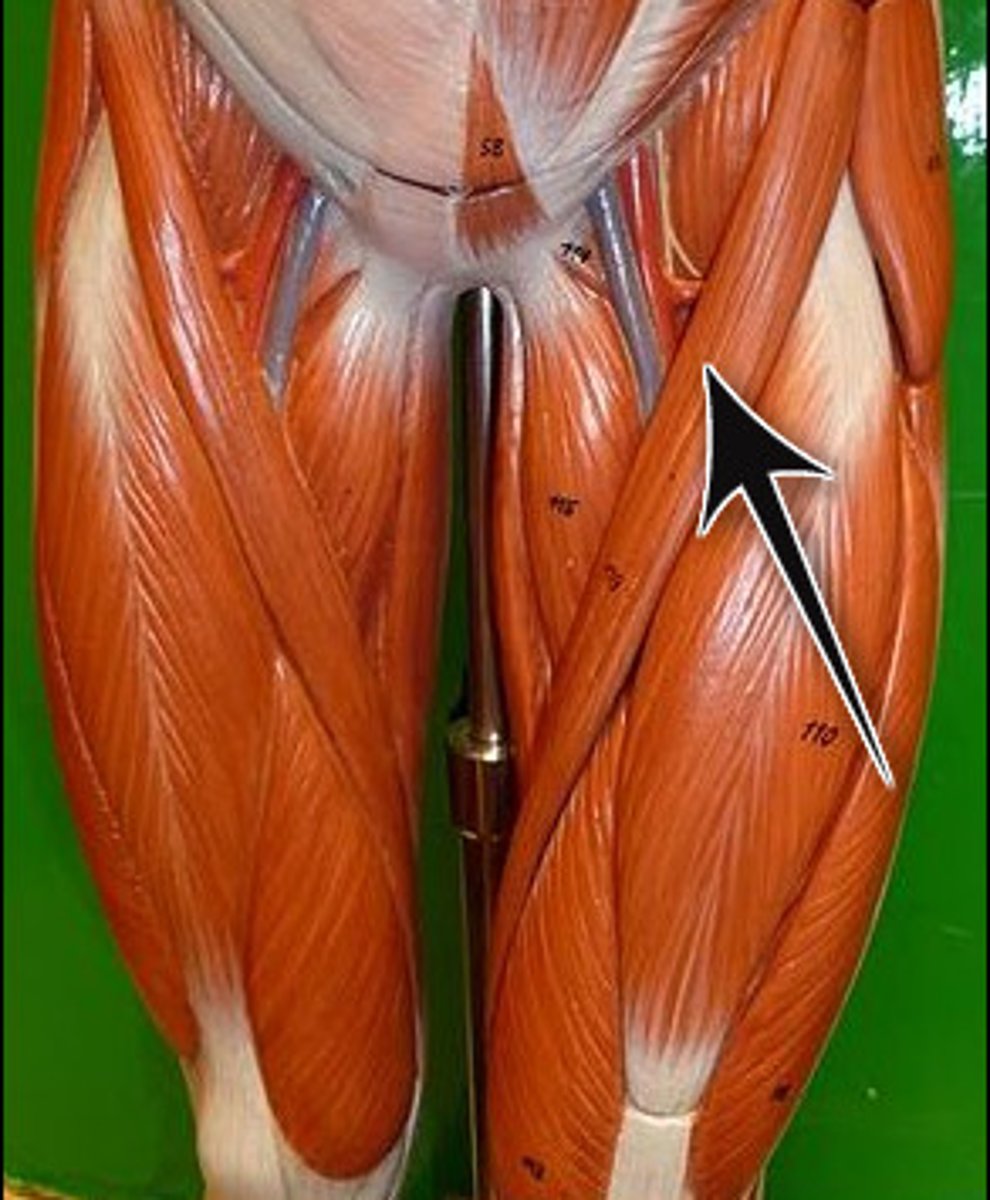
What are the major knee flexors?
Hamstrings (Biceps femoris, Semitendinosus, Semimembranosus) and Sartorius.
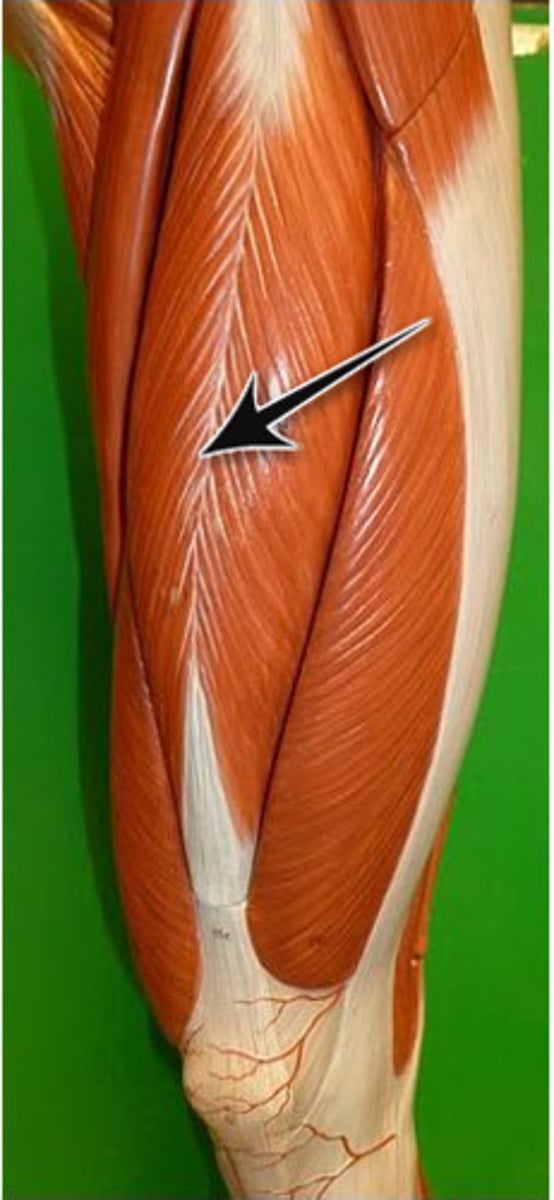
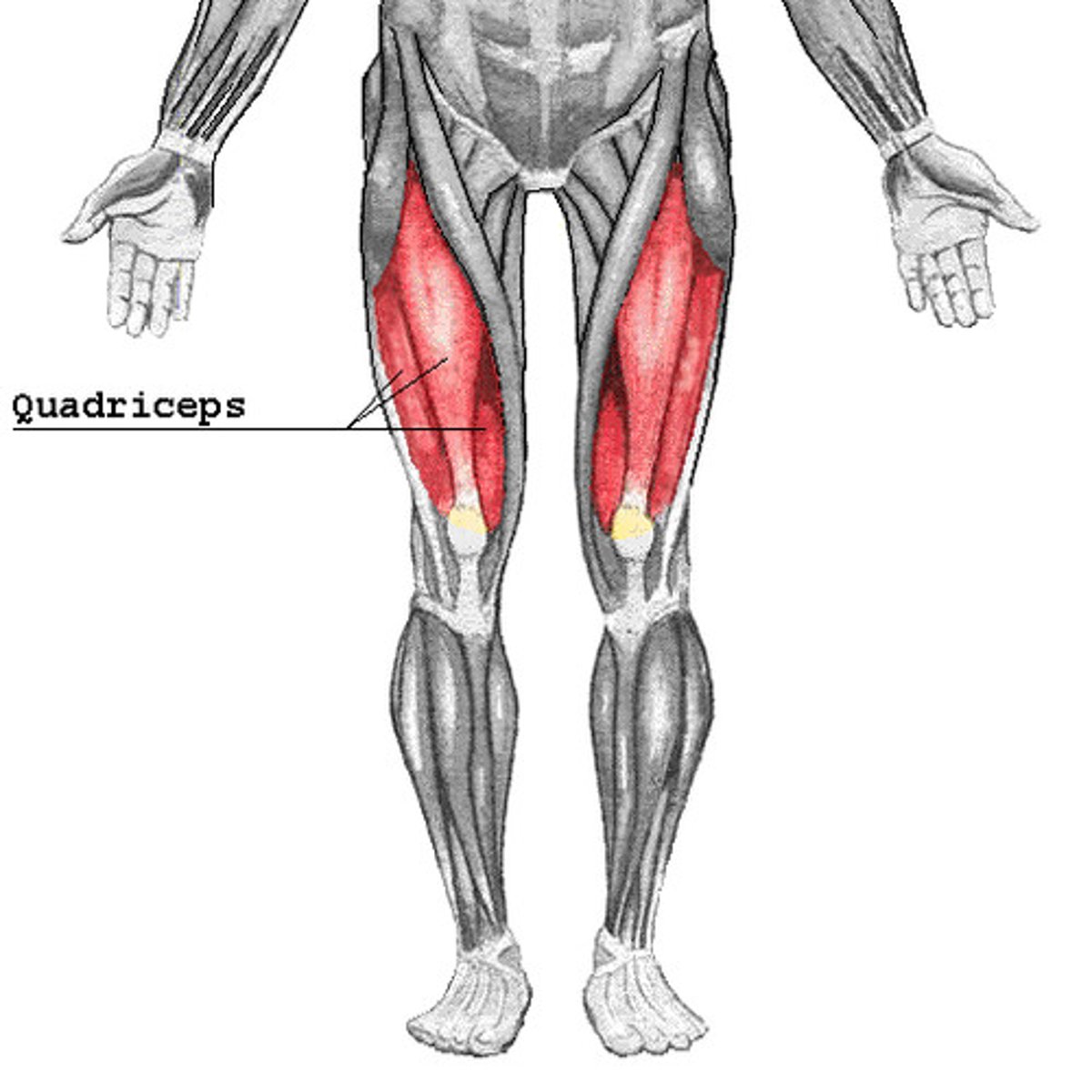
What is the role of the vastus muscles?
They assist in extending the knee.
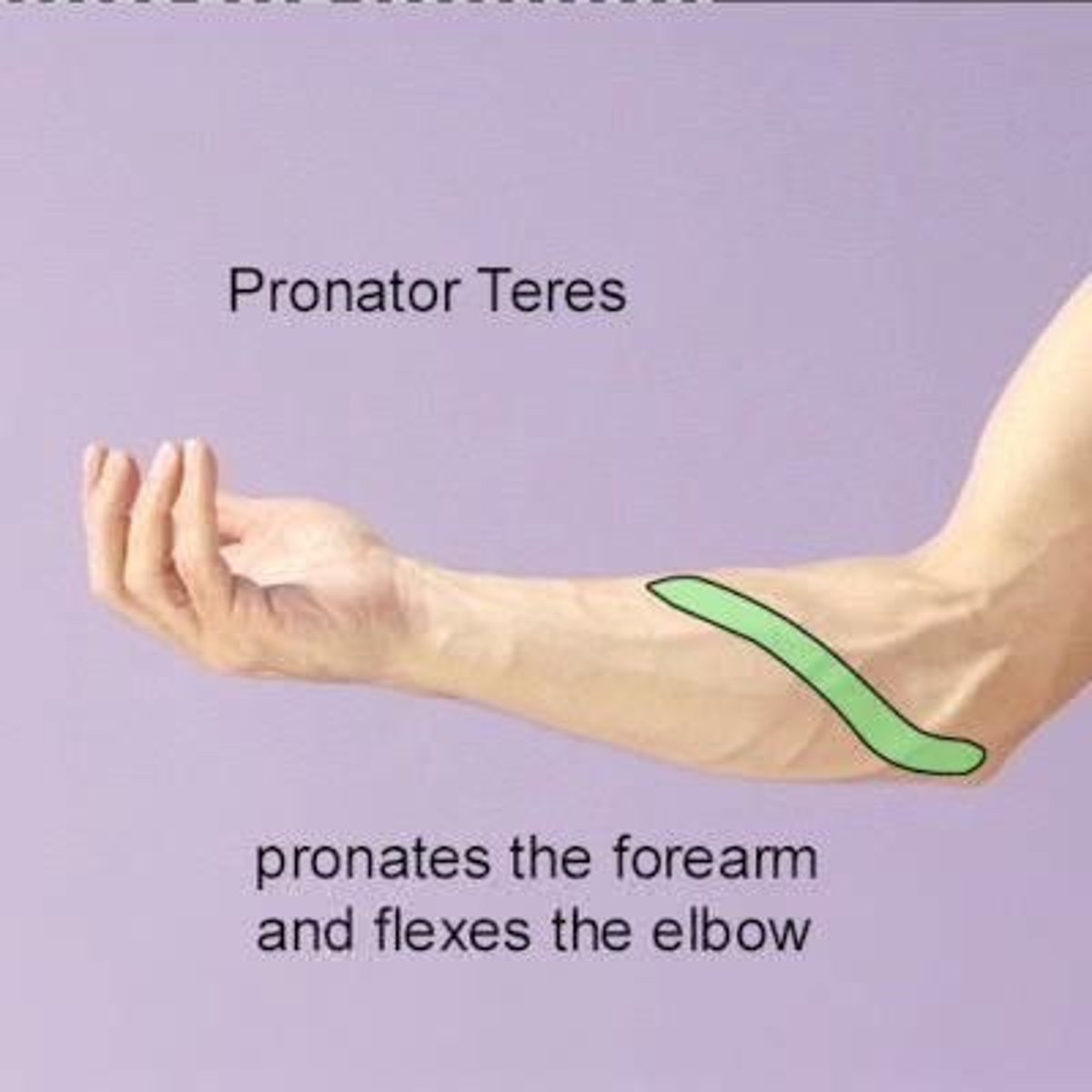
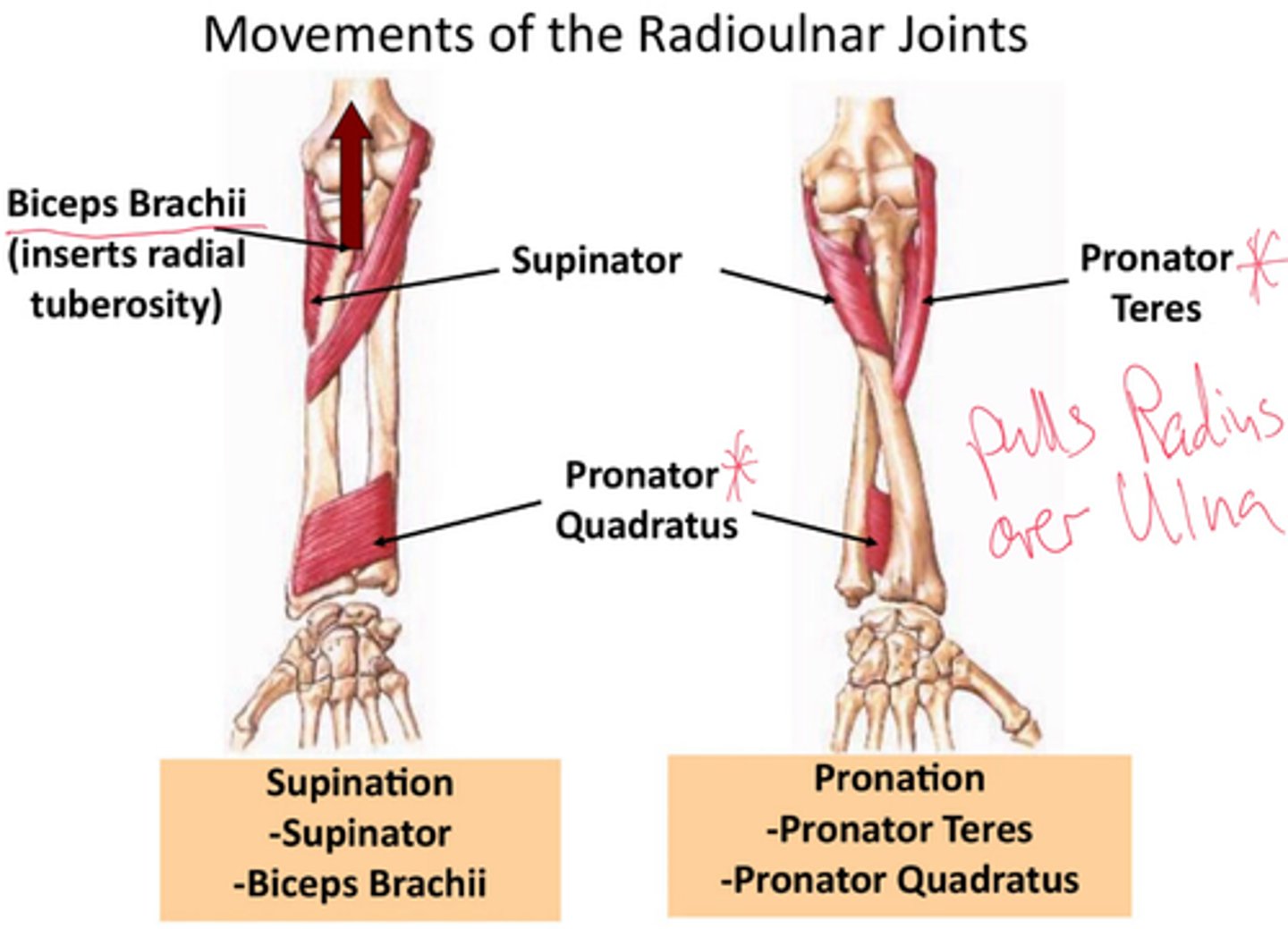
What is the function of the pronator teres?
Pronation of the forearm.
What is the action of the supinator muscle?
Supination of the forearm.
What is the significance of the rotator cuff muscles?
They stabilize the head of the humerus within the glenoid cavity.
What is the insertion point for the vastus lateralis?
Tibial tuberosity via the patellar ligament.
What is the role of the hamstrings during knee flexion?
They contract to flex the knee.
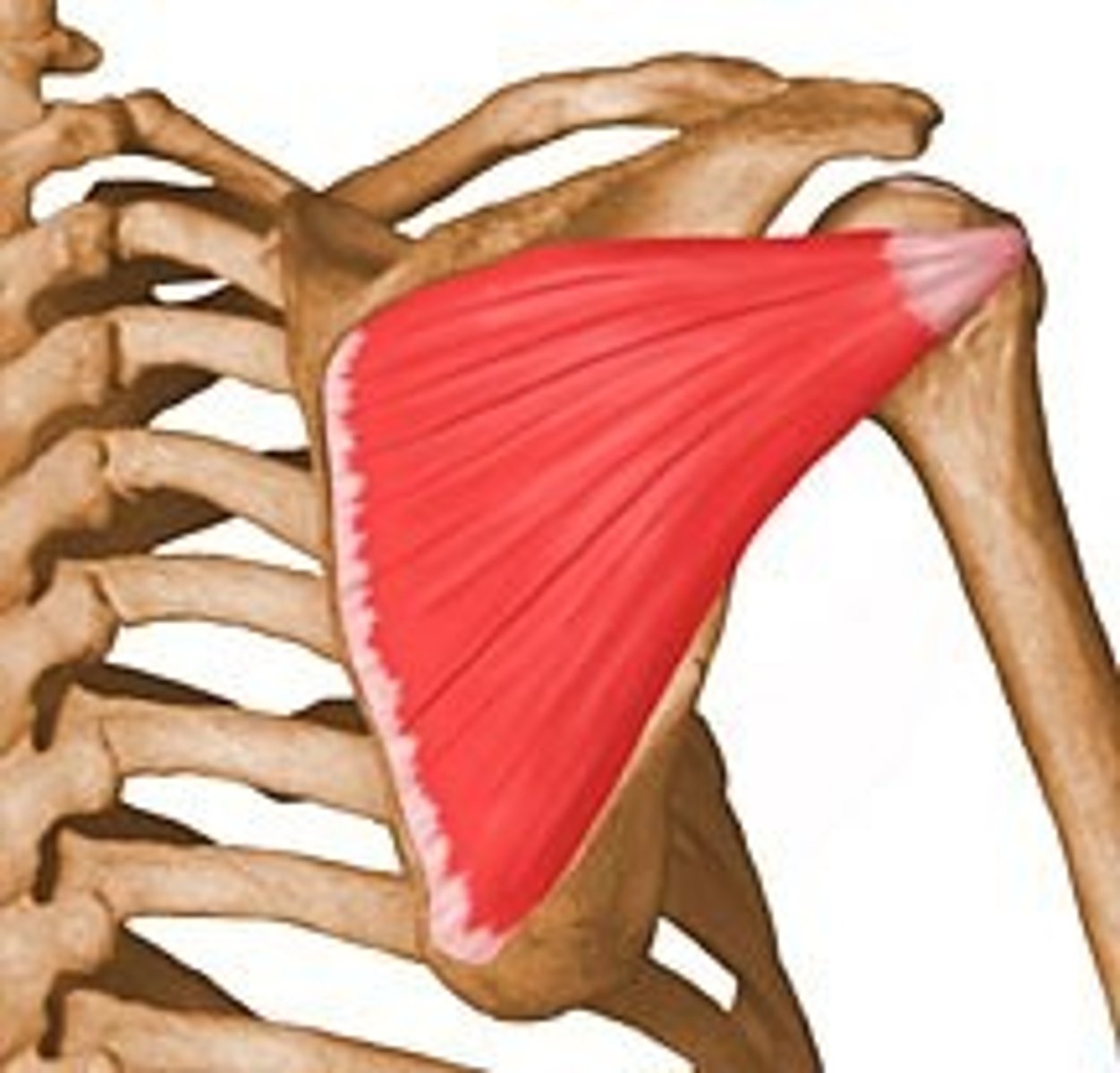
What is the action of the teres major?
Adduction and medial rotation of the humerus.

What joint allows for flexion and extension at the knee?
Tibiofemoral joint.

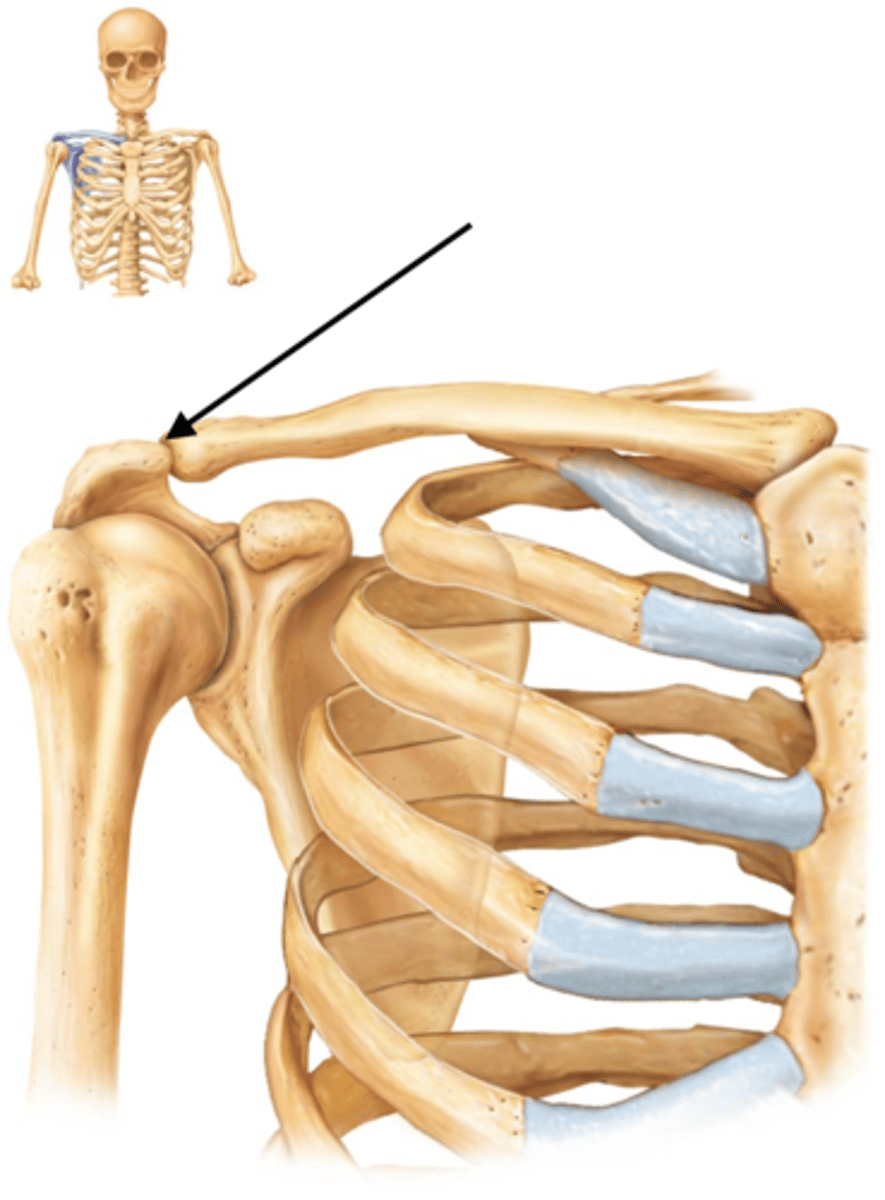
What type of joint is the sternoclavicular joint?
Gliding joint.
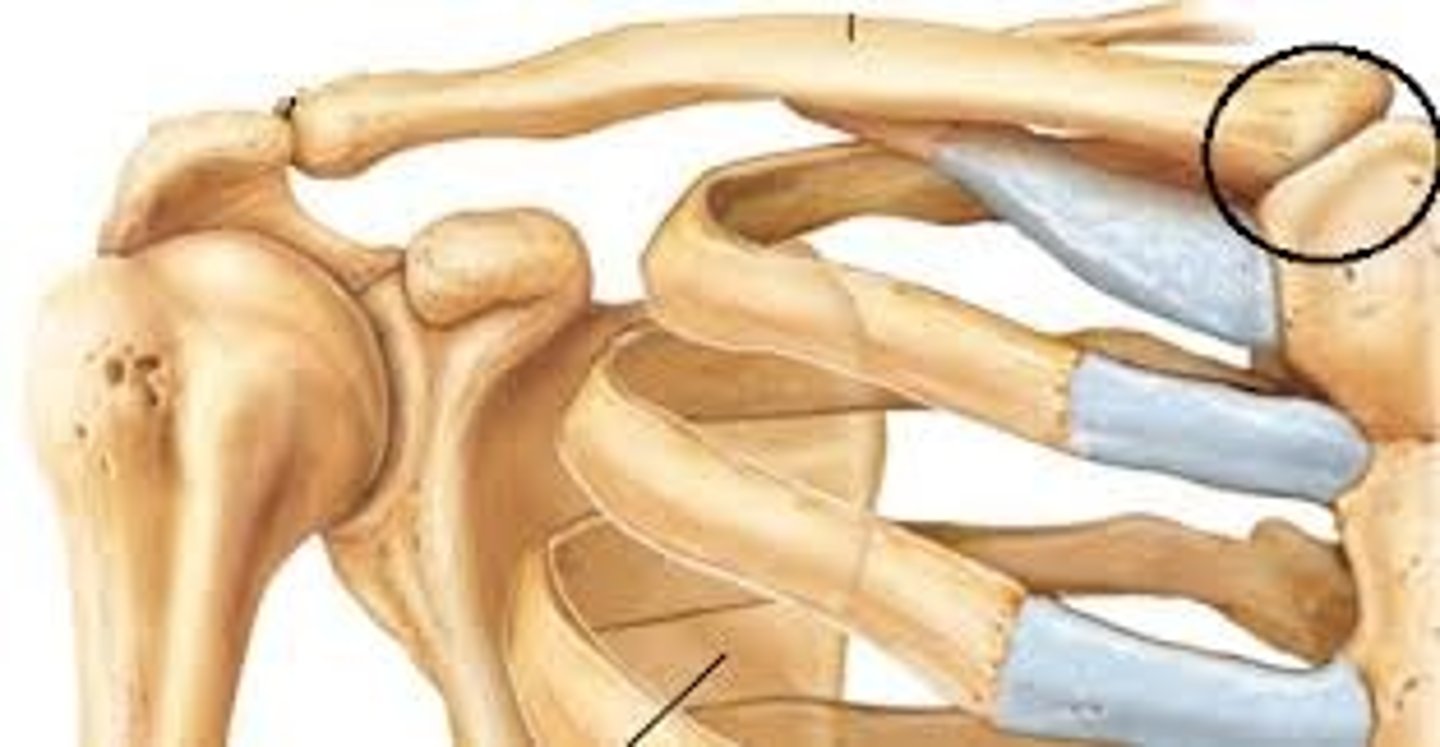
What type of joint is the acromioclavicular joint?
Gliding joint.
What is the origin of the subscapularis?
Subscapular fossa of scapula.
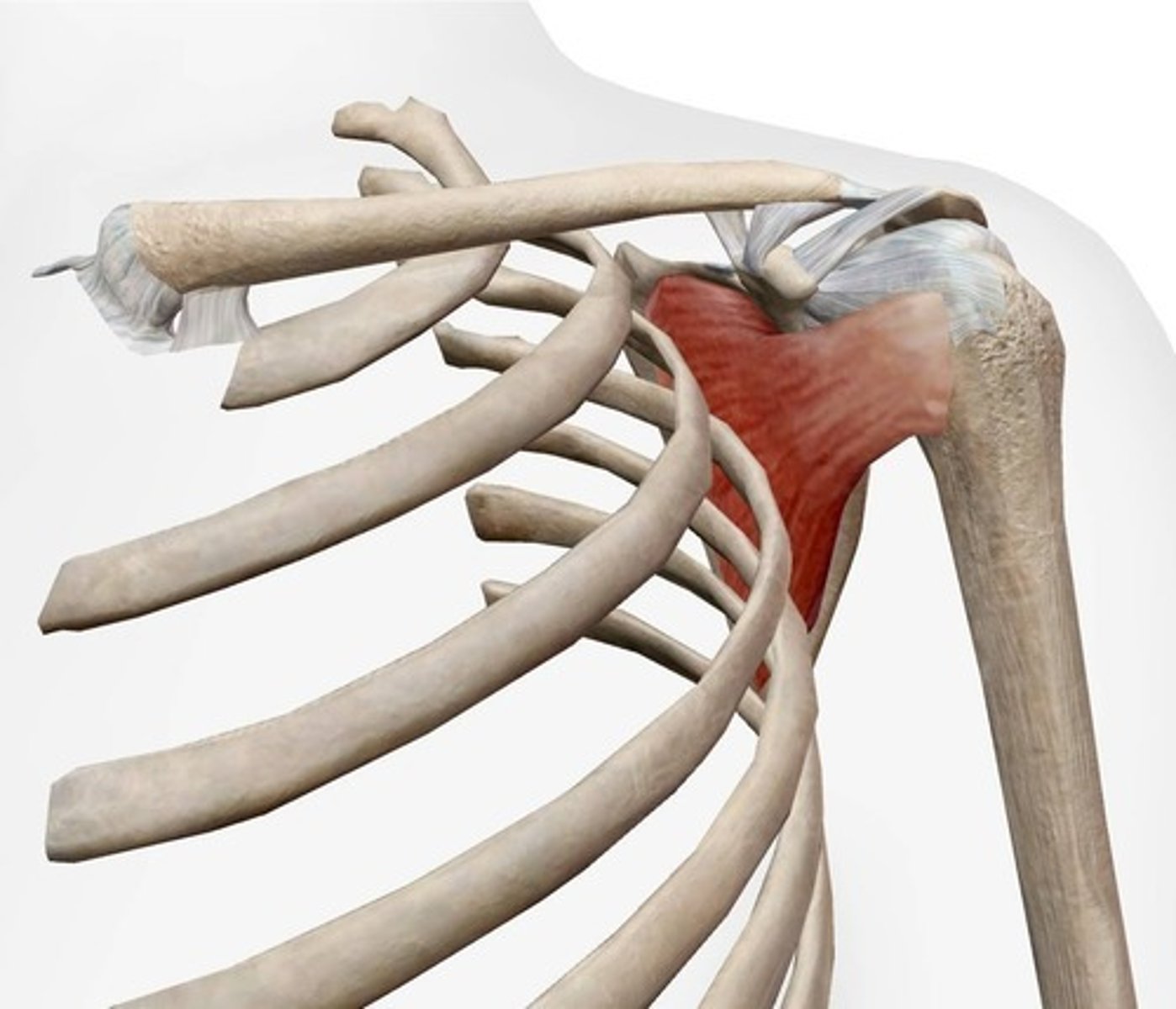
What is the insertion of the subscapularis?
Lesser tubercle of humerus.
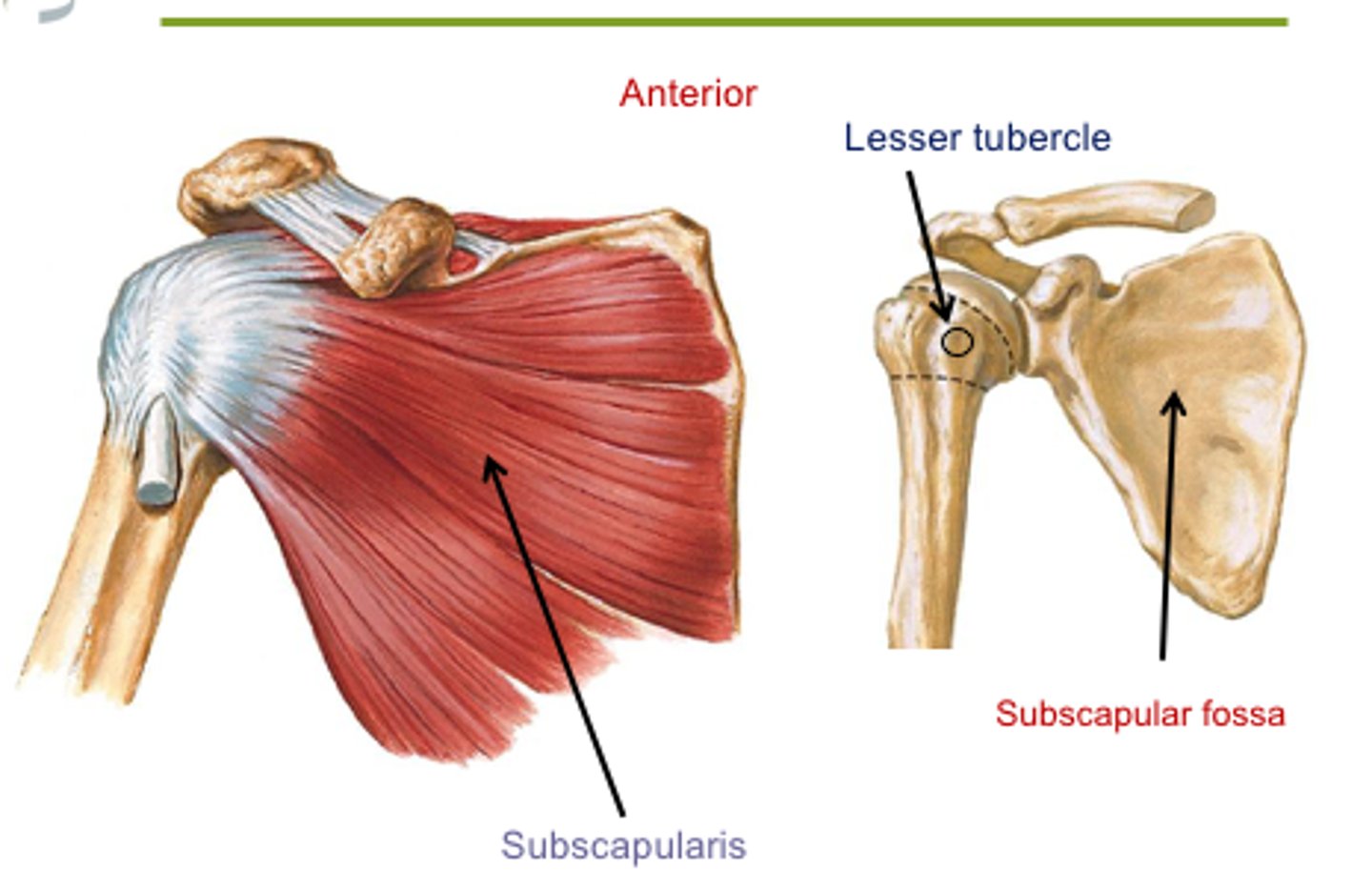
What action does the subscapularis muscle perform?
Medial rotation of the humerus.
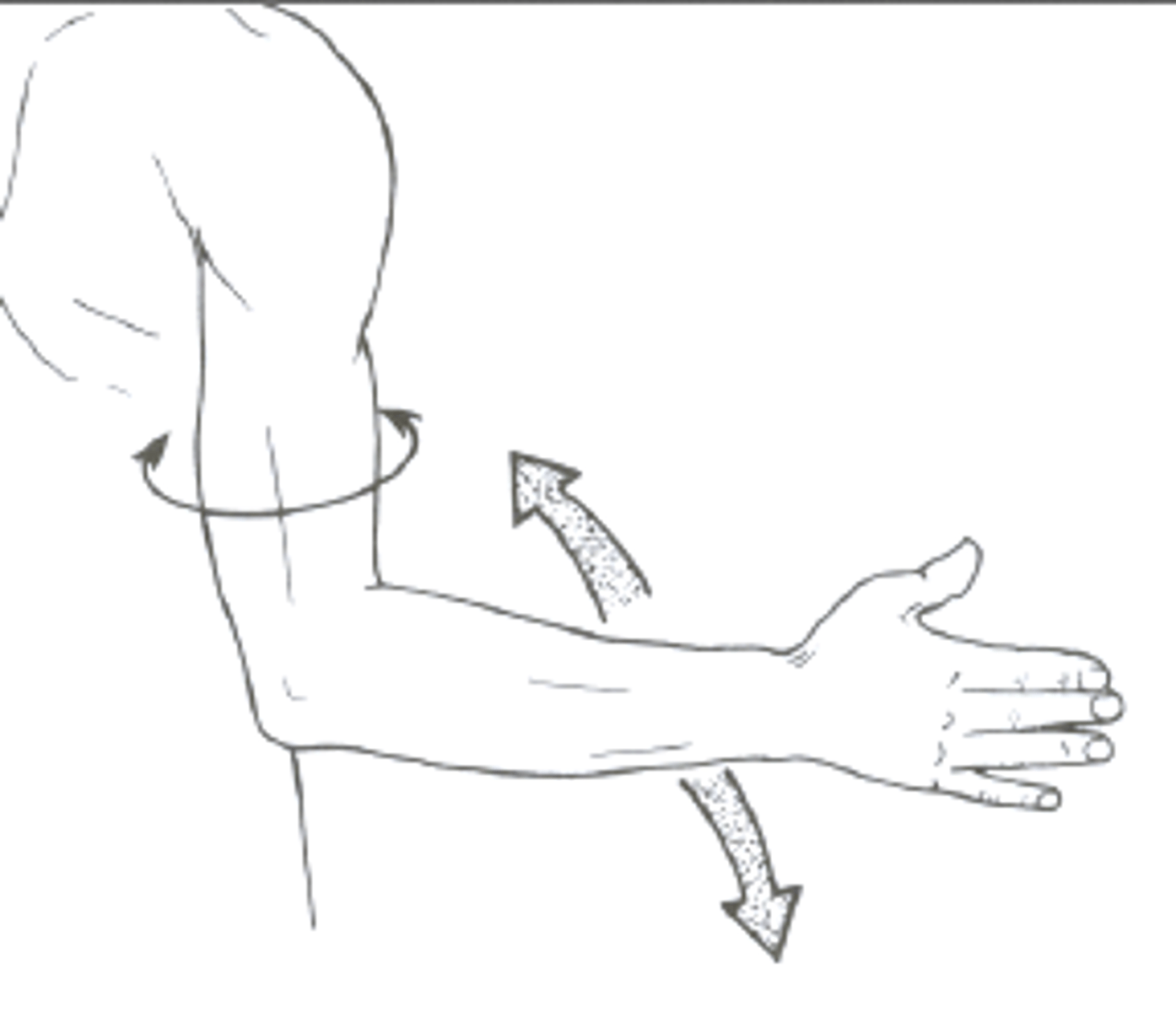
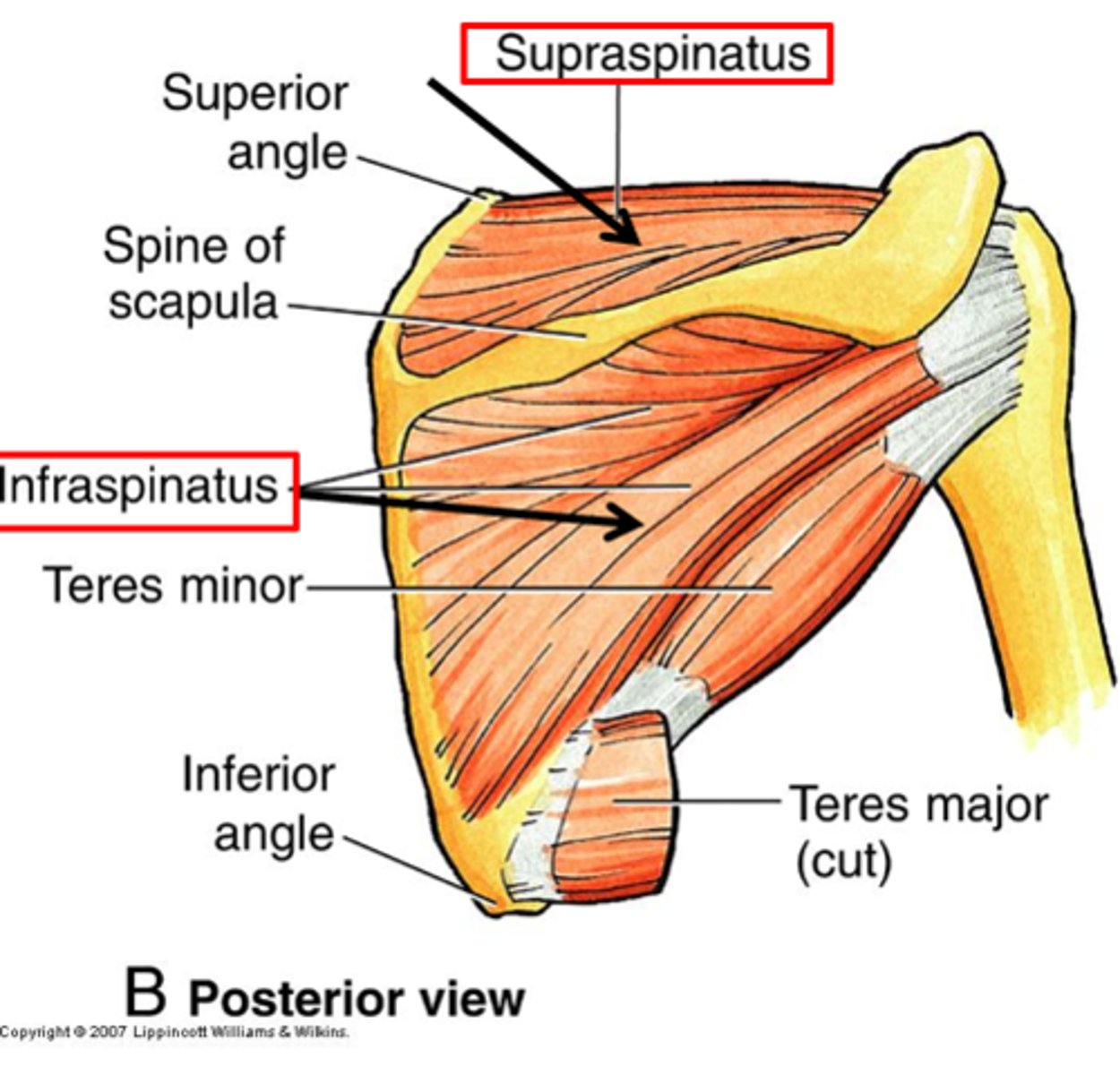
What is the origin of the supraspinatus?
Supraspinous fossa of scapula.
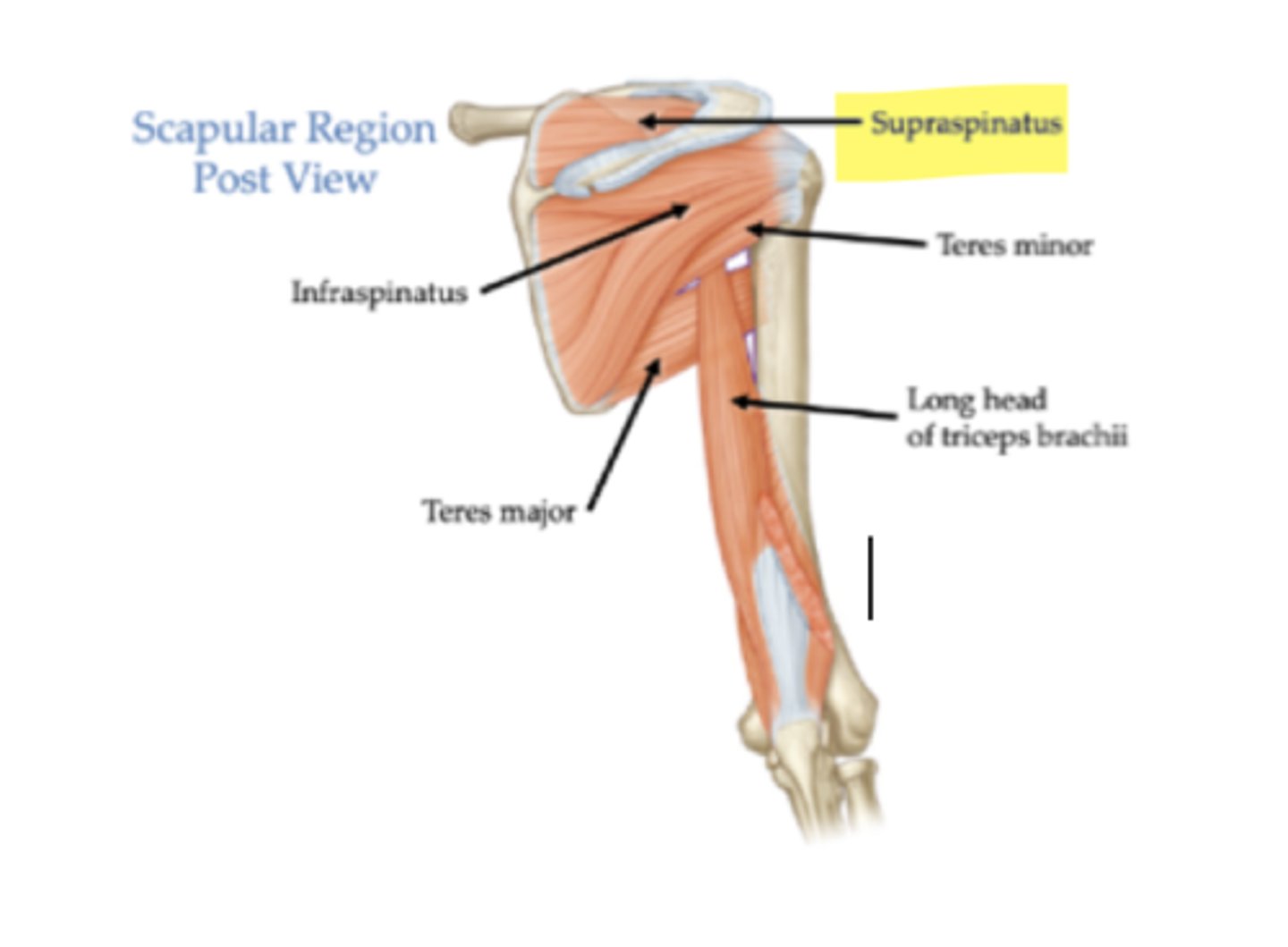
What is the insertion of the supraspinatus?
Greater tubercle of the humerus.
What is the primary action of the supraspinatus?
Abduction of the humerus.
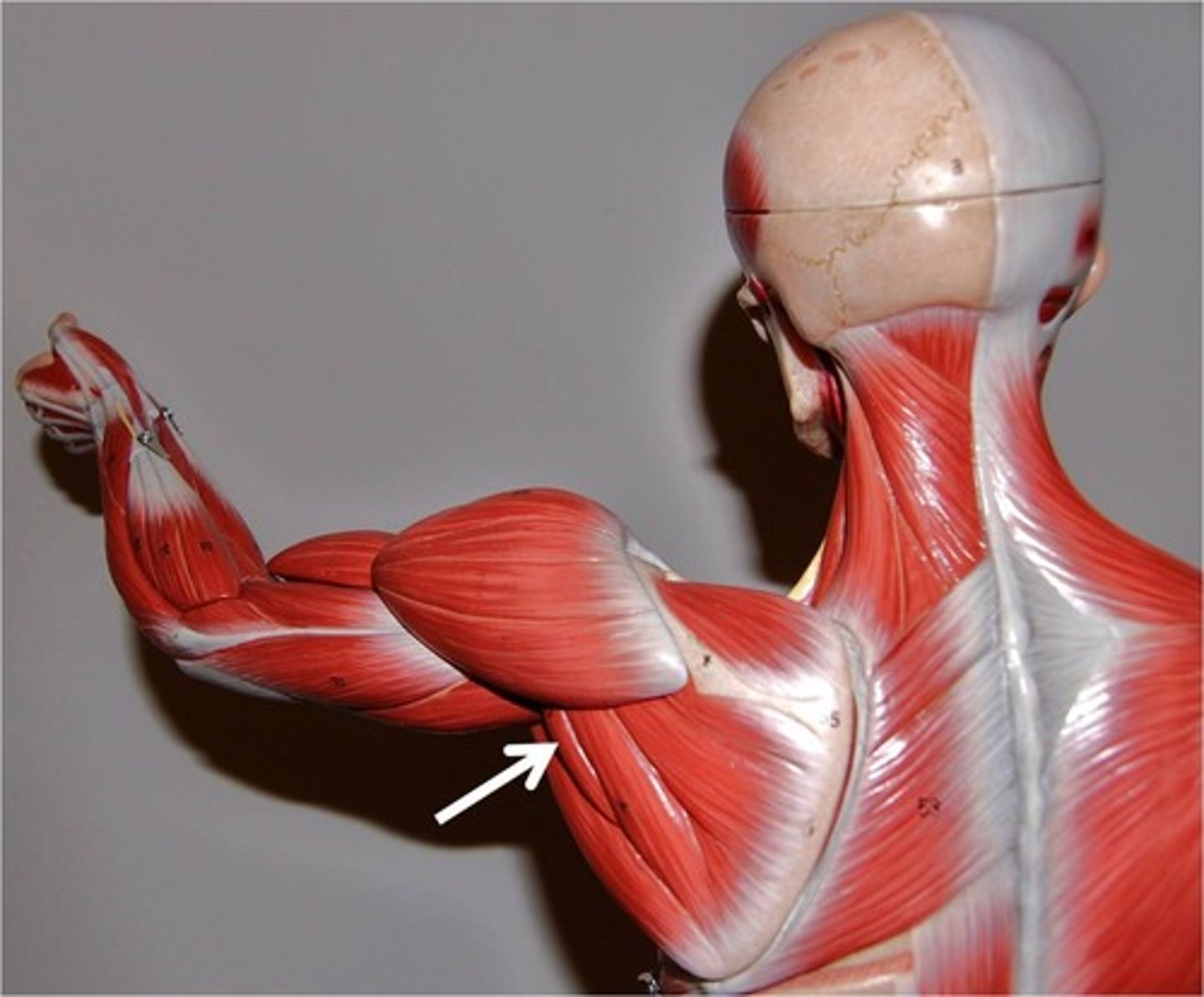
What is the origin of the infraspinatus?
Infraspinous fossa of scapula.

What is the insertion of the infraspinatus?
Greater tubercle of the humerus.

What is the primary action of the infraspinatus?
Lateral rotation of humerus.
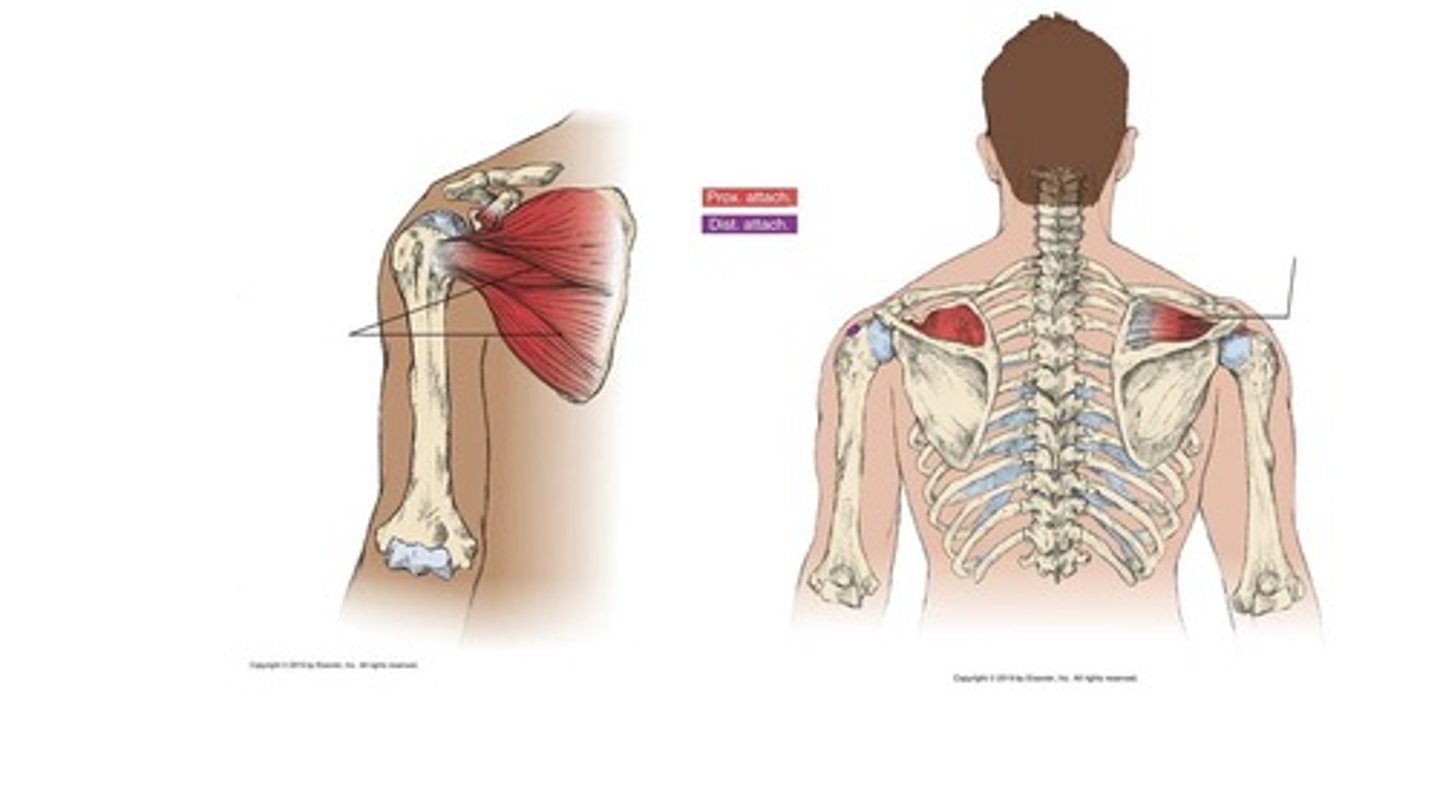
What is the origin of the teres minor?
Lateral border of scapula.
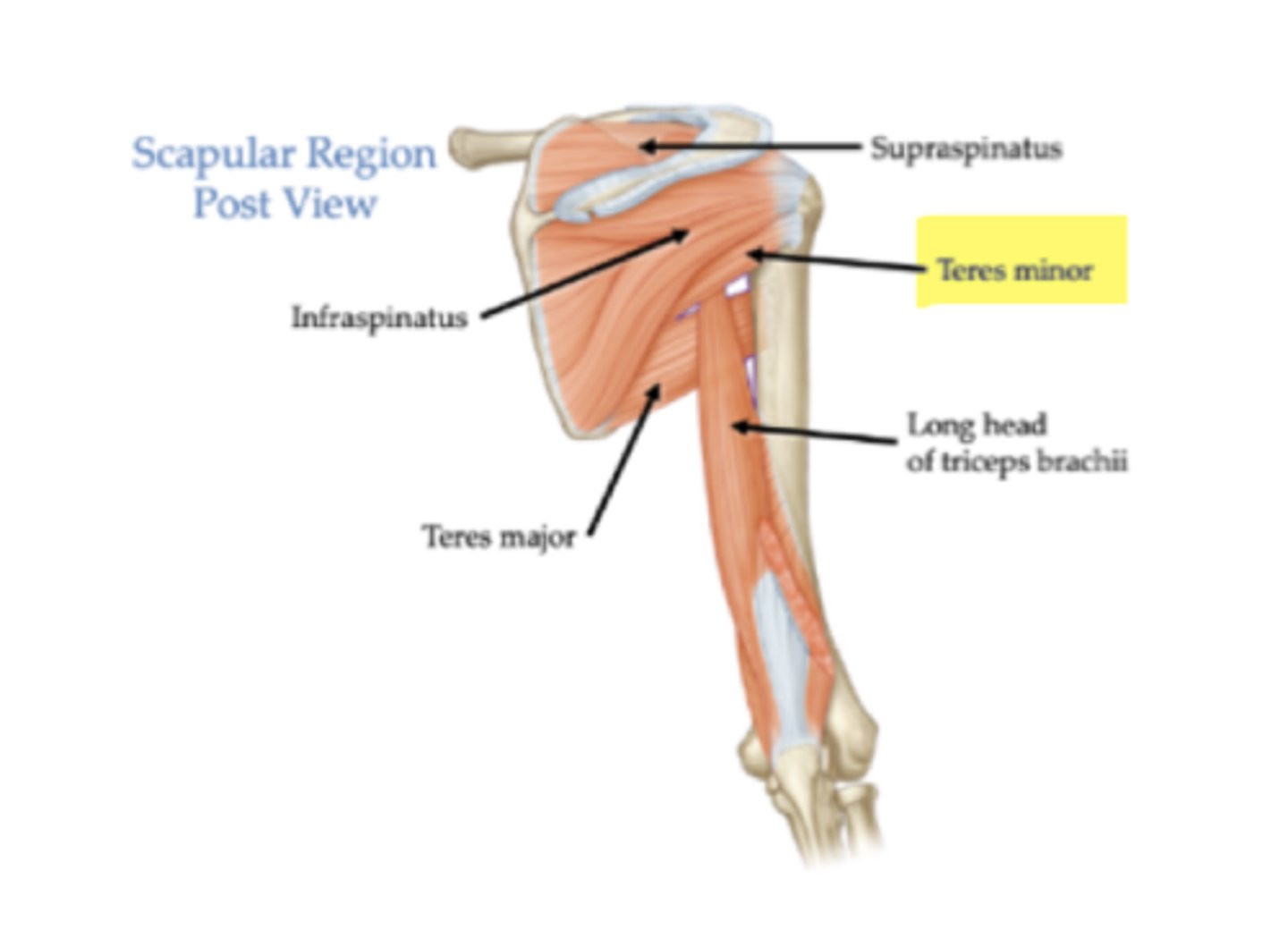
What is the insertion of the teres minor?
Greater tubercle of the humerus.
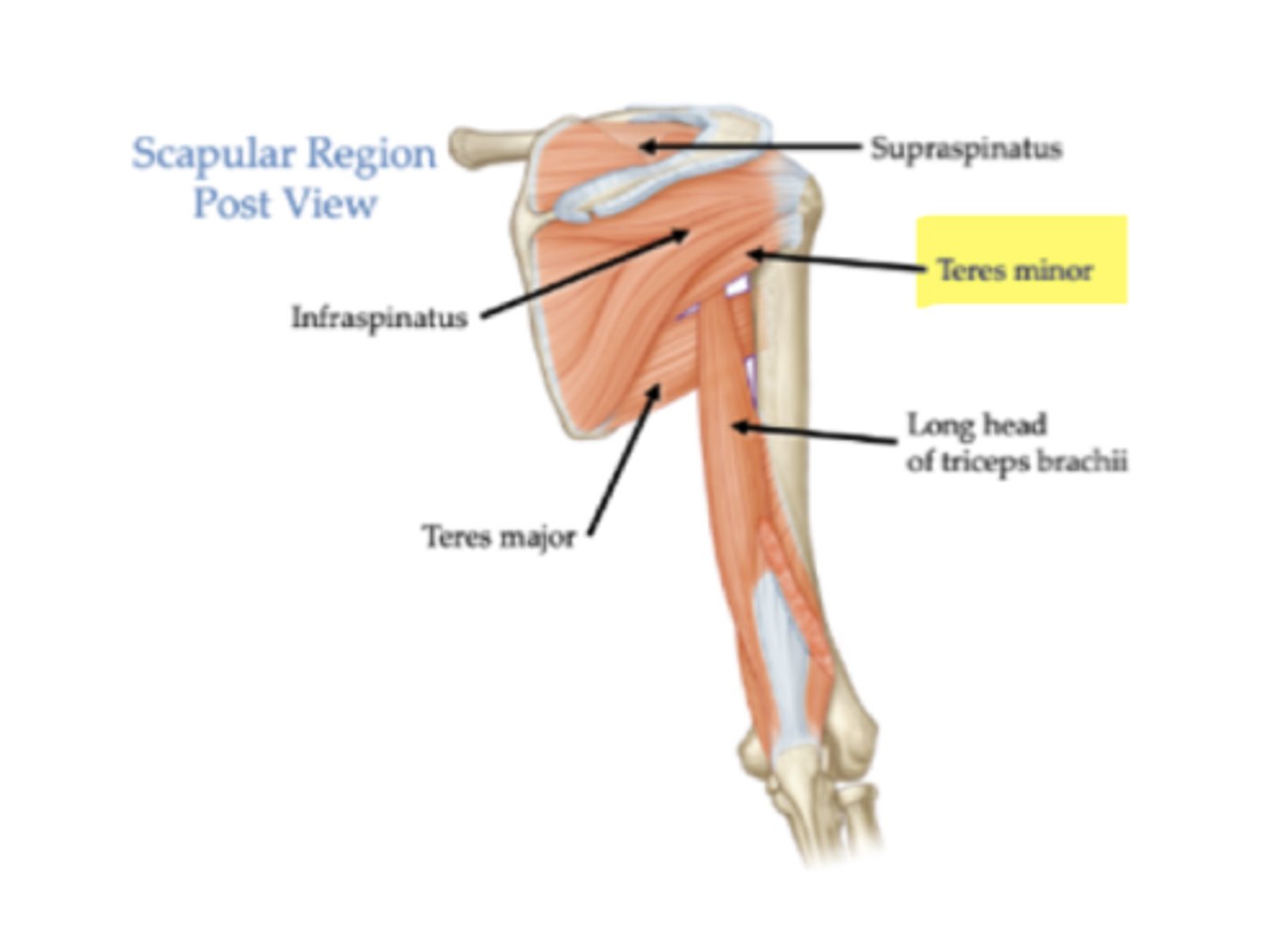
What is the primary action of the teres minor?
Lateral rotation of humerus.
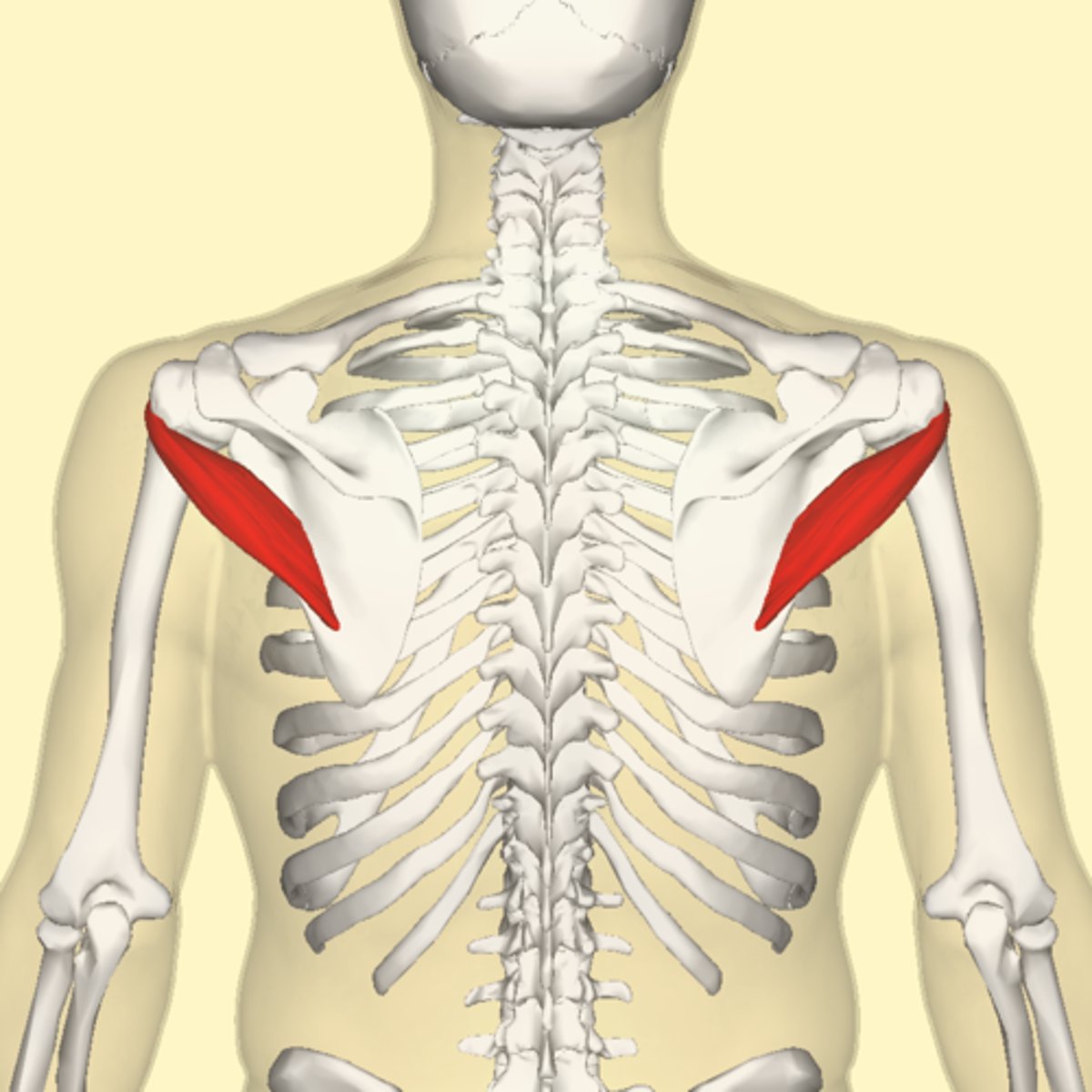
What is the origin of the teres major?
Inferior angle (point of scapula)
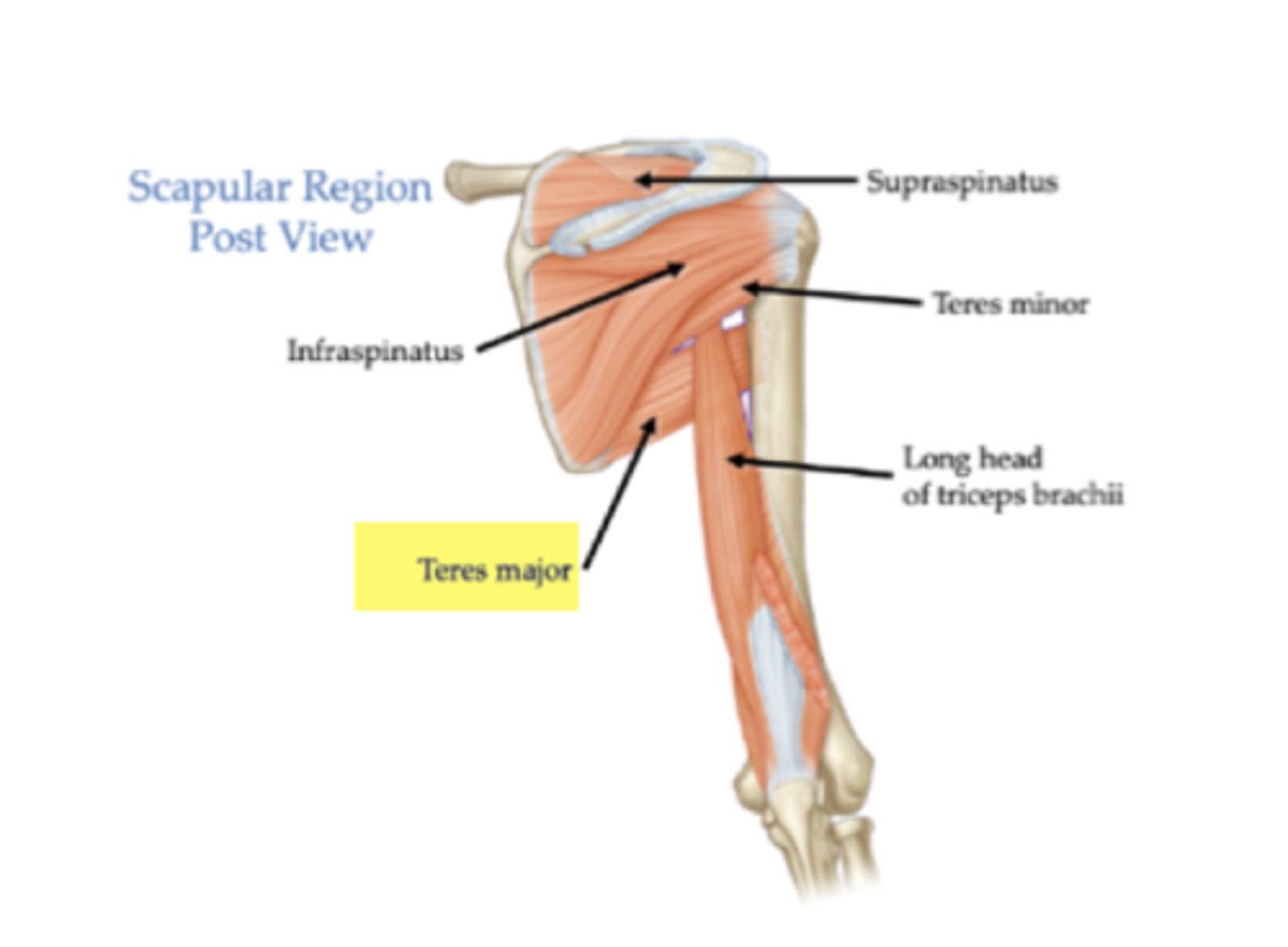
What is the insertion of the teres major?
Intertubercular sulcus of the humerus
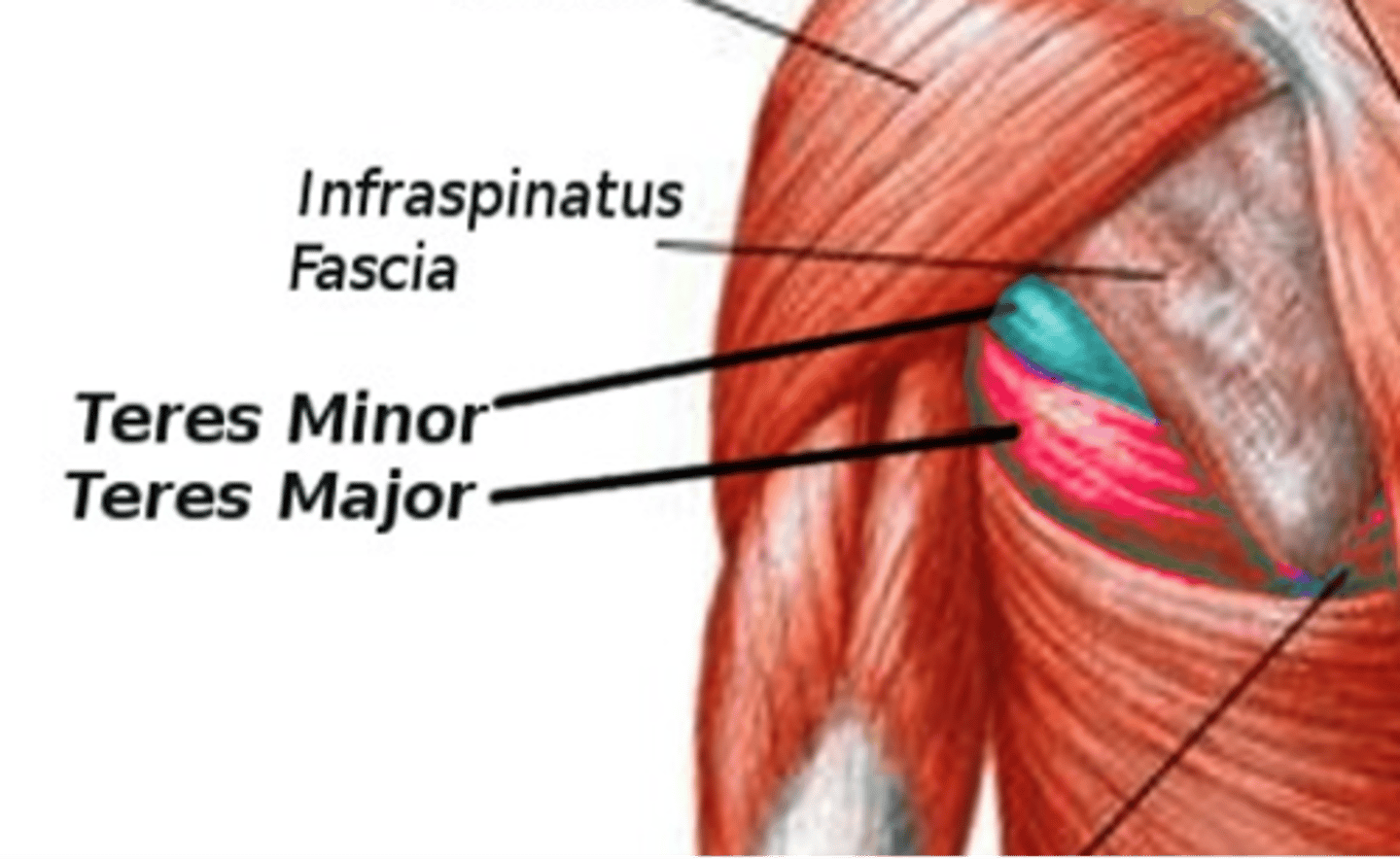
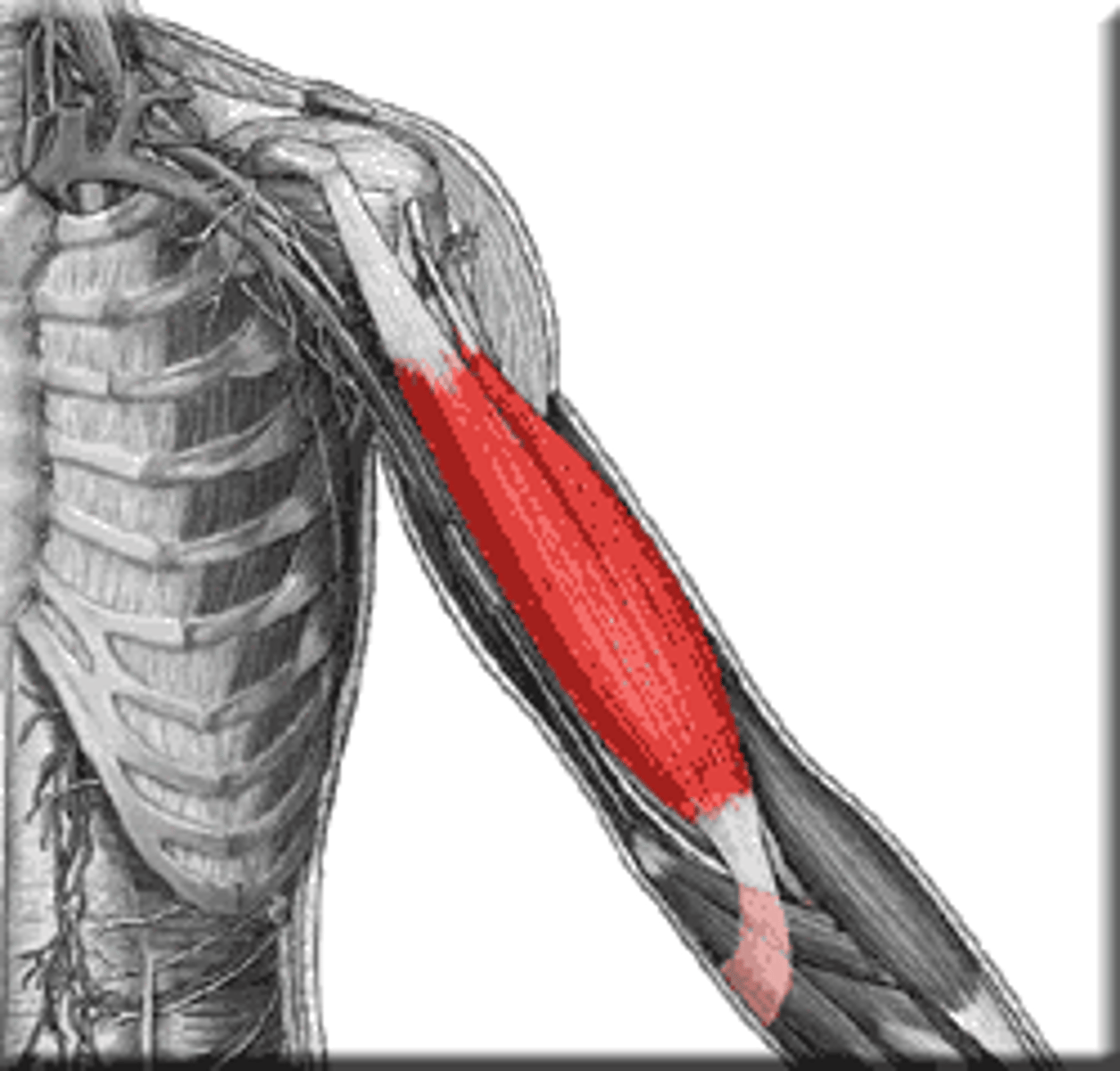
What is the primary action of the teres major?
Adduction of humerus.
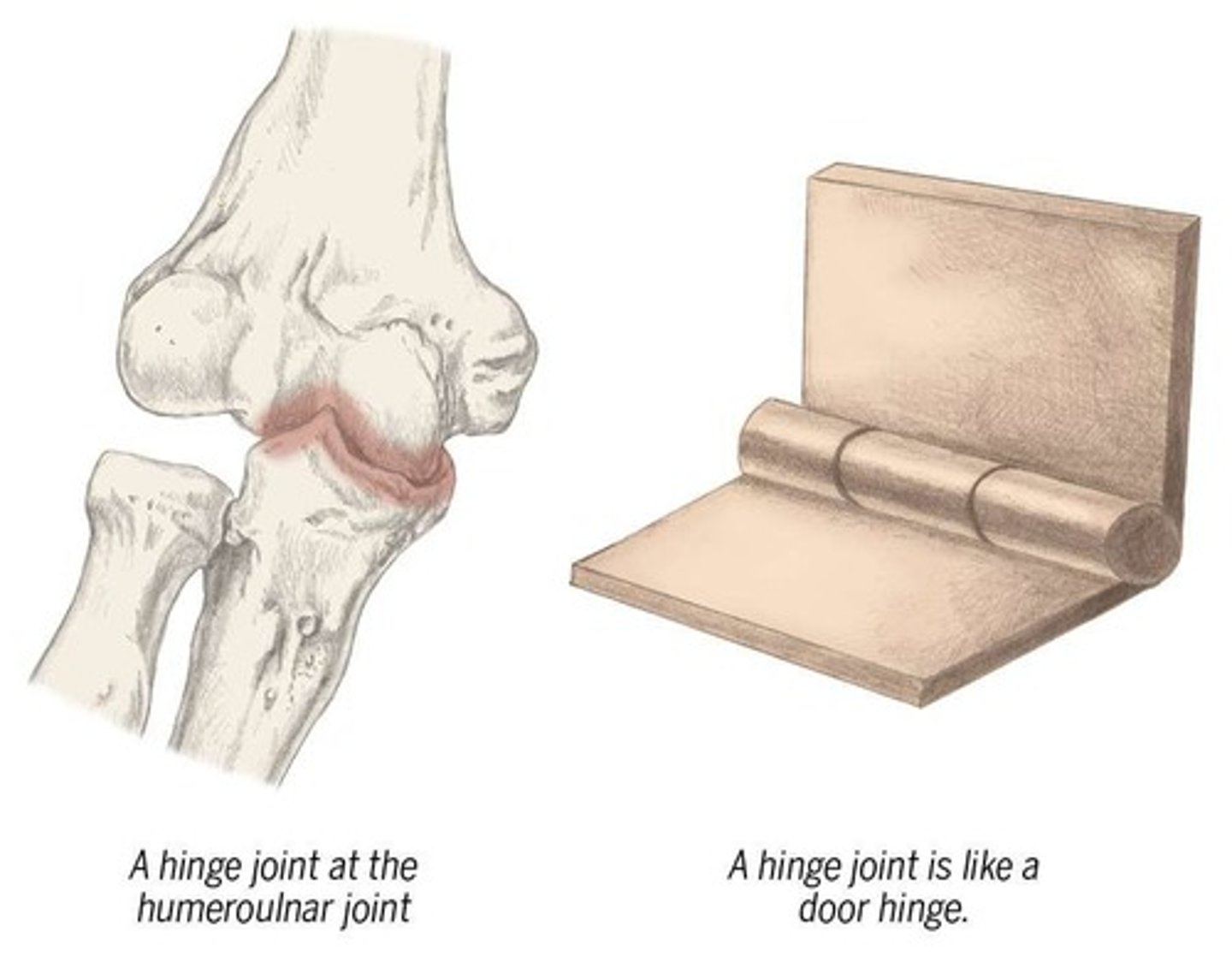
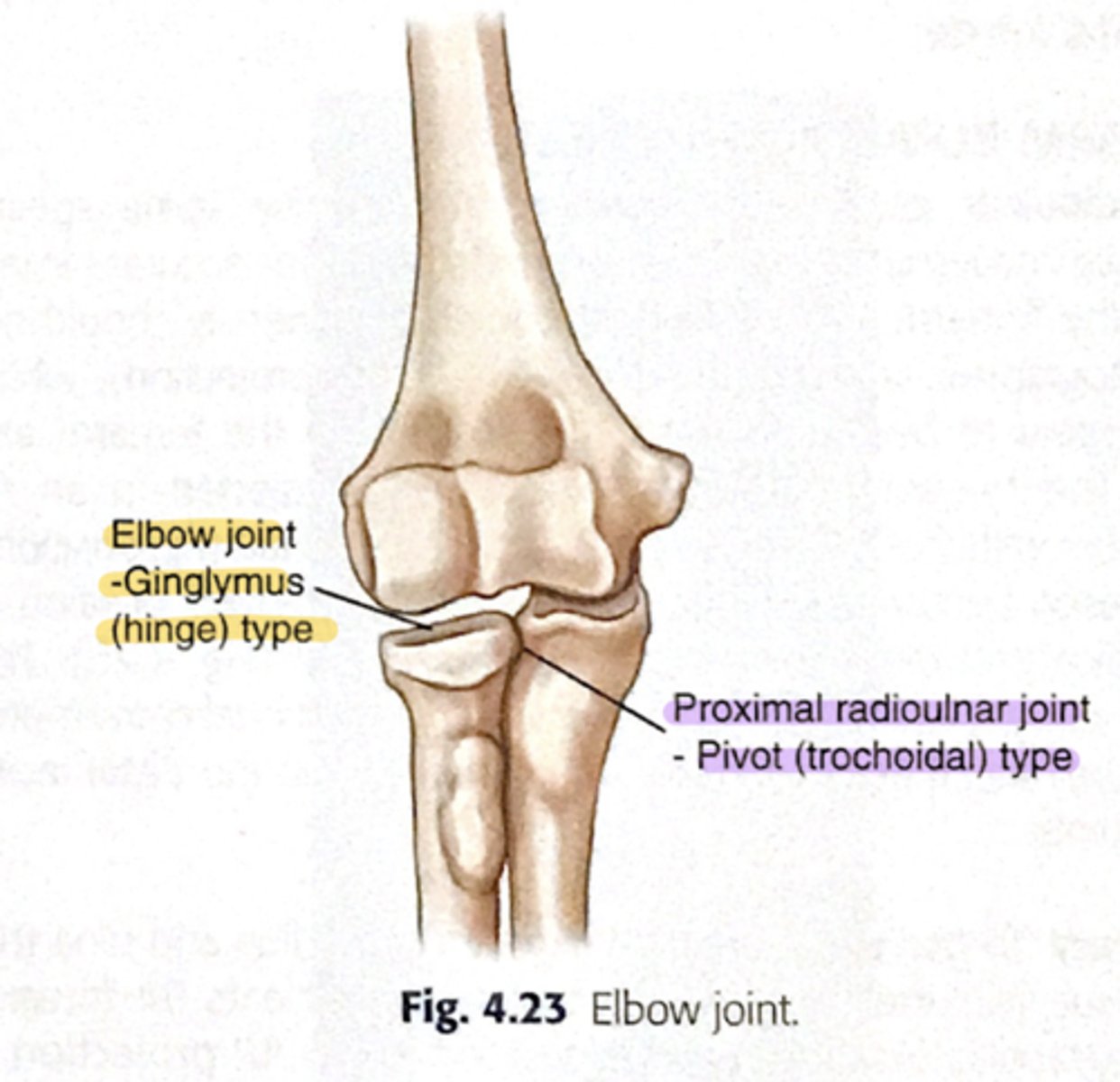
What type of joint is the humeroulnar joint?
Hinge joint.
What type of joint is the humeroradial joint?
Limited ball-and-socket joint.
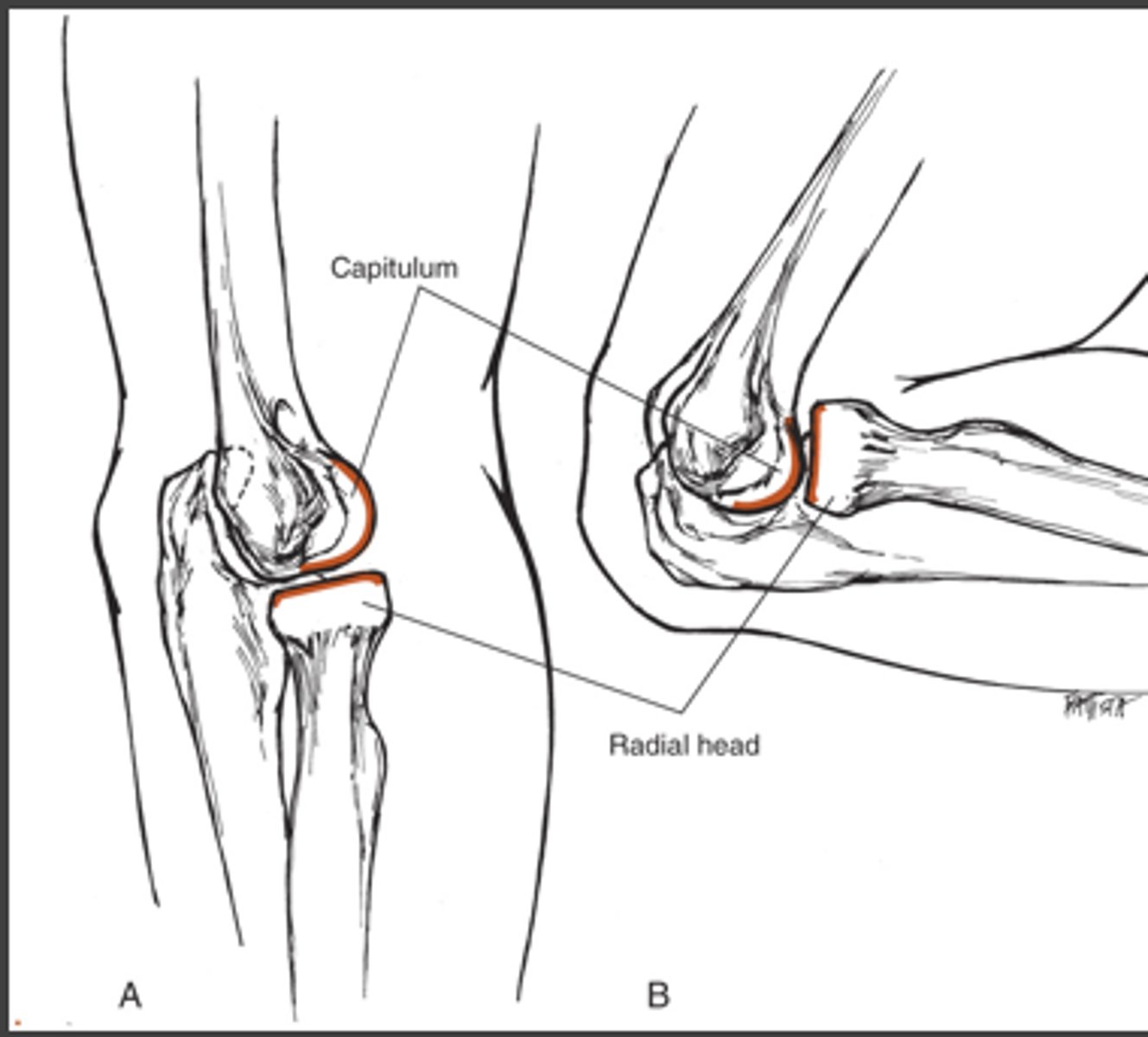
What type of joint is the proximal radioulnar joint?
Pivot joint.
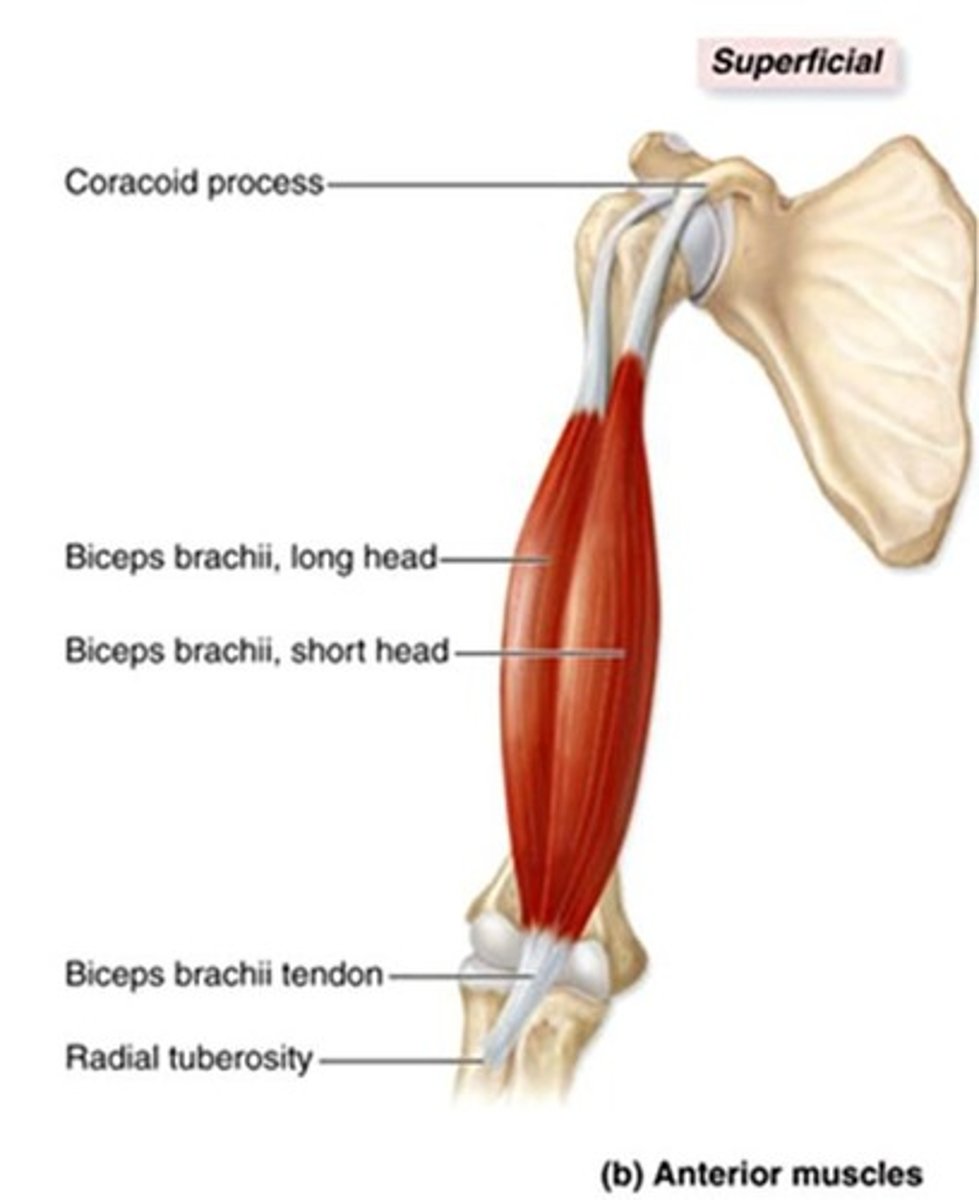
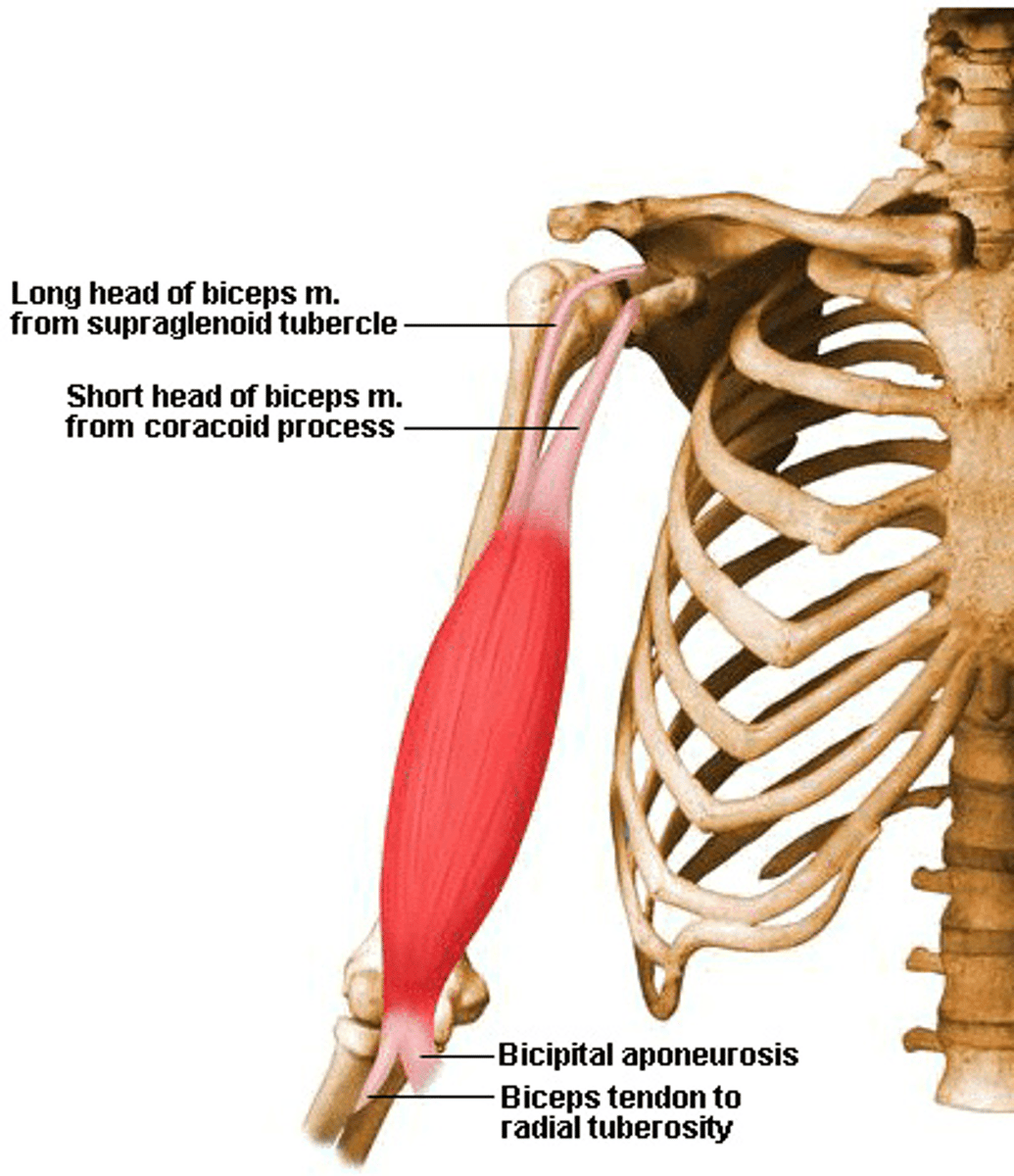
What is the origin of the biceps brachii?
Short heat: coraCoid process of scapula
Long head: superior to glenoid cavity on scapula.
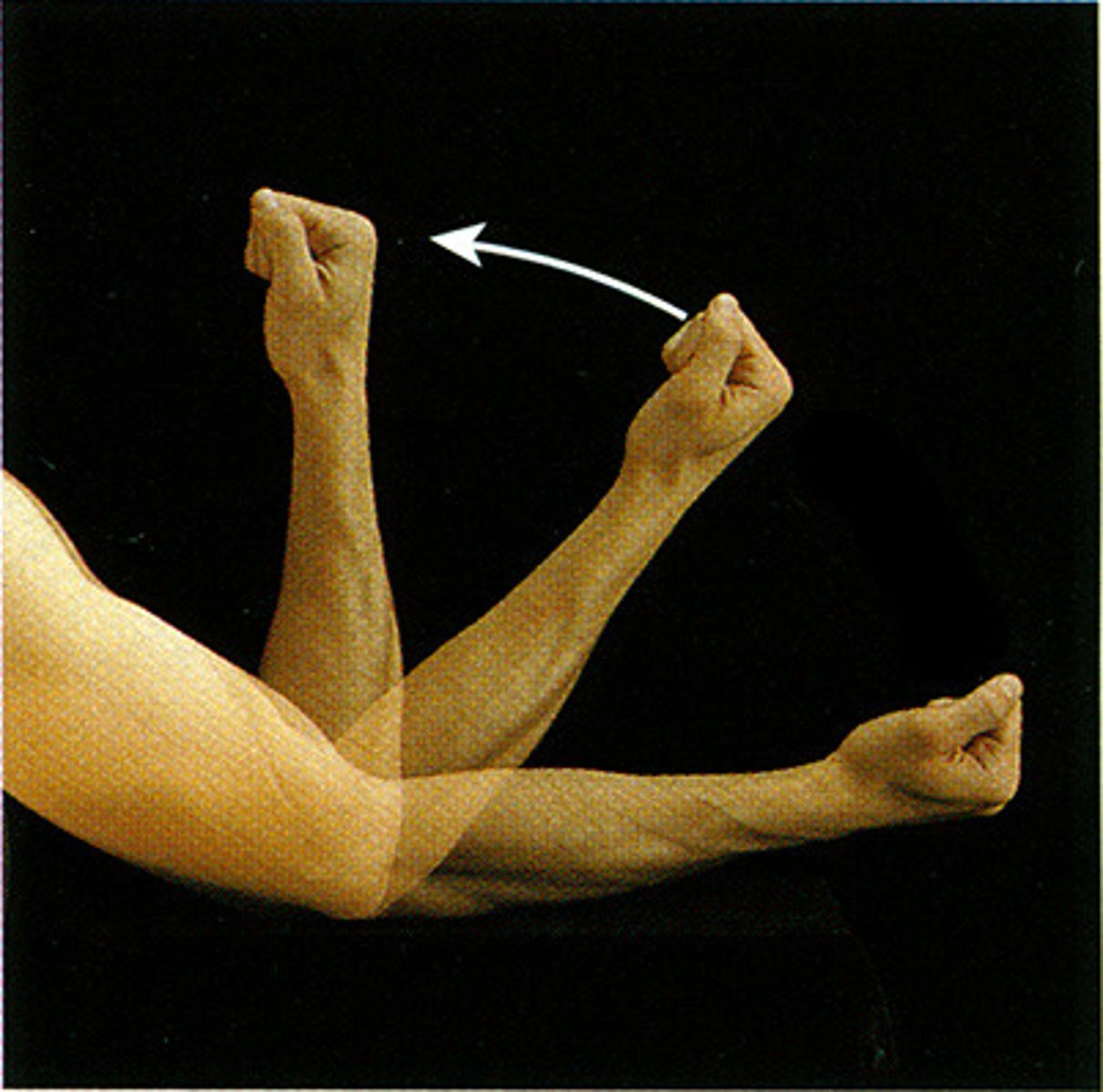
What is the action of the biceps brachii at the elbow?
Flexion at the elbow.
What is the insertion of the biceps brachii?
Radial tuberosity of radius
What is the origin of the triceps brachii?
Long head: inferior to glenoid cavity
Lateral head: lateral edge of superior humerus
Medial head: medial surface of mid-humerus
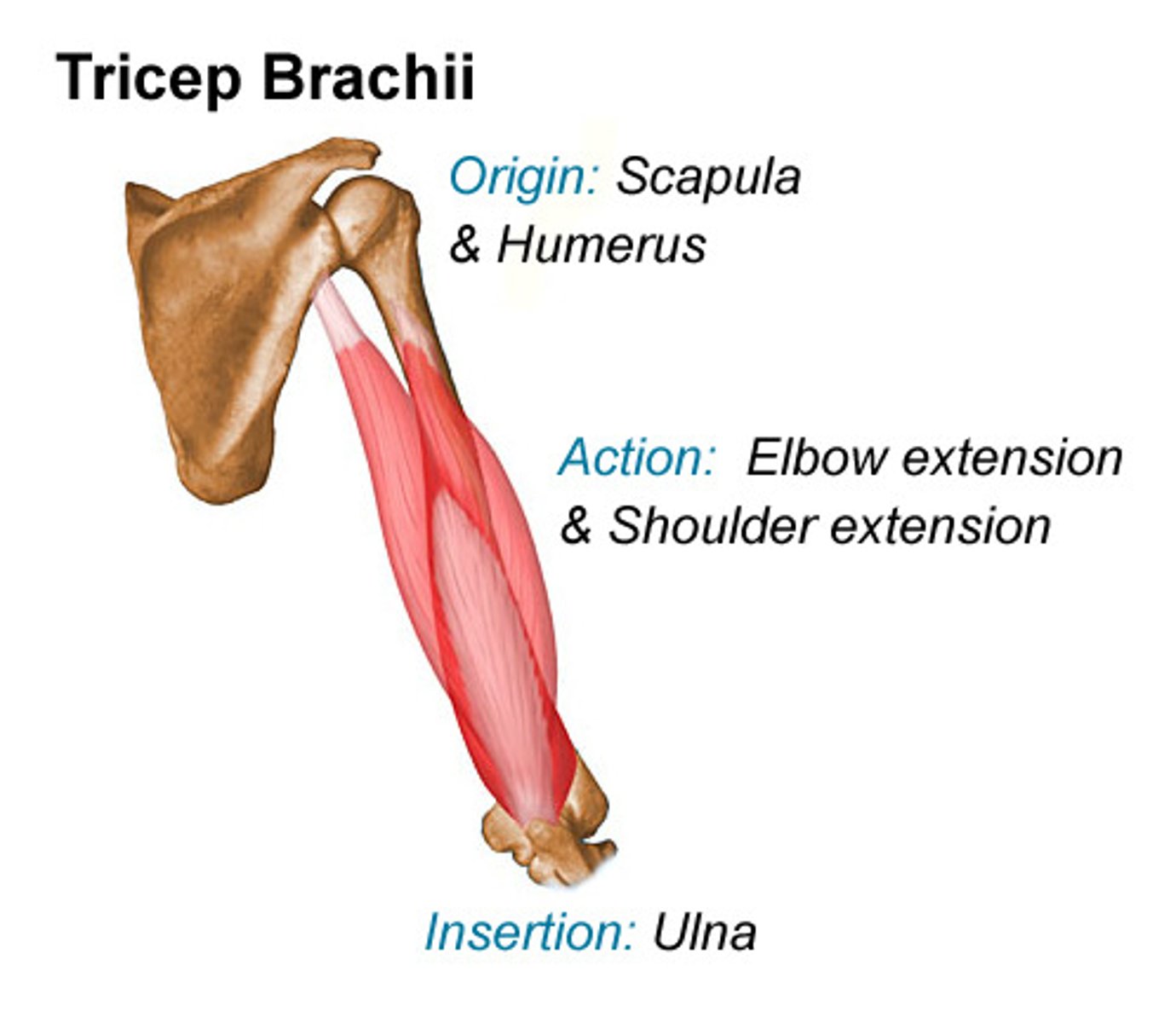
What is the insertion of the triceps brachii?
Olecranon of ulna

What is the primary action of the triceps brachii?
Extension at the elbow.
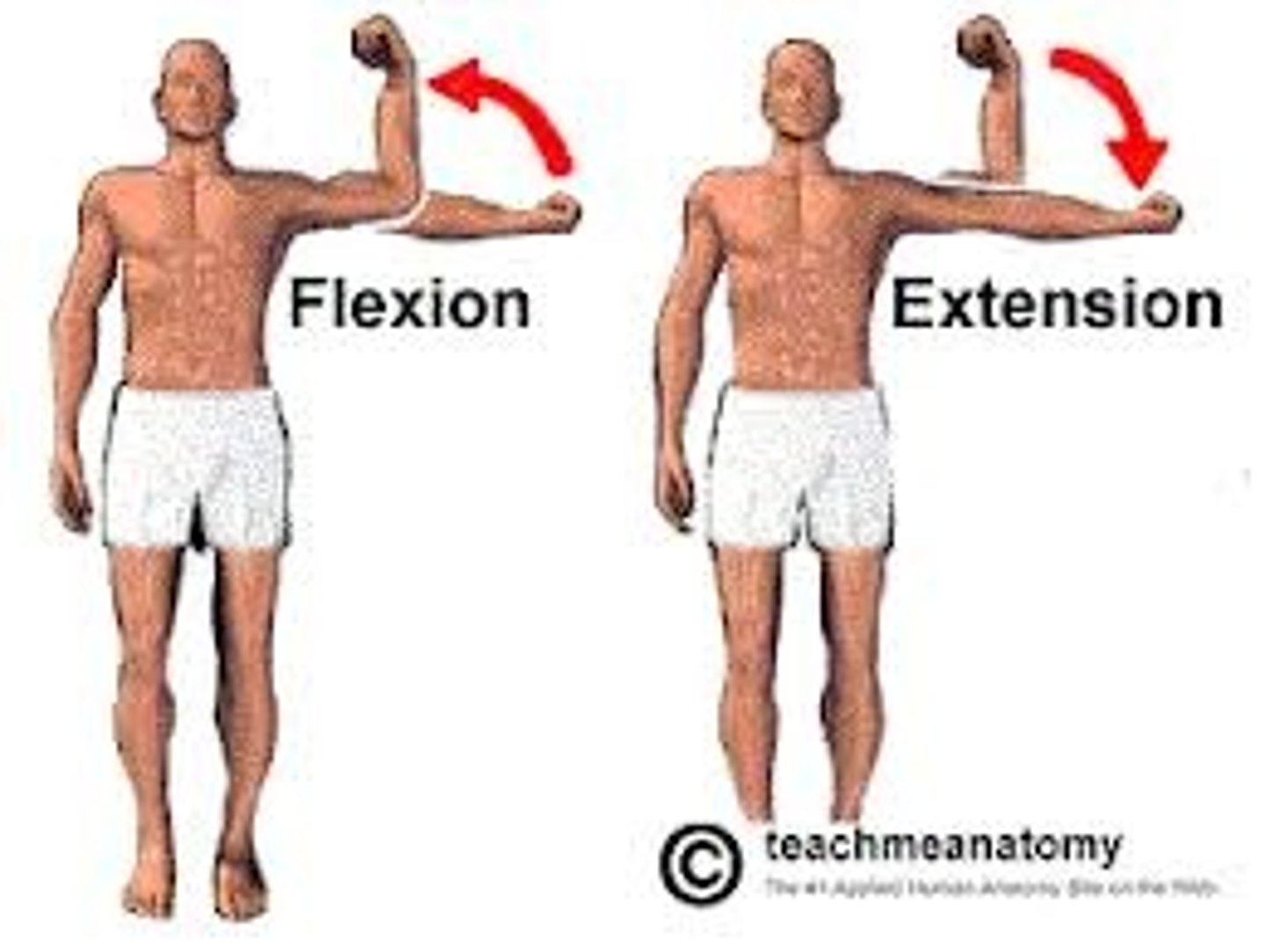
What is an antagonistic movement?
Muscle movements that oppose one another.
What is the origin of the pronator teres?
Medial epicondyle of humerus.
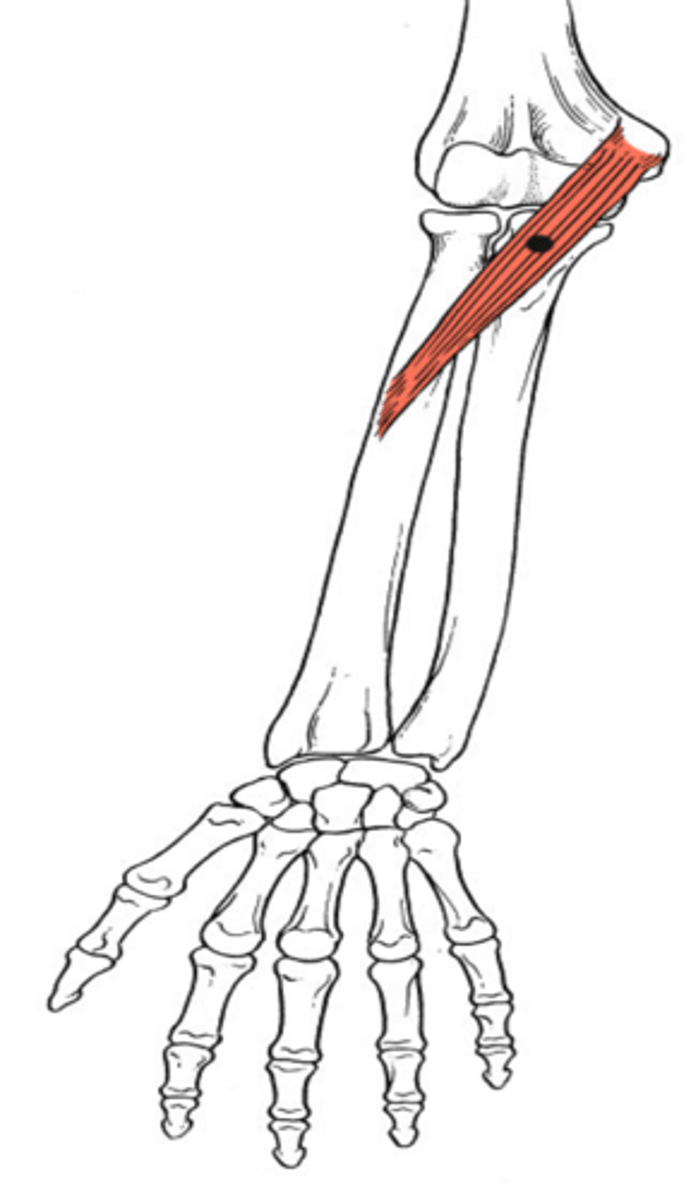
What is the insertion of the pronator teres?
Lateral edge of mid-radius
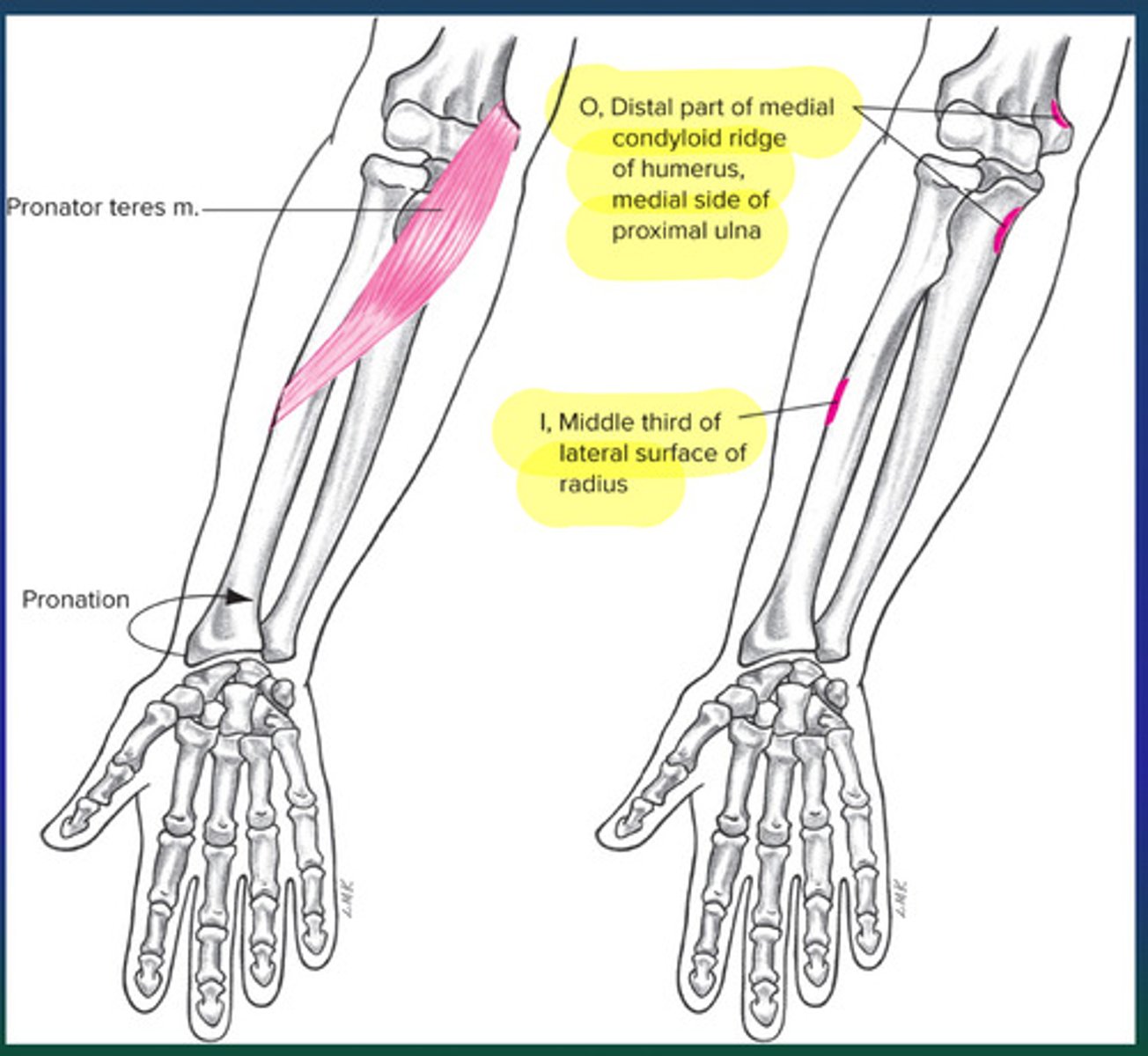
What is the primary action of the pronator teres?
Pronation of the head of the radius
What is the origin of the supinator?
Lateral epicondyle of the humerus
Radial notch of the ulna
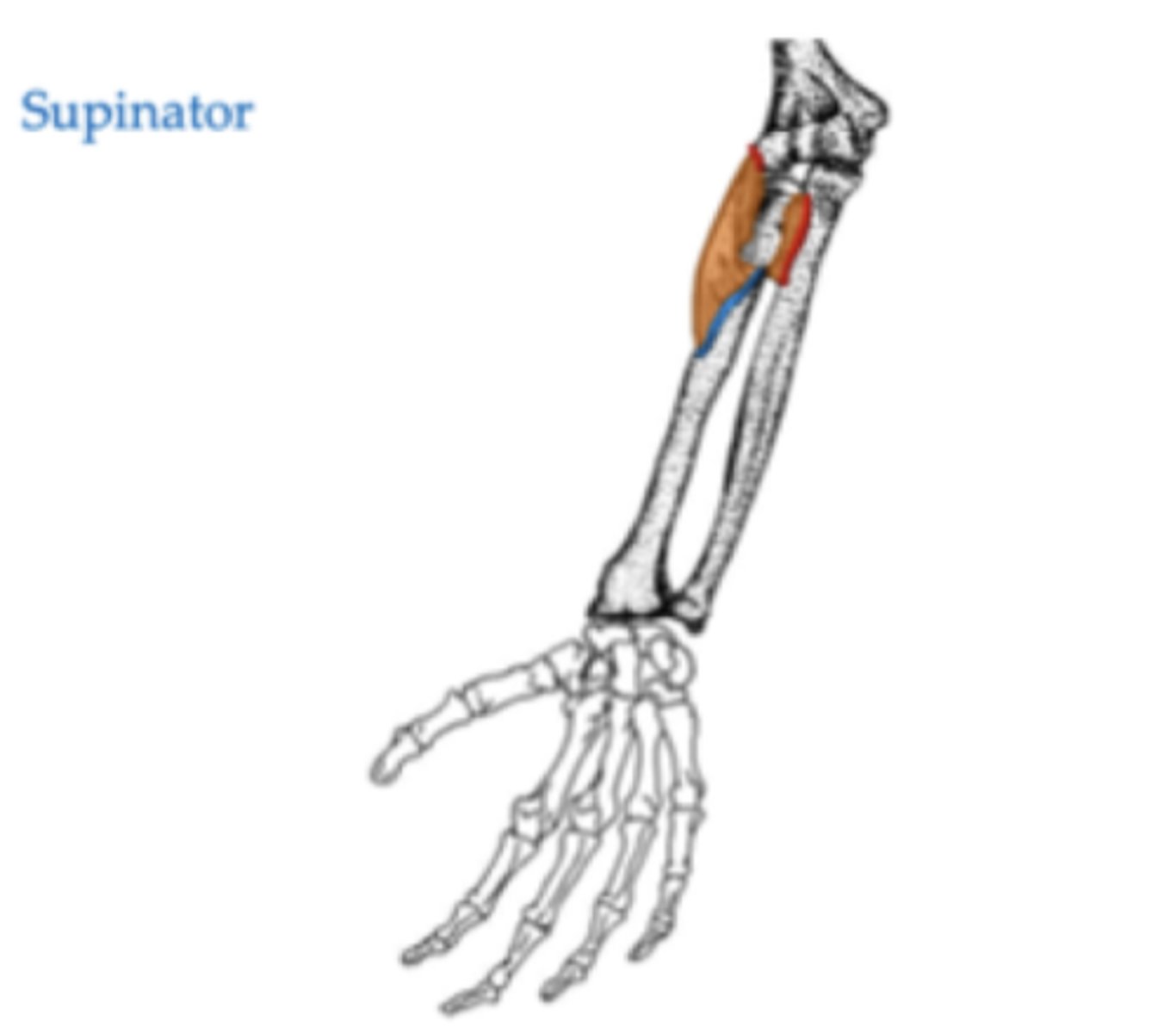
What is the insertion of the supinator?
Lateral surface of radius (more proximal)

What is the primary action of the supinator?
Supination

What type of joint is the acetabulofemoral joint?
Ball-and-socket joint.
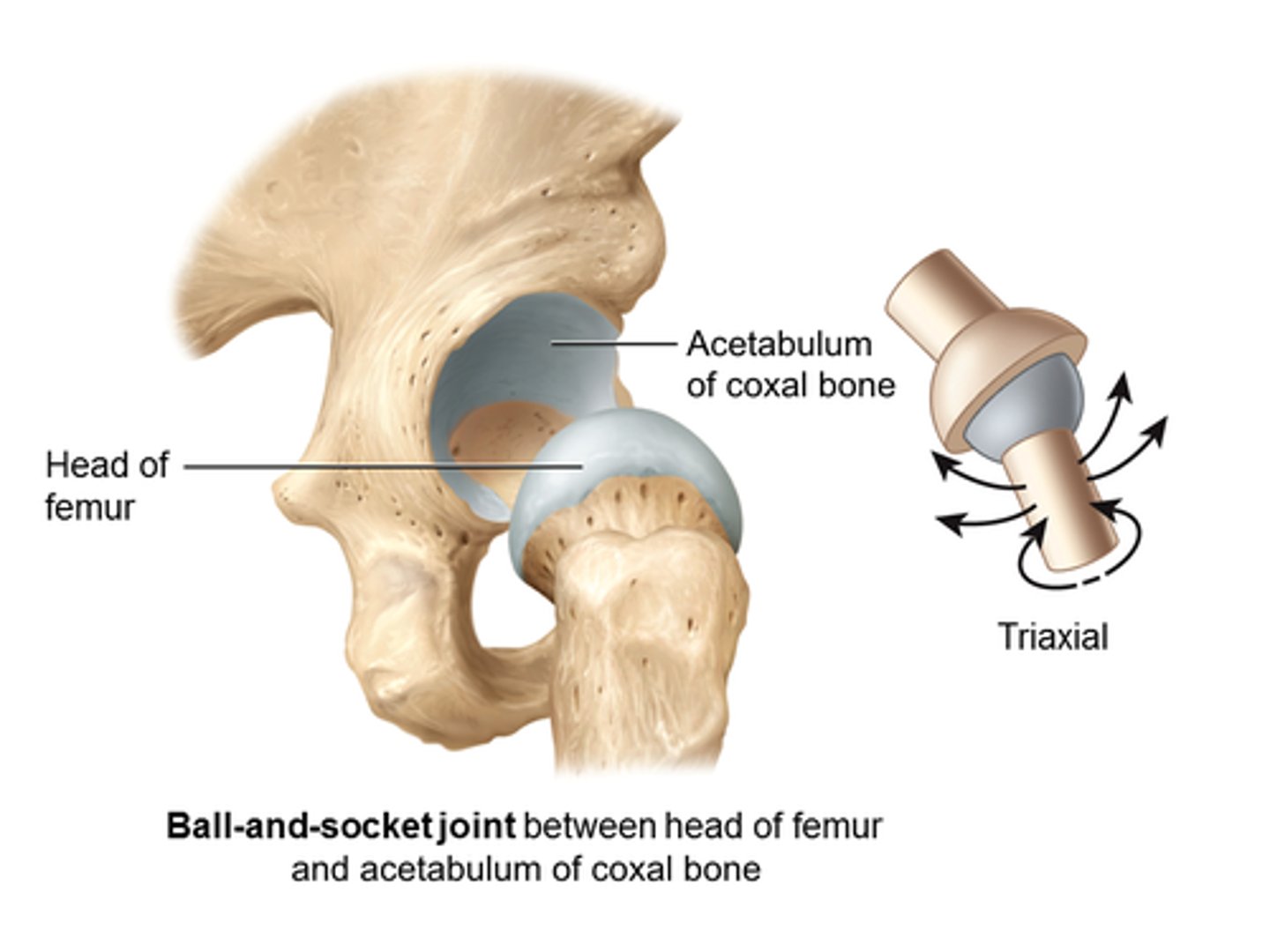
What type of joint is the sacroiliac joint?
Gliding joint.
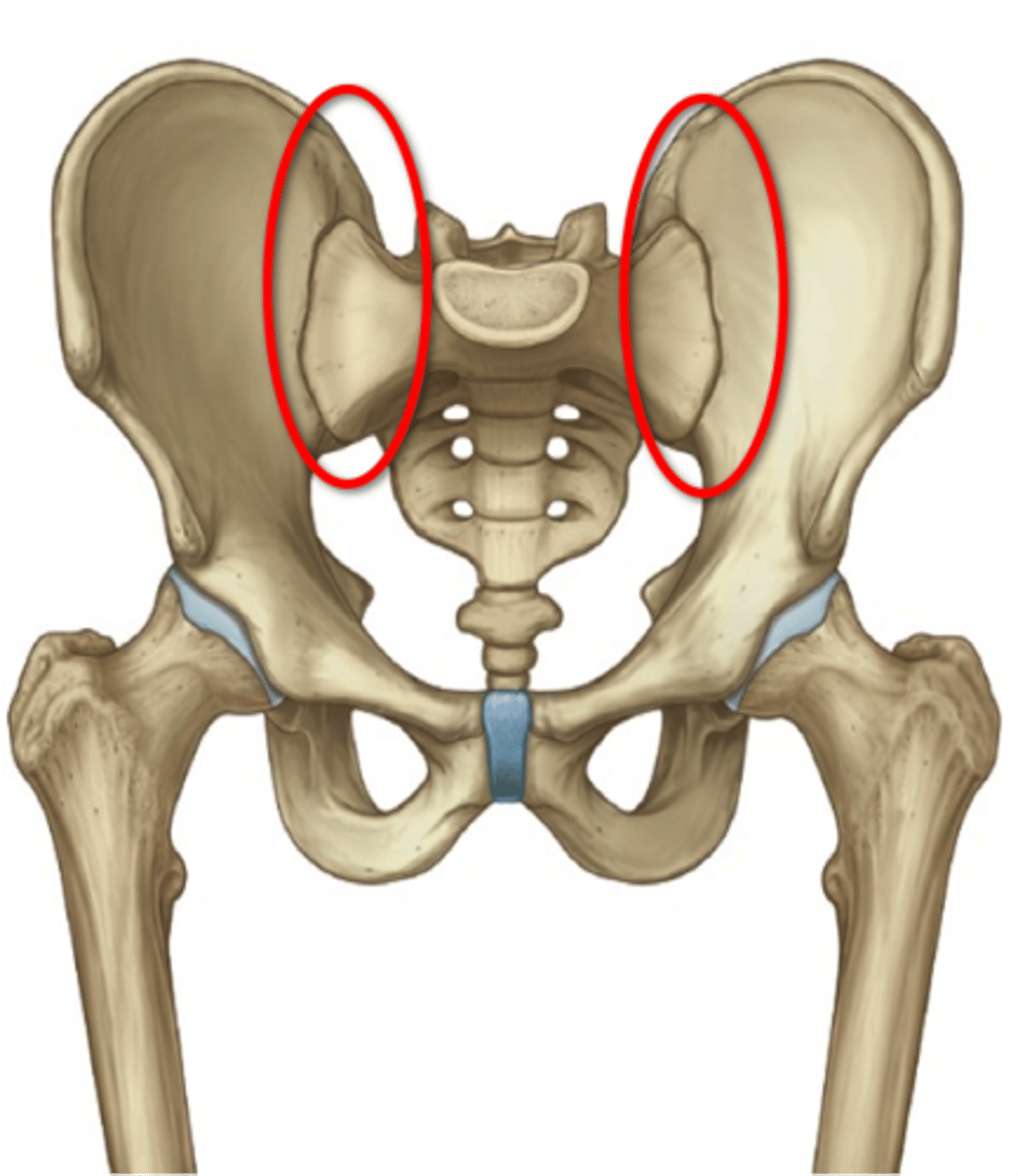
What type of joint is the pubic symphysis joint?
Non-synovial joint.
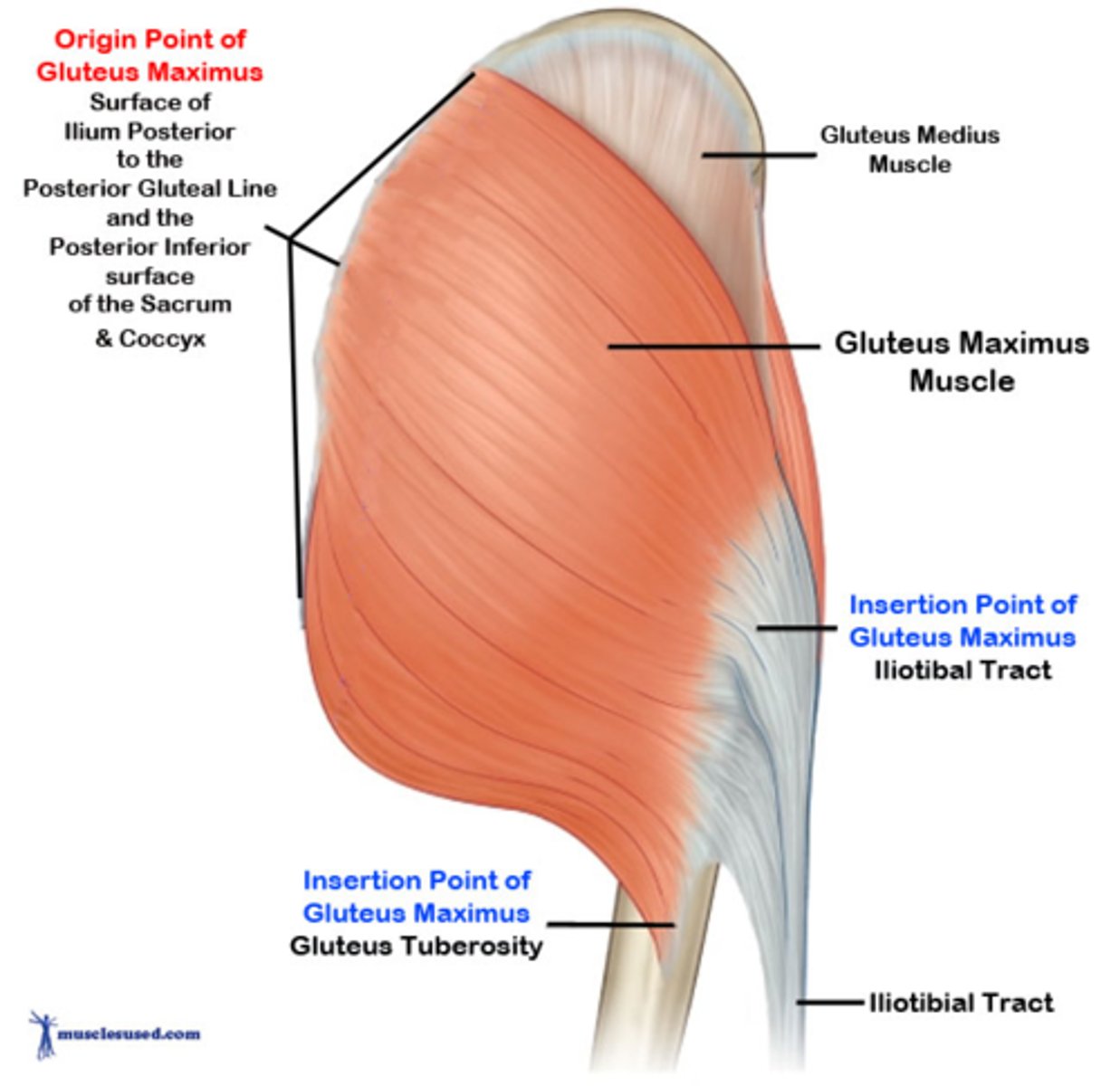
What is the origin of the gluteus maximus?
Posterior iliac crest (and lateral edge of sacrum)
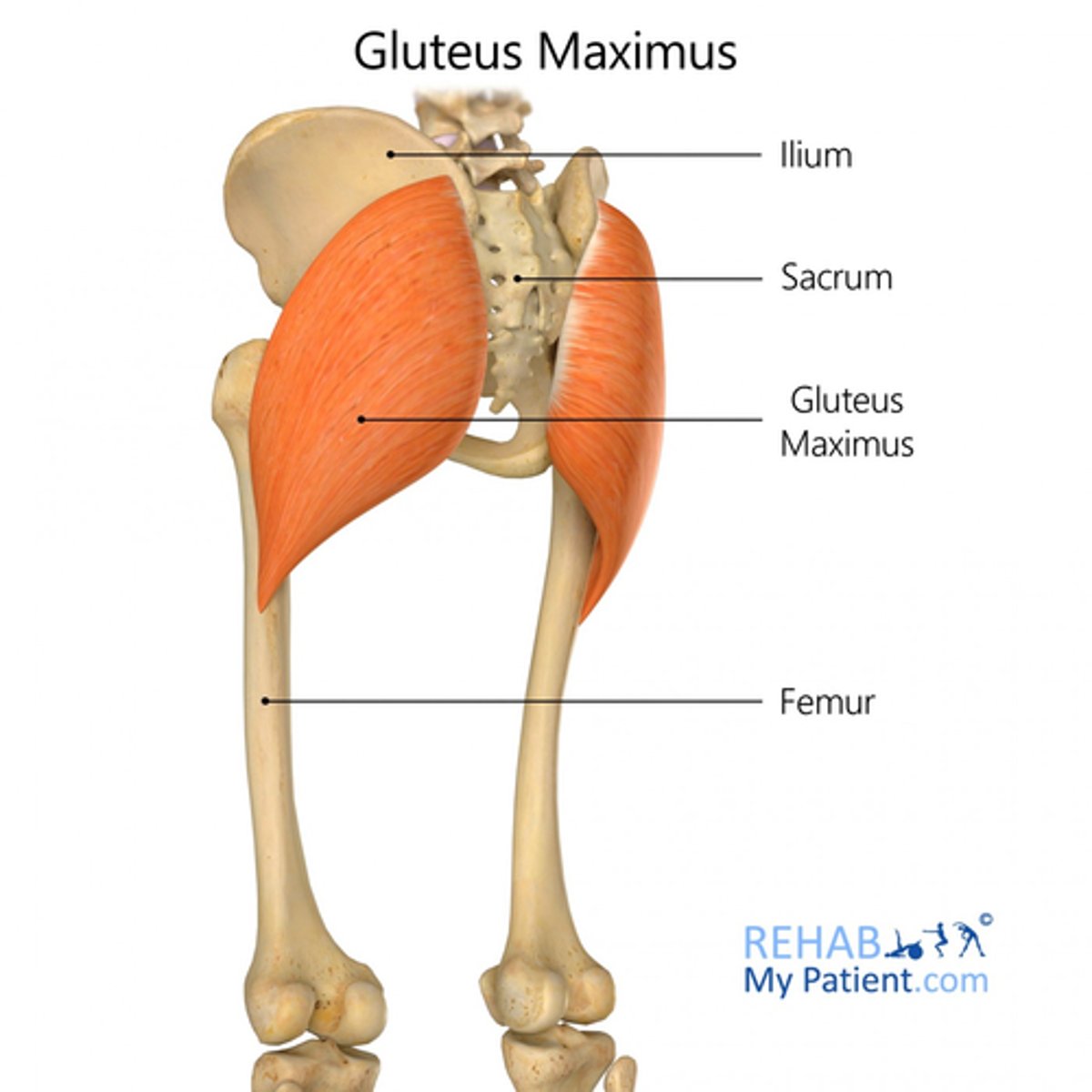
What is the action of the gluteus maximus?
Lateral rotation and extension of the femur.

What is the action of the gluteus medius?
Abduction and medial rotation of the femur.

What is the primary action of the adductor magnus?
Adduction of the femur.
What is the insertion of the gluteus maximus?
Posterior superior femur (gluteal tuberosity)
What is the origin of the gluteus medius?
Iliac crest

What is the insertion of the gluteus medius?
Greater trochanter of femur.
What is the origin of the adductor magnus?
Inferior ramus of pubis
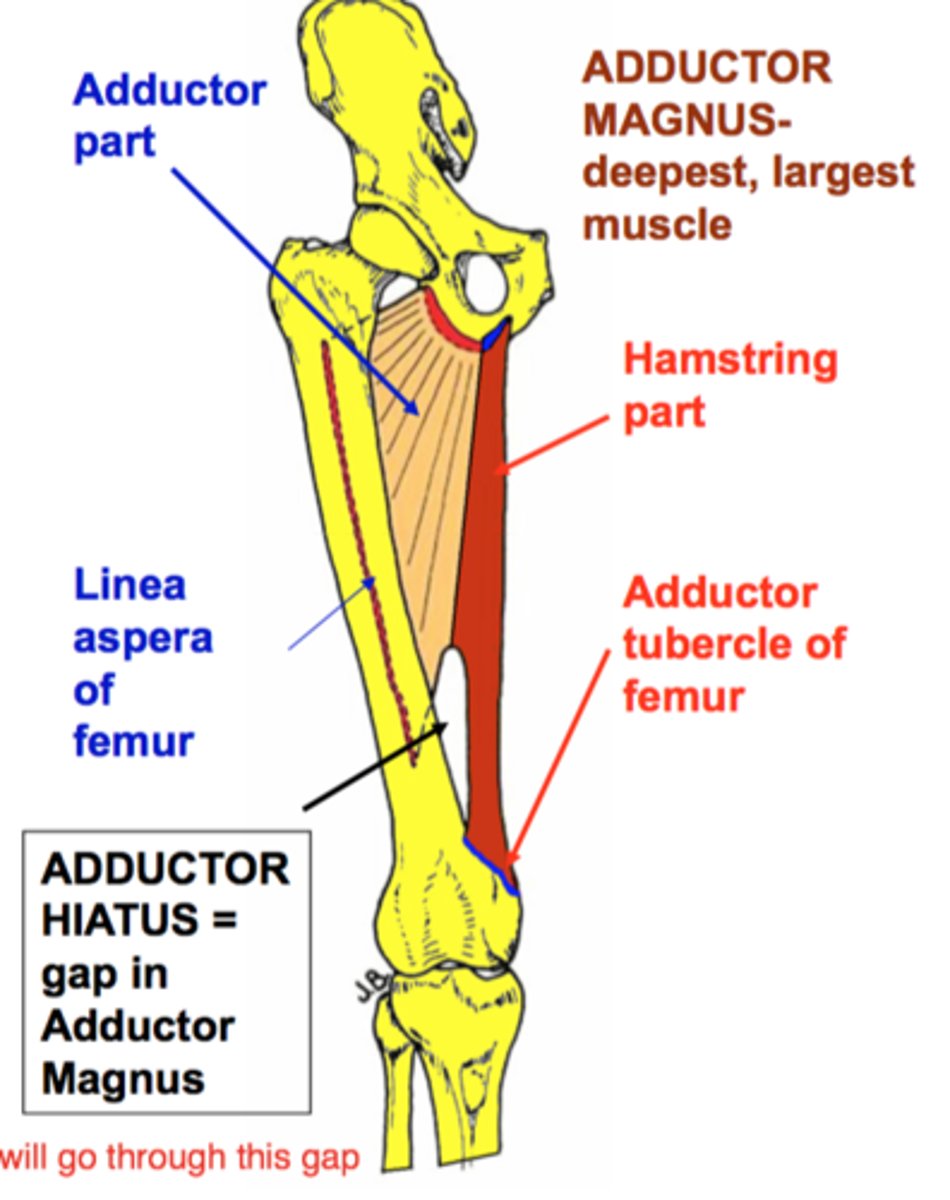
What is the insertion of the adductor magnus?
Linea aspera of femur.

What type of joint is the tibiofemoral joint?
Hinge joint.
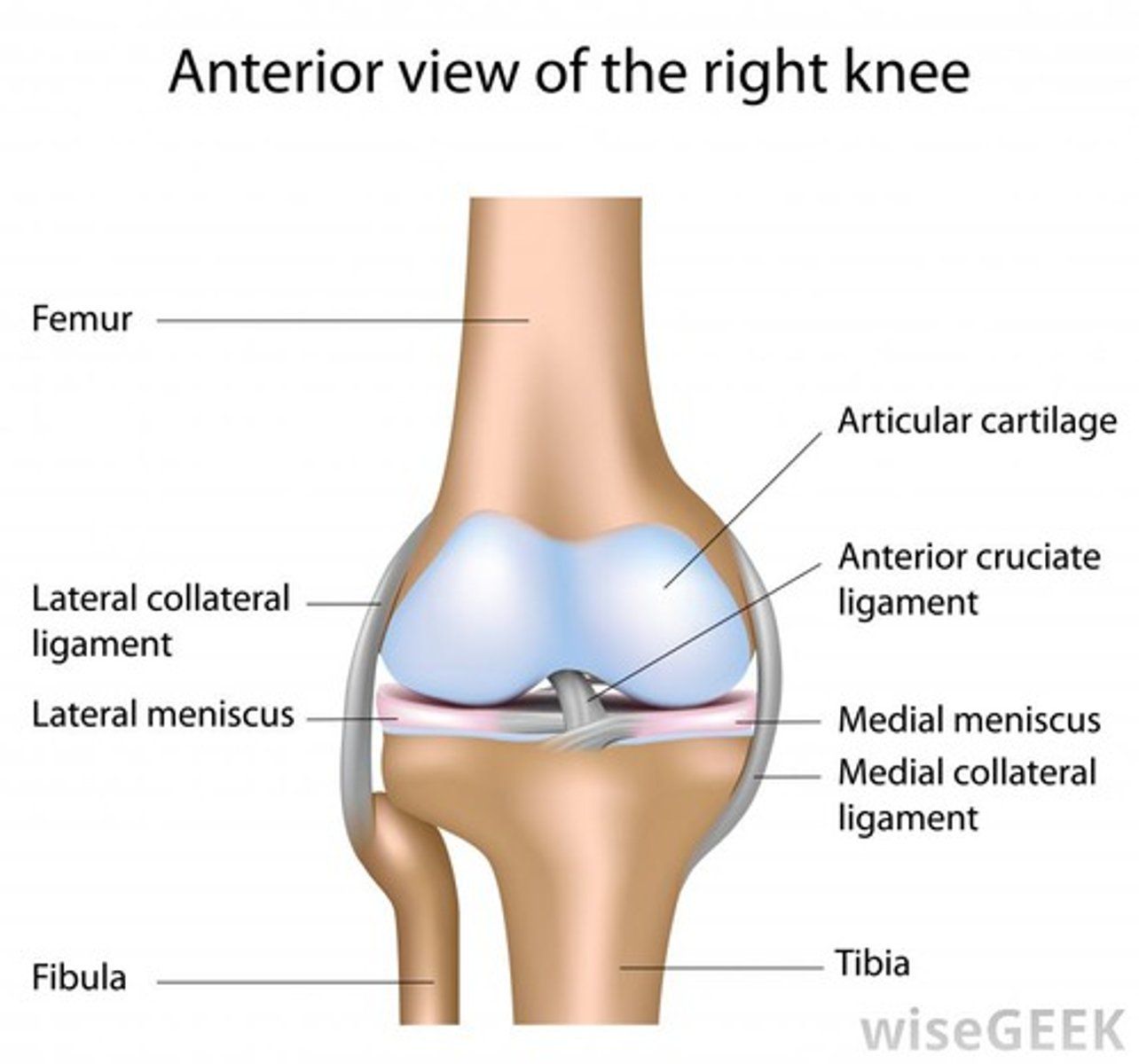
What type of joint is the femoropatellar joint?
Gliding joint.
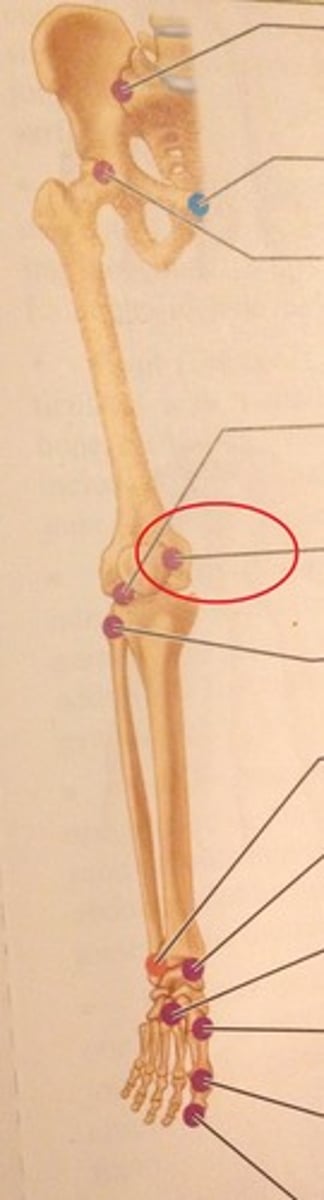
What type of joint is the proximal tibiofibular joint?
Non-synovial joint.

What are the major knee extensor muscles?
Quadriceps femoris (quads)
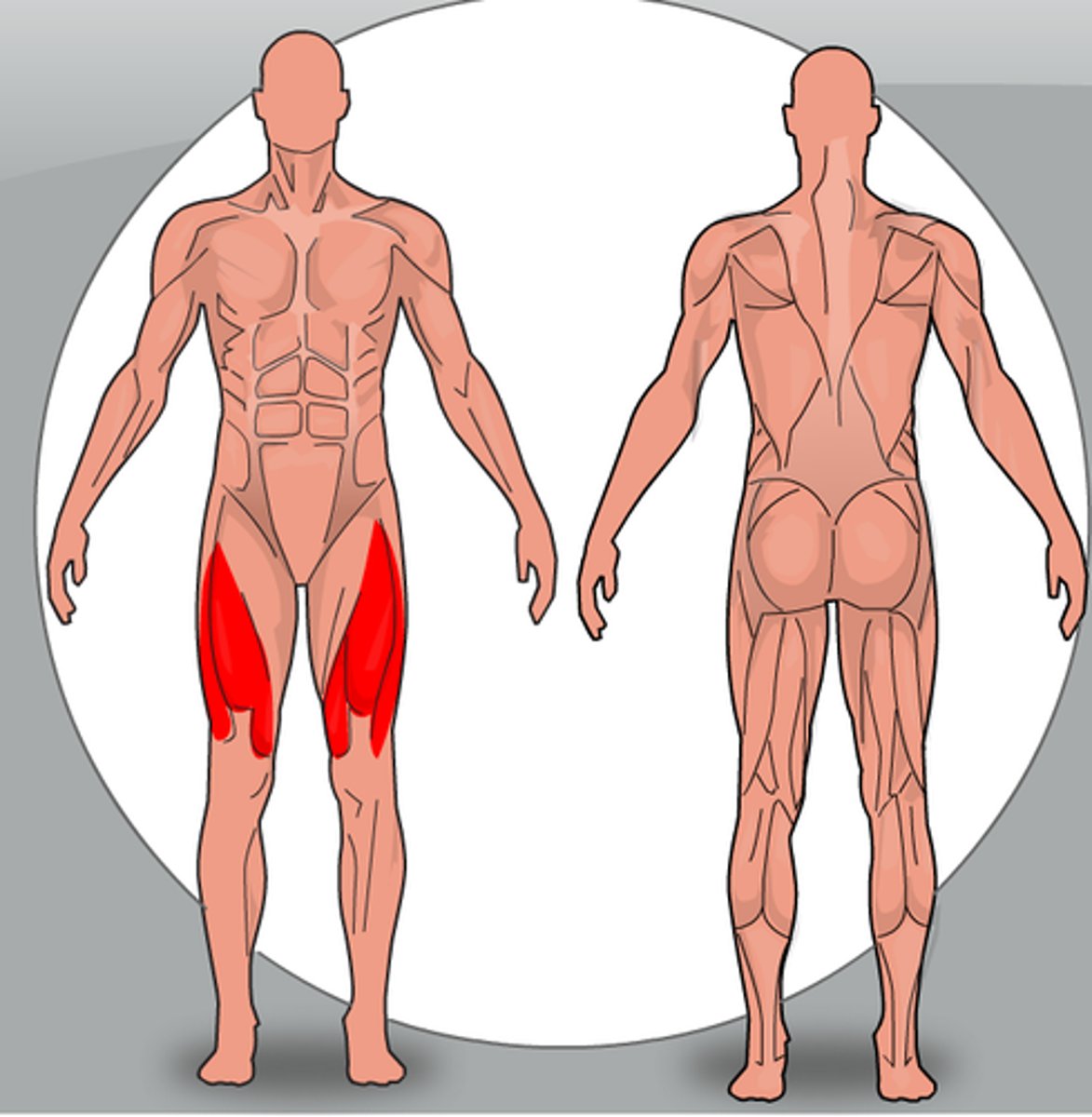
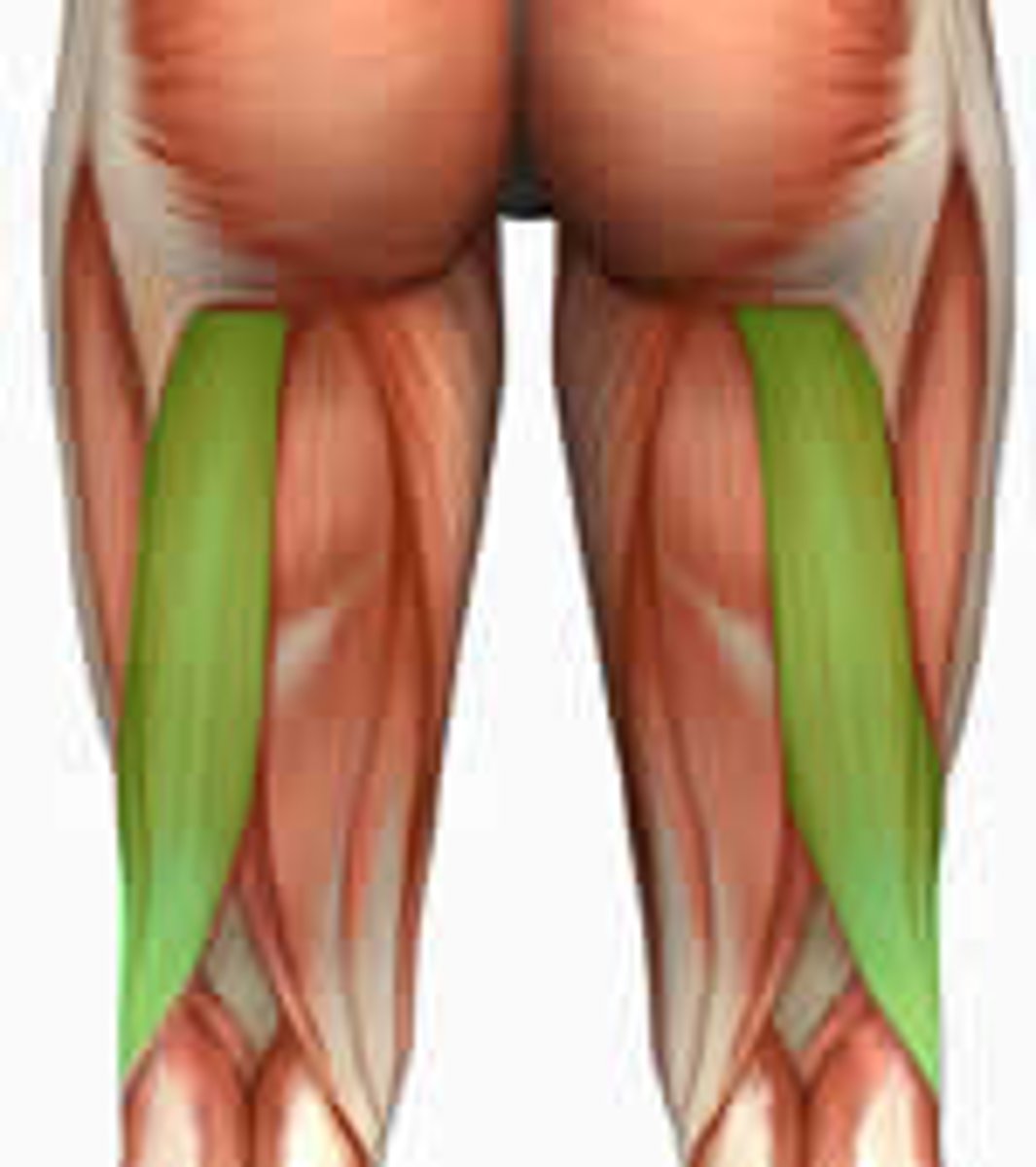
Which muscle originates from the ischial tuberosity and flexes the knee?
Biceps femoris.
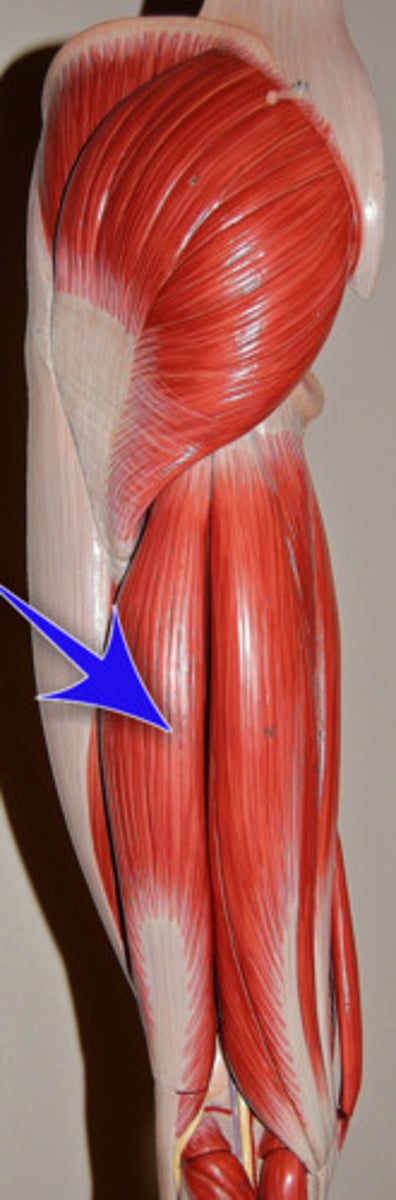
What muscle inserts at the head of the fibula and lateral condyle of tibia?
Biceps femoris.
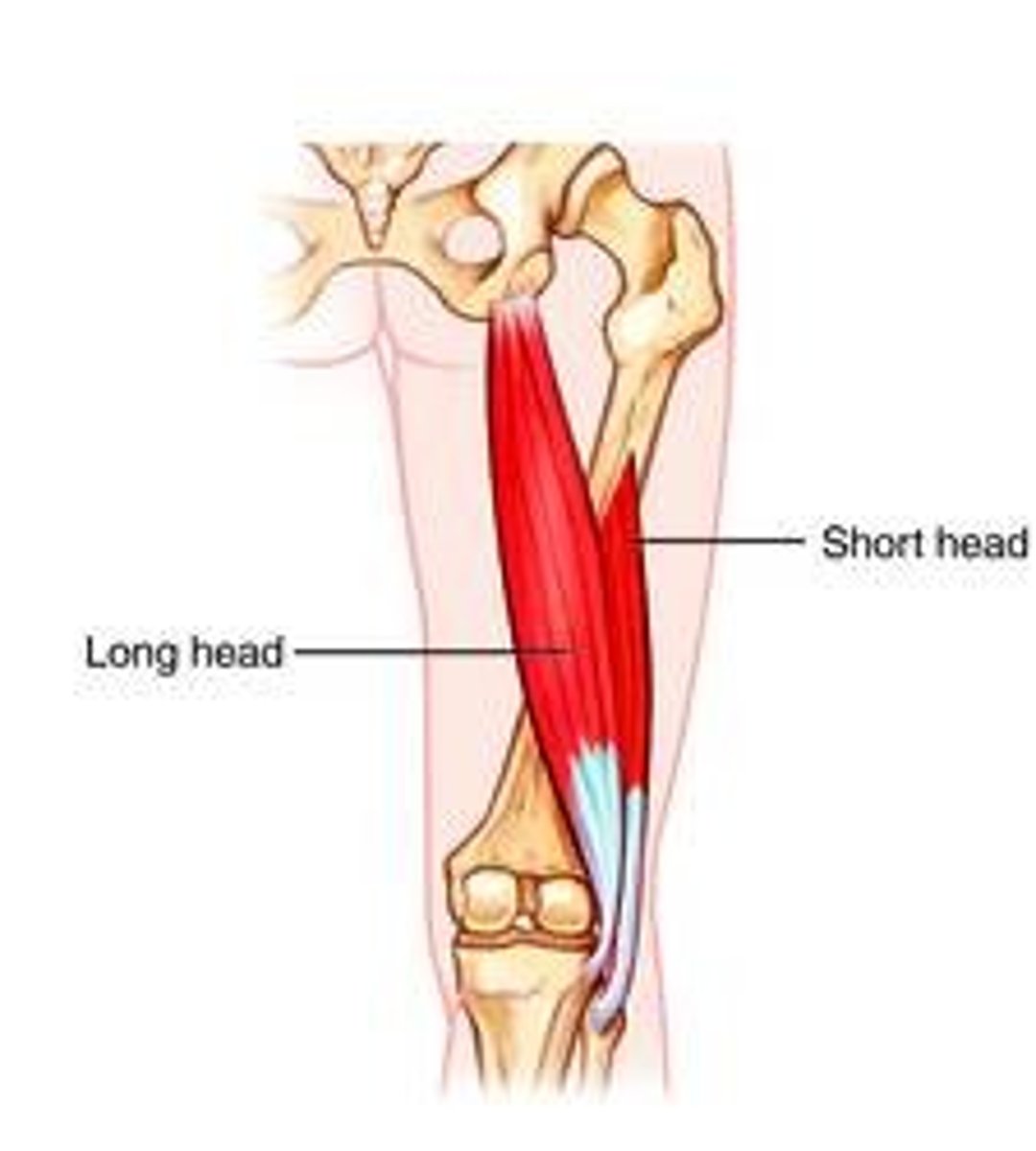
What is the primary action of the biceps femoris?
Flexion at the knee.
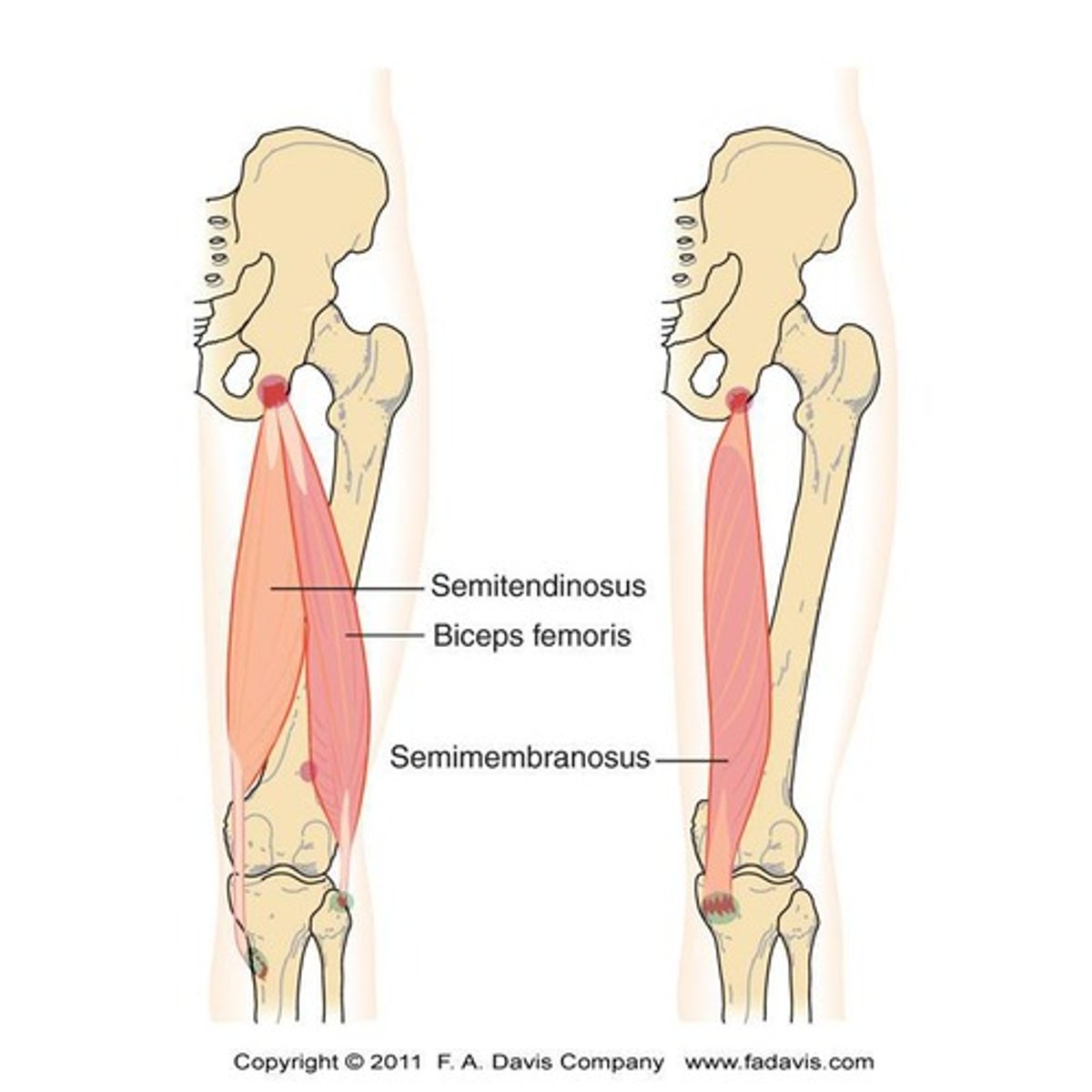
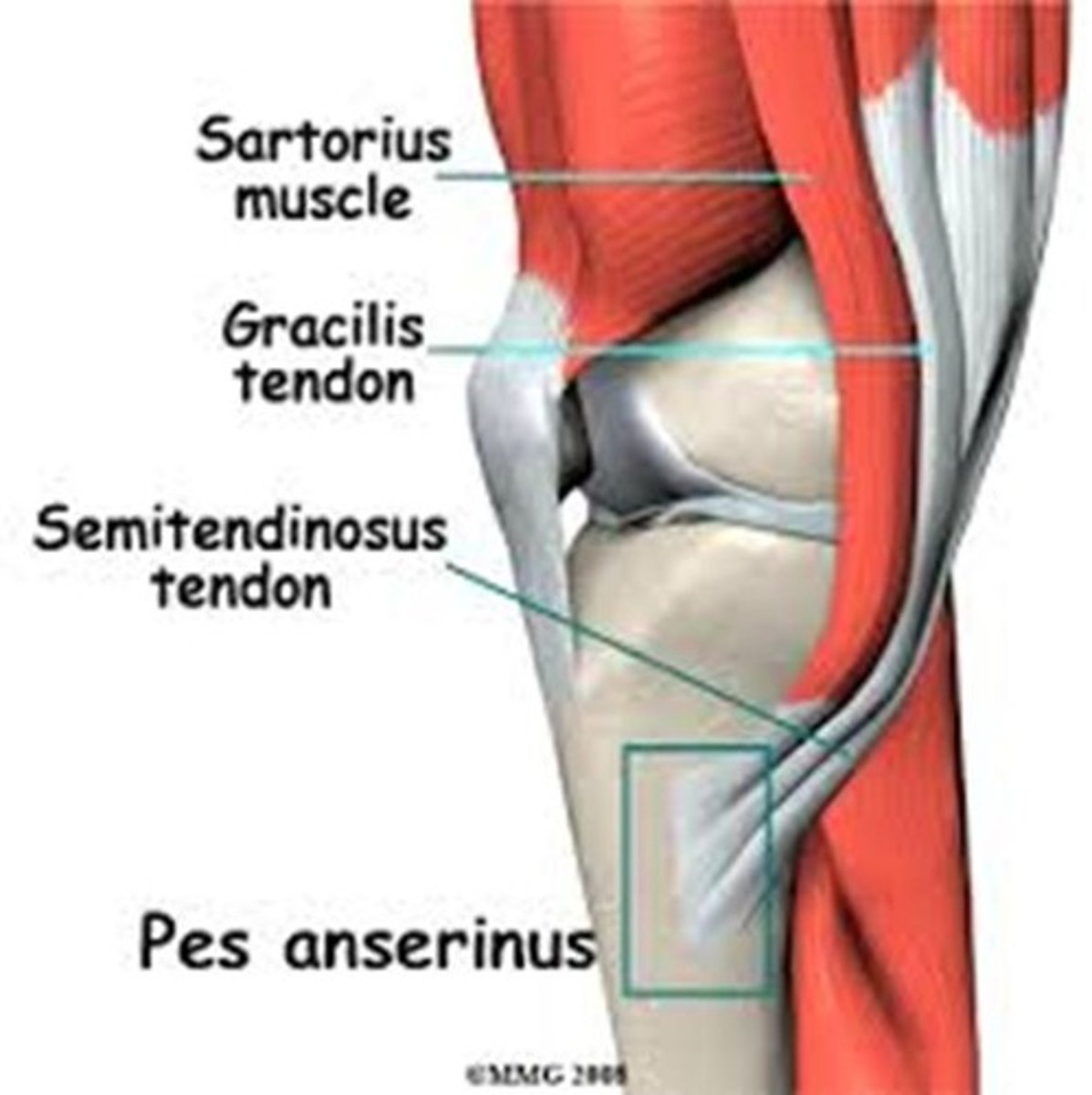
What is the origin of the semitendinosus?
Ischial tuberosity
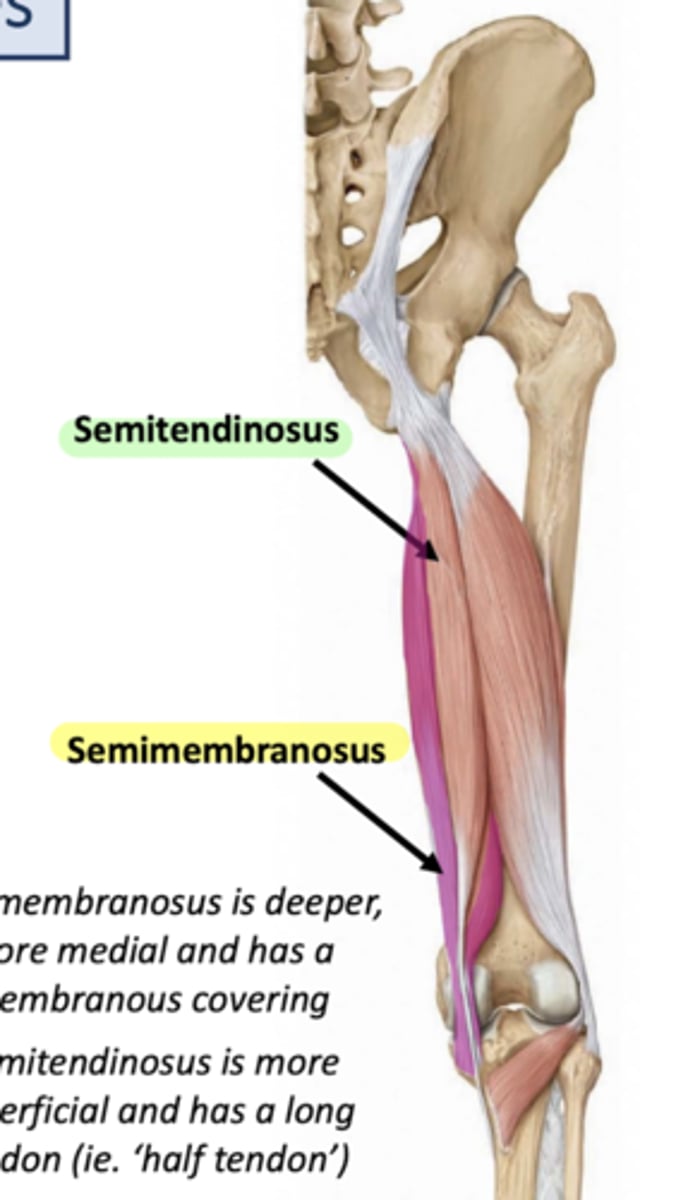
What is the primary action of the semitendinosus?
Flexion at the knee.
What is the insertion of the semitendinosus?
Posterior surface of medial condyle of tibia.
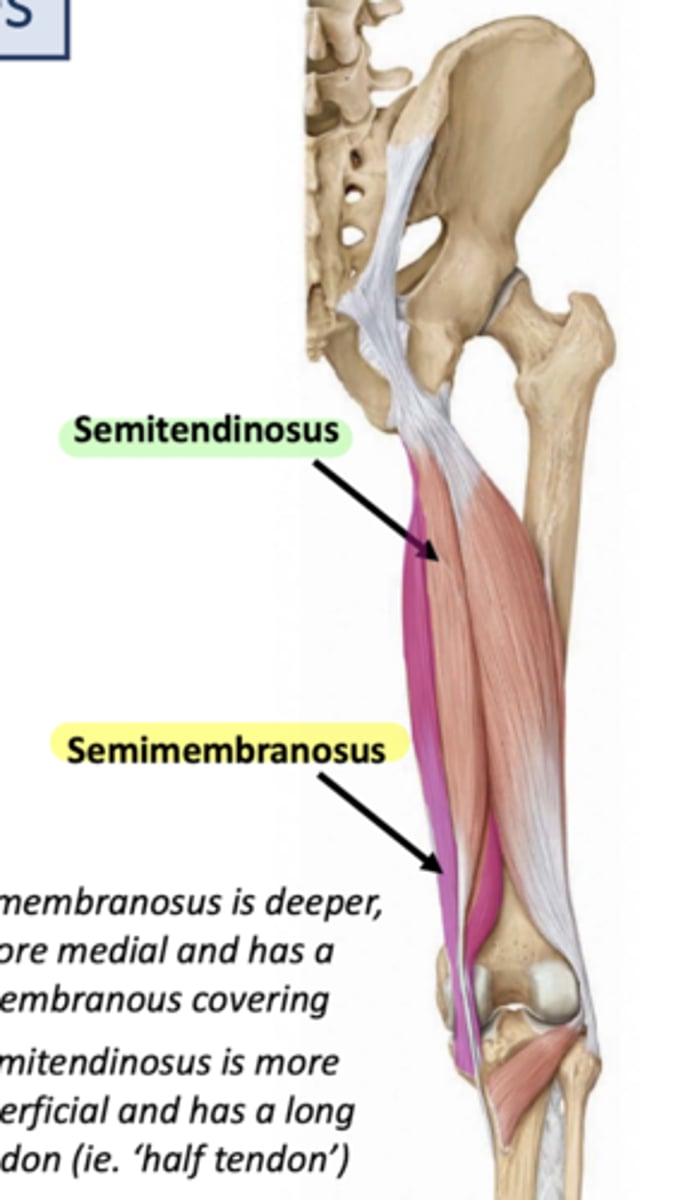
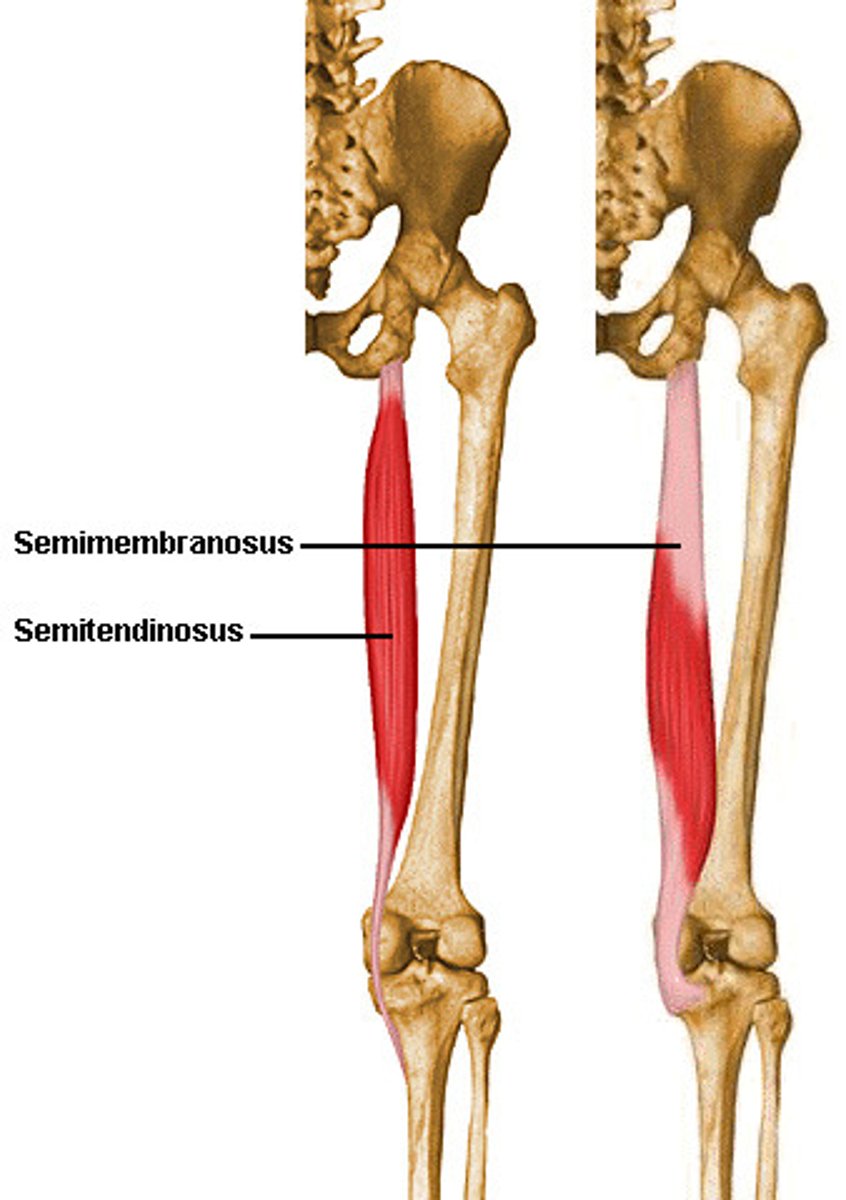
What is the origin of the semimembranosus?
Ischial tuberosity
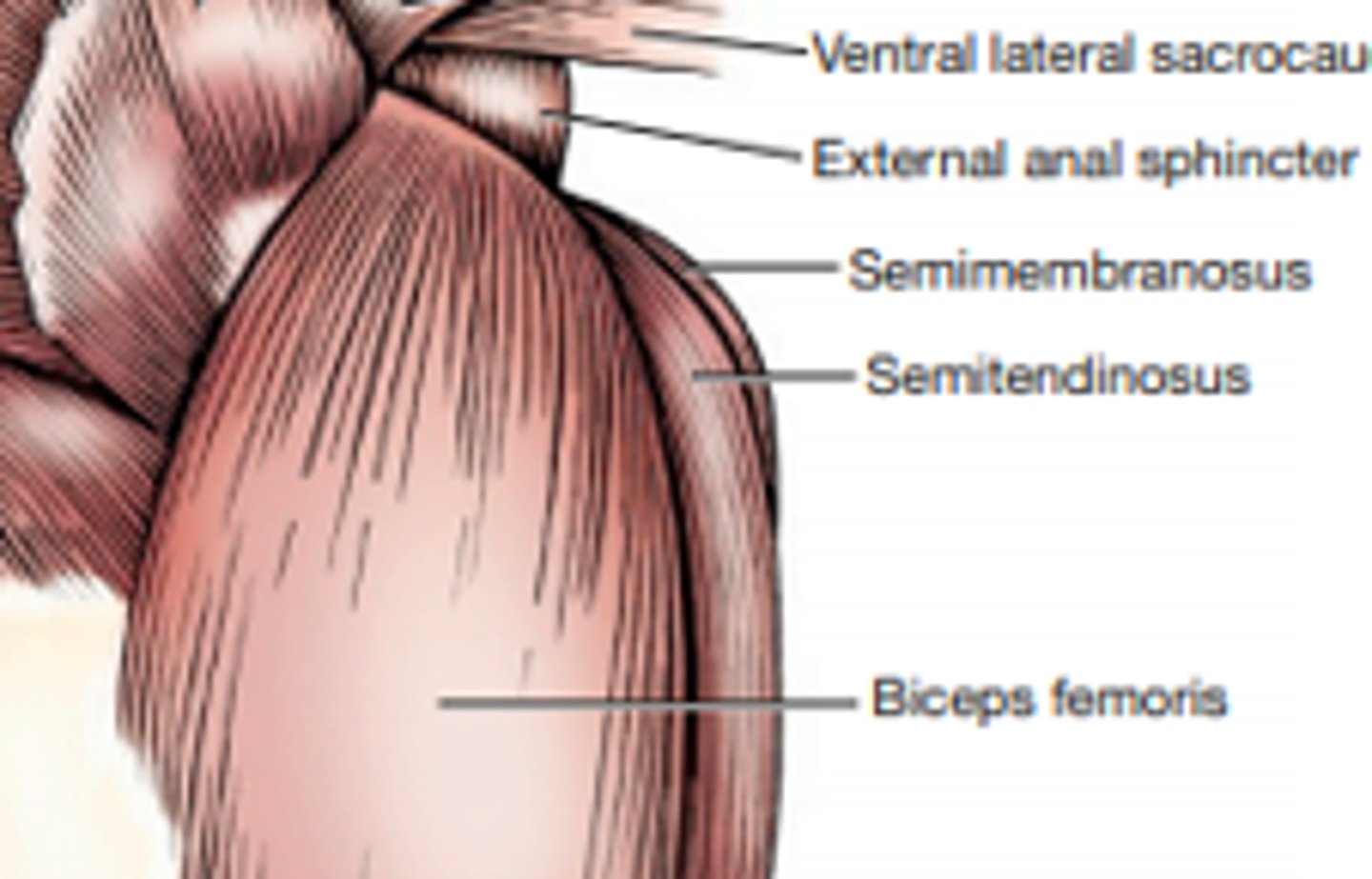
What is the insertion of the semimembranosus?
Medial condyle of tibia

What is the primary action of the semimembranosus?
Flexion at the knee.
What is the origin of the sartorius?
Anterior iliac crest
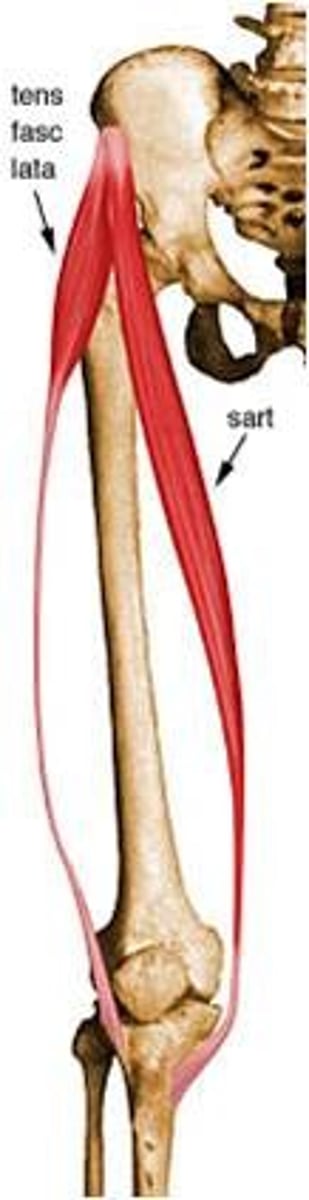
What is the insertion of the sartorius?
Medial surface of tibial tuberosity

What is the primary action of the sartorius?
Flexion at the knee and hip
What is the origin of the rectus femoris?
Inferior to the anterior iliac crest
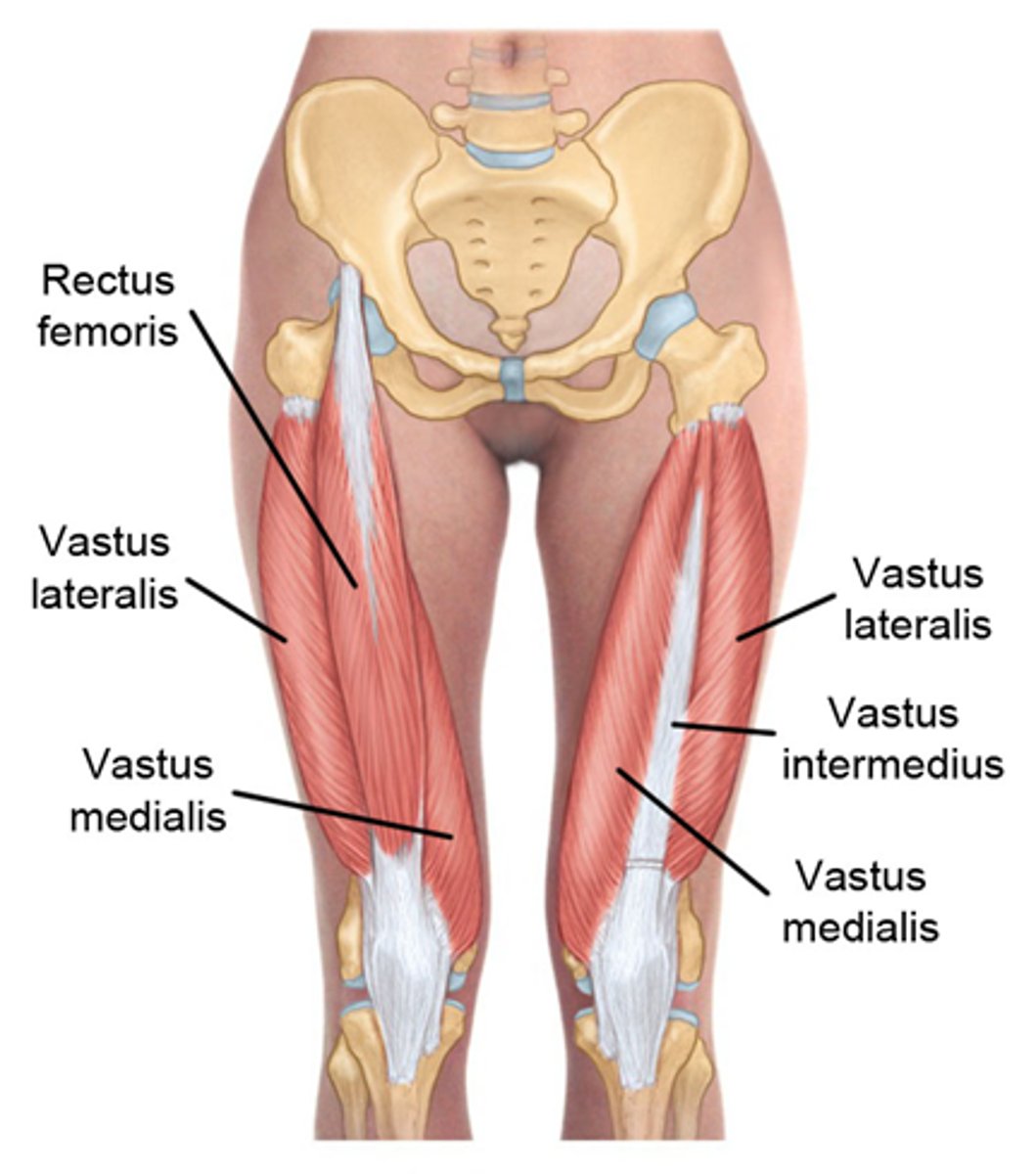
What is the action of the rectus femoris at the knee?
Extension at the knee.
What is the insertion of the rectus femoris?
Tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament

What is the origin of the vastus intermedius?
Anterior-proximal surface of femur
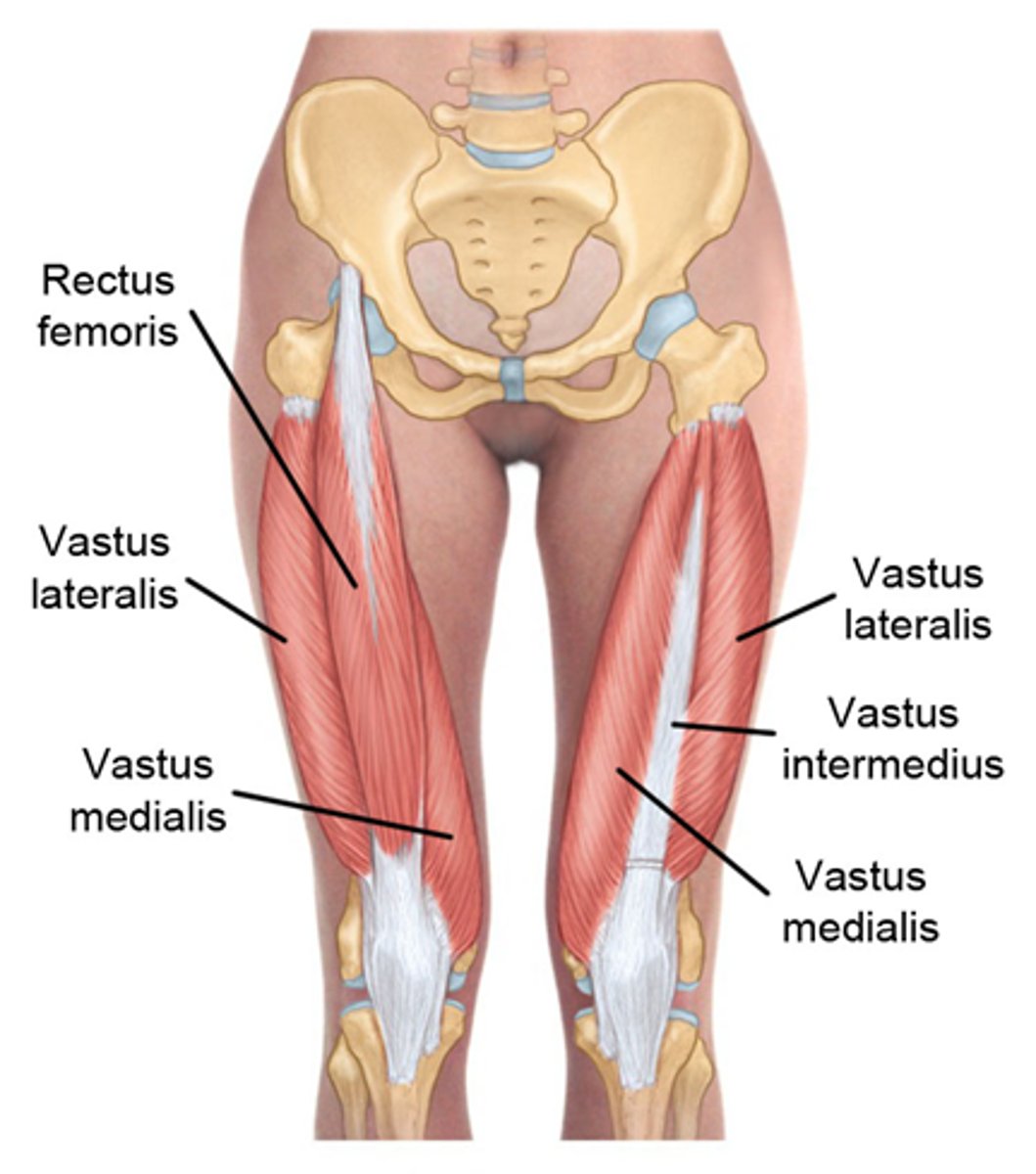
What is the insertion of the vastus intermedius?
Tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament

What is the primary action of the vastus intermedius?
Extension at the knee
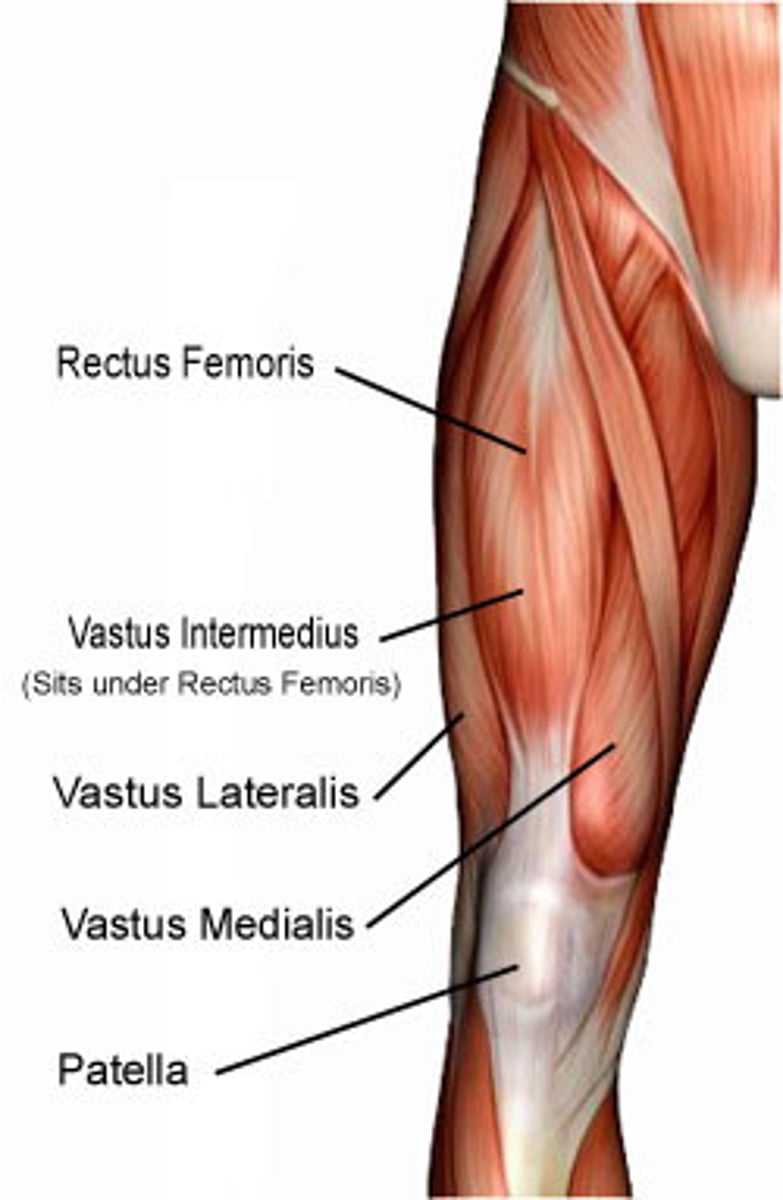
What is the origin of the vastus lateralis?
Intertrochanteric line (near greater trochanter)
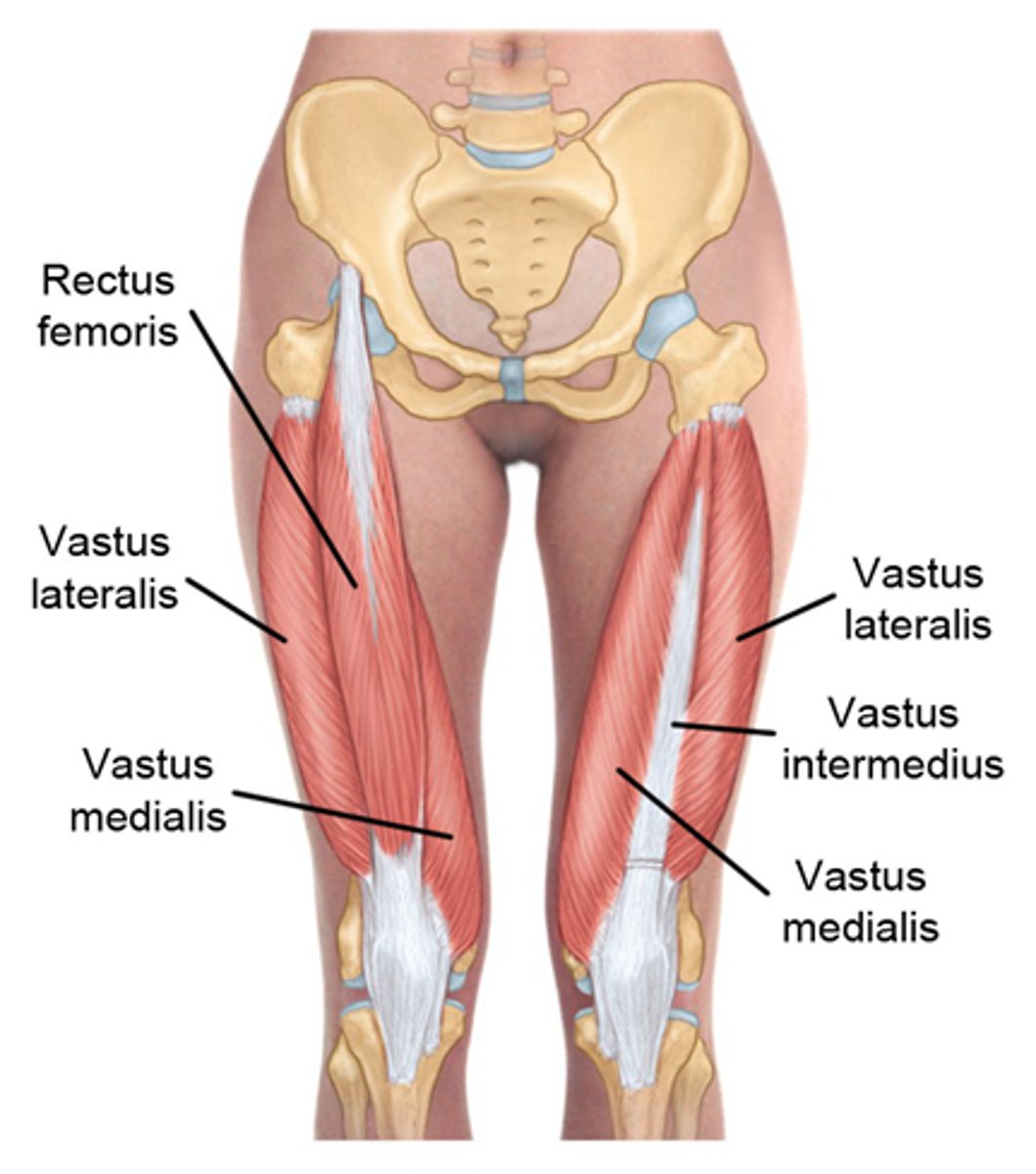
What is the insertion of the vastus lateralis?
Tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament
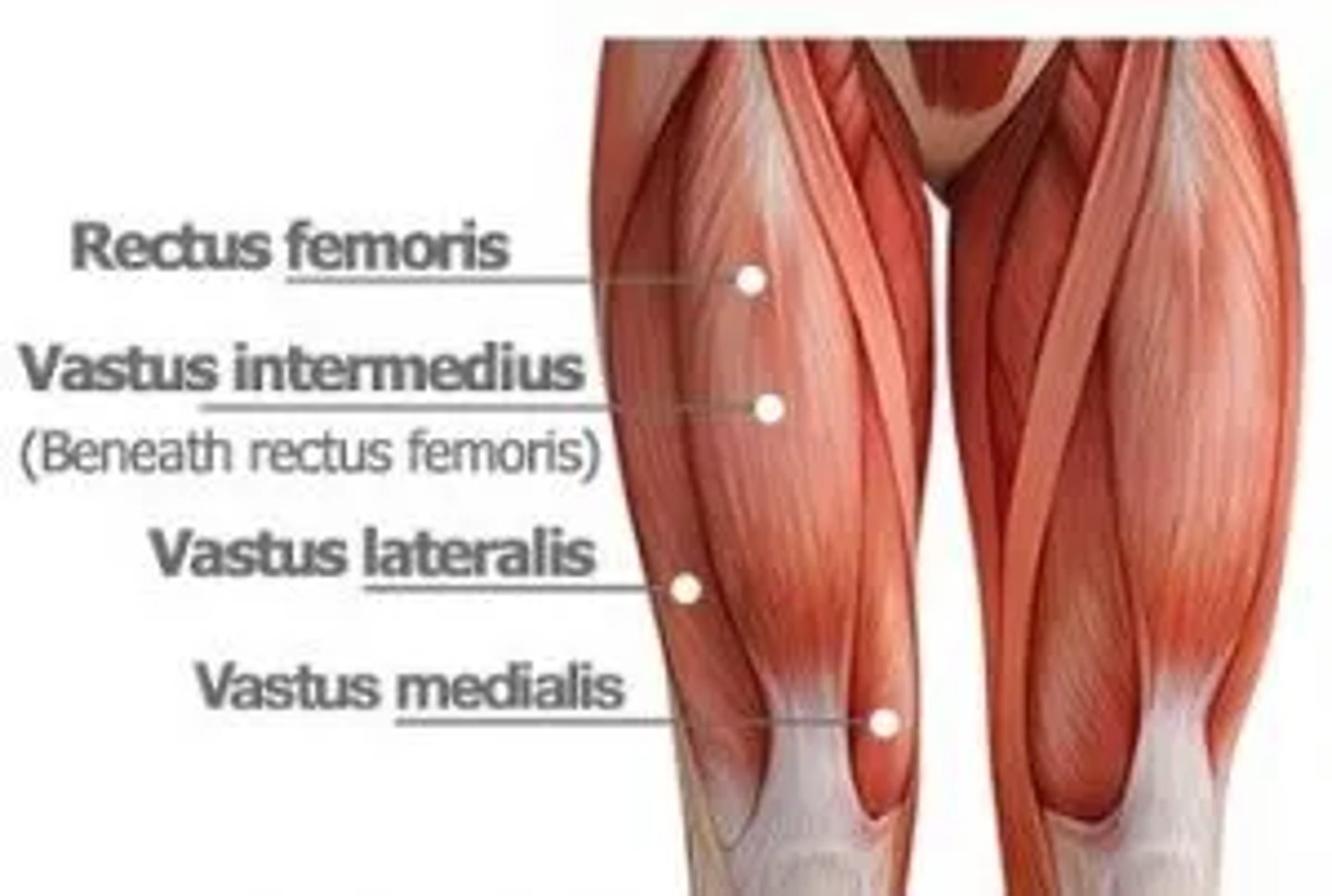
What is the primary action of the vastus lateralis?
Extension at the knee
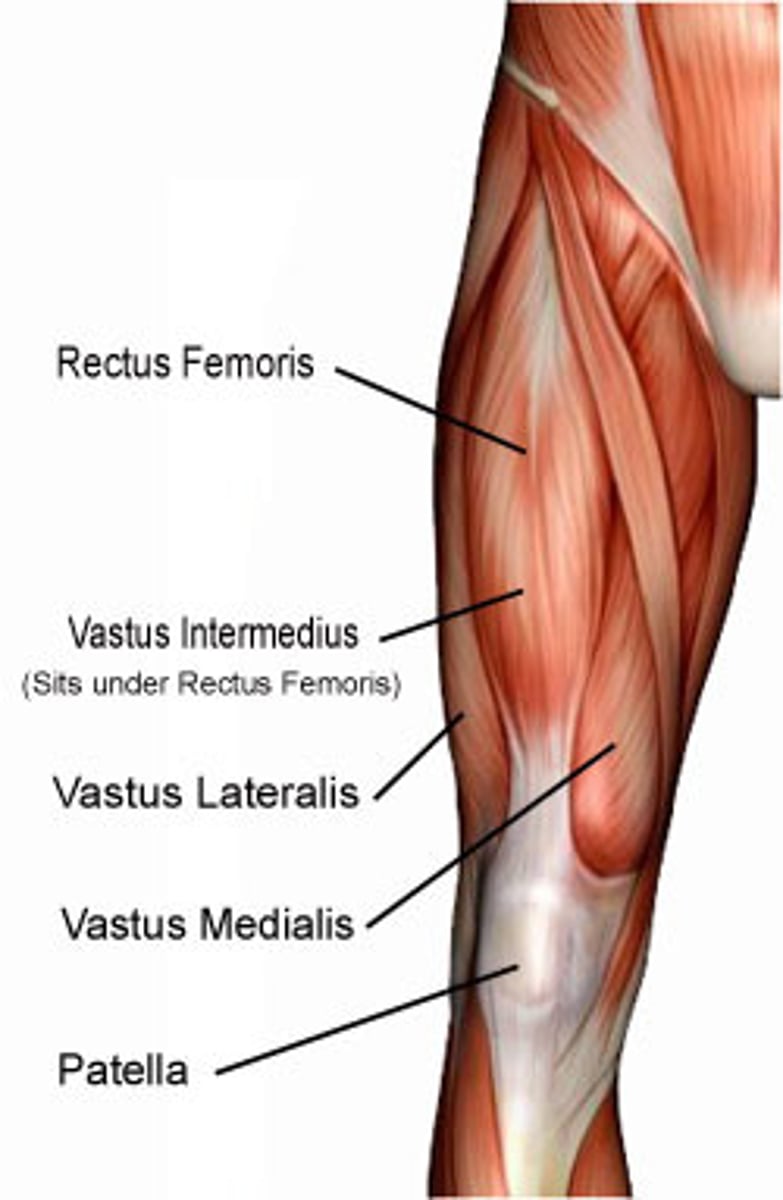
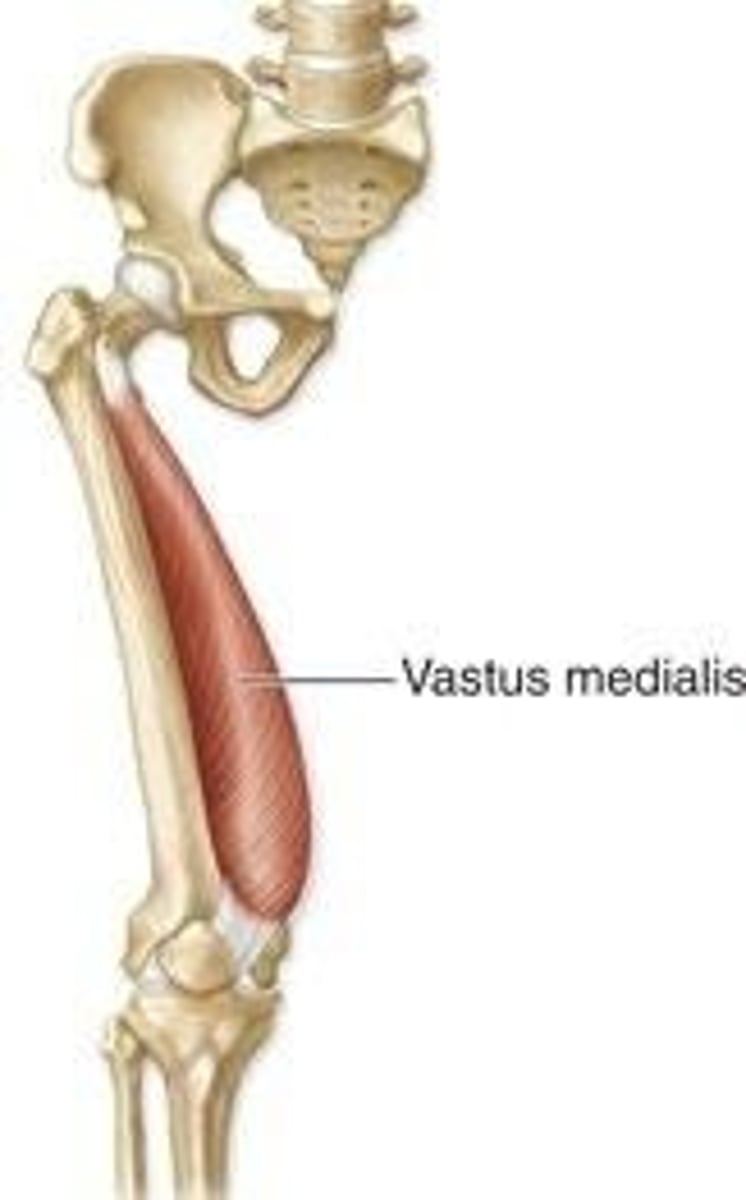
What is the origin of the vastus medialis?
Medial surface of femur (below lesser trochanter)
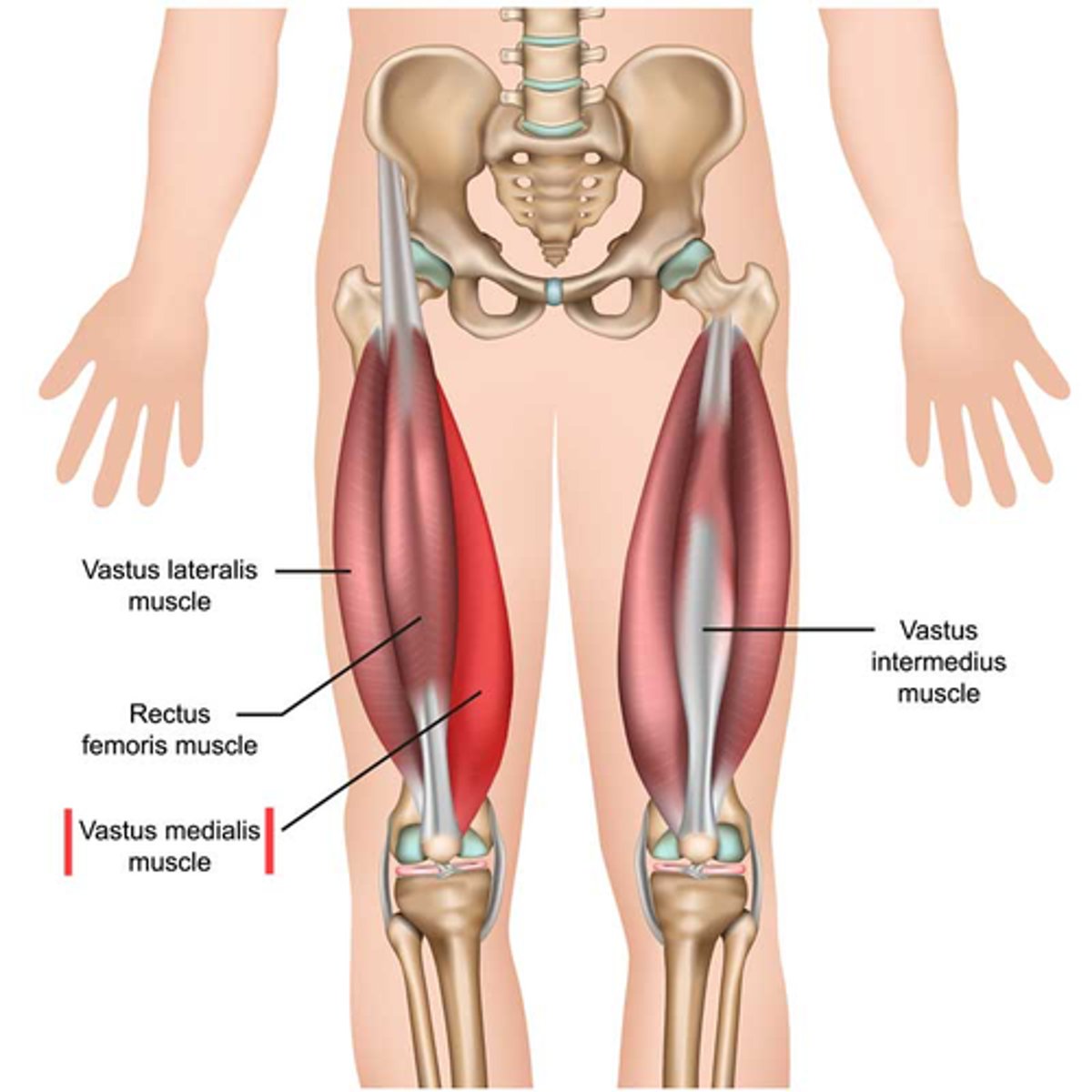
What is the insertion of the vastus medialis?
Tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament

What is the primary action of the vastus medialis?
Extension at the knee