PSYCH 3230 EXAM 1 - MILLER
1/244
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
245 Terms
Insurance, legal responsibility, and disability
The three important ramifications that color the way we interrupt behavior
Is there a single definition to normal or abnormal psychology?
No- everything exists on a continuum and is dimensional
Lazy, weak, or crazy. Weak in character. Dangerous to self or others, they are hopeless, and the freud "and all, be all mentality"
common myths to mental illness
Drapetomania, Childhood masturbation disorders, and homosexuality
3 common controversial diagnosis from the past
"harmful dysfunction; hybrid of value judgement; and biological disadvantage"
Wakefield's definition of abnormal behavior
Disorders as a pure value concept
Judge behavior of desirability according to social norms and ideals. This is problematic because it gives the decision makers a lot of power.
Disorders as whatever professionals treat
"problematic approach"- treat issues as they come along. This is how clinics work today.
The people that will come in are fairly normal and have Internal issues.
The people that don't come in have "scary" External disorders.
What is the issues with "disorder as whatever professionals treat" ?
Disorders as a Statistical Deviance
plays a large role in intellectual disability- BUT just because someone is dumb it doesn't mean that have a disorder.
Disorders as a Biological Disadvantage
- disorder if it causes lowered reproductive fitness.
- disorder if a mental mechanism is not preforming correctly to its specific function.
-Disorder when mechanism fails to preform correctly AND it causes impairment.
Disorders as distress or suffering
this is normal and happens to everyone
Psychological Dysfunction
breakdown in cognitive, emotional, or behavioral functioning
Personal Distress/Disability
It is difficult to preform expected roles. Some disorders may emphasize one over another.
Atypical cultural response
reaction is outside cultural norms
Dyscontrol: when you lose control and can't stop yourself
Maladaptivity: functional impairment
Tom Widiger defines abnormal psychology with two constructs...
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-5)
a widely accepted system of classifying psychological problems and disorders.
1. Fitting a pattern; with at least half the traits
2. Cause dysfunction or subjective distress
3. Are present for a specific duration
4. Are based on Prototypes
The four criteria for Behavior (DSM-5)
1. start with "what brings you in"
2. distinguish clinically significant dysfunction from common human experience
3. Describe demographics, relative symptoms, age of onset, and any precipitating factors
Clinical description
Prevalence
The number or proportion of cases of a particular disorder
Incidence
The number of new cases of a disorder during a given period of time
Episodic
Time-limited
Chronic
Course of disorder can be...
onset of disorder
Acute or insidious
Acute onset
relatively severe, but self-limiting
Insidious onset
Development of a disorder that occurs gradually over an extended period. Harder to treat.
good or guarded
prognosis can either be...
Etiology
the study of the causes of diseases
treatment development
How can we help alleviate psychological suffering?Includes pharmacological, psychosocial, and/or combined treatments
treatment outcome research
A way of systematically measuring which therapies work best for which problems
Supernatural, Biology, and Psychological
the three dominant traditions for explaining psychology
supernatural
believed deviant was because of a battle of "Good vs. Evil". It was caused by demonic possession, witchcraft, sorcery, or movement of moon and stars. They treated these with exoticism and torture. This could have a placebo effect.
BIOLOGICAL
Hippocrates
believed disorders could be treated like any other disease and there were natural causes to disorders. Like brain trauma, genes, and brain pathology.
BIOLOGICAL
Galen: Humoral theory
personality is a balance of four basic bodily fluids.
Galenic-Hippocratic Tradition
-linked abnormality with brain chemical imbalances
-foreshadowed modern views
Syphilis: sexually transmitted disease that caused hallucinations. Pasteur cured it with penicillin.
This provided a biological basis for madness.
"mental illness= physical illness"
Why did biological treatments come of age?
1930's biological treatments
insulin shock therapy, brain surgery, ECT
1950's biological treatments
medicines became available- Neuroleptics
1970's biological treatments
discovered Benzodiazepines
Psychological tradition
Plato and Aristotle
believed social and cultural environment and early learning experiences impacted psych
moral therapy
psychosocial approach in the 19th century that involved treating patients as normally as possible in normal environments. Emphasized a nurturing environment
- worked best in small groups
- Mental hygiene movement -> Custodial Care
- rise of biological tradition and notion that mental illness was die to brain pathology= incurable
Why did moral therapy decline?
- Psychoanalysis
- Humanism
- Behaviorism -> Cognitive- Behaviorism
How does Psychological tradition reemerge in the 1900s
Psychoanalysis major players
Brueur and Freud
Brueur
had patients describe problems under hypnosis. He discovered the "Unconscious mind' and "Catharsis"
unconscious mind
under hypnosis a person would reveal material that was outside their explicit awareness
catharsis theory
a release of emotional tension after discussing emotionally painful events and feelings
Freudian Theory
the structure and function of the mind: ID, EGO, and SUPEREGO
Id
contains a reservoir of unconscious psychic energy that, according to Freud, strives to satisfy basic sexual and aggressive drives. The id operates on the pleasure principle, demanding immediate gratification.
your primary process.
Libido
source of sexual desire and aggressive motives
Eros
instinctual drive for sex, pleasure, and fulfillment
Thanatos
death instinct
Ego
the largely conscious, "executive" part of personality that, according to Freud, mediates among the demands of the id, superego, and reality. The ego operates on the reality principle, satisfying the id's desires in ways that will realistically bring pleasure rather than pain. This is your secondary process.
Superego
represents moral ideals form family and society. develops as a result of being rewarded or punished for different behaviors. Its main purpose is to counteract drive for sex and aggression. it is unconscious.
Intrapsychic conflict -> Anxiety-> defense mechanism
if the ego can not mediate between the superego and id...
defense mechanism
in psychoanalytic theory, the ego's protective methods of reducing anxiety by unconsciously distorting reality
Affiliation
deal with conflict by turning to others for help and support
Humor
Emphasizing the amusing or ironic aspects of the conflict or stressor
Sublimation
deal with stressor by channeling potentially maladaptive feelings or impulses into socially acceptable behavior
Displacement
psychoanalytic defense mechanism that shifts sexual or aggressive impulses toward a more acceptable or less threatening object or person, as when redirecting anger toward a safer outlet
Intellectualization
a coping mechanism in which the person analyzes a situation from an emotionally detached viewpoint
reaction formation
- Preventing unacceptable thoughts or behaviors from being expressed by exaggerating opposite thoughts or types of behaviors.
EX: Jane hates nursing. She attended nursing school to please her parents. During career day, she speaks to prospective students about the excellence of nursing as a career.
Repression
Involuntary blocking of unpleasant feelings and experiences from ones awareness.
EX: An accident victim can remember nothing about the accident
Projection
people disguise their own threatening impulses by attributing them onto others
The psychosexual stages of development by Freud
the 5 basic stages that represent gratifying basic needs and satisfy drive for physical pleasure
Oral Stage (0-18 months)
pleasure centers on the mouth- sucking, biting, chewing
Anal Stage (18-36 months)
pleasure focuses on bowel and bladder elimination; coping with demands for control
Phallic (3-6 years)
pleasure zone is the genitals; coping with incestuous sexual feelings
Latency Stage (6 to puberty)
Sexual feelings become dormant
-no zone (when cooties come into play)
libido is focused on school, friends, sports, etc.
Genital Stage (puberty on)
sexual feelings re-emerge and are oriented toward others
Oedipus complex
a boy's sexual desires toward his mother and feelings of jealousy and hatred for the rival father, but is fearful of dad for "castration anxiety" and then identifies with father.
Electra complex
the unconscious desire of girls to replace their mother and win their father's romantic love. "Penis envy", this is resolved once they develop healthy hetero relationships with males.
psychodynamic theory
therapy deriving from the psychoanalytic tradition that views individuals as responding to unconscious forces and childhood experiences, and that seeks to enhance self-insight.
1. focus on affect and patients expressions of emotions
2. explore avoidance of topics to engage in behaviors that hinder therapy
3. identify patterns of behavior, thoughts, and feelings
4. emphasis on role of past experiences
5. focus on interpersonal relationships
6. emphasis on therapeutic relationship
7. explore patients fantasies, dreams, and wishes
psychodynamic theory- how to apply it
Humanistic Theory
notion that there is positive qualities to people and hat they strive for improvement and excellence- this can be achieved through self actualization
Self Actualization
attain highest potential by overcoming the Hierarchy of needs
hierarchy of needs
Maslow's pyramid of human needs, beginning at the base with physiological needs that must first be satisfied before higher-level safety needs and then psychological needs become active
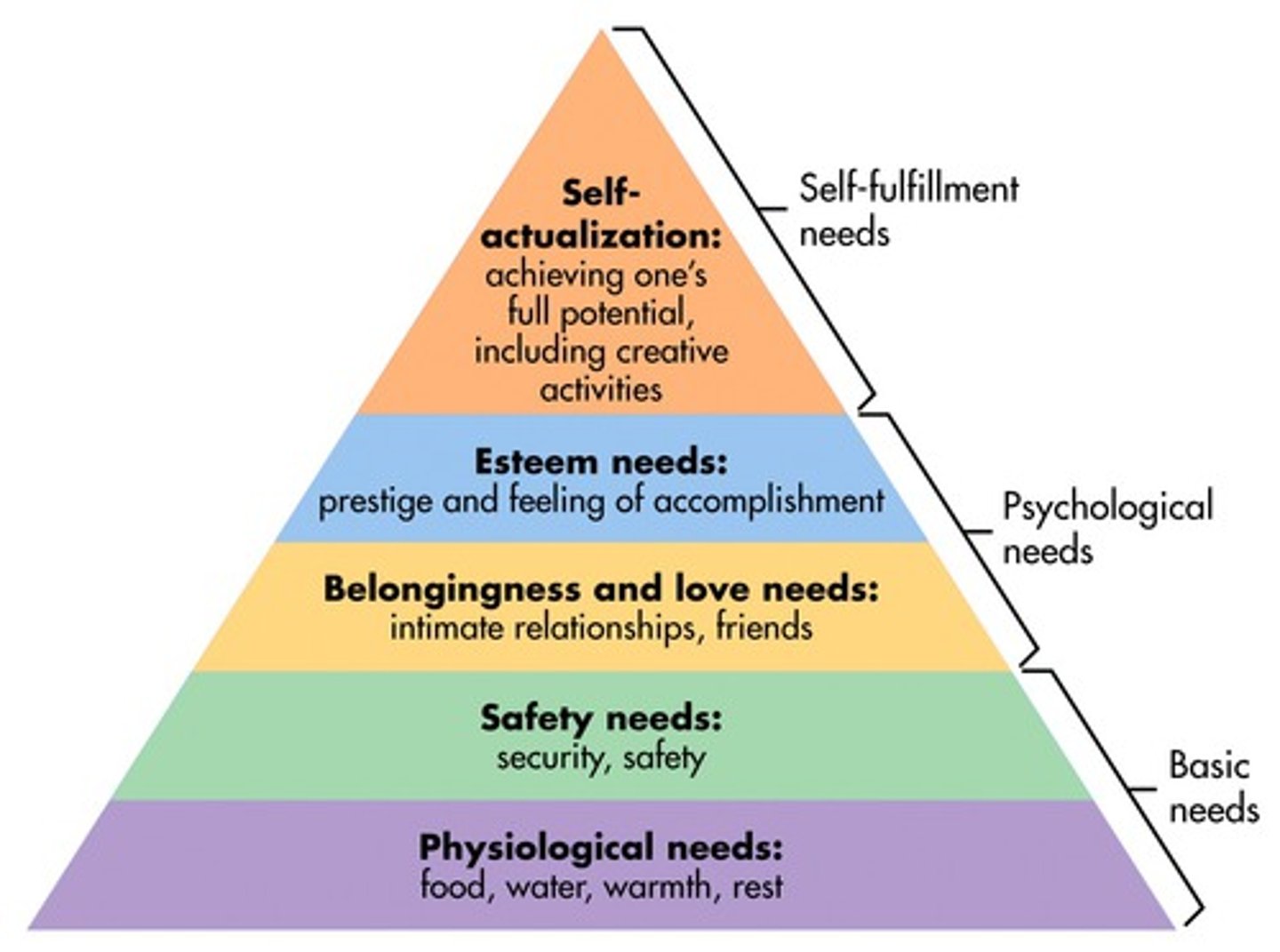
Carl Rodgers Client-Centered Therapy
- therapist must convey empathy and an unconditional positivity with minimal therapist interpretation.
- belief that the patient has all the resources that need to solve their own problems if given emotional support.
- client/therapist relationship is the most important part
Behaviorism
A theoretical orientation based on the premise that scientific psychology should study only observable behavior
classical conditioning
a type of learning founded by Pavlo and Watson. Pairs a Neutral stimulus with and unconditioned stimuli
- unconditioned stimuli (food)
- unconditioned response (saliva)
- conditioned stimuli (bell)
- conditioned response (saliva)
operant conditioning
a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher (skinner and thorndike)
Thorndike's Law of Effect
behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely
Skinner Reinforcement Theory
a consequence that will increase the behavior. Can be pos or neg
Skinner Punishment Theory
a consequence that will decrease the behavior. Can be pos or neg
Skinner Shaping
Successful reinforcement of desired behaviors
the reactionary movement against psychoanalysis and nonscientific approaches
why did behaviorism turn into Behavioral Therapy?
Wolpe, Beck, and Bandura
Who pioneered behavioral therapy?
Behavior Therapy
a time-limited, direct, here-and-now approach. Has widespread support.
said that learning could affect genes by turning them on. This is because genetic structure is malleable and receptive to the environment (epigenetic)
Eric Kandel and gene-environment interactions
COMT gene
Adolescent onset of marijuana use -> Adult Psychosis. Why?
gene-environment correlation
our genes influence the environments to which we are exposed which can influence psych disorders
Passive, Evocative, and Proactive
3 types of correlations
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
somatic: voluntary movements
autonomic: involuntary movements
change
Therapy can ____ brain functions
Conditioning and Cognitive Processes
animal research in learning led to important insights into psychopathology
ex: classical conditioning needs to be consistent
prepared learning
evolutionary predisposition to learn some pairings of feared stimuli over others owing to their survival value
heart disease: due to decreased pumping of the heart
anger and hostility are linked strongly to
has a strong effect on psych and certain disorders have a strong gender link
male= external disorders
females=internal disorders
Gender effects in psychopathology
The principle of equifinality and Multi-finality
concept in developmental psych
one-dimensional models
- explain behavior in terms of a single cause
- could mean a paradigm, school, or conceptual approach
- tend to ignore information from other areas
Multidimensional Models
Interdisciplinary, eclectic, and integrative.
"System" of influences that cause and maintain suffering
Draw upon information from several sources
Abnormal behavior results from multiple influences